Submitted:
28 March 2023
Posted:
29 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
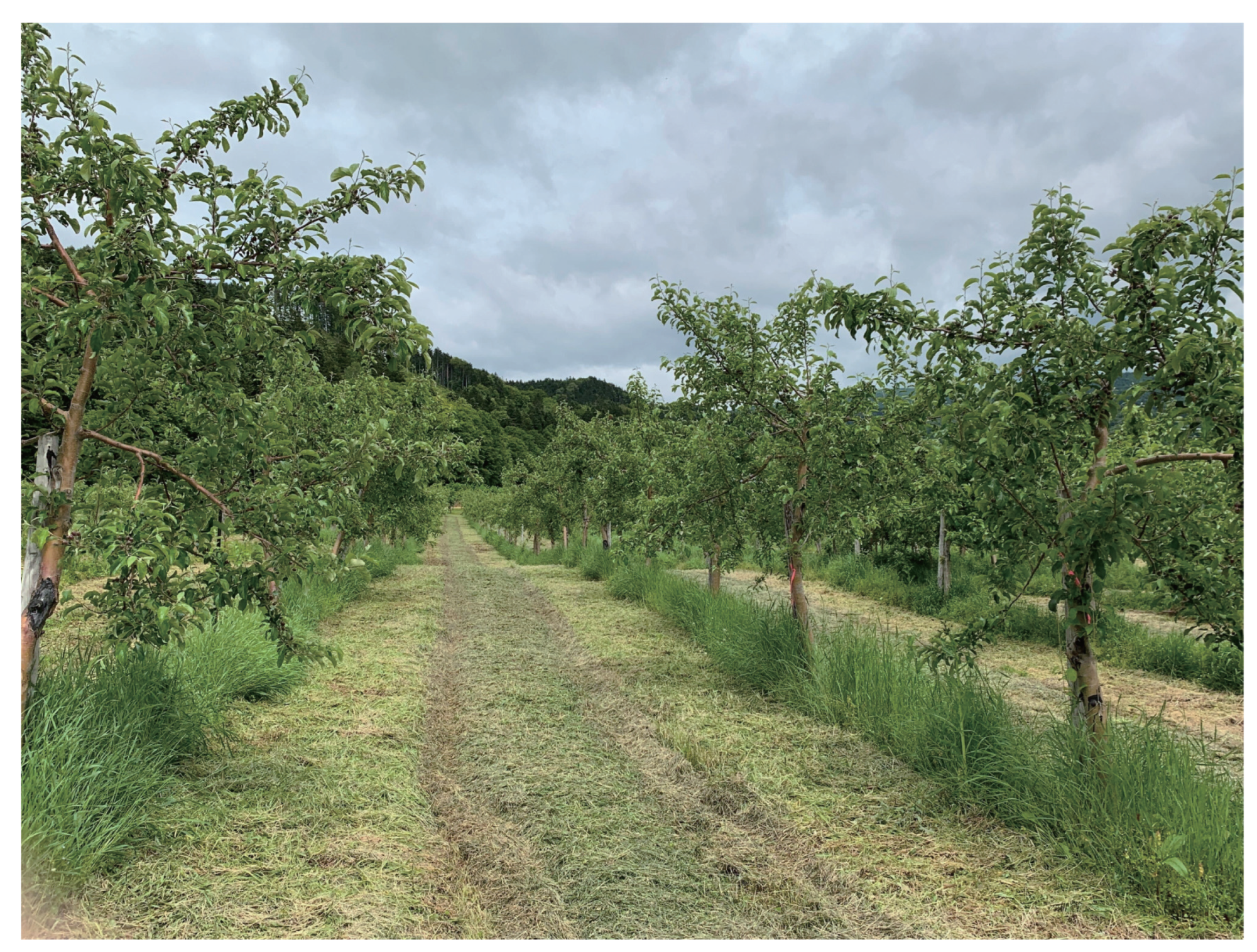
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Use Instrument
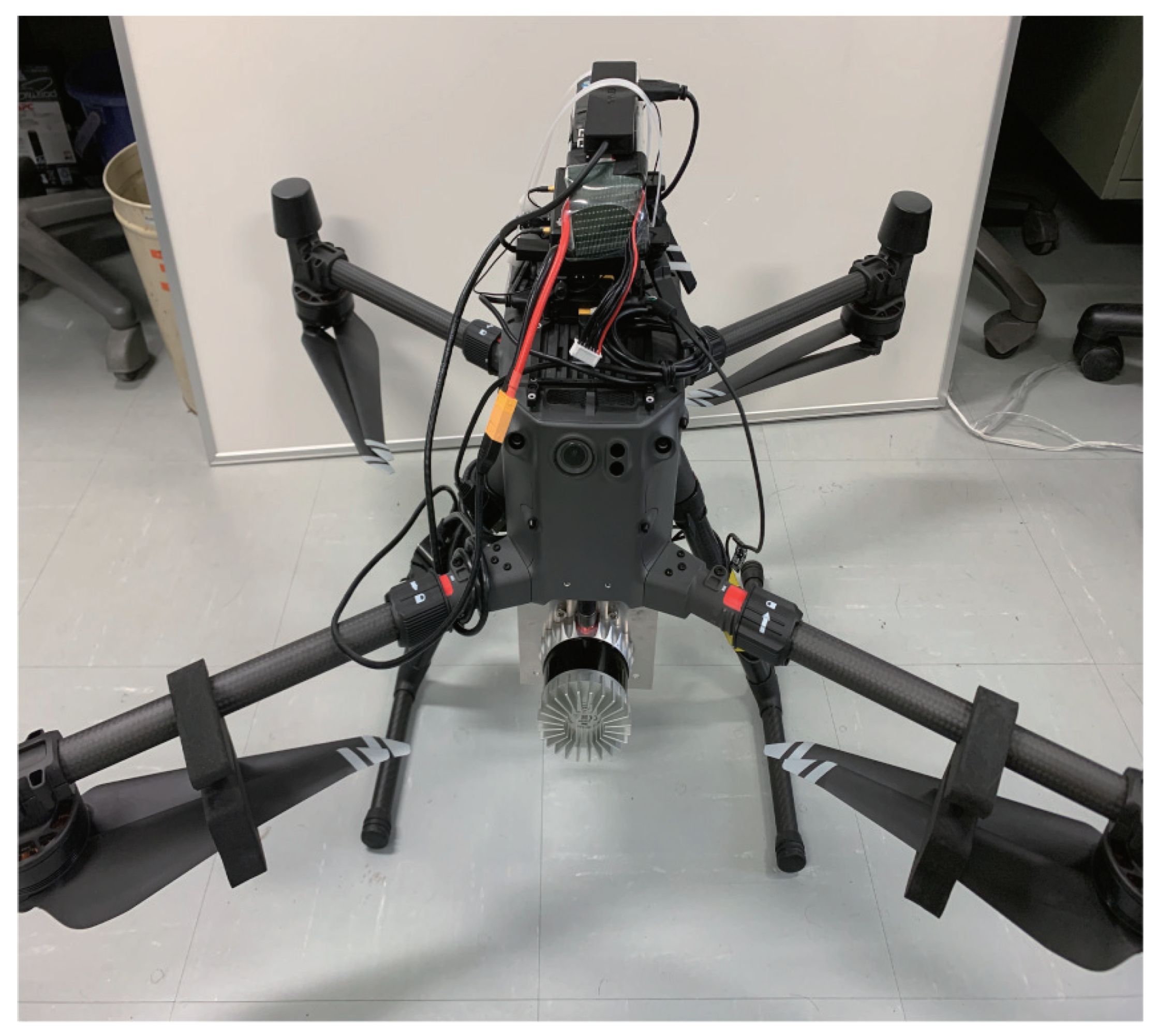
2.2.1. UAV DJI Matrice 300 RTK
2.2.2. Laser Scanner OS1-64
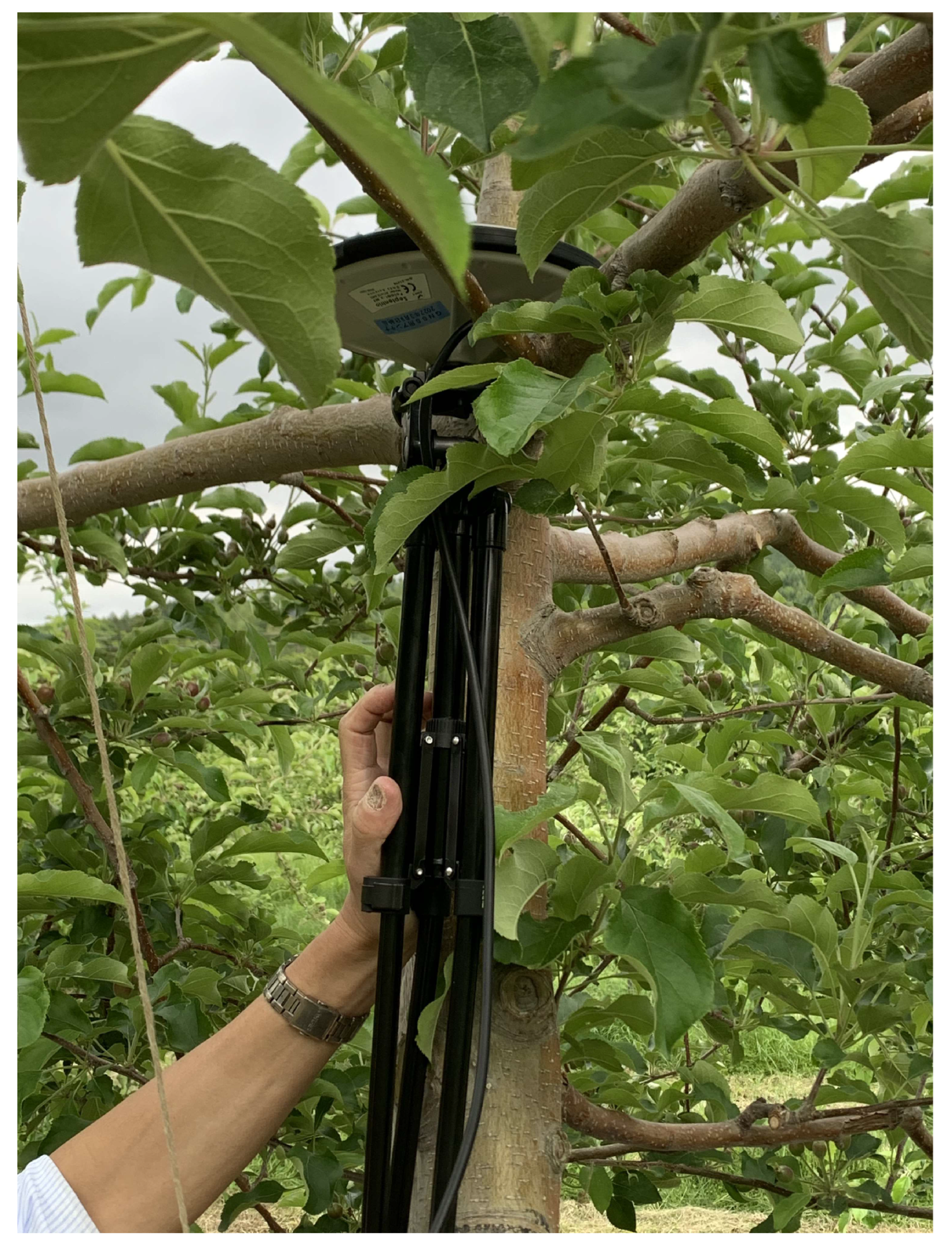
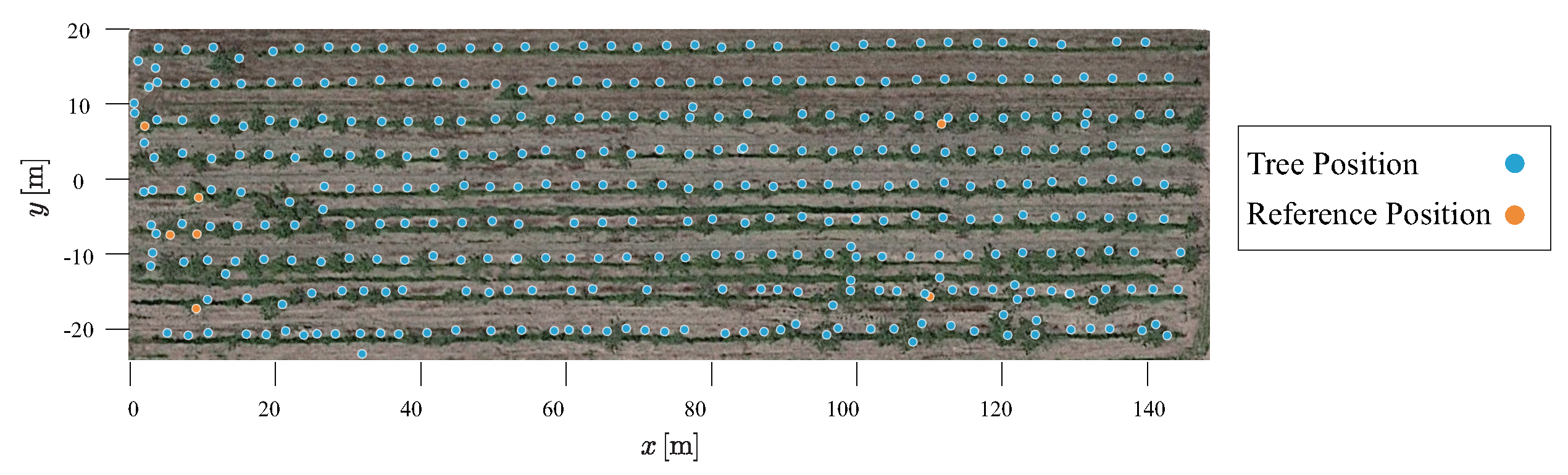
2.3. Acquisition of Standing Tree Location
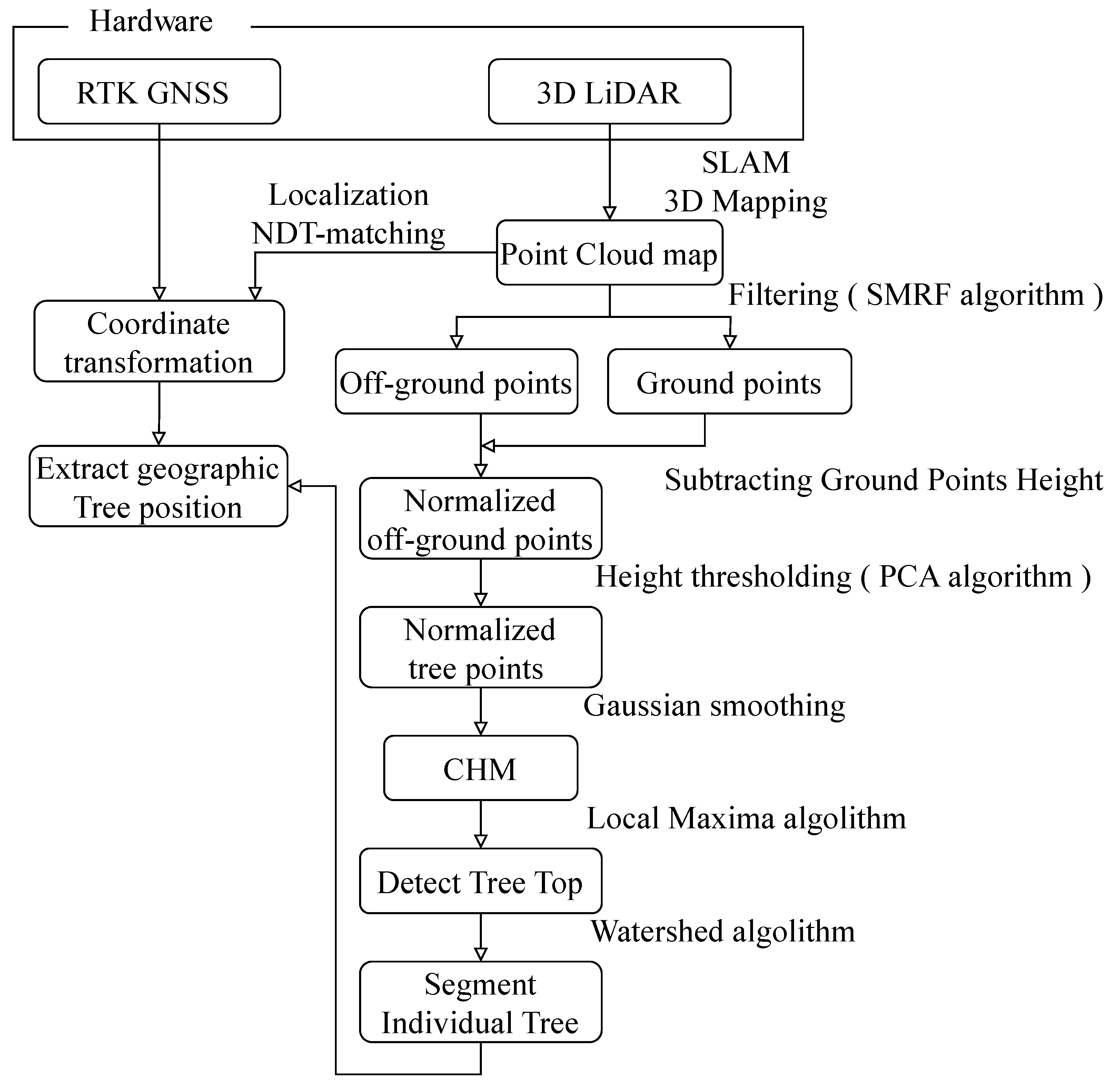
2.4. Processing Strategy
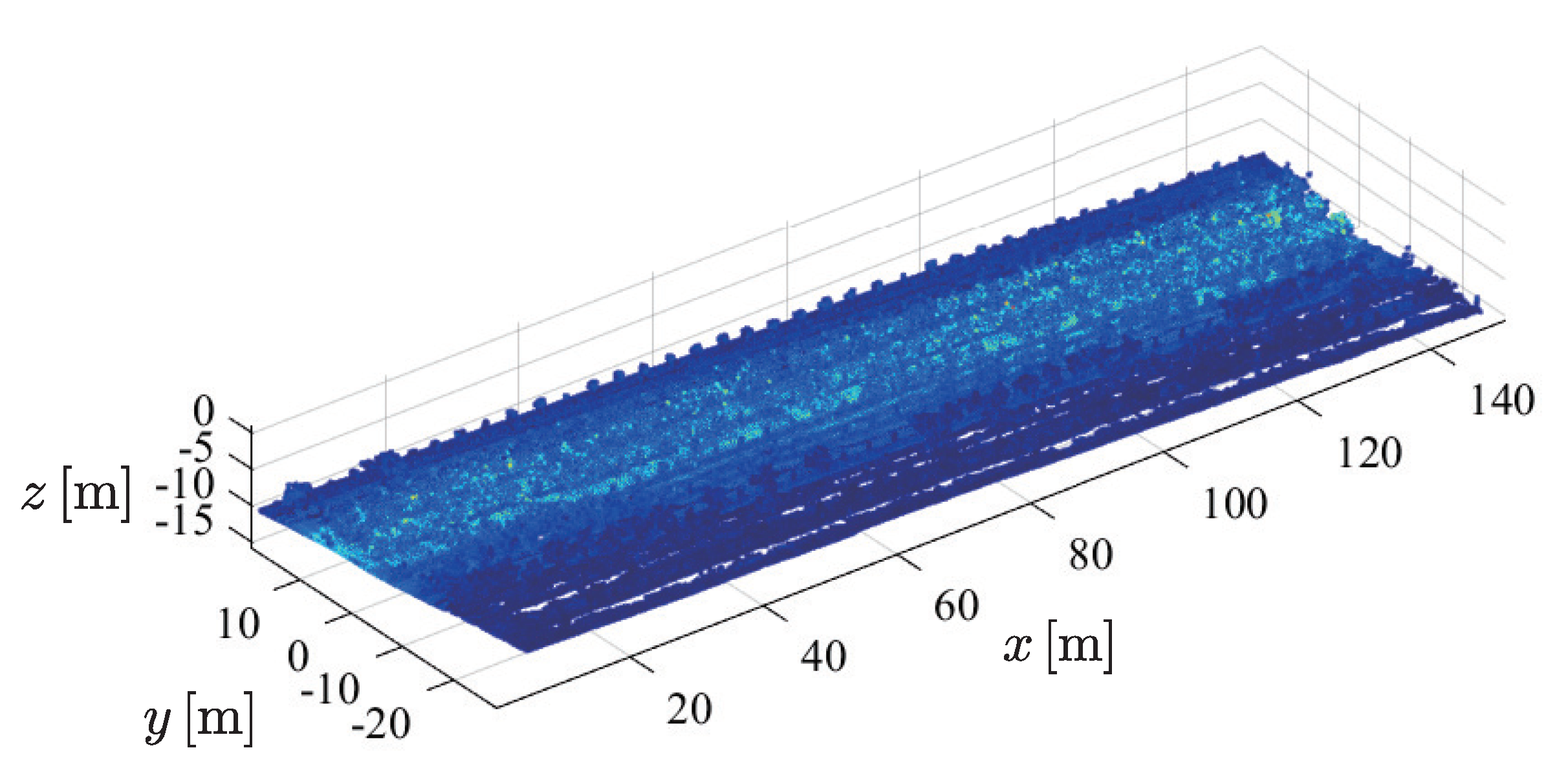
2.4.1. Point Cloud Normalization
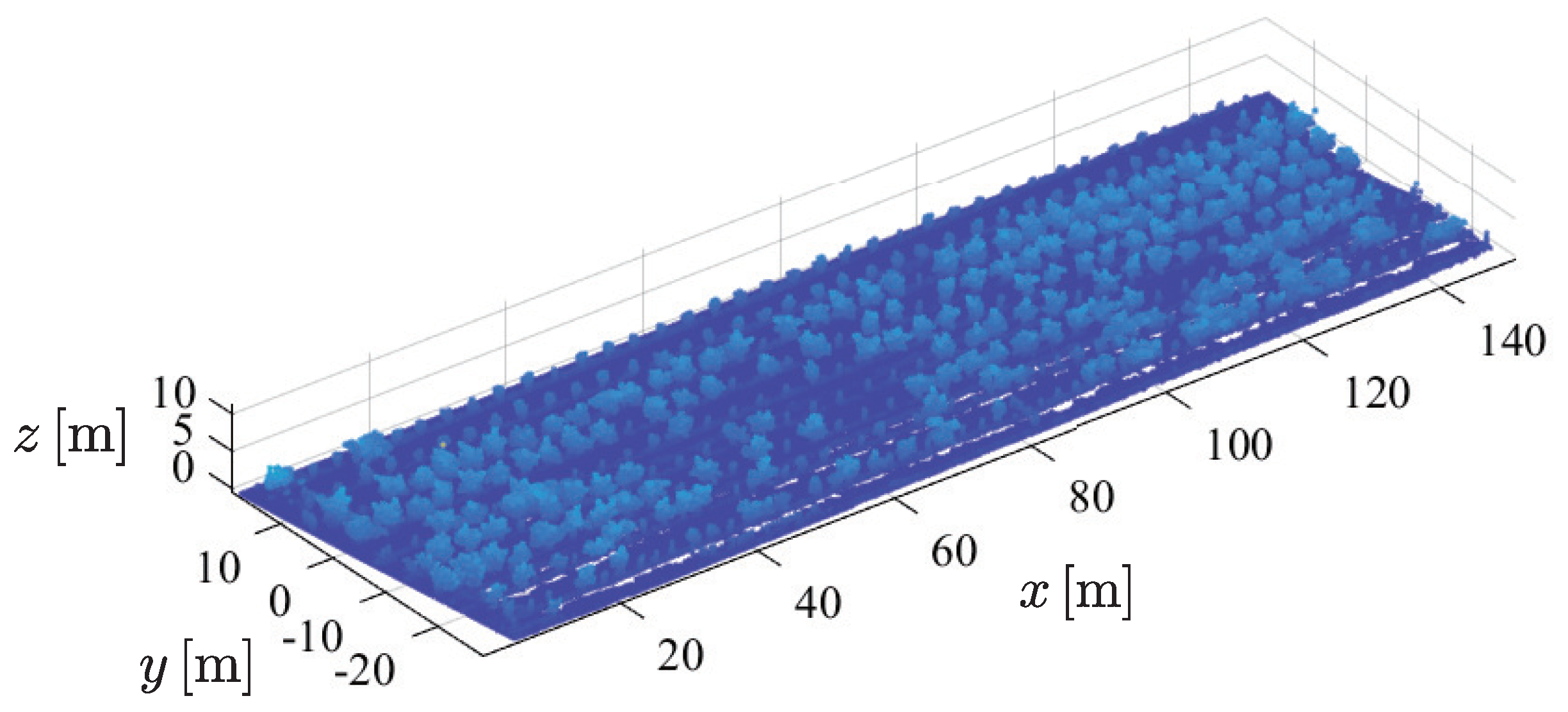
2.4.2. Remove Grass Point Cloud
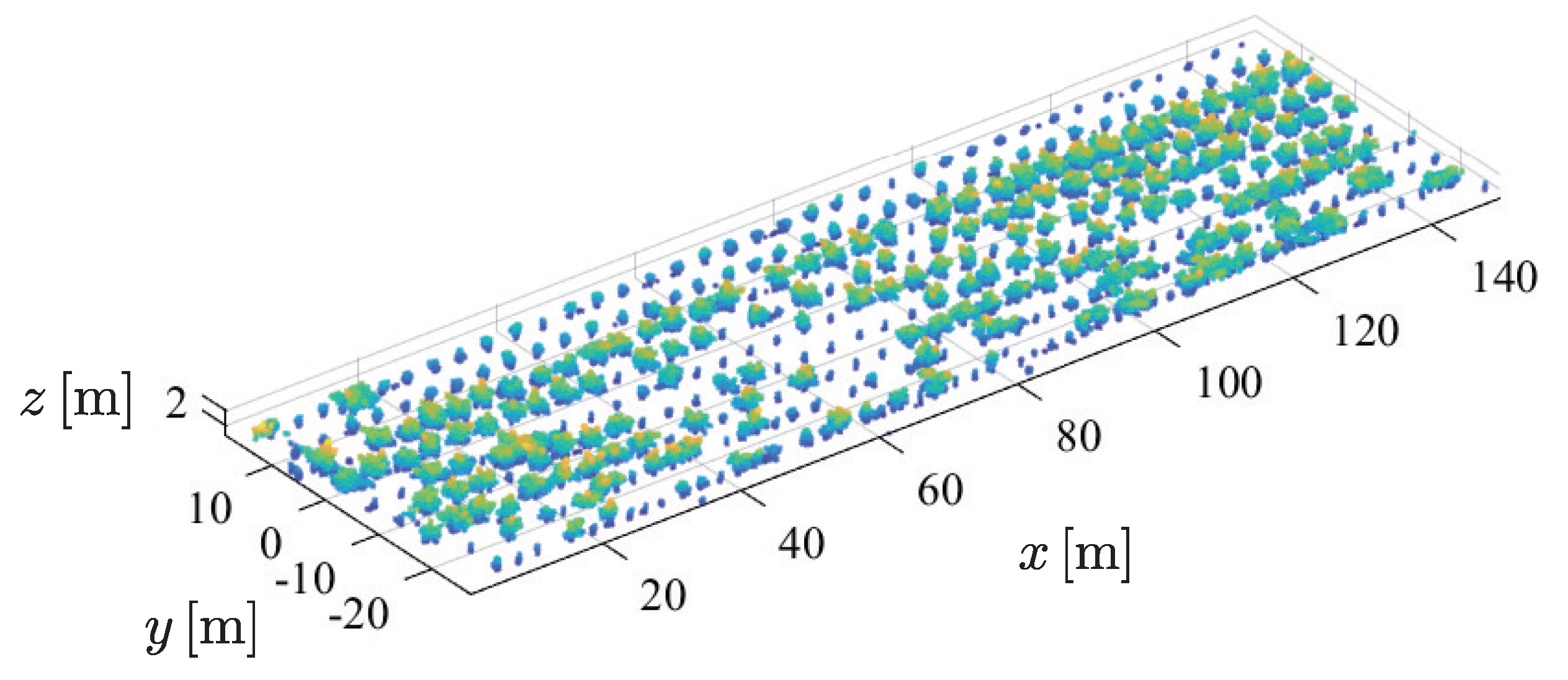
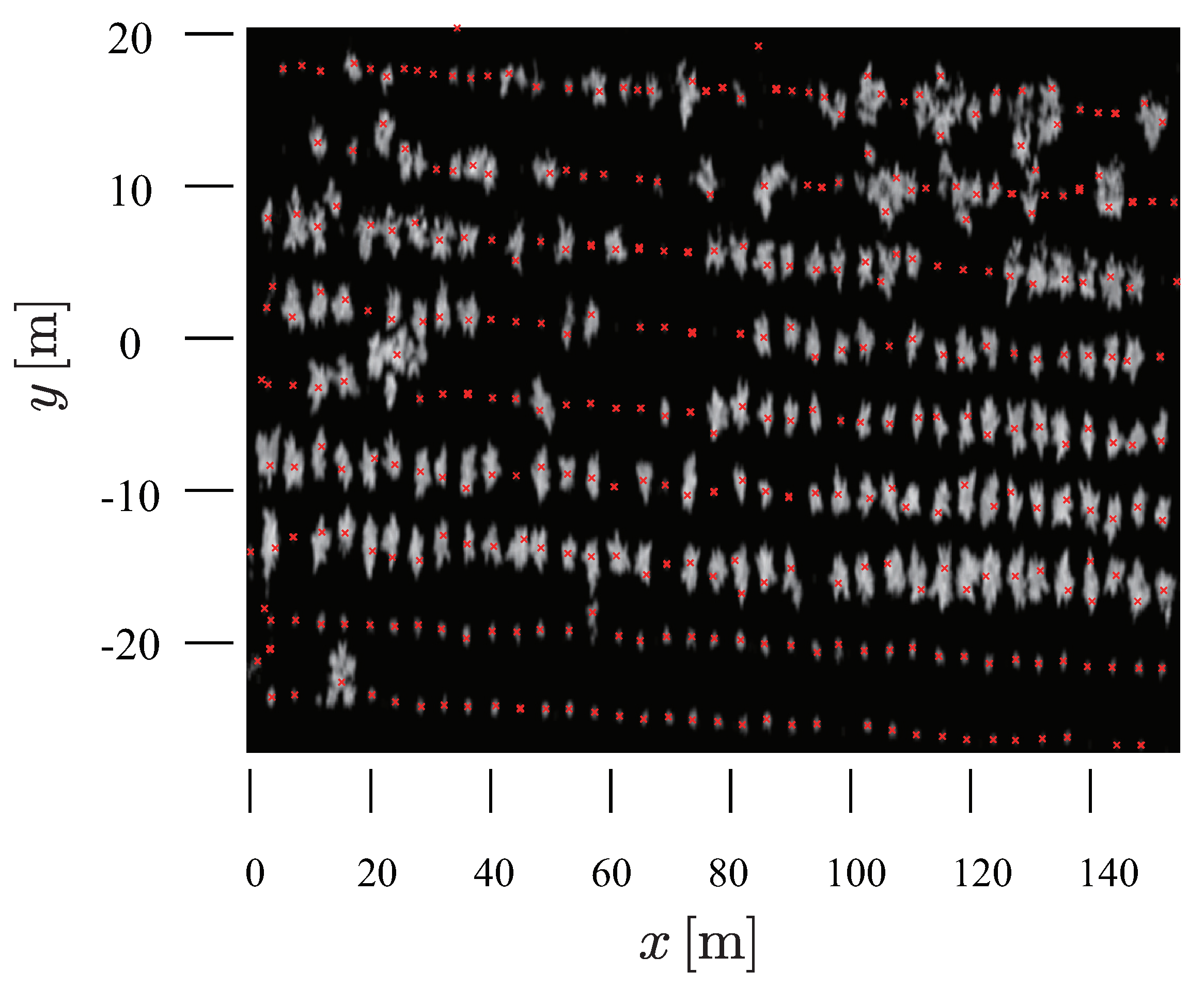
2.4.3. Canopy Height Model (CHM) Creation and Individual Tree Detection
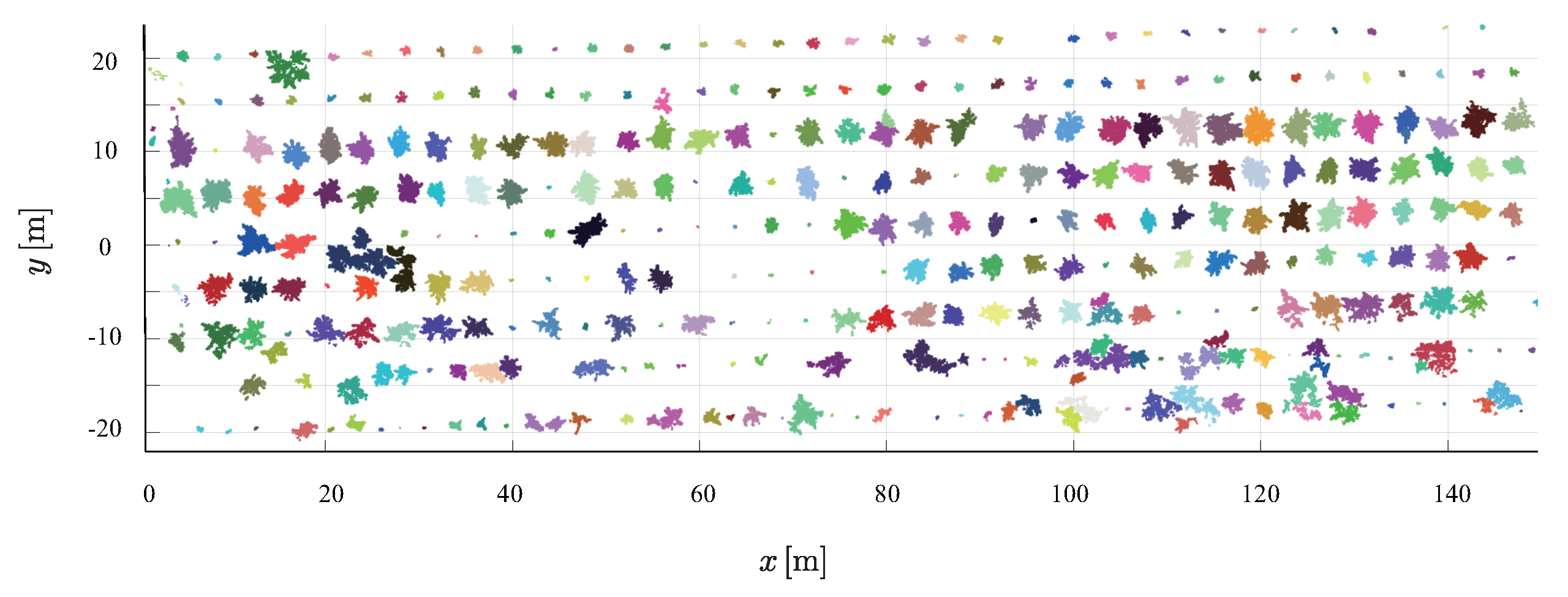
2.4.4. Segment Individual Trees
2.4.5. Alignment of GNSS Coordinate System and Map Coordinate System
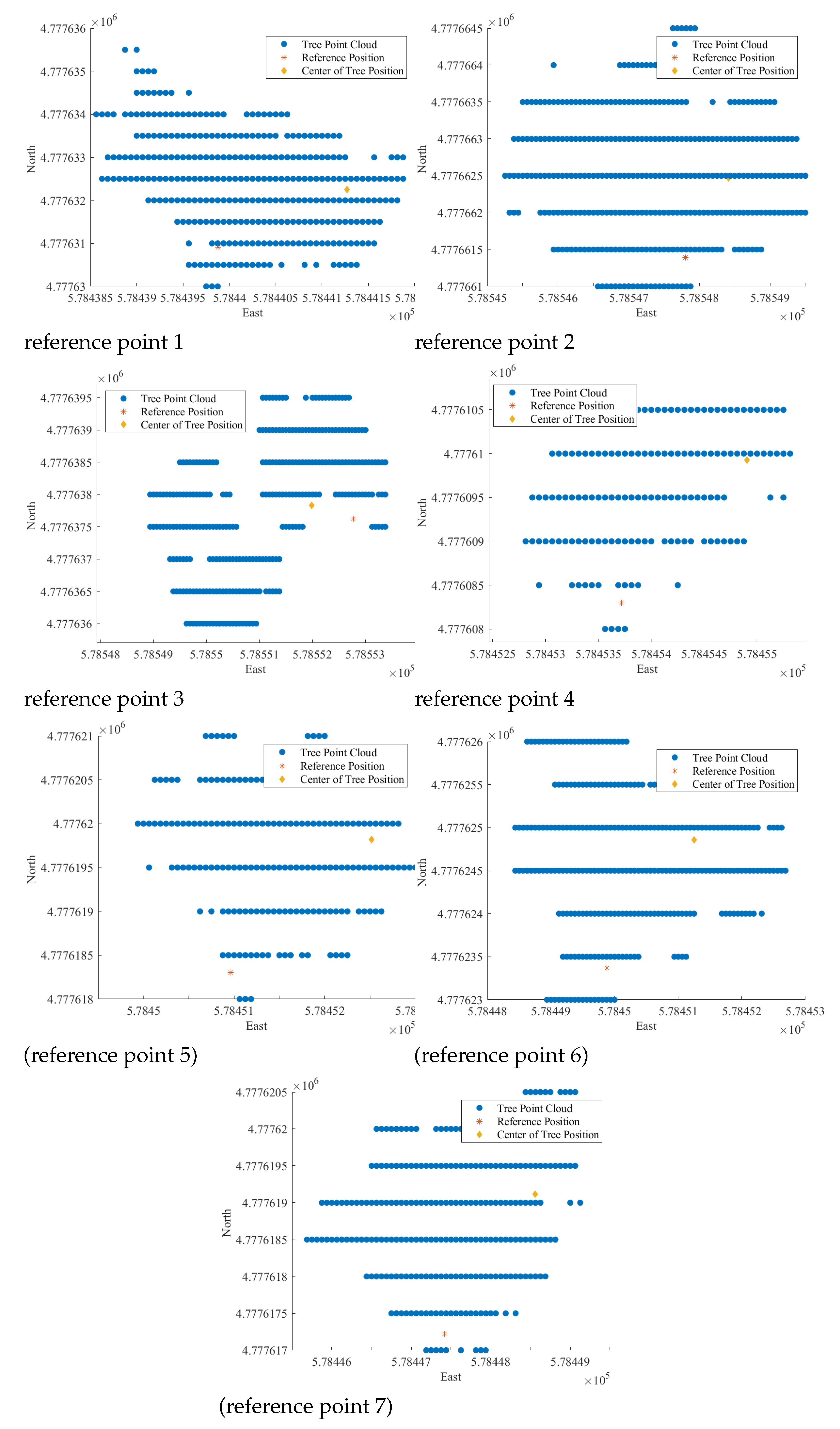
2.5. Statistical Analsis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
References
