1. Introduction
The development of aluminum has drawn much attention since it is a key strategic metal resource in China. The melting point of alumina, the raw material for its production, is 2054°C, while that of aluminum is 660°C [
1]. Since the melting point of the mixture of cryolite and alumina will be lower than that of pure alumina after melting, most current aluminum production methods are cryolite-alumina molten salt electrolysis [
2]. However, with the emphasis on energy saving and emission reduction, more and more attention has been paid to the research of low-temperature electrolysis. The K
3AlF
6-Na
3AlF
6-AlF
3 electrolyte system has become a research hotspot in the research of low-temperature molten salt electrolyte, which has the advantage of lowering the electrolysis temperature while still maintaining strong dissolved Al
2O
3. At the same time, the study of inert anodes has received a great deal of attention, with zirconium boride based ceramic composites being the most attractive to researchers. Compared with nickel ferrate based ceramic composites, zirconium boride based ceramic composites have superior mechanical properties and chemical stability in the high temperature environments of molten salt.
After extensive research, it has been found that the addition of different additives to the molten salt system will change the physical and chemical properties of the molten salt electrolyte [
3].The selection of the appropriate additive components can bring the temperature, viscosity, density and other parameters of the molten salt electrolyte to the ideal state, resulting in lower energy consumption for aluminum production and bringing it closer to the national requirements for environmental protection and emission reduction [
4,
5].The introduction of other ions into the low-temperature molten salt system will affect not only the combination pattern of ions in the system, but also the migration and diffusion of ions in the system [
4].
Since the electrolysis of aluminum is generally carried out at high temperatures above 1173 K [
6], it is challenging to study the effect of additives on the molten salt system through practical experiments [
4]. In response to this difficulty, many researchers began to use molecular dynamics simulations to analyze molten salt systems. Lv [
7] used Factsage to explore the effect of different levels of AlF
3, CaF
2, LiF, and MgF
2 on the solubility of Al
2O
3 in the molten salt system of xNaF·AlF
3-Al
2O
3-CaF
2-MgF
2-LiF. The comprehensive analysis concluded that when the content of AlF
3 was 10%-15%, the addition of AlF
3, CaF
2, LiF, and MgF
2 would reduce the solubility of electrolyte Al
2O
3, and the strong and weak effects were in the order of LiF>MgF
2>CaF
2>AlF
3. Han [
8] studied the ionic structure in the LiF-NaF-AlF
3-Al
2O
3 molten salt system using IPMD and FPMD simulations, and the comprehensive analysis concluded that there are Al-F complex ions and Al-O-F complex ions in the LiF-NaF-AlF
3-Al
2O
3 molten salt system, and also the presence of Li+ decreases the coordination number between Al-F. Tian [
9] used molecular dynamics methods to explore the effects of different levels of AlF
3 on the structure and properties of the Na
3AlF
6-AlF
3 molten salt system, and the comprehensive analysis concluded that the conductivity of the molten salt system gradually decreased with the increase of AlF
3 content, and ionic groups with Al-F coordination number greater than 6 may be formed in the melt.
Based on the previous studies, this paper systematically investigates the effect of Zr, B, C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta elements in the inert anode in the molten salt electrolyte system using zirconium boride based metal-ceramic inert anode into the K3AlF6-Na3NaF6-AlF3 electrolyte system by using molecular dynamics method. The physicochemical properties of ions in the K3AlF6-Na3AlF6-AlF3 molten salt system containing elements that may be present in inert anode materials at 1.01 MPa and 1173 K were systematically investigated.
2. Effect of Zr and B ions on K3AlF6-Na3AlF6-AlF3 molten salt system
2.1. Computational Methods
This calculation uses the Material Studio software to set a given number of various ions in a periodic box. The Foeite module in MS (UFF force field with a time step of 1 fs) was used to simulate the dynamic processes of the molten salt. The Coulomb effect of the simulated ions was processed using the Ewald summation algorithm for the system, with the buffer width and energy calculation accuracy set to 0.5 Å and 0.5 kcal/mol. The cut-off radius for short-range interactions was set to half the length of the simulated box sides. The simulated molten salt tank was heated to 4000 K at a pressure of 1.01 MPa under an isothermal isobaric system and a structural relaxation of 100 ps was performed. The particle number, pressure and temperature of the molten salt system were set to remain constant during the simulation. The superheated liquid was then cooled to the target molten salt melting point of 1173 K at 1 K/ps in the canonical system and the molten salt model continued to undergo 100 ps of structural relaxation.
Table 1.
he number of atoms in the simulation system and the size of the system.
Table 1.
he number of atoms in the simulation system and the size of the system.
| Additive |
Number of particles |
Box side length/ Å |
| Al |
Na |
K |
F |
Zr |
B |
| No addition |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
0 |
0 |
43.6 |
| 0.1wt%Zr4+
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
1 |
0 |
43.6 |
| 0.2wt%Zr4+
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
2 |
0 |
43.6 |
| 0.3wt%Zr4+
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
3 |
0 |
43.6 |
| 0.4wt%Zr4+
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
4 |
0 |
43.6 |
| 0.5wt%Zr4+
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
5 |
0 |
43.6 |
| 0.1wt%B2-
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
0 |
2 |
43.6 |
| 0.5wt%B2-
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
0 |
4 |
43.6 |
| 0.3wt%B2-
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
0 |
6 |
43.6 |
| 0.4wt%B2-
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
0 |
8 |
43.6 |
| 0.5wt%B2-
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
0 |
10 |
43.6 |
| 0.1wt%ZrB2
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
1 |
2 |
43.6 |
| 0.2wt%ZrB2
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
2 |
4 |
43.6 |
| 0.3wt%ZrB2
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
6 |
6 |
43.6 |
| 0.4wt%ZrB2
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
4 |
8 |
43.6 |
| 0.5wt%ZrB2
|
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
5 |
10 |
43.6 |
2.2. Coordination number
The coordination number is the number of target particles within a certain distance of the central particle, and the coordination number between ions can be obtained by integrating the radial distribution function [
10].The specific formula is as follows.
