Submitted:
03 February 2023
Posted:
10 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
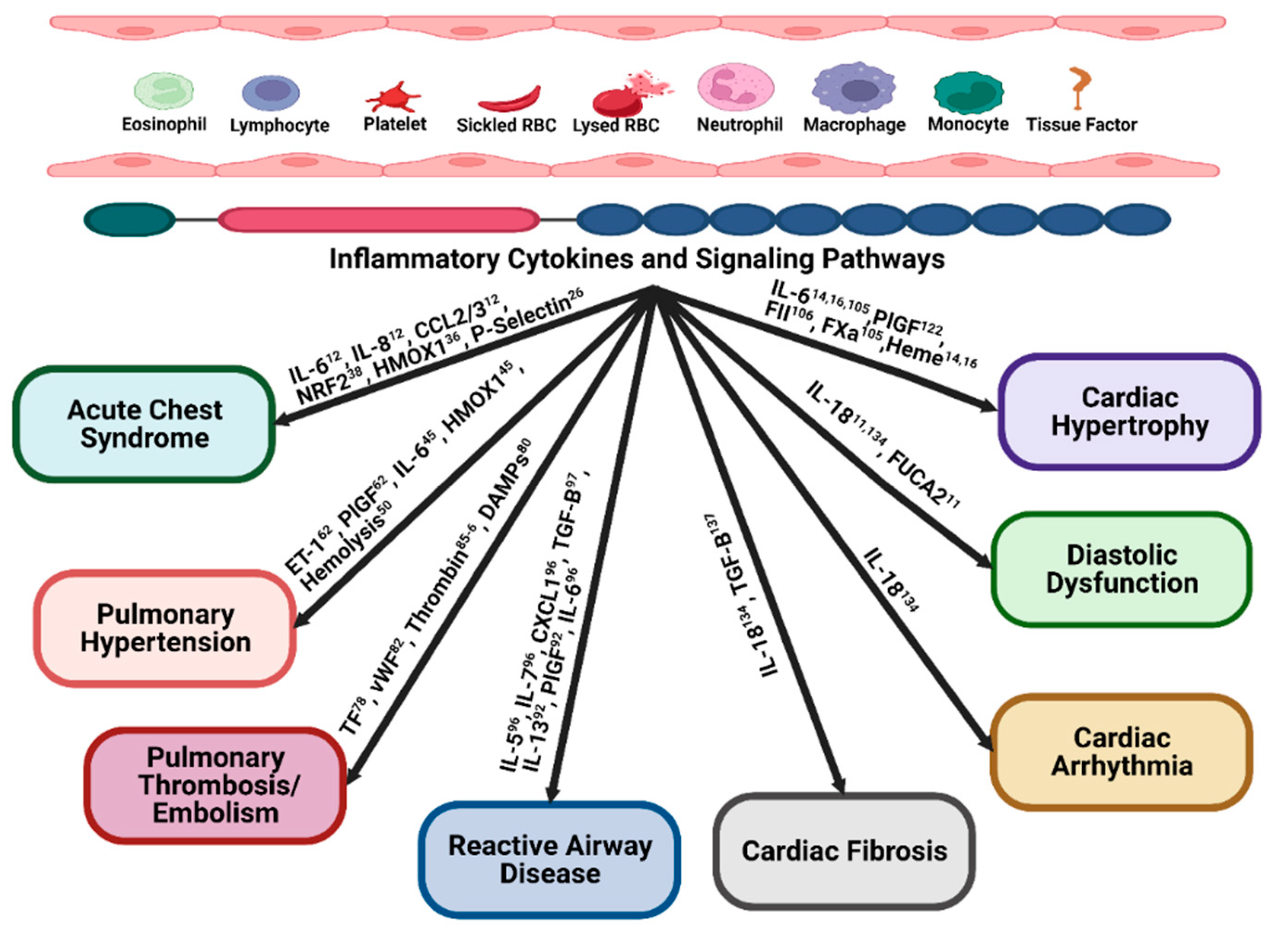
Inflammation and acute chest syndrome.
