Introduction
Water contamination has become a serious threat to the public health and environment on planet Earth. In addition to causing immediate health effects such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea, water contamination can have long term effects such as cancer, reproductive problems, and developmental delays [
1,
2]. Among various water pollution resources heavy metals are the most significant owing to the fact that they are toxic even at low concentration and non-biodegradable. Moreover, heavy metals can accumulate in the food chain through plants and fish. Heavy metal containing wastewater is mostly generated by agricultural and industrial activities. Industries such as mineral processing, leather tanneries, textile dyes, petroleum refineries and electroplating often emit large quantity of wastewater exceeding the permissible limit set by World Health Organization (WHO) [
3]. Effective management of heavy metal pollution in water requires a comprehensive approach that involves monitoring, regulation, and prevention measures.
Mercury (Hg) is among one of the top 5 most toxic heavy metals of concern by WHO and its emission to environment from anthropogenic sources was estimated to be 2200 tons in 2015 [
4]. Anthropogenic sources include, fossil fuel burning (24% specifically coal), iron and steel industry, cement production, metal smelting and chlor-alkali industry and waste disposal. [
5] Mercury ion (Hg
+2) is significantly toxic and can cause damage to kidneys and lungs while methylmercury (organic form) consumption can result in serious brain dysfunction issues. As its non-biodegradable, the only solution to mercury pollution problem is its removal or immobilization in the environment.
Mercury eradication from wastewater can be achieved via numerous techniques including ion-exchange, membrane separation, electrochemical treatment, chemical precipitation, adsorption, coagulation, flocculation, and membrane separation. [
6,
7] Despite the availability of variety of methods/techniques to remove mercury and other heavy metals from water, majority of these techniques cannot be used on a commercial scale due to their high cost, production of harmful sludge, and low efficiency.[
8] Adsorption, however, offers many advantages such as its excellent removal efficiency, low cost, abundantly available raw materials, flexibility, and low energy consumption. [
8] Therefore, lots of research has been done in this regard and a wide range of materials, including but not limited to clay, biomass, carbon-based adsorbents, and functionalized silica, have been tested for their adsorption capabilities. [
9,
10] Nonetheless, there are certain limitations that need to be eliminated if adsorption must be applied on industrial scale for efficient wastewater treatment; for instance, the adsorbents which have highest efficiency are either expensive (activated carbon) or have low uptake efficiency when manufactured from abundantly available cheap sources (biosorbents). [
5] This results in an increased demand to develop low cost adsorbents with high removal efficiency that are not only able to eradicate ionic mercury Hg(II) but also can be employed on large scale for the removal of other commonly encountered mercury forms such as organomercury, liquid mercury, inorganic mercury complexed with organic ligands and mercury vapours. [
11]
These efforts to develop a general sorbent that can not only handle various forms of mercury with high removal efficiency but is also made of abundantly available raw materials have been going on for some time. [
12] Elemental sulfur is one such raw material that is produced in excess of 50 million tons per year as a by-product of petroleum processing industry. [
13] And this amount is increasing as more and more sulfur rich crude oil is now being processed to meet the energy needs of the entire World. Though sulfur has the ability to capture and subsequently stabilize mercury,[
14] it has some practical constraints like its flammability, inability to mix effectively with wastewater for mercury removal in batch processing, and caking tendency which could result in high hydraulic pressure drop during filtration. Additionally, it poses a threat to the environment by producing methylmercury which is a highly toxic chemical, and it is formed when sulfur is reduced to sulfate by sulfate-reducing bacteria in the soil and sediments.[
15]
Recently, much attention has been paid to sulfur polymers synthesized by inverse vulcanization due to many merits of inverse vulcanization process which align with greener chemistry approach such as no solvent requirement, flexibility in terms of organic monomer choice and minimum by-products. Inverse vulcanized sulfur polymers contain 50-80% sulfur which are synthesized by reacting elemental sulfur and organic monomers. [
16] The process is instigated by high temperature (>159
oC) ring opening of S
8 (homolytic scission of S-S bond) generating thiyl diradical which subsequently reacts with either S to form polysulfide or form C-S bond with unsaturated organic molecules forming polymeric sulfur. The major difference between inverse vulcanization and vulcanization process is the sulfur content and its role. In classic vulcanization process sulfur acts as crosslinker with making up only 1-3% of vulcanized rubber. [
17] While in inverse vulcanization an unsaturated organic compound in small quantity acts as crosslinker to form polysulfide polymers with sulfur content ranging from 50-80%. These sulfur polymers are promising way to make use of abundantly produced petroleum industry waste product in varied application areas such as energy storage LiS batteries, water purification, controlled fertilizer release, nanotechnology and adhesive material [
18,
19].
