1. Introduction
The autonomous parvovirus Minute Virus of Mice (MVM) is lytic in murine hosts and in transformed human cells [
1]. The viral genome is single stranded with inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) at either end that serve as packaging signals and as origins of replication [
2]. MVM expresses two non-structural proteins, NS1 and NS2. While NS1 is essential for virus replication, NS2 is required only in murine hosts [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. MVM depends on host cell cycle entry into S-phase to initiate viral replication, utilizing host DNA polymerase delta and alpha to amplify its genome [
9,
10]. Virus replication proceeds via a partial strand-displacement process known as rolling hairpin replication [
11]. MVM established viral replication centers known as Autonomous Parvovirus-Associated Replication (APAR) bodies in the nuclear environment that colocalize with cellular replication and repair proteins [
12,
13,
14]. Vigorous MVM replication leads to a potent pre-mitotic cell cycle block at the G2/M border mediated by transcriptional silencing of host Cyclin B1 [
15,
16].
It has become increasingly clear that DNA viruses associate with host cell DNA damage response (DDR) proteins in the nuclear environment [
17,
18]. These DDR proteins colocalize with viral replication centers. In particular, DNA viruses like HPV and HBV associate with persistent cellular DDR sites, known as fragile sites [
19,
20,
21,
22]. Cellular fragile sites are induced by collisions between the host cell replication and transcription machinery and are stabilized by host topoisomerases and cohesin [
23,
24,
25]. We have previously discovered that MVM genomes localize to cellular DDR sites in order to establish efficient infection [
26]. Particularly a subset of cellular fragile sites induced early in S phase (referred to as Early Replicating Fragile sites, or ERFs), are preferred regions for MVM to establish replication centers with the help of NS1 [
27]. We have previously discovered that NS1 transports the viral genome to cellular DDR sites by binding to the viral genome and to heterologous DNA molecules containing NS1 binding elements [
27]. However, the cellular signaling pathways that drive MVM localization (either NS1 or the viral genome) to cellular DDR sites remain unknown.
DNA viruses modulate the cellular DDR pathways using distinct strategies for their benefit. The related parvovirus Adeno-Associated Virus 2 (AAV2) induces a cellular DDR that is driven by signaling by the PI3-kinase-like-kinase DNA-PK [
28]. However, DNA-PK signaling does not regulate MVM replication [
14]. Instead MVM life cycle is dependent on signaling by the ATM kinase pathway [
13,
14,
26]. As MVM replication proceeds, it inactivates signaling by the ATR kinase pathway that normally responds to single-stranded DNA breaks [
29]. Based on these findings, we have previously proposed that ATR inactivation is a mechanism for MVM pathogenesis, which has evolved to enable MVM to inactivate the cellular signals that sense the single-stranded DNA virus genomes that may inhibit the viral life cycle [
29,
30].
In this study, we establish NS1 as a proxy marker for cellular DNA damage during MVM infection. Using this marker, we elucidate the cellular DDR pathways that modulate how MVM localizes to cellular sites of DNA damage. Strikingly, we have discovered that MVM localization to sites of cellular damage and early replication is dependent on signaling by the ATR kinase pathway, destined to be inactivated by MVM, and not the ATM or DNA-PK pathways. Our findings suggest that the single-stranded break repair processes aid in the establishment of MVM replication at the onset of infection.
2. Materials and Methods
Cell lines and virus, Viral infections
Male murine A9 and female human U2OS cells were propagated in 10 percent Serum Plus (Sigma Aldrich) containing DMEM media (Gibco) supplemented with Gentamicin at 37 degrees Celsius and 5 percent carbon dioxide. A9 and U2OS cells were used as representative model systems for these studies because MVMp infects mouse cells and transformed human cells respectively. Cell lines are routinely authenticated for mycoplasma contamination, and background levels of DNA damage are monitored by γH2AX staining. As A9 cells have smaller nuclei and higher background γH2AX levels relative to U2OS, imaging-based studies of NS1 localization to cellular DDR sites can be difficult to discern microscopically using this system. Therefore, U2OS cells were predominantly used for the laser microirradiation followed by imaging experiments. Wild-type MVMp virus was produced as previously described [
26] and genome copies were quantified by Southern blotting [
31]. MVMp infection was carried out at a Multiplicity of Infection (MOI) of 25 in all imaging assays. MVMp infection for western blot analysis was carried out at an MOI of 10.
Cell synchronization, and drug treatments
A9 cells were parasynchronized in G0 phase of the cell cycle by isoleucine deprivation for 42 hours as previously described [
32,
33]. Cells were infected with MVM upon release into complete DMEM medium (described above) for 16 hours for imaging and 24 hours for western analysis. For western blots, cells were pulsed with ATR inhibitor (Berzosertib, Selleckchem S7102) 12 hours post infection. The cells enter S phase approximately 12 hours post release [
16]. For immunofluorescence, U2OS cells were infected with MVMp virus or transfected with NS1 expression plasmid for 16 hours and treated with inhibitors 30 minutes prior to laser micro-irradiation unless otherwise indicated.
Table 1.
Summary of inhibitors used.
Table 1.
Summary of inhibitors used.
| Inhibitor |
Target |
Supplier |
Catalog Number |
Dosage |
| Olaparib |
PARP |
Selleckchem |
S1060 |
1 µM |
| TDRL-505 |
RPA binding |
Millipore Sigma |
5.30535 |
50 µM |
| Caffeine |
ATM and ATR |
Millipore Sigma |
W222402 |
2.5 µM and 7.5 µM |
| KU-55933 |
ATM |
Selleckchem |
S1092 |
7 µM |
| Berzosertib |
ATR |
Selleckchem |
S7102 |
2 µM and 4 µM |
| NU7441 (KU-57788) |
DNA-PK |
Selleckchem |
S2638 |
10 µM |
| CAS 17374-26-4 |
CK2 |
Millipore Sigma |
218697 |
10 µM |
| CHIR-124 |
CHK1 |
Selleckchem |
S2683 |
10 µM |
The NS1 open reading frame containing a mutation in the splice site for NS2 was cloned into the pcDNA3.1 mammalian expression vector as previously described [
14,
27]. Plasmids were transfected into U2OS cells for at least 16 hours using the LipoD293 transfection reagent (SignaGen Laboratories).
