1. Introduction
The endogenous circadian clock temporally coordinates the diurnal variation of most metabolic processes to anticipate the daily changes in the light /dark cycle and nutrient availability to adjust the eating and fasting schedule to the optimal time of the day [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6].
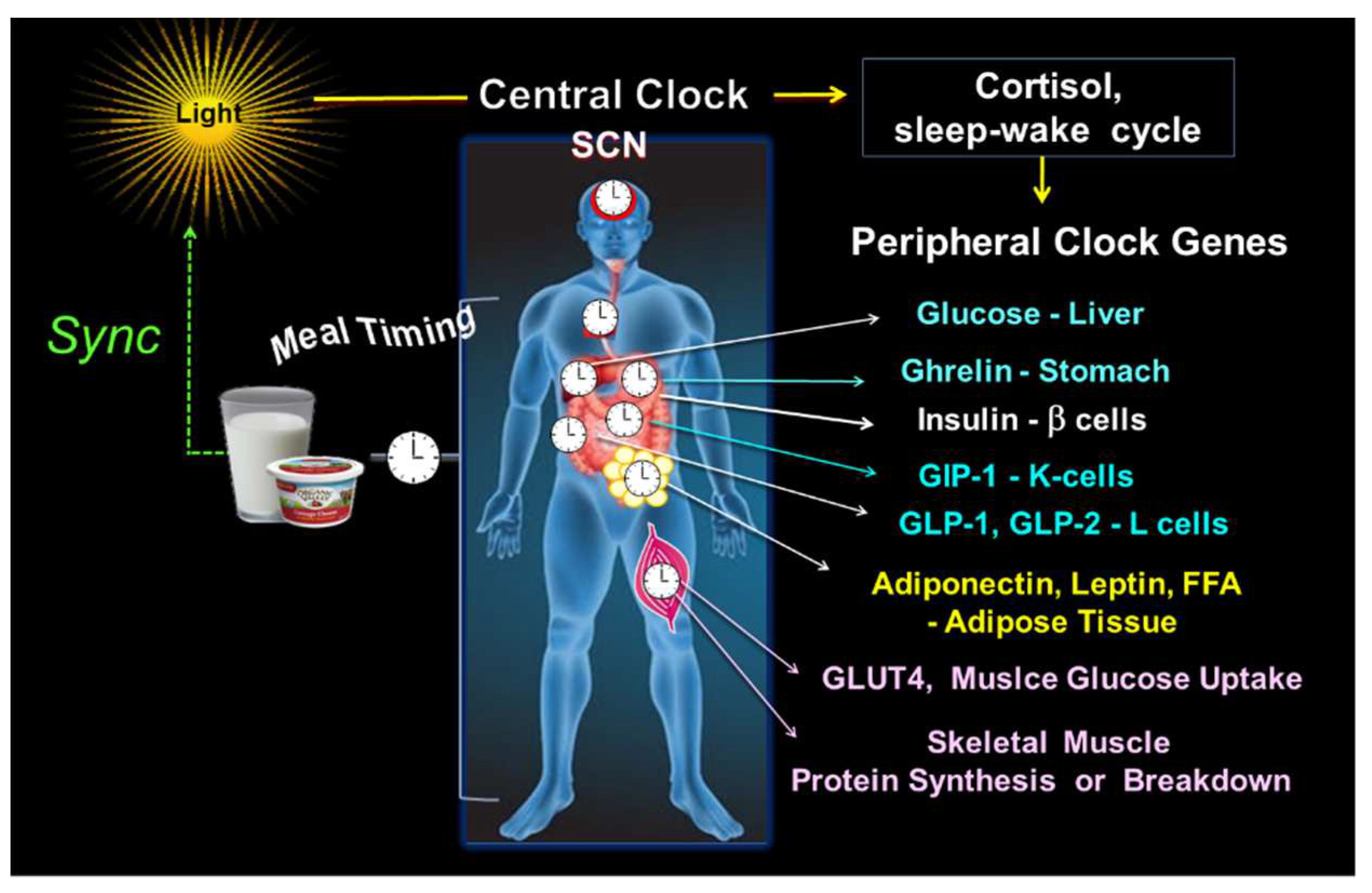
The circadian coordination requires an alignment between the central clock in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which is responsive to light inputs, with the peripheral clock genes disseminated in almost all the tissues (i.e., β-cells, muscle, liver), mostly entrained to the hour of food intake [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
Evidence suggests that the metabolic conditions for food intake are optimal in the morning [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. Specifically, the first meal of the day, consumed at the beginning of the activity phase (early-timed breakfast), is a powerful “zeitgeber” or starter of peripheral clock genes expression [
4,
8,
9,
19,
20,
21,
22]. It enhances enzymes and hormones involved in the regulation of body weight [
19,
23,
24,
25], overall glycemia [
18,
26,
27,
28,
29], muscle synthesis [
30,
31,
32], and appetite [
12,
25,
33]. Further, the diet-induced thermogenesis is significantly higher after high energy breakfast vs. an isocaloric dinner, highlighting the importance of the first meal of the day in achieving metabolic homeostasis [
25,
34,
35,
36,
37].
While many studies documented the metabolic advantage of early-timed breakfast [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26], growing evidence shows that the "lack of breakfast" or delayed breakfast until noon, also known as "extended postabsorptive state," at the transition from overnight fast to fed state, has the potential to desynchronize clock gene expression and regulation of metabolism [
19,
20,
21,
22,
38]. The omission of breakfast has been associated with higher body mass indices, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and the risk for developing T2D [
19,
23,
28,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43]. The circadian misalignment and disrupted clock gene expression arising from fasting until noon lead to increased glycemia, and appetite scores, deficient insulin, and incretin responses after subsequent meals [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
27,
38,
44,
45,
46], and reduced energy expenditure [
25,
34,
35,
36,
37]. Further, the lack of breakfast activates muscle protein breakdown to provide the liver with glucogenic amino acids for neoglucogenesis, which may result in a loss of skeletal muscle mass [
30,
31,
32,
41,
45,
46,
47].
This review aims to discuss the circadian misalignment derived from the lack of breakfast and the ensuing deleterious effects on clock genes expression, body weight, glucose metabolism, muscle mass, and energy expenditure. We will provide a general overview of the circadian clock molecular mechanism and its role in aligning metabolic processes to the active and resting phases. The clock-controlled postprandial and postabsorptive glucose metabolism and the transition or switch from overnight fast to a fed state. Finally, we will discuss what time of the day is most appropriate for fasting and eating to achieve optimal control of body weight, energy expenditure, and glucose metabolism.
2. Circadian Clock Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of central and peripheral clocks consists of transcriptional/translational positive and negative feedback loops coordinating an extensive clock gene network to maintain a self-sustained daily ~24 h oscillation [
1,
2,
3]. The clock gene set includes
BMAL1 (brain and muscle ARNT-like 1),
CLOCK (circadian locomotor output cycles kaput), three period genes (
PER1, PER2, and PER3), two cryptochrome genes (
CRY1 and
CRY2), the reverse erythroblastosis virus (
REV-ERB α, β, δ, and γ
), and retinoic acid-related orphan receptor (
ROR α, β, and γ
) [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55].
The transcriptional activators
CLOCK and
BMAL1 dimerize, forming the CLOCK: BMAL1 complex, which associates with
Sirtuin 1 (
SIRT1) deacetylase. CLOCK: BMAL1 complex rhythmically binds E-box-like promoter sequences to activate the transcription of
PER and
CRY repressor genes. The resulting PER and CRY proteins interact to form PER: CRY dimers in the cytoplasm. Upon reaching a critical threshold concentration in the cytoplasm, PER: CRY dimers translocate back to the nucleus, repressing their own CLOCK: BMAL1 transcription [
1,
2,
3,
7,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55]. The blockage of CLOCK: BMAL1 transcription persists until all PER: CRY dimers are degraded, and then the cycle begins again, thus maintaining the ~ 24 h oscillation. The blockage of CLOCK: BMAL1 is reversed by the action of casein kinase I epsilon (CKIε
), allowing the resumption of a new ~ 24h transcription cycle. Further, CKIε also phosphorylates and partially reactivates the
BMAL1-driven transcription [
1,
48,
49].
In another major transcriptional loop, CLOCK: BMAL1 complex encodes the transcription of repressor proteins
REV-ERBs and the activators
RORs, (α, β, and γ), forming an additional stabilizing loop with
BMAL1, further maintaining a ~24h rhythm in B
MAL1 transcription [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56].
The oxidized form NAD+ activates
SIRT1 and interacts with
CLOCK:
BMAL1 in a circadian manner, promoting the deacetylation and degradation of
PER2 and is a crucial factor in glucose metabolism [
3,
7,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55]. In addition, the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) positively interacts with
SIRT1 [
56].
Figure 1.
Another subset of clock-controlled genes (CCGs), transcriptional factors, and clock proteins include all members of the PPAR family [α, β, γ, δ], and PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), which feeds back into the clock, producing additional bidirectional regulation of metabolism and circadian rhythms [
53,
54,
55]. Hence,
CLOCK: BMAL1-driven transcription of
PERs, CRYs, REV-ERBα, RORα genes, and PGC-1α promote the expression of tissue-specific clock-controlled genes, activating many rhythmic metabolic and hormonal outputs, i.e., β-cell secretion, GLUT-4 activity, muscle glucose uptake, and incretin, i.e., glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) response. The clock gene-driven hepatic glucose production promotes glycogenolysis enzyme glucose 6-phosphatase (HG6-P) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) in the gluconeogenesis pathway. PGC-1α plays a role in lipid metabolism (lipogeneses and nocturnal lipolysis [
7,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64,
65,
66,
67,
68].