Polysulfides (PS) have great tendency to remove Hg
+2 from wastewater due to their high sulfur content and according to soft acid-base theory sulfur as soft base has reasonable affinity for soft acid Hg
+2. As discussed, polysulfides can be synthesized from inverse vulcanization process by using various co-monomers like waste cooking oil, limonene [
20], diisopropyl benzene (DIB) [
21], dicyclopentadiene [
22], and myrcene [
23]. However, despite their high S content all these polysulfides (PS) demonstrated poor Hg
+2 remediation capability hence can’t be considered for practical applications. Such outcomes require further inspection of the parameters and properties of PS to warrant practical applications. The use of organic comonomer in inverse vulcanization rendered PS hydrophobic and hence low dispersibility in aqueous media (no hydrogen bond formation).[
24] Hg
+2 ions cannot reach the binding sites due to low wettability which leads to low adsorption capacity of PS. This implies that only high sulfur contents are not enough to guarantee good adsorption affinity, the metal and PS polymer surface interaction also plays critical role. [
25]
To overcome this challenge hydrophilic PS can be developed by utilizing monomers rich in oxygen containing functional groups (-OH, -C=O, -COOH) in inverse vulcanization process. The comonomers that can be employed should have boiling point in the melting range of sulfur. Methacrylic acid is one such acid which is an organic acid soluble in both water and most organic solvents with boiling point of 161