Where ρ
0 denotes the mean number density of the target particle, g(r) is the radial distribution function, r takes the position of the first trough of the radial distribution function, and the N value obtained by integration is the coordination number of the target particle within the first coordination layer [
11,
12].
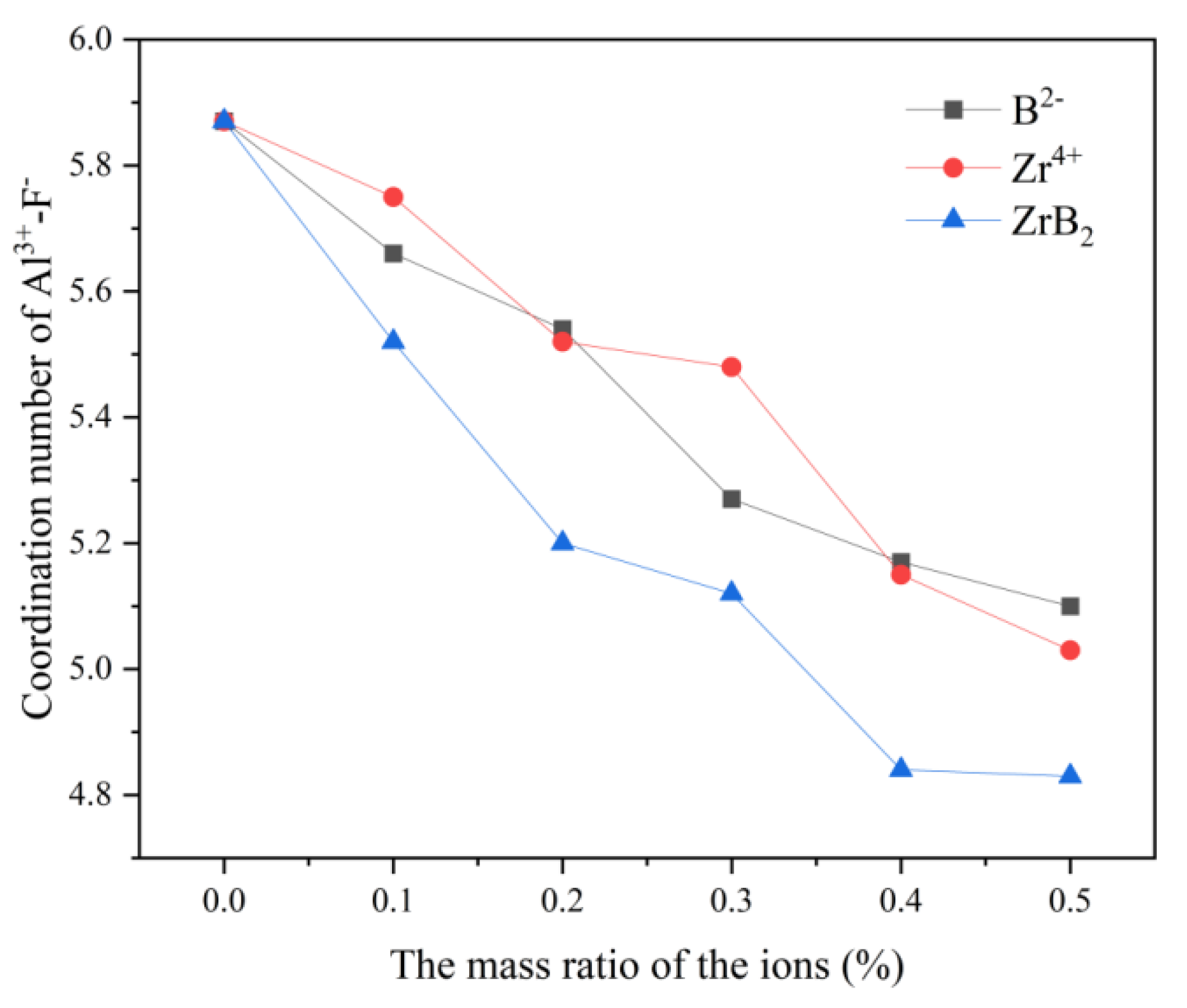
In
Figure 1, the maximum value of the coordination number of all three curves is 5.87 at no addition, and the minimum value is also at 0.5% addition, 5.1 for the B
2- curve, 5.03 for the Zr
4+ curve, and 4.83 for ZrB
2 curve. The coordination number of F
- around Al
3+ decreases continuously as the B
2- and Zr
4+ content increases. In the study of the KF-AlF
3 system, Ma [
13] pointed out that [AlF
5]
2- and [Al
2F
7]
- are present in very small amounts in the system, so it can be speculated that the decrease in the coordination number may be due to the addition of ZrB
2, which reduces the Al-F interaction force and promotes the transition process of [AlF
6]
3-→[AlF
4]
-.
2.3. Conductivity
The electrical conductivity can be obtained from the Nemst-Einstein equation [
14].
Where N denotes the number of anions and cations per unit volume, q denotes the electronic charge, D
- and D
+ denote the diffusion coefficients of anions and cations, respectively, and k
B is the Boltzmann constant. The calculation results are shown in
Figure 2.
