Submitted:
25 February 2023
Posted:
27 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Eye tracking applied to road safety
1.2. The visual behavior of road users
2. Method
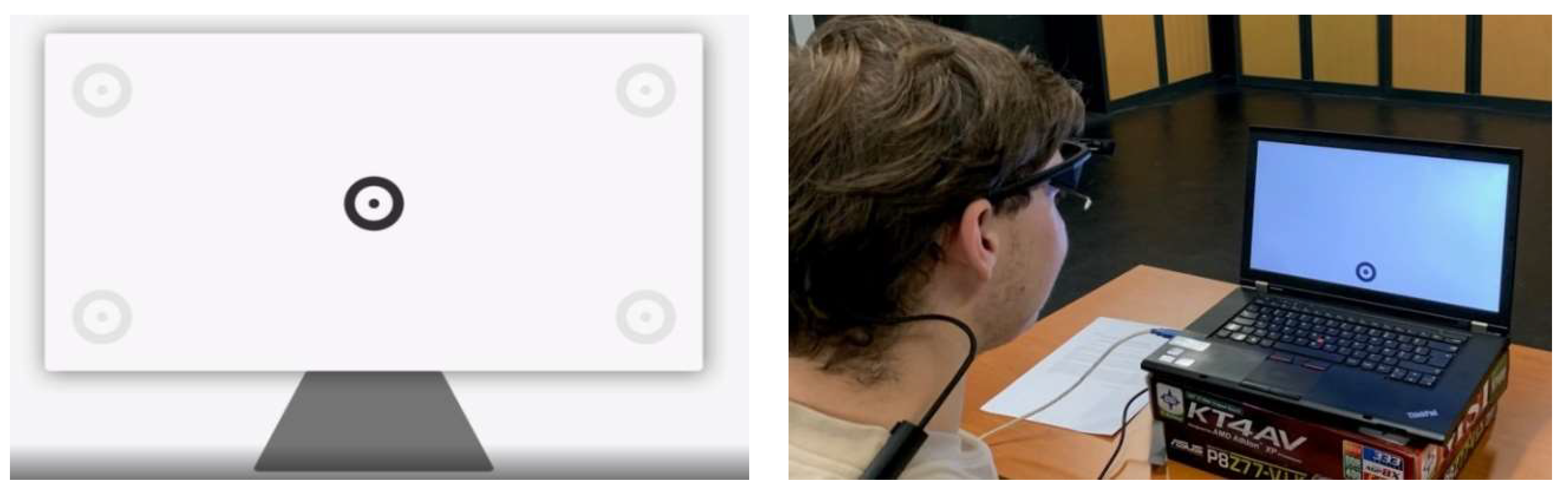
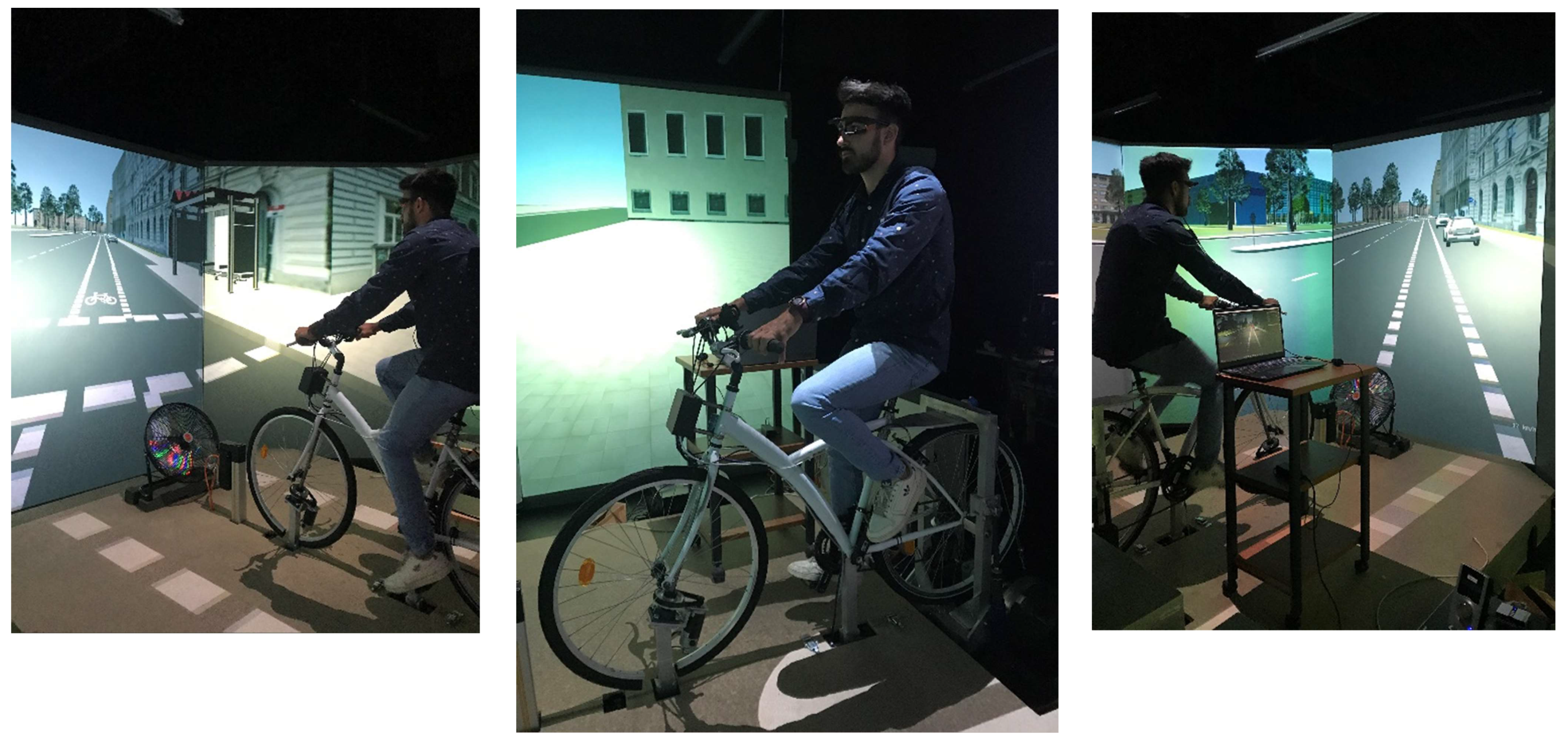
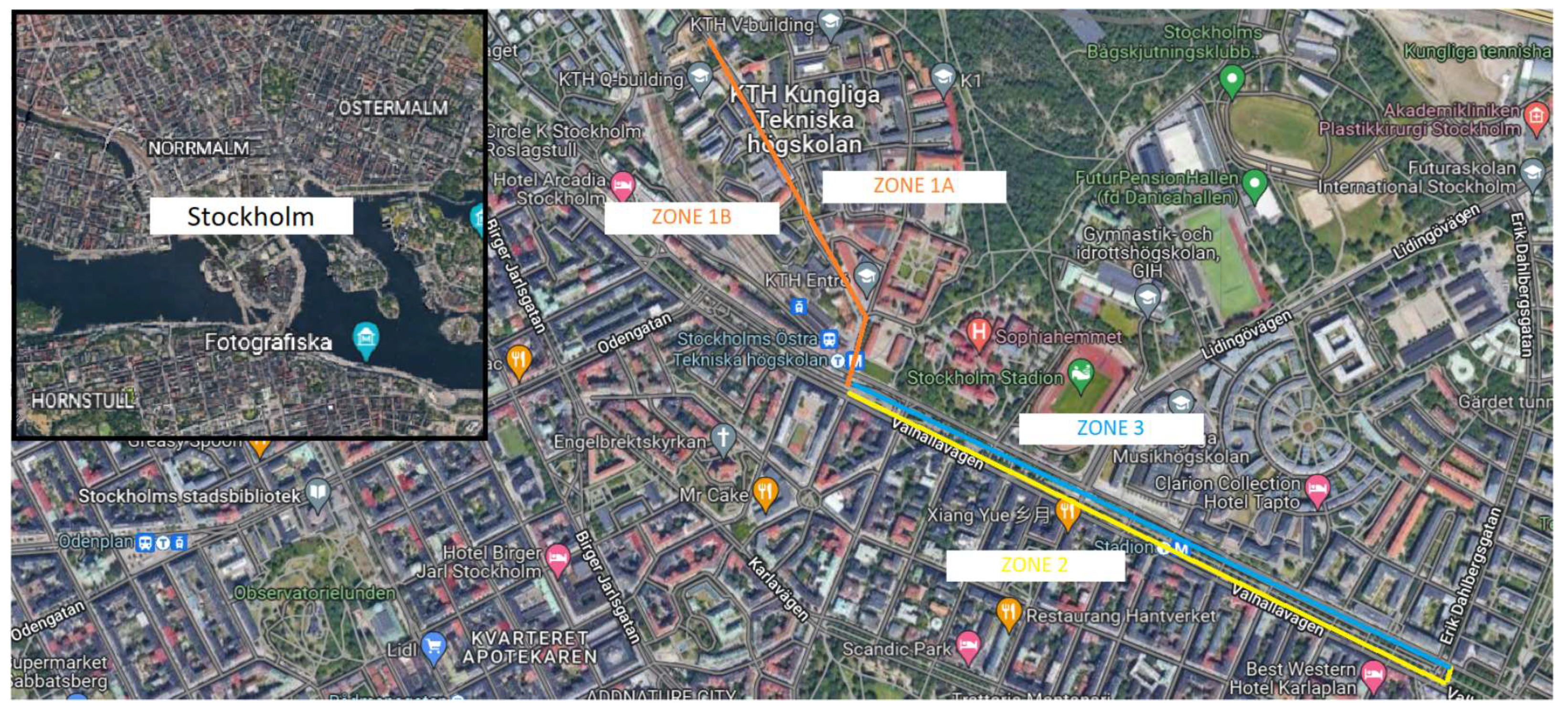
2.1. Experimental Procedure
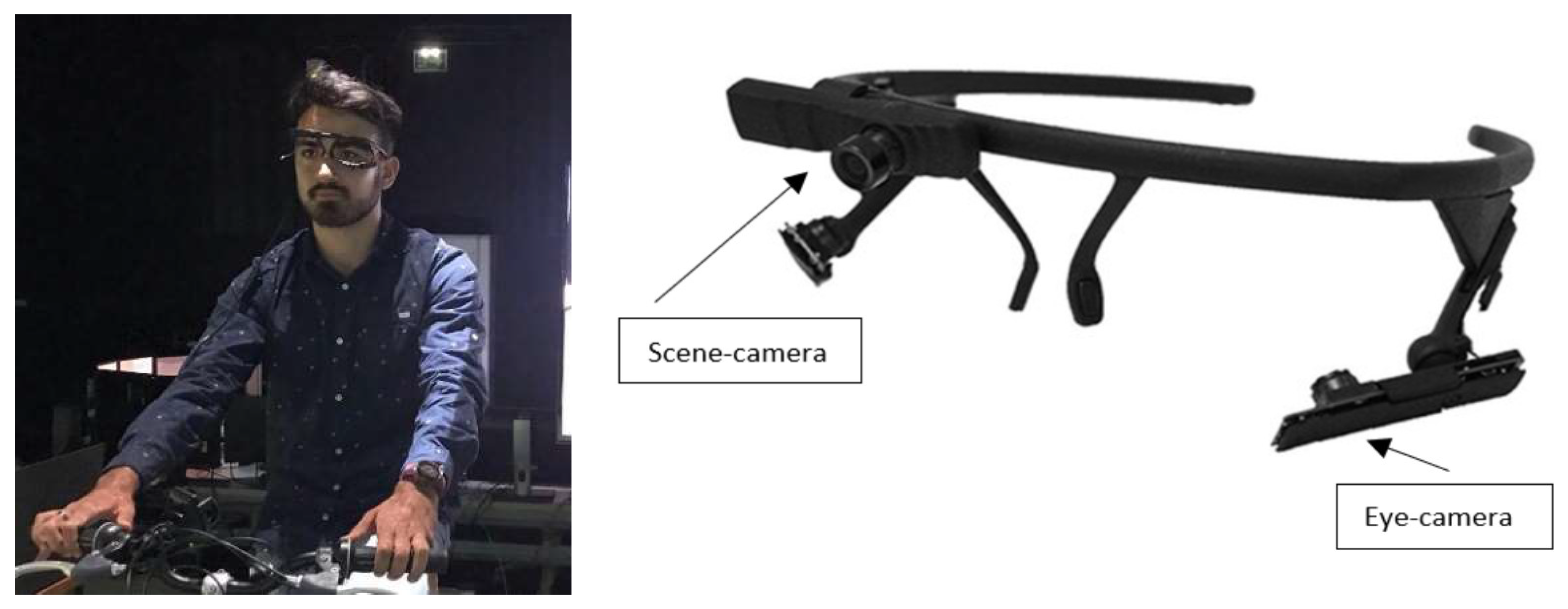
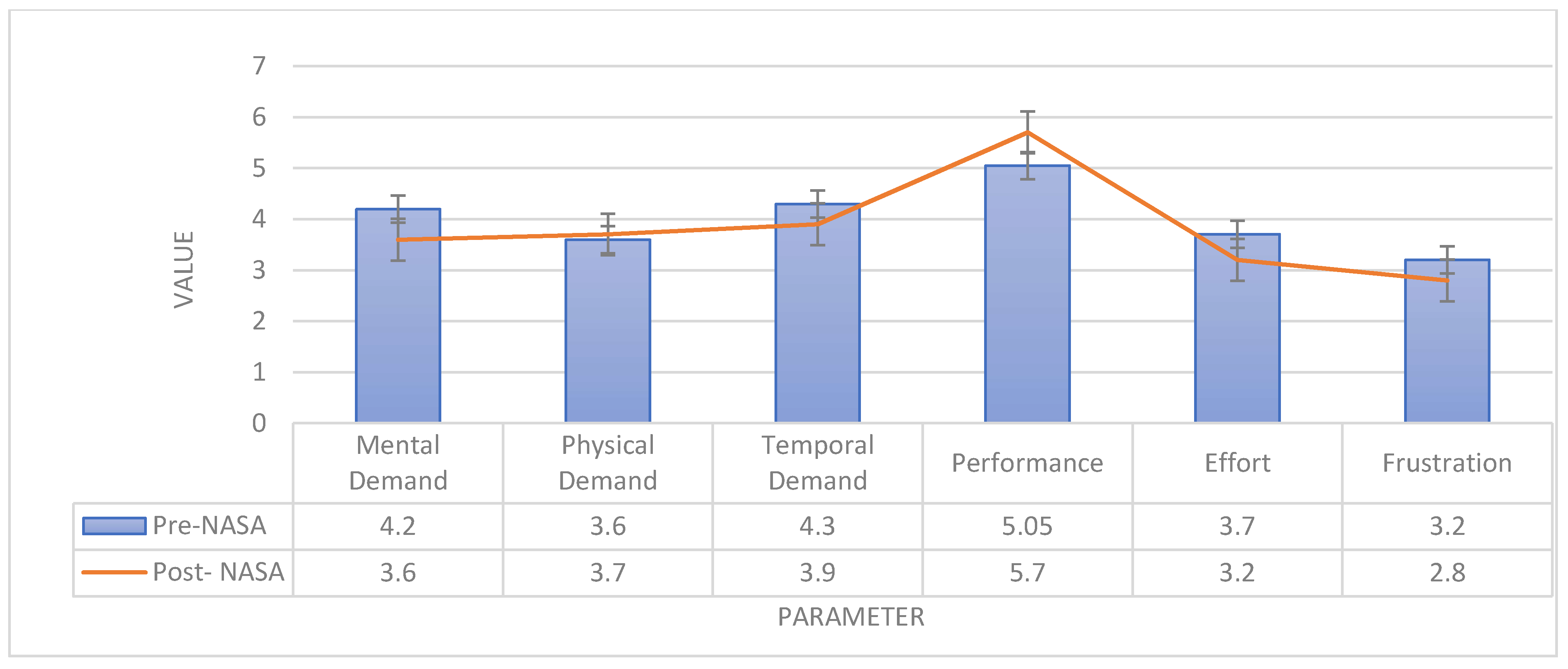
2.2. Instrument and data analysis
- -
- infrastructure, which includes sidewalks and streets;
- -
- users, correlated with the car, parked car, pedestrian and bicycle;
- -
- signs, considering horizontal, vertical, pedestrian passage and traffic lights;
- -
- background, with buildings, vegetation, street lamp and sky;
- -
- bicycle test, such as handlebar, pedals and GPS.
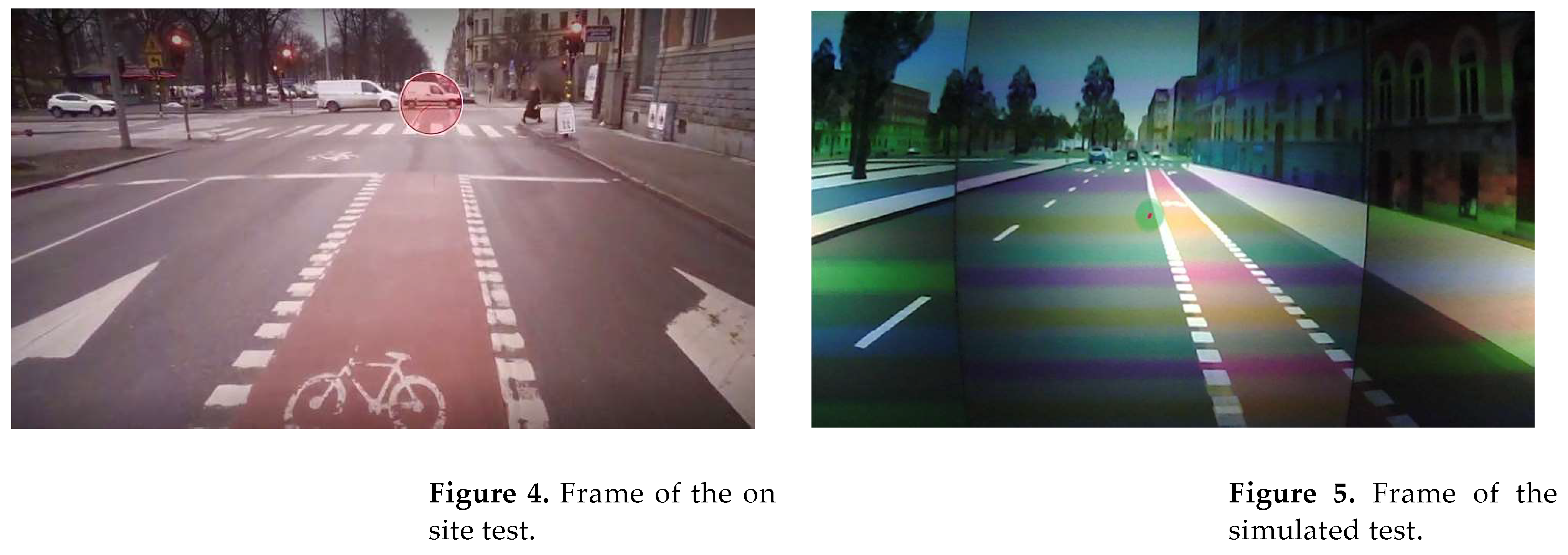

3. Discussion and results
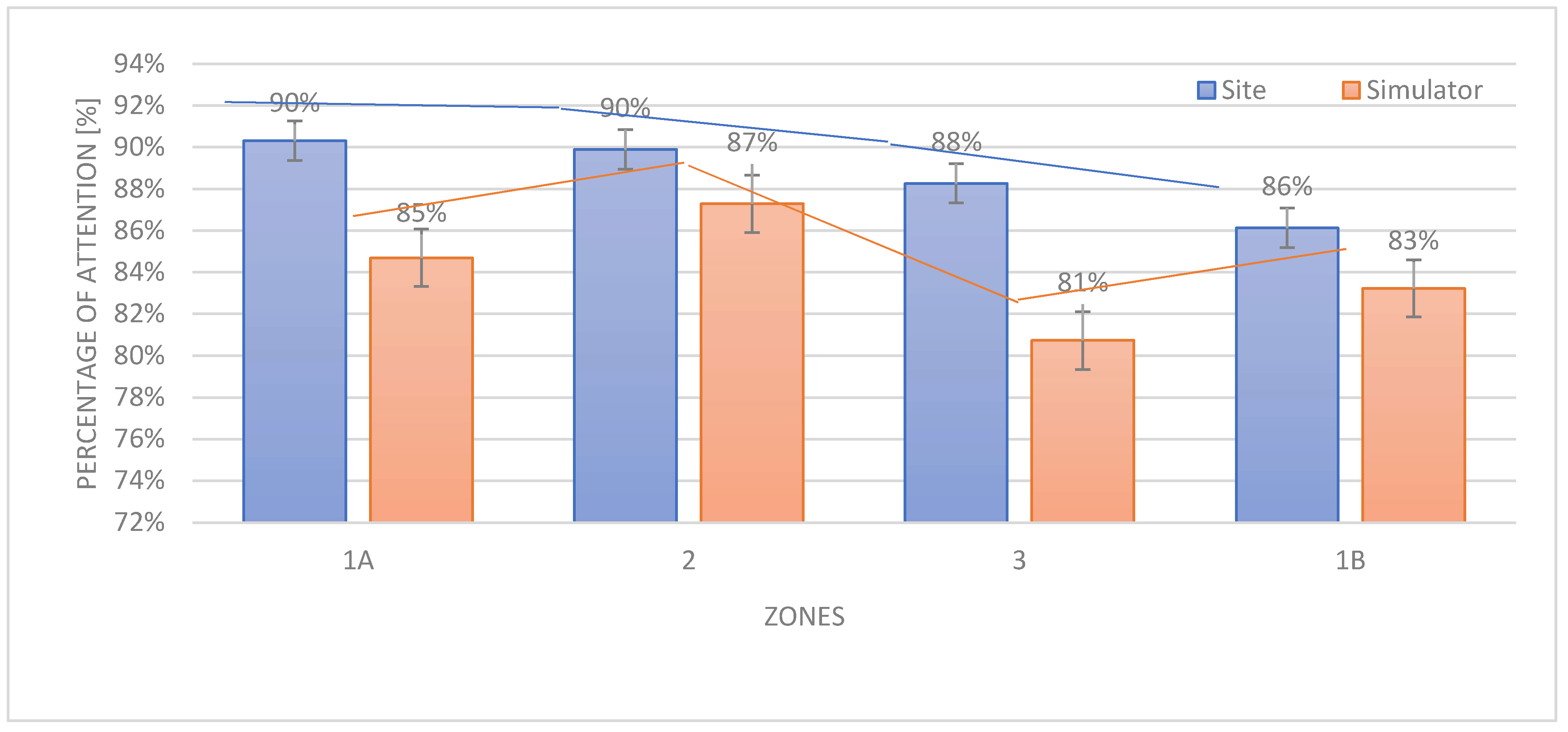
3.1. On-site test
3.2. Simulated test
3.3. Comparison