oC. In a recent study, hydrophilic PS was prepared by using methacrylic acid (PS-MA) and then blended with polyacrylonitrile (PAN) to form a fibrous composite whose adsorption characteristics were studied for Hg
+2 removal. [
26]
In study we have prepared a Polysulfide-methacrylic acid polymer (Poly(S_MA)) by inverse vulcanization process which was further impregnated with amine to introduce more functional groups on polymer surface which can adsorb Hg+2. Previously no work has been done in this specific category and this type of polymer is being employed first time for Hg+2 remediation to the best for our knowledge. Due to lack of fundamental literature on Poly (S_MA), a comprehensive characterization study was carried out to understand the binding mechanism. The adsorption performance of Poly(S-MA) was thoroughly evaluated in terms of kinetics, capacity and thermodynamics. -
Experimental
Materials
Elemental sulfur (assay 99.9%) and Methacrylic acid were procured from PC laboratory reagents, Malaysia and Merck, Malaysia, respectively. Polyethylenime (PEI) and ethanol was purchased from Sigma Aldrich, USA.
Synthesis of Poly(S-MA)
To produce poly(S-MA), 4 g of sulfur and 8 g of sodium chloride were heated at 180
oC in a 30 ml glass vial using thermoset oil bath to initiate the ring opening process of the sulfur under continuous stirring [