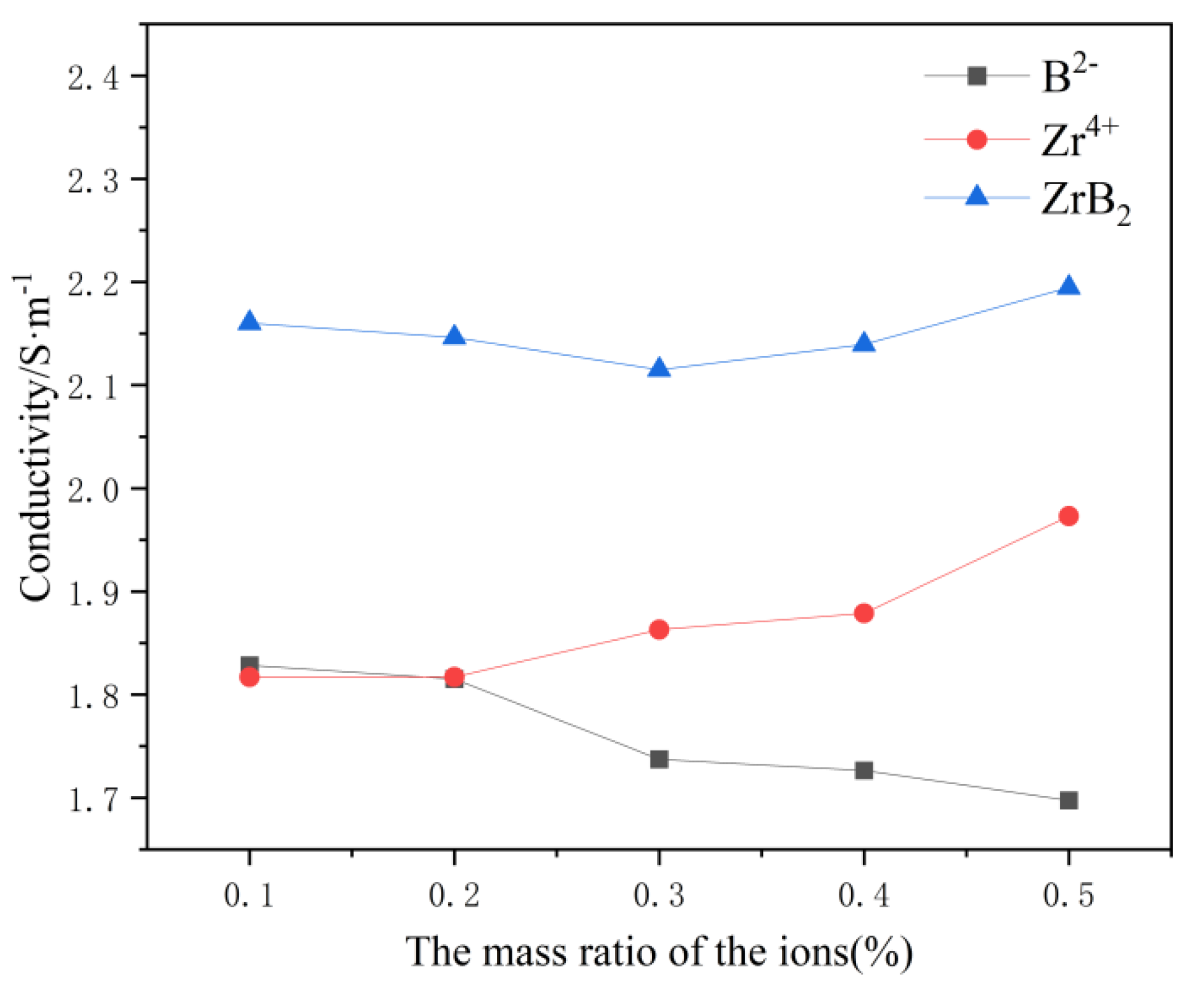
In
Figure 2, the conductivity of the system gradually decreases with increasing B
2- content and gradually increases with increasing Zr
4+ content. Presumably because the presence of Zr
4+ ions intensifies the transformation process of [AlF
6]
3-→[AlF
4]
-,and the presence of B
2- ions intensifies the chemistry reaction between a certain Al-F, such as [AlF
6]
3-→[Al
2F
7]
-. Thus, when ZrB
2 is added, the element that plays a dominant role in influencing the conductivity change should be identified in the calculation. By differentiating the B
2- and Zr
4+ change curves, it can be concluded that B
2- plays a dominant role in influencing the conductivity change when the content of ZrB
2 is lower than 0.3wt%, and the conductivity of the system will gradually decrease with the increase of the ZrB
2 content at this time. When the content of ZrB
2 is greater than 0.3wt%, Zr
4+ plays a dominant role in influencing the change of conductivity, and the conductivity of the system gradually increases with the increase of ZrB
2 content.
2.4. Viscosity
Viscosity is an important physical parameter of molten salt electrolytes, and its magnitude has a great influence on the choice of mass transfer methods and dynamics. Viscosity can usually be calculated from the Stokes-Einstein relationship as follows [
15].
Where D
+ is the cation diffusion coefficient, k
B is the Boltzmann constant (taken as 1.38×10
-23J·K
-1), and R
+ is the kinetic diameter of the ion, which is taken as 1.9×10
-10 for the calculation.
