1. Introduction
Influenza infection causes substantial morbidity and mortality in pregnant women and young children. Immunization of pregnant women with an influenza vaccine is effective in reducing the risk of influenza [
1] and has been reported to be safe for mothers and their foetuses[
2] It also reduces the risk of influenza in infants during the first six months of life[
2,
3] In 2009-10 India witnessed an influenza (H1N1) pandemic[
4]. Influenza is still endemic in some part of countries, including Pune, the city in Maharashtra State that was most severely affected during the pandemic[
5]. In 2012, the World Health Organization (WHO) Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) recommended that any country with an influenza immunization program should prioritize pregnant women[
6]. Following the WHO recommendation and considering the endemic situation and availability of global data on influenza vaccine effectiveness in 2015, the Maharashtra state government proposed local health care authorities of endemic regions to vaccinate high-risk populations, such as pregnant women, with seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine free of charge. Since then, only selected civic hospitals in Pune have been vaccinating pregnant women with the trivalent Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (IIV3), mainly Vaxigrip. Vaccine coverage in the area was reported to be low because of frequent interruptions in vaccine supply and inadequate promotion of antenatal vaccination by healthcare providers from both the private and government sectors. Although there are no major safety concerns reported for maternal influenza vaccines, opinions on the effect of influenza vaccination on adverse birth outcomes vary[
7,
8,
9].
Observational studies conducted in Canada and Australia did not find an association between influenza vaccination during pregnancy and adverse foetal or perinatal outcomes [
10,
11]; however, another study conducted by Donahue et al. reported a possible association between influenza vaccination administered very early in the first trimester and spontaneous abortion [
12]. A review of previous studies on the safety of influenza immunization among pregnant women revealed that no studies have examined the influence of influenza vaccination on adverse birth outcomes in pregnant Indian women. This lack of evidence among pregnant women may present a barrier to endorsing the influenza vaccination. In addition, the effect of vaccination may vary by population- or geographic-specific factors, such as influenza seasonality and baseline rates of low birth weight or preterm births. Therefore, this study aimed to examine vaccine safety by comparing the incidence of adverse birth outcomes (including spontaneous abortion, preterm birth, low birth weight, and congenital anomalies) between vaccinated and unvaccinated pregnant women in Pune. In Pregnant women with underlying illnesses, such as hypertension or diabetes, the incidence of adverse birth outcomes is higher. The safety of influenza vaccination was evaluated based on background characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting and Study-Population
This cross-sectional, observational study was conducted at the Yashwantrao Chavan Memorial Hospital (YCM), a tertiary care civic hospital in Pune. Pregnant women attending Antenatal Care (ANC) were offered a trivalent injectable influenza vaccine, mainly Vaxigrip by the hospital. Vaccination was recommended during the second or third trimester of pregnancy however we also noticed that few pregnant women received vaccine in first trimester of their pregnancy. It was also noted that most women receiving the vaccine in the YCM Hospital preferred delivery in the maternity ward of the same hospital. The study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of KEM Hospital Research Centre Pune
(KEMHRC/ RVM/EC/2383). The ICMR’s Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical and Health Research on Human Participants (2017)[
13] were followed. We approached women who delivered in the YCM hospital and were admitted to the obstetric ward between October 2019 and March 2020. Voluntarily provided written Informed Consent was obtained from each participant to access their records and for interviews to check their socioeconomic status, medical history, past pregnancy status, alcohol consumption, and tobacco consumption using a structured questionnaire. Maternal characteristics were collected from all the participants.
2.2. Intervention
Influenza vaccination during pregnancy was defined as a vaccine received between the first day (date) of the last menstrual period and the end of pregnancy, and it was the focus of exposure in this study. The vaccination status of the participants was ascertained from the influenza vaccination stamp on their Ante Natal Care (ANC) card. The vaccination date and gestational week of vaccine administration were recorded.
2.3. Outcomes
Pregnancy-induced hypertension, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, chorioamnionitis (premature preterm rupture of membranes or PPROM), spontaneous and/or preterm birth, and birth outcomes, including congenital anomalies, low birth weight (< 2500 g) (LBW), very low birth weight (< 1500 g), APGAR scores at 1 and 5 min, NICU or neonatal care unit hospitalization, respiratory distress syndrome, and mechanical ventilation. The Brighton Collaboration guidelines were used to diagnose pregnancy and birth complications [
14]. The expected date of delivery was calculated from the last menstrual period (LMP) date. If the LMP date was not confirmed, the antenatal USG scan dates were used to calculate the estimated delivery date.
2.4. Covariates
In the first encounter with the participants in the obstetric wards of the hospital, information was obtained regarding socio-demographics, age, education, smoking, medical and obstetric history, complications during pregnancy, and vaccination status of influenza vaccine as an independent variable.
2.5. Statistical Methods for Analysis
The demographic and clinical characteristics of the study participants were descriptively analysed. Continuous variables were estimated as mean ± standard deviation (SD), while counts and percentages were used to describe categorical variables. To evaluate whether there was an association between influenza vaccination status and each outcome variable, chi-squared tests of association were applied to the variables. For all multivariable models, different levels of education, maternal health risk factors (such as age, gravidity, smoking, and alcohol intake), pre-existing health conditions, history of surgical operations, or abortions were among the variables selected as potential confounders based on available literature [15,16].
