Submitted:
13 February 2023
Posted:
14 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. WRF Model Setup and Perturbation Methods Description
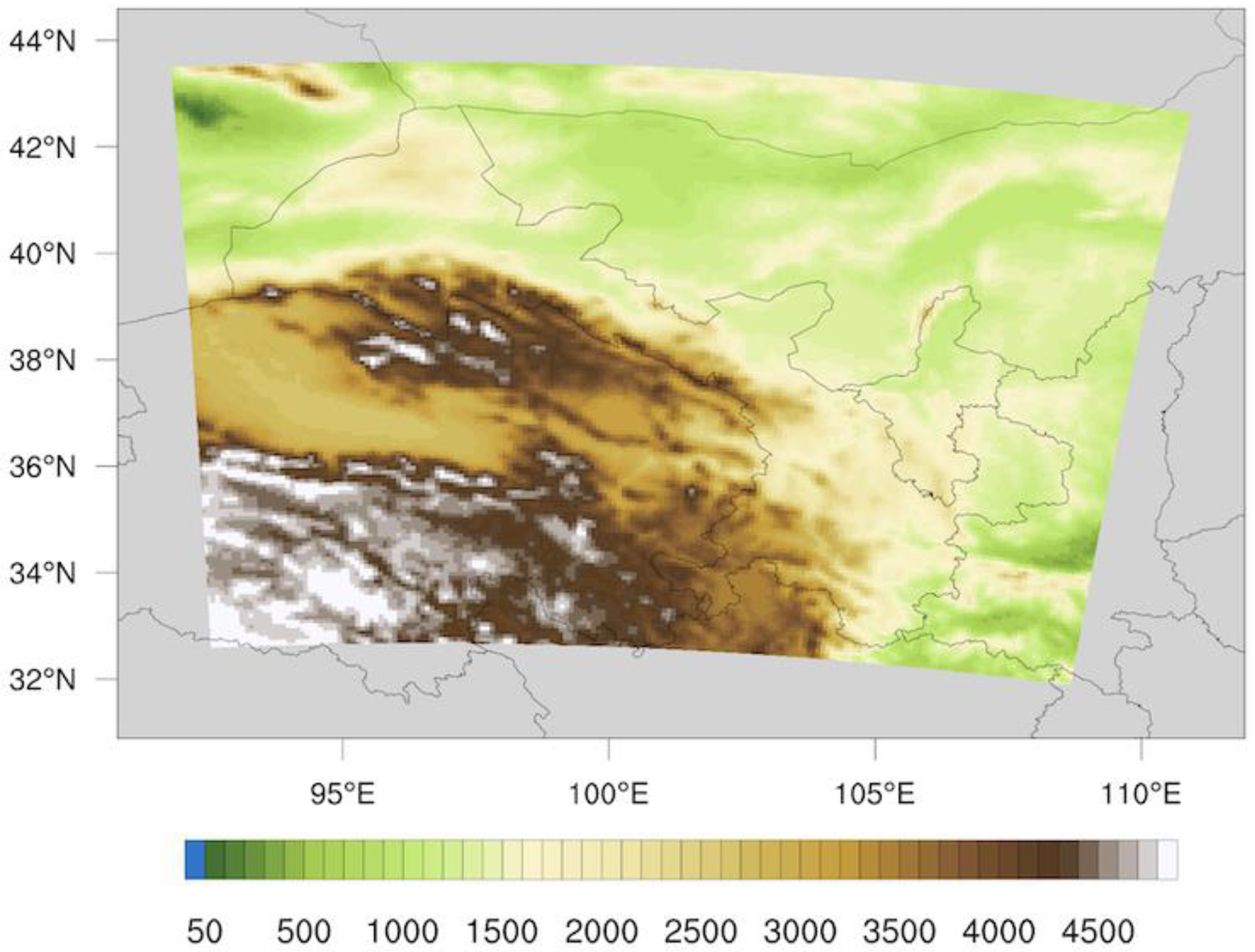
2.1. WRF Model Setup
