1. Introduction
Mobile robots and autonomous driving both require accurate and reliable state estimation. It is challenging for traditional GNSS/INS to achieve high accuracy localization requirements in indoor and urban environments.
In recent years, some developments have been made in both visual and LiDAR SLAM. Due to the wide field of view and detailed texture information that cameras provide, vision-base slam can estimate a 6-DOF(six-degree of freedom) state. However, it is easily affected by lighting shifts, low texture and repetitive texture environments [1,2]. Compared to cameras, LiDAR has more direct, accurate and reliable depth information for SLAM systems, allowing for robust state estimation even in challenging environments [3].
1.1. Localization and Mapping Based on LiDAR and Inertial
The most widely used SLAM technique in urban areas is a localization and mapping algorithm based on LiDAR [4]. Because lidar can accurately estimate the depth of the point cloud. We can categorize these investigations using representations of LiDAR measurements as a basis. The widely used and basic method ICP (Iterative Closest Point Approach) [5] uses LiDAR point clouds directly. Recent studies have proposed a variety of representations such as grid cells, features of LiDAR pointclouds and surface elements. The primary distinction between these algorithms is matching search. In particular, to increase computational efficiency, variations of ICP approaches match associated points using downsampled points and various data structures like kd-trees, ikd-trees, incremental voxels, and projection depth maps [6–8]. The use of projection geometry for nearest neighbor search was proposed in [7,9]. SuMa [9], a powerful 3D LiDAR based SLAM system that employs a shader language for parallel processing, is proposed by Behley et al. Using the input point clouds, they execute spherical image projection and correlate it, treating these points as the closest points. In addition, this paper indicates that motion drift can be greatly decreased through surface element-based map creation and matching. Deep learning in recent years has made significant advancements. Many scholars have developed approaches based on deep learning [10,11] for LiDAR motion estimation using projected LiDAR features.
Zhang et al. [12] propose LiDAR odometry and mapping (LOAM), which is a LiDAR slam solution based on LiDAR featrues. Instead of using complete pointclouds in ICP, planar and edge point features are matched in LOAM to provide real-time and low-drift state estimation.t consists of the odometry system and the mapping system. The odometry module performs point to edge/plane matching method at high frequency, and the mapping module runs at lower frequency to perform scan to map matching which can get more precise pose estimations. During the nearest-neighbor search in the former module, kd-trees are built for each feature set from each LiDAR scan. In the mapping module, it uses these LiDAR features to construct a global map and optimize poses further. In the KITTI odometry benchmark site, LOAM have achieved the best performance and placed first [13]. In order to further enhance performance, numerous LiDAR slam frameworks based on LOAM have been proposed. F-LOAM [14] uses a non-iterative two-stage distortion compensation approach to boost the system’s real-time perfoemance and compute efficiently. Nevertheless, there is still no sub-module for global optimization, such as a loop detection strategy. It will lead to significant cumulative errors over long periods of time in large-scale environments. HDL SLAM [15] is a multi-sensor fusion framework that can combine LiDAR, imu and GNSS sensors, however the reliability of the frame to frame registration is low because it is based on the NDT algorithm. LeGo-LOAM [16] extracts two types of points in the feature extraction module: ground and non-ground points. It significantly improves feature registration efficiency. Then, the LiDAR mapping module receives its initial value via two-step registration. Moreover, a keyframe selection strategy and loopback detection method are added to the backend for better global localization consistency and real-time performance. However, because of the loose coupling of IMU and lidar, running in a wide range of scenarios still leads to large cumulative errors. Liu et al. [17] proposes a feature extraction method and computed descriptors based on deep learning. It also uses two-stage state estimation and experiments in a long-range environment. Ye et al. [18] proposed a tightly coupled LiDAR SLAM algorithm, LIO-Mapping, built on VINS and LOAM. For feature extraction and state estimation, a LiDAR front-end component in LOAM takes the role of the visual front-end component in VINS-Mono. Unfortunately, due to the size of the optimization issue, real-time execution on an unmanned vehicle is challenging. LiLi-OM [19] presents an adaptive key frame selection strategy that can be used for solid state LiDAR and conventional LiDAR. In addition, it introduces a method with metric weights in sensor fusion. To further increase processing speed and trajectory accuracy, LIO-SAM [20] proposes a tightly-coupled LiDAR-inertial odometry system based on the framework iSAM2(incremental smoothing and mapping) [21]. The factor graph optimization can also incorporate GPS and loop closure factors. An algorithm for loosely coupled adaptive covariance estimation is proposed by Zhang et al. [22]. Better experimental results are achieved compared to the LIO system with a tightly coupled framework. Liu et al. [3] propose a feature extraction algorithm to extract rod-shaped and planar features, which reduces computational consumption and improves the accuracy of the LIO.
In addition to optimization-based LIO systems, filter-based LIO systems have emerged in recent years. The error state kalman filter is used in [23] to propose a filter-based method for LiDAR-inertial odometry that estimates the robot’s pose state. FAST-LIO [24] proposes a new method to calculate kalman gain to accelerate the system. FAST-LIO2 [25] directly uses the original lidar points to performs scan-to-map registration and proposes the ikd-Tree structure to reduce the time consumption of map updation compared with the static k-d tree structure. Faster-LIO [26] proposes the iVox structure to organize voxels through a hash table and uses a LRU cache to realize the map points addition and deletion, whose parallel accelerated version can achieve a performance that completely surpasses the performance of ikd-Tree. However, these exsiting SLAM systems are assumed to perform in a static environment. In fact, when an autonomous system navigates in a realistic environments, the spatial structure will become more complex as more moving objects, such as moving people and cars, enter the environment. Therefore, for pose estimation and mapping, the online removal of dynamic objects is essential.
1.2. Dynamic Points Removal Approaches in SLAM
In the real world, moving objects like cars and pedestrians are common. However, the excellent SLAM systems mentioned above are designed assuming a static environment and cannot robustly perform in dynamic scenes. Moving objects must be recognized and eliminated from the LiDAR point clouds in order to provide accurate position and navigation. The following is a summary of the relevant methods:
Model-based approaches: These approaches are based on the simple prior model. For example, the ground is required to be removed firstly in [27,28]. [29] is based on the concept that most moving objects in urban scenes will inevitably come into contact with the ground.
Voxel map-based approaches: These approaches construct a voxel map and track the emitted ray from LiDAR. When the end point of a lidar ray hit a voxel, it is considered as being occupied. Moreover, the LiDAR beam is regarded of as traveling across free voxels. The voxel probability in the voxel map can be computed in this way. However, there methods are computationally expensive. Even with engineering acceleration in latest method[30]. Processing a large number of 3D points online is still difficult [31]. In addition, these methods need a highly accurate localization information which is a challenging to SLAM. In [32], an offline approach for labeling dynamic points in LiDAR scans based on occupancy maps is introduced, and the labeled results are used as a training datasets for deep learning-based LiDAR SLAM methods.
Visibility-based approaches: In contrast to building a voxel map, the visibility-based approaches just need to compare the visibility difference rather than maintaining a large voxel map.[33–35]. Specifically, the seen point should be considered dynamic if the view of the previously observed point blocks out the view of the current point. RF-LIO[36] proposes an adaptive dynamic object rejection method based on removert, which can perform SLAM in real time.
Learning-based method: The performance of semantic segmentation and detection methods based on deep learning have been significantly improved. Ruchti et al. [37] integrate a neural network and Octree Map to estimate the occupancy probability. Point clouds in a grid with low occupancy probability are considered as dynamic points. Chen et al. [38] propose a fast moving object segmentation network to divide the LiDAR scan to dynamic and still object. The network is able to operate even faster than the LiDAR frequency. Wang et al. [39] propose a 3D neural network SANet and add it to LOAM for semantic segmentation to segment dynamic objects. Jeong et al. [40] proposed a 2D lidar odometry and mapping based on CNN which used the fault detection of scan matching in dynamic environments.
This paper mainly aims to improve the accuracy of LIO under the dynamic urban environments. The following are the main contributions of this paper:
An online and effective dynamic points detection method on the spatial dimension is optimized and intergrated. This approach fully utilizes the height information to the ground of the point clouds to detect dynamic points.
An indexed point-based dynamic points propagation and removal algorithm is proposed to remove more dynamic points in local map along the spatial and temporal dimension and detect dynamic points in history keyframes.
In the LiDAR odometry module, we propose a delayed removal strategy for keyframes. And a lite slide window method is utilized to optimize the poses from scan-to-map module. We assign dynamic weights to the well-matched LiDAR feature points in the history keyframes in the sliding window.