Figure 1.
3. Synchrony between central and peripheral clock genes
The light-entrained central clock in SCN coordinates peripheral clocks through sympathetic-pathway signals, setting the sleep-wake cycle and hormonal signaling, primarily adrenal glucocorticoids. [
1,
2,
3,
4,
7]. This alignment allows anticipating the secretion of specific hormones and antagonistic factors at a “specific time of the day,” leading to an appropriate temporal sequence of hormonal, digestive, absorptive, and metabolic functions [
5,
7,
8,
9,
10,
49,
50].
Thus, the clock timing system adjusts to the active and resting phase, the oscillation of hepatic glucose output [
56,
58], ghrelin secretion [
59], insulin sensitivity, and β-cell responsiveness [
58,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64]. It also regulates the diurnal variation of the postprandial secretion of incretins, i.e., GLP-1 and glucagon-like peptide-2 (GLP-2) in the intestinal L-cells, gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) in intestinal K-cells [
65,
66], and leptin and adiponectin secretion in the adipose tissue [
55,
67]. Notably, the clock genes in skeletal muscle regulate GLUT-4 activity, muscle glucose uptake [
60,
68], muscle protein synthesis during the postprandial state, and muscle protein breakdown in the postabsorptive state [
30,
31,
32,
41].
Figure 2.
4. Circadian variation of metabolism during active and resting phase
The coordination between central and peripheral clocks generates the diurnal variation of the metabolic processes throughout the active and resting phases to ensure the consumption of “the right meals at the right and optimal time of the day.” [
5,
49,
69,
70].
4.1. Clock controlled active and resting phase
The diurnal variation of melatonin and cortisol, and the sleep-wake cycle driven by the light/dark controlled SCN clock, split the daily metabolic outputs into the active phase (biological day) and resting phase (biological night) [
71]. The active phase in humans begins upon waking up between 06:00 and 08:00 and continues until 22:00 when the nocturnal rise of melatonin initiates the resting phase [
6,
72,
73]. The morning peak of cortisol is an important starting signal. It prepares the body for waking up and consuming the first meal of the day (i.e., breakfast) to cover the increase in the energetic demands of the active phase [
74].
4.2. Clock controlled metabolism is enhanced in the early hours of the active phase
The clock-gene regulation enhances most metabolic pathways at dawn, in the early hours of the active phase, and shortly after waking up [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
69,
70]. The secretion of ghrelin peaks at 08:00, increasing appetite and food intake in the early morning [
59]. Adiponectin levels also rise in the morning, peaking at 11:00 and declining at 20:00 [
74,
75,
76]. The morning rise of adiponectin stimulates via activation of AMPK, the fatty acid oxidation, insulin sensitivity, muscle glucose uptake, and glycolysis while reducing hepatic glucose production during the morning hours. These mechanisms increase glucose utilization and decrease fat accumulation in the early hours suggesting fewer fattening effects from the meal ingested in the early morning [
6,
74,
75,
76]. The decreased adiponectin in the evening induces metabolic change toward insulin-mediated anabolic processes. Thus, the postprandial insulin response in the evening stimulates fat storage and lipogenesis by activating fatty acid synthesis [
75,
76]. In contrast, the rise of leptin n the evening reduces fat accumulation and increases nocturnal lipolysis [
74].
The clock gene regulation also enhances insulin sensitivity, β-cell responsiveness, GLUT-4 activity, muscle glucose uptake, post-meal incretin (i.e., GLP-1, GLP-2, and GIP) secretion, and incretin-mediated insulinotropic effect in the early hours of the active phase [
58,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64,
65,
66,
68]. As a result, the glycemic response is significantly higher after identical meals consumed in the evening compared to the morning [
18,
36,
58,
78].
The resting energy expenditure (REE) also displays circadian oscillation showing its lowest levels during the resting phase, while the respiratory quotient (RQ), reflecting macronutrient utilization, is at its highest score in the early hours of the active phase [
80]. Moreover, the circadian clock enhances diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT) or energy expenditure after meals consumed in the early active phase compared to the evening [
34,
35,
36,
37]. Therefore, the early hours of the active phase (i.e., breakfast) are optimal for food intake and especially for CH consumption, while in the evening and nighttime, it is likely more convenient to reduce the energy and CH intake [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
69,
70,
77,
78,
79].
4.3. Potential benefits of early-timed breakfast
Feeding/fasting misalignment, i.e., small breakfast or breakfast omission and higher caloric intake in the evening, e.g., in shift workers, are associated in preclinical and clinical studies with circadian clock disruption [
19,
22] and increased risk of developing obesity, hyperglycemia, and diabetes [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
38,
39,
40]. Studies on time-restricted eating (TRE) consisting of an eating window restricted to the early hours of the day (eTRE) and fasting during the late hours and night are associated with improved regulation of weight loss and overall glucose levels compared to late TRE, with extended fasting until noon and eating window in the afternoon and evening [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
15,
16,
77,
79].
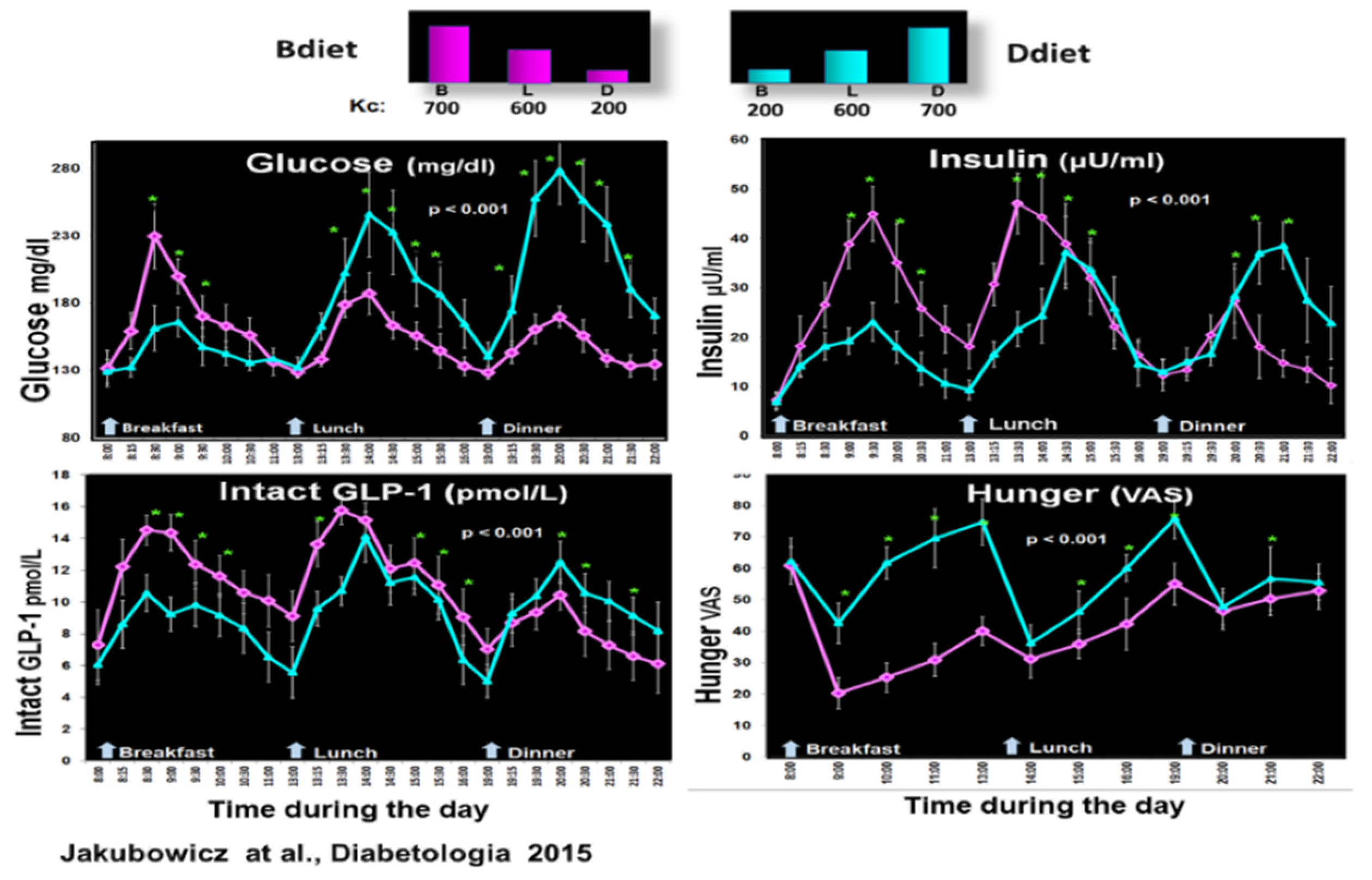
Our group further explored whether shifting most energy and CH to the early hours of the day is an effective meal-timing approach for weight loss and reduction of overall daily glycemia. We compared the effects of a high-energy breakfast diet (Bdiet) versus a high-energy dinner diet (Ddiet) in overweight and obese women over 12 weeks [
17]. The high-energy breakfast diet (Bdiet) consisted of (700kcal breakfast, 500kcal lunch, and 200kcal dinner), while the high-energy dinner diet (Ddiet) had the reverse schedule (200kcal breakfast, 500kcal lunch, 700kcal dinner). Bdiet led to more efficient weight loss, reduced overall daily glucose and insulin resistance, and lower hunger scores and ghrelin levels than Ddiet. In summary, greater weight loss was observed in the Bdiet group, with energy intake shifted towards early rather than late hours in the day [
17].