2.2. Description of the Initial Condition Perturbation Methods
2.2.1. BGM Method
2.2.1. Blending
3. Data and Metrics for Evaluation
3.1. Observation Data
3.2. Evaluation Methods
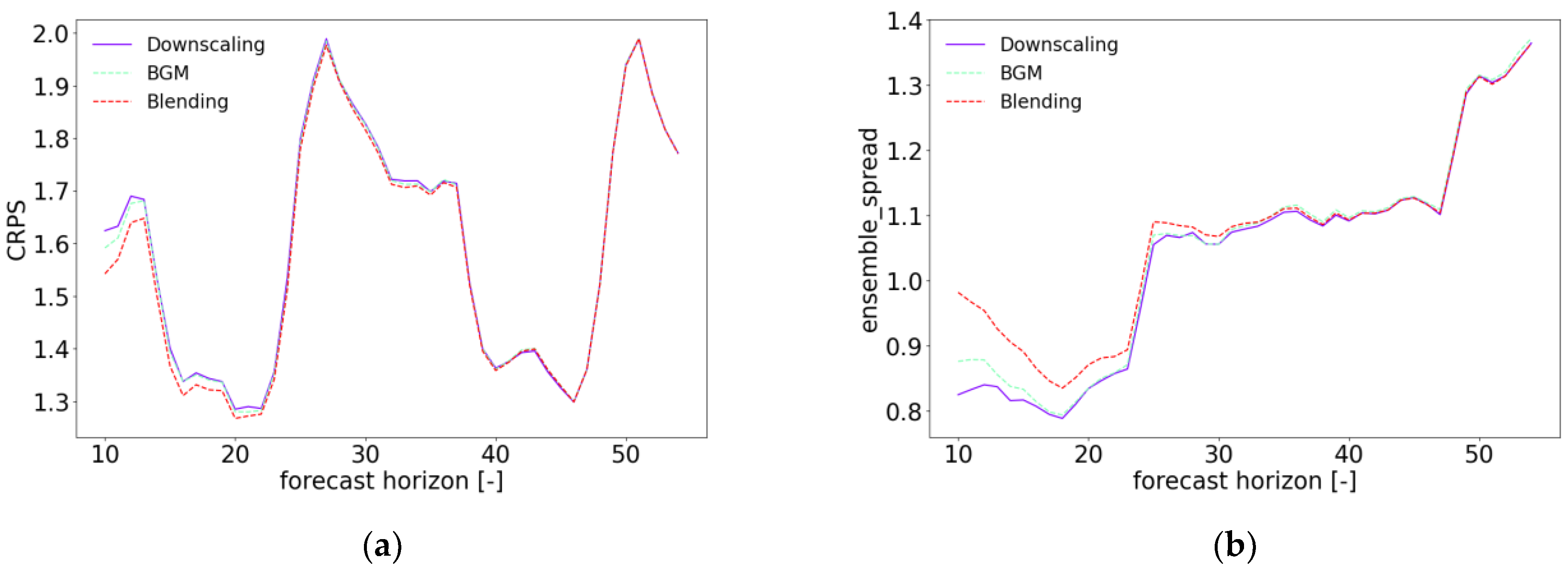