2. Materials and Methods
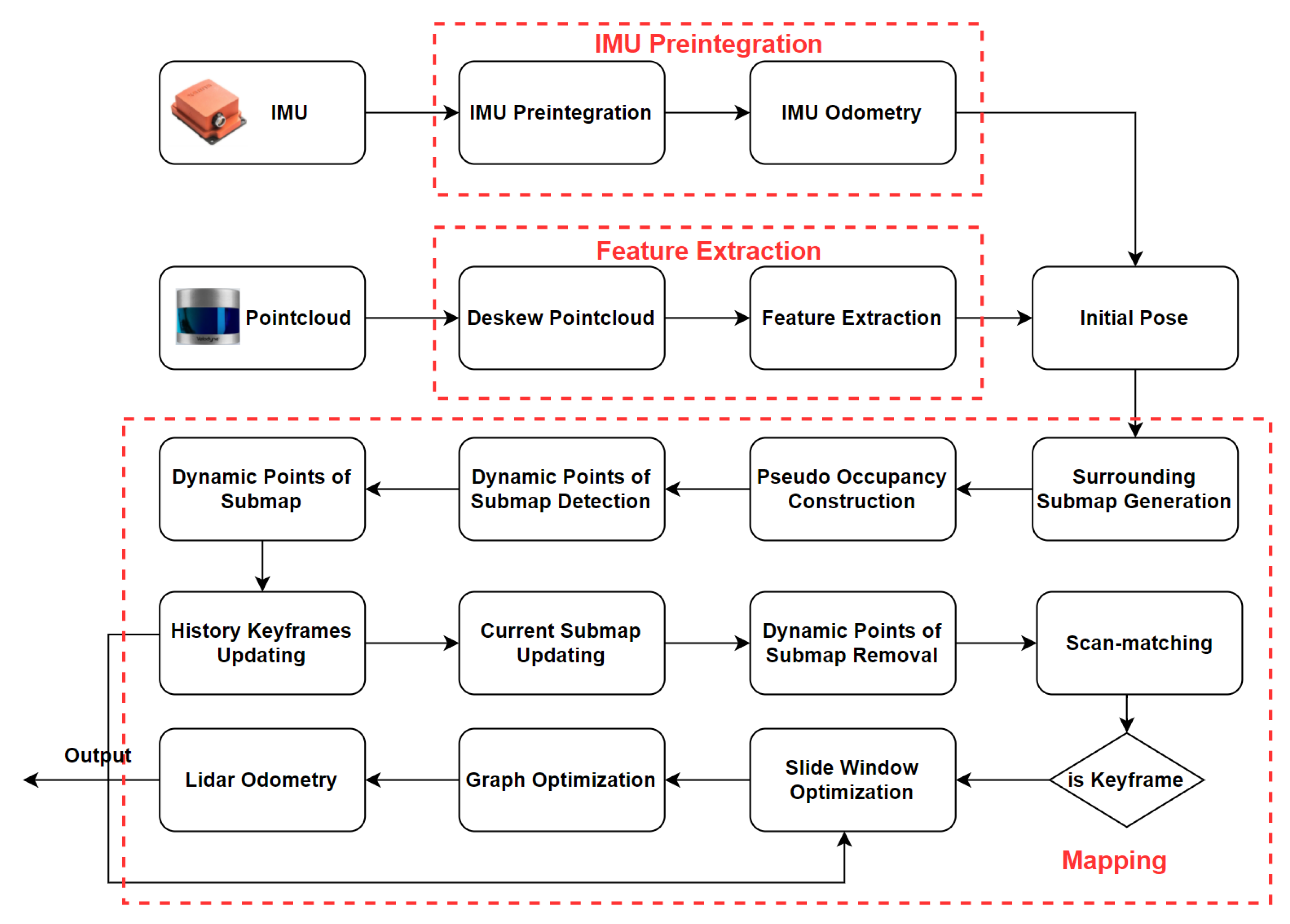
An overview of our ID-LIO is shown in the
Figure 1. Our system includes three main modules. The first module is IMU pre-integration. It is employed to estimate system motion and get an initial pose result for pointcloud decomposition and LiDAR odometry. Second, the feature extraction module includes de-skewed pointclouds and feature extraction. In the de-skewed pointclouds part, point clouds from a raw LiDAR scan are de-skewed using the pose from the IMU integration. In feature extraction part, the roughness of the points is computed in order to extract the planar and edge features.
Last, the key component of our LIO system is the mapping module. To achieve dynamic points in local map removal online before scan-to-map module, several critical steps are as follows: (i) IMU odometry is used to estimate the initial pose. (ii) The raw LiDAR scan and the matching local map are constructed individually the pseudo occupancy using the initial pose of IMU odometry. (iii) The main moving objects of the local map are detected by comparing the height difference of pseudo occupancy in the scan and local map. (iv) Through a comparison of the dynamic observation numbers of map points with the threshold, we can finally remove the primary moving points from the local map. After the history keyframes are updated, the dynamic points in the previous keyframes can also be labled. (v) If the current frame is determined to be a keyframe, only the LiDAR scan-to-map residuals with dynamic weight are optimized via the lite slide window optimization method.
2.1. IMU Preintegration
The raw IMU measurements include acceleration
and angular velocity
. The measured values are all under the IMU coordinate system
B, which is the same as the frame of motion body. The IMU measurement model is expressed as:
Where
b is the bias and
is white noise. The raw measured values of IMU are affected by them. The gravity vector is
in the world frame
W. It only affects the measurement of the accelerometer.
In our work, we assume that
is the current frame and
i is the previous frame. When
and
come, the initial pose state between frame
i and frame
can be estimated using the IMU preintegration approach:
Where
is the attitude rotation,
is velocity and
is position.
2.2. Indexed Point Initialization
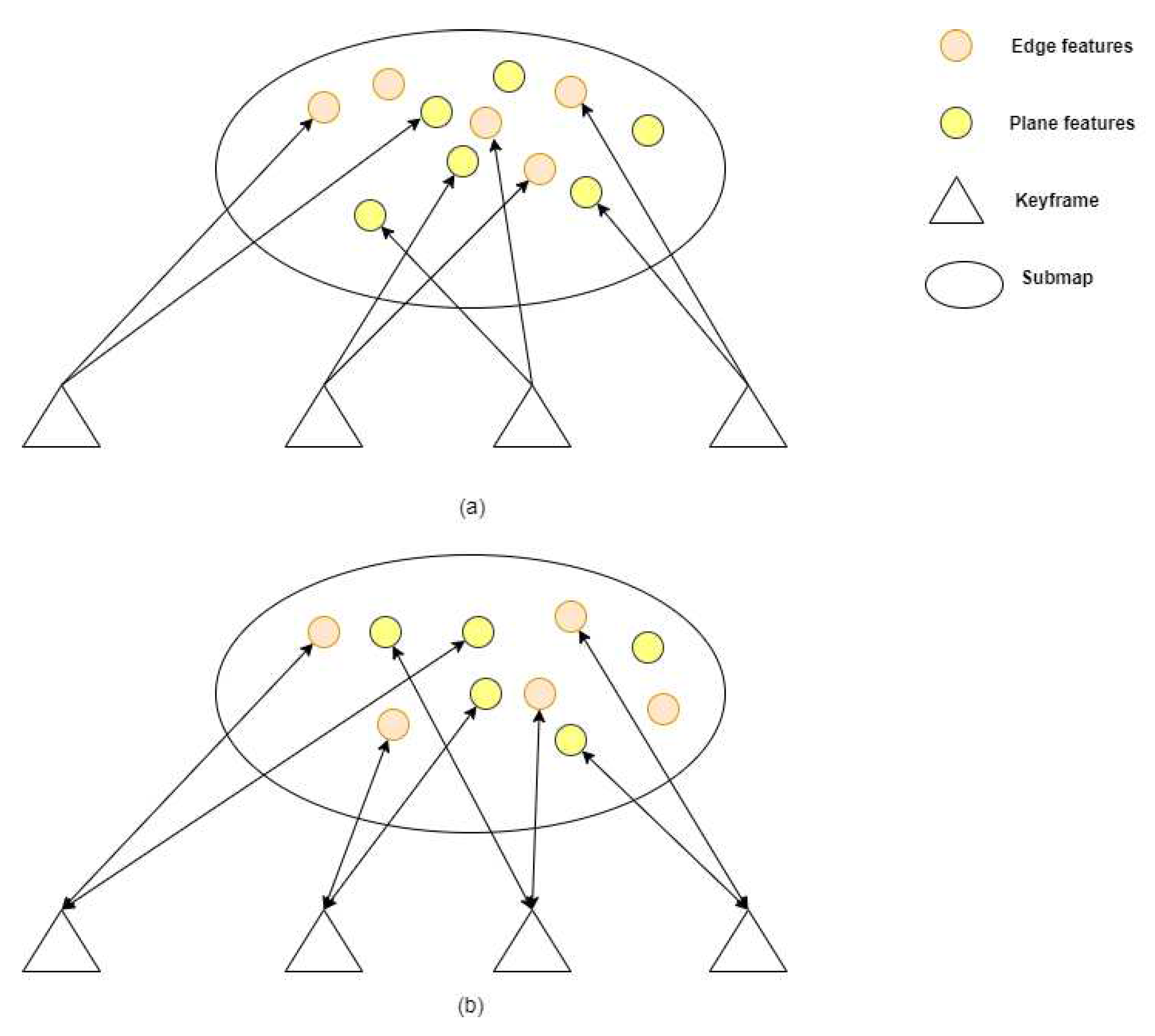
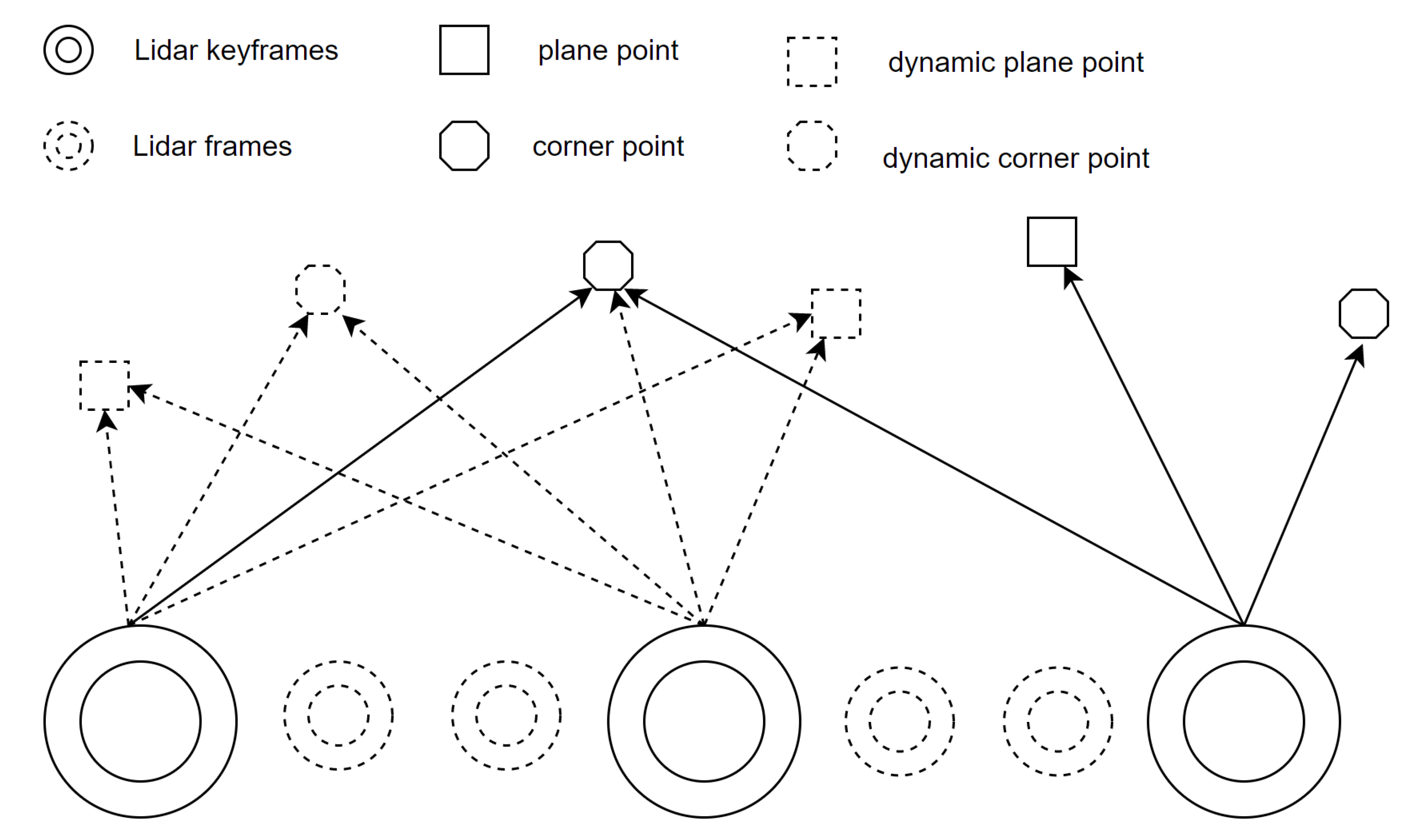
In our work, we concentrate on feature point clouds in keyframes. We denote the extracted edge and planar features from a lidar scan at time step t+1 as and respectively. All the features extracted at time t+1 compose a lidar keyframe , where . A number of keyframes of edge points close to the current t+1 moment together constitutes the local edge pointcloud map corresponding to the current frame, where . And indicates the number of frames that make up the current local corner point map. Similarly, the local plane pointcloud map at t+1 moment is represented as , where . and compose a local map corresponding to the current keyframe , where .
