1. Introduction
A surprising feature of myonecrotic disease caused by clostridia is the absence of phagocytic cells at the infection site [
1]. Circulating monocytes are recruited at the injury site where they differentiate into tissue macrophages. These macrophages eliminate infectious agents, eliminate damaged cells, and repair tissue [
2,
3]. Recent studies suggest that extracellular proteins (as a whole or fractions) secreted by clostridia can cause membrane pores in phagocytic cells and phagosome membranes [
2,
4]. Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Bacillus, Listeria, and Clostridium, are capable of producing programmed cell death (apoptosis) in eukaryotic cells. One of the secreted virulence factors that can induce apoptosis is the bacterial wall component, lipoteichoic acid, although the available data are contradictory [
5]. Many apoptogenic components in gram-positive bacteria have been identified, including the exotoxin-like-lethal factor of Bacillus anthracis [
6,
7], cytosin-like listeriolysin O of Listeria monocytogenes [
8,
9], and hemolysin-like hemolysin β of Streptococcus agalactiae [
10,
11].
Clostridium septicum is an anaerobic gram-positive terminal endospore-forming bacillus [
12]. This bacterium exerts its pathogenic action through different extracellular toxins, leading to death by toxic shock, necrosis, and inflammation at the infection site [
13]. The cytotoxicity of the alfa toxin of
C. septicum has been the most investigated in different cellular lines. For example, it has been found that the toxicity mechanism depends on the eukaryotic cell type used to assess cytotoxicity [
14]. Indeed, the protoxin form of
C. septicum αtoxin causes a significant cytolytic effect in eukaryotic cells [
15]. Furthermore, this protoxin causes pores in the cell membrane and triggered apoptosis [
14]. Because of the extensive tissue damage and high mortality observed in the non-traumatic gas gangrene 67-100% caused by
C. septicum both in humans and in animals, it is noteworthy that besides the cytolytic activity of α-toxin, other exotoxins secreted by the bacterium may participate in the death of host tissue cells [
16]. However, studies on the identification of
C. septicum exotoxin/s that causes macrophage death are rare [
15]. Autophagy, also known as programmed cell death type II, is a distinctive cellular event characterized by the formation of autophagosomes and the degradation of organelles and intracellular materials within autophagosomes fused with lysosomes [
17]. In addition to occurring at a basal level, this process is enhanced in response to stress conditions such as starvation, radiation, or pharmacological agents [
18]. Whether exotoxins secreted by
C. septicum cause autophagy in macrophages remains a matter of discussion [
19]. Herein, we aimed to investigate the effects of partially purified fractions of proteins secreted by the culture of
C. septicum on the mechanism of macrophage death, which may help explain bacterial evasion of the innate immune response at the infection site.
2. Results
C. septicum PPFs kill mouse peritoneal macrophages
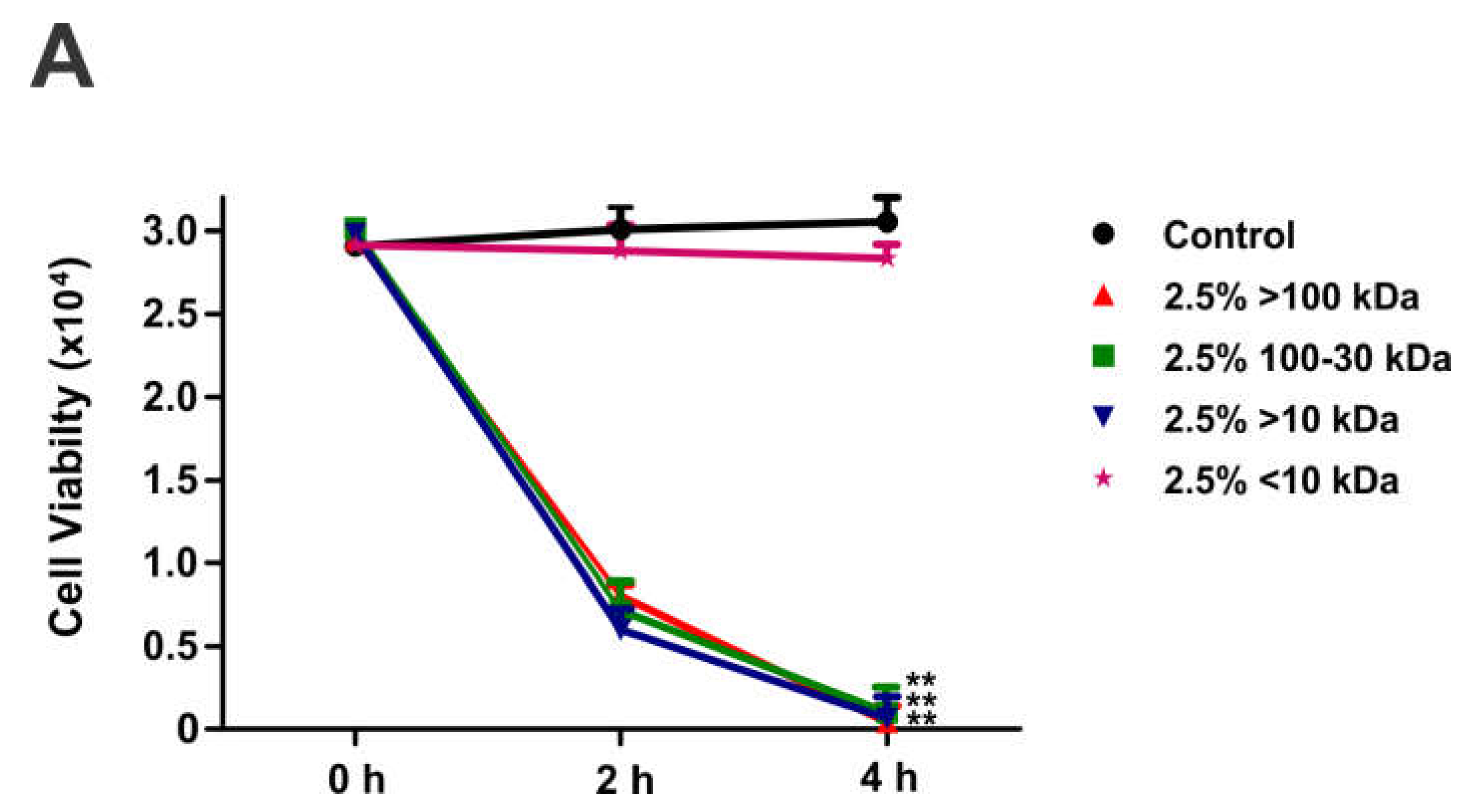
To test the effect of PPFs on macrophage viability, trypan blue assay was performed (
Figure 1). After 2 or 4h of incubation with 2.5% (v/v) PPF<10kDa in the culture medium, the macrophage viability was not affected. However, incubation with 2.5% PPF>10 kDa 100-30 kDa and <100kDa caused approximately 85% cell death after 2h of incubation and almost 100% cell death after 4h.