27,
28,
29]. After the which 4 g of methacrylic acid were added in the mixture in a dropwise manner to avoid sudden temperature drop and left the mixture to react for 1 hour. After 1 hour the polymer obtained was removed from glass vial and placed in a conical flask containing 200 ml deionized water and shaken for 48 h at room temperature at speed of 220 rpm to remove sodium chloride from polymer to generate pores followed by overnight drying of the polymer using oven. After which dried was grounded using mortar and pestle. The obtained powdered polymer was used for further experimentation.
Amination of Poly(S-MA)
For amine impregnation, firstly a 50/50 vol% polyethyleneimine and ethanol mixture was prepared. Then poly(S-MA) was placed in an amine solution following by continuous shaking for 24 h. After this, the excess liquid was removed from the mixture and the obtained solid material was used as adsorbent.
Characterization of Poly(S-MA) and Amine@Poly(S-MA)
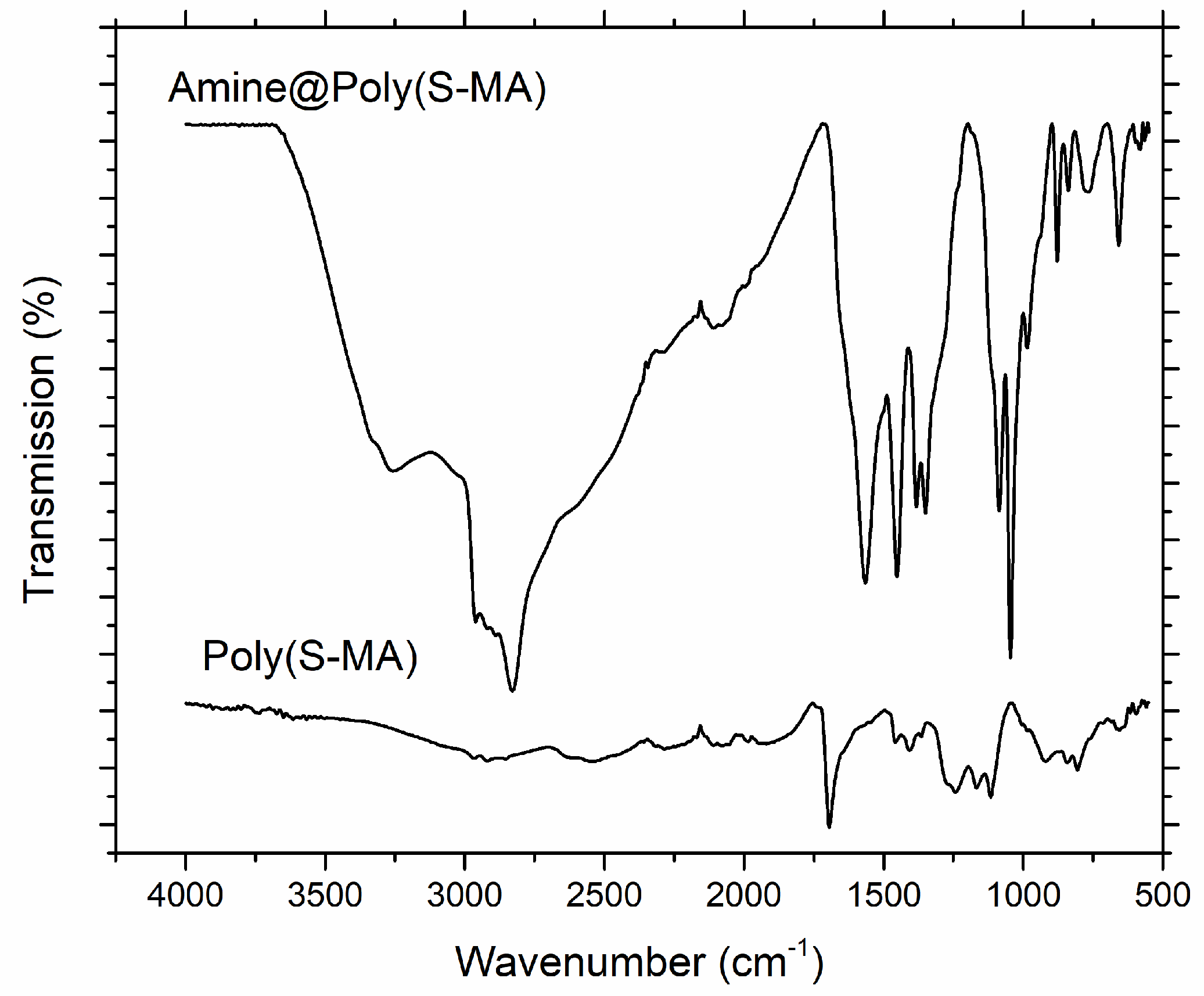
PerkinElmer Frontier Spectrometer was used investigate and compare the chemical composition of poly(S-MA) and amine@poly(S-MA) using attenuated total reflectance (ATR) with 4 cm-1 resolution, 8 scan frequency and 4000-500 cm-1 range.
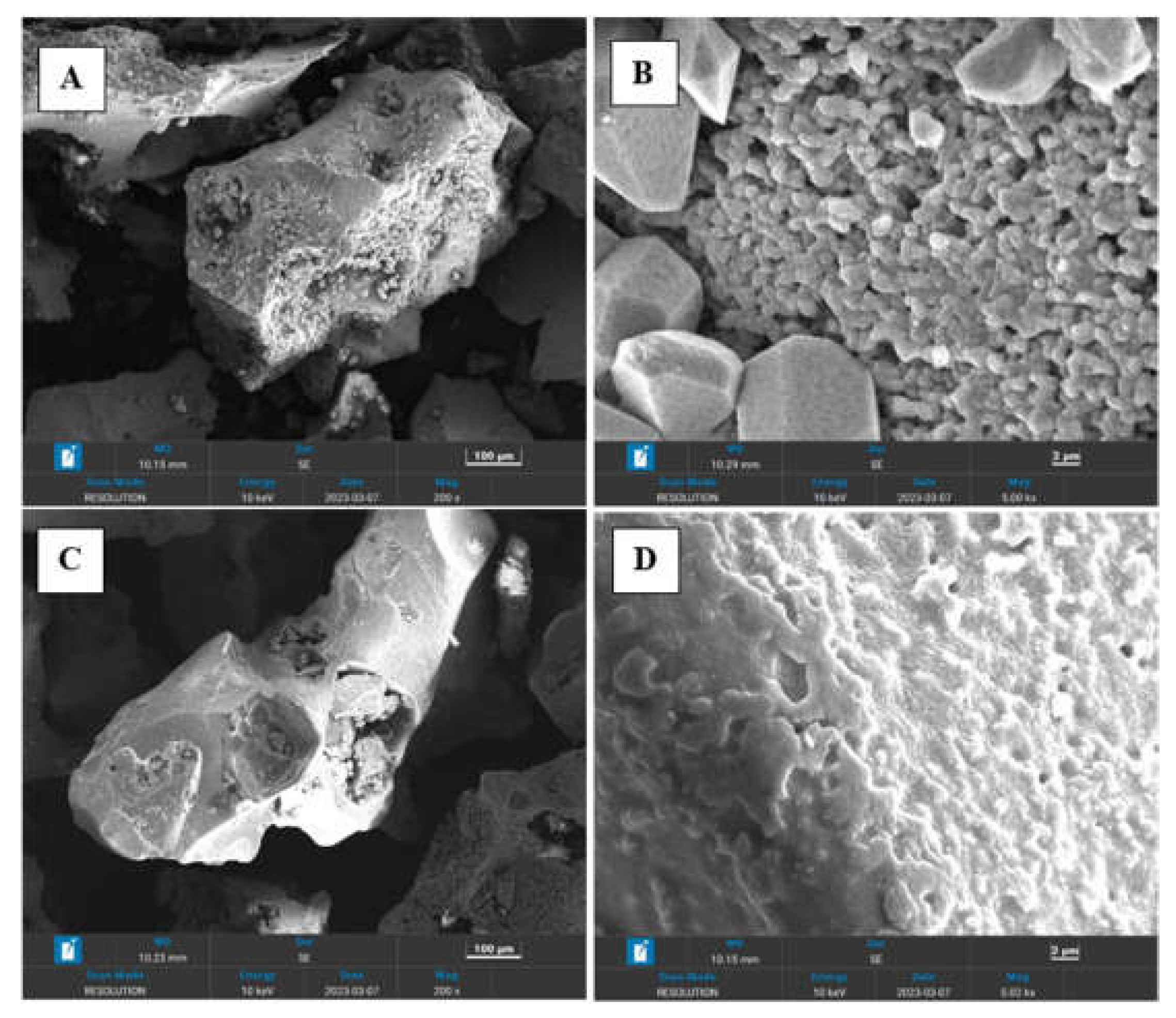
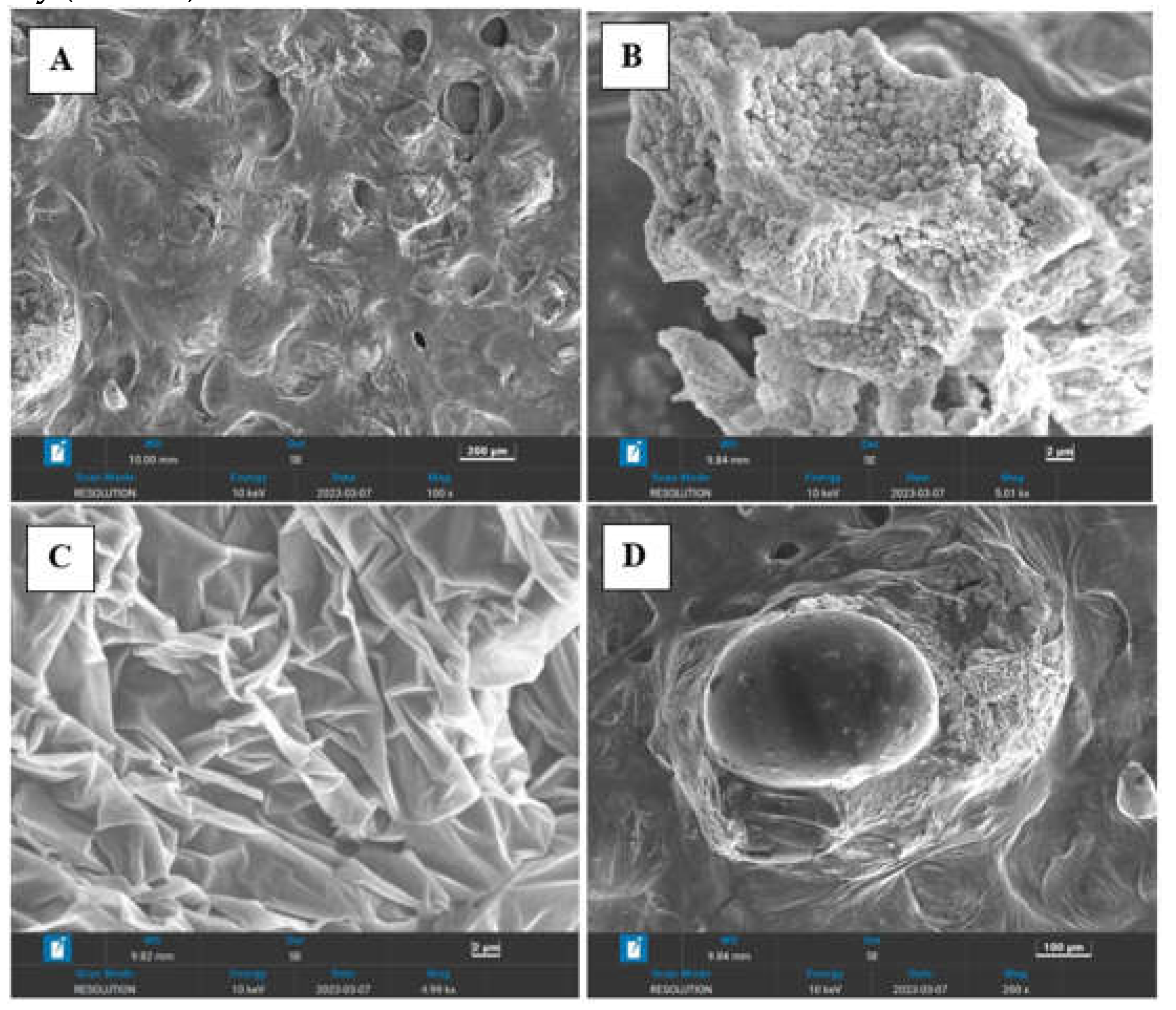
Morphology of the both copolymers was investigated using Zeiss SUPRA 55VP microscope equipped with INCAx-act EDX oxford spectroscope.