Figure 3.
The difference between common points and index points.
Figure 3.
The difference between common points and index points.
In order to better find the point and then update the status of the point, a new type of point is defined. This operation storing extra information besides the 3D position of a point is motivated by
Directed Geometry Point [41]. In our work, a point
P is a vector with size 7:
where the first
sub-vector
denotes the point 3D position, and the second
vector
store the index information of point
p.
records point index in
and
indicates which keyframe point
belongs to in keyframe set. Besides,
is the category of the point.
is dynamic observation number(DON) which records the number of times the point was observed as a dynamic point.
In addition, we don’t initialize every lidar scan. When current lidar scan is selected as a keyframe, we initialize the points of this keyframe. This is because the local map is composed of multiple keyframes. The state of feature points in keyframe are what we care about. And the difference between common point and indexed point is shown in the Figure. In Figure (a), the local map consists of multiple keyframes composed of common points. In Figure (b), because of the indexed point, we can know which keyframe the points in the local map come from. And this part is used in Chapter 2.4.
2.3. Dynamic Points Detection
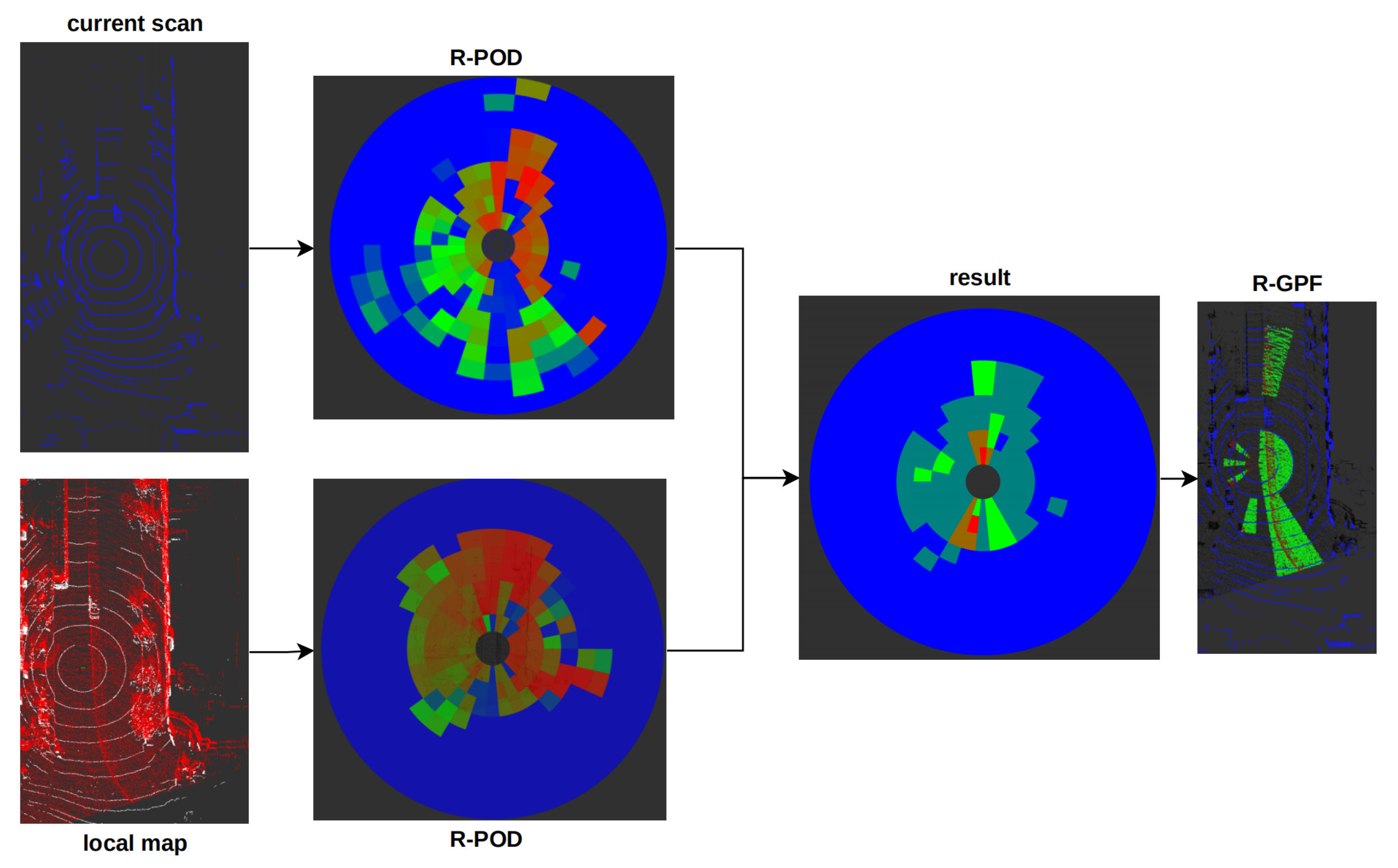
For dynamic points detection in high dynamic urban environments and in the process of SLAM, the offline post-processed ERASOR [29] method is optimized and integrated into the SLAM online system. As shown in
Figure 4, we can see the overview of the online dynamic points detection method.
2.3.1. Problem Definiton
We first denote the current lidar frame and corresponding voxel submap at time step
t+1 as
and
respectively. The former is a full query lidar scan and the latter is a feature map which is composed of some keyframes around
found by sliding window method. Note that
is in the world frame
W. However,
is in frame
B. And we need to transform frame
to the world coordinate system
W before the moving point detection to get
and record the current position of the motion robot
in frame
W firstly, which can be formulated as follows:
where
is the relative transformation between
and
from IMU odometry, Equation (
7) represents the conversion of all point cloud coordinates in the
to the
.
2.3.2. Pseudo Occupancy-based Removal Method
First, we divide the lidar frame
and the submap
to
Region-Wise Pseudo Occupancy Descriptor (R-POD)
and
respectively which is similar to Scan Context:
where
is rings number and
is sectors number.
is the
-th bin of R-POD. Let
. Each
includes the point clouds that meet the formula as follows:
where
;
;
and
is the maximum detection distance of lidar. Then we calculate the maximum height difference
and
in each bin.Thereafter, we could get the potentially dynamic bins in
if :
Finally, we use Region-Wise Ground Plane Fitting (R-GPF) to get ground points in dynamic bins and get the ground plane. The dynamic points are points in dynamic bin expect the ground points. And all dynamic points in dynamic bins consist of the final dynamic points set
. Therefore, we can get the dynamic set
, where
:
2.4. Dynamic Points Propagation and Removal
ERAOSR [29] is an offline method which using the long sequence local map. However, we need to eliminate dynamic points in the online process of SLAM. The short sequences we can only get in the SLAM, which will decrease the performance of dynamuc points removal. Therefore, we propose the dynamic points removal method based on spatial and temporal dimension to improve the removal performance.
In our work, we don’t remove dynamic points in a submap when getting the dynamic points set after the dynamic points detection module like RF-LIO. We judge the feature point is dynamic not only according to the difference between current lidar scan and submap but also the history difference. We propagate these points to history keyframes based on indexed point in part 2.2. Then we perform the dynamic points removal. If a feature point is a dynamic feature point, the frequency with which the feature point is judged to be a dynamic feature point will be high. Thus, the Dynamic Observation Numbers (DON) of a point is used to determine whether the point is dynamic in the temporal dimension. The Dynamic Points Propagation and Removal process is summarized in Algorithm 1.
Where
is a threshold used to distinguish dynamic feature points and static feature points. If
is small, there will be many static points misclassified as dynamic points. If
is large, we cannot remove dynamic feature points better. In our system ,
is set to 3 and 3 is an emprical value. It ensures a balance between the removal of dynamic points and the retention of static points.
|
Algorithm 1: Dynamic Points Propagation and Removal Algorithm |
 |
2.5. Lidar Odometry
This module includes scan-to-map matching and front-end optimization. To describe this section clearly, we start with the scan-to-map matching module, which is follwed by the front-end optimization module.
2.5.1. Feature-Based Scan-to-Map Matching
The sensor motion between two consecutive LiDAR scans is estimated using the front end of SLAM. There are a variety of scan-matching methods. And the fundamental method of this module is same with LOAM. We compute the roughness of each point in each LiDAR frame. Then we extract edge and planar features for this new scan. The formula for calculating roughness is as follows:
where
represents the target point, and
is in the same ring of LiDAR scan. The edge and planar features from the lidar frame
are denoted as
and
respectively. Then the feature points in
and
are transformed to
W and obtain
. IMU preintegration provides the initial transformation. By using the nearest neighbor search method, we are able to locate its correlating feature points in
. Thus, the following formula can be used to calculate the distance between a target point and its related edge:
Where
is an edge feature point, and
are two different points on the corresponding edge-line. Similarly, the distance from a target point to its associated plane can be calculated as follows:
Where
is an planar feature point, and
are three different points on the corresponding plane.
At last, we can estimate the pose between current frame and local map by solving the optimization problem:
2.5.2. Front-End Optimization
Within the scanning-to-mapping part, the local map is used with dynamic points removed. However, we use lidar scan in which dynamic points are existed. Because in a single lidar frame there are not enough sparse lidar points to use the dynamic point removal method as described above [42]. Therefore, we propose a delayed removal strategy for keyframe and build a cost function including LiDAR measurements only with a dynamic observations-related weight jointly motivated by VINS-Mono. To get more accurate odometry for each key frame of LiDAR, we optimize the pose states in the light-weight sliding window iteratively.