C. septicum PPFs produced morphologic changes compatible with cells death in mouse peritoneal macrophages
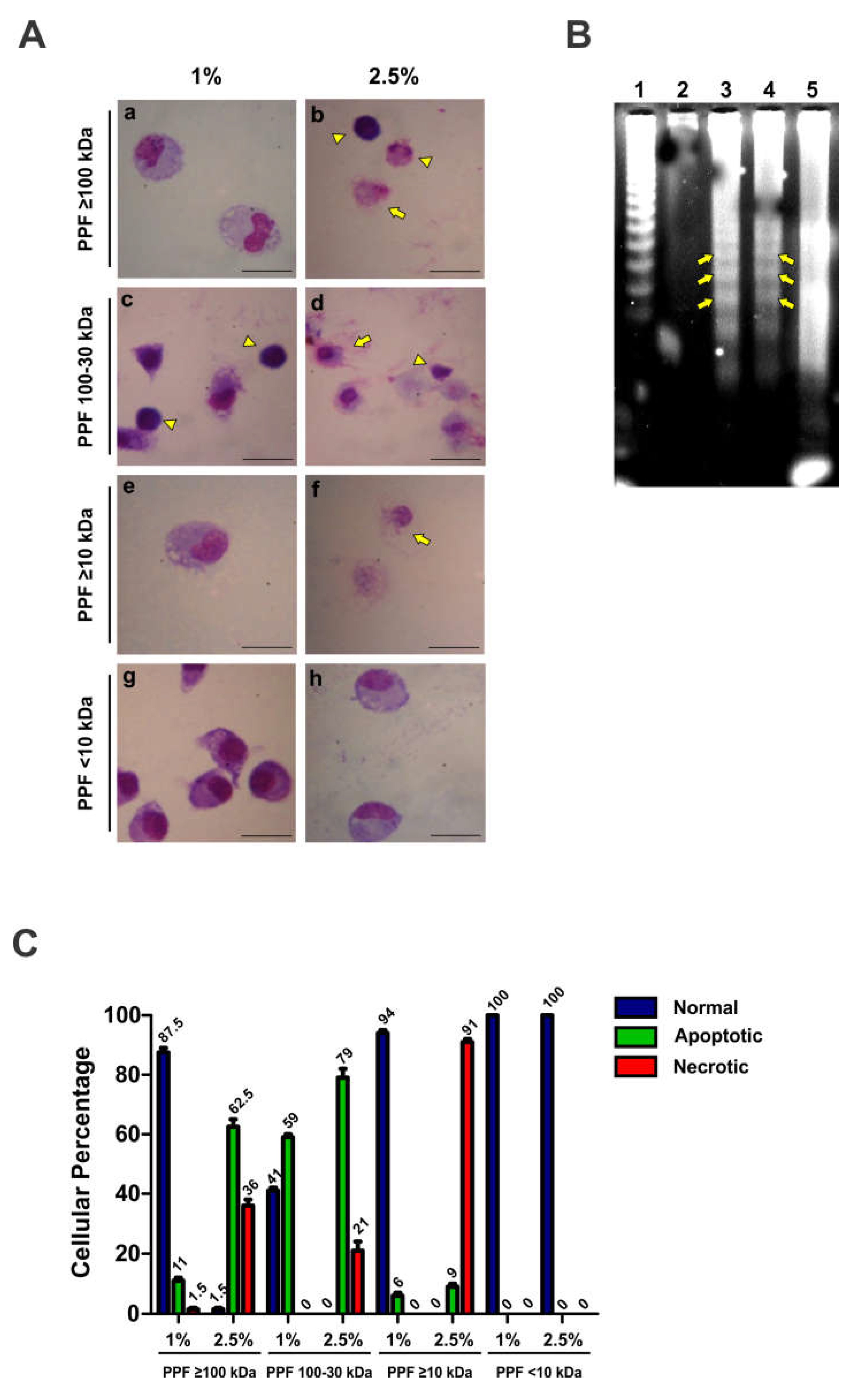
To test the mechanism of PPF-induced cytotoxicity caused by PPFs, mouse peritoneal macrophages were treated with 1% or 2.5% PPF ≥100, 100-30, ≥10, and <10kDa for 4h. Morphological changes in macrophages were observed using optical microscopy after Giemsa staining (
Figure 2A). A marked apoptotic effect (pycnotic nucleus) was observed upon exposure to 2.5% PPF≥100 kDa (
Figure 2A, panels and a b). We also observed morphological changes compatible with apoptosis upon treatment with PPF100-30kDa (
Figure 2A, panel c) at low concentrations and necrosis at high concentrations (
Figure 2A, panel d). A similar effect was observed upon treatment of macrophages with PPF<10kDa (
Figure 2A, panel f). Treatment with PPF<10kDa did not show any morphological effects on the cells (
Figure 2A, panels g-h). Differential cell morphology analysis, as the percentages of normal, apoptotic, and necrotic cells, is shown in
Figure 2B.
An electrophoretic DNA leader pattern is usually observed in cells that die via apoptosis. We observed that treatment of macrophages with 2.5% PPF≥100kDa resulted in DNA-leader fragmentation (
Figure 2C, Line 3, yellow arrows). This pattern was not observed in DNA isolated from macrophages treated for 4h with 1% PPF≥100kDa (
Figure 2C, line 2). In contrast, macrophages treated with 1% PPF100-30kDa showed the typical apoptotic pattern of DNA fragmentation, indicated with yellow arrows in
Figure 2C, Line 4. However, higher PPF100-30kDa concentrations in the culture medium caused a DNA-random fragmentation pattern compatible with a necrosis cell death mechanism (
Figure 2C, Line 5).