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Acerra, E.M.; Lantieri, C.; Simone, A.; Di Flumeri, G.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Vignali, V. The Impact of the Adaptive Cruise Control on the Drivers’ Workload and Attention. 2022; Available at SSRN 4281921. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlstrom, C.; Kircher, K.; Kircher, A. A gaze-based driver distraction warning system and its effect on visual behavior. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2013, 14, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, H.; Nilsson, L. Oool-4575(93)E0003-P Changes in driver behaviour as a function of handsfree mobile phones-a simulator study. Accid. Anal. and Prev. 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, J.E.; Hurst, P.M. Collisions between cyclists and motorists in New Zealand. Accident Analysis & Prevention 1983, 15, 137–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.; Flannagan, C.; Xiong, H.; Sayer, J. Eye glance behavior associated with cell-phone use: Examination with naturalistic driving data. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society; Human Factors an Ergonomics Society Inc., 2014; pp. 2112–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beratis, I.N.; Pavlou, D.; Papadimitriou, E.; Andronas, N.; Kontaxopoulou, D.; Fragkiadaki, S.; Yannis, G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Mild Cognitive Impairment and driving: Does in-vehicle distraction affect driving performance? Accid Anal Prev 2017, 103, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucchi, A.; Sangiorgi, C.; Vignali, V. Traffic Psychology and Driver Behavior. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 2012, 53, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulling, A.; Duchowski, A.T.; Majaranta, P.; SIGCHI (Group: U.S.); ACM SIGMOBILE, Association for Computing Machinery. Special Interest Group on Spatial Information; Microsoft Research; ACM Digital Library. UbiComp (Conference) (13th: 2011: Beijing, C., n.d. PETMEI 11. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Pervasive Eye Tracking & Mobile Eye-Based Interaction, Beijing, China, 18 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Caird, J.K.; Willness, C.R.; Steel, P.; Scialfa, C. A meta-analysis of the effects of cell phones on