In our LIO system, the states in the sliding window that need to be optimized are defined as
, where we optimize the poses of the n keyframes before the current moment
t. And
. For a sliding window of size n, these states are obtained by minimizing the final cost function which is described as:
In this cost function,
denotes edge-line geometric terms of LiDAR and
means the planar LiDAR error terms. The process of front-end optimization is shown in
Figure 5. Based on the previous LiDAR term calculation of each scan, the LiDAR term incorporates geometric constraints with dynamic weight from the Dynamic Points Propagation and Removal module (see
Section 2.4) into the cost function scheme. The term is donated as:
and the dynamic observations-related weight is defined as:
where
is the distance from the
i-th target edge point to its corresponding edge and
is the distance from target planar point to its corresponding plane in
Section 2.5.1,
is a dynamic observations-related weight,
is the dynamic observations of the
i-th feature point. In this paper, we set the value of dynamic weight as of the DON. It indicates that the higher the DON, the less important the corresponding residuals
d are in the cost function
r.
3. Results
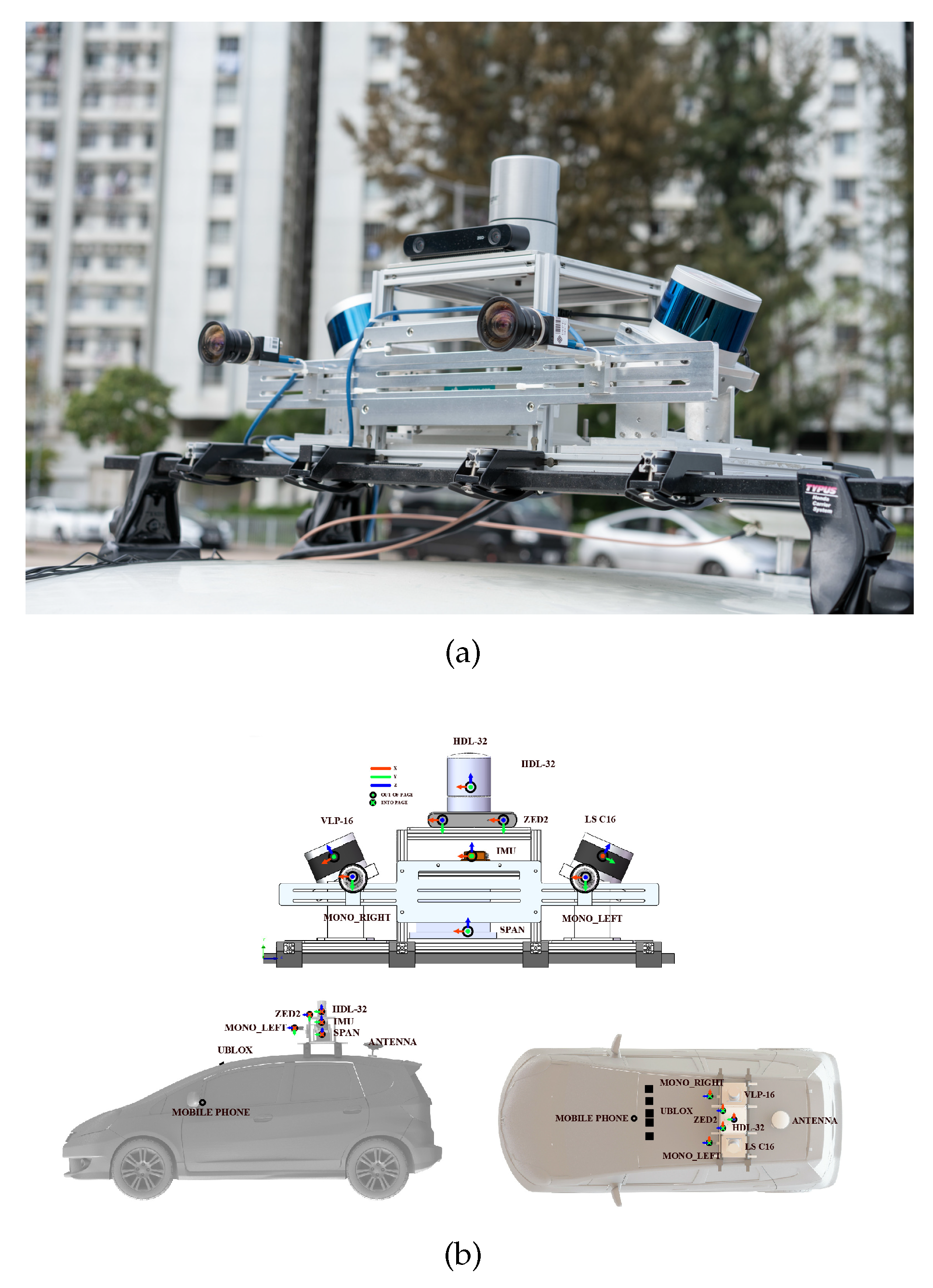
3.1. Experimental Setup
We validate our system ID-LIO by conducting a set of experiments on public datasets. And ID-LIO is contrasted with FAST-LIO2, Faster-LIO and LIO-SAM. Compared with the LIO-SAM, the ID-LIO employs the same feature extraction module, loopback detection strategy and optimization method for the back-end using GTSAM. And we use evo [43] to evaluate accuracy. The ablation experiment demonstrates the effect of our proposed methods. The proposed methods are executed on a computer with Intel i5 CPU and 32G RAM. Ubuntu 18.04 with the Robot Operating System(ROS) Melodic [44] is our computer system. The datasets used for validation include UrbanNav datasets in HongKong(UNHK) [45] and UrbanLoco datasets in California(ULCA) [46]. The UrbanNav-HK-Data20190428 is a dataset containing some movable objects, which is defined as a low dynamic dataset. And we define the others in UNHK and ULCA as high dynamic datasets because they contain masses of movable objects. As shown in
Table 1, the data information is listed in detail. The sensors suite of UBHK dataset is shown in
Figure 6.
3.2. Dynamic Observations Number Analysis
The impact of the appropriate DON value on the removal results of dynamic objects is very critical. Consequently, the purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate that the approach mentioned in
Section 2.4 is accurate. Setting the correct DON threshold is important. If the DON value is too low, the static points may be incorrectly regarded as dynamic points. If it is too larger, many moving points may be wrongly identified as static points. In the implementation of our algorithm, we set the DON value to 3. It can ensure that static points and dynamic points are correctly distinguished. To further prove the rationality of this threshold value, we choose three dynamic urban datasets. We test the LIO-SAM using the different thresholds between 1 and 6. DON1 to 6 means the value of DON is 1 to 6. The RMSE(Root Mean Square Error) of absolute trajectory error(ATE) of them is shown in
Table 2, which demonstrates that the fixed threshold 3 can provide more reliable and accurate pose estimation.
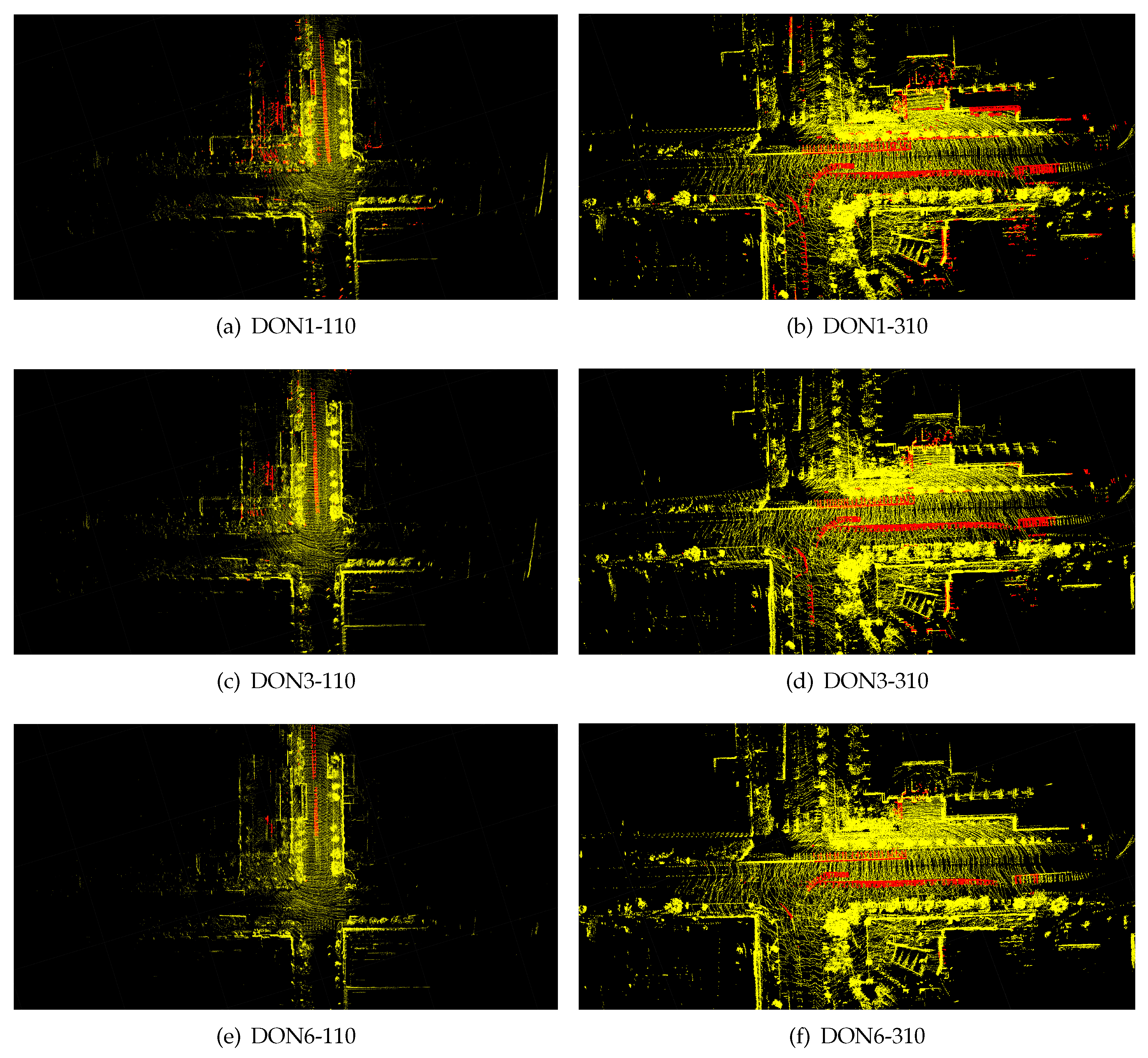
ULCA-MarktStreet is chosen for our analysis. As shown in
Figure 9, there are two kinds of red point set in figures. Red cloud points on the street indicate dynamic objects by moving cars and the more red points, the better. However, red cloud points at other places indicate static objects that have been incorrectly removed and the less red points, the better. If the threshold is 1, more dynamic points are removed. At the same time many static points are incorrectly removed. If the threshold is 6, more static points are preserved. However, many dynamic points are also preserved in comparison with DON1. Neither of these two extreme cases applies to dynamic point removal. However, DON3 can achieve better rejection results. It retains most of the static points of the local map while removing more dynamic points.