C. septicum PPF≥100kDa induces apoptosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages
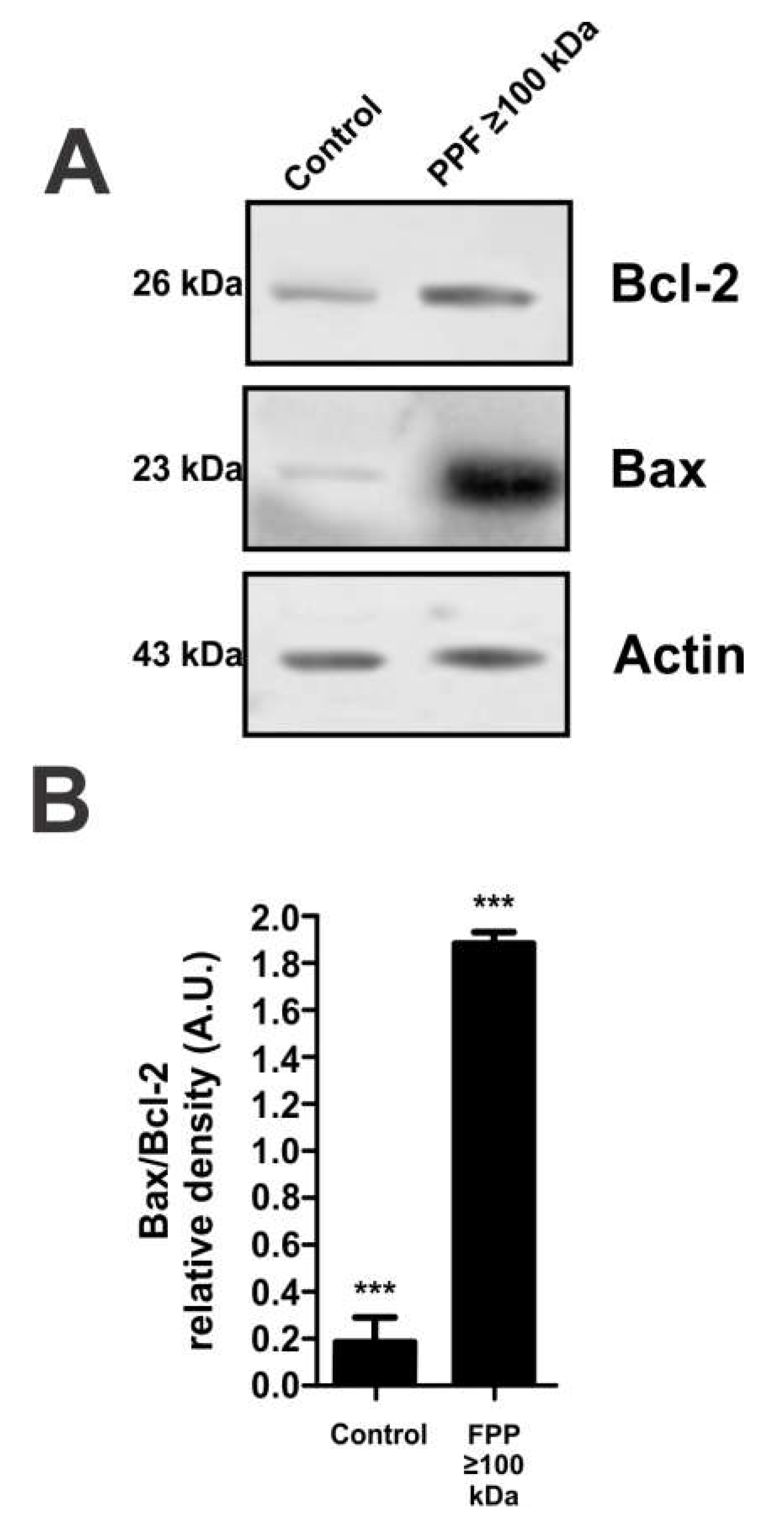
To further corroborate the cell death mechanism triggered by PPF≥100kDa exposure, Bcl-2 and Bax were measured by western blotting using β-actin as a loading control. Compared to the control, exposure of mouse peritoneal macrophages to 4h 2.5% PPF≥100 kDa caused a slight increase in the expression of the anti-apoptotic proteinBcl-2. However, the same treatment caused an almost 10-times increment in the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein-Bax (
Figure 3A). In agreement with these data, semiquantitative analysis of the band intensities shown in Figure. 3B indicates an almost 10-times increment in Bax2 expression.