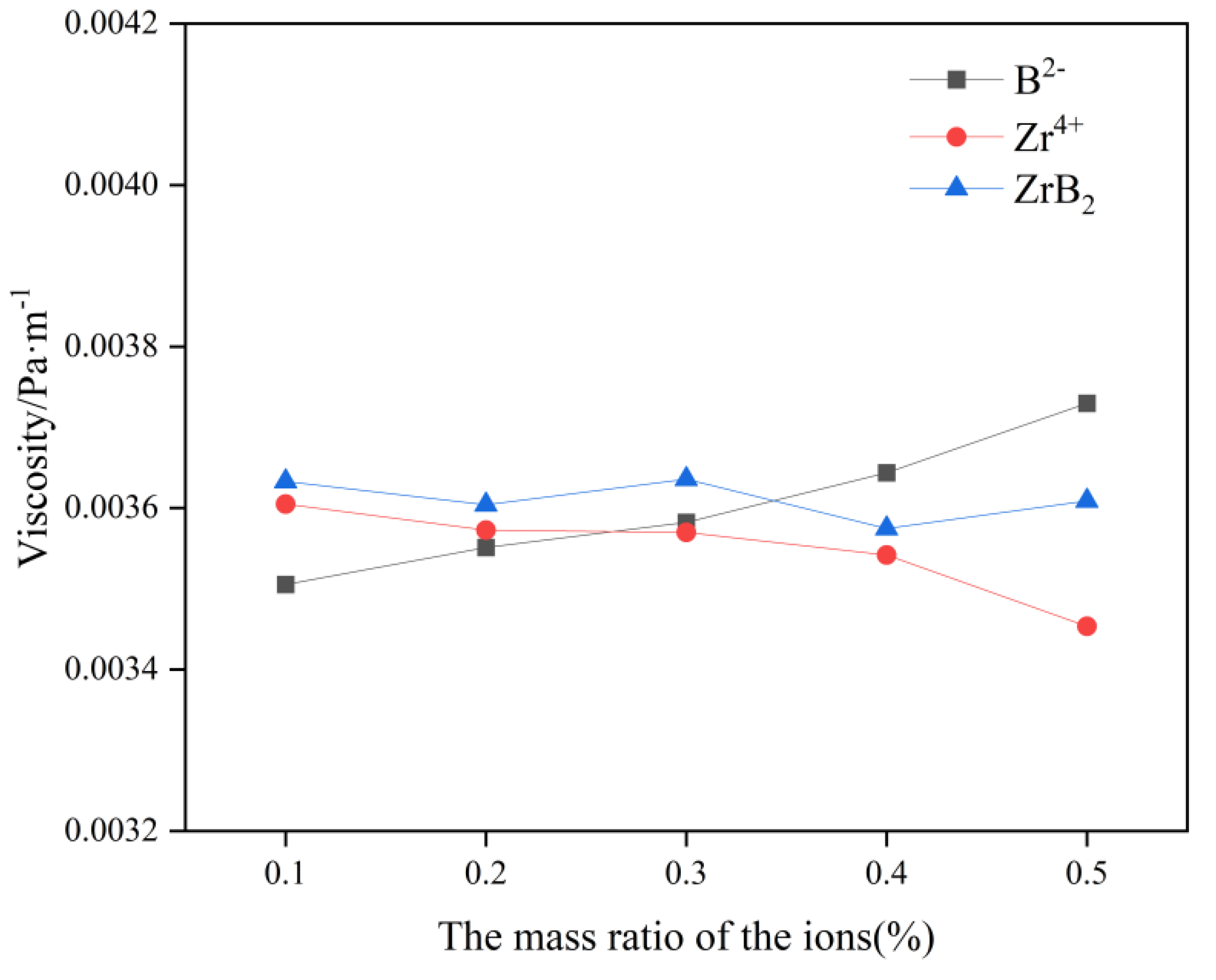
In
Figure 3, the viscosity of this molten salt electrolyte system gradually increases with the increase of B
2- content, which indicates that the addition of B
2- increases the polymerization degree of electrolyte molten salt ions and affects the electrolysis production to a certain extent. The viscosity of this molten salt electrolyte system gradually decreases with the increase of Zr
4+ content, which indicates that the addition of Zr
4+ effectively reduces the polymerization of the electrolyte molten salt ions, and this facilitates electrolysis production. As a result, when ZrB
2 is added, the element that plays a dominant role in influencing the viscosity change should be identified in the calculation. By differentiating the B
2- and Zr
4+ change curves, it can be concluded that Zr
4+ plays a dominant role in influencing the viscosity change when the content of ZrB
2 is lower than 0.4 wt%, at which time the system viscosity will gradually decrease with the increase of ZrB
2 content. When the content of ZrB
2 is greater than 0.4wt%, B
2- plays a dominant role in influencing the change of viscosity, and the viscosity of the system will gradually increase with the increase of ZrB
2 content.
3. Effect of Zr, B, C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta ions on K3AlF6-Na3AlF6-AlF3 molten salt system
3.1. Computational Methods
Since the electrolysis system did not change, the parameters of the box used were set as follows: Density 2 g/cm3. Then, selected the Ensemble of Dynamics as NPT to keep the box size constant for parameter setting, Temperature as 4000K, Pressure as 0.00101GPa, and Total simulation time as 100ps. And then selected the Ensemble of Dynamics as NVT to keep the box size constant for parameter setting, Temperature as 1173K.
Table 2.
The number of atoms in the simulation system and the size of the system.
Table 2.
The number of atoms in the simulation system and the size of the system.
|
AdditiveZrB2
|
Number of particles |
Box side length/ Å |
| Al |
Na |
K |
F |
Zr |
B |
C |
W |
Ti |
Hf |
Nb |
Ta |
| 0.1wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
43.7 |
| 0.2wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
43.7 |
| 0.3wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
3 |
6 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
43.7 |
| 0.4wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
4 |
8 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
43.8 |
| 0.5wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
5 |
10 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
43.8 |
| 0.1wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
43.6 |
| 0.2wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
43.6 |
| 0.3wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
3 |
6 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
43.7 |
| 0.4wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
4 |
8 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
43.7 |
| 0.5wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
5 |
10 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
43.7 |
| 0.1wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
1 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
43.6 |
| 0.2wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
2 |
4 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
43.7 |
| 0.3wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
3 |
6 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
43.7 |
| 0.4wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
4 |
8 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
43.7 |
| 0.5wt% |
610 |
780 |
270 |
2890 |
5 |
10 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
43.7 |
3.2. Radial distribution function
The radial distribution is mainly used to observe the bonding between two molecules or atoms. First, select two kinds of atoms or molecules, set them into two kinds of Sets, and then analyze the radial distribution of the two Sets. For this analysis, this paper select two kinds of atoms (Al and F). The formula of the radial distribution function is as follows [
16].