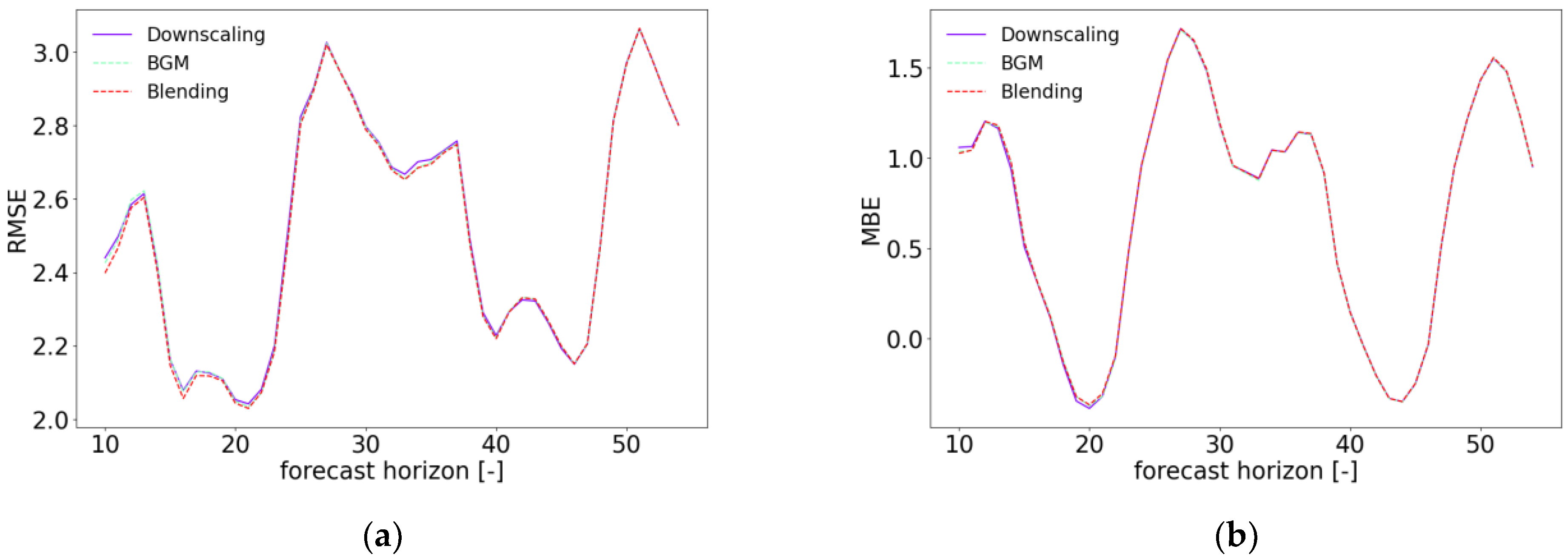
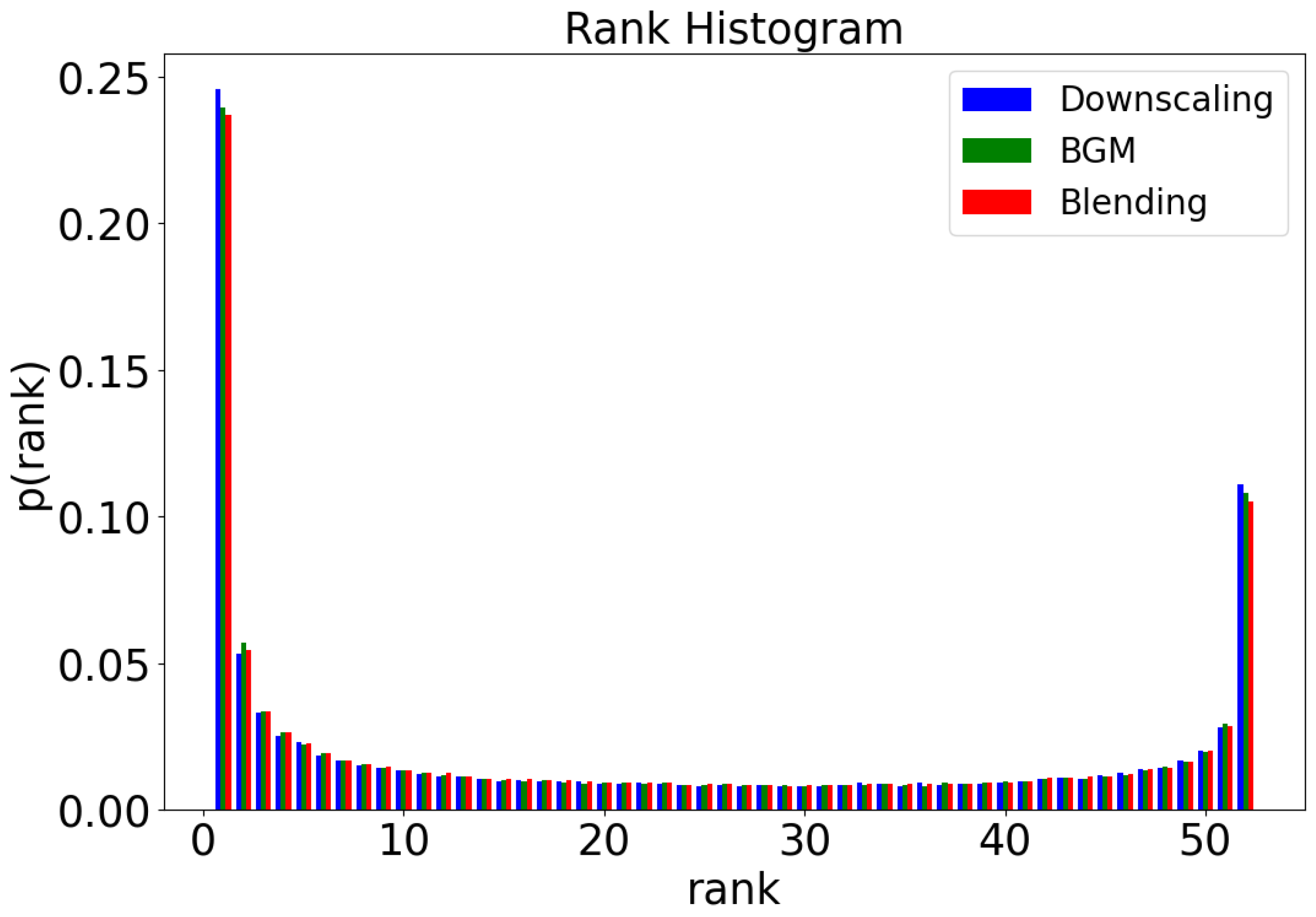
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Wind Energy Council GWEC Global Wind Report 2022. 2021.