C. septicum PPF≥100kDa induces autophagy in mouse peritoneal macrophages.
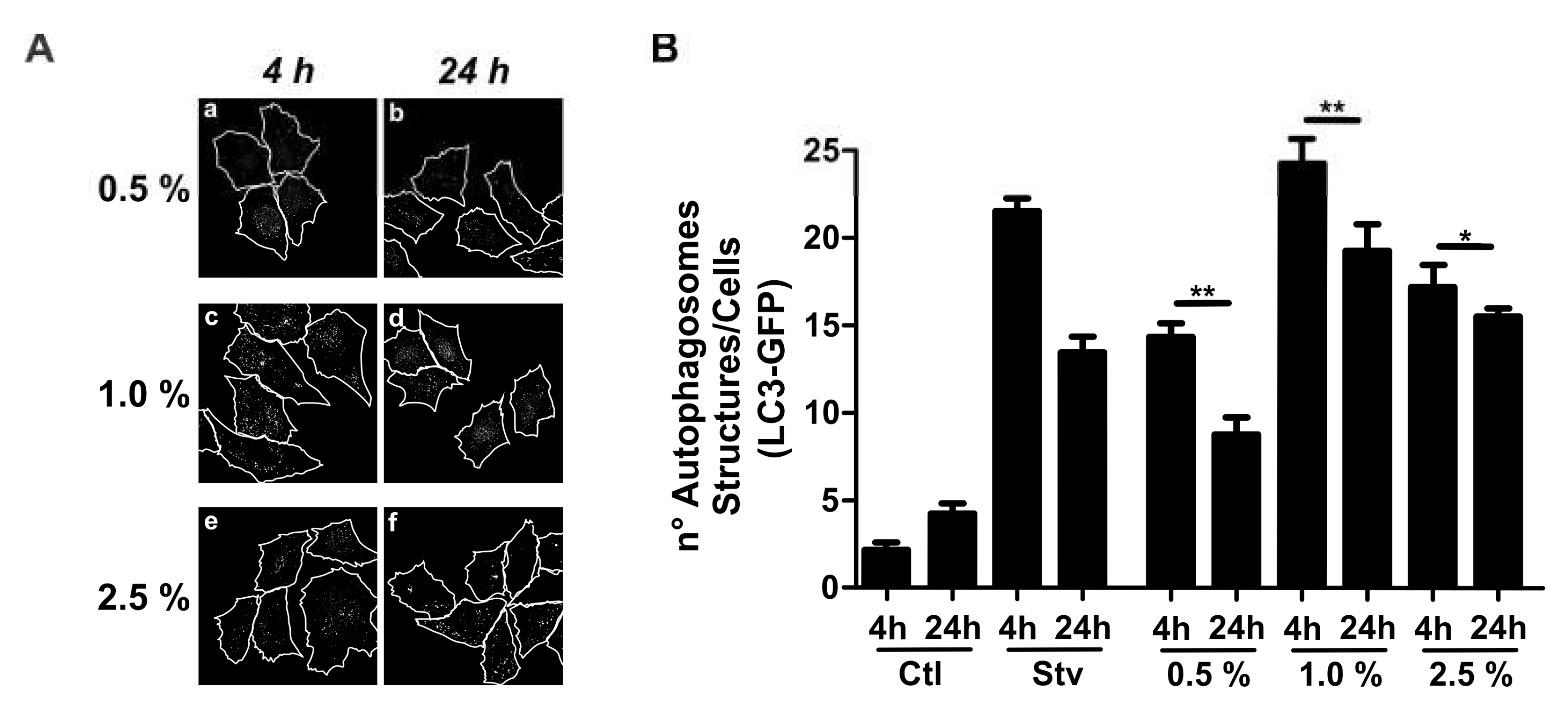
Morphologically, macrophages incubated with 1% PPF≥100 kDa showed no significant signs of apoptosis or necrosis, but showed extensive development of cytoplasmic vacuoles (
Figure 1A, panel a). This morphological pattern raises the question of whether PPF can cause autophagy. Light chain 1 of microtubule-associated protein 1 (LC3) is the mammalian homolog of the autophagy protein in yeast Atg8, which is added to autophagosome membranes when autophagy occurs. Therefore, we measured the expression of the autophagic protein LC3 in CHO cells stably overexpressing the LC-3-green-fluorescent protein (GFP). These cells were incubated for 4h or 24h with 0.5%, 1%, or 2.5% PPF≥100kDa.
Figure 4A shows a confocal image of the cell localization of LC3-GFP in mouse peritoneal macrophages exposed to different concentrations of PPF≥100kDa for 4h and 24h. An image analysis of
Figure 4A is shown in
Figure 4B. The data indicated that the exposure of mouse peritoneal macrophages to PPF≥100kDa caused a higher expression of LC3-GFP at 4h than at 24h of incubation (
Figure 4B). Nevertheless, autophagy-induced apoptosis may indicate a possible mechanism for apoptotic cell death triggered by this PPF fraction in mouse peritoneal macrophages.
To confirm whether autophagy is involved in cell death caused by exposure of mouse peritoneal macrophages to 1% PPF≥100kDa for 4h we measured the conversion of free cytosolic LC3B (LC3B-I) to LC3B conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine (LC3B-II). This conversion was time dependent, starting from the first hour of exposure to PPF (
Figure 5A). The LC3 II/LC3 I ratio, which indicates the conversion rate of LC3 I to LC3 II, increased over time in macrophages incubated with PPF of ≥100kDa 1% (
Figure 5B). These data are consistent with autophagy-induced apoptosis and may indicate a possible mechanism for apoptotic cell death triggered by this PPF fraction in mouse peritoneal macrophages.
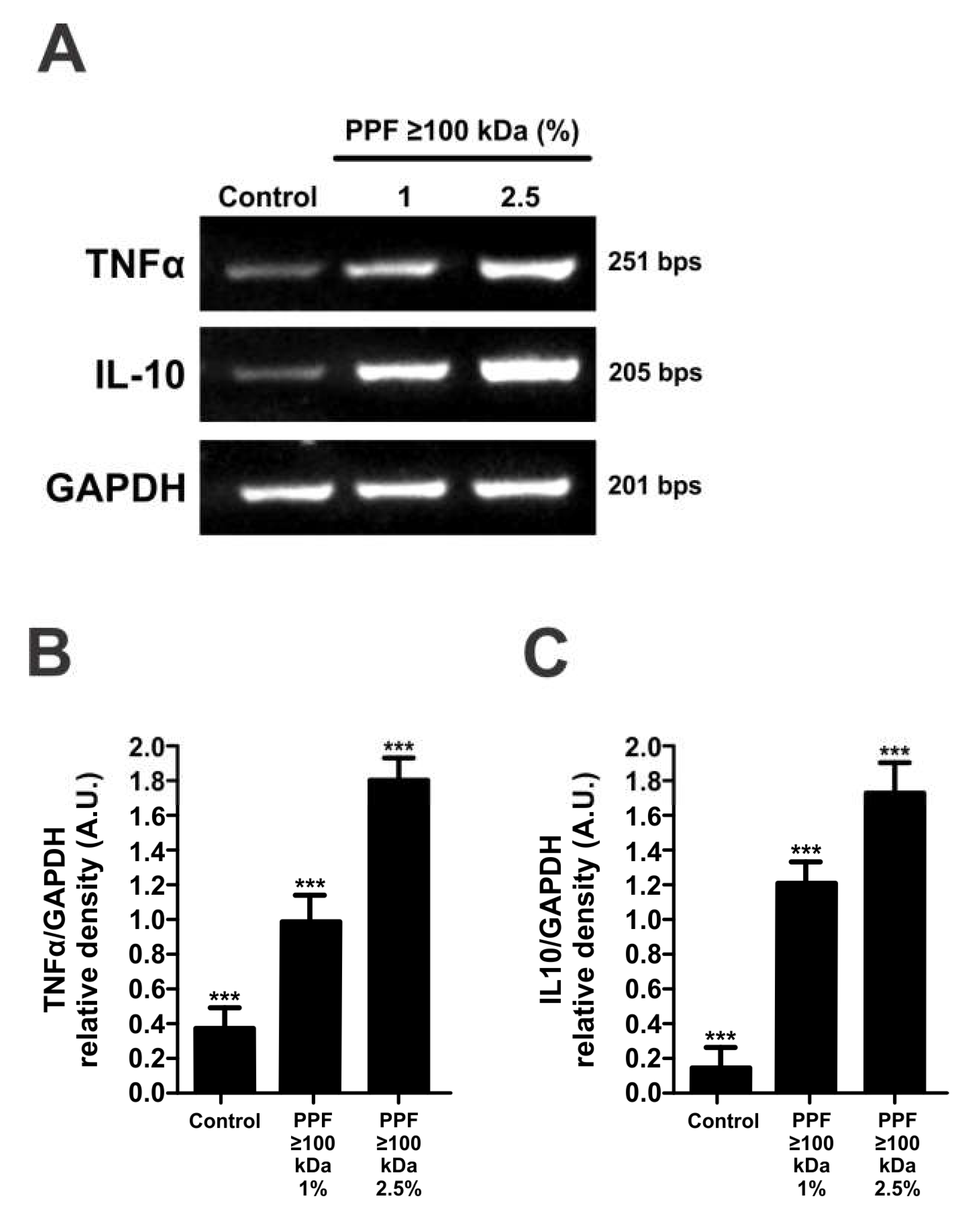
C. septicum PPF ≥100kDa affects cytokine expression in mouse peritoneal macrophages.
Several members of the Clostridium family secrete proteins that induce the expression of tumor necrosis factorα (TNFα) and interleukin-10 (IL-10), in monocytic cell lines. As a cell response to PPF≥100kDa the expression of these cytokines may increase. To test our hypothesis, we performed RT-PCR analysis of IL-10 and TNFα mRNAs in macrophages exposed to 1 and 2.5% PPF≥100kDa (
Figure 6A). The semi-quantitative analysis of band intensities in relation to GAPDH mRNA is shown in
Figure 6B,C. This result indicates that
C. septicum PPF≥100kDa can induce the cytokine-mediated response of macrophages, which may be responsible for triggering autophagy and further cell death by apoptosis.
3. Discussion
Exposure of mouse peritoneal macrophages to
C. septicum PPF≥100kDa triggers cell responses consisting of pro-autophagy cytokines (IL-10 and TNFα), autophagy, and cell death by apoptosis. These data support a possible mechanism by which extracellular proteins secreted by bacteria can modulate the innate immune response at the infection site, which can serve as a critical pathogenic factor. One of the characteristic features of myonecrotic diseases caused by clostridia is the absence of phagocytic cells at the site of infection [
20,
21,
22]. This observation suggests an important modulation strategy used by
C. septicum to evade the innate immune response by preventing the accumulation of phagocytic cells, such as polymorphonuclear cells, monocytes, and macrophages, at the site of infection [
2,
3]. It has been shown that certain bacterial cytotoxins, acting alone or together, are capable not only of producing pores in the membrane of cells of the immune system [
2]. Within gram-positive microorganisms, Clostridia can induce apoptosis in eukaryotic cells [
22]. Little information is available regarding the molecules that modulate the apoptotic pathway, and the molecular mechanisms differ with respect to gram-negative bacteria. The cytotoxicity of the α-toxin of