Laser micro-irradiation for immunofluorescence
Laser micro-irradiation was performed on 1 million U2OS cells cultured on glass bottomed dishes (MatTek Corp.) infected with MVMp at an MOI of 25 or transfected with 1 µg of NS1-expression vectors for 16–20 hours. Cells were sensitized with 3.5 μl of Hoechst dye (ThermoFisher Scientific) 5 minutes prior to micro-irradiation. Samples were irradiated using a Leica Stellaris DMI8 confocal microscope using 63X oil objective and 2X digital zoom with a 405 nm laser using 25 percent power at 10 Hz frequency for 2 frames per field of view. Regions of interest (ROIs) were selected across the nucleus (edges of the nuclei were demarcated and visualized by Hoechst staining). Samples were processed for immunofluorescence imaging and analysis (described below) immediately after micro-irradiation.
Immunofluorescence assays
U2OS cells were pre-extracted with CSK Buffer (10 mM PIPES pH 6.8, 100 mM Sodium Chloride, 300 mM Sucrose, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM Magnesium Chloride) and CSK with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 3 minutes each before fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes at room temperature. Cells were washed in PBS before being permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 minutes at room temperature. Samples were blocked with 3% BSA in PBS for 20 minutes, incubated with the primary antibody diluted in 3% BSA solution for 20 minutes, washed in PBS and incubated with secondary antibody (tagged with the appropriate Alexa-Fluor conjugated fluorophores) for 20 minutes. Samples were washed in PBS and mounted on glass bottomed dishes with DAPI Fluoromount (Southern Biotech). Images were taken and processed on Leica Stellaris DMI8 Confocal microscope with 63X oil objective lens.
Western Blot Analysis
Cells were collected at specified time point and pellets were lysed on ice for 15 minutes in complete Radio-Immuno-Precipitation Assay (RIPA) buffer (20 mM Tris HCL pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCL, 10% glycerol, 1% NP-40, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM trisodium pyrophosphate, 20 mM sodium fluoride, 2 mM sodium orthovanadate and 1x protease inhibitor cocktail (MedChemExpress). Cell lysate was collected following centrifugation for 15 minutes at 17,000 X g at 4 degrees Celsius. Protein sample concentration was calculated using BCA assay (Bio-Rad). 5X protein loading dye (1M Tris-HCl pH 8, 30% Glycerol, 100mM DTT, 10mM EDTA, 350mM SDS, Bromophenol blue) was added to samples and boiled at 95°C for 5 min.
Equivalent protein levels were loaded onto a 10% SDS-PAGE gel for electrophoresis and was subsequently transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were blocked for 30 minutes in 5% milk in TBS (20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.6) with 0.5% Tween-20. Membranes were incubated with the primary antibody in 5% milk in TBST for 1 hour followed by three 5-minute washes in TBST prior to incubation with HRP conjugated secondary antibody and ladder conjugate (Bio-Rad) in 5% milk in TBST for 30 minutes. All incubations were performed at room temperature. The membrane was incubated 5 minutes with Clarity Western ECL Blotting Substrate (Bio-Rad) before imaging using a Li-COR-Fortessa scanner and analysis with Image Studio Lite software.
Antibodies
Primary antibodies used in immunofluorescence (IF) and western blot analysis (WB).
The mouse anti-NS1 monoclonal antibody (clone 2C9b) has been previously generated and extensively validated by the Pintel lab [
14,
26,
27].
Table 2.
Summary table of antibodies used. .
Table 2.
Summary table of antibodies used. .