The intergroup statistical comparison of the distribution of categorical variables was performed using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact probability test if more than 20% had an expected frequency of less than 5. The intergroup statistical comparison of the distribution of means of continuous variables was performed using an independent sample t-test. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to obtain statistically significant and independent determinants of the incidence of abnormal outcome measures (such as delivery outcome and incidence of neonatal complications). The underlying normality assumption was tested before subjecting the continuous variables to t-test.
In the entire study, p-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All data were statistically analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS version 24.0, IBM Corporation, USA) for MS Windows.
3. Results
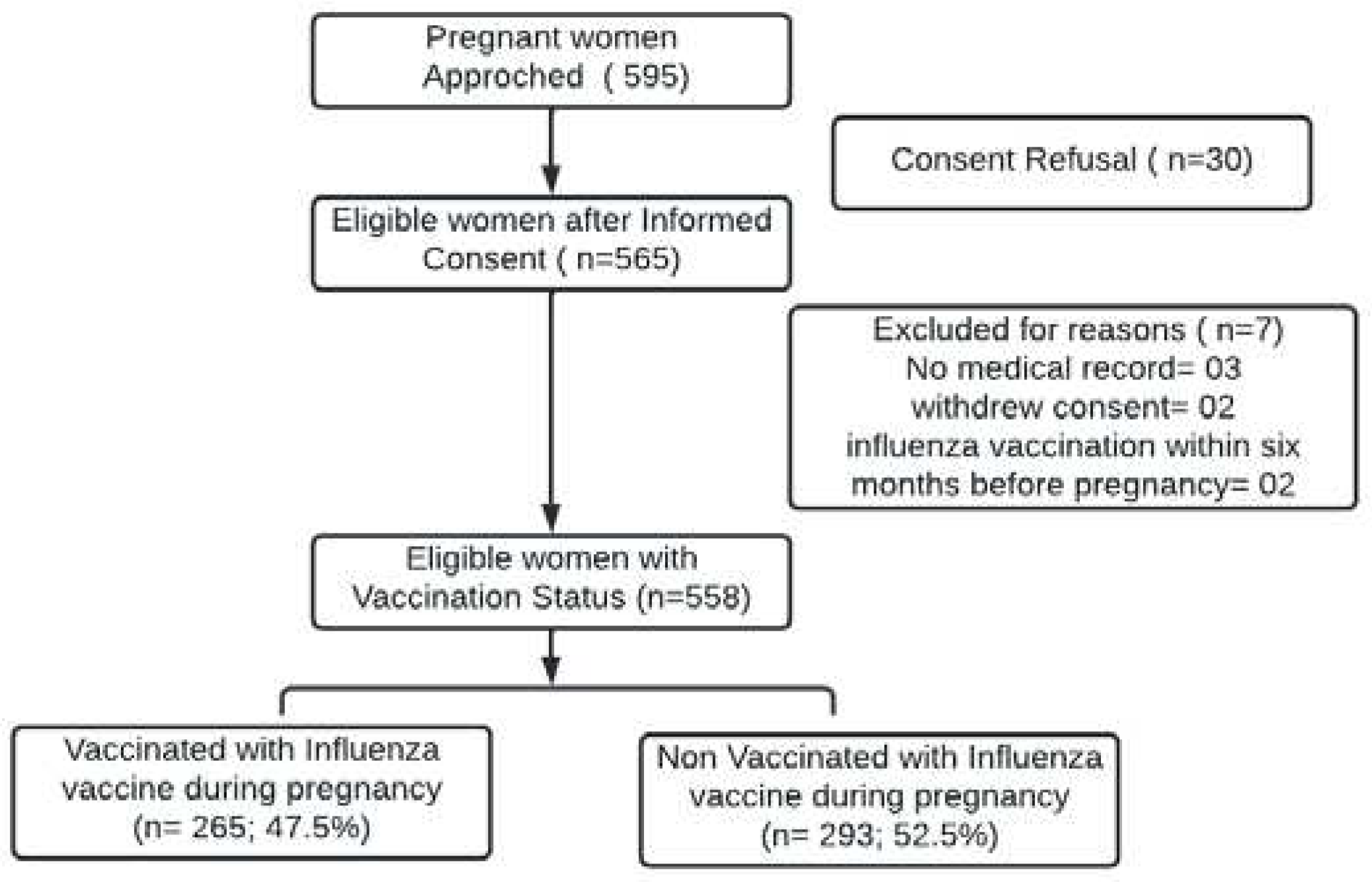
We approached 595 eligible women admitted to the obstetrics ward. Thirty women refused to provide informed consent. Written informed consent was obtained from 565 women and were further screened. Of the 565 women screened, two withdrew consent during screening and three participants had no mother and child protection card or medical notes; hence, they were excluded from our final analyses. Two women who had received influenza vaccination within six months prior to their pregnancy were excluded. The final cohort comprised 558 women (Fig. 1).
Of the 558 women recruited from the obstetric ward, 265 (47.5%) received an influenza vaccine during their pregnancy. Maternal characteristics did not differ significantly between vaccinated and unvaccinated women. At recruitment, the mean maternal age of the pregnant women was 24.7 years (SD 4.4) (range:18-45 years), and the median gestational age at influenza vaccination was 24 weeks (IQR 22-28 years), with 21.1% (118 of 558) presenting for their study clinic visit in the third trimester of pregnancy. Higher educational level was found to be significantly associated with vaccine acceptance (p<0.001) (
Table 1).