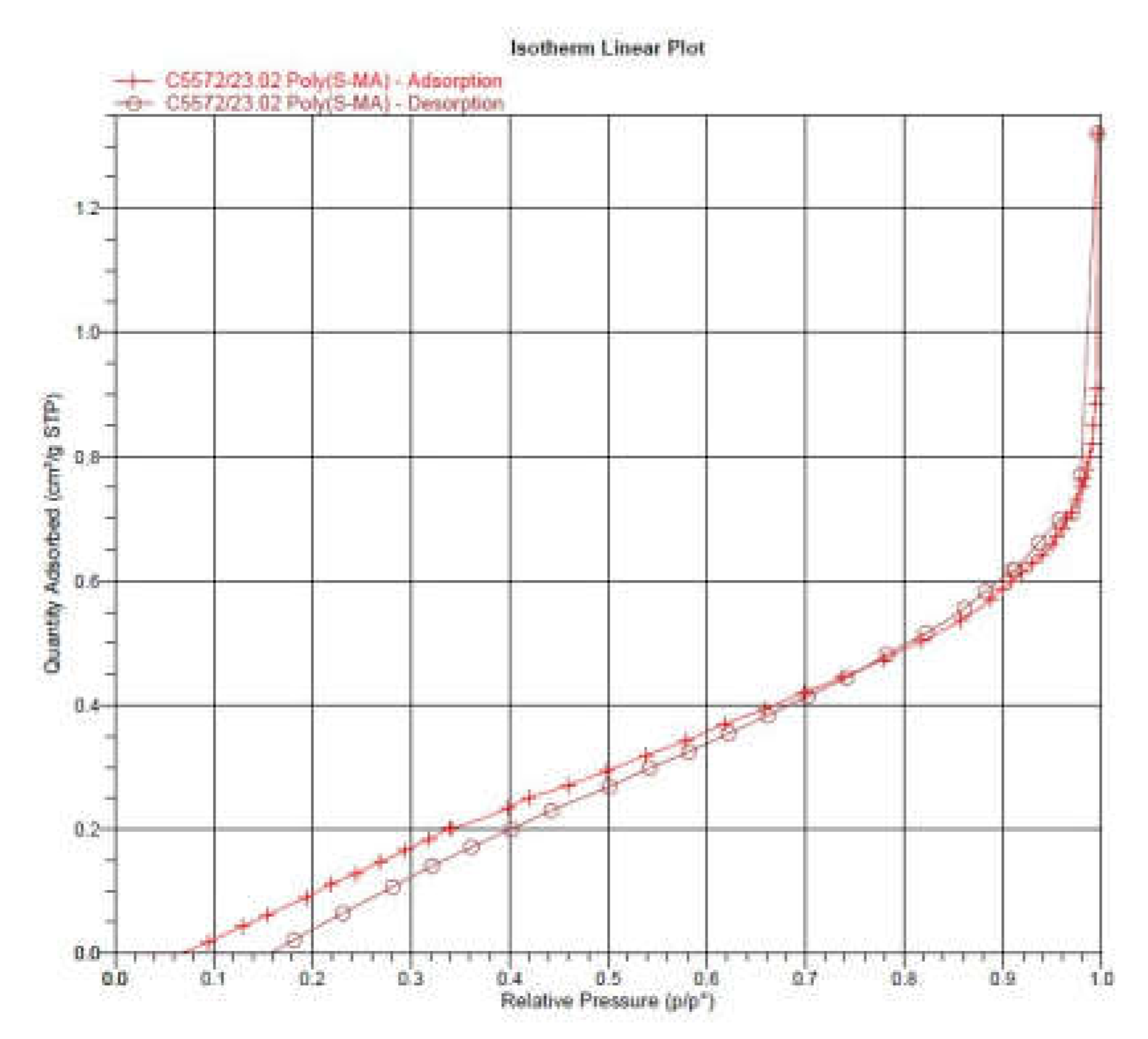
The specific surface area of poly(S-MA) and amine@poly(S-MA) was evaluated using Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms. Isotherms were obtained using Micrometrics Instruments ASAP 2020 at -196 oC. Before surface area analysis the samples were degassed at 60 oC for 6 h. BJH method was also employed to investigate the pore volume and size/dimensions.
Batch Mercury Adsorption Tests
A 1000 ppm mercury chloride stock solution was prepared by dissolving mercury chloride in 1 L of distilled. Later this solution was used to prepare various known concentrated solution accordingly for experiments.
Adsorption test was carried by placing 0.05 g of copolymer in a 50 ml of mercury contaminated water with an initial concentration of 50 ppm in a 250 ml conical flask. The mixture was then placing in incubator shaker for desired time at 220 rpm speed, pH=6 and room temperature. The pH of the mercury solution in all experiments was maintained at 6 as the maximum adsorption capacity was achieved at this pH in our preliminary experiments. After the desired time the mixture was removed from shaker and the treated solution was then analysed. Cold Vapor-Atomic Absorption method was utilized to evaluate the mercury concentration of water samples using calibration curve method. The calibration curve for mercury was first obtained using Agilent model 65 CV-AA using conventional hollow cathode lamp. The empirical equation yielded from calibration curve was then used to calculate the mercury concentration by measuring light absorbance using CV-AA of the treated solution.
Removal efficiency and mercury adsorption capacity of the developed copolymer can be calculated using Eq. (1) and Eq. (2)
In which initial and equilibrium mercury concentration are represented by Co (mg/l) and Ce (mg/l) in each solution, respectively. W (g) and V (l) are weight of dry adsorbent and volume of the solution, respectively.
Equilibrium Isotherms and Kinetics
Equilibrium Isotherms
To investigate the equilibrium isotherm of the mercury adsorption using amine functionalized copolymer, batch adsorption experiments were conducted at different initial mercury concentration keeping other parameters fixed. To carried out this, 0.05 g of amine@poly(S-MA) was placed in a 50 ml of mercury solution with different initial concentration (i.e., 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50) in a 250 ml conical flask and the pH was maintained at 6. The solution stirred at 220 rpm for 3 h at room temperature using incubator shaker. The remaining mercury concentration was measured using CV-AA.