- Soman, S.S.; Zareipour, H.; Member, S.; Malik, O.; Fellow, L. A Review of Wind Power and Wind Speed Forecasting Methods With Different Time Horizons. In Proceedings of the North American Power Symposium, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinson, P. Wind Energy: Forecasting Challenges for Its Operational Management. Stat. Sci. 2013, 28, 564–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.E. Strategies and Decision Support Systems for Integrating Variable Energy Resources in Control Centers for Reliable Grid Operations; 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, L.; Farhan, S.; Gao, S.; Liao, X. Wind Power Day-Ahead Prediction with Cluster Analysis of NWP. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.W.; Lu, H.J.; Chang, Y.R.; Lee, Y.D. An Improved Neural Network-Based Approach for Short-Term Wind Speed and Power Forecast. Renew. Energy 2017, 105, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.W.; Grimit, E.; Nijssen, B. Potential Benefits of a Dedicated Probabilistic Rapid Ramp Event Forecast Tool. 2009 IEEE/PES Power Syst. Conf. Expo. PSCE 2009 2009, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Bias-Correction Method for Wind-Speed Forecasting. Meteorol. Zeitschrift 2019, 28, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, A.M.; Leahy, P.G.; Marvuglia, A.; McKeogh, E.J. Current Methods and Advances in Forecasting of Wind Power Generation. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, M.; Venkaiah, C.; Kumar, D.M.V. Current Advances and Approaches in Wind Speed and Wind Power Forecasting for Improved Renewable Energy Integration: A Review. Eng. Reports 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifi, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, Z.; Lotfian, S. A Critical Review of Wind Power Forecasting Methods—Past, Present and Future. Energies 2020, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, N. Lorenz Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Pu, Z. Beating the Uncertainties: Ensemble Forecasting and Ensemble-Based Data Assimilation in Modern Numerical Weather Prediction. Adv. Meteorol. 2010, 2010, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneiting, T.; Raftery, A.E. Atmospheric Science. Weather Forecasting with Ensemble Methods. Science (80-. ). 2005, 310, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The Quiet Revolution of Numerical Weather Prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, Z.; Kalnay, E. Ensemble Forecasting at NMC: The Generation of Perturbations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 74, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buizza, R.; Houtekamer, P.L.; Toth, Z.; Pellerin, G.; Wei, M.; Zhu, Y. A Comparison of the ECMWF, MSC, and NCEP Global Ensemble Prediction Systems. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1076–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buizza, R.; Palmer, T.N. Palmer The Singular-Vector Sturcture of the Atmospheric Global Circulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 1434–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F.; Buizza, R.; Palmer, T.N.; Petroliagis, T. The ECMWF Ensemble Prediction System: Methodology and Validation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 122, 73–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtekamer, P.L.; Derome, J. Methods for Ensemble Prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 1995, 123, 2181–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtekamer, P.L.; Lefaivre, L.; Derome, J. A System Simulation Approach to Ensemble Prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 1996, 124, 1225–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, D.; Luo, Y.; Peng, J.; Wobus, R. Performance of the New NCEP Global Ensemble Forecast System in a Parallel Experiment. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 1989–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, S.; Deng, X. Ensemble Forecast Systems and Future Applications at MSC. In Proceedings of the 8th NCEP Ensemble User Workshop, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson, L.; Bidlot, J.R.; Bonavita, M.; Brown, A.R.; Browne, P.A.; De Chiara, G.; Dahoui, M.; Lang, S.T.K.; McNally, T.; Mogensen, K.S.; et al. ECMWF Activities for Improved Hurricane Forecasts. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Jiaqi, L.; Mengye, Z. Wind Curtailment in China and Lessons from the United States; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- NS Energy Staff Writer Profiling Ten of the Biggest Onshore Wind Farms in the World. Available online: https://www.nsenergybusiness.com/features/worlds-biggest-onshore-wind-farms/ (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Dong, C.; Qi, Y.; Dong, W.; Lu, X.; Liu, T.; Qian, S. Decomposing Driving Factors for Wind Curtailment under Economic New Normal in China. Appl. Energy 2018, 217, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, D.; Milligan, M.; Jordan, G.; Piwko, R. The Value of Wind Power Forecasting Preprint; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Prósper, M.A.; Casal, C.O.; Fernández, F.C.; Miguez-Macho, G. Wind Power Forecasting for a Real Onshore Wind Farm on Complex Terrain Using WRF High Resolution Simulations. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidle, F.; Wang, Y.; Smet, G. On the Impact of the Choice of Global Ensemble in Forcing a Regional Ensemble System. Weather Forecast. 