5. Circadian clock regulation of postprandial and postabsorptive glucose metabolism and the transition (switch) from overnight fast to postprandial fed state
The alignment of the fasting/feeding cycle with the circadian clock engages dynamic feedback to the clock gene regulatory network. It regulates the insulin and glucagon-dependent metabolic tissues and the circadian oscillation of glucose metabolism throughout the postabsorptive and postprandial states and during the shift or transition from postabsorptive to postprandial or fed state at dawn [
3,
4,
38,
45].
In the active phase (postprandial state) which starts upon the consumption of the early-timed breakfast, the glucose and insulin response to the influx of dietary CH, initiates the translocation of GLUT4, the skeletal muscle glucose uptake, and the reduction of liver glucose production [
38,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85]. While, in the resting phase (postabsorptive state), the glucose metabolism consists of hepatic glucose production (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis) [
3,
4,
38,
45].
The expression of
BMAL-1,
RORα,
SIRT1, and AMPK is essential during the fed or postprandial state for the regulation of the diurnal variation of β-cells responsiveness [
58,
62,
63,
64,
65,
66], insulin sensitivity [
60,
61], GLUT-4 activity, and muscle glucose uptake [
60,
68]. During the overnight fast (postabsorptive state), the expression of
REVERBα, RORα, SIRT1, and
PGC-1α in the liver is critical for the regulation of the nocturnal hepatic glucose production, namely glycogenolysis and gluconeogenic pathways, to maintain adequate blood glucose during overnight sleep [
56,
57,
86].
Figure 3.
5.1. Clock controlled metabolism during postprandial state
At dawn, shortly after waking up, the postprandial rise of glucose, insulin, and incretins (i.e., GLP-1) after breakfast upregulate the transcription of clock genes expression [
21,
22,
38,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85,
86,
87], improving insulin sensitivity, β-cells responsiveness [
58,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64], GLUT-4 activity, and muscle glucose uptake [
60,
68].
Thus, the early-timed breakfast enhances glycolysis and glycogen synthesis to use glucose as fuel and to replenish glycogen stores [
38,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85]. It also decreases adipose tissue lipolysis, reducing the blood-free fatty acids (FFA) and further facilitating insulin-stimulated glucose uptake during the remaining hours of the active phase [
81,
82].
At the molecular level, it has been documented that early-timed breakfast upregulates CLOCK,
BMAL1, RORα,
SIRT1, AMPK, and
PER2 clock gene expression [
21,
22,
38,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85,
86,
87] and several transcriptional factors such as CH response element binding protein (
ChREBP), that promote the activity of hexokinase (HK) and 6-phosphofructokinase (PFK), key enzymes in skeletal muscle glycolysis, enhancing glucose utilization as the primary fuel during postprandial state [
38,
81,
82,
83].
The early-timed breakfast positively influences the SRIT1-AMPK interaction, which further benefits insulin sensitivity, GLUT-4 translocation, and muscle glucose uptake [
7,
56,
60,
61,
86,
87,
88,
89]
, improving the glucose and insulin postprandial responses in the morning versus evening [
7,
56,
86].
At the same time the increased
CLOCK and PER2 expression activates the transcription of glycogen synthase 2 (GYS2), and hepatic glycogen synthesis [
38,
84,
85]. Therefore, the excess of postprandial glucose is transported to the liver and stored as glycogen, while glycogenolysis is inhibited [
38,
84,
85].
BMAL-1 and RORα also regulate the diurnal variation of postprandial incretin (i.e., GLP-1) secretion. Indeed, the GLP-1 response is higher after meals consumed in the early hours of the day (i.e., early timed breakfast) compared to isocaloric evening meals [
18,
65,
66]
5.2. Influence of high energy breakfast versus high energy dinner on clock controlled postprandial glucose metabolism
Based on several reports showing that the first meal of the day has a powerful resetting effect on the clock gene network [
21,
22,
38,
81,
82,
83,
84,
85,
86,
87], the temporal synchronization between breakfast with light at dawn might be critical for achieving metabolic homeostasis [
19,
21,
22,
88,
89,
90].
Therefore, our group explored in a crossover design whether a high-energy breakfast diet (Bdiet) versus a high-energy dinner diet (Ddiet) improves postprandial and overall glycemia in participants with T2D [
18]. Bdiet consisted of 3 meals; high-energy and CH breakfast (700kcal, with 54% of daily CH), medium-sized lunch (600kcal, with 36% of daily CH), and low in energy and CH dinner (200kcal, with only 10% of daily CH intake). The participants ate breakfast between 8:00-10:00, lunch between 13:00-15:00, and dinner between 18:00-20:00. Ddiet had a reversed plan, including a small breakfast, similar lunch, and a large energy dinner [
18].
There was a significant reduction in overall glucose excursions and hunger scores in Bdiet vs. Ddiet. In parallel, postprandial insulin, C-peptide, intact GLP-1, and total GLP-1 secretion were significantly enhanced in Bdiet [
18].
Figure 4.
The higher and faster insulin response, especially the first phase of insulin secretion, after breakfast, lunch, and dinner in Bdiet compared to Ddiet, suggests an improvement of β-cell responsiveness and β-cell memory [
91,
92]. The increased overall GLP-1 in Bdiet also enhances the insulinotropic effect and may further explain the reduction of overall glycemic excursions in Bdiet [
18,
93]. Other reports also suggest that shifting more energy to the early hours of the day has a metabolic advantage on overall glycemia compared to diet interventions (DI), with more energy assigned to afternoon/evening hours [
4,
5,
6,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
79].
5.3. Clock controlled metabolism during postabsorptive state
The circadian clock also plays a pivotal role during the postabsorptive state. The physiological postabsorptive state is the overnight fast (i.e., 23:00–07:00). It refers to a 6–12 h period from the last meal until the next meal. During postabsorptive state the blood glucose levels are maintained mainly through hepatic glucose production [
38,
45,
81]
After the last meal of the day, at the beginning of the nocturnal sleep, the insulin/glucagon ratio initially increases to stimulate glucose storage as glycogen in the liver [
45]. Following the digestion of this meal, and as the nocturnal fasting progresses, the insulin/glucagon ratio decreases, then the liver shifts into releasing glucose into the blood (via glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis) to maintain a constant concentration of glucose
[45,81,93]. Therefore, during the overnight fast, the glucose metabolism gradually moves from an anabolic into a catabolic state [
38,
45,
81,
93].
During the postabsorptive state, the liver also takes up the free fatty acids (FFAs) released into the circulation from the lipolysis of adipose tissue to provide energy for the liver and generate ketones for use by other tissues [
38,
83,
84]. The liver also breaks down glycogen and amino acids to generate glucose for the brain [
30,
31,
32,
38].
At the molecular level, during the overnight fast, the
BMAL1: CLOCK complex promotes the expression of
REVERBα, RORα, SIRT1, and
PGC-1α in the liver. The glucagon-mediated cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) is upregulated. It stimulates the rhythms of enzymes involved in the postabsorptive nocturnal hepatic glucose production, namely the hepatic glucose 6-phosphatase (HG6-P) in the glycogenolysis pathway and the gluconeogenic enzyme, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) [
56,
57,
86,
94,
95].
Figure 1 and 3
Therefore, the circadian clock coordinates the nocturnal oscillation of hepatic glucose output; the glycogenolysis pathway, which is more active in the first part of the overnight sleep, and the gluconeogenesis, more active during the second part of the overnight fast before waking up [
56,
57,
86,
94,
95]. In addition,
REV-ERBα, RORα, and the
BMAL1 transcription of
PPARα and
PGC-1α in the adipose tissue regulate the nocturnal lipolysis [
52,
55,
96].
Figure 1.
5.4. Clock-controlled glucose metabolism during the transition (switch) from overnight fast to postprandial state
The circadian clock coordinates changes in insulin secretion and action to ensure appropriate substrate switching between tissues to meet metabolic needs in the transition from postabsorptive to postprandial state [
38,
45,
97,
98].
After the early-timed breakfast, the blood glucose levels across the day depend mainly on insulin-mediated muscular glucose uptake [
38,
98]
. This switch to insulin-mediated muscular glucose uptake is crucial to prevent postprandial hyperglycemia after breakfast and the subsequent meals across the day [
38,
45,
50]. Simultaneously, with breakfast consumption, the hepatic clock switches from the resting phase glycogenolysis to postprandial phase glycogenesis [
4,
50].
The increase of
AMPK expression after a nocturnal fast significantly enhances GLUT-4 translocation and muscle glucose uptake once the day's first meal is consumed, ensuring circadian changes of metabolic efficiency, thus improving morning versus evening glucose and postprandial insulin responses [
7,
56,
86].