Three well known isotherm adsorption models including Langmuir, Freundlich and Redlich-Peterson (in their non-linear form) were fitted to the obtained adsorption data from varying initial concentration to investigate the adsorption nature of amine@poly(S-MA).
Langmuir isotherm Eq. (3) represents Langmuir isotherm model. This isotherm explains the monolayer adsorption without lateral interactions assuming the homogenous flat surface of the adsorbent with identical binding sites and adsorbates behaves ideally.
Where qe (mg/g) and Ce (mg/l) are mercury concentration and adsorption capacity at equilibrium, respectively. QL (maximum adsorption capacity, mg/g) and KL (mass transfer coefficient, l/mg) are Langmuir adsorption constants.
Freundlich isotherm Eq. (4) depicts Freundlich isotherm model which explains multilayer adsorption unlike Langmuir isotherm on heterogenous adsorbent surface with non-uniform adsorption heat.
Where qe (mg/g) and Ce (mg/l) are mercury concentration and adsorption capacity at equilibrium, respectively. KF (mg/g) (l/mg)(1/n) is adsorption constant whereas n is heterogeneity factor showing the intensity of adsorption.
Redlich-Peterson isotherm Eq. (5) shows Redlich-Peterson isotherm model which is appropriate for all types of surfaces either heterogenous or homogenous as it explains the features of both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm.
Where qe (mg/g) and Ce (mg/l) are mercury concentration and adsorption capacity at equilibrium, respectively. AR ( l/mg) and KR (l/g) are model constants whereas g is exponential factor.