Table 3.
Average bond lengths of Al-F ion pairs in molten salt systems using different additives.
Table 3.
Average bond lengths of Al-F ion pairs in molten salt systems using different additives.
| Other elements |
ZrB2 Additive |
| 0.1wt% |
0.2wt% |
0.3wt% |
0.4wt% |
0.5wt% |
| No addition |
3.15 |
3.13 |
3.13 |
3.11 |
3.11 |
| W |
3.03 |
3.03 |
3.03 |
3.01 |
3.01 |
| C |
3.15 |
3.13 |
3.13 |
3.11 |
3.11 |
| Ti, Hf, Nb, Ta, C |
3.19 |
3.19 |
3.17 |
3.17 |
3.15 |
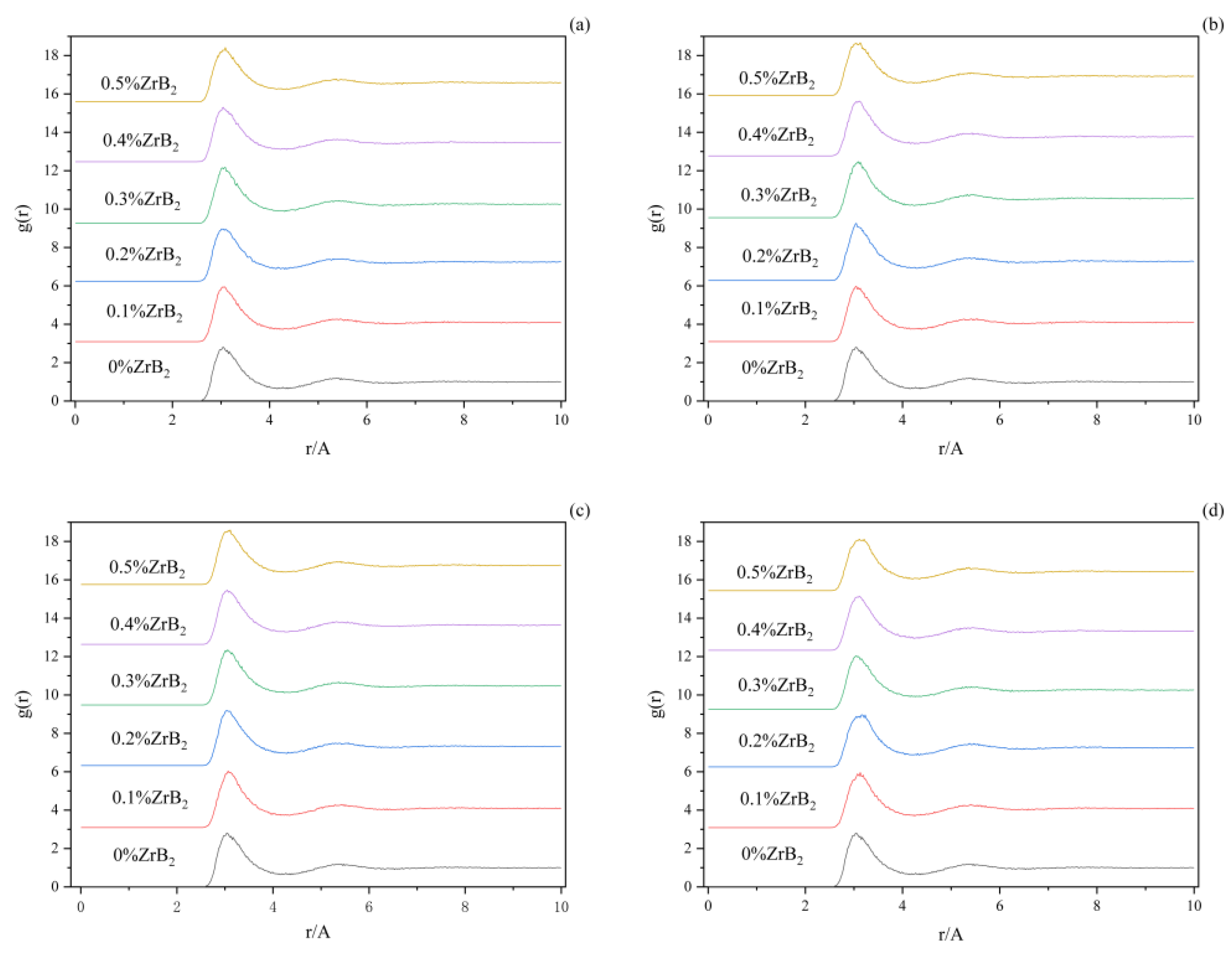
Figure 4 shows the radial distribution functions among the Al-F ions when adding ZrB
2 at the proportions of 0 wt%, 0.1 wt%, 0.2 wt%, 0.3 wt%, 0.4 wt%, 0.5 wt%, and different trace elements to the K
3AlF
6-Na
3AlF
6-AlF
3 molten salt electrolyte system. In (a), the position of the first wave of Al-F varies with the ZrB
2 content from 0~0.5% with 3.17 A, 3.15 A, 3.13 A, 3.13 A, 3.11 A, and 3.11 A. In (b), the average bond length of Al-F decreases with increasing ZrB
2 content. In the Al-F comparison plot (a), (b), (c), and (d). it can be found that plot (a) and (c) are not significantly different from each other, indicating that the addition of C ions has no significant effect on the F and Al ions of this molten salt system. With the addition of different additives in the (b) and (d) plots, it can be obviously found that the sharpness of the first front of Al-F has changed, which indicates that the W ions and Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta ions in the molten salt species make the distribution of F ions around Al ions more uniform. Taking the (d) as an example, it can be found that the sharpness of the first front of Al-F becomes significantly slower with the increase of ZrB
2 content, indicating that the distribution of F ions around Al ions is more uniform under the joint effect of Zr ions and B ions [
17].