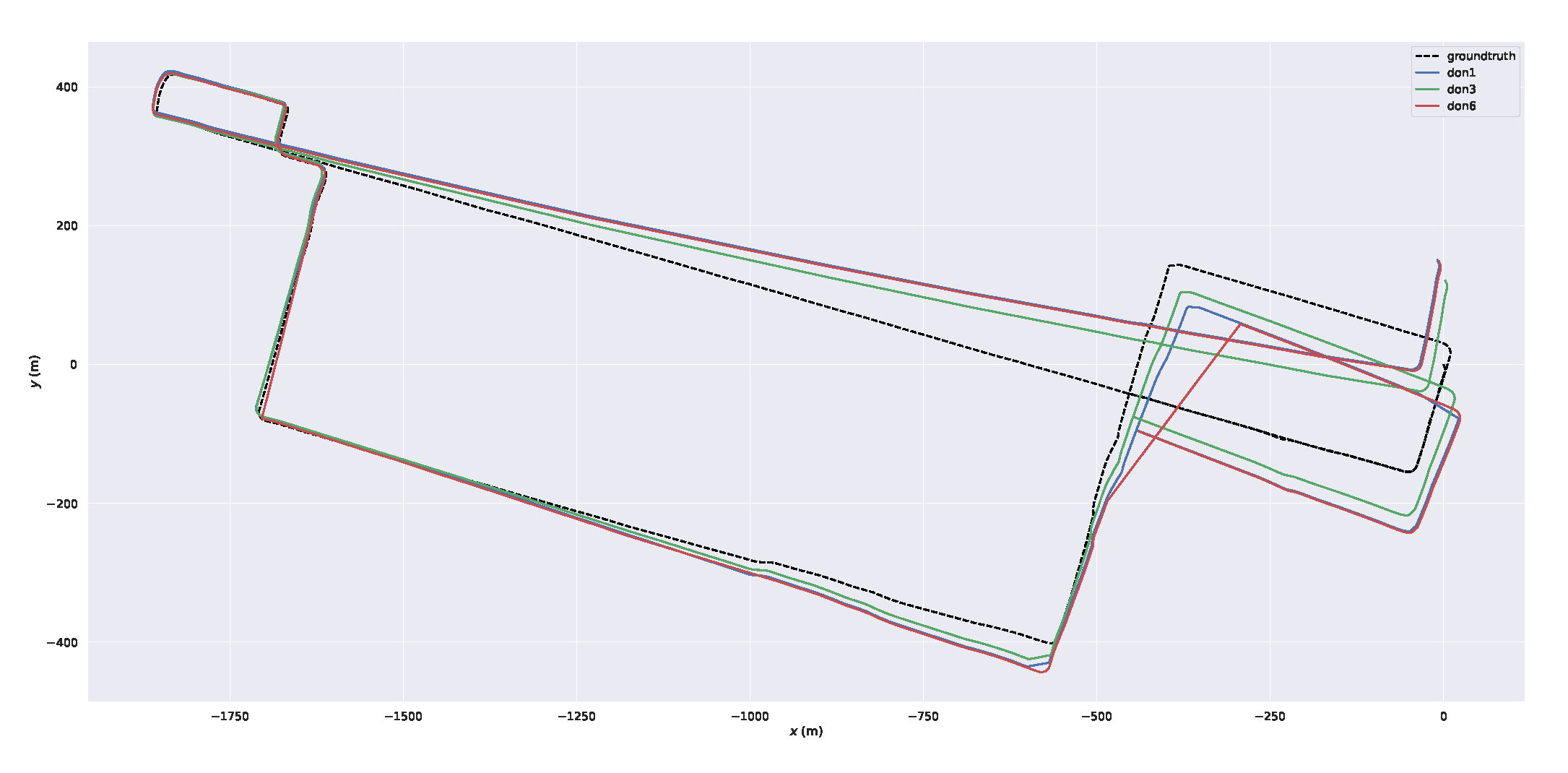
Figure 7 shows the trajectories of different DON with our system in ULCA-MarktStreet in X-Y plot when the threshold is 1, 3 and 6. This figure performs the total error for three distinct thresholds. It can be seen that the trajectory corresponding to don3 is closer to the ground truth. Because the don3 system achieves a balance between dynamic point removal and static point retention.
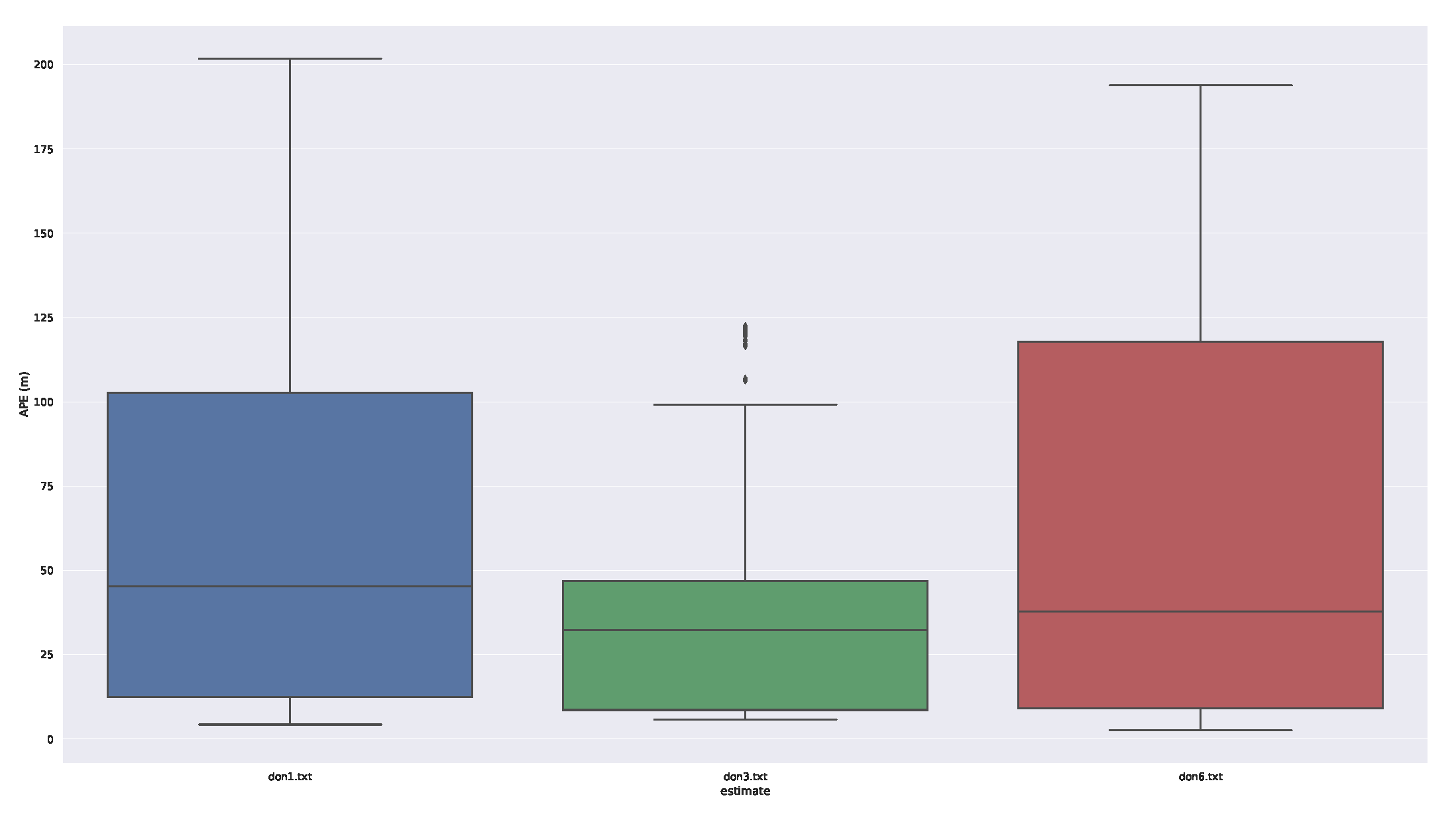
Box diagram of the deviation is shown in
Figure 8, which allows us to better view the magnitude of the deviation. Moreover, the DON3 system has the smallest error.
Figure 8.
Box diagram of the deviation.
Figure 8.
Box diagram of the deviation.
Figure 9.
The removal results of local maps corresponding to different DON thresholds. On the left is the local map corresponding to keyframe 110 in keyframe sequences. The right is the local map corresponding to keyframe 310.
Figure 9.
The removal results of local maps corresponding to different DON thresholds. On the left is the local map corresponding to keyframe 110 in keyframe sequences. The right is the local map corresponding to keyframe 310.
3.3. Comparison of Dynamic Removal Strategy for Local Map
To further demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed removal strategy based on the pseudo occupancy and indexed point in the spatial and temporal dimension(denoted as LIO-SAM+Spatial+Temporal), we make comparisons with the removal strategy based on the pseudo occupancy in the spatial dimension only(denoted as LIO-SAM+Spatial). The ATE of mapping thread are shown in
Table 3.