C. septicum has been widely studied in different animal cell lines, and it has been shown that its toxic activity varies depending on the cell type used to assess the toxicity mechanism [
14]. Moreover, it has been reported that both the protoxin and the active α-toxin exert their cytolytic effect on mammalian cells by forming membrane pores [
23], but the involvement of autophagy has rarely been reported. It has been reported that
C. septicum can secrete, in addition to the α-toxin, a series of toxins and enzymes that have not been characterized so far, and thus their participation in cytotoxicity is unknown. This information is critical for understanding the modulation of the innate immune system responses and activity at the infection site. Interestingly, our results indicate that the exposure of mouse peritoneal macrophages to PPF≥100kDa induces apoptosis. The exotoxins found in this PPF may include the
C. septicum α-toxin; however, several authors have reported that the mechanism of cell death induced by this exotoxin does not involve apoptosis, but necrosis. Importantly, α-toxin has been found in PPF100-30kDa [
24,
25,
26]. Our data clearly showed a characteristic DNA ladder fragmentation pattern in macrophages treated with 2.5% PPF≥100kDa. At the same concentration, PPF100-30kDa caused a broad and random DNA fragmentation pattern consistent with a necrosis cell death mechanism. These results were supported by the morphological pattern of macrophages treated with the same concentration of PPFs. In addition, we found that the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax increased markedly in macrophages treated with PPF ≥100kDa, whereas Bcl-2 expression remained almost unchanged. These results may indicate that the proteins of the PPF≥100kDa fraction induce apoptosis and that this effect is due to exotoxins other than α-toxin. In contrast, incubation of macrophages with low concentrations of
C. septicum PPF≥100 kDa caused autophagy, but the mechanism remains unclear. Autophagy is a lysosomal degradation pathway essential for the cellular response to stressors aimed at preserving cellular survival, differentiation, development, and homeostasis [
27,
28]. LC3 typically localizes to the cytosol under normal conditions and translocates to autophagosomal membranes when autophagy is triggered. There are two forms of LC3, LC3-I and LC3-II. LC3-I is the non-lipidated form with a molecular weight of 16 kDa, and LC3-II is the lipidated form with a molecular weight of 14 kDa. Conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II indicates the formation of autophagosomes. Thus, changes in the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio are indicative of autophagic activity [
29]. Moreover, the exposure of macrophages to 1% PPF≥100kDa induced autophagy over time (until 4 h). Autophagy is an important process that induces apoptotic cell death in response to microbial toxins [
1]. In addition, autophagy induced by PPF could be classified as cell death associated with autophagy, giving an advantage to
C. septicum during infection. The transcriptomic response to
C. septicum PPF≥100kDa involves the expression of several survival mRNAs encoding several proteins involved in immunomodulation mechanisms, including autophagy and apoptosis. Among these transcripts, IL-10 and TNFα mRNA [
30] are critical for triggering autophagy, which can lead to apoptosis. It has been reported that these cytokines induce autophagy and apoptosis in macrophages [
31,
32]; however, the mechanism remains to be fully understood. However, our data suggest that exposure of mouse peritoneal macrophages to
C. septicum PPF≥100kDa can trigger a cell response, including induction of TNF and IL-10 expression. These cytokines trigger autophagy, which leads to programmed cell death. Our data suggest that exotoxins secreted by
C. septicum and contained in a PPF≥100kDa obtained under conditions similar to those found in tissue microenvironments cause apoptosis in macrophages. Our findings are consistent with a novel mechanism by which exotoxins produced by