| Antibody |
Supplier |
Catalog Number |
Application |
| Tubulin (Clone DM1A) |
Sigma |
05-829 |
WB |
| Mre11 |
Cell Signaling |
4895 |
WB |
| RPA phospho-Ser4, Ser8 |
Thermo Fisher |
A300-245A |
IF |
| EXO1 phospho-Ser746 |
Sigma |
ABE1066 |
IF |
| CHK1 phospho-Ser345 |
Cell Signaling |
23415 |
IF |
| NBS1 phospho-ser95 |
Cell Signaling |
3002 |
IF |
| MDC1 phospho-T4 |
Abcam |
Ab35967 |
IF |
| anti-Mouse-AF568 |
Thermo Scientific |
A11004 |
IF |
| anti-Rabbit-AF488 |
Thermo Scientific |
A11034 |
IF |
| Anti-mouse IgG, HRP-linked |
Cell Signaling |
7076 |
WB |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-linked |
Cell Signaling |
7074 |
WB |
3. Results
3.1. NS1 is a proxy marker for cellular DNA Damage during MVM infection.
Upon infecting host cells, MVM genomes and non-structural proteins localize to pre-existing as well as induced cellular sites of DNA damage [
26,
27]. This localization is driven by NS1 associating with ACCA motifs on the MVM genome [
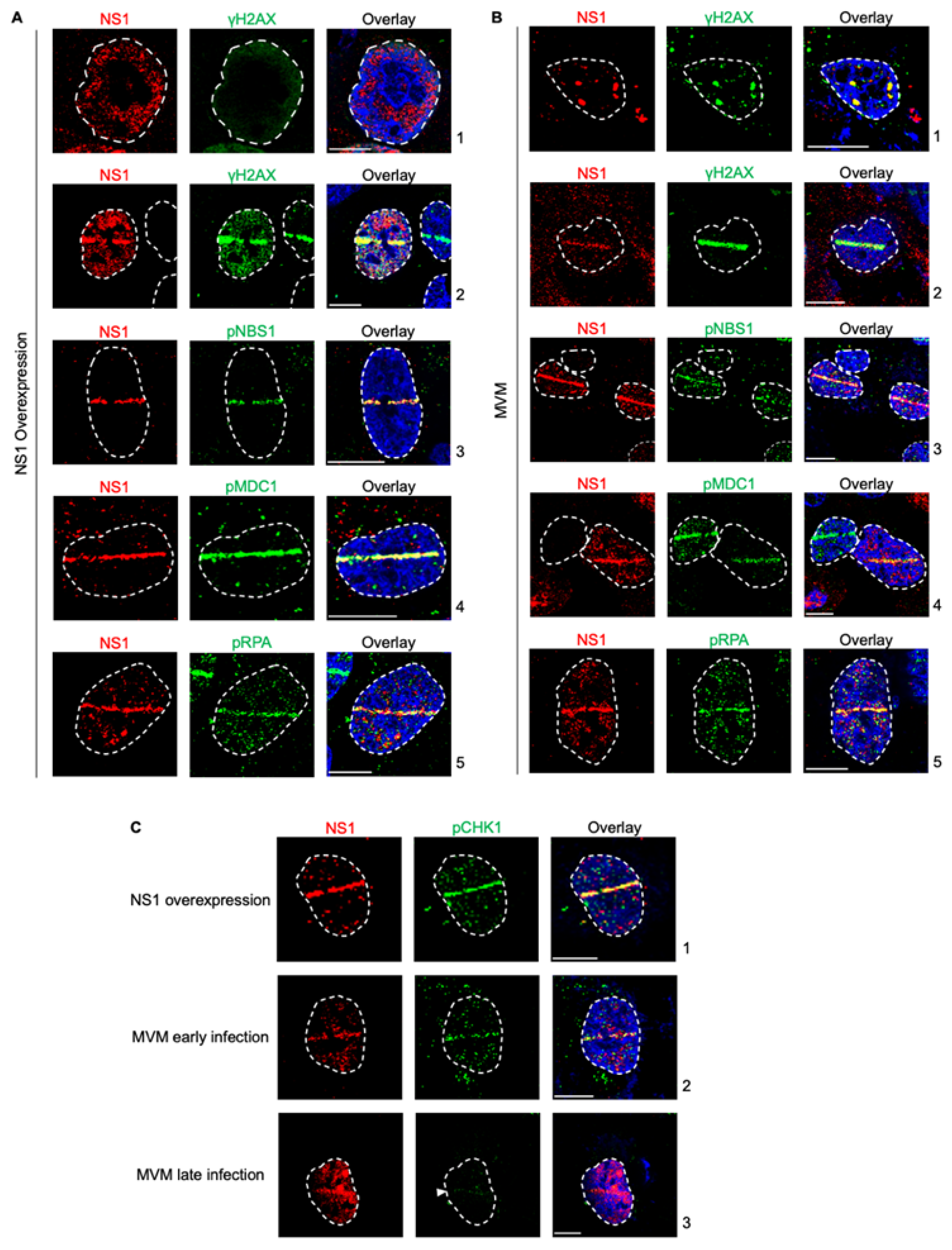
27]. However, NS1 on its own activates a cytotoxic program in host cells. Therefore, to determine whether activation of this cytotoxic program by ectopic NS1 perturbs the host’s ability to recognize cellular DNA breaks, we expressed NS1 by transient transfection and monitored whether host cells recognize induced cellular DNA breaks using laser microirradiation followed by immunofluorescence. Using relocalized NS1 as a marker for induced DNA damage, we monitored the ability of cellular DDR proteins to recognize micro-irradiated sites. As shown in Fig. 1A, NS1 relocalized to γH2AX sites, consistent with previously observed findings (Fig. 1A, compare panel 1 to 2, [
27]). This relocalization was also evident when monitored by staining for phosphorylated NBS1 (Fig. 1A, panel 3), phosphorylated MDC1 (Fig. 1A, panel 4) and phosphorylated RPA (Fig. 1A, panel 5). Therefore, we have extended our observations of NS1 localization during ectopic expression and MVM infection to additional DDR pathways proteins, finding NS1 relocalized to DDR sites marked by phosphorylated NBS1, MDC1 and RPA. Importantly, this interaction of NS1 with host DDR recognition markers does not impact their ability to recognize additional cellular DNA breaks.
Figure 1.
NS1 is a proxy marker for cellular DNA Damage during MVM infection. (A) U2OS cells transfected with NS1-expressing vectors for 16 hours were damaged across the nucleus using laser micro-irradiation and monitored by NS1-DDR staining as indicated. (B) U2OS cells infected with MVM at an MOI of 25 for 16 hours were damaged across the nucleus using laser micro-irradiation and monitored by NS1-DDR staining as indicated. (C) Relocalization of NS1 produced during different stages of MVM infection or ectopic expression were monitored by relocalization to DDR sites marked by phosphorylated CHK1. Viral non-structural protein NS1 (red), respective DDR markers (green) and pan-nuclear content was visualized by DAPI staining (blue). White dashed lines demarcate the nuclear boundaries, white bars represent 10 micrometers and white arrows indicate the location of the laser micro-irradiated stripe.
Figure 1.
NS1 is a proxy marker for cellular DNA Damage during MVM infection. (A) U2OS cells transfected with NS1-expressing vectors for 16 hours were damaged across the nucleus using laser micro-irradiation and monitored by NS1-DDR staining as indicated. (B) U2OS cells infected with MVM at an MOI of 25 for 16 hours were damaged across the nucleus using laser micro-irradiation and monitored by NS1-DDR staining as indicated. (C) Relocalization of NS1 produced during different stages of MVM infection or ectopic expression were monitored by relocalization to DDR sites marked by phosphorylated CHK1. Viral non-structural protein NS1 (red), respective DDR markers (green) and pan-nuclear content was visualized by DAPI staining (blue). White dashed lines demarcate the nuclear boundaries, white bars represent 10 micrometers and white arrows indicate the location of the laser micro-irradiated stripe.