2016, 31, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, N.E.; Arribas, A.; Mylne, K.R.; Robertson, K.B.; Beare, S.E. The MOGREPS Short-Range Ensemble Prediction System. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 134, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelin, S.; Son, J.; Swinbank, R.; Mccabe, A.; Roberts, N.; Tennant, W. The Met Office Convective-Scale Ensemble, MOGREPS-UK. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 2846–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Fan, S. Study on the Construction of Initial Condition Perturbations for the Regional Ensemble Prediction System of North China. Atmosphere (Basel). 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Kunii, M.; Honda, Y. The Regional Model-Based Mesoscale Ensemble Prediction System, MEPS, at the Japan Meteorological Agency. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, N.E.; Mylne, K.R. Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter Perturbations for a Regional Ensemble Prediction System. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 135, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAITO, K.; HARA, M.; KUNII, M.; SEKO, H.; YAMAGUCHI, M. Comparison of Initial Perturbation Methods for the Mesoscale Ensemble Prediction System of the Meteorological Research Institute for the WWRP Beijing 2008 Olympics Research and Development Project ( B08RDP ). Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2011, 63, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, J.F. Mismatching Perturbations at the Lateral Boundaries in Limited-Area Ensemble Forecasting: A Case Study. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 356–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bellus, M.; Wittmann, C.; Steinheimer, M.; Weidle, F.; Kann, A.; Ivatek-Šahdan, S.; Tian, W.; Ma, X.; Tascu, S.; et al. The Central European Limited-Area Ensemble Forecasting System: ALADIN-LAEF. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bellus, M.; Geleyn, J.F.; Ma, X.; Tian, W.; Weidle, F. A New Method for Generating Initial Condition Perturbations in a Regional Ensemble Prediction System: Blending. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 2043–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhi, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Study on Multi-Scale Blending Initial Condition Perturbations for a Regional Ensemble Prediction System. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huva, R.; Song, G.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, Y. Comprehensive Physics Testing and Adaptive Weather Research and Forecasting Physics for Day-Ahead Solar Forecasting. Meteorol. Appl. 2021, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, J.-O.J. The WRF Single-Moment 6-Class Microphysics Scheme (WSM6). J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bougeault, P.; Lacarrere, P. Parameterization of Orography-Induced Turbulence in a Mesobeta-Scale Model. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 1872–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleim, J.E.; Xiu, A. Development and Testing of a Surface Flux and Planetary Boundary Lyaer Model for Application in Mesoscale Models. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1995, 34, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, A.; Pleim, J.E. Development of a Land Surface Model. Part I: Application in a Mesoscale Meteorological Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain–Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.-D.; Suarez, M.J. Technical Report Series on Global Modeling and Data Assimilation Volume 15: A Solar Radiation Parameterization for Atmospheric Studies; 1999; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, Z.; Kalnay, E. Ensemble Forecasting at NCEP and the Breeding Method. Mon. Weather Rev. 1997, 125, 3297–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese GB/T 19963-2011; Technical Rule for Connecting Wind Farm to Power System. China.
- Hersbach, H. Decomposition of the Continuous Ranked Probability Score for Ensemble Prediction Systems. Weather Forecast. 2000, 15, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloughter, J.M.L.; Gneiting, T.; Raftery, A.E. Probabilistic Wind Speed Forecasting Using Ensembles and Bayesian Model Averaging. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2010, 105, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamill, T.M. Interpretation of Rank Histograms for Verifying Ensemble Forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.S.; Loughe, A.F. The Relationship between Ensemble Spread and Ensemble Mean Skill. Mon. Weather Rev. 1998, 126, 3292–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 4th ed; Academic Press, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- The Climate Corporation Proper Scoring Rules for Evaluating Probabilistic Forecasts in Python.
| Experiment | Initial Condition Perturbations | Lateral Condition Perturbations |
|---|---|---|
| Downscaling | Dynamical downscaling of ECMWF EPS | ECMWF EPS |
| BGM | WRF BGM | ECMWF EPS |
| Blending | Blending ECMWF EPS with WRF BGM | ECMWF EPS |
| 10 to 13 Hours | 28 to 51 Hours | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Downscaling | BGM | Blending | Downscaling | BGM | Blending | |
| RMSE | 2.531 | 2.530 | 2.508 | 2.582 | 2.579 | 2.577 |
| MBE | 1.122 | 1.112 | 1.113 | 0.722 | 0.721 | 0.725 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