3.1. Outcomes
3.1.1. Pregnancy Outcomes
Of the 558 women, 43 (7.7%) had spontaneous abortions at < 20 weeks gestation. Though the number of spontaneous abortion cases were low in vaccinated group than that of unvaccinated the difference was not statistically significant. At recruitment, the mean maternal age of the pregnant women was 24.7 years (SD 4.4) (range:15-38 years), and the median gestational age was 28 weeks and enrolled in the first trimester of pregnancy.
3.1.2. Birth Weight Variable
Birth weight (gm) is a continuous numerical variable compared across vaccination status modalities. The distribution of birth weight (g) was not normal among the different groups (p = no: <0.001, yes:0.001). Infants born to vaccinated mothers were estimated to be 113.95 g heavier than infants born to unvaccinated mothers. In the present study, the mean birth weight was found to be 2633.57 (Table-2).
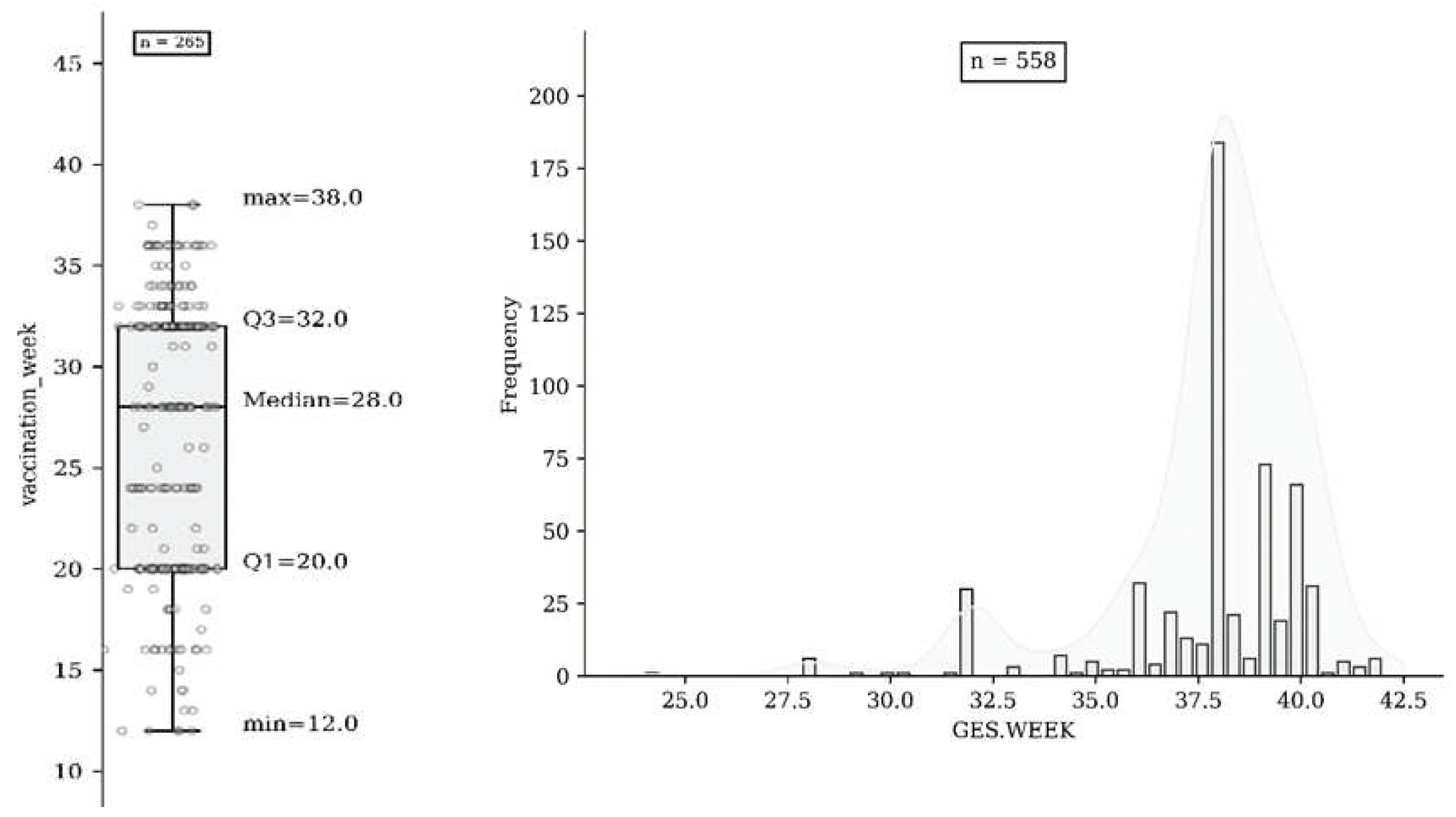
The overall uptake of influenza vaccination was 47.5% (265 558); of these, 1.9% (n = 5) were vaccinated in the first trimester, 40.4% (n = 107) in the second trimester, and 57.7% (n = 153) in the third trimester (Fig. 2a & 2b). A total of 77.8 % of uneducated women in the study (n=84/108) did not receive influenza vaccination during pregnancy. Of the 558 study participants, 43 (7.7%) had spontaneous abortions, three had stillbirths (0.53%), and 555 (99.47%) delivered a live infant. The mean gestational age at delivery was 37.8 weeks (SD 2.4 weeks). There was no association with spontaneous abortion in women who were vaccinated against influenza before 20 weeks of gestation. Our model showed that influenza vaccination during pregnancy was not associated with maternal hypertensive disorders, including gestational hypertension. Overall, 9.3% (52 of 558) of pregnancies resulted in preterm births. There was no difference in stillbirth rates between vaccinated (n = 1) and unvaccinated women (n = 2). Our time-dependent analysis showed no association between influenza vaccination through 37 weeks of gestation and preterm birth or preterm premature rupture of the membranes.
