Submitted:
21 April 2023
Posted:
23 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. H.pylori infection status
- Lack of gastric mucosal atrophy in endoscopy or Kimura–Takemoto Classification of C-1 [18];
- Absence of gastric atrophy in resected specimens as per pathological examinations;
- Negative clinical findings observed for at least one of the following three tests: the 13C-urea breath test (UBT; cutoff value <2.5%, Otsuka, Tokushima, Japan), the H.pylori stool antigen test (Premier Platinum H.pylori SA; Meridian, Cincinnati, OH, USA), or lack of serum immunoglobulin G antibodies against H.pylori (H.pylori Ab; cutoff value <3 U/mL, Eiken, Tokyo, Japan);
2.3. Immunohistochemical examination and phenotypic classification
2.4. Histopathological classification of RSGL
2.5. Clinicopathological assessment
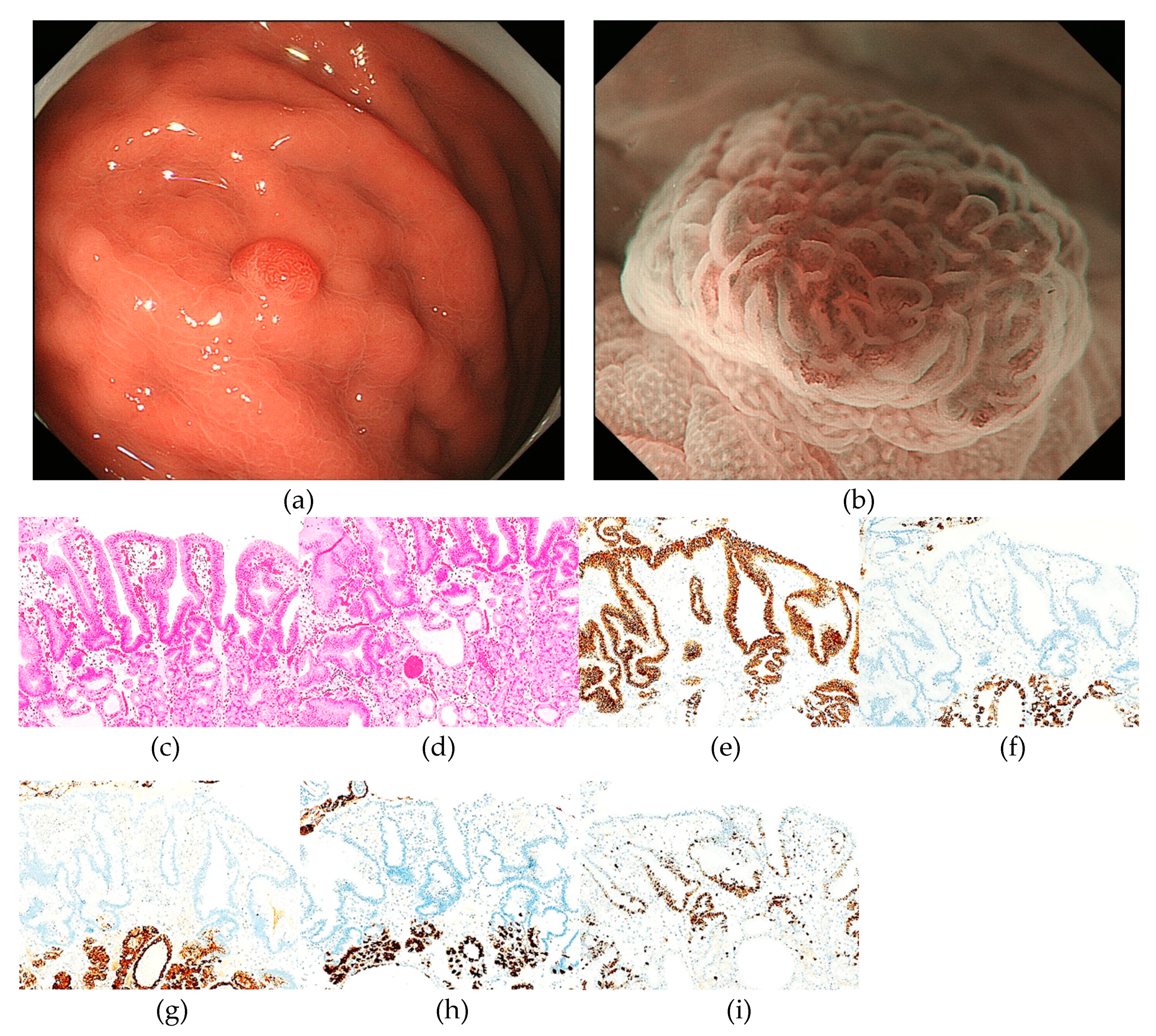
2.6. Endoscopic Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological features of RSGLs
3.2. Immunohistochemical features of RSGLs
3.3. Endoscopic features of RSGLs
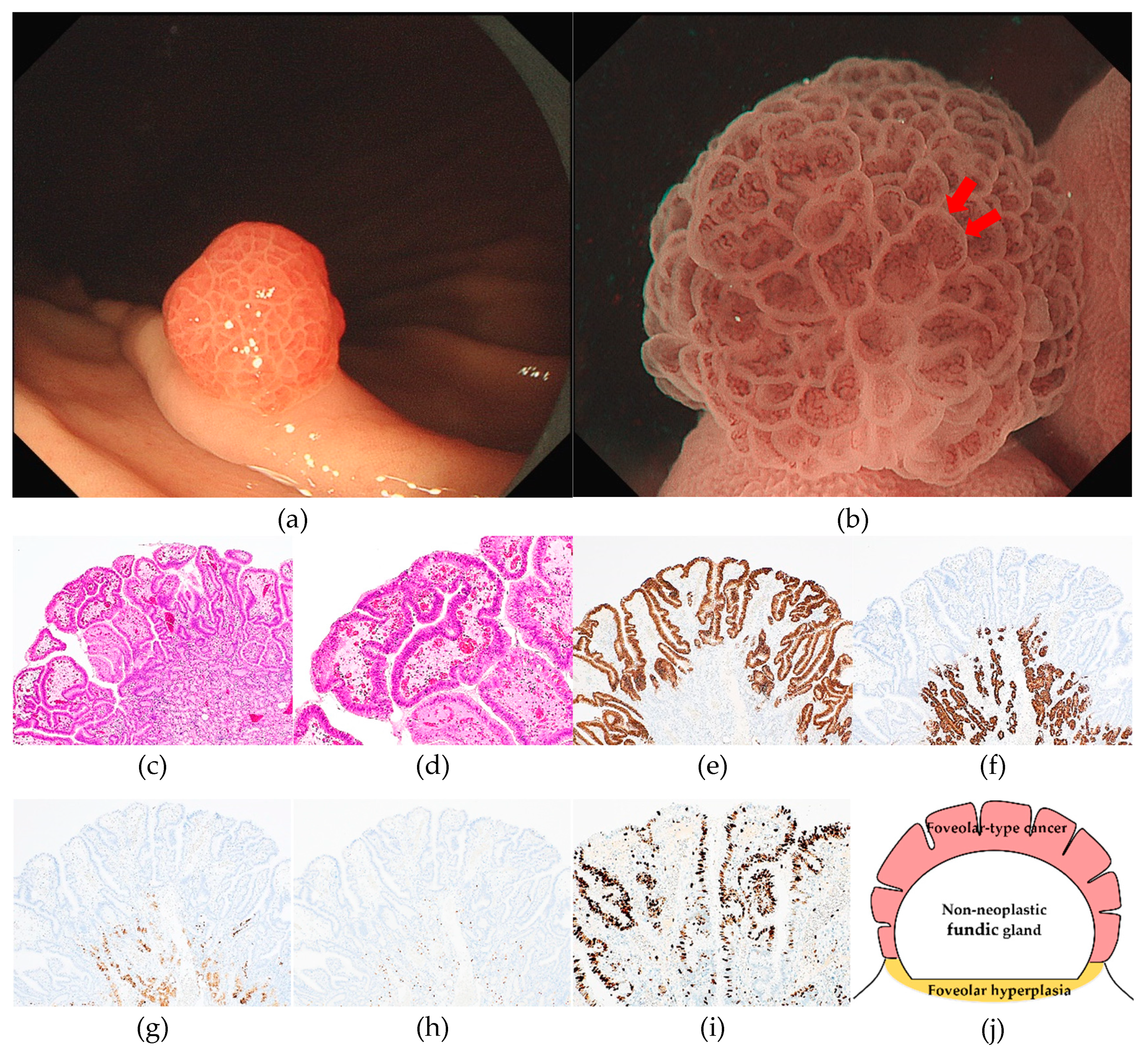
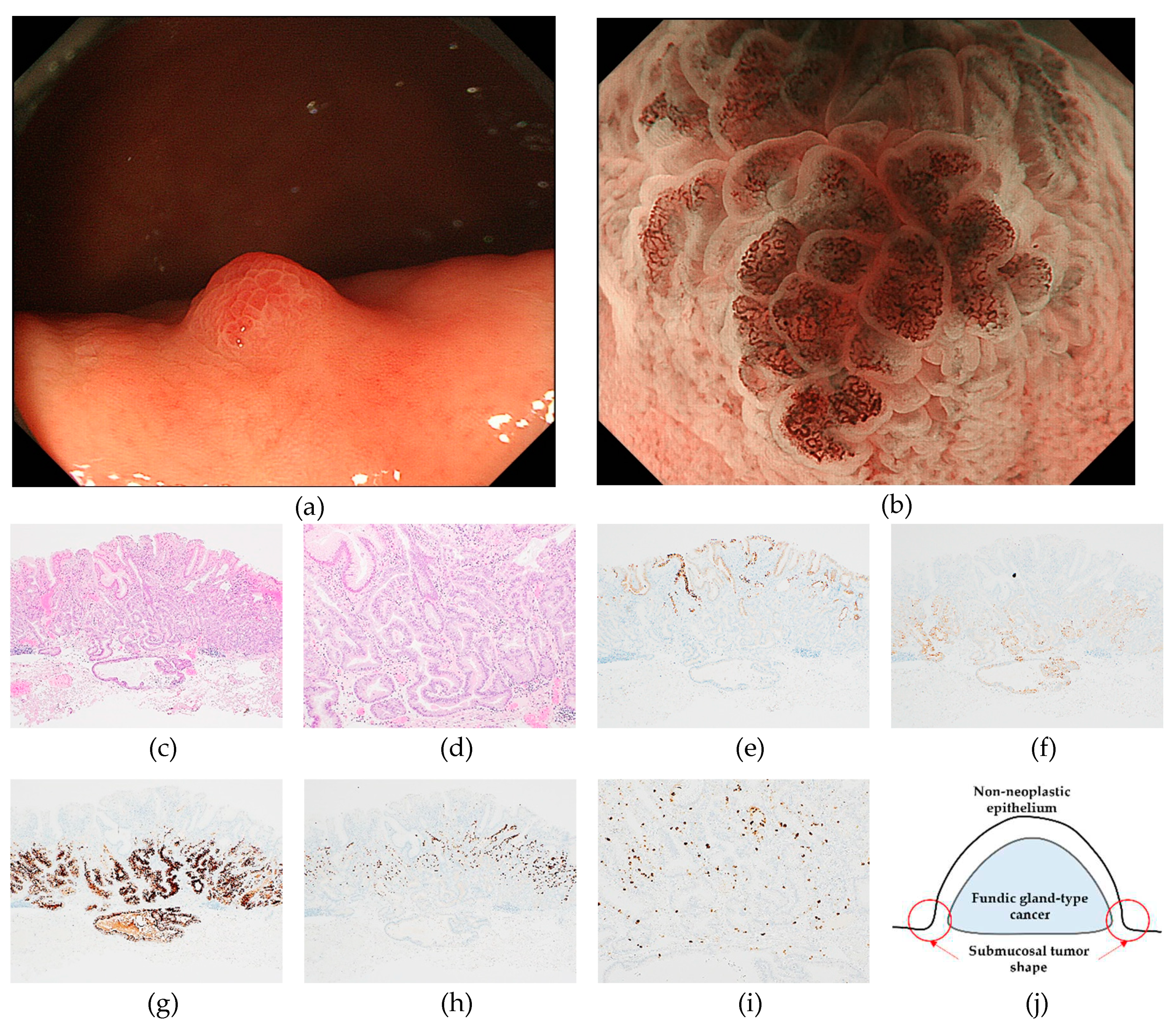
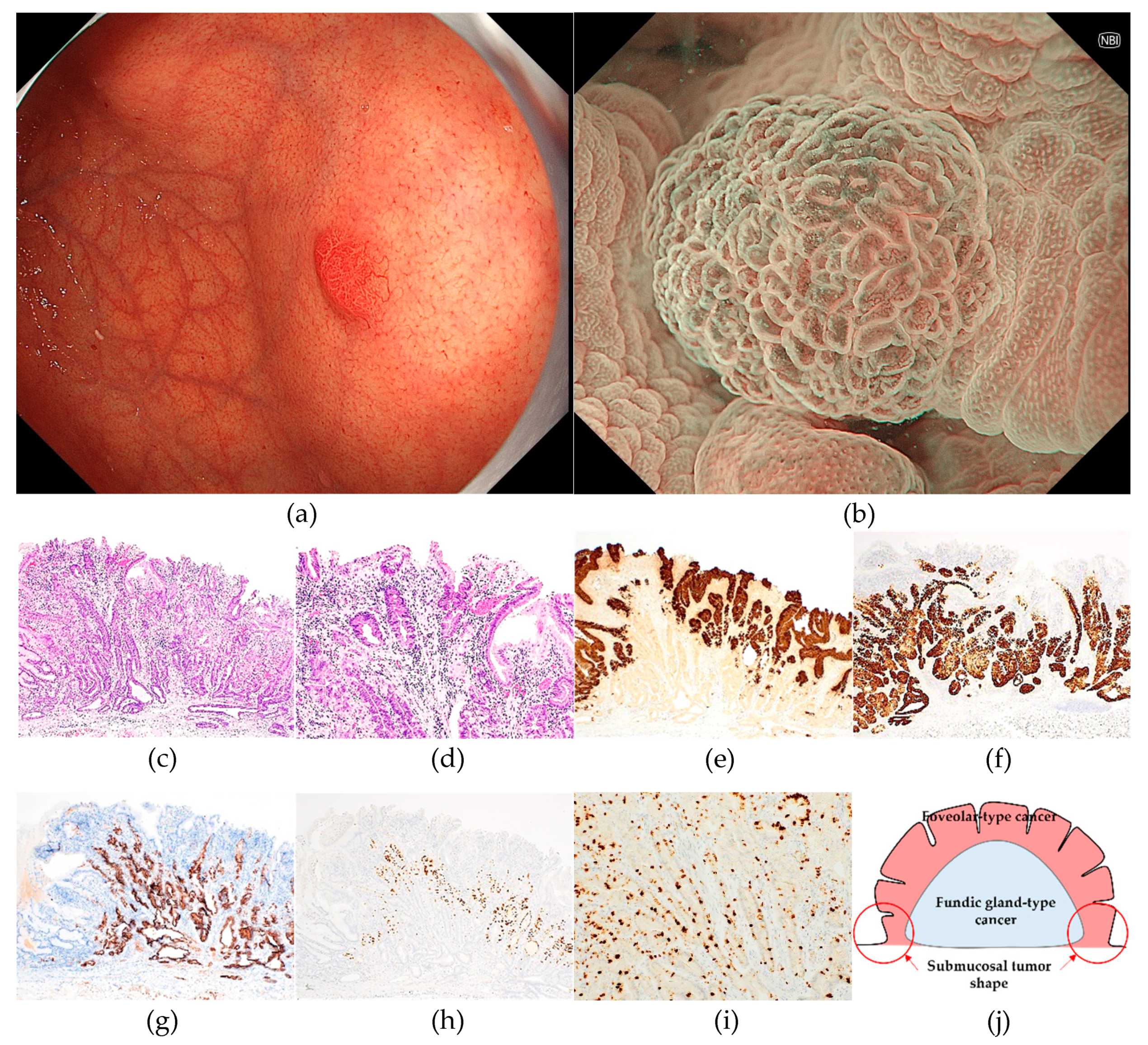
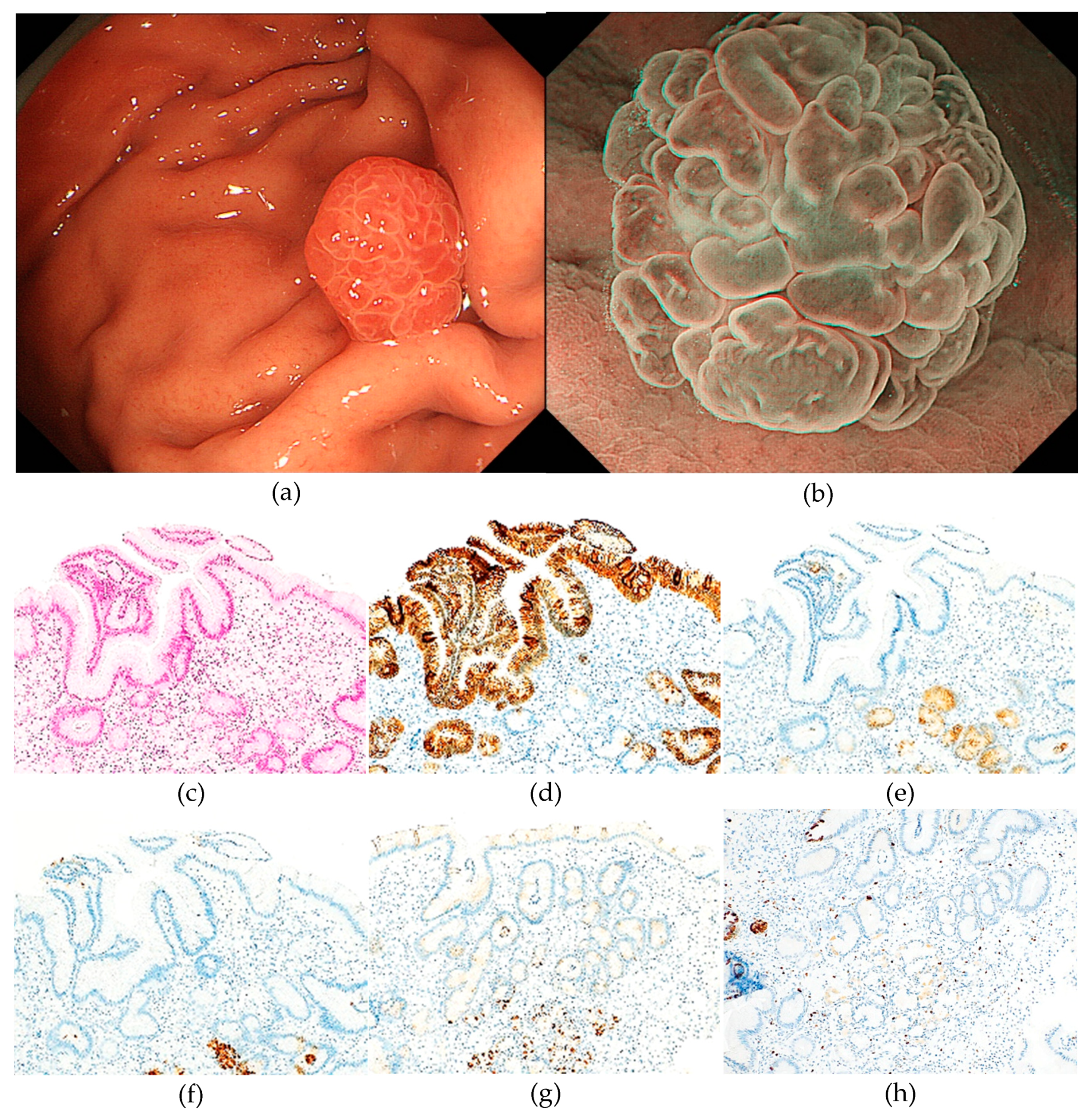
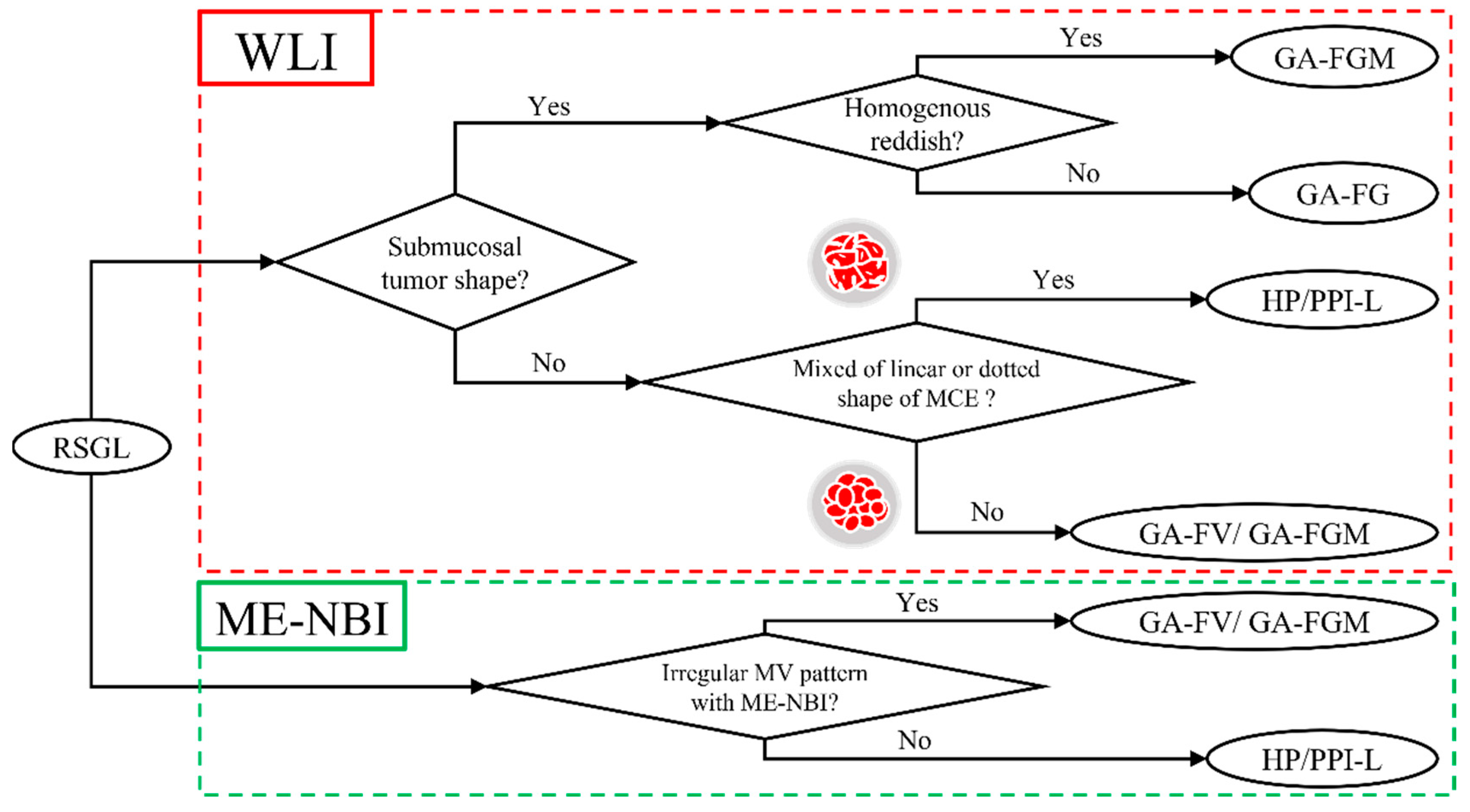
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon, 7-14 June 1994. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 1994, 61, 1–241. [Google Scholar]
- Uemura, N.; Okamoto, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsumura, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamakido, M.; Taniyama, K.; Sasaki, N.; Schlemper, R.J. Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med 2001, 345, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Ito, M.; Takata, S.; Tanaka, S.; Yoshihara, M.; Chayama, K. Low prevalence of Helicobacter pylori-negative gastric cancer among Japanese. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Kato, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ishigaki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Haneda, M.; Mabe, K.; Shimizu, Y. Frequency of Helicobacter pylori -negative gastric cancer and gastric mucosal atrophy in a Japanese endoscopic submucosal dissection series including histological, endoscopic and serological atrophy. Digestion 2012, 86, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, A.; Kaise, M.; Inoshita, N.; Toba, T.; Nomura, K.; Kuribayashi, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Furuhata, T.; Kikuchi, D.; Matsui, A.; et al. Characterization of Helicobacter pylori-Naïve Early Gastric Cancers. Digestion 2018, 98, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, T.; Araki, H.; Saigo, C.; Takada, J.; Kubota, M.; Ibuka, T.; Suzui, N.; Miyazaki, T.; Shimizu, M. Endoscopic and Pathological Characteristics of Helicobacter pylori Infection-Negative Early Gastric Cancer. Dig Dis 2020, 38, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, C.; Hirasawa, K.; Tateishi, Y.; Ozeki, Y.; Sawada, A.; Ikeda, R.; Fukuchi, T.; Nishio, M.; Kobayashi, R.; Makazu, M.; et al. Clinicopathological features of early gastric cancers arising in Helicobacter pylori uninfected patients. World J Gastroenterol 2020, 26, 2618–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, Y.; Baba, Y.; Mukai, K.; Asakawa, H.; Nose, K.; Tsuruga, S.; Tochio, T.; Kumazawa, H.; Tanaka, H.; Matsusaki, S.; et al. Gastric adenocarcinoma coexisting with a reddish semipedunculated polyp arising from Helicobacter pylori-negative normal gastric mucosa: a report of two cases. Clin J Gastroenterol 2018, 11, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibagaki, K.; Fukuyama, C.; Mikami, H.; Izumi, D.; Yamashita, N.; Mishiro, T.; Oshima, N.; Ishimura, N.; Sato, S.; Ishihara, S.; et al. Gastric foveolar-type adenomas endoscopically showing a raspberry-like appearance in the Helicobacter pylori -uninfected stomach. Endosc Int Open 2019, 7, E784–e791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, N.; Ueyama, H.; Ikemura, M.; Uchida, R.; Utsunomiya, H.; Abe, D.; Oki, S.; Suzuki, N.; Ikeda, A.; Akazawa, Y.; et