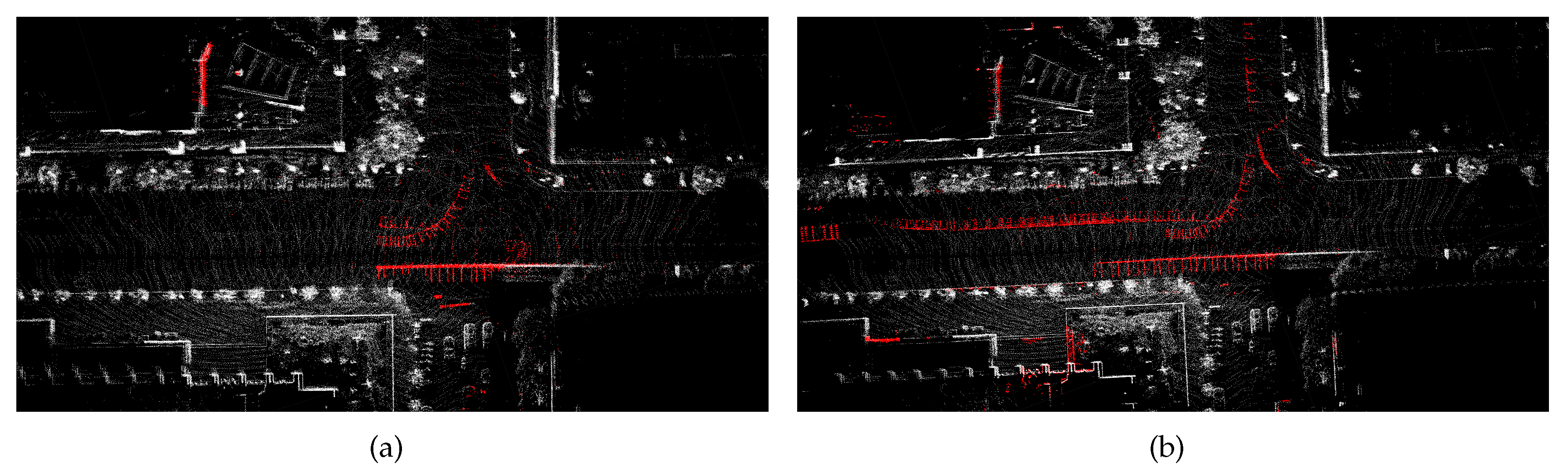
Figure 10a shows dynamic points removal results by these two methods. The red points on the street are dynamic traces by moving cars.
Figure 10b identifies part of the dynamic feature points. In contrast, our method based on spatial and temporal dimension sucessfully removes most of the dynamic traces. After the trajectories of both systems are aligned with ground truth, we acquire the error maps for these two approaches. And we illustrate them in
Figure 11.
3.4. Comparison of Delayed Removal Strategy for Keyframe
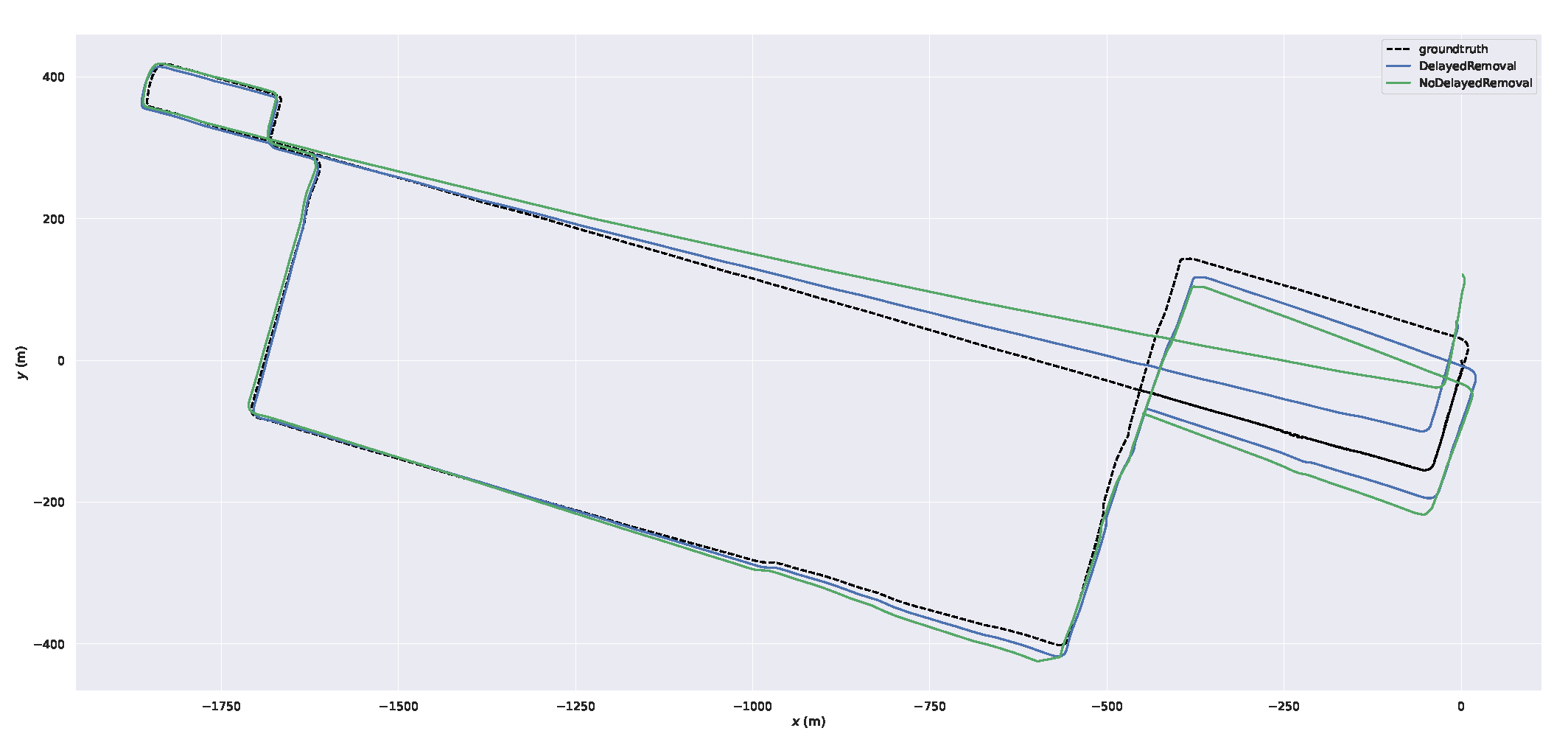
During the scan-to-map matching, both of dynamic points in map and LiDAR scan can result in significant deviation. According to the moving points in local map, we can get the dynamic points in keyframes. When we do the slide window optimization, the dynamic lidar terms will get the dynamic weights. Although we can not remove dynamic points in current key frame, it will be removed in the next slide window optimization. Therefore, we conduct this experiment to prove the efficiency of the delayed removal strategy.
Figure 13 shows the removal result.
Figure 13a,b shows the real environment with moving cars and people corresponding to the current frame.
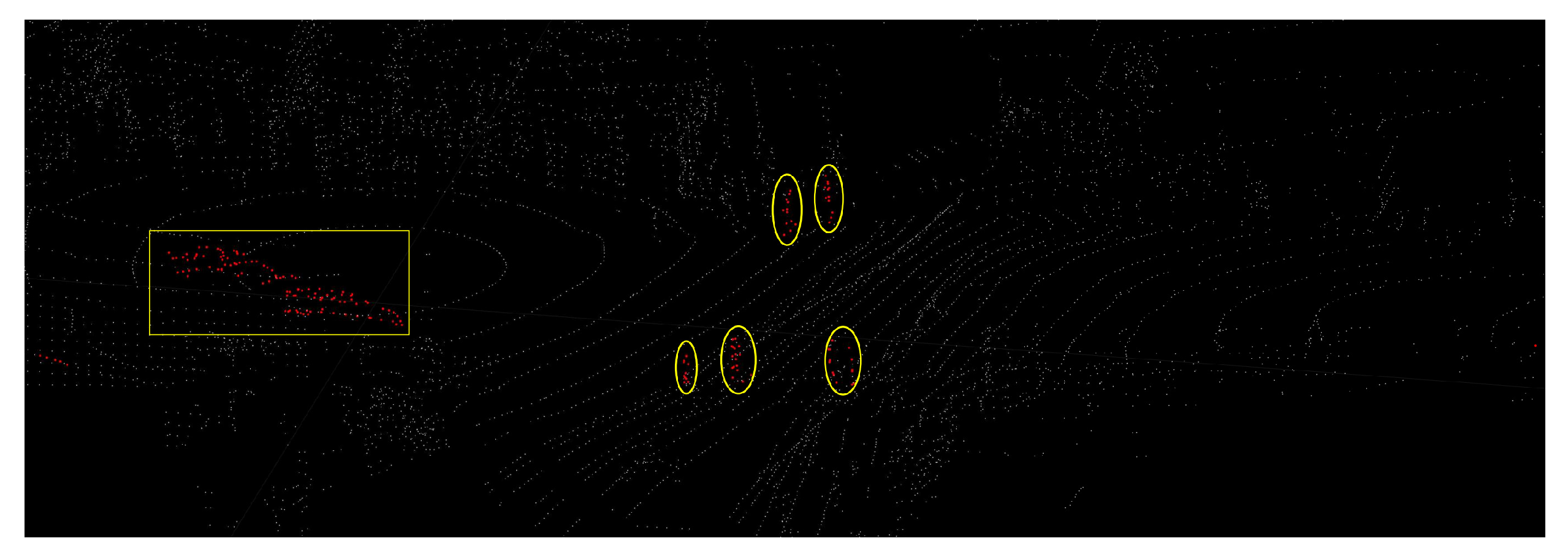
Figure 13d shows a keyframe with red dynamic points after the delayed removal strategy. And we mark the dynamic cars and people with red points.
Figure 13c shows a static keyframe after removing dynamic points of this keyframe.
The goal of this experiment is to demonstrate the effectiveness of the delayed removal method for dynamic points in history keyframes. We use dynamic point propagation method to obtain dynamic points in historical keyframes on the based of dynamic local map feature points.
Figure 13f shows the dynamic traces in the local map.
Figure 13e shows the dynamic points in this keyframe obtained by the dynamic point propagation method. For example, red points marked by yellow rectangles in
Figure 13e. There are five people walking on the road. These red points are part of the red points in the yellow rectangle in
Figure 13f. Similarly, the car in the yellow oval in
Figure 13e is part of the red points in the yellow oval in
Figure 13f. The error maps of the ID-LIO with delayed removal strategy and without this strategy are shown in
Figure 14. We can obtain that the trajectory our system with this method is closer to the ground truth.
Table 4.
RMSE ATE for our system without delayed removal strategy(denoted as Ours+No Delayed Removal) to ours with the strategy(donated as Ours + Delayed Removal).
Table 4.
RMSE ATE for our system without delayed removal strategy(denoted as Ours+No Delayed Removal) to ours with the strategy(donated as Ours + Delayed Removal).
| Sequence/ATE |
Ours + No Delayed Removal |
Ours + Delayed Removal |
| UNHK-Data20190428 |
5.96 |
5.99 |
| UNHK-TST |
4.86 |
1.06 |
| ULCA-MarktStreet |
49.26 |
28.02 |
Figure 12.