While ectopic NS1 did not perturb the cellular detection of DNA damage, MVM replication is known to utilize ATM kinase signalling and inactivate the ATR kinase pathways [
14,
29]. To determine whether the actively replicating MVM genome inhibits the recognition of cellular DNA breaks, we analyzed the localization of cellular DDR proteins to laser micro-irradiated stripes during viral infection using NS1 as the DDR marker. As shown in Fig. 1A, laser microirradiation of U2OS cells during MVM infection led to relocalization of NS1 to the induced cellular DDR sites marked by γH2AX, consistent with previously published findings (Fig. 1B, compare panel 1 to 2, [
27]). Using relocalized NS1 as a marker for induced DNA damage, we monitored the ability of cellular DDR proteins to recognize these sites. As shown in Fig. 1A, DDR sites monitored by NS1 staining colocalized with DNA break recognition markers such as phosphorylated NBS1 (Fig. 1B, panel 3), phosphorylated MDC1 (Fig. 1B, panel 4) and phosphorylated RPA (Fig. 1B, panel 5). These findings showed that MVM-infected cells still retain the ability to recognize additional cellular DNA breaks.
MVM infection leads to the inactivation of the ATR kinase pathway by inhibiting the single stranded break transducer TopBP1 [
29]. To confirm that NS1 is a alternative marker for cellular DDR during all stages of MVM infection, we performed laser microirradiation followed by immunofluorescence for NS1 and phosphorylated CHK1, which is activated downstream of ATR/TopBP1 [
29]. Ectopically expressed NS1 robustly relocalized with cellular DDR sites that are marked by phospho CHK1 (Fig. 1C, panel 1). Similarly, during early infection, when phosphorylation of CHK1 is still possible, NS1 colocalized with phospho CHK1 to mark cellular DDR sites (Fig. 1C, panel 2). However, during late stages of infection when CHK1 activation is inhibited, NS1 is still able to relocalize to the cellular DDR sites (Fig. 1C, panel 3). These findings indicated that NS1 is a marker for cellular DNA breaks throughout all stages of MVM infection.
3.2. NS1 localization to cellular DDR sites is independent of ATM and DNA-PK signaling but depends on ATR signaling.
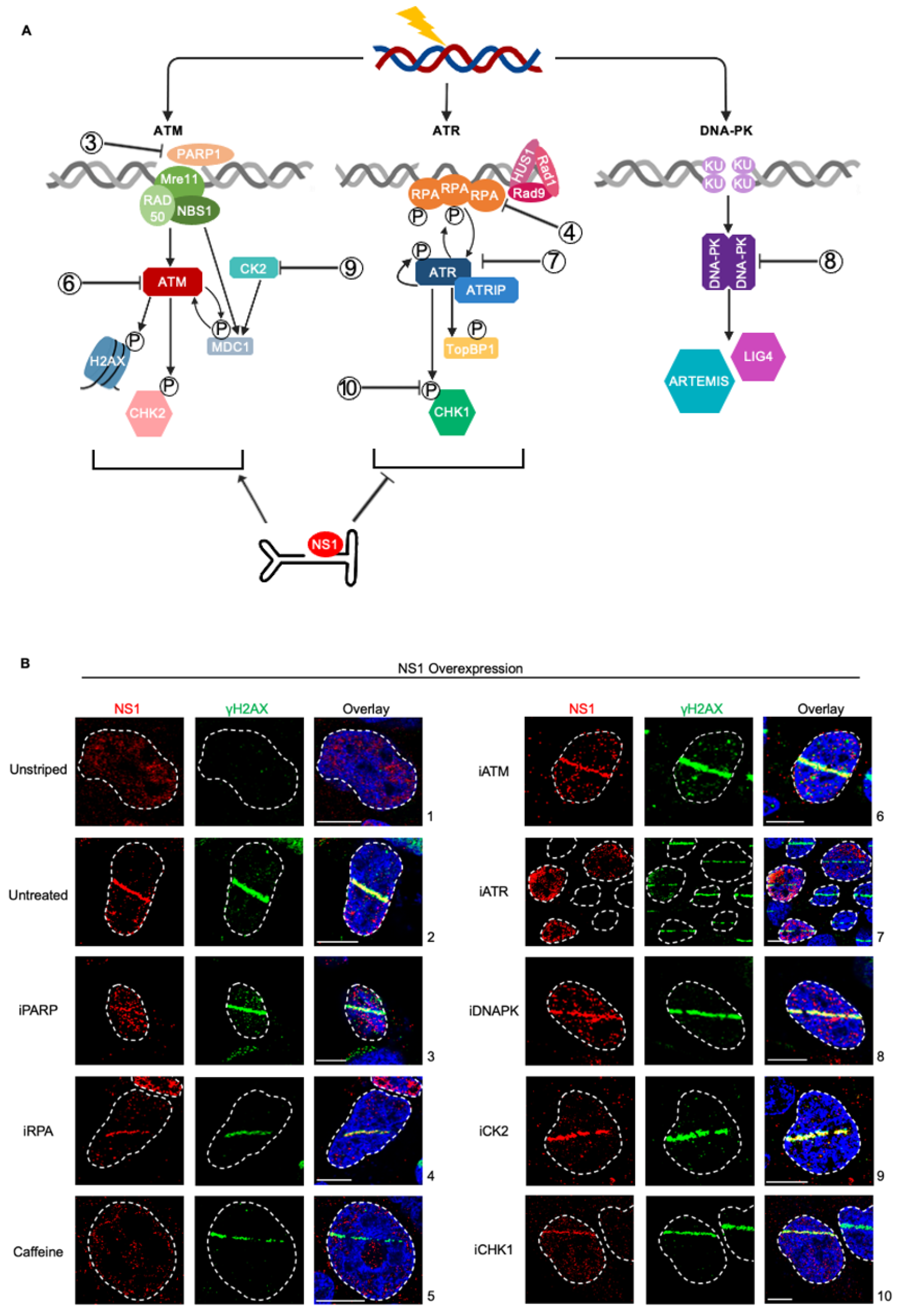
To systematically determine which cellular DDR signals drive the relocalization of NS1 to cellular sites of DNA damage, we used well-characterized DDR inhibitors in U2OS cells transfected with an NS1 expression vector combined with laser micro-irradiation assays [
27]. We investigated proteins in the ATR, ATM, and DNA-PK DDR pathways to determine which signals drive NS1 relocalization (Fig. 2A, inhibitors indicated by numbers). Inhibition of PARP polymerase that signals the initial activation of cellular DDR signals and local chromatin remodelling [
34] did not impact NS1 relocalization (Fig. 2B, panel 3). Similarly, NS1 still relocalized to sites of DDR under inhibition of the single-strand DNA binding protein RPA (Fig. 2B, panel 4). However, in the presence of the pan ATM and ATR inhibitor caffeine, NS1 did not relocalize to sites of DDR (Fig. 2B, panel 5), remaining as diffuse foci around the nucleus. To distinguish if this phenotype was driven distinctly by the ATM or ATR pathways we used specific small-molecule inhibitors. While inhibition of ATM had no impact on NS1 relocalization (Fig. 2B, panel 6), inhibition of ATR consistently resulted in a loss of relocalization (Fing. 2B, panel 7). This suggested that the ATR signaling pathway is involved in the relocalization of NS1 to sites of DDR. Interestingly, the inhibition of the downstream ATR effector CHK1 did not impact the re-localization of NS1 to the laser micro-irradiated DDR site (Fig. 2B, panel 10).