The radius of the first peak of the radial distribution function indicates the average bond length of the ion pair [
18]. Table 3 shows the average bond length of Al-F ion pairs in the molten salt system with different additives, which also corresponds to the four figures of abcd, respectively. It can be noticed that the average bond length of the molten salt system with the addition of W decreases, indicating that the addition of W results in a weaker interaction between Al-F, while the average bond length of the molten salt system with the addition of Ti, Hf, Nb, Ta, and C increases, indicating that the addition of Ti, Hf, Nb, Ta, and C leads to an enhanced Al-F interaction. The interaction between Al and F represents the coordination ability between Al and F. It is therefore possible to predict the trend of the effect of the addition of W, Ti, Hf, Nb, Ta, and C elements on the coordination number of Al and F in the electrolyte system by virtue of these variation patterns.
3.3. Coordination number
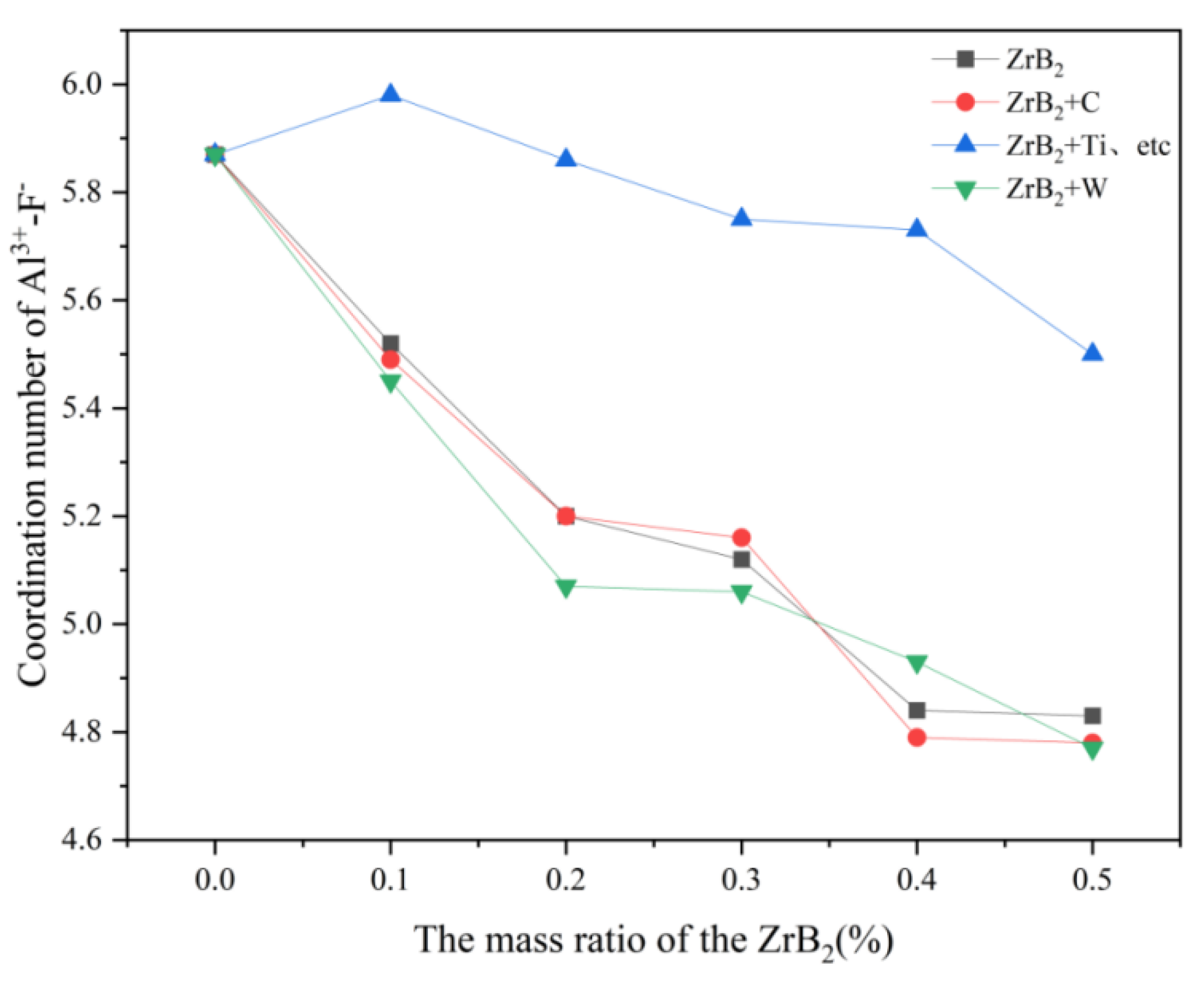
In
Table 4, the coordination number between Al-F decreases after adding ZrB
2 to the system, indicating that the interaction between Al-F is gradually decreasing with the addition of ZrB
2 and the number of fluorine bridges formed in the system is also gradually decreasing. In the addition of 0.1% ZrB
2 into the melt system, the coordination number F between Al was significantly reduced, which also indicated a shortening of the interaction F between Al [
19].
Table 4.