The trajectories of our system with delayed removal strategy and without the strategy.
Figure 12.
The trajectories of our system with delayed removal strategy and without the strategy.
Figure 13.
Keyframe with red dynamic points after the delayed removal strategy.
Figure 13.
Keyframe with red dynamic points after the delayed removal strategy.
Figure 14.
Error map of our system with delayed removal strategy and without the strategy.
Figure 14.
Error map of our system with delayed removal strategy and without the strategy.
3.5. Results on Low and High Dynamic Datasets
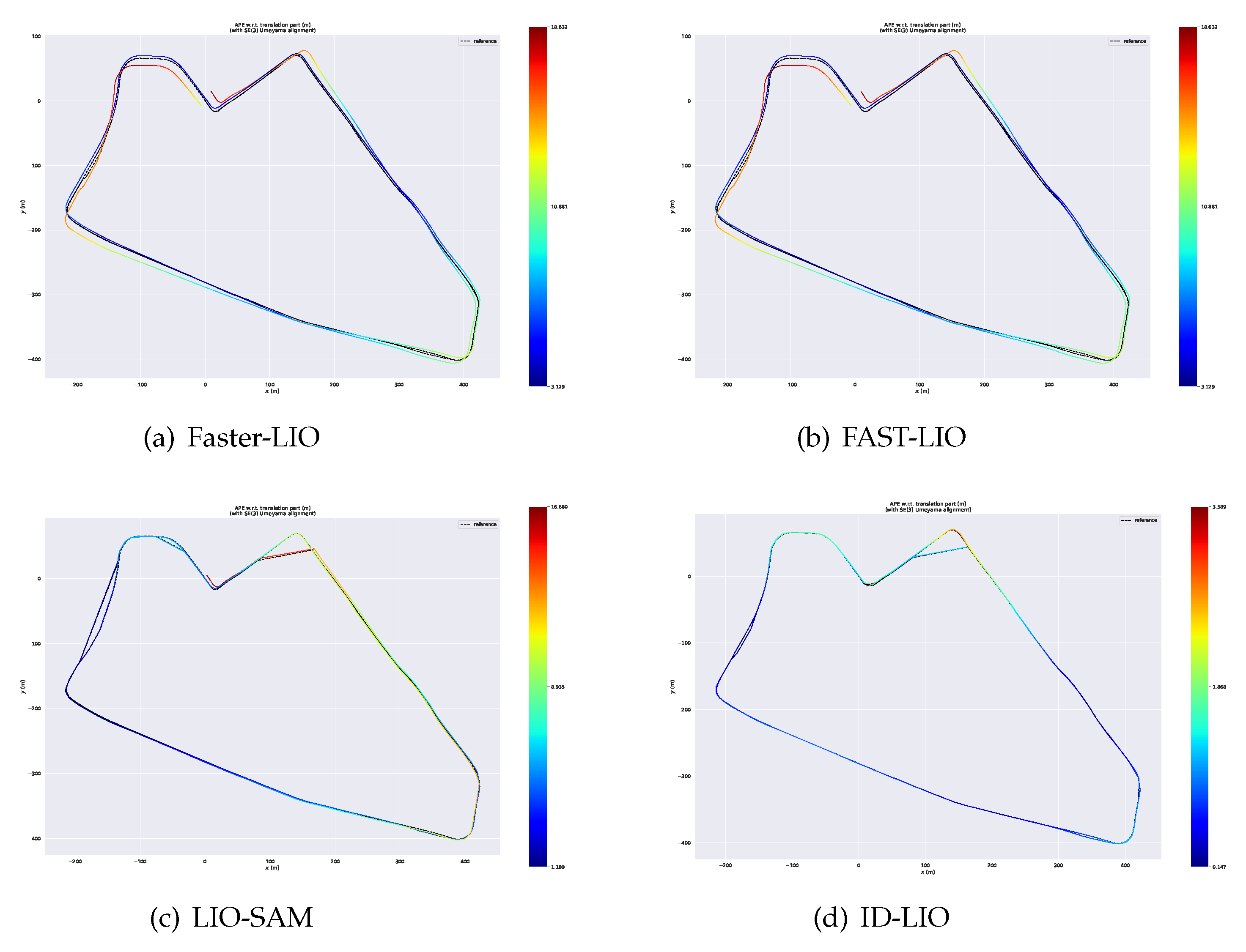
We have evaluated our ID-LIO system on 6 datasets with ground truths in the UrbanNav and UrbanLoco datasets. And we compared the results with LIO-SAM, Fast-LIO, Faster-LIO and the ground truths. For quantitative evaluation, we compute the ATE for these three methods on different datasets using the evaluation tool EVO and the results are shown in
Table 5.
After the trajectories of these four systems are aligned with ground truth, we acquire the error maps for these approaches. And we illustrate them in
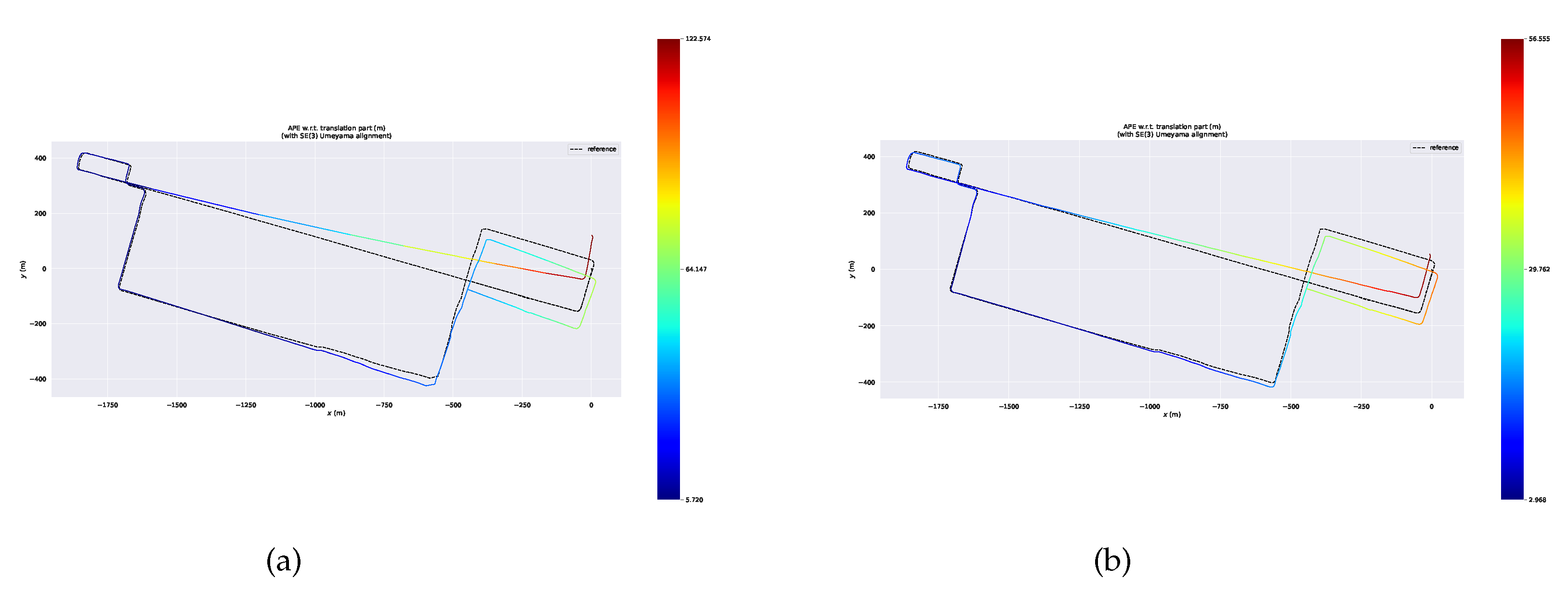
Figure 15, from which we can see that the error of each position calculated by our system is less than 1.10 m, while the error of Faster-LIO, FAST-LIO and LIO-SAM can be up to 9.81m, 9.34m and 7.51m, respectively.
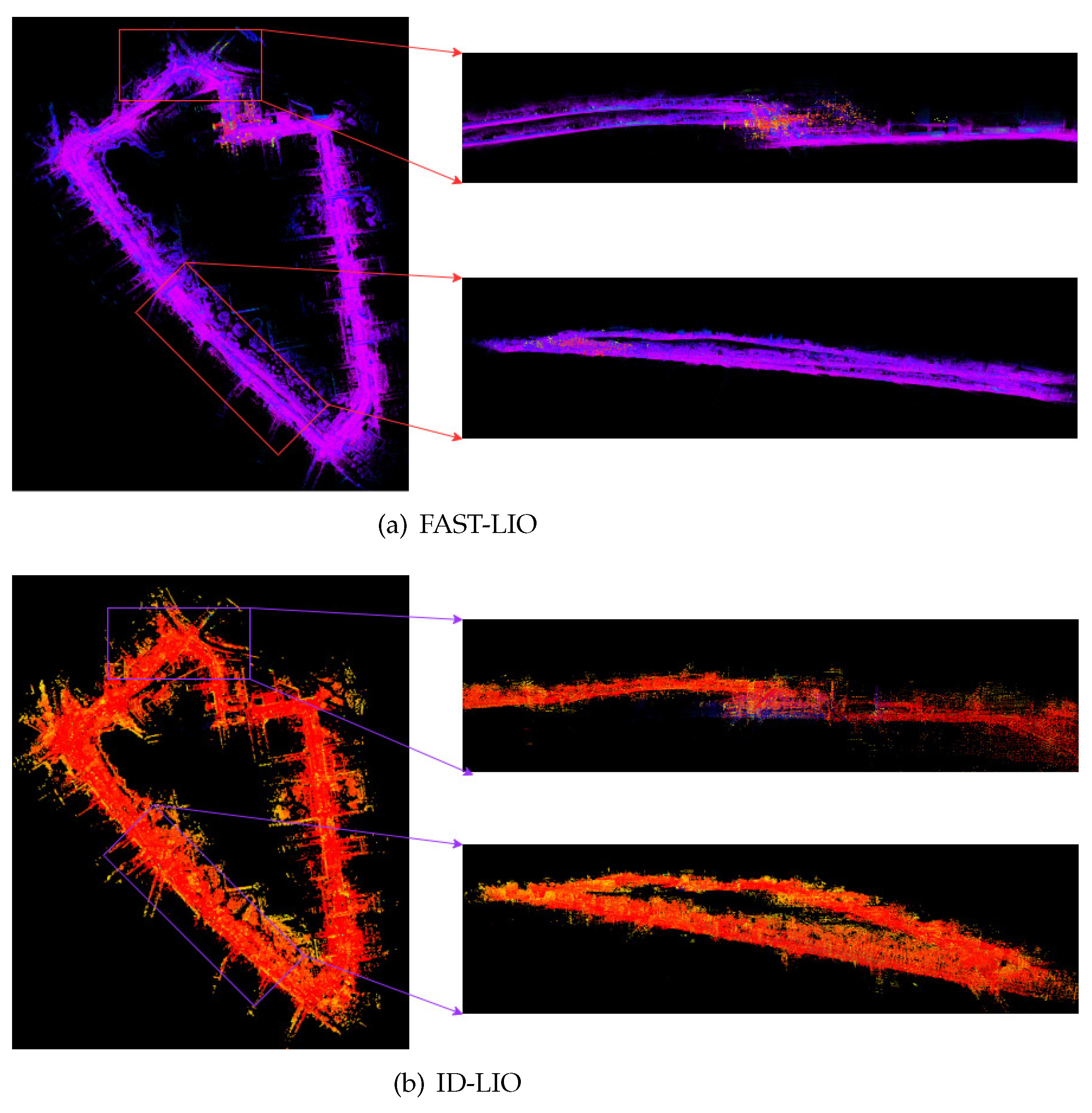
Finally, we compare the differences between the point cloud maps of FAST-LIO and ID-LIO. We can see that Fast-LIO is the least effective because it does not have back-end loopback detection, and LIO-SAM is unable to detect closed-loop accurately because there are many dynamic objects in the urban environment, resulting in inaccurate poses obtained by scan2map. Our ID-LIO adopts a dynamic point detection and rejection algorithm, and achieves better loops back results compared to LIO-SAM.