al. Clinicopathological and Endoscopic Features of Raspberry-Shaped Gastric Cancer in Helicobacter pylori-Uninfected Patients. Digestion 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatagai, N.; Ueyama, H.; Iwano, T.; Uchida, R.; Utsunomiya, H.; Abe, D.; Oki, S.; Suzuki, N.; Ikeda, A.; Akazawa, Y.; et al. Raspberry-shaped Gastric Tumor in Patients without Helicobactor pylori Infection. Stomach and Intestine 2022, 57, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, C.; Shibagaki, K.; Mikami, H.; Izumi, D.; Yamashita, N.; Mishiro, T.; Oshima, N.; Ishimura, N.; Sato, S.; Ishihara, S.; et al. Multiple Foveolar-type Adenomas and a Foveolar Hyperplasia in a Patient Not Infected with Helicobacter pylori, Report of a Case. Stomach and Intestine 2019, 54, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Shibagaki, K.; Mishiro, T.; Fukuyama, C.; Takahashi, Y.; Itawaki, A.; Nonomura, S.; Yamashita, N.; Kotani, S.; Mikami, H.; Izumi, D.; et al. Sporadic foveolar-type gastric adenoma with a raspberry-like appearance in Helicobacter pylori-naïve patients. Virchows Arch 2021, 479, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, S.; Montgomery, E.; Vieth, M. Foveolartype adenoma. WHO classification of digestive system tumours. 5th ed 2019, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ueyama, H.; Yao, T.; Akazawa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Kurahara, K.; Oshiro, Y.; Yamada, M.; Oda, I.; Fujioka, S.; Kusumoto, C.; et al. Gastric epithelial neoplasm of fundic-gland mucosa lineage: proposal for a new classification in association with gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland type. J Gastroenterol 2021, 56, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueyama, H.; Yao, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Hirakawa, K.; Oshiro, Y.; Hirahashi, M.; Iwashita, A.; Watanabe, S. Gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic gland type (chief cell predominant type): proposal for a new entity of gastric adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2010, 34, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueyama, H.; Yao, T.; Nagahara, A. A gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic gland type. Stomach and Intestine 2018, 53, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Takemoto, T. An Endoscopic Recognition of the Atrophic Border and its Significance in Chronic Gastritis. Endoscopy 1969, 1, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, K.; Nakamura, A.; Sekine, A. Characteristic endoscopic and magnified endoscopic findings in the normal stomach without Helicobacter pylori infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2002, 17, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Kato, M.; Matsuda, K.; Abiko, S.; Tsuda, M.; Mizushima, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ono, S.; Kudo, T.; Shimizu, Y.; et al. Gastric Hyperplastic Polyps Associated with Proton Pump Inhibitor Use in a Case without a History of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Intern Med 2017, 56, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, K.; Imai, Y.; Fujimori, K.; Arai, S.; Inao, M.; Nakayama, N.; Nagoshi, S.; Ban, S.; Mochida, S. Cases of Gastric Fundic Gland Polyps Increasing in the Size during the Long-term Therapy with Proton Pump Inhibitor. Gastroenterol Endosc 2009, 51, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoi, K.; Yasunaga, Y.; Matsuura, N.; Ikezoe, S.; Morita, K.; Masuda, E.; Yanagawa, K.; Fukushima, J.; Inui, Y.; Kohro, T.; et al. Fundic Gland Polyp with Dysplasia Developed during Long-term Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy, Report of a Case. Stomach and Intestine 2012, 47, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, R.; Akazawa, Y.; Ueyama, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Iwano, T.; Utsunomiya, H.; Oki, S.; Abe, D.; Suzuki, N.; Ikeda, A.; et