3.1.3. Birth Outcomes
Influenza vaccination during pregnancy had no effect on the risk of congenital anomalies (P =0.672). There was no evidence of an increased risk of LBW associated with the receipt of inactivated influenza vaccine during any trimester of pregnancy. Maternal influenza vaccination was protective against delivering Very LBW term infants in our univariate and multivariate analyses. There was no association between maternal influenza vaccination and adverse infant outcomes, including low APGAR scores at 1 min (OR 1.13, 95% CI, 0.30 to 4.26) and 5 min (OR 0.90, 95% CI 0.22 to 3.64), admission to the neonatal care unit (OR 0.75, 95% CI, 0.23 to 2.48), mechanical ventilation (OR 0.68, 95% CI, 0.15 to 3.04), and respiratory distress syndrome (OR 1.09, 95% CI, 0.33 to 3.60).
3.2. Figures, Tables and Schemes
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for subject disposition.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for subject disposition.
Table 1.
Maternal characteristics of vaccinated and unvaccinated pregnant women who delivered at an obstetric hospital in Pune between October 2019 and March 2020.
Table 1.
Maternal characteristics of vaccinated and unvaccinated pregnant women who delivered at an obstetric hospital in Pune between October 2019 and March 2020.
| Parameters |
Vaccinated
(n=265) |
Unvaccinated
(n=293) |
Total
(n=558) |
p-value |
| No. of participants |
265 (47.5%) |
293 (52.5%) |
558 |
|
| Maternal Age (years) |
|
|
|
|
| Age (yrs) |
24.8 ± 4.5 |
24.7 ± 4.4 |
24.7± 4.4 |
|
| <18 |
2 (0.8%) |
6 (2%) |
8 |
p = 0.424NS
|
| 18 to 30 |
228 (86%) |
251 (85.7%) |
479 |
|
| >30 |
35 (13.2%) |
36 (12.3%) |
71 |
|
| Parity |
|
|
|
|
| Primiparous |
132 (49.8%) |
129 (44%) |
261 |
p = 0.171 NS
|
| Multiparous |
133 (50.2%) |
164 (56%) |
297 |
|
| Maternal Education |
|
|
|
|
| Illiterate |
24 (9.1%) |
84 (28.7%) |
108 |
p< 0.001*
|
| Primary |
118 (44.5%) |
121 (41.3%) |
239 |
|
| Secondary |
70 (26.4%) |
60 (20.5%) |
130 |
|
| Graduation |
53 (20%) |
27 (9.2%) |
80 |
|
| Post-graduation |
0 (0%) |
1 (0.3%) |
1 |
|
| Gestational maturity |
|
|
|
|
| Extremely/early pre-term |
3 |
9 |
12 |
p=0.01*
|
| Pre-term/Late pre-term |
32 |
51 |
83 |
|
| Term/mature |
226 |
220 |
446 |
|
| Post-term |
4 |
13 |
17 |
|
| Smoking |
|
|
|
|
| No |
262 (98.9%) |
293 (100%) |
555 |
0.106NS
|
| Yes |
3 (1.1%) |
0 |
3 |
|
| Alcohol |
|
|
|
|
| No |
265 (100%) |
293 (100%) |
558 |
-- |
| Influenza vaccine at |
n (%) |
NA |
|
|
| 1st Trimester |
5 (1.9%) |
|
|
|
| 2nd Trimester |
107 (40.4%) |
|
|
|
| 3rd Trimester |
153 (57.7%) |
|
|
|
Mean (SD) Gest. Week of vaccine administration
|
26.8 ± 6.9 |
NA |
- |
|
Table-1 shows that the distribution of maternal education differed significantly between groups of non-vaccinated and vaccinated participants (P-value<0.05). A significantly higher proportion of vaccinated participants had a relatively higher level of education and vice versa (P-value<0.05). *P-value<0.05.
Table 2.
Delivery Characteristics and outcomes according to maternal influenza vaccination status with unadjusted (univariate) and adjusted (multivariate) odds ratios.
Table 2.
Delivery Characteristics and outcomes according to maternal influenza vaccination status with unadjusted (univariate) and adjusted (multivariate) odds ratios.