- Yousefi, M.R.; Razdari, A.M. Application of GIS and GPS in precision agriculture (a review). International Journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research 2015, 3, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, A.; Lamb, D.H.B.L.J. Optical remote sensing applications in viticulture - a review. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research 2002, 8, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longchamps, L.; Tisseyre, B.; Taylor, J.; Sagoo, L.; Momin, M.; Fountas, S.; Manfrini, L.; Ampatzidis, Y.; Schueller, J.; Khosla, R. Yield sensing technologies for perennial and annual horticultural crops: A review. Precision Agriculture 2022, 23, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, S.C.; Baysal-Gurel, F. Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) Technology and Applications in Agriculture. Agronomy 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasingam, N.; Ashan Salgadoe, A.S.; Powell, K.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Natarajan, S. A review of UAV platforms, sensors, and applications for monitoring of sugarcane crops. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 2022, 26, 100712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Chapman, S.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, B. Dynamic monitoring of NDVI in wheat agronomy and breeding trials using an unmanned aerial vehicle. Field Crops Research 2017, 210, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delalieux, S.; van Aardt, J.; Keulemans, W.; Schrevens, E.; Coppin, P. Detection of biotic stress (Venturia inaequalis) in apple trees using hyperspectral data: Non-parametric statistical approaches and physiological implications. European Journal of Agronomy 2007, 27, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Guan, Q.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liang, D.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. New Optimized Spectral Indices for Identifying and Monitoring Winter Wheat Diseases. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2014, 7, 2516–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zude-Sasse, M.; Fountas, S.; Gemtos, T.; Abu-Khalaf, N. Applications of precision agriculture in horticultural crops. European Journal of Horticultural Science 2016, 81, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Huang, W.; Huang, S.; Cui, B.; Dong, Y.; Guo, A.; Ren, Y.; Jin, Y. Recognition of Banana Fusarium Wilt Based on UAV Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roma, E.; Laudicina, V.A.; Vallone, M.; Catania, P. Application of Precision