C. septicum deplete innate immune cells, which are critically involved in host defense at the infection site.
4. Conclusions
Exposure of mouse peritoneal macrophages to C. septicum PPF≥100kDa triggers cell responses consisting of pro-autophagy cytokines (IL-10 and TNFα), autophagy, and cell death by apoptosis.
These data support a possible mechanism by which extracellular proteins secreted by bacteria can modulate the innate immune response at the infection site, which can serve as a critical pathogenic factor.
We found that the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax increased markedly in macrophages treated with PPF ≥100kDa, whereas Bcl-2 expression remained almost unchanged
These results may indicate that the proteins of the PPF≥100kDa fraction induce apoptosis and that this effect is due to exotoxins other than α-toxin.
Our findings are consistent with a novel mechanism by which exotoxins produced by C. septicum deplete innate immune cells, which are critically involved in host defense at the infection site.
5. Materials and Methods
Clostridium septicum. The ATCC 12464 strain of C. septicum was obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). This strain was preserved under anaerobic conditions in a cooked meat culture (MCC) medium at room temperature. An anaerobic environment was achieved using the Vaseline-Paraffin (VAS-PAR) method. Both cell and cell supernatants were obtained when the bacterial culture reached the logarithmic growth phase. The evolution of the cultures was followed by changes in optical density at 580 nm (DO580) using a Metrolab VD 40 spectrophotometer (Pirt, 1970). The early logarithmic phase of the culture was obtained between 4 and 6 h of incubation.
Preparation C. septicum partially purified fractions (PPF). To obtain the cell-free supernatant (CFS), the cultures in the logarithmic growth phase were centrifuged at 5,500 × g for 10 min at 4°C (SIGMA, 3K30 centrifuge). The pelleted cells were then separated from the supernatant. The PPFs were obtained from the CFS by ultracentrifugation fractionation according to the molecular weight cut-off using Millipore 100kDa and 30kDa cut-off concentrators, and an Amicon Ultra-0.5 concentrator of cut-off = 10 kDa at 5,000 × g at 4°C and a recovery spin of 1,000 × g. CFS was concentrated approximately 20-times. PPF was used immediately after being obtained in subsequent tests to avoid any activity loss due to freezing and thawing. PPF was recovered in sterile Eppendorf tubes. The molecular weight (MW) range of the four PPFs used in this study was as follows: (i) ≥100 kDa (PPF≥100 kDa); (ii) 100 kDa at 30 kDa (PPF100-30 kDa), (iii) ≥10 kDa (PPF≥10 kDa), and (iv) <10 kDa (PPF<10 kDa).
Isolation and culture of elicited mouse peritoneal macrophages. Elicited peritoneal macrophages were obtained from Rockland mice having between 18 g–20 g of body weight. Groups of two animals were intraperitoneally injected with 1 ml of a sterile 10% protease peptone suspension (Difco) to increase the number of macrophages in the peritoneum. After 48h, peritoneal cells were isolated by lavage of the peritoneal cavity twice with 10 ml of ice-cold sterile saline solution (pH 7.4). The cell suspension was centrifuged at 4oC at 3,000 xg for 15 min. The pelleted peritoneal cells were rinsed twice with ice-cold sterile saline solution. The viability of isolated peritoneal cells was assessed using the trypan blue uptake assay. Isolation of macrophages from the peritoneal-cell suspension was performed by selective adherence to a tissue plate in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% antibiotic-antimycotic mix (Gibco®), and 25 μg/ml amphotericin B. After selection of peritoneal macrophages, the monolayer was rinsed with sterile saline to eliminate non-adherent cells, and fresh medium was added to the macrophage monolayer.
Treatment of macrophages with different PPFs. Macrophages (2×106) were plated in 12- or 24-well plates and incubated for 4 h at 37°C and 5% CO2. After rinsing the monolayers with fresh medium, the macrophages were treated with 1% to 2.5% (%v/v) PPFs in the culture medium for different periods in a cell incubator.
CHO cell culture and autophagy analysis. The hamster-ovarian epithelial cell lineCHO-K1 (catalog #CCL-61), stably transfected to overexpress pEGFP-LC3, was grown in α-MEM supplemented with 10% FBS, streptomycin (50 μg/ml), and penicillin (50 IU/ml). For autophagy analysis, cells were rinsed three times with ice-cold sterile PBS and incubated in Earle's Balanced Salt Solution (EBSS) at 37°C for different periods in the presence or absence of different concentrations of PPFs. Starvation, a positive control for autophagy, was induced by rapamycin treatment (50 µg/ml). GFP expression in CHO cells was assessed by confocal imaging using an Olympus Confocal FV1000 microscope. Autophagy was assessed by counting, in the confocal images, the number of LC3 dots per cell and by normalizing the results according to the respective control (cells without any treatment). Confocal images from 10-random fields were quantified, representing approximately 80 cells per experiment.
Observation of morphological changes. Morphological changes in macrophages exposed to PPFs were evaluated without staining (40X) or after Giemsa staining. Giemsa staining was performed on 3 mm circular coverslips placed at the bottom of 6-well plates. The cells were treated with PPFs, fixed with methanol, and stained with Giemsa (1/24) for 30 min. The program FV10-ASW 3.0, was used for living-cell image analysis. The observed morphological changes were expressed as the number of apoptotic or necrotic cells observed in 100 cells analyzed.