driver performance. Accid Anal Prev 2008, 40, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Chintamani, K.K.; Pandya, A.K.; Ellis, R.D. NASA TLX: Software for assessing subjective mental workload. Behav Res Methods 2009, 41, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. The Research Framework of Eye-tracking Based Mobile Device Usability Evaluation. In Proceedings of the PETMEI ’11: 1st international workshop on pervasive eye tracking & mobile eye-based interaction; 2011; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Bonetti, L.; Vignali, V.; Bichicchi, A.; Lantieri, C.; Simone, A. Driver’s visual attention to different categories of roadside advertising signs. Appl Ergon 2019, 78, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crundall, D.; Underwood, G.; Chapman, P. Driving experience and the functional field of view. Perception 1999, 28, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crundall, D.; van Loon, E.; Underwood, G. Attraction and distraction of attention with roadside advertisements. Accid Anal Prev 2006, 38, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waard, D.; Westerhuis, F.; Lewis-Evans, B. More screen operation than calling: The results of observing cyclists’ behaviour while using mobile phones. Accid Anal Prev 2015, 76, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, J.S.; Stannard, S.J.; McManus, B.; Wittig, S.M.O.; Sisiopiku, V.P.; Stavrinos, D. The Impact of Billboards on Driver Visual Behavior: A Systematic Literature Review. Traffic Inj Prev 2015, 16, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukic, T.; Ahlstrom, C.; Patten, C.; Kettwich, C.; Kircher, K. Effects of Electronic Billboards on Driver Distraction. Traffic Inj Prev 2013, 14, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitch, G.M.; Bartholomew, P.R.; Hanowski, R.J.; Perez, M.A. A. Drivers' visual behavior when using handheld and hands-free cell phones. Journal of safety research 2015, 54, 105–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadsby, A.; Watkins, K. Instrumented bikes and their use in studies on transportation behaviour, safety, and maintenance. Transp Rev 2020, 40, 774–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, N.; Acerra, E.M.; Lantieri, C.; Simone, A.; Rupi, F.; Vignali, V. Urban Mid-Block Bicycle Crossings: The Effects of Red Colored Pavement and Portal Overhead Bicycle Crossing Sign. Coatings 2022, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, N.; Acerra, E.; Vignali, V.; Lantieri, C.; Simone, A.; Imine, H. Road Safety Review update by using innovative technologies to investigate driver behaviour. Transportation research procedia 2020, 45, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godley, S.T.; Triggs, T.J.; Fildes, B.N. Driving simulator validation for speed research. Accident Analysis and Prevention 2002. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C. Driver distraction: An initial examination of the ‘attention diverted by’contributory factor codes from crash reports and focus group research on perceived risks. no. code 2005, 350, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, P.A.; Lesch, M.; Simmons, L. The distraction effects of phone use during a crucial driving maneuver. Accident Analysis and Prevention 2003.