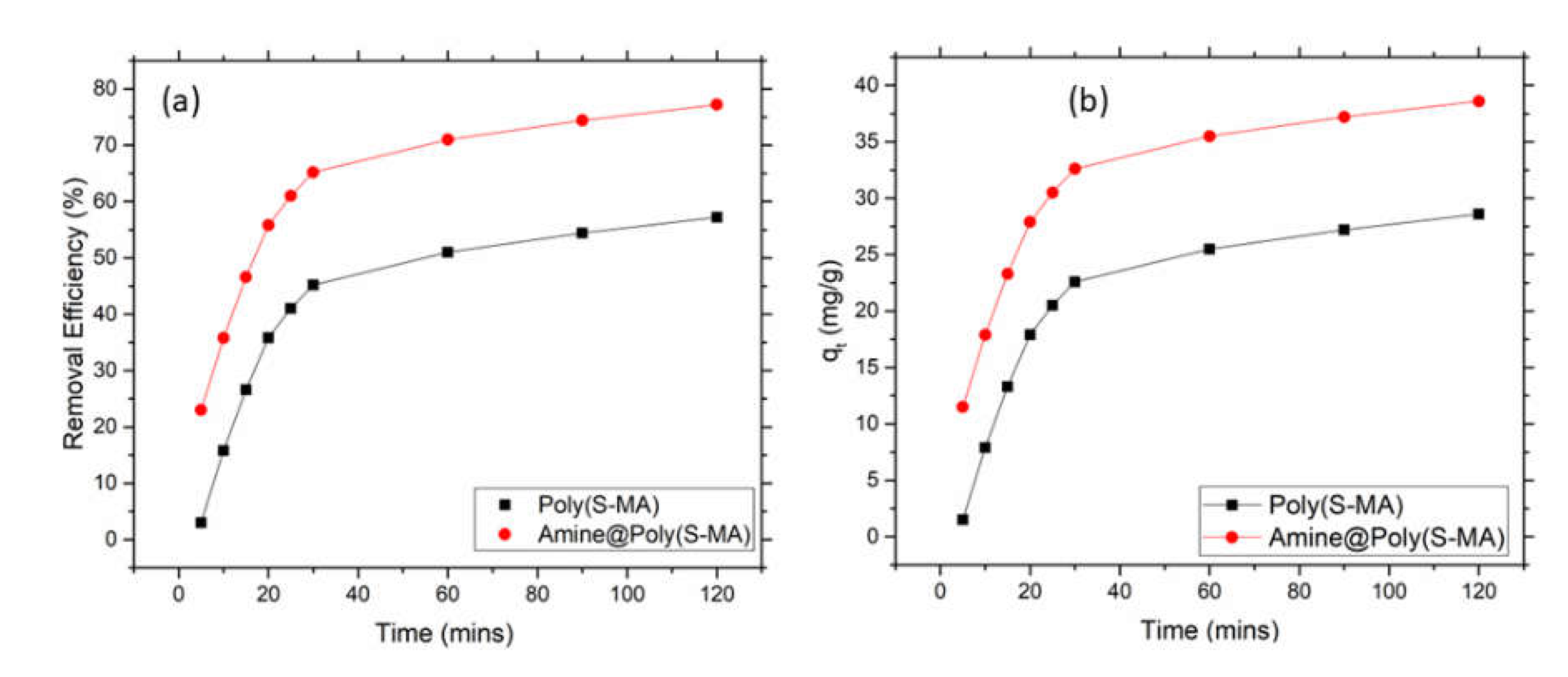
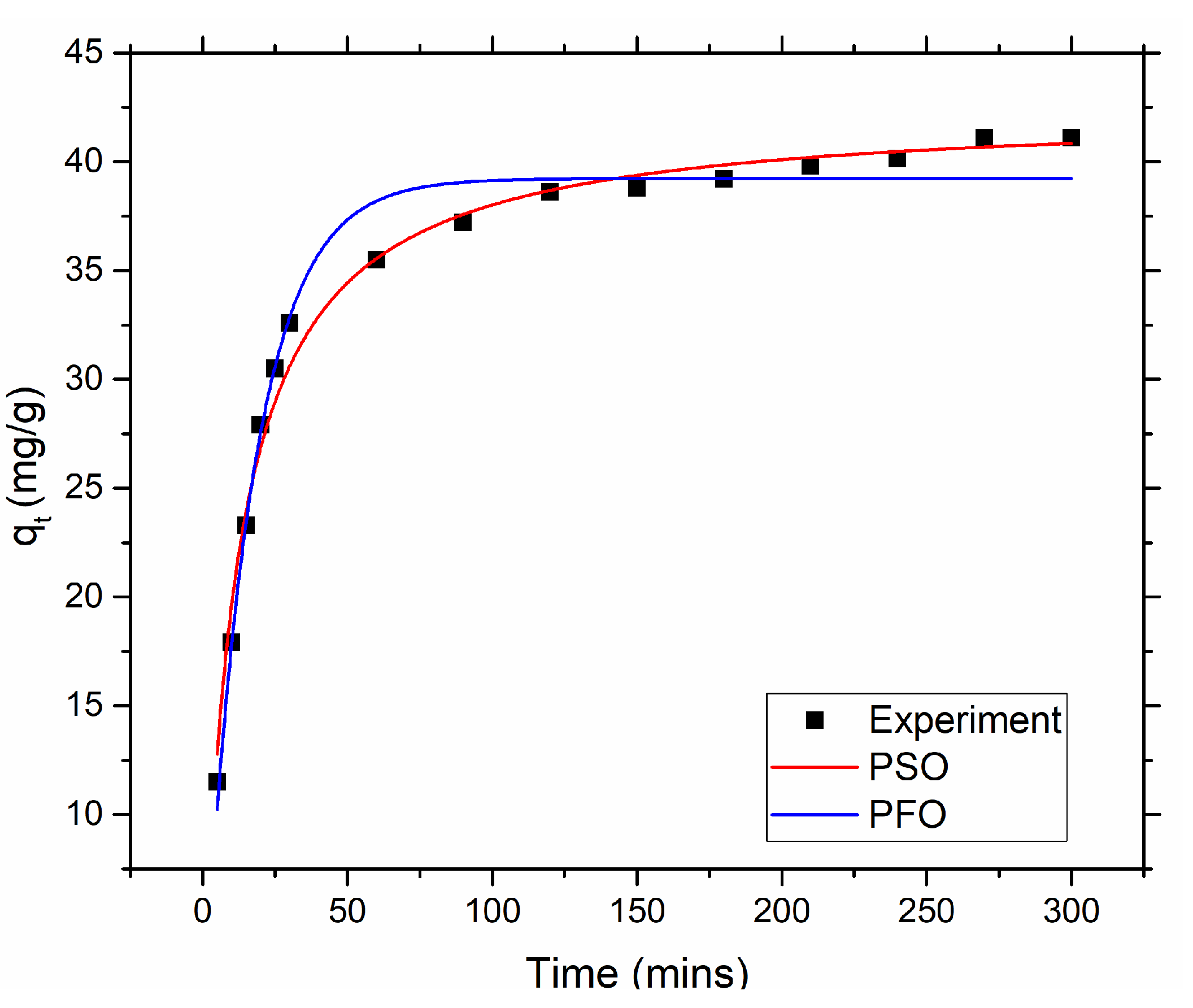
Kinetics of Mercury Adsorption
To investigate the kinetics of mercury adsorption, batch adsorption test was carried out with 50 ppm initial mercury concentration and different adsorption time while fixing other parameters. To carried out this, 0.05 g of amine@poly(S-MA) was placed in a 50 ml of mercury solution with 50 ppm initial concentration in a 250 ml conical flask and the pH was maintained at 6. The solution stirred at 220 rpm for specific time ranging from 5 to 300 mins at room temperature using incubator shaker. The remaining mercury concentration was measured using CV-AA. Non-linear form of pseudo first and second order kinetic models were fitted the obtained adsorption kinetic data. In almost every case either one of model can explain the adsorption kinetics.
Pseudo first order (PFO) Eq. (6) depicts the pseudo first order kinetic model which assumes that physisorption dominates the chemisorption and rate of adsorption increases with the increase of number of vacant active sites.
Where qt is the amount of mercury adsorbed at t time, qe (mg/g) is mercury adsorption capacity at equilibrium, and K1 (1/min) is the rate constant.
Pseudo second order (PSO) Eq. (7) shows pseudo second order model which assumes chemical absorption dominated physisorption and rate of adsorption is directly proportional to the square of number of vacant active sites.