al. Fundic Gland Polyp with Gastric-type Adenoma during Long-term Proton Pump Inhibitor Administration, Report of a Case. Stomach and Intestine 2022, 57, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Anagnostopoulos, G.K.; Ragunath, K. Magnifying endoscopy for diagnosing and delineating early gastric cancer. Endoscopy 2009, 41, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, M.; Yao, K.; Kaise, M.; Kato, M.; Uedo, N.; Yagi, K.; Tajiri, H. Magnifying endoscopy simple diagnostic algorithm for early gastric cancer (MESDA-G). Dig Endosc 2016, 28, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueyama, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Nagahara, A.; Hayashi, T.; Yao, T.; Watanabe, S. Gastric adenocarcinoma of the fundic gland type (chief cell predominant type). Endoscopy 2014, 46, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Yao, K.; Tanabe, H.; Nimura, S.; Kanemitsu, T.; Miyaoka, M.; Ohtsu, K.; Ueki, T.; Kinjo, K.; Ota, A.; et al. Characteristic Endoscopic Findings and Clinical Pathology Associated with Gastric Adenocarcinoma of Fundic Gland Mucosa Type in Patients without H. pylori Infection. Stomach and Intestine 2020, 55, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Yao, K.; Nimura, S.; Tanabe, H.; Kanemitsu, T.; Miyaoka, M.; Ono, Y.; Ueki, T.; Iwashita, A. Characteristic endoscopic findings of gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland mucosa type. Gastric Cancer 2021, 24, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ueyama, H.; Yao, T.; Iwano, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Utsunomiya, H.; Uchida, R.; Abe, D.; Oki, S.; Suzuki, N.; et al. Endoscopic Features of Gastric Epithelial Neoplasm of Fundic Gland Mucosa Lineage. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, S.; Ali, R.; Bateman, A.C.; Dasgupta, K.; Deshpande, V.; Driman, D.K.; Gibbons, D.; Grin, A.; Hafezi-Bakhtiari, S.; Sheahan, K.; et al. Gastric foveolar dysplasia: a survey of reporting habits and diagnostic criteria. Pathology 2017, 49, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishiro, T.; Shibagaki, K.; Fukuyama, C.; Kataoka, M.; Notsu, T.; Yamashita, N.; Oka, A.; Nagase, M.; Araki, A.; Kawashima, K.; et al. KLF4 Mutation Shapes Pathologic Characteristics of Foveolar-Type Gastric Adenoma in Helicobacter pylori-Naive Patients. Am J Pathol 2022, 192, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| RSGC | RSBGL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-FV | GA-FG | GA-FGM | HP | PPI-L | |
| Patients (n = 54) | n = 36 | n = 2 | n = 4 | n = 12 | n = 4 |
| Age (mean), years (range) | 56.1 (29–81) | 65.5 (51–80) | 51.3 (40–63) | 65.5 (46–76) | 67.8 (54–81) |
| Sex (male/female) | 27/9 | 0/2 | 2/2 | 6/6 | 2/2 |
| PPI administration (+/-) | 9/27 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 4/8 | 4/0 |
| Smoking history (+/-) | 22/14 | 1/1 | 2/2 | 6/6 | 1/3 |
| Alcoholic history (+/-) | 13/23 | 1/1 | 1/3 | 3/9 | 0/4 |
| Survival periods (mean), months (range) | 26.2 (1–141) | 77.0 (45–109) | 24.3 (1–76) | NA | NA |
| Outcome | One death due to another disease | All alive NED | All alive NED | NA | NA |
| Lesions (n = 65) | n = 43 | n = 2 | n = 4 | n = 12 | n = 4 |
| Endoscopic findings | |||||
| Location (U/M/L) | 27/16/0 | 2/0/0 | 4/0/0 | 7/4/1 | 1/1/2 |
| (GC/LC/Ant/Post) | 42/0/0/1 | 2/0/0/0 | 0/0/2/2 | 7/5/0/0 | 2/2/0/0 |
| Size (average), mm | 3.3 (2–6) | 8.5 (5–12) | 8.0 (4–15) | 4.8 (1–15) | 8.5 (3–20) |
| Therapy method (biopsy/CFP/EMR/ESD) | 5/18/20/0 | 0/0/0/2 | 0/0/1/3 | 4/6/2/0 | 2/1/1/0 |
| Pathological findings | |||||
| Invasion depth (M/SM) | 43/0 | 0/2 | 1/3 | NA | NA |
| Distance of SM invasion (average), μm (range) | NA | 250 (200–300) | 433 (300–700) | NA | NA |
| Lymphatic invasion (+/-) | 0/43 | 0/2 | 0/4 | NA | NA |
| Venous invasion (+/-) | 0/43 | 0/2 | 0/4 | NA | NA |
| Lateral margin (+/-) | 0/43 | 0/2 | 0/4 | NA | NA |
| Vertical margin (+/-) | 0/43 | 0/2 | 0/4 | NA | NA |