4. Discussion
According to the public datasets experiments, we performed two ablation experiments firstly. Compared to LIO-SAM with online ERASOR dynamic points removal method in the spatial dimension(LIO-SAM + spatial), the removal effect, position accuracy and robustness is significantly improved in LIO-SAM with dynamic removal method based on indexed point. Our LIO system with removing dynamic points in keyframes has lower drift compared with pur system without delayed removal strategy. In addition, compared to FAST-LIO, faster-lio and LIO-SAM, our system has lower drift in low dynamic and high dynamic enviroments.
In this paper, we proposed an improved and robust LIO system in dynamic environments. A dynamic points removal method based on pseudo occupancy and indexed point is used for local map before scan-to-map registration. It reduces the influence of dynamic points on feature matching and improves pose accuracy. In addition, we propose a delayed removal strategy for keyframes and the optimization based on sliding window incorporates the LIDAR measurement with dynamic weights to reduce error from dynamic points in keyframes which further improves the pose accuracy.
For the future work, we note that it is important to improve the real-time of LIO system. In our system, we need to construct local map for scan-to-map registration and pseudo occupancy map for dynamic points removal repetitively. It is time-consuming. We will focus on spatial data structure for local map addition and deletion to improve the system’s efficiency. It is also important to note that the LIO system is susceptible to Z direction drift in a vast scenario. In the future, the ground constraint will be added to reduce the drift on the Z-axis.
Author Contributions
Funding acquisition, Wanliang Wang; Investigation,Weizhuang Wu; Methodology, Weizhuang Wu; Supervision, Wanliang Wang; Writing—original draft, Weizhuang Wu; Writing—review editing, Weizhuang Wu. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61873240.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicablee.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MDPI |
Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ |
Directory of open access journals |
| TLA |
Three letter acronym |
| LD |
Linear dichroism |
References
- He, G.; Yuan, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Hu, H. An integrated GNSS/LiDAR-SLAM pose estimation framework for large-scale map building in partially GNSS-denied environments. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2020, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Monocular visual odometry based on depth and optical flow using deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2020, 70, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Hu, L.; He, J. A Method for Reconstructing Background from RGB-D SLAM in Indoor Dynamic Environments. Sensors 2023, 23, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Cho, Y.; Shin, Y.S. Nonparametric Background Model-Based LiDAR SLAM in Highly Dynamic Urban Environments. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2022, 23, 24190–24205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In Proceedings of the Sensor fusion IV: Control paradigms and data structures. Spie, 1992, Vol. 1611, pp. 586–606.
- Pomerleau, F.; Colas, F.; Siegwart, R.; Magnenat, S. Comparing ICP variants on real-world data sets: Open-source library and experimental protocol. Autonomous Robots 2013, 34, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, J.; Grisetti, G. NICP: Dense normal based point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE, 2015, pp. 742–749.
- Ren, Z.; Wang, L.; Bi, L. Robust GICP-based 3D LiDAR SLAM for underground mining environment. Sensors 2019, 19, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. Efficient Surfel-Based SLAM using 3D Laser Range Data in Urban Environments. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems; 2018; Vol. 2018, p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Wen, C.; Cheng, M.; Li, J. Lo-net: Deep real-time lidar odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2019; pp. 8473–8482. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.; Kim, G.; Kim, A. Unsupervised geometry-aware deep lidar odometry. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2020; pp. 2145–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Singh, S. LOAM: Lidar odometry and mapping in real-time. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems. Berkeley, CA, 2014, Vol. 2, pp. 1–9.
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? In the kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE; 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.L.; Xie, L. F-loam: Fast lidar odometry and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE; 2021; pp. 4390–4396. [Google Scholar]
- Koide, K.; Miura, J.; Menegatti, E. A portable three-dimensional LIDAR-based system for long-term and wide-area people behavior measurement. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 2019, 16, 1729881419841532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B. Lego-loam: Lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE; 2018; pp. 4758–4765. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Niu, X.; Chang, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. LiDAR Odometry by Deep Learning-Based Feature Points with Two-Step Pose Estimation. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Tightly coupled 3d lidar inertial odometry and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2019; pp. 3144–3150. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Li, M.; Hanebeck, U.D. Towards high-performance solid-state-lidar-inertial odometry and mapping. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 5167–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Meyers, D.; Wang, W.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. Lio-sam: Tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS). IEEE; 2020; pp. 5135–5142. [Google Scholar]
- Kaess, M.; Ranganathan, A.; Dellaert, F. iSAM: Incremental smoothing and mapping. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2008, 24, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, W.; Huang, F.; Chen, X.; Hsu, L.T. Coarse-to-Fine Loosely-Coupled LiDAR-Inertial Odometry for Urban Positioning and Mapping. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Ye, H.; Pranata, C.E.; Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M. Lins: A lidar-inertial state estimator for robust and efficient navigation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2020; pp. 8899–8906. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, F. Fast-lio: A fast, robust lidar-inertial odometry package by tightly-coupled iterated kalman filter. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cai, Y.; He, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F. Fast-lio2: Fast direct lidar-inertial odometry. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2022, 38, 2053–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Xiao, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Gao, X. Faster-LIO: Lightweight tightly coupled LiDAR-inertial odometry using parallel sparse incremental voxels. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 4861–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.; Caselitz, T.; Tipaldi, G.D.; Burgard, W. Motion-based detection and tracking in 3d lidar scans. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2016; pp. 4508–4513. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, A.; Caselitz, T.; Tipaldi, G.D.; Burgard, W. Rigid scene flow for 3d lidar scans. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE; 2016; pp. 1765–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.; Hwang, S.; Myung, H. ERASOR: Egocentric ratio of pseudo occupancy-based dynamic object removal for static 3D point cloud map building. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 2272–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, A.; Wurm, K.M.; Bennewitz, M.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. OctoMap: An efficient probabilistic 3D mapping framework based on octrees. Autonomous robots 2013, 34, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.; Nüchter, A. The peopleremover—removing dynamic objects from 3-d point cloud data by traversing a voxel occupancy grid. IEEE robotics and automation letters 2018, 3, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfreundschuh, P.; Hendrikx, H.F.; Reijgwart, V.; Dubé, R.; Siegwart, R.; Cramariuc, A. Dynamic object aware lidar slam based on automatic generation of training data. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2021; pp. 11641–11647. [Google Scholar]
- Pomerleau, F.; Krüsi, P.; Colas, F.; Furgale, P.; Siegwart, R. Long-term 3D map maintenance in dynamic environments. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2014; pp. 3712–3719. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, D.; Tang, T.; Barfoot, T. Mapless online detection of dynamic objects in 3d lidar. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV). IEEE; 2019; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Kim, A. Remove, then revert: Static point cloud map construction using multiresolution range images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE; 2020; pp. 10758–10765. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Xiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Sun, H. RF-LIO: Removal-First Tightly-coupled Lidar Inertial Odometry in High Dynamic Environments. arXiv, 2022; arXiv:arXiv:2206.09463. [Google Scholar]
- Bescos, B.; Fácil, J.M.; Civera, J.; Neira, J. DynaSLAM: Tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2018, 3, 4076–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.J.; Xie, F.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Fei, Q. DS-SLAM: A semantic visual SLAM towards dynamic environments. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). IEEE; 2018; pp. 1168–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; You, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. LiDAR-Based SLAM under Semantic Constraints in Dynamic Environments. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Lee, H. CNN-Based Fault Detection of Scan Matching for Accurate SLAM in Dynamic Environments. Sensors 2023, 23, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Cao, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, J. A novel 3D LIDAR SLAM based on directed geometry point and sparse frame. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2020, 6, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Shen, B.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Pan, J. DynamicFilter: An Online Dynamic Objects Removal Framework for Highly Dynamic Environments. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2022; pp. 7988–7994. [Google Scholar]
- Sanfourche, M.; Vittori, V.; Le Besnerais, G. eVO: A realtime embedded stereo odometry for MAV applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. IEEE; 2013; pp. 2107–2114. [Google Scholar]
- Będkowski, J.; Pełka, M.; Majek, K.; Fitri, T.; Naruniec, J. Open source robotic 3D mapping framework with ROS—robot operating system, PCL—point cloud library and cloud compare. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI). IEEE; 2015; pp. 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, L.T.; Kubo, N.; Wen, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Suzuki, T.; Meguro, J. UrbanNav: An open-sourced multisensory dataset for benchmarking positioning algorithms designed for urban areas. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021); 2021; pp. 226–256. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Fahandezh-Saadi, S.; Bai, X.; Zhan, W.; Tomizuka, M.; Hsu, L.T. UrbanLoco: A full sensor suite dataset for mapping and localization in urban scenes. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE; 2020; pp. 2310–2316. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).