Inflammation and pulmonary hypertension
Inflammation and pulmonary thrombosis/ embolism
Inflammation and reactive airway disease or airway hyper-activity (AHR)
Inflammatory mediators and cardiac hypertrophy
Inflammation and diastolic dysfunction
Inflammation and cardiac arrhythmia
Inflammation and cardiac fibrosis
Conclusions and future perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piel, F.; Hay, S.; Gupta, S.; Weatherall, D.; Williams, T. Global burden of sickle cell anaemia in children under five, 2010-2050: modelling based on demographics, excess mortality, and interventions. PLoS Med 2013, 10, e1001484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piel, F.; Patil, A.; Howes, R.; Nyangiri, O.; Gething, P.; Dewi, M.; Temperley, W.; Williams, T.; Weatherall, D.; Haya, S. Global epidemiology of sickle haemoglobin in neonates: a contemporary geostatistical model-based map and population estimates. Lancet 2013, 381, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzhugh, C.; Lauder, N.; Jonassaint, J.; Telen, M.; Zhao, X.; Wright, E.; Gilliam, F.; De Castro, L. Cardiopulmonary complications leading to premature deaths in adult patients with sickle cell disease. Am J Hematol 2010, 85, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladwin, M. Cardiovascular complications and risk of death in sickle-cell disease. Lancet 2016, 387, 2565–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, V.; Rosing, D.R.; Thein, S.L. Cardiovascular complications of sickle cell disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2020. [CrossRef]
- Alfaddagh, A.; Martin, S.S.; Leucker, T.M.; Michos, E.D.; Blaha, M.J.; Lowenstein, C.J.; Jones, S.R.; Toth, P.P. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Am J Prev Cardiol 2020, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.D.; Aday, A.W.; Rose, L.M.; Ridker, P.M. Residual Inflammatory Risk on Treatment With PCSK9 Inhibition and Statin Therapy. Circulation 2018, 138, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Ellims, A.H.; Beale, A.L.; Taylor, A.J.; Murphy, A.; Dart, A.M. Systemic inflammation is associated with myocardial fibrosis, diastolic dysfunction, and cardiac hypertrophy in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Am J Transl Res 2017, 9, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Kong, B.; Yang, H.; Dai, C.; Fang, J.; Qin, T.; Huang, H. Key Player in Cardiac Hypertrophy, Emphasizing the Role of Toll-Like Receptor 4. Front Cardiovasc Med 2020, 7, 579036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.R.; Yuan, T.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhao, J.L.; Li, M.T.; Fang, L.H.; Du, G.H. Immunity and inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension: From pathophysiology mechanisms to treatment perspective. Pharmacol Res 2022, 180, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.D.; Desai, A.A.; Sysol, J.R.; Abbasi, T.; Patel, A.R.; Lang, R.M.; Gupta, A.; Garcia, J.G.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Machado, R.F. Genome-Wide Analysis Identifies IL-18 and FUCA2 as Novel Genes Associated with Diastolic Function in African Americans with Sickle Cell Disease. PloS one 2016, 11, e0163013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allali, S.; de Montalembert, M.; Rignault-Bricard, R.; Taylor, M.; Brice, J.; Brousse, V.; Talbot, J.M.; Moulin, F.; Heilbronner, C.; Hermine, O.; Maciel, T.T. IL-6 levels are dramatically high in the sputum from children with sickle cell disease during acute chest syndrome. Blood advances 2020, 4, 6130–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbotosho, O.T.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Ghosh, S.; Villanueva, F.S.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Kato, G.J. Heme Induces IL-6 and Cardiac Hypertrophy Genes Transcripts in Sickle Cell Mice. Frontiers in Immunology 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, A.V.; Liu, J.; Tsai, H.P.; Zeng, L.; Yang, S.; Asnani, A.; Kim, J. Excess heme upregulates heme oxygenase 1 and promotes cardiac ferroptosis in mice with sickle cell disease. Blood 2022, 139, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karoor, V.; Swindle, D.; Pak, D.I.; Strassheim, D.; Fini, M.A.; Dempsey, E.; Stenmark, K.R.; Hassell, K.; Nuss, R.; Buehler, P.W.; Irwin, D.C. Evidence supporting a role for circulating macrophages in the regression of vascular remodeling following sub-chronic exposure to hemoglobin plus hypoxia. Pulmonary circulation 2021, 11, 20458940211056806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbotosho, O.T.