Where qt is the amount of mercury adsorbed at t time, qe (mg/g) is mercury adsorption capacity at equilibrium, and K1 (1/min) is the rate constant.
Equilibrium Isotherm of Mercury Adsorption
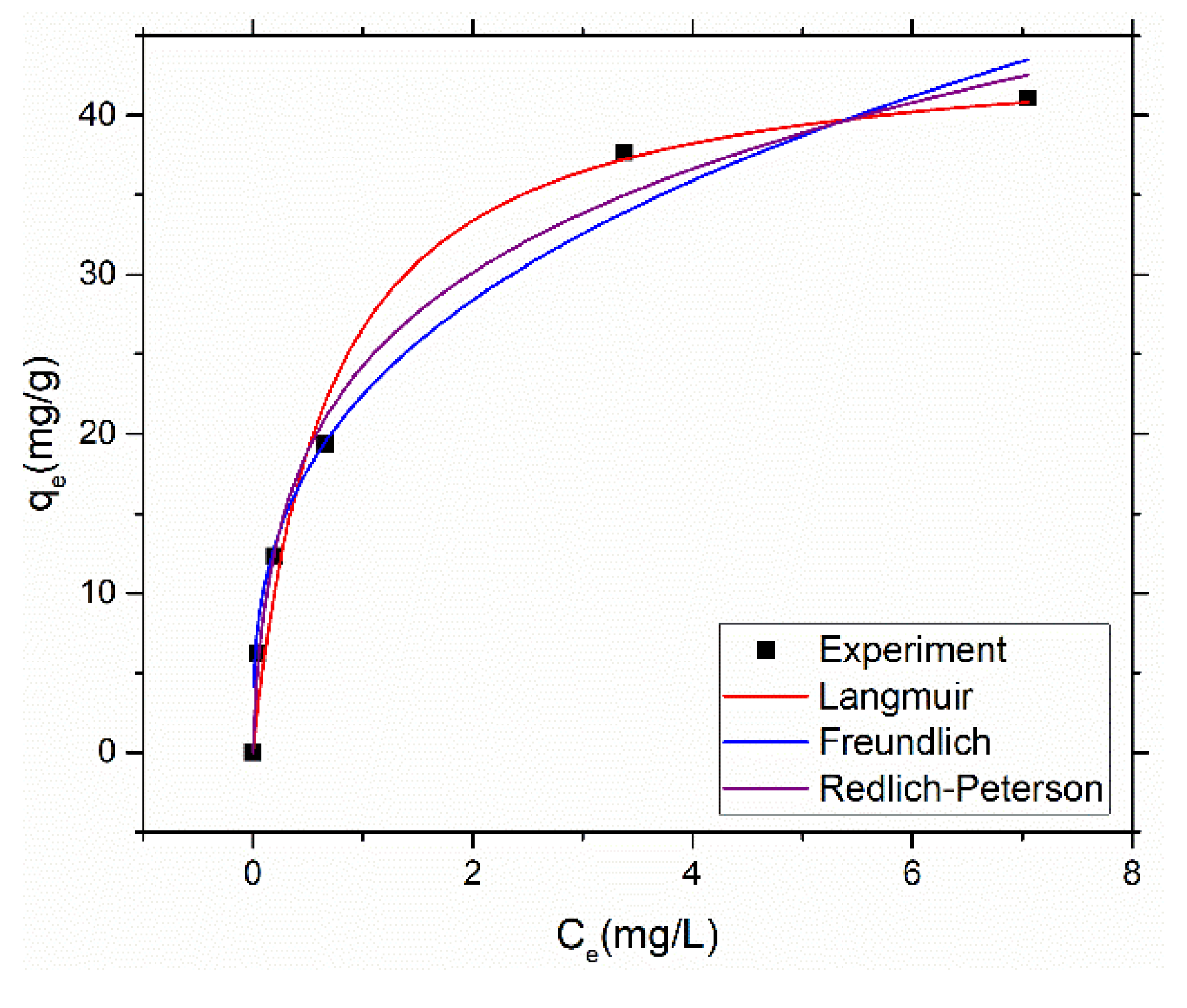
Mercury adsorption data with initial mercury concentration ranging from 10 to 50 ppm while keeping other parameters constant as explained early was fitted to Langmuir, Freundlich and Redlich-Peterson isotherm model to understand the nature of adsorption.
Figure 6 shows the plotted isotherms for mercury adsorption using above stated models.
Table 3 presents the coefficient of determination and other model parameters obtained by non-linear regression of the adsorption data using the above three models.
High R2 values of 0.976, 0.982 and 0.99 for Freundlich, Langmuir and Redlich-Peterson, respectively shows that all three models are capable of describing the adsorption data. Nevertheless, Redlich-Peterson has shown highest value which demonstrates that the adsorption data have characteristics of both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. In simple words, the adsorption of mercury on amine@poly(S-MA) obeys the principle of both monolayer (adsorption on homogenous surface) and multilayer (adsorption on heterogenous surface). The value of isotherm exponent of Redlich-Peterson model is 0.76 which shows that it deviates from Langmuir model.
The maximum adsorption capacity (monolayer) of the amine@poly(S-MA) is 44.7 mg/g estimated using Langmuir model which is far better as compared to other inverse vulcanized copolymer utilized as mercury adsorbent.