Delivery
Characteristics |
Not vaccinated (n=293) |
Vaccinated (n=265) |
Total (n=558) |
p-value |
Unadjusted (Univariate) or
Crude Odds ratio (COR) |
Adjusted (Multivariate)
Odds ratio (AOR)#
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COR |
95% CI |
p-value |
AOR |
95% CI |
p-value |
| Gestational age |
37.6 ± 2.60 |
38.09 ± 2.19 |
37.83 ± 2.43 |
0.02* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Full term |
252 (86%) |
228 (86%) |
480 (86%) |
0.02* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Post term |
8 (2.7%) |
18 (6.8%) |
26 (4.7%) |
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| Pre-term* |
33 (11.3%) |
19 (7.2%) |
52 (9.3%) |
|
1.64 |
0.91 – 2.97 |
0.09NS
|
1.69 |
0.92 – 2.99 |
0.14NS
|
| Birth weight |
2579.45 ± 602.41 |
2693.4 ± 503.51 |
2633.57 ± 560.05 |
0.02* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Normal |
204 (69.6%) |
191 (72.1%) |
395 (70.8%) |
0.12NS
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| LBW |
66 (22.5%) |
64 (24.2%) |
130 (23.3%) |
|
0.97 |
0.65 – 1.44 |
0.86NS
|
0.86 |
0.74 – 1.54 |
0.61NS
|
| VLBW |
23 (7.8%) |
10 (3.8%) |
33 (5.9%) |
|
2.15 |
1.00 – 4.64 |
0.05* |
2.29 |
1.03 – 5.58 |
0.03* |
| Mode of delivery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Normal |
75 (25.6%) |
66 (24.9%) |
141 (25.3%) |
0.85NS
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| LSCS |
218 (74.4%) |
199 (75.1%) |
417 (74.7%) |
|
0.96 |
0.66– 1.41 |
0.85NS
|
0.97 |
0.78 – 1.85 |
0.47NS |
| Pregnancy outcome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Live birth |
291 (99.3%) |
264 (99.6%) |
555 (99.5%) |
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| Still birth |
2 (0.7%) |
1 (0.4%) |
3 (0.5%) |
0.99NS
|
1.81 |
0.16 – 20.13 |
0.63NS
|
1.8 |
0.18 – 24.64 |
0.56NS
|
| Baby’s sex |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Male |
154 (52.6%) |
144 (54.3%) |
298 (53.4%) |
0.67NS
|
1 |
-- |
|
|
|
|
| Female |
139 (47.4%) |
121 (45.7%) |
260 (46.6%) |
|
1.07 |
0.77 – 1.50 |
0.67NS
|
-- |
|
|
| Spontaneous Abortion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
267 (91.1%) |
248 (93.6%) |
515 (92.3%) |
|
1 |
-- |
|
|
|
|
| Yes |
26 (8.9%) |
17 (6.4%) |
43 (7.7%) |
0.3NS
|
1.42 |
0.75 – 2.68 |
0.3NS
|
-- |
|
|
| Gestational Hypertension** |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
278 (94.9%) |
257 (97.0%) |
535 (95.9%) |
|
1 |
-- |
|
|
|
|
| Yes |
15 (5.1%) |
8 (3.0%) |
23 (4.1%) |
0.22NS
|
1.73 |
0.72 – 4.16 |
0.22NS
|
-- |
|
|
| Chorioamnionitis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
291 (99.3%) |
262 (98.9%) |
553 (99.1%) |
|
1 |
-- |
|
|
|
|
| Yes |
2 (0.7%) |
3 (1.1%) |
5 (0.9%) |
0.58NS
|
0.6 |
0.10 – 3.62 |
0.58NS
|
-- |
|
|
| P-value for comparing mean gestational age and mean birthweight by independent sample t test. The rest of the P-values by Chi-Square test. P-value<0.05 is considered to be statistically significant. *P-value<0.05, NS – Statistically non-significant. #Adjusted for maternal age, education, gravidity using logistic regression analysis. |
As shown in
Table 2, the distribution of gestational age differed significantly between the non-vaccinated and vaccinated groups (P-value<0.05). A significantly higher proportion of non-vaccinated participants had a higher incidence of preterm gestation than vaccinated participants (P-value<0.05). On univariate statistical analysis, the distribution of outcome measures, such as pregnancy outcome (still birth), preterm gestation, LBW, and LSCS mode of delivery, were not significantly associated with vaccination status (P-value>0.05). In univariate statistical analysis, the distribution of outcome measures, such as VLBW, was significantly associated with vaccination status (P-value<0.05).
On multivariate statistical analysis, the distribution of outcome measures such as pregnancy outcome (still birth), preterm gestation, LBW, and LSCS mode of delivery was not significantly associated with vaccination status after adjusting for confounders such as maternal age, education, and gravidity (P-value>0.05). On multivariate statistical analysis, the distribution of outcome measures, such as VLBW, was significantly associated with vaccination status (p <0.05). Non-vaccinated mothers were twice as likely to have VLBW babies as vaccinated mothers after adjusting for maternal age, education, and gravidity (P-value>0.05).
Table 3.
Pregnancy and birth outcomes following influenza vaccination in pregnancy at obstetric hospital with unadjusted (Univariate) and adjusted (Multivariate) odds ratios.
Table 3.
Pregnancy and birth outcomes following influenza vaccination in pregnancy at obstetric hospital with unadjusted (Univariate) and adjusted (Multivariate) odds ratios.