6. Effect of fasting until noon (extended postabsorptive state) on clock genes mRNA expression and regulation of body weight, glucose metabolism, appetite, and energy expenditure
In the same way like eating at an inappropriate time can cause metabolic disturbances, the lack of meals during the activity phase may negatively affect the metabolism. As mentioned, skipping or delaying breakfast until noon is associated with weight gain, increased risk for T2D, and cardiovascular diseases [
10,
19,
23,
39,
40,
41,
99].
While early-timed breakfast is a known powerful zeitgeber for clock genes in peripheral tissues, the absence or delayed breakfast until noon has the potential to cause asynchrony of clock genes expression and disrupted regulation of metabolic outputs [
10,
15,
20,
22,
44].
6.1. Effect of fasting until noon on clock genes mRNA expression and glucose, insulin, and incretin responses after subsequent meals
Several studies documented that the absence of the day's first meal, equivalent to a delayed breakfast until noon, leads to disrupted and blunted rhythmicity of clock gene expression in animal models [
19,
21,
41] and humans [
22]. It was also shown that fasting until noon causes an increase in the glycemic response and diminished insulin response after a subsequent meal [
22,
44,
45,
100,
101,
102]. Moreover, the delayed breakfast until noon, in the context of TRE modality consisting of fasting until noon and eating window in the afternoon and evening, has been associated with deficient control of body weight [
15,
16,
39,
40,
79,
103], increased overall glycemia [
28,
42,
43], hunger scores and appetite hormones, i.e., ghrelin, and decreased energy expenditure [
10,
15,
25,
104,
105,
106].
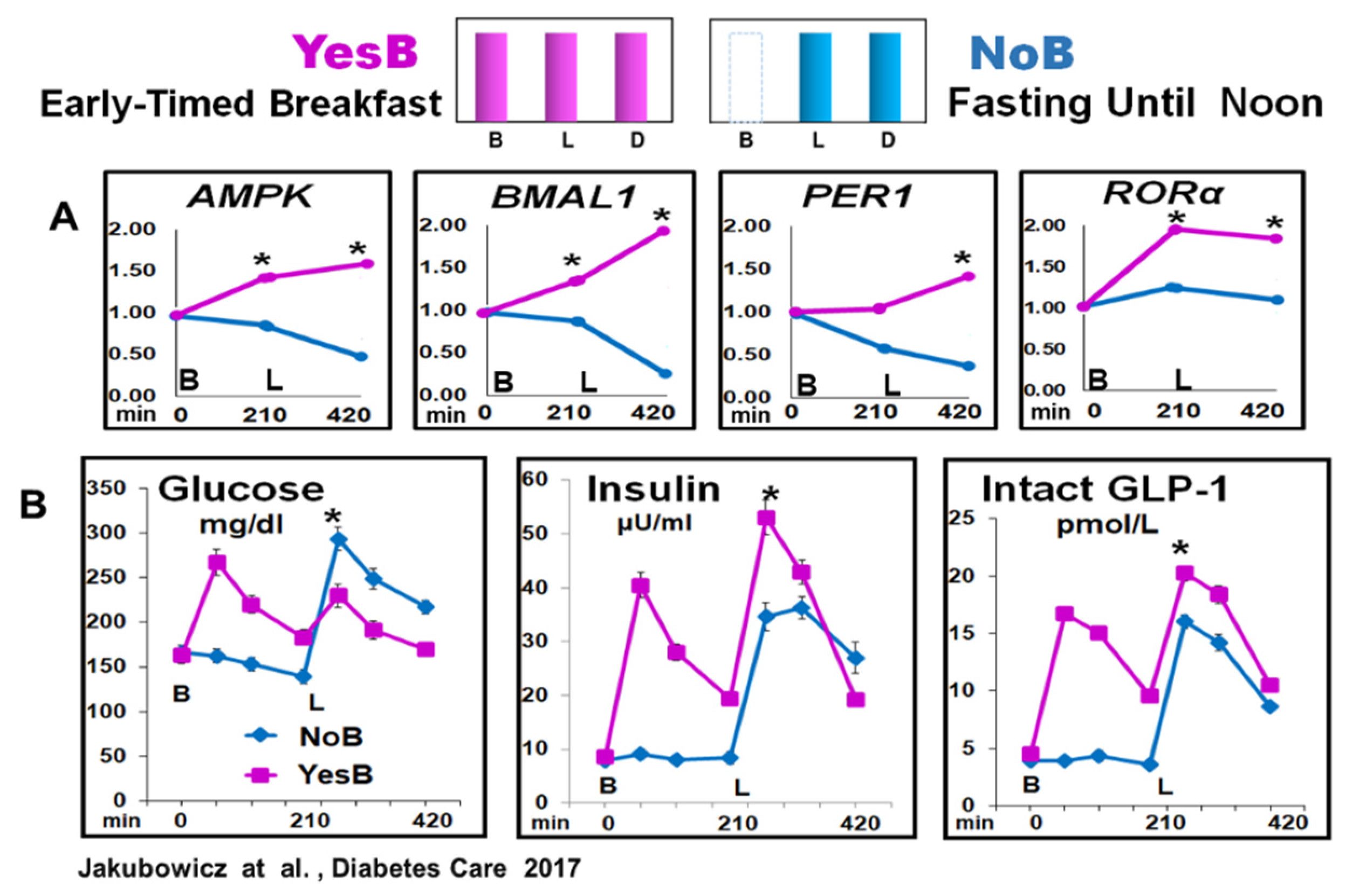
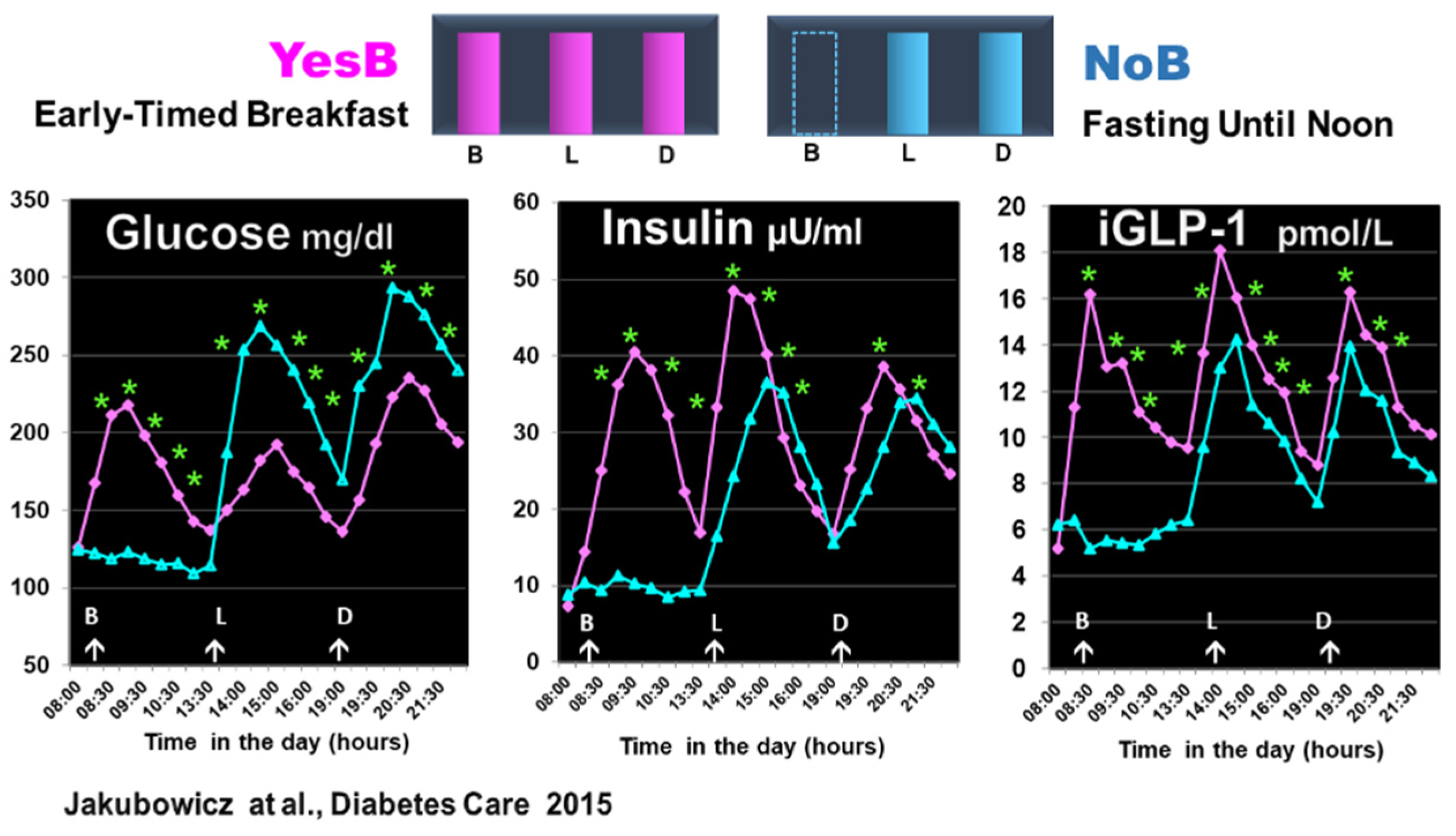
Therefore, in healthy and T2D individuals, we explored the effect of extended postabsorptive fasting until noon versus breakfast consumption on clock gene mRNA expression and glycemic, insulin, and incretin excursions after subsequent isocaloric lunch [
22]. The participants were randomly assigned in crossover to single-test day, either to early breakfast consumption at 8:00, lunch, and dinner (YesB), or to another testing day (NoB) with only lunch and dinner but the omission of breakfast [
22].