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Ghosh, S.; Villanueva, F.S.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Kato, G.J. Heme Induces IL-6 and Cardiac Hypertrophy Genes Transcripts in Sickle Cell Mice. Frontiers in immunology 2020, 11, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichinsky, E.P.; Styles, L.A.; Colangelo, L.H.; Wright, E.C.; Castro, O.; Nickerson, B. Acute chest syndrome in sickle cell disease: clinical presentation and course. Cooperative Study of Sickle Cell Disease. Blood 1997, 89, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichinsky, E.P.; Neumayr, L.D.; Earles, A.N.; Williams, R.; Lennette, E.T.; Dean, D.; Nickerson, B.; Orringer, E.; McKie, V.; Bellevue, R.; Daeschner, C.; Manci, E.A. Causes and outcomes of the acute chest syndrome in sickle cell disease. National Acute Chest Syndrome Study Group. The New England journal of medicine 2000, 342, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Bakshi, N.; Krishnamurti, L. Acute Chest Syndrome in Children with Sickle Cell Disease. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol 2017, 30, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennewitz, M.F.; Jimenez, M.A.; Vats, R.; Tutuncuoglu, E.; Jonassaint, J.; Kato, G.J.; Gladwin, M.T.; Sundd, P. Lung vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease mediated by arteriolar neutrophil-platelet microemboli. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e89761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Vichinsky, E. Pulmonary complications of sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med 2008, 359, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, C.A.; Rehberg, M.; Lerchenberger, M.; Berberich, N.; Bihari, P.; Khandoga, A.G.; Zahler, S.; Krombach, F. Ccl2 and Ccl3 mediate neutrophil recruitment via induction of protein synthesis and generation of lipid mediators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2009, 29, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koltsova, E.K.; Sundd, P.; Zarpellon, A.; Ouyang, H.; Mikulski, Z.; Zampolli, A.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Ley, K. Genetic deletion of platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha but not its extracellular domain protects from atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost 2014, 112, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anea, C.B.; Lyon, M.; Lee, I.A.; Gonzales, J.N.; Adeyemi, A.; Falls, G.; Kutlar, A.; Brittain, J.E. Pulmonary platelet thrombi and vascular pathology in acute chest syndrome in patients with sickle cell disease. Am J Hematol 2016, 91, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, M.A.; Novelli, E.; Shaw, G.D.; Sundd, P. Glycoprotein Ibalpha inhibitor (CCP-224) prevents neutrophil-platelet aggregation in Sickle Cell Disease. Blood Adv 2017, 1, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Flage, B.; Weidert, F.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F. P-selectin plays a role in haem-induced acute lung injury in sickle mice. British journal of haematology 2019, 186, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbotosho, O.T.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Kato, G.J. The Worst Things in Life are Free: The Role of Free Heme in Sickle Cell Disease. Frontiers in immunology 2020, 11, 561917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, G.J.; Steinberg, M.H.; Gladwin, M.T. Intravascular hemolysis and the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. The Journal of clinical investigation 2017, 127, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Kanias, T.