Coordination number between Al-F in molten salt systems using different additives.
Table 4.
Coordination number between Al-F in molten salt systems using different additives.
| Other elements |
ZrB2 Additive |
| 0.1wt% |
0.2wt% |
0.3wt% |
0.4wt% |
0.5wt% |
| No addition |
5.52 |
5.20 |
5.12 |
4.84 |
4.83 |
| W |
5.45 |
5.07 |
5.06 |
4.93 |
4.77 |
| C |
5.49 |
5.20 |
5.16 |
4.80 |
4.78 |
| Ti, Hf, Nb, Ta, C |
5.98 |
5.86 |
5.75 |
5.73 |
5.50 |
In
Figure 5, it can be concluded that the addition of C and W ions decreases the coordination number of F- around Al
3+ in the K
3AlF
6-Na
3AlF
6-AlF
3 molten salt electrolyte system, and the effect of W ions in decreasing the coordination number of F- around Al3+ is more obvious, presumably because of C and W ions. The hypothetical reason is that the C and W ions intensify the transition process of [AlF
6]
3-→[AlF
4]
-, where the effect of W is more effective. With the addition of Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta ions, the coordination number of F- around Al
3+ in this molten salt system increases significantly, probably because Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta ions inhibit the transition process of [AlF
6]
3-→[AlF
4]
-.
3.4. Conductivity
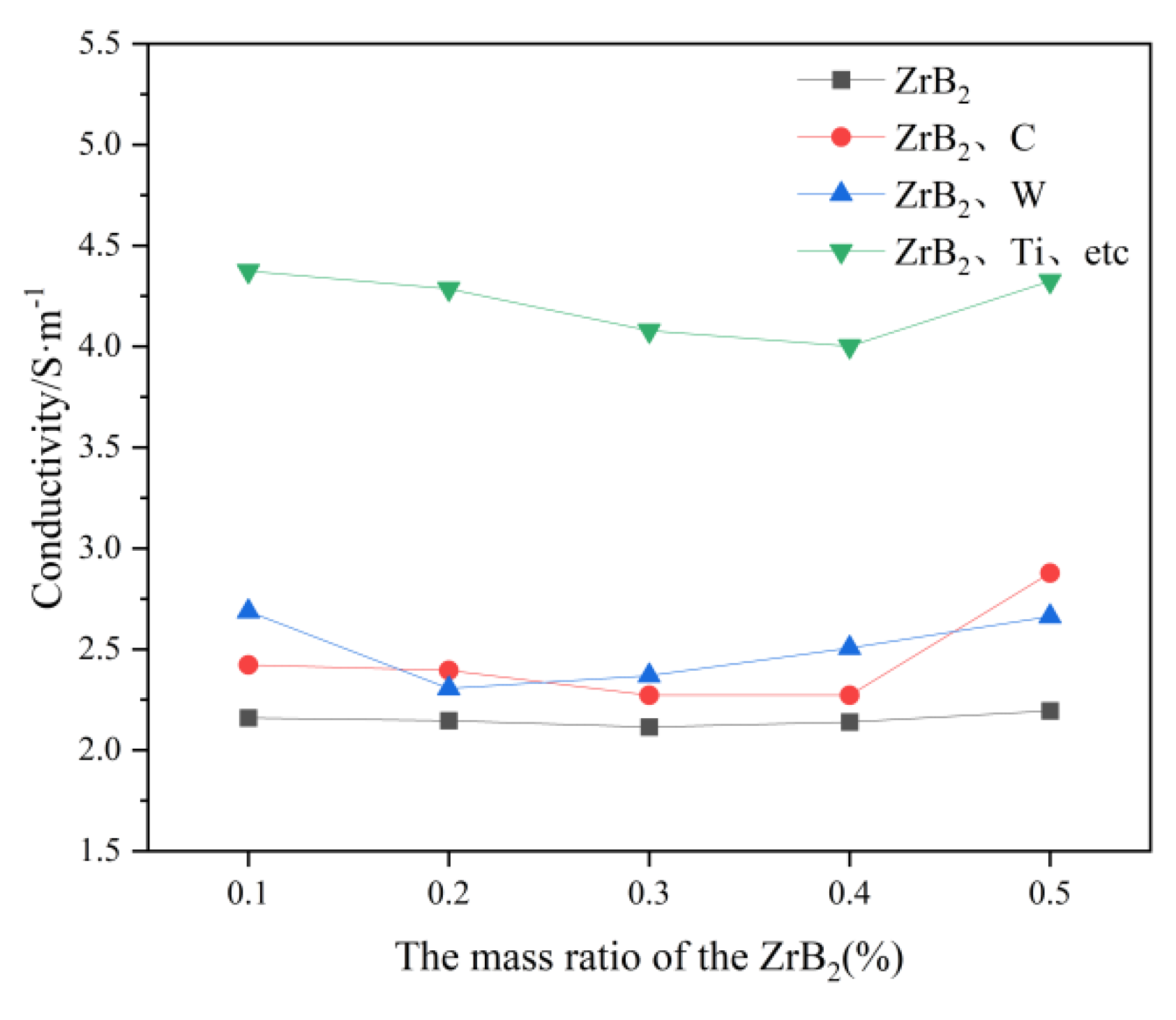
In
Figure 6, it can be obtained that the conductivity of the molten salt electrolyte is increased by the increase of C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta. However the effect of C and W on the conductivity is relatively small, probably because the addition of C and W increases the number of ions in the electrolyte. In contrast the addition of Ti, Hf, Nb and Ta has a more pronounced effect on the increase in conductivity, presumably because Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta aggravate the process of a certain decomposition reaction in the molten salt electrolyte. It is assumed that Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta aggravate the process of a certain decomposition reaction in the molten salt electrolyte, causing a significant shift in the ion number.