Surprisingly, although NS1 has been previously shown to interact with the cellular Casein Kinase II (CK2, [
35]) and CK2 interacts with MDC1 to transduce the signals to γH2AX [
13,
36], inhibition of CK2 activity did not attenuate the relocalization of NS1 to laser-microirradiated γH2AX sites (Fig. 2B, panel 9). Inhibition of DNA-PK signaling did not impact the ability of NS1 to localize to laser micro-irradiated sites (Fig. 2B, panel 8), suggesting NS1 relocalization discriminates between the cellular DDR PI3-kinase-like kinases [
17].
Figure 2.
NS1 localization to cellular DDR sites is independent of ATM and DNA-PK signaling but depends on ATR signaling. (A) U2OS cells were transfected with NS1 overexpression vector for 16 hours, treated with the indicated DDR inhibitors 30 minutes prior to laser micro-irradiation and processed for NS1-γH2AX colocalization. Viral non-structural protein is depicted by NS1 (red), cellular DDR by γH2AX (green) and pan-nuclear content was visualized by DAPI staining (blue). White dashed lines demarcate the nuclear boundaries and white bars represent 10 micrometers. The concentrations of the inhibitors used are shown in Materials and Methods. (B) Schematic of cellular DNA damage response mediated by PI3-Kinase-like-Kinases with the relevant proteins inhibited in part (A) indicated as shown. .
Figure 2.
NS1 localization to cellular DDR sites is independent of ATM and DNA-PK signaling but depends on ATR signaling. (A) U2OS cells were transfected with NS1 overexpression vector for 16 hours, treated with the indicated DDR inhibitors 30 minutes prior to laser micro-irradiation and processed for NS1-γH2AX colocalization. Viral non-structural protein is depicted by NS1 (red), cellular DDR by γH2AX (green) and pan-nuclear content was visualized by DAPI staining (blue). White dashed lines demarcate the nuclear boundaries and white bars represent 10 micrometers. The concentrations of the inhibitors used are shown in Materials and Methods. (B) Schematic of cellular DNA damage response mediated by PI3-Kinase-like-Kinases with the relevant proteins inhibited in part (A) indicated as shown. .
3.3. ATR signaling regulates the early replication of MVM and formation of viral replication centers in the nuclear compartment.
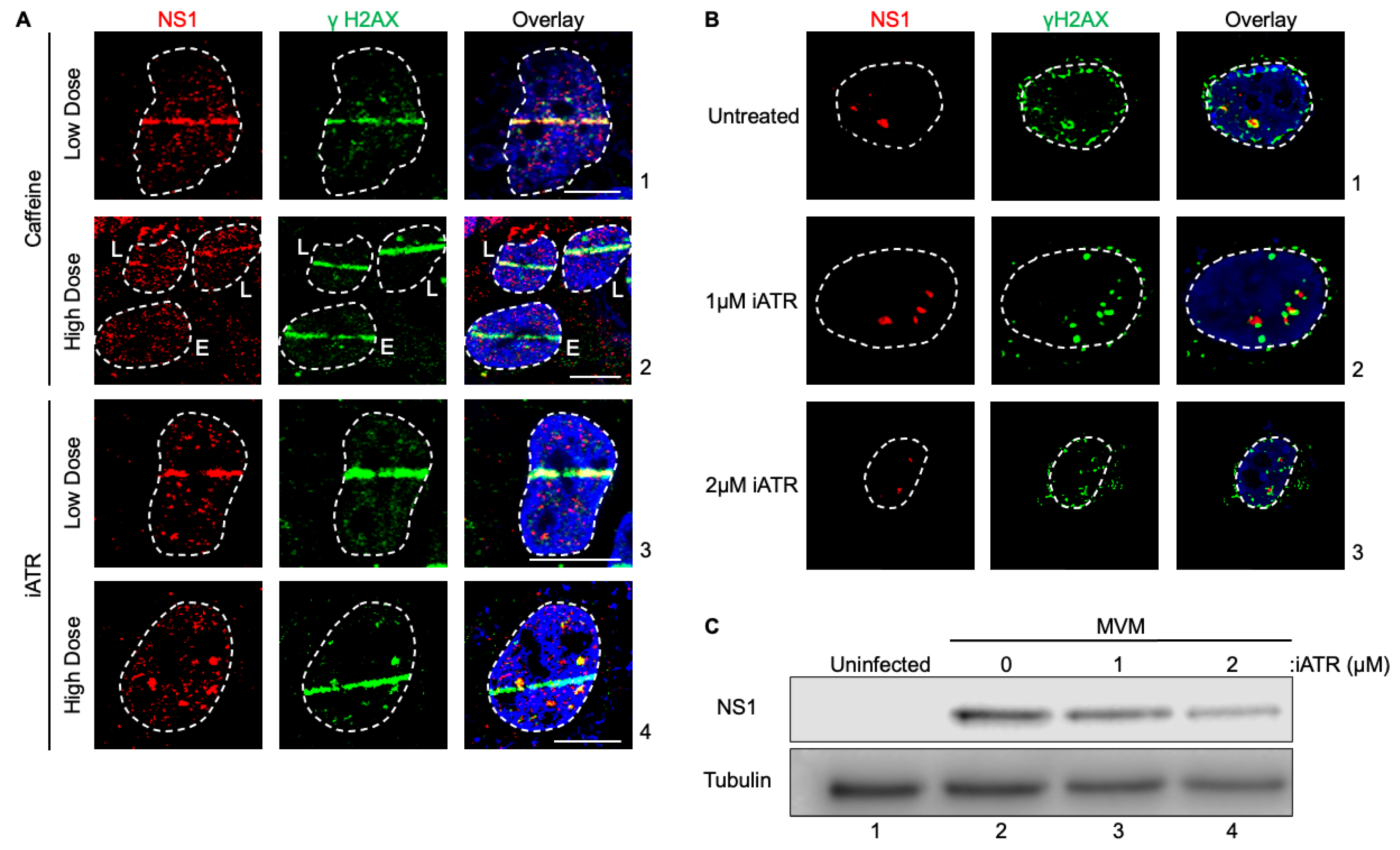
Since ATR inhibition during NS1 expression attenuated ectopic NS1 localization to cellular DDR sites, we hypothesized that ATR signaling may drive MVM localization during the early stages of infection. To test this hypothesis, we pulsed MVM infected U2OS cells with Caffeine and ATR inhibitor for 30 minutes prior to laser microirradiation. Interestingly, during MVM infection, U2OS cells treated with 2.5 mM caffeine or 1 μM iATR for 30min prior to microirradiation did not inhibit relocalization (Fig. 3A, panels 1 and 3). However when treated with a higher caffeine, NS1 relocalization was attenuated in MVM infected cells at early stages of infection (Fig. 3A, panels 2, compare cell i to ii). Similarly, MVM remained as defined foci within the nucleus when treated with high doses of iATR rather than relocalizing to the cellular DDR sites. MVM’s localization with cellular DDR sites enhances its ability to replicate [