Agriculture for the Sustainable Management of Fertilization in Olive Groves. Agronomy 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothou, A.; Toth, C.; Spyros, K.; Georgopoulos, A. An approach to optimize reference ground control requirements for estimating LiDAR/IMU boresight misalignment. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.; Lucieer, A.; Watson, C.S. An Automated Technique for Generating Georectified Mosaics from Ultra-High Resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Imagery, Based on Structure from Motion (SfM) Point Clouds. Remote. Sens. 2012, 4, 1392–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, L.; Ding, X.; Guo, B. The precise multimode GNSS positioning for UAV and its application in large scale photogrammetry. Geo-spatial Information Science 2016, 19, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Lucieer, A.; Wallace, L. Direct Georeferencing of Ultrahigh-Resolution UAV Imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2014, 52, 2738–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, F.; Dall’Asta, E.; Diotri, F.; Forlani, G.; Morra di Cella, U.; Roncella, R.; Santise, M. Testing Accuracy and Repeatability of UAV Blocks Oriented with GNSS-Supported Aerial Triangulation. Remote Sensing 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, G.; Diotri, F.; Cella, U.M.d.; Roncella, R. Indirect UAV strip georeferencing by on-board GNSS data under poor satellite coverage. Remote sensing 2019, 11, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.; Mora, O.E.; Starek, M.J. Evaluating the performance of sUAS photogrammetry with PPK positioning for infrastructure mapping. Drones 2021, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Ablanedo, E.; Chandler, J.H.; Rodríguez-Pérez, J.R.; Ordóñez, C. Accuracy of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and SfM photogrammetry survey as a function of the number and location of ground control points used. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Habib, A. Quality control and crop characterization framework for multi-temporal UAV LiDAR data over mechanized agricultural fields. Remote Sensing of Environment 2021, 256, 112299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štroner, M.; Urban, R.; Línková, L. A New Method for UAV Lidar Precision Testing Used for the Evaluation of an Affordable DJI ZENMUSE L1 Scanner. Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozkow, G.; Wieczorek, P.; Karpina, M.; Walicka, A.; Borkowski, A. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF sUAS EQUIPPED WITH VELODYNE HDL-32E LiDAR SENSOR. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2017, XLII-2/W6, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Choi, D.; Bolkas, D. GNSS-IMU-assisted colored ICP for UAV-LiDAR point cloud registration of peach trees. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2022, 197, 106966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, E.; Jozkow, G.; Walicka, A.; Borkowski, A. Apple orchard inventory with a LiDAR equipped unmanned aerial system. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2019, 82, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, P.; Straßer, W. The Normal Distributions Transform: A New Approach to Laser Scan Matching. 2003, 3, 2743–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingel, T.J.; Clarke, K.C.; McBride, W.A. An improved simple morphological filter for the terrain classification of airborne LIDAR data. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2013, 77, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews: Computational statistics 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, I.; Anttila, P.; Pitkänen, J. The performance of a local maxima method for detecting individual tree tops in aerial photographs. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2006, 27, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Baldocchi, D.; Gong, P.; Kelly, M. Isolating individual trees in a savanna woodland using small footprint lidar data. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing 2006, 72, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; de Mendonça, B.A.F.; Silva, C.A.; Klauberg, C.; de Saboya Ribeiro, A.S.; de Araújo, E.J.G.; Monte, M.A.; Cardil, A. Optimizing individual tree detection accuracy and measuring forest uniformity in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) plantations using airborne laser scanning. Ecological Modelling 2019, 409, 108736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, P.; Gomes, M.F. Detection and counting of orchard trees from VHR images using a geometrical-optical model and marked template matching. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2016, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.; McKay, N.D. A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.; Niemann, K.O.; Goodenough, D.G. Local maximum filtering for the extraction of tree locations and basal area from high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sensing of environment 2000, 73, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Hu, B.; Noland, T.; Li, J. An individual tree crown delineation method based on multi-scale segmentation of imagery. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2012, 70, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Yang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Lei, L.; Zhao, C. Extracting apple tree crown information from remote imagery using deep learning. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2020, 174, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dimensions | 810 × 670 × 430 mm (L×W×H) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 9 kg |
| Max Flight Time | 55 min |
| Max Speed | 23 m/s |
| GNSS | GPS+GLONASS+BeiDou+Galileo |
| RTK Positioning Accuracy | Vertical : 1.5 cm + 1 ppm; Horizontal : 1 cm+1 ppm |
| Horizontal channels | 64 |
| Points Per Second | 5,242,880 |
| Range | 120 m |
| Range Resolution | 0.1 cm |
| Field of View | Vertical : 45°(+22.5°to -22.5°); Horizontal : 360° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