The prolonged fasting, ~ 16 hours until noon (21:00 to 12:00), NoB acutely disrupted clock gene expression, and downregulated
AMPK and
BMAL1, PER1, and RORα mRNA expression before and after lunch. It was associated with significantly higher glucose, deficient and delayed insulin, and lower intact GLP-1 responses after lunch vs. YesB. In contrast, cutting the overnight fast at 8:00, with high energy breakfast on YesB day, led to a resetting effect of these key metabolic clock gene mRNA expression, and significant reduction of postprandial glycemia, and enhanced and faster insulin and GLP-1 post-lunch responses [
22].
Figure 5 It has been documented that the upregulation of
AMPK, shown in YesB day, significantly enhances GLUT-4 translocation, muscle glucose uptake, and postprandial insulin response leading to reduced post-meal glycemic excursions [
56]. However, this increased
AMPK expression occurs only upon consuming an early-timed breakfast, ensuring metabolic efficiency and improving glucose and insulin postprandial responses. [
7,
56,
86]. Further,
AMPK is also positively linked to
SIRT1 and its beneficial effects on insulin sensitivity, β-cell proliferation, and viability [
61,
86]. It suggests that the disturbed clock genes expression triggered by the absence of breakfast may be the underlying mechanism of the higher glycemia and deficient insulin, and intact GLP-1 postprandial responses [
22].
In another single-day crossover study in T2D, comparing YesB versus NoB testing days, we have found that the deleterious effects of fasting until noon, i.e., increased glucose and deficient insulin and GLP-1 responses after lunch, were also observed after dinner on the NoB day [
44].
Figure 6.
The omission or lack of the day's first meal was associated with poor β-cell memory and β-cell responsiveness at the next meals [
91,
92]. Further, fasting until noon may induce lysosomal degradation of nascent insulin secretory granules and less β-cell secretory granule biogenesis [
92], underscoring the poor and delayed postprandial insulin response to lunch and dinner on NoB day [
44]. These results align with other studies showing that omission of breakfast or late TRE is associated with increased postprandial and overall glycemia [
15,
100,
101,
102,
103,1628].
6.2. Effect of fasting until noon at the switch from overnight fast to fed state on clock-controlled glucose metabolism and skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown.
Hepatic glucose production (via glycogenolysis) maintains blood glucose levels during the overnight (resting) fast. After waking up at dawn, once an early-timed breakfast is consumed, the hepatic clock switches from resting phase glycogenolysis to postprandial (active phase) glycogenesis [
4,
50]. The omission of early-timed breakfast is a challenge that activates several surviving mechanisms, switching to alternative metabolic pathways in the liver and muscle to ensure glucose availability [
20,
41,
47]. In response to extended fasting after waking up, once glucose levels begin to fall, the rise of glucagon levels leads to the increase of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glucose production, thus restoring blood glucose levels [
20,
38,
41,
47]. Therefore, the hepatic glucose production, which usually occurs during the overnight fast, is shifted to the early hours of the active phase [
20,
41,
47].
At the molecular level, the omission of breakfast affects the clock genes mRNA expression and clock proteins, resulting in blunted and delayed rhythmicity of BMAL1 and REV-ERBα both in the liver and skeletal muscle [
20,
38,
46]. In addition, the prolonged postabsorptive state implicated in the omission of breakfast activates clock gene-mediated gluconeogenesis by increasing transcriptional factors involving glucagon-mediated cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB)- transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2). It reactivates the transcription of gluconeogenic genes and gluconeogenesis during the active phase to further facilitate hepatic glucose production [
20,
47,
107,
108].
The response to the extended morning fast involves massive gluconeogenesis, requiring skeletal muscle protein breakdown to provide glucogenic amino acids (mainly alanine) as a substrate to replace liver glycogen and to supply glucose to the brain [
20,
30,
31,
32,
41,
46,
47,
107]. Although the transportation of alanine to the liver and its conversion to glucose via gluconeogenesis provides an effective mechanism to maintain blood glucose levels during an extended-postabsorptive state, it uses a large protein reserve from skeletal muscle on the day when breakfast is omitted. [
38,
107,
109]. It was shown in mice that the omission of breakfast, besides delaying clock-gene expression in the liver, adipose tissue, and muscle, are associated with a risk for obesity and sarcopenia with significant loss of muscular mass [
41].
Long-term omission or delayed breakfast until noon may increase the risk of losing skeletal muscle mass and sarcopenia in those who frequently skip breakfast [
30,
31,
32]. Therefore, early breakfast consumption aligned with the circadian transition from a nocturnal fasting state to a fed state might be critical for the appropriate regulation of glucose metabolism while preserving muscle mass
6.3. Influence of fasting until noon on circadian clock-controlled regulation of body weight, appetite, and energy expenditure
Dietary interventions (DI) for weight loss typically focus on the magnitude of the energy deficit. However, growing evidence shows that the timing of fasting and food intake can influence the metabolic response [
10,
13,
14,
15,
16]. The omission of or delayed breakfast until noon is associated with weight gain, which frequently cannot be explained by differences in reported caloric intake [
19,
23,
39,
40].
Previous studies have shown that an early-timed high-energy breakfast was associated with more significant weight loss than a high-energy dinner [
10,
15,
17,
103,
105,
106]. Likewise, the modality of early TRE, consisting of early-timed breakfast and fasting in the late hours of the day, is more efficient for achieving weight loss than fasting until noon and eating later in the day [
15,
79].
Fasting in the morning is apparently less beneficial for weight loss than fasting in the evening [
10,
15,
16,
79,
103]. Indeed, breakfast omission has been proposed as a key modifiable risk factor for obesity [
103,
104,
105,
106]. The underlying mechanism linking breakfast omission with obesity and less efficient weight loss is unknown. However, higher energy expenditure and diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT) in the morning versus evening may play a role in the beneficial effect of early-timed breakfast on weight loss outcomes [
10,
34,
35,
36,
37].
The endogenous circadian clock regulates energy expenditure (EE), and in humans, EE is at its lowest levels during the biological night. The respiratory quotient (RQ), reflecting macronutrient utilization, also varies by circadian phase and is highest in the early morning [
80]. Several studies have documented that diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT ) is higher in the morning than in the evening [
34,
35,
36,
37]. Hence, isocaloric meals lead to a 2.5-fold higher DIT in the morning than in the evening. Therefore, consuming a large dinner meal rather than an extensive breakfast may promote obesity. [
36]. However, it remains unclear whether a diet intervention (DI) with a delayed breakfast until noon influences diet-induced thermogenesis and 24-h energy expenditure [
105,
106].
Therefore, a recent randomized crossover study was conducted to determine whether fasting until noon and late evening meals are associated with decreased energy expenditure and changes in appetite and whether molecular pathways in adipose tissues are involved [
25]. The participants were assigned in a crossover design to two isocaloric diet interventions (DI), with three meals but different meal timing. In the “early meal” DI period, participants ate early breakfast, lunch, and dinner at about 09:00, 13:00, and 17:00. In the “late-meal” DI, the participants skipped breakfast, began eating lunch at 13:00, ate dinner at 17:00 and added a late supper at 21:00, to compensate for the skipped breakfast [
25]. The study showed that fasting until noon and late-meal DI was associated with significantly increased hunger VAS scores, decreased leptin, and increased ghrelin levels [
25]. These findings align with previous reports showing that consuming a morning-loaded diet significantly lowers hunger scores [
13,
17,
18,
29,
33].
Adipose tissue gene expression analyses during the fasting until noon DI period showed alterations in lipid metabolism pathways, e.g., TGF-β signaling and modulation of receptor tyrosine kinases, in a direction consistent with increased adipogenesis and decreased lipolysis [
25].
Further, fasting until 13:00 in the late-meal DI protocol led to a significant decrease in energy expenditure compared to the early-meal DI with early-timed breakfast [
25]. Although skipping breakfast in the late-meal DI protocol was associated with decreased energy expenditure, we cannot rule out that this effect was also related to the late-timed supper at 21:00. However, this seems unlikely since the early-timed breakfast triggers a greater increase in DIT compared to the evening meal [
34,
35,
36,
37].
The decreased energy expenditure in the fasting until noon DI schedule suggests that skipping breakfast may increase the risk of obesity and reduce the efficacy of DIs aimed at weight loss [
11,
12,
19,
23,
25,
39,
40,
103,
104,
105,
106]. The early-timed high-energy breakfast may assist in weight loss DI through appetite suppression [
13,
17,
18,
29,
33]. Further, it provides a mechanistic explanation of greater efficiency of the weight loss outcomes from the DI with more energy shifted to the early hours of the day [
10,
11,
12,
17,
18,
29,
33,
110].