26]. Because of its inability to localize under conditions where ATR is inhibited, we hypothesized that ATR inhibition will attenuate MVM APAR body formation and replication. Consistent with this hypothesis, in the presence of the ATR inhibitor, MVM infected cells showed smaller APAR bodies (Fig. 3B, compare panels 1 to 3) and lower levels of NS1 in whole-cell lysates (Fig. 3C, compare lane 2 to 4). Taken together, these findings confirmed that inhibition of the ATR signaling pathway attenuates the ability of MVM-NS1 to localize to cellular sites of DNA damage, thereby regulating how viral replication centers are established.
Figure 3.
ATR signaling regulates the early replication of MVM and formation of viral replication centers in the nuclear compartment. (A) U2OS cells were transfected with MVM for 16 hours. Cells were treated with 2.5 mM (panel 1) or 7.5 mM (panel 2) caffeine, 1 µM (panel 3) or 2 µM (panel 4) iATR for 30 minutes prior to laser micro-irradiation and processed for NS1-γH2AX colocalization. Panel 2 shows cells in early (E) and late (L) stages of infection by NS1 staining (red). (B) Syncronized A9 cells were infected with MVM for 16 hours and treated with iATR 4 hours prior to processing for colocalization of MVM APAR bodies, indicated by NS1, and cellular γH2AX. Viral non-structural protein is depicted by NS1 (red), cellular DDR by γH2AX (green) and pan-nuclear content was visualized by DAPI staining (blue). White dashed lines demarcate the nuclear boundaries and white bars represent 10 micrometers. (C) Western blot analysis of synchronized A9 cells mock infected (lane 1) or infected with MVM for 24 hours (lane 2-4). Cells were treated with iATR 4 hours prior to collection (lanes 3 and 4) and antibodies were used against NS1 and tubulin as a loading control. .
Figure 3.
ATR signaling regulates the early replication of MVM and formation of viral replication centers in the nuclear compartment. (A) U2OS cells were transfected with MVM for 16 hours. Cells were treated with 2.5 mM (panel 1) or 7.5 mM (panel 2) caffeine, 1 µM (panel 3) or 2 µM (panel 4) iATR for 30 minutes prior to laser micro-irradiation and processed for NS1-γH2AX colocalization. Panel 2 shows cells in early (E) and late (L) stages of infection by NS1 staining (red). (B) Syncronized A9 cells were infected with MVM for 16 hours and treated with iATR 4 hours prior to processing for colocalization of MVM APAR bodies, indicated by NS1, and cellular γH2AX. Viral non-structural protein is depicted by NS1 (red), cellular DDR by γH2AX (green) and pan-nuclear content was visualized by DAPI staining (blue). White dashed lines demarcate the nuclear boundaries and white bars represent 10 micrometers. (C) Western blot analysis of synchronized A9 cells mock infected (lane 1) or infected with MVM for 24 hours (lane 2-4). Cells were treated with iATR 4 hours prior to collection (lanes 3 and 4) and antibodies were used against NS1 and tubulin as a loading control. .
4. Discussion
In this study, we have validated that NS1 is a bonafide marker for parvovirus-induced cellular DNA damage. Additionally, we have systematically perturbed the major cellular DDR signaling pathways, determining that ATM, PARP and DNA-PK are not involved in regulating NS1 localization to induced cellular DDR sites. Strikingly, ATR inhibition inhibits NS1 relocalization, leading to attenuated MVM replication. Taken together, these findings suggest that although ATR signaling is inactivated by MVM infection at late stages, it is required at the early stages of the viral infection to initially establish APAR bodies.