DNA leader-fragmentation analysis. After the indicated incubation periods with PPFs, macrophage monolayers were rinsed with ice-cold PBS and then lysed with 350 µL of lysis buffer (NaCl (1 M), sucrose, (1M), Tris (1M), EDTA (1 M), and SDS (10%), pH 8.6). Cell lysates were centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 10 min. The DNA contained in the supernatant was precipitated by the addition of three volumes of isopropanol and 5M NaCl, and the mixture was incubated overnight at -20 °C. Afterward, the mixture was centrifuged at 12,000 xg for 10 min and the pellet were resuspended in 750 μl of Tris-EDTA buffer (0.25M sodium chloride, 0.05M Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 20 mM EDTA, sodium dodecyl sulfate (1% SDS) (w/v) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (4% PVP) (w/v), pH 7,6. Then 10 μl of DNA was mixed with 2.5 μl of sample buffer (0.1% bromophenol blue, 15% glycerol), resolved on a 1% agarose gel electrophoresis (90V/cm for 1h) and finally, the gel was stained with 1% GelRed ™ (Genbiotech), and the image was acquired using a UV-transilluminator.
RNA extraction and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). RNA isolation and reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR) were performed to measure the expression of genes encoding inflammatory cytokines upon treatment of mouse peritoneal macrophages with different PPFs. After exposure to PPFs, the culture medium was removed, and the macrophage monolayer was rinsed twice with sterile PBS (pH 7.4). Total RNA was isolated and purified using Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen, Cat#) as described by the manufacturer. The purified RNA pellet was resuspended in 50 μl of RNAse-free water. mRNA was retrotranscribed to cDNA according to the M-MLV Transcripta protocol (PB-L Productos Bio-Logicos). Amplification of the cDNA fragments was carried out using 20 μl of the reaction mixture (10X reaction buffer, 2.5 μl, 50 mM MgCl2, 0.75 μl, 10 mM dNTPs (dATP, dTTP, dCTP, dGTP), 1 μl; 10 mM Forward (F) and Reverse (R) oligonucleotides, 1.25 μl of each, 13 μl nuclease-free H20 (added first) and finally 0.25ul of Taq DNA Pol (5 IU/μl). Five microliters of cDNA were used for annealing. The amplification protocols used for each sequence were those recommended by the GenBank NCBI (
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The primers used to amplify the resulting cDNAs were as follows: TNFα, F: CCGAGGCAGTCAGATCATCTT and R: AGCTGCCCCTCAGCTTGA; IL-10, F: TTACCTGGAGGAGGTGATGC and R: GGCTTTGTAGACCCCCTTCT; GAPDH (housekeeping gene), F: ATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGAC and R: GCACGTCAGATCCACAACAG. Samples (10 μl) were mixed with 2.5 μl of sample buffer and separated by agarose gel (1.9%) electrophoresis at 90V/cm for 1h. Afterward, the gel was stained with a 1% solution of GelRed ™ (Genbiotech), and the bands were visualized and acquired under UV trans-illumination. The size of the resulting amplicons was determined by comparison with a molecular weight marker (100 bp PB-L® Ladder).
Western blot. Briefly, macrophages were treated with PPFs, lysed with 150 μl of native sample buffer per well, and scraped. The cell lysate was boiled for 4-5 min and 400 μl of the reducing agent DTT (1%, v/v) was added. Samples were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and then immunostained with primary antibodies (anti-Bcl-1, anti-Bax). Immunocomplexes were detected using anti-rabbit IgG-horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody. The immunocomplexes were then developed using the LumiPico® ECL Kit, following the manufacturer's instructions (ShineGene, catalog #ZK00902).
Statistics. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SE) from three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism software using one-way ANOVA and/or Student’s two-tailed t-test followed by Tukey’s comparisons test.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Ortiz Flores RM, Mattar Domínguez MA and Cortiñas TI; methodology, Ortiz Flores RM and Mattar Domínguez MA; software, Ortiz Flores RM; validation, Gomez Mejiba SE and Mattar Domínguez MA; formal analysis, Ortiz Flores RM and Sasso, CV; investigation, Ortiz Flores RM, Cáceres CS and Sasso CV; resources, Mattar Domínguez MA; data curation, Gomez Mejiba SE and Mattar Domínguez MA; writing—original draft preparation, Ortiz Flores RM and Sasso CV; writing—review and editing, Gomez Mejiba SE and Mattar Domínguez MA; visualization, Gomez Mejiba SE and Mattar Domínguez MA; supervision, Cortiñas TI and Mattar Domínguez MA; project administration, Mattar Domínguez MA; funding acquisition, Cortiñas TI and Mattar Domínguez MA. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Animals were housed and cared at the Animal Resource Facilities, Faculty of Chemistry, Biochemistry and Pharmacy, National University of San Luis. Mice were handled according to the Institutional Committee for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals guidelines.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to thank the research support provided by the Universidad Nacional de San Luis (San Luis, Argentina) and the Instituto de Histología y Embriología - Universidad Nacional de Cuyo (Mendoza, Argentina).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- X.-R. Wang and B. Cull, “Apoptosis and Autophagy: Current Understanding in Tick–Pathogen Interactions,” Front Cell Infect Microbiol, vol. 12, p. 784430 23, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. K. O’Brien and S. B. Melville, “Effects of Clostridium perfringens Alpha-Toxin (PLC) and Perfringolysin O (PFO) on Cytotoxicity to Macrophages, on Escape from the Phagosomes of Macrophages, and on Persistence of C. perfringens in Host Tissues,” Infect Immun, vol. 72, no. 9, pp. 5204–5215, Sep. 2004. [CrossRef]
- E. Bryant and D. L. Stevens, “Expression of activational markers on circulating leukocytes from baboons with group A streptococcal (GAS) bacteremia,” Adv Exp Med Biol, vol. 418, pp. 801–804, [Online]. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9331773.