7. Conclusions
The circadian clock controls the diurnal variation of most metabolic processes through dynamic bidirectional synchronization between fasting /feeding cycles and light input. It regulates the glucose and other metabolic processes during fasted and fed states and during the switch from an overnight fast to a postprandial fed state.
The early-timed breakfast at dawn shortly after waking up has a powerful resetting effect on the clock gene network and is crucial for transitioning from an overnight fast to a fed state. Glucose, insulin, GLP-1, and other postprandial signals rising after early-timed breakfast upregulate clock genes and transcription factors, improving glucose and other metabolic processes throughout the remainder of the active phase. In contrast, postponing the first meal of the day creates a metabolic challenge at the hour when the clock gene network is anticipating early-timed meal consumption
In this review, we have shown that the misalignment of the feeding fasting cycle, and particularly the lack of early-timed breakfast, leads to deleterious effects on clock gene expression, disrupted regulation of body weight, increased overall glycemia and postprandial glucose, along with deficient insulin and incretin responses after subsequent meals. Skipping breakfast activates skeletal muscle protein breakdown as part of a survival mechanism to provide glucogenic amino acids to the liver. Moreover, the delayed breakfast until noon increases hunger scores and even may cause a lowering effect on energy expenditure. It may further increase the risk of obesity and reduce the efficacy of DI aimed at weight loss.
Although many more studies are needed to explore the underlying mechanism of these deleterious effects of breakfast omission, it seems that shifting caloric intake toward the beginning of the active phase (i.e., early-timed breakfast) may confer a metabolic advantage, especially in the context of weight loss and overall glycemia, by coordinating food intake to coincide with optimal circadian timing.
Author Contribution “Conceptualization, D.J.; methodology, D.J. and R.R.; software, R.R.; validation, D.J., R.R. and O.T.; formal analysis, D.J. and R.R.; investigation, D.J., R.R. and O.T.; resources, D.J. and R.R.; data curation, D.J. and O.T.; writing—original draft preparation, D.J. and R.R.; writing—review and editing, D.J. and R.R.; visualization, R.R..; supervision, O.T. and R.R.; project administration, O.T.; funding acquisition, O.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.” All author: Equal effort and contribution to this manuscript
Funding
No funding for this review
Institutional Review Board Statement
N/A
Informed Consent Statement
N/A
Data Availability Statement
N/A
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest
References
- Cox, K.H.; Takahashi, J.S. Circadian clock genes and the transcriptional architecture of the clock mechanism. Journal of molecular endocrinology. 2019, 63, R93–R102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwasser, A.M.; Turek, F.W. Neurobiology of Circadian Rhythm Regulation. Sleep medicine clinics. 2015, 10, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koronowski, K.B.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Communicating clocks shape circadian homeostasis. Science (New York, N.Y.). 2021, 371, eabd0951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickel, L.; Sung, H.K. Feeding Rhythms and the Circadian Regulation of Metabolism. Frontiers in nutrition. 2020, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddick-Collins, L.C.; Johnston, J.D.; Morgan, P.J.; Johnstone, A.M. The Big Breakfast Study: Chrono-nutrition influence on energy expenditure and bodyweight. Nutr. Bull. 2018, 43, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlot, A.; Hutt, F.; Sabatier, E.; Zoll, J. Beneficial Effects of Early Time-Restricted Feeding on Metabolic Diseases: Importance of Aligning Food Habits with the Circadian Clock. Nutrients, 2021, 13, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, H.; Asher, G. Crosstalk between metabolism and circadian clocks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hutchison, A.T.; Heilbronn, L.K. Carbohydrate intake and circadian synchronicity in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021, 24, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoogian, E.N.; Chow, L.S.; Taub, P.R.; Laferrère, B.; Panda, S. Time-restricted eating for the prevention and management of metabolic diseases. Endocr Rev. 2021, 22, bnab027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton DJ,; Mode, W. J.A.; Slater, T. Optimising intermittent fasting: evaluating the behavioural and metabolic effects of extended morning and evening fasting. Nutr Bull. 2020, 45, 444–455.
- Poggiogalle, E.; Jamshed, H.; Peterson, C.M. Circadian regulation of glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism in humans. Metabolism. 2018, 84, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E.; Beyl, R.A.; Poggiogalle, E.; Hsia, D.S.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Reduces Appetite and Increases Fat Oxidation But Does Not Affect Energy Expenditure in Humans. Obesity. 2019, 27, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddick-Collins, L.C.; Morgan, P.J.; Fyfe, C.L.; Filipe, J.A.N.; Horgan, G.W.; Westerterp, K.R.; Johnston, J.D.; Johnstone, A.M. Timing of daily calorie loading affects appetite and hunger responses without changes in energy metabolism in healthy subjects with obesity. Cell metabolism. 2020, 34, 1472–1485.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.P.; Ellacott, K.L.J.; Chen, H.; McGuinness, O.P.; Johnson, C.H. Time-optimized feeding is beneficial without enforced fasting. Open biology. 2021, 11, 210183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, O.; Martin, B.; Stote, K.S.; Golden, E.; Maudsley, S.; Najjar, S.S.; Ferrucci, L.; Ingram, D.K.; Longo, D.L.; Rumpler, W.V.; Baer, D.J.; Egan, J.; Mattson, M.P. Impact of reduced meal frequency without caloric restriction on glucose regulation in healthy, normal-weight middle-aged men and women. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Barnea, M.; Wainstein, J.; Froy, O. High caloric intake at breakfast vs. dinner differentially influences weight loss of overweight and obese women. Obesity. 2013, 21, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Wainstein, J.; Ahrén, B.; Bar-Dayan, Y.; Landau, Z.; Rabinovitz, H.R.; Froy, O. High-energy breakfast with low-energy dinner decreases overall daily hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomised clinical trial. Diabetologia. 2015, 58, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Hanzawa, F.; Kim, D.; Sun, S.; Laurent, T.; Umeki, M.; Ikeda, S.; Mochizuki, S.; Oda, H. Delayed first active-phase meal, a breakfast skipping model, led to increased body weight and shifted the circadian oscillation of the hepatic clock and lipid metabolism-related genes in rats fed a high-fat diet. PLoS ONE. 2018, 13, e0206669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinouchi, K.; Magnan, C.; Ceglia, N.; Liu, Y.; Cervantes, M.; Pastore, N.; Huynh, T.; Ballabio, A.; Baldi, P.; Masri, S.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Fasting Imparts a Switch to Alternative Daily Pathways in Liver and Muscle. Cell reports. 2018, 25, 3299–3314.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Sun, L.; Zhuge, F.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, R.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Kato, H.; Fu, Z. Differential roles of breakfast and supper in rats of a daily three-meal schedule upon circadian regulation and physiology. Chronobiol. Int. 2011, 28, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Wainstein, J.; Landau, Z.; Raz, I.; Ahren, B.; Chapnik, N.; Ganz, T.; Menaged, M.; Barnea, M.; Bar-Dayan, Y.; et al. Influences of Breakfast on Clock Gene Expression and Postprandial Glycemia in Healthy Individuals and Individuals With Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care. 2017, 40, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, R.; Tomi, R.; Shinzawa, M.; Yoshimura, R.; Ozaki, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Ide, S.; Nagatomo, I.; Nishida, M.; Yamauchi-Takihara, K.; Kudo, T.; Moriyama, T. Associations of Skipping Breakfast, Lunch, and Dinner with Weight Gain and Overweight/Obesity in University Students: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshed, H.; Beyl, R.A.; Manna, D.L.D.; Yang, E.S.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early time-restricted feeding improves 24-hour glucose levels and affects markers of the circadian clock, aging, and autophagy in humans. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujović, N.; Piron, M.J.; Qian, J.; Chellappa, S.L.; Nedeltcheva, A.; Barr, D.; Heng, S.W.; Kerlin, K.; Srivastav, S.; Wang, W.; Shoji, B.; Garaulet, M.; Brady, M.J.; Scheer, F.A.J.L. Late isocaloric eating increases hunger, decreases energy expenditure, and modifies metabolic pathways in adults with overweight and obesity. Cell metabolism. 2022, 34, 1486–1498.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Furutani, A.; Sasaki, H.; Takahashi, M.; Shibata, S. Effect of a High Protein Diet at Breakfast on Postprandial Glucose Level at Dinner Time in Healthy Adults. Nutrients. 2022, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, F.; Ogata, H.; Omi, N.; Nagasaka, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hibi, M.; Tokuyama, K. Effect of breakfast skipping on diurnal variation of energy metabolism and blood glucose. Obesity research & clinical practice. 2014, 8, e201–e298. [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, H.; Hatamoto, Y.; Goto, Y.; Tajiri, E.; Yoshimura, E.; Kiyono, K.; Uehara, Y.; Kawanaka, K.; Omi, N.; Tanaka, H. Association between breakfast skipping and postprandial hyperglycaemia after lunch in healthy young individuals. The British journal of nutrition 2019, 122, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Landau, Z.; Tsameret, S.; Wainstein, J.; Raz, I.; Ahren, B.; Chapnik, N.; Barnea, M.; Ganz, T.; Menaged, M.; Mor, N.; Bar-Dayan, Y.; Froy, O. Reduction in Glycated Hemoglobin and Daily Insulin Dose Alongside Circadian Clock Upregulation in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Consuming a Three-Meal Diet: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care. 2019, 42, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.; Moore, D.R. A Muscle-Centric Perspective on Intermittent Fasting: A Suboptimal Dietary Strategy for Supporting Muscle Protein Remodeling and Muscle Mass. Frontiers in nutrition. 