| Foveolar hyperplasia around tumor (+/-) | 41/0 | 0/2 | 3/1 | NA | NA |
| Covered or mixed non-neoplastic epithelium (+/-) | 13/28 | 2/0 | 1/3 | NA | NA |
| RSGC, raspberry-shaped gastric cancer; RSBGL, raspberry-shaped benign gastric lesion; GA-FV, gastric adenocarcinoma of foveolar type; GA-FG, gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland type; GA-FGM, gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland mucosa type; HP, hyperplastic polyp; PPI-L, proton pump inhibitor-related lesion; U, upper third; M, middle third; L, lower third; GC, greater curvature; LC, lesser curvature; Ant, anterior wall; Post, posterior wall; CFP, cold forceps polypectomy; EMR, endoscopic mucosal resection; ESD, endoscopic submucosal dissection; M, mucosal layer; SM, submucosal layer; NA, not assessed; NED, no evidence of disease. | |||||
| RSGC | RSBGL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-FV | GA-FG | GA-FGM | HP | PPI-L | |
| Lesions | n = 40 | n = 2 | n = 4 | n = 9 | n = 4 |
| MUC5AC (+/-) | 40/0 | 0/2 | 4/0 | 9/0 | 4/0 |
| MUC6 (+/-) | 0/40 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 9/0 | 3/1 |
| MUC2 (+/-) | 0/40 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 0/9 | 0/4 |
| CD10 (+/-) | 0/40 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 0/9 | 0/4 |
| Gastric phenotype (+/-) | 40/0 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 9/0 | 4/0 |
| pepsinogen-Ⅰ (+/-) | 0/40 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 4/5 | 4/0 |
| H+/K+-ATPase (+/-) | 0/40 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 3/6 | 4/0 |
| Ki-67 MIB-1 labeling index (%) (mean) | 42.8 | 15.0 | 22.5 | NA | NA |
| (range) | 5-80 | 10-20 | 10-30 | NA | NA |
| p53 over expression (+/-) | 0/40 | 0/2 | 0/4 | NA | NA |
| RSGC, raspberry-shaped gastric cancer; RSBGL, raspberry-shaped benign gastric lesion; GA-FV, gastric adenocarcinoma of foveolar type; GA-FG, gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland type; GA-FGM, gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland mucosa type; HP, hyperplastic polyp; PPI-L, proton pump inhibitor-related lesion | |||||