- He, Q.; Fan, X.; Ma, D. Full bicycle dynamic model for interactive bicycle simulator. J Comput Inf Sci Eng 2005, 5, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpers, R.; Heiden, W.; Kutz, M.; Scherfgen, D.; Hartmann, U.; Bongartz, J.; Schulzyk, O. FIVIS bicycle simulator: an immersive game platform for physical activities. In Proceedings of the 2008 Conference on Future Play: Research, Play, Share; 2008; pp. 244–247. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Yang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Sze, N.N.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J. Effects of using mobile phones while cycling: A study from the perspectives of manipulation and visual strategies. Transp Res Part F Traffic Psychol Behav 2021, 83, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.B. Various approaches for driver and driving behavior monitoring: A review. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., 2013; pp. 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, S.J.; Cole, K.S.; Stanny, C.J. Effects of distraction and experience on situation awareness and simulated driving. Transp Res Part F Traffic Psychol Behav 2007, 10, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Q.; Lee, S. Gaze and eye tracking: Techniques and applications in ADAS. Sensors (Switzerland) 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircher, K.; Ahlstrom, C. Minimum Required Attention: A Human-Centered Approach to Driver Inattention. Hum Factors 2017, 59, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovácsová, N.; Cabrall, C.D.D.; Antonisse, S.J.; de Haan, T.; van Namen, R.; Nooren, J.L.; Schreurs, R.; Hagenzieker, M.P.; de Winter, J.C.F. Cyclists’ eye movements and crossing judgments at uncontrolled intersections: An eye-tracking study using animated video clips. Accid Anal Prev 2018, 120, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.S.; Yang, G.H.; Lee, C.W.; Shin, J.C.; Park, Y.; Jung, B.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, K.; Han, S.H.; Yoo, B.H.; et al. KAIST interactive bicycle simulator. Proc IEEE Int Conf Robot Autom 2001, 3, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantieri, C.; Costa, M.; Vignali, V.; Acerra, E.M.; Marchetti, P.; Simone, A. Flashing in-curb LEDs and beacons at unsignalized crosswalks and driver’s visual attention to pedestrians during nighttime. Ergonomics 2021, 64, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lee, J.D. Combining cognitive and visual distraction: Less than the sum of its parts. Accid Anal Prev 2010, 42, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantuano, A.; Bernardi, S.; Rupi, F. Cyclist gaze behavior in urban space: An eye-tracking experiment on the bicycle network of Bologna. Case Stud Transp Policy 2017, 5, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, H.S.; Whitehead, A.E.; Marchant, D.; Polman, R.C.; Williams, E.L. An investigation of expertise in cycling: Eye tracking, Think Aloud and the influence of a competitor. Psychol Sport Exerc 2020, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabatilan, L.B.; Aghazadeh, F.; Nimbarte, A.D.; Harvey, C.C.; Chowdhury, S.K. Effect of driving experience on visual behavior and driving performance under different driving conditions. Cognition, Technology and Work 2012, 14, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hern, S.; Oxley, J.; Stevenson, M. Validation of a bicycle simulator for road safety research. Accid Anal Prev 2017, 100, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, C.W.; Jou, R.C. Cyclists’ red-light running behaviours: An examination of risk-taking, opportunistic, and law-obeying behaviours. Accid Anal Prev 2014, 62, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, A.; Lantieri, C.; Imine, H.; Simone, A. Light vehicle model for dynamic car simulator. Transport 2016, 31, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planek, T.W.; Sinelnikov, S.; Thomas, J.; Kolosh, K.; Porretta, K. Letter from the Editors - Fourth international symposium on naturalistic driving research. J Safety Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räsänen, M.; Koivisto, I.; Summala, H. Car Driver and Bicyclist Behavior at Bicycle Crossings Under Different Priority Regulations. Journal of Safety Research 1999. [CrossRef]
- Recarte, M.A.; Nunes, L.M. Effects of Verbal and Spatial-Imagery Tasks on Eye Fixations While Driving. J Exp Psychol Appl 2000, 6, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recarte, M.A.; Nunes, L.M. Mental Workload While Driving: Effects on Visual Search, Discrimination, and Decision Making. J Exp Psychol Appl 2003, 9, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, M.A.; Hallett, C.; Gordon, C.P. Driver distraction and driver inattention: Definition, relationship and taxonomy. Accid Anal Prev 2011, 43, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, M.S.; Long, C.S.; Fichman, M.; Davidson, J.H.; Scudder, K.N.; Kim, M.; Katti, R.; Poon, G.; Harris, M.D. Evaluating cyclist biometrics to develop urban transportation safety metrics. Accid Anal Prev 2021, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, J.P.; Kroeze, P.A.; Sweers, W.; Wüst, J.C. Road factors and bicycle-motor vehicle crashes at unsignalized priority intersections. Accid Anal Prev 2011, 43, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, P.; den Brinker, B. What do cyclists need to see to avoid single-bicycle crashes? Ergonomics 2011, 54, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinar, D.; Tractinsky, N.; Compton, R. Effects of practice, age, and task demands, on interference from a phone task while driving. Accid Anal Prev 2005, 37, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoman, M.; Imine, H. Subjective validity of bicycle simulators. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Advances in Vehicular Systems, Technologies and Applications; 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shoman, M.; Imine, H.; Johansson, K.; Wallqvist, V. Bicycle instrumentation and analysis of the output signals. Highlights of Vehicles, under submission. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shoman, M.; Imine, H. Bicycle Simulator Improvement and Validation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 55063–55076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoman, M.; Simone, A.; Vignali, V. Looking behavior to vertical road signs on rural roads. MOJ Civil Engineering 2018, 4, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrinos, D.; Mosley, P.R.; Wittig, S.M.; Johnson, H.D.; Decker, J.S.; Sisiopiku, V.P.; Welburn, S.C. Visual behavior differences in drivers across the lifespan: A digital billboard simulator study. Transp Res Part F Traffic Psychol Behav 2016, 41, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnros, J. Driving behaviour in a real and a simulated road tunnel—a validation study. Accident Analysis & Prevention 1998, 30, 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Vansteenkiste, P.; Zeuwts, L.; Cardon, G.; Philippaerts, R.; Lenoir, M. The implications of low quality bicycle paths on gaze behavior of cyclists: A field test. Transp Res Part F Traffic Psychol Behav 2014, 23, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, V.; Cuppi, F.; Acerra, E.; Bichicchi, A.; Lantieri, C.; Simone, A.; Costa, M. Effects of median refuge island and flashing vertical sign on conspicuity and safety of unsignalized crosswalks. Transportation research part F: traffic psychology and behaviour 2019, 60, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villing, J. Towards Dialogue Strategies for Cognitive Workload Man. Accident Analysis and Prevention 2015, 41, 924–930. [Google Scholar]
- Von Stülpnagel, R. Gaze behavior during urban cycling: Effects of subjective risk perception and vista space properties. Transp Res Part F Traffic Psychol Behav 2020, 75, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Stülpnagel, R. Gaze behavior during urban cycling: Effects of subjective risk perception and vista space properties. Transp Res Part F Traffic Psychol Behav 2020, 75, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.H.; Stanton, N.A.; Chowdhury, I. Self Explaining Roads and situation awareness. Saf Sci 2013, 56, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, I. Signals are informative but slow down responses when drivers meet bicyclists at road junctions. Accid Anal Prev 2005, 37, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, I. Drivers overtaking bicyclists: Objective data on the effects of riding position, helmet use, vehicle type and apparent gender. Accid Anal Prev 2007, 39, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bao, S.; Du, W.; Ye, Z.; Sayer, J.R. Examining drivers’ eye glance patterns during distracted driving: Insights from scanning randomness and glance transition matrix. J Safety Res 2017, 63, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yao, L.; Zhang, K. The red-light running behavior of electric bike riders and cyclists at urban intersections in China: An observational study. Accid Anal Prev 2012, 49, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Zones | Total frames | Total fixation duration [sec] | Fixation duration of attention [sec] | Fixation duration of inattention [sec] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 23359 | 934.36 | 845.32 | 89.04 |
| 2 | 50545 | 2021.8 | 1756.34 | 265.46 |
| 3 | 44412 | 1776.48 | 1547.36 | 229.13 |
| 1B | 29924 | 1196.96 | 1032.01 | 164.93 |
| Categories | Total frames | Total fixation duration [sec] | Average Percentage [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sidewalk | 3013 | 121 | 2 |
| Street | 101635 | 4065 | 78 |
| Car | 5916 | 237 | 5 |
| Parked car | 2818 | 113 | 2 |
| Pedestrian | 5617 | 225 | 4 |
| Bicycle | 1417 | 57 | 1 |
| Horizontal Signs | 803 | 32 | 1 |
| Vertical Signs | 755 | 30 | 1 |
| Pedestrian passage | 2138 | 86 | 2 |
| Traffic light | 5414 | 217 | 4 |
| Categories | Total frames | Total fixation duration [sec] | Average Percentage [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings | 3066 | 123 | 16 |
| Vegetation | 774 | 31 | 4 |
| Street lamps | 601 | 25 | 3 |
| Sky | 7 | 0.28 | 0 |
| Handlebar | 2136 | 85 | 11 |
| Pedals | 721 | 29 | 4 |
| Gps | 11410 | 456 | 61 |
| Zones | Total frames | Total fixation duration [sec] | Fixation duration of attention [sec] | Fixation duration of inattention [sec] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 12168 | 487 | 386 | 101 |
| 2 | 24315 | 973 | 813 | 159.48 |
| 3 | 16712 | 668 | 492 | 176.24 |
| 1B | 8771 | 351 | 297 | 53.6 |
| Categories | Total frames | Total fixation duration [sec] | Average Percentage [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sidewalk | 19203 | 768 | 9 |
| Street | 159839 | 6394 | 78 |
| Car | 9355 | 374 | 5 |
| Parked car | 4053 | 162 | 2 |
| Pedestrian | 3272 | 131 | 2 |
| Bicycle | 2026 | 81 | 1 |
| Horizontal Signs | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vertical Signs | 25 | 1 | 0 |
| Pedestrian passage | 2782 | 111 | 1 |
| Traffic light | 5476 | 219 | 3 |
| Categories | Total frames | Total fixation duration [sec] | Average Percentage [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings | 23795 | 952 | 64 |
| Vegetation | 11535 | 461 | 31 |
| Street lamps | 45 | 2 | 0 |
| Sky | 1106 | 44 | 3 |
| Handlebar | 744 | 30 | 2 |
| Pedals | 17 | 0.68 | 0 |
| Gps | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