Mass spectrometry studies investigating the host proteins that associate with MVM NS1 have previously discovered that NS1 interacts with the host protein Casein Kinase 2 (CK2, [
37]). These findings suggested that CK2 might play a role in serving as a connecting link between NS1 and cellular DDR sites, particularly in light of CK2’s established role in connecting between MDC1 and NBS1 [
38]. However, the CK2 inhibitor did not impact the relocalization of MVM-NS1 to cellular DDR sites. These findings suggest that the role of CK2 in regulating MVM life cycle is independent of the localization of NS1 (and by extension MVM) to cellular DDR sites.
Much of our understanding of virus-host interactions comes from transfection of viral proteins ectopically. However, our findings in this study suggests there are phenotypic differences in how viral proteins interact with the host during infection versus ectopic expression. This may be due to the absence of the replicating viral genomes. Alternately, it is possible that active virus replication causes global changes that modulate NS1-DDR interactions differently. While the inhibition of ATR obliterates NS1 relocalization to sites of DNA damage in overexpression, during infection the presence of increasing MVM DNA molecules and additional viral protein expression presents the potential for additional redundant pathways to be activated, that can then induce relocalization. This may be contributing to why relocalization is inhibited in cells at early stages of infection but not late stages.
While relocalization was only attenuated during early infection by inhibiton of ATR, APAR body formation was still impacted and correlated with decreased overall virus replication. Previous work investigating APAR body formation has shown that while at lower resolutions NS1 appears to be directly associated with γH2AX, at higher resolution, MVM APAR bodies form in distinct pockets surrounded or directly next to γH2AX [
26]. However, at higher resolution, MVM APAR bodies form in distinct pockets surrounded or directly next to γH2AX [
26]. Our observations with the ATR inhibitor suggest that while NS1 initially associates with γH2AX to form APAR bodies, the lack of relocalization to additional γH2AX sites resulting in smaller APAR bodies suggest a defect in expanding to new cellular DDR sites. This is further supported by decreased levels of NS1 later in infection.
An attractive mechanism by which PIKKs may regulate NS1 localization to cellular DDR sites is via phosphorylation of their SQ/TQ motifs. Cellular Serine/Threonine residues that are associated with glutamine residues on the primary amino acid sequence are phosphorylation targets of ATM and ATR kinases [
39]. Further supporting this assertion, the Rep 68/78 protein of AAV2 localizes to cellular DDR sites in an ATM/ATR-dependent manner [
40]. In line with these expectations, the MVM NS1 protein contains two SQ and two TQ motifs. We hypothesize that these are the residues that serve as the phyosphorylation substrates for ATM and ATR kinases. However, based on our current findings, it remains unknown why these sites might be specifically targeted by ATR and not ATM. Future studies will focus on dissecting these conundrums on parvovirus-host interactions.
Prior studies on MVM pathogenesis established that MVM infection inactivates CHK1 (downstream of ATR) by inhibiting the activation of the transducer TopBP1 [
29]. However, our findings suggest that while ATR may be inactivated at late stages, it is required at the early stages of infection to establish viral replication centers in the nuclear compartment. Perhaps ATR interaction at early stages facilitate the opening of the viral genome for access by host replication proteins, whereas at late stages this enhances genome instability and chromosome fragmentation. Alternately, it is possible that ATR inactivation at the late stages of infection is a mechanism evolved by parvoviruses to evade integration into the host genome. It remains unclear, however, whether this requirement for ATR pathway inactivation is induced on the viral genome or on the host genome. Interestingly, Adenovirus infection induces distinct virus and host-mediated ATM signals [
41]. We speculate that MVM, by virtue of being a single-stranded DNA virus, interacts with the host ATR pathway via a similar route. Future studies will elucidate how distinct single-stranded DNA repair pathways on the viral versus cellular genomes drive viral pathogenesis and can be used for oncolytic virotherapies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.I.S.L. and K.M; methodology, C.I.S.L. and K.M; validation, C.I.S.L. and K.M; formal analysis, C.I.S.L. and K.M; investigation, C.I.S.L. and K.M; data curation, C.I.S.L. and K.M; writing—original draft preparation, C.I.S.L. and K.M; writing—review and editing, C.I.S.L. and K.M; visualization, C.I.S.L. and K.M; supervision, K.M.; project administration, K.M.; funding acquisition, K.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by NIH/NIAID K99/R00 Pathway to Independence Award, grant number AI148511 to K.M. and The Wisconsin Partnership Program’s New Investigator Award (PERC Grant G-4942) to K.M.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge members of the Majumder Lab for critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cotmore, S.F.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Chiorini, J.A.; Mukha, D.V.; Pintel, D.J.; Qiu, J.; Soderlund-Venermo, M.; Tattersall, P.; Tijssen, P.; Gatherer, D.; et al. The family parvoviridae. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotmore, S.F.; Tattersall, P. Parvoviruses: Small does not mean simple. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 517–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotmore, S.F.; Tattersall, P. The ns-1 polypeptide of minute virus of mice is covalently attached to the 5' termini of duplex replicative-form dna and progeny single strands. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotmore, S.F.; Christensen, J.; Nüesch, J.P.; Tattersall, P. The ns1 polypeptide of the murine parvovirus minute virus of mice binds to dna sequences containing the motif [acca]2-3. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Tattersall, P. Parvovirus initiator protein ns1 and rpa coordinate replication fork progression in a reconstituted dna replication system. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6518–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotmore, S.F.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Tattersall, P. Replication initiator protein ns1 of the parvovirus minute virus of mice binds to modular divergent sites distributed throughout duplex viral dna. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13015–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouw, M.; Pintel, D.J. Amino acids 16–275 of minute virus of mice ns1 include a domain that specifically binds (acca)2–3-containing dna. Virology 1998, 251, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeger, L.K.; Cater, J.; Pintel, D.J. The small nonstructural protein (ns2) of the parvovirus minute virus of mice is required for efficient dna replication and infectious virus production in a cell-type-specific manner. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 6166–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Horlein, R.; Rommelaere, J.; Willwand, K. Cyclin a activates the dna polymerase delta -dependent elongation machinery in vitro: A parvovirus dna replication model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5522–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Rommelaere, J.; Cziepluch, C. In vivo accumulation of cyclin a and cellular replication factors in autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice-associated replication bodies. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4394–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, P.; Ward, D.C. Rolling hairpin model for replication of parvovirus and linear chromosomal dna. Nature 1976, 263, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, P.J.; Jensen, K.T.; Burger, L.R.; Pintel, D.J.; Lorson, C.L. Minute virus of mice ns1 interacts with the smn protein, and they colocalize in novel nuclear bodies induced by parvovirus infection. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3892–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, Z.; Mihaylov, I.S.; Cotmore, S.F.; Tattersall, P. Recruitment of dna replication and damage response proteins to viral replication centers during infection with ns2 mutants of minute virus of mice (mvm). Virology 2011, 410, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, R.O.; Landry, S.; Davis, M.E.; Weitzman, M.D.; Pintel, D.J. Parvovirus minute virus of mice induces a dna damage response that facilitates viral replication. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, R.O.; Pintel, D.J. Parvovirus-induced depletion of cyclin b1 prevents mitotic entry of infected cells. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, M.S.; Majumder, K.; Pintel, D.J. Minute virus of mice inhibits transcription of the cyclin b1 gene during infection. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, N.J.; Price, A.M.; Weitzman, M.D. Take your pikk: Tumour viruses and dna damage response pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzman, M.D.; Fradet-Turcotte, A. Virus dna replication and the host dna damage response. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2018, 5, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, A.; Markowitz, T.E.; Katz, J.P.; Pipas, J.M.; McBride, A.A. Recurrent integration of human papillomavirus genomes at transcriptional regulatory hubs. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitelson, M.A.; Lee, J. Hepatitis b virus integration, fragile sites, and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, A.A. Human papillomaviruses: Diversity, infection and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.K.; Shen, K.; McBride, A.A. Papillomavirus genomes associate with brd4 to replicate at fragile sites in the host genome. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canela, A.; Maman, Y.; Jung, S.; Wong, N.; Callen, E.; Day, A.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.R.; Pekowska, A.; Zhang, H.; Rao, S.S.P. , et al. Genome organization drives chromosome fragility. Cell. 2017, 170, 507–521.e518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, J.H.; Faryabi, R.B.; Callén, E.; Wong, N.; Malhowski, A.; Chen, H.T.; Gutierrez-Cruz, G.; Sun, H.W.; McKinnon, P.; Wright, G. , et al. Identification of early replicating fragile sites that contribute to genome instability. Cell. 2013, 152, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canela, A.; Maman, Y.; Huang, S.N.; Wutz, G.; Tang, W.; Zagnoli-Vieira, G.; Callen, E.; Wong, N.; Day, A.; Peters, J.M. , et al. Topoisomerase ii-induced chromosome breakage and translocation is determined by chromosome architecture and transcriptional activity. Mol. Cell. 2019, 75, 252–266.e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Wang, J.; Boftsi, M.; Fuller, M.S.; Rede, J.E.; Joshi, T.; Pintel, D.J. Parvovirus minute virus of mice interacts with sites of cellular dna damage to establish and amplify its lytic infection. Elife 2018, 7, e37750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Boftsi, M.; Whittle, F.B.; Wang, J.; Fuller, M.S.; Joshi, T.; Pintel, D.J. The ns1 protein of the parvovirus mvm aids in the localization of the viral genome to cellular sites of dna damage. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1009002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.A.; Carson, C.T.; Schuberth, C.; Weitzman, M.D. Adeno-associated virus replication induces a dna damage response coordinated by dna-dependent protein kinase. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6269–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, R.O.; Pintel, D.J. The atr signaling pathway is disabled during infection with the parvovirus minute virus of mice. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10189–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Etingov, I.; Pintel, D.J. Protoparvovirus interactions with the cellular dna damage response. Viruses 2017, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cater, J.E.; Pintel, D.J. The small non-structural protein ns2 of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice is required for virus growth in murine cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73(Pt. 7), 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoborg, R.V.; Pintel, D.J. Accumulation of mvm gene products is differentially regulated by transcription initiation, rna processing and protein stability. Virology 1991, 181, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Boftsi, M.; Pintel, D.J. Viral chromosome conformation capture (v3c) assays for identifying trans-interaction sites between lytic viruses and the cellular genome. Bio Protoc. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray Chaudhuri, A.; Nussenzweig, A. The multifaceted roles of parp1 in dna repair and chromatin remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 18, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüesch, J.P.; Rommelaere, J. Ns1 interaction with ckii alpha: Novel protein complex mediating parvovirus-induced cytotoxicity. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4729–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, S.; Zhao, H.; Liao, J.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Xu, B.; Stern, D.F.; Xu, X.; Ye, K. Structural mechanism of the phosphorylation-dependent dimerization of the mdc1 forkhead-associated domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 3898–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüesch, J.P.; Rommelaere, J. A viral adaptor protein modulating casein kinase ii activity induces cytopathic effects in permissive cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12482–12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spycher, C.; Miller, E.S.; Townsend, K.; Pavic, L.; Morrice, N.A.; Janscak, P.; Stewart, G.S.; Stucki, M. Constitutive phosphorylation of mdc1 physically links the mre11-rad50-nbs1 complex to damaged chromatin. J. Cell. Biol. 2008, 181, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackford, A.N.; Jackson, S.P. Atm, atr, and dna-pk: The trinity at the heart of the dna damage response. Mol. Cell. 2017, 66, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boftsi, M.; Whittle, F.B.; Wang, J.; Shepherd, P.; Burger, L.R.; Kaifer, K.A.; Lorson, C.L.; Joshi, T.; Pintel, D.J.; Majumder, K. The adeno-associated virus 2 (aav2) genome and rep 68/78 proteins interact with cellular sites of dna damage. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 31, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, G.A.; O'Shea, C.C. Viral and cellular genomes activate distinct dna damage responses. Cell. 2015, 162, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).