| Variables |
Not vaccinated
(n=293) |
Vaccinated
(n=265) |
Total
(n=558) |
P-value |
Unadjusted (Univariate)
Crude Odds ratio (COR) |
Adjusted (Multivariate)
Odds ratio (AOR) |
| |
|
|
|
|
COR |
95% CI |
p-value |
AOR |
95% CI |
p-value |
| APGAR score (1-min) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ≥7 |
288 (98.3%) |
261 (98.5%) |
549 (98.4%) |
0.85NS
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| <7 |
5 (1.7%) |
4 (1.5%) |
9 (1.6%) |
|
1.13 |
0.30 – 4.26 |
0.85NS
|
1.05 |
0.43 – 4.84 |
0.72NS
|
| APGAR score (5-min) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ≥7 |
289 (98.6%) |
261 (98.5%) |
550 (98.6%) |
0.99NS
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| <7 |
4 (1.4%) |
4 (1.5%) |
8 (1.4%) |
|
0.9 |
0.22– 3.64 |
0.88NS
|
0.92 |
0.23 – 3.78 |
0.60NS
|
| NICU required |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Not required |
288 (98.3%) |
259 (97.7%) |
547 (98%) |
0.64NS
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| Required |
5 (1.7%) |
6 (2.3%) |
11 (2%) |
|
0.75 |
0.23 – 2.48 |
0.64NS
|
0.87 |
0.29 – 2.85 |
0.55NS
|
| Mechanical ventilation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Not required |
290 (99%) |
261 (98.5%) |
551 (98.7%) |
0.71NS
|
1 |
-- |
|
1 |
-- |
|
| Required |
3 (1%) |
4 (1.5%) |
7 (1.3%) |
|
0.68 |
0.15 – 3.04 |
0.51NS
|
0.72 |
0.21 – 4.00 |
0.40NS
|
| Respiratory distress |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
287 (98%) |
260 (98.1%) |
547 (98%) |
0.89NS
|
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
-- |
| Yes |
6 (2%) |
5 (1.9%) |
11 (2%) |
|
1.09 |
0.33 – 3.60 |
0.89NS
|
1.1 |
0.35 – 3.95 |
0.72NS
|
| Foetal distress |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
282 (96.2%) |
257 (97%) |
539 (96.6%) |
0.63NS
|
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
-- |
| Yes |
11 (3.8%) |
8 (3%) |
19 (3.4%) |
|
1.25 |
0.49 – 3.16 |
0.63NS
|
0.29 |
0.51 – 3.87 |
0.40NS
|
| Congenital anomaly |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
291 (99.3%) |
262 (98.9%) |
553 (99.1%) |
0.67NS
|
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
-- |
| Yes |
2 (0.7%) |
3 (1.1%) |
5 (0.9%) |
|
0.6 |
0.09 – 3.62 |
0.58NS
|
0.81 |
0.10 – 3.87 |
0.47NS
|
| High risk pregnancy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
238 (81.2%) |
218 (82.3%) |
456 (81.7%) |
0.75NS
|
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
-- |
| Yes |
55 (18.8%) |
47 (17.7%) |
102 (18.3%) |
|
1.07 |
0.70 – 1.65 |
0.75NS
|
1.1 |
0.74 – 1.88 |
0.71NS
|
| Complications before or during delivery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
238 (81.2%) |
218 (82.3%) |
456 (81.7%) |
0.75NS
|
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
-- |
| Yes |
55 (18.8%) |
47 (17.7%) |
102 (18.3%) |
|
1.07 |
0.70 – 1.65 |
0.75NS
|
1.09 |
0.72 – 1.74 |
0.70NS
|
| Complications after delivery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
283 (96.6%) |
261 (98.5%) |
544 (97.5%) |
0.18NS
|
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
-- |
| Yes |
10 (3.4%) |
4 (1.5%) |
14 (2.5%) |
|
2.31 |
0.71 – 7.44 |
0.16NS
|
2.85 |
0.88 – 9.85 |
0.09NS
|
| P-values by Chi-Square test. Adjusted for maternal age, education, gravidity using logistic regression analysis. P-value<0.05 is considered to be statistically significant. NS – Statistically non-significant. |
Table 3 shows that (on univariate statistical analysis), the distribution of the incidence of various neonatal complications such as Abnormal APGAR score (1-min and 5-min), NICU requirement, requirement of mechanical ventilation, occurrence of respiratory distress, occurrence of fetal distress, occurrence of congenital anomaly, occurrence of high-risk pregnancy, occurrence of complications before or during delivery, and occurrence of complications after delivery were not significantly associated with vaccination status (P-value>0.05).
On multivariate statistical analysis, the distribution of the incidence of various neonatal complications such as Abnormal APGAR score (1-min and 5-min), NICU requirement, requirement of mechanical ventilation, occurrence of respiratory distress, occurrence of fetal distress, occurrence of congenital anomaly, occurrence of high-risk pregnancy, occurrence of complications before or during delivery, and occurrence of complications after delivery were not significantly associated with vaccination status after adjusting for confounders such as maternal age, education, and gravidity (P-value>0.05).
Figure 2.
(a) Vaccination based on number of Gestation. Weeks of participants (n=265); (b) Gestational Weeks of participants (n=558).
Figure 2.
(a) Vaccination based on number of Gestation. Weeks of participants (n=265); (b) Gestational Weeks of participants (n=558).
4. Discussion
Reports published earlier shows that the influenza virus infection was associated with an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm births, stillbirths, low birthweight, and miscarriage [
17,
18,
19]. Antenatal influenza vaccination is the best strategy to avoid both morbidity and mortality among pregnant women and infants; however, there are always concerns about the safety of influenza vaccines in terms of their effects on birth outcomes.
The findings of our study, conducted in an Indian setting, suggest that the prevention of infection by influenza vaccination during pregnancy was not associated with adverse birth outcomes. This result is consistent with randomized controlled trials conducted in other countries, such as South Africa and Nepal [
1,
20]. Several other studies and meta-analysis also demonstrated that antenatal vaccination with seasonal inactivated influenza vaccines does not increase the risk of foetal death, adverse foetal and birth outcomes, low birth weight, spontaneous abortion, or congenital malformations [
15,
16,
20,
21,
22].