| RSGC | RSBGL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-FV | GA-FG | GA-FGM | HP | PPI-L | |
| WLI | n = 43 | n = 2 | n = 4 | n = 12 | n = 4 |
| Redness (homogenous/heterogeneous) | 41/2 | 0/2 | 3/1 | 11/1 | 4/0 |
| Shape of MCE (polygonal or curved) (+/-) | 43/0 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 12/0 | 4/0 |
| Shape of MCE (linear or dotted) (+/-) | 3/40 | 1/1 | 3/1 | 9/3 | 4/0 |
| Whitish area around tumor (+/-) | 30/13 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 4/8 | 1/3 |
| Submucosal tumor shape (+/-) | 0/43 | 2/0 | 2/2 | 0/12 | 0/4 |
| Multiple white and flat elevated lesions (+/-) | 5/38 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 2/10 | 1/3 |
| Fundic gland polyp (+/-) | 33/10 | 2/0 | 1/3 | 9/3 | 4/0 |
| ME-NBI | n = 33 | n = 2 | n = 4 | n = 11 | n = 3 |
| MESDA-G (cancer/non-cancer) | 30/3 | 1/1 | 3/1 | 0/11 | 0/3 |
| Demarcation line (+/-) | 33/0 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 11/0 | 3/0 |
| Microvascular pattern (irregular/regular/absent) | 30/0/3 | 1/1/0 | 3/0/1 | 0/9/2 | 0/2/1 |
| Microsurface pattern (irregular/regular/absent) | 0/33/0 | 0/2/0 | 0/4/0 | 0/11/0 | 0/3/0 |
| Irregular inner edge shape of MCE (+/-) | 30/3 | 1/1 | 4/0 | 0/11 | 0/3 |
| RSGC, raspberry-shaped gastric cancer; RSBGL, raspberry-shaped benign gastric lesion; GA-FV, gastric adenocarcinoma of foveolar type; GA-FG, gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland type; GA-FGM, gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic-gland mucosa type; HP, hyperplastic polyp; PPI-L, proton pump inhibitor-related lesion; WLI, white-light imaging; ME-NBI, magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging; MESDA-G, magnifying endoscopy simple diagnostic algorithm for early gastric cancer | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