2021, 8, 640621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, S.; Kim, H.K.; Hirooka, R.; Tanaka, M.; Shimoda, T.; Chijiki, H.; Kojima, S.; Sasaki, K.; Takahashi, K.; Makino, S.; Takizawa, M.; Takahashi, M.; Tahara, Y.; Shimba, S.; Shinohara, K.; Shibata, S. Distribution of dietary protein intake in daily meals influences skeletal muscle hypertrophy via the muscle clock. Cell reports. 2021, 36, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamerow, M.M.; Mettler, J.A.; English, K.L.; Casperson, S.L.; Arentson-Lantz, E.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Layman, D.K.; Paddon-Jones, D. Dietary protein distribution positively influences 24-h muscle protein synthesis in healthy adults. The Journal of nutrition. 2014, 144, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Froy, O.; Wainstein, J.; Boaz, M. Meal timing and composition influence ghrelin levels, appetite scores and weight loss maintenance in overweight and obese adults. Steroids 2012, 77, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Fadda, M.; Castiglione, A.; Ciccone, G.; De Francesco, A.; Fedele, D.; Guggino, A.; Parasiliti Caprino, M.; Ferrara, S.; Vezio Boggio, M.; Mengozzi, G.; Ghigo, E.; Maccario, M.; Broglio, F. Is the timing of caloric intake associated with variation in diet-induced thermogenesis and in the metabolic pattern? A randomized cross-over study. International journal of obesity. 2015, 39(12), 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.J.; Garcia, J.I.; Myers, S.; Yang, J.N.; Trienekens, N.; : Scheer, F.A. The human circadian system has a dominating role in causing the morning/evening difference in diet-induced thermogenesis. Obesity. 2015, 23, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, J.; Herzog, N.; Janka, S.; Baumann, T.; Kistenmacher, A.; Oltmanns, K.M. Twice as High Diet-Induced Thermogenesis After Breakfast vs Dinner On High-Calorie as Well as Low-Calorie Meals. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2020, 105, dgz311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romon, M.; Edme, J.L.; Boulenguez, C.; Lescroart, J.L.; Frimat, P. Circadian variation of diet-induced thermogenesis. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 1993, 57, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bideyan, L.; Nagari, R.; Tontonoz, P. Hepatic transcriptional responses to fasting and feeding. Genes & development 2021, 35, 635–657. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Q.; Pu, Y.; Guo, M.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, W.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y. Skipping breakfast is associated with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity research & clinical practice. 2020, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Otaki, N.; Obayashi, K.; Saeki, K.; Kitagawa, M.; Tone, N.; Kurumatani, N. Relationship between Breakfast Skipping and Obesity among Elderly: Cross-Sectional Analysis of the HEIJO-KYO Study. The journal of nutrition, health & aging. 2017, 21, 501–504. [Google Scholar]
- Kiriyama, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kim, D.; Sun, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Oda, H. Skipping breakfast regimen induces an increase in body weight and a decrease in muscle weight with a shifted circadian rhythm in peripheral tissues of mice. The British journal of nutrition. 2022, 128, 2308–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimitphong, H.; Siwasaranond, N.; Saetung, S.; Thakkinstian, A.; Ongphiphadhanakul, B.; Reutrakul, S. The relationship among breakfast time, morningness–eveningness preference and body mass index in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reutrakul, S.; Hood, M.M.; Crowley, S.J.; Morgan, M.K.; Teodori, M.; Knutson, K.L. The relationship between breakfast skipping, chronotype, and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowicz, D.; Wainstein, J.; Ahren, B.; Landau, Z.; Bar-Dayan, Y.; Froy, O. Fasting Until Noon Triggers Increased Postprandial Hyperglycemia and Impaired Insulin Response After Lunch and Dinner in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Care. 2015, 38, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriadis, G.D.; Maratou, E.; Kountouri, A.; Board, M.; Lambadiari, V. Regulation of Postabsorptive and Postprandial Glucose Metabolism by Insulin-Dependent and Insulin-Independent Mechanisms: An Integrative Approach. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, B.A.; Wen, Y.; Riley, L.A.; Zhang, X.; England, J.H.; Harfmann, B.D.; Schroder, E.A.; Esser, K.A. The endogenous molecular clock orchestrates the temporal separation of substrate metabolism in skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle. 2015, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erion, D.M.; Kotas, M.E.; McGlashon, J.; Yonemitsu, S.; Hsiao, J.J.; Nagai, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Murray, S.F.; Bhanot, S.; Cline, G.W.; Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I.; Gillum, M.P. cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB)-regulated transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2) promotes glucagon clearance and hepatic amino acid catabolism to regulate glucose homeostasis. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2013, 288, 16167–16176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, E.J.; Woolf, M.F.; Kang, H.; Woolf, P.; Hurst, W.; Camacho, F.; Vielhaber, E.L.; Giovanni, A.; Virshup, D.M. Control of mammalian circadian rhythm by CKIepsilon-regulated proteasome-mediated PER2 degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Tahara, Y.; Tsubosaka, M.; Fukazawa, M.; Ozaki, M.; Iwakami, T.; Nakaoka, T.; Shibata, S. Chronotype and social jetlag influence human circadian clock gene expression. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronowski, K.B.; Kinouchi, K.; Welz, P.S.; Smith, J.G.; Zinna, V.M.; Shi, J.; Samad, M.; Chen, S.; Magnan, C.N.; Kinchen, J.M.; Li, W.; Baldi, P.; Benitah, S. A.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Defining the Independence of the Liver Circadian Clock. Cell. 2019, 177, 1448–1462.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaumond, F.; Dardente, H.; Giguère, V.; Cermakian, N. Differential control of Bmal1 circadian transcription by REV-ERB and ROR nuclear receptors. Journal of biological rhythms. 2005 20, 391–403. [CrossRef]
- Preitner, N.; Damiola, F.; Lopez-Molina, L.; Zakany, J.; Duboule, D.; Albrecht, U.; Schibler, U. The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell. 2002, 110, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, G. PPARs Integrate the Mammalian Clock and Energy Metabolism. PPAR research. 2014, 653017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Latre, A.; Eckel-Mahan, K. Interdependence of nutrient metabolism and the circadian clock system: Importance for metabolic health. Molecular metabolism, 2016, 5, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froy, O.; Garaulet, M. The circadian clock in white and brown adipose tissue: Mechanistic, endocrine, and clinical aspects. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.E.; Liu, Y.; Dentin, R.; Pongsawakul, P.Y.; Liu, A.C.; Hirota, T.; Nusinow, D.A.; Sun, X.; Landais, S.; Kodama, Y.; Brenner, D.A.; Montminy, M.; Kay, S.A. Cryptochrome mediates circadian regulation of cAMP signaling and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Joshi, N.; Miles, J.; Carter, R.E.; Rizza, R.A.; Basu, R. Paradigm shifts in nocturnal glucose control in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3801–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, A.; Man, C.D.; Nandy, D.K.; Levine, J.A.; Bharucha, A.E.; Rizza, R.A.; Basu, R.; Carter, R.E.; Cobelli, C.; Kudva, Y.C.; et al. Diurnal pattern to insulin secretion and insulin action in healthy individuals. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistlberger, R.E. Neurobiology of food anticipatory circadian rhythms. Physiology & behavior. 2011, 104, 535–545. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, F.; Ge, X.; Yan, T.; Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhai, Q. SIRT1 Improves Insulin Sensitivity under Insulin-Resistant Conditions by Repressing PTP1B. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.V.; Bensellam, M.; Wauters, E.; Rees, M.; Giry-Laterriere, M.; Mawson, A.; Ly, L.Q.; Biankin, A.V.; Wu, J.; Laybutt, D.R.; Rooman, I. Pancreas-specific Sirt1-deficiency in mice compromises β-cell function without development of hyperglycemia. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, e0128012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, J.; Imai, S.I. A clock ticks in pancreatic β cells. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadacca, L.A.; Lamia, K.A.; DeLemos, A.S.; Blum, B.; Weitz, C.J. An intrinsic circadian clock of the pancreas is required for normal insulin release and glucose homeostasis in mice. Diabetologia. 2011, 54, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Su, Z. Identification of insulin as a novel retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor α target gene. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Lozano, M.; Mingomataj, E.L.; Wu, W.K.; Ridout, S.A.; Brubaker, P.L. Circadian secretion of the intestinal hormone GLP-1 by the rodent L cell. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3674–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancolin, A.D.; Martchenko, A.; Mitova, E.; Gurges, P.; Michalchyshyn, E.; Chalmers, J.A.; Doria, A.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Adriaenssens, A.E.; Reimann, F.; et al. The core clock gene, Bmal1, and its downstream target, the SNARE regulatory protein secretagogin, are necessary for circadian secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1. Mol. Metab. 2020, 31, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrens, S.M.T.; Christou, S.; Isherwood, C.; Middleton, B.; Gibbs, M.A.; Archer, S.N.; Skene, D.J.; Johnston, J.D. Meal Timing Regulates the Human Circadian System. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1768–1775.