Our observation regarding the improvement in birth weight among neonates in the vaccinated group is like that of a randomized controlled trial conducted in Bangladesh, which showed that maternal influenza vaccination during pregnancy was associated with an increase in the mean birth weight of babies born during the influenza season[
23]. Interestingly, a pooled analysis of randomized control trials conducted in Nepal, Mali, and South Africa showed no overall association between maternal vaccination and low birth weight [
24]. Therefore, the lack of a biologically plausible mechanism for the suggested association raises concerns for any interpretation of positive correlations between vaccination and an increase in mean birth weight among infants. The improvement in health conditions in the absence of influenza and other cofactors might have improved the birth weights of the neonates of vaccinated mothers.
A case-control study conducted by Donahue
et al. reported an association between spontaneous abortion and vaccination with inactivated influenza vaccine within a 28-day exposure period, but only among women who had received an A(H1N1)-containing vaccine in the previous influenza season[
12]. However, this study failed to gain confidence due to the difficulty in interpreting the data. We did not find any association between spontaneous abortion and inactivated influenza vaccination during pregnancy.
Another study conducted by Eick
et al. indicated a significant association between influenza vaccination in pregnant women and a reduced risk of influenza virus infection or hospitalization for influenza-like illnesses up to six months of age [
25]. This study also demonstrated that maternal influenza vaccination during pregnancy reduces the risk of hospitalization in pregnant women due to respiratory illnesses and other complications during pregnancy. The first trimester is a significant period for embryogenesis of major organs, and pregnant women are hesitant to vaccinate during this period. The results of this study suggest no adverse effects on birth outcomes, even if influenza vaccination is administered during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
Our study had several strengths and limitations. The pregnancy outcome data were directly received from the delivery records, and the information captured from the participants through a questionnaire for medical history was also confirmed from the physician’s notes and hospital records simultaneously, which improved the quality of the data. Vaccinated and non-vaccinated participants were exposed to the same season and had similar seasonal influenza effects.
The limitations include that comparatively few participants were recruited because of the interrupted supply of influenza vaccine and the lack of access to hospital facilities during the COVID-19 pandemic-related lockdown across the country. Second, the inclusion of subjects across all seasons to match the transmission dynamics of influenza disease in the region would have been useful for studying the effectiveness of the influenza vaccine during pregnancy. The data were collected from the obstetrics ward of the hospital which is one of the selected hospitals offering maternal influenza vaccine. Most of the women which delivers in this hospital attend their ANC visits in same hospital. So the comparatively high influenza vaccine uptake reported in this study which might not be correct representative of the region. Also, the pregnancy outcome data were collected from women admitted in the obstetrics ward, some important data such as termination of pregnancies and few cases of still births might be missed, as those cases generally do not stay for a long duration in the hospital.
5. Conclusions
Our data provided reassuring evidence that an injectable inactivated trivalent influenza vaccine is safe during pregnancy. There was no increased risk of adverse birth outcomes, regardless of the trimester in which vaccination was performed. We also observed that vaccine uptake for influenza vaccination among pregnant women is good in the Pune area, provided that there is an uninterrupted supply of vaccine. The findings of this study underscore the importance of maternal influenza vaccination in preventing influenza in both pregnant women and their infants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: HS, PK, and AK; Methodology: HS, PK, CU, MA; Software: HS, AP; Validation: HS, PK, and AK; Formal analysis: HS, AP; Investigation: HS; Resources: PK, MA; Data curation: HS, PK, AP, MA; Writing–original draft preparation:HS, PK, MA, AP; Writing-review and editing: HS, AK, SS, CU; Visualization: HS, AK, SS, CU; Supervision: AK, SS, CU; Project administration: HS, AK; Funding acquisition: HS. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Ethics Committee Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the KEM Hospital Research Centre Ethics Committee Pune (KEMHRC/ RVM/EC/2383 dated March 14, 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all study participants, and consent was obtained from all participants to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request due to ethical restrictions and confidentiality. The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data were not publicly available due to confidentiality and ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We thank TDR, the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases, co-sponsored by UNICEF, UNDP, the World Bank, and WHO for providing financial support for establishing a network and organizing training for safety reporting of maternal influenza vaccines within civic hospitals in Pune.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the study design, collection, analyses, interpretation of data, writing of the manuscript, or decision to publish the results.