- D. L. Stevens, M. J. Aldape, and A. E. Bryant, “Life-threatening clostridial infections,” Anaerobe, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 254–259, Apr. 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Lotz et al., “Highly purified lipoteichoic acid activates neutrophil granulocytes and delays their spontaneous apoptosis via CD14 and TLR2,” J Leukoc Biol, vol. 75, no. 3, pp. 467–477, Mar. 2004. [CrossRef]
- S. G. Popov et al., “Effect of Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells,” FEBS Lett, vol. 527, no. 1–3, pp. 211–215, Sep. 2002. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Park, F. R. Greten, Z.-W. Li, and M. Karin, “Macrophage Apoptosis by Anthrax Lethal Factor Through p38 MAP Kinase Inhibition,” Science (1979), vol. 297, no. 5589, pp. 2048–2051, Sep. 2002. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Carrero, B. Calderon, and E. R. Unanue, “Type I Interferon Sensitizes Lymphocytes to Apoptosis and Reduces Resistance to Listeria Infection,” Journal of Experimental Medicine, vol. 200, no. 4, pp. 535–540, Aug. 2004. [CrossRef]
- A. Guzmán et al., “Apoptosis of mouse dendritic cells is triggered by listeriolysin, the major virulence determinant of Listeria monocytogenes,” Mol Microbiol, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 119–126, Apr. 1996. [CrossRef]
- Ring, C. Depnering, J. Pohl, V. Nizet, J. L. Shenep, and W. Stremmel, “Synergistic Action of Nitric Oxide Release from Murine Macrophages Caused by Group B Streptococcal Cell Wall and β-Hemolysin/Cytolysin,” J Infect Dis, vol. 186, no. 10, pp. 1518–1521, Nov. 2002. [CrossRef]
- G. Y. Liu et al., “Sword and shield: Linked group B streptococcal β-hemolysin/cytolysin and carotenoid pigment function to subvert host phagocyte defense,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 101, no. 40, pp. 14491–14496, Oct. 2004. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Katlic, W. M. Derkac, and W. S. Coleman, “Clostridium septicum infection and malignancy.,” Ann Surg, vol. 193, no. 3, pp. 361–4, Mar. 1981. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Hickey et al., “Molecular and Cellular Basis of Microvascular Perfusion Deficits Induced by Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium septicum,” PLoS Pathog, vol. 4, no. 4, p. e1000045, Apr. 2008. [CrossRef]
- L. Kennedy et al., “Pore-Forming Activity of Alpha-Toxin Is Essential for Clostridium septicum -Mediated Myonecrosis,” Infect Immun, vol. 77, no. 3, pp. 943–951, Mar. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M. J. Aldape, A. E. Bryant, and D. L. Stevens, “Spontaneous C. septicum gas gangrene: A literature review,” Anaerobe, vol. 48, pp. 165–171, Dec. 2017. [CrossRef]
- G. Dedemadi, I. Sakellariou, A. Kolinioti, P. Lazaridis, and E. Anagnostou, “Clostridium septicum myonecrosis: a destructive and lethal condition.,” Am Surg, vol. 77, no. 6, pp. e101–2, Jun. 2011, [Online]. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21679616.
- J. Klionsky et al., “Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy.,” Autophagy, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 445–544, Apr. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Y.-J. Chen et al., “Platonin induces autophagy-associated cell death in human leukemia cells,” Autophagy, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 173–183, Feb. 2009. [CrossRef]
- C. C. Mihalache and H.-U. Simon, “Autophagy regulation in macrophages and neutrophils,” Exp Cell Res, vol. 318, no. 11, pp. 1187–1192, Jul. 2012. [CrossRef]
- C. A. O. Junior, R. O. S. Silva, F. C. F. Lobato, M. A. Navarro, and F. A. Uzal, “Gas gangrene in mammals: a review,” Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 175–183, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. A. Keyel, M. E. Heid, and R. D. Salter, “Macrophage responses to bacterial toxins: a balance between activation and suppression,” Immunol Res, vol. 50, no. 2–3, pp. 118–123, Aug. 2011. [CrossRef]
- C. Ren, H. Zhang, T. Wu, and Y. Yao, “Autophagy: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Reversing Sepsis-Induced Immunosuppression,” Front Immunol, vol. 8, p. 1832 27, Dec. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. B. Hang’ombe, M. Mukamoto, T. Kohda, N. Sugimoto, and S. Kozaki, “Cytotoxicity of Clostridium septicum alpha-toxin: its oligomerization in detergent resistant membranes of mammalian cells,” Microb Pathog, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 279–286, Dec. 2004. [CrossRef]
- T. I. Cortiñas, M. A. Mattar, and A. M. Stefanini de Guzmán, “Alpha-Toxin Production byClostridium septicumat Different Culture Conditions,” Anaerobe, vol. 3, no. 2–3, pp. 199–202, Apr. 1997. [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, M. Awad, J. Cheung, T. Hiscox, D. Lyras, and J. Rood, “The Pore-Forming α-Toxin from Clostridium septicum Activates the MAPK Pathway in a Ras-c-Raf-Dependent and Independent Manner,” Toxins (Basel), vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 516–534, Feb. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Knapp et al., “Clostridium septicum alpha-toxin forms pores and induces rapid cell necrosis,” Toxicon, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 61–72, Jan. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Doherty and E. H. Baehrecke, “Life, death and autophagy,” Nat Cell Biol, vol. 20, no. 10, pp. 1110–1117, Oct. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Bialik, S. K. Dasari, and A. Kimchi, “Autophagy-dependent cell death – where, how and why a cell eats itself to death,” J Cell Sci, vol. 131, no. 18, p. 215152, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Tanida, T. Ueno, and E. Kominami, “LC3 and Autophagy,” 2008, pp. 77–88. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Turner, B. Nedjai, T. Hurst, and D. J. Pennington, “Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease,” Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research, vol. 1843, no. 11, pp. 2563–2582, Nov. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xu, S. O. Kim, Y. Li, and J. Han, “Autophagy Contributes to Caspase-independent Macrophage Cell Death,” Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 281, no. 28, pp. 19179–19187, Jul. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Djavaheri-Mergny et al., “NF-κB Activation Represses Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-induced Autophagy,” Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 281, no. 41, pp. 30373–30382, Oct. 2006. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).