3.5. Viscosity
In
Figure 7, the addition of C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta ions will slightly reduce the viscosity of the K
3AlF
6-Na
3AlF
6-AlF
3 molten salt electrolyte system, while the addition of Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta ions is more effective in reducing the viscosity of this molten salt electrolyte system. However, the viscosity of this molten salt electrolyte is generally considered to be stable because the content of ZrB
2 varies in a small range.
4. Conclusion
In order to reveal the impact of adding Zr, B, C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta to the low-temperature electrolytic aluminum system on the system’s physicochemical properties, simulations were carried out using molecular dynamics methods. The following main conclusions were obtained.
1. The coordination number of F- around Al3+ decreases with the increase of B2- and Zr4+ contents. The interaction force between Al-F may be reduced by the joint action of B2- and Zr4+, which promotes the transition process of [AlF6]3-→[AlF4]-.
2. The addition of C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta will make the viscosity of the molten salt electrolyte slightly decrease, but since the fluctuation range is small, it can be concluded that the viscosity of the molten salt electrolyte is relatively stable.
3. The conductivity of the molten salt electrolyte was increased by the addition of C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb and Ta. However, the effect of C and W on the conductivity was relatively small, probably because the addition of C and W increased the number of C and W ions in the electrolyte, which led to an increase in the total number of ions, hence the slight fluctuation in conductivity. In contrast, the addition of Ti, Hf, Nb and Ta had a more pronounced effect on the increase in conductivity.
4. The effect of the addition of C, W, Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta on the coordination number of Al-F is not immediately apparent. However, the addition of W decreases the coordination number of Al-F, presumably because the presence of W ions intensifies the transformation process of [AlF6]3-→[AlF4]-, whereas the addition of Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta increases the coordination number of Al-F. As the Al-F coordination number increases, it is speculated that Ti, Hf, Nb, and Ta speed up the decomposition reaction between a certain Al-F, for example [Al2F7]-→[AlF4]-, which increases the coordination number between the Al-F and the number of ions in the electrolyte.
References
- Wei Ding. Experimental analysis of the combustion of aluminum foil in air[J]. Mathematical and physical study, 2011(07): 106-107.
- Yi Wang, Shengxiang Deng. Numerical simulation of magnetic field of 400kA aluminum electrolyzer based on COMSOL[J]. Light Metals, 2022(11): 30-34. [CrossRef]
- Shengshou Wang. A review of physicochemical properties of aluminum electrolytes[C]// National Aluminum Electrolysis Energy Conservation Technology Exchange. 2006.
- Yongzhi Wang. Study on the influence of additives on the structure and properties of aluminum electrolytic molten salt system[D]. Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2015.
- Ning Zhang, Wei Chen. Exploration of energy-saving and emission reduction technology for electrolytic aluminum production[J].China Metal Bulletin, 2017(11): 100-101.
- Yuping Zhu, Yedong He, DeRen Wang. Oxidation and electrolytic corrosion behavior of Fe-40Cr-2Ce alloy anodes at 900°C[J]. Journal of Materials Heat Treatment, 2011, 32(11): 6. [CrossRef]
- Xiaojun Lv, Yajing Shuang, Lingyun Hu. Theoretical calculation of the initial crystal temperature and alumina solubility of aluminum electrolytes[J]. Light Metals, 2015, No.443(09): 27-31. [CrossRef]
- Shuo Han, Honglei Xu, Peng Zhen. Molecular dynamics simulation of Li-rich aluminum electrolyte system[J]. Light Metals, 2021, No.515(09): 29-33. [CrossRef]
- Guocai Tian, Yongzhi Wang. Molecular dynamics simulation study of the effect of AlF3 on the structure and properties of cryolite molten salt system[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 40(03): 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Yayun Zhang, Mian Chen, Ya Deng. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Temperature and Pressure Effects on Hydration Characteristics of Montmorillonites[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018(10): 22. [CrossRef]
- Cikit S, Akdeniz Z, Madden P A. Structure and Raman Spectra in Cryolitic Melts: Simulations with an ab Initio Interaction Potential[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 118 (2014), 1064-1070. [CrossRef]
- Nazmutdinov Renat R, Zinkicheva Tamara T. A spectroscopic and computational study of Al(III) complexes in cryolite melts: Effect of cation nature[J]. Chemical Physics, (412), 22–29. [CrossRef]
- Nan Ma, Jinglin You, Guangchao Wei. High-temperature Raman spectroscopy and quantum chemical calculations of molten salt microstructures of K3AlF6-Al2O3 system[C]//. Abstracts of the 19th National Conference on Light Scattering. 2017: 144.
- R.A. McKee. A generalization of the nernst-Einstein equation for self-diffusion in high defect concentration solids[J]. Solid State Ionics, 5(none), 133–136. [CrossRef]
- Searles, Debra J, Evans Denis J. The fluctuation theorem and Green–Kubo relations[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 112(22), 9727. [CrossRef]
- Xiaojun Lv, Zhenming Xu. Theoretical investigation on local structure and transport properties of NaF-AlF3 molten salts under electric field environment[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1117, 105–112. [CrossRef]
- Xianwei Hu, Zhaowen Wang. Raman spectra of the ionic structure of acidic NaF-AlF3 molten salts[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2008(10): 1914-1919. [CrossRef]
- Zongwei Li, Jue Kou, Tichang Sun, Zekun Chen. Molecular dynamics simulation of CaO dephosphorylation mechanism during direct reduction of high phosphorus hematite[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Mineral Processing Part), 2022(06): 35-42.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2022.06.055.
- Yanli Jiang, Xin Tang, Fan Gao. Molecular dynamics study of cryolite-alumina molten salts[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2016, 33(02): 325-329. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).