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyar, K.A.; Ciciliot, S.; Wright, L.E.; Biensø, R.S.; Tagliazucchi, G.M.; Patel, V.R.; Forcato, M.; Paz, M.I.P.; Gudiksen, A.; Solagna, F.; et al. Muscle insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism are controlled by the intrinsic muscle clock. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Parr, E.B.; Devlin, B.L.; Hawley, J.A.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Human metabolomics reveal daily variations under nutritional challenges specific to serum and skeletal muscle. Mol Metab. 2018, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Hilton, M.F.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Shea, S.A. Adverse metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of circadian misalignment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnocchi, D.; Bruscalupi, G. Circadian Rhythms and Hormonal Homeostasis: Pathophysiological Implications. Biology. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, K.L.; Berry, R.; Frank, S.J.; Young, M. E. Circadian clock control of endocrine factors. Nature reviews. Endocrinology 2014, 10, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skene, D.J.; Arendt, J. Human circadian rhythms: physiological and therapeutic relevance of light and melatonin. Annals of clinical biochemistry. 2006, 43(Pt 5), 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, A.; Peng, C.K.; Chan, J.L.; Mietus, J.E.; Goldberger, A.L.; Mantzoros, C.S. Diurnal and ultradian dynamics of serum adiponectin in healthy men: comparison with leptin, circulating soluble leptin receptor, and cortisol patterns. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism. 2003, 88, 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in the integrated regulation of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. International journal of obesity. 2008, 32 (Suppl 7), S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. International journal of molecular sciences. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHill, A.W.; Phillips, A.J.; Czeisler, C.A.; Keating, L.; Yee, K.; Barger, L.K.; Garaulet, M.; Scheer, F.A.; Klerman, E.B. Later circadian timing of food intake is associated with increased body fat. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2017, 106, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, L.M.; Shi, J.W.; Hampton, S.M.; Frost, G. Effect of meal timing and glycaemic index on glucose control and insulin secretion in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cienfuegos, S.; Gabel, K.; Kalam, F.; Ezpeleta, M.; Wiseman, E.; Pavlou, V.; Lin, S.; Oliveira, M.L.; Varady, K.A. Effects of 4- and 6-h time restricted feeding on weight and cardiometabolic health: a randomized controlled trial in adults with obesity. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 366–378.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitting, K.M.; Vujovic, N.; Yuan, R. K.; Isherwood, C. M.; Medina, J.E.; Wang, W.; Buxton, O.M.; Williams, J.S.; Czeisler, C. A.; Duffy, J.F. Human Resting Energy Expenditure Varies with Circadian Phase. Current biology: CB. 2018, 28, 3685–3690.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, G.; Mitrou, P.; Lambadiari, V.; Maratou, E.; Raptis, S.A. Insulin effects in muscle and adipose tissue. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2011, 93 Suppl 1, S52–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, F.; Fielding, B.; Ilic, V.; Macdonald, I.A.; Summers, L.; Frayn, K.N. Adipose tissue blood flow response is related to aspects of insulin sensitivity. Diabetes. 2002, 51, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, L. Energy metabolism in the liver. Compr Physiol. 2014, 4, 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, R.; Oishi, K.; Ishida, N. CLOCK regulates circadian rhythms of hepatic glycogen synthesis through transcriptional activation of Gys2. J Biol Chem. 2010, 285, 22114–22121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zani, F.; Breasson, L.; Becattini, B.; Vukolic, A.; Montani, J.-P.; Albrecht, U.; Provenzani, A.; Ripperger, J.A.; Solinas, G.
PER2 promotes glucose storage to liver glycogen during feeding and acute fasting by inducing Gys2 PTG and G L expression
. Mol Metab 2013, 2, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G.; Ross, F.A.; Hawley, S.A. AMPK: A nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.D.; Lamia, K.A. AMPK at the crossroads of circadian clocks and metabolism. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 366, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wefers, J.; Van Moorsel, D.; Hansen, J.; Connell, N.J.; Havekes, B.; Hoeks, J.; Van Marken Lichtenbelt, W.D.; Duez, H.; Phielix, E.; Kalsbeek, A.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Hesselink, M.K.C.; Kersten, S.; Staels, B.; Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Schrauwen, P. Circadian misalignment induces fatty acid metabolism gene profiles and compromises insulin sensitivity in human skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018, 115, 7789–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, C.; Vetter, C.; Devore, E.E.; Ramin, C.A.; Speizer, F.E.; Willett, W.C.; Schernhammer, E.S. Mismatch of sleep and work timing and risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015, 38, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, H.; Genzer, Y.; Cohen, R.; Chapnik, N.; Madar, Z.; Froy, O. Timed high-fat diet resets circadian metabolism and prevents obesity. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagn Korsgaard, T.; Colding-Jørgensen, M. Time-dependent mechanisms in β-cells glucose sensing. J. Biol. Phys. 2006, 32, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goginashvili, A.; Zhang, Z.; Erbs, E.; Spiegelhalter, C.; Kessler, P.; Mihlan, M.; Pasquier, A.; Krupina, K.; Schieber, N.; Cinque, L.; Morvan, J.; Sumara, I.; Schwab, Y.; Settembre, C.; Ricci, R. Insulin granules. Insulin secretory granules control autophagy in pancreatic β cells. Science 2015, 347, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrington, A. Control of glucose uptake and release by the liver in vivo. Diabetes. 1999, 48, 1198–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, A.; Arita, E.; Matsumoto, E.; Oohira, A.; Iwase, K.; Hiwasa, T.; Yokote, K.; Shibata, S.; Takiguchi, M. Systemic oscillator-driven and nutrient-responsive hormonal regulation of daily expression rhythms for gluconeogenic enzyme genes in the mouse liver. Chronobiol. Int. 2019, 36, 591–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Mendoza, M.; Rivera-Zavala, J.B.; Díaz-Muñoz, M. Daytime restricted feeding modifies the daily variations of liver gluconeogenesis: Adaptations in biochemical and endocrine regulators. Chronobiol. Int. 2014, 31, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvers, D.J.; Jongejan, A.; Atiqi, S.; Vreijling, J.P.; Limonard, E.J.; Endert, E.; Baas, F.; Moerland, P.D.; Fliers, E.; Kalsbeek, A.; Kalsbeek, A.; Bisschop, P.H. Diurnal rhythms in the white adipose tissue transcriptome are disturbed in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes compared with lean control individuals. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menting, J.G.; Whittaker, J.; Margetts, M.B.; Whittaker, L.J.; Kong, G.K.; Smith, B.J.; Watson, C.J.; Zakova, L.; Kletvikova, E.; Jiracek, J.; et al. How insulin engages its primary binding site on the insulin receptor. Nature 2013, 493, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullmann, S.; Kleinridders, A.; Small, D.M.; Fritsche, A.; Haring, H.U.; Preissl, H.; Heni, M. Central nervous pathways of insulin action in the control of metabolism and food intake. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Onge, M.P.; Ard, J.; Baskin, M.L.; Chiuve, S.E.; Johnson, H.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.; Varady, K. ; American Heart Association Obesity Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young; Council on Clinical Cardiology; and Stroke Council. Meal Timing and Frequency: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017, 135, e96–e121. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Tura, A.; Mari, A.; Ko, S.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Song, K.H.; Yoon, K.H.; Lee, K.W.; Ahn, Y.B. Potentiation of the early-phase insulin response by a prior meal contributes to the second-meal phenomenon in type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol.—Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, A.; Gerrard, J.; Taylor, R. The second-meal phenomenon in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, F.; Ogata, H.; Omi, N.; Nagasaka, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hibi, M.; Tokuyama, K. Effect of breakfast skipping on diurnal variation of energy metabolism and blood glucose. Obesity research & clinical practice. 2014, 8, e201–e298. [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka, M.; Hatamoto, Y.; Tajiri, E.; Matsumoto, N.; Tanaka, S.; Yoshimura EHatamoto, Y.; Tajiri, E.; Matsumoto, N.; Tanaka, S.; Yoshimura, E. An Earlier First Meal Timing Associates with Weight Loss Effectiveness in A 12-Week Weight Loss Support Program. Nutrients. 2022, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, J.; Takahashi, J.S. Circadian integration of metabolism and energetics. Science (New York, N.Y.). 2010, 330, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.C.; Hopkins, C.M.; Ruggieri, M.; Spaeth, A.M.; Ahima, R.S.; Zhang, Z.; Taylor, D.M.; and Goel, N. Prolonged, controlled daytime versus delayed eating impacts weight and metabolism. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 650–657.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, K.P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Buchowski, M.; Hughey, J.J.; Chen, H.; Powers, J.; Page, T.; and Johnson, C.H. Eating breakfast and avoiding late-evening snacking sustains lipid oxidation. PLoS Biol 2020, 18, e3000622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felig, P.; Pozefsky, T.; Marliss, E.; Cahill, G.F., Jr. Alanine: key role in gluconeogenesis. Science (New York, N.Y.). 1970, 167, 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altarejos, J.Y.; Montminy, M. CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, R. The Effect of Fasting on Human Metabolism and Psychological Health. Disease markers. 2022, 5653739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, S.; Longo, V.D. Breakfast keeps hunger in check. Cell metabolism. 2022, 34, 1420–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).