References
- Madhi SA, Cutland CL, Kuwanda L, Weinberg A, Hugo A, Jones S, et al. Influenza Vaccination of Pregnant Women and Protection of Their Infants. New England Journal of Medicine 2014;371:918–31. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1401480. [CrossRef]
- Bratton KN, Wardle MT, Orenstein WA, Omer SB. Maternal influenza immunization and birth outcomes of stillbirth and spontaneous abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2015;60:e11–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciu915. [CrossRef]
- Zaman K, Roy E, Arifeen SE, Rahman M, Raqib R, Wilson E, et al. Effectiveness of maternal influenza immunization in mothers and infants. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1555–64. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0708630. [CrossRef]
- Broor S, Krishnan A, Roy DS, Dhakad S, Kaushik S, Mir MA, et al. Dynamic Patterns of Circulating Seasonal and Pandemic A(H1N1)pdm09 Influenza Viruses From 2007–2010 in and around Delhi, India. PLoS One 2012;7:e29129. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029129. [CrossRef]
- Chadha M, Prabhakaran AO, Choudhary ML, Biswas D, Koul P, Kaveri K, et al. Multisite surveillance for influenza and other respiratory viruses in India: 2016–2018. PLOS Global Public Health 2022;2:e0001001. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0001001. [CrossRef]
- Programme L, Gpelf L. Weekly epidemiological record Relevé épidémiologique hebdomadaire 2017;92:557–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61877. [CrossRef]
- Omer SB, Goodman D, Steinhoff MC, Rochat R, Klugman KP, Stoll BJ, et al. Maternal influenza immunization and reduced likelihood of prematurity and small for gestational age births: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS Med 2011;8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000441. [CrossRef]
- Legge A, Dodds L, Macdonald NE, Scott J, Mcneil S. Rates and determinants of seasonal influenza vaccination in pregnancy and association with neonatal outcomes 2014;186:13–8. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.130499. [CrossRef]
- Fell DB, Platt RW, Lanes A, Wilson K, Kaufman JS, Basso O, et al. Fetal death and preterm birth associated with maternal influenza vaccination: Systematic review. BJOG 2015;122:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.12977. [CrossRef]
- Giles ML, Krishnaswamy S, Macartney K, Cheng A. The safety of inactivated influenza vaccines in pregnancy for birth outcomes: a systematic review. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2019;15:687–99. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2018.1540807. [CrossRef]
- Chambers CD, Johnson DL, Xu R, Luo YJ, Louik C, Mitchell AA, et al. Safety of the 2010–11, 2011–12, 2012–13, and 2013–14 seasonal influenza vaccines in pregnancy: Birth defects, spontaneous abortion, preterm delivery, and small for gestational age infants, a study from the cohort arm of VAMPSS. Vaccine 2016;34:4443–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.06.054. [CrossRef]
- Donahue JG, Kieke BA, King JP, DeStefano F, Mascola MA, Irving SA, et al. Association of spontaneous abortion with receipt of inactivated influenza vaccine containing H1N1pdm09 in 2010–11 and 2011–12. Vaccine 2017;35:5314–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.06.069. [CrossRef]
- Mathur R. INDIAN COUNCIL OF MEDICAL RESEARCH 2017 NATIONAL ETHICAL GUIDELINES FOR BIOMEDICAL AND HEALTH RESEARCH INVOLVING HUMAN PARTICIPANTS. 2017.
- Kochhar S, Bauwens J, Bonhoeffer J. Safety assessment of immunization in pregnancy. Vaccine 2017;35:6469–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.09.033. [CrossRef]
- McMillan M, Porritt K, Kralik D, Costi L, Marshall H. Influenza vaccination during pregnancy: A systematic review of fetal death, spontaneous abortion, and congenital malformation safety outcomes. Vaccine 2015;33:2108–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.02.068. [CrossRef]
- Jeong S, Jang EJ, Jo J, Jang S. Effects of maternal influenza vaccination on adverse birth outcomes: A systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis. PLoS One 2019;14:e0220910. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220910. [CrossRef]
- Regan AK, Feldman BS, Azziz-Baumgartner E, Naleway AL, Williams J, Wyant BE, et al. An international cohort study of birth outcomes associated with hospitalized acute respiratory infection during pregnancy. Journal of Infection 2020;81:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.057. [CrossRef]
- Song JY, Park KV, Han SW, Choi MJ, Noh JY, Cheong HJ, et al. Paradoxical long-term impact of maternal influenza infection on neonates and infants. BMC Infect Dis 2020;20:502. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-020-05236-8. [CrossRef]
- Newsome K, Alverson CJ, Williams J, McIntyre AF, Fine AD, Wasserman C, et al. Outcomes of infants born to women with influenza A(H1N1)pdm09. Birth Defects Res 2019;111:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdr2.1445. [CrossRef]
- Kozuki N, Katz J, Englund JA, Steinhoff MC, Khatry SK, Shrestha L, et al. Impact of maternal vaccination timing and influenza virus circulation on birth outcomes in rural Nepal. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2018;140:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12341. [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson JF, Strom P, Lundholm C, Cnattingius S, Ekbom A, Ortqvist A, et al. Maternal vaccination against H1N1 influenza and offspring mortality: population based cohort study and sibling design. BMJ 2015;351:h5585–h5585. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h5585. [CrossRef]
- McHugh L, Marshall HS, Perrett KP, Nolan T, Wood N, Lambert SB, et al. The Safety of Influenza and Pertussis Vaccination in Pregnancy in a Cohort of Australian Mother-Infant Pairs, 2012–2015: The FluMum Study. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2019;68:402–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciy517. [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff MC, Edwards K, Keyserling H, Thoms ML, Johnson C, Madore D, et al. A randomized comparison of three bivalent Streptococcus pneumoniae glycoprotein conjugate vaccines in young children: Effect of polysaccharide size and linkage characteristics. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1994. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006454-199405000-00007. [CrossRef]
- Omer SB, Clark DR, Madhi SA, Tapia MD, Nunes MC, Cutland CL, et al. Efficacy, duration of protection, birth outcomes, and infant growth associated with influenza vaccination in pregnancy: a pooled analysis of three randomised controlled trials. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:597–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30479-5. [CrossRef]
- Eick AA, Uyeki TM, Klimov A, Hall H, Reid R, Santosham M, et al. Maternal Influenza Vaccination and Effect on Influenza Virus Infection in Young Infants. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2011;165:104. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2010.192. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).