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B. Hemolysis and cell-free hemoglobin drive an intrinsic mechanism for human disease. J Clin Invest 2012, 122, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F. Erythroid DAMPs drive inflammation in SCD. Blood 2014, 123, 3689–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, D.; Fuchs, T.A.; Manwani, D.; Wagner, D.D.; Frenette, P.S. Heme-induced neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to the pathogenesis of sickle cell disease. Blood 2014, 123, 3818–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rank, B.H.; Carlsson, J.; Hebbel, R.P. Abnormal redox status of membrane-protein thiols in sickle erythrocytes. J Clin Invest 1985, 75, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, C.D.; Wang, X.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Hogg, N.; Cannon, R.O., 3rd; Schechter, A.N.; Gladwin, M.T. Cell-free hemoglobin limits nitric oxide bioavailability in sickle-cell disease. Nat Med 2002, 8, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.M.; Sysol, J.R.; Singla, S.; Smith, P.; Sandusky, G.E.; Wang, H.; Natarajan, V.; Dudek, S.M.; Machado, R.F. Cortactin loss protects against hemin-induced acute lung injury in sickle cell disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2022, 322, L890–L97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adisa, O.A.; Hu, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Aryee, D.; Osunkwo, I.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F. Association between plasma free haem and incidence of vaso-occlusive episodes and acute chest syndrome in children with sickle cell disease. British journal of haematology 2013, 162, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, C.J.; Boulet, S.L.; Ellingsen, D.; Pyle, M.E.; Barron-Casella, E.A.; Casella, J.F.; Payne, A.B.; Driggers, J.; Trau, H.A.; Yang, G.; Jones, K.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Hooper, W.C.; DeBaun, M.R. Heme oxygenase-1 gene promoter polymorphism is associated with reduced incidence of acute chest syndrome among children with sickle cell disease. Blood 2012, 120, 3822–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Adisa, O.A.; Chappa, P.; Tan, F.; Jackson, K.A.; Archer, D.R.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F. Extracellular hemin crisis triggers acute chest syndrome in sickle mice. The Journal of clinical investigation 2013, 123, 4809–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hazra, R.; Ihunnah, C.A.; Weidert, F.; Flage, B.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F. Augmented NRF2 activation protects adult sickle mice from lethal acute chest syndrome. British journal of haematology 2018, 182, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alishlash, A.S.; Sapkota, M.; Ahmad, I.; Maclin, K.; Ahmed, N.A.; Molyvdas, A.; Doran, S.; Albert, C.J.; Aggarwal, S.; Ford, D.A.; Ambalavanan, N.; Jilling, T.; Matalon, S. Chlorine inhalation induces acute chest syndrome in humanized sickle cell mouse model and ameliorated by postexposure hemopexin. Redox Biol 2021, 44, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, O.S.; Brambilla, D.J.; Rosse, W.F.; Milner, P.F.; Castro, O.; Steinberg, M.H.; Klug, P.P. Mortality in sickle cell disease. Life expectancy and risk factors for early death. N Engl J Med 1994, 330, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, F.; Bachir, D.; Inamo, J.; Lionnet, F.; Driss, F.; Loko, G.; Habibi, A.; Bennani, S.; Savale, L.; Adnot, S.; Maitre, B.; Yaici, A.; Hajji, L.; O'Callaghan, D.S.; Clerson, P.; Girot, R.; Galacteros, F.; Simonneau, G. A hemodynamic study of pulmonary hypertension in sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med 2011, 365, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, R.I.; Lanzkron, S. T DC;DeCastro, L.; Desai, A.A.; Ataga, K.I.; Cohen, R.T.; Haynes, J.; Osunkwo, I.; Lebensburger, J.D.; Lash, J.P.; Wun, T.; Verhovsek, M.; Ontala, E.; Blaylark, R.; Alahdab, F.; Katabi, A.; Mustafa, R.A. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for sickle cell disease: cardiopulmonary and kidney disease. Blood advances 2019, 3, 3867–3897. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adedeji, M.O.; Cespedes, J.; Allen, K.; Subramony, C.; Hughson, M.D. Pulmonary thrombotic arteriopathy in patients with sickle cell disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2001, 125, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.C.; Gladwin, M.T.; Straub, A.C. Sickle cell disease: at the crossroads of pulmonary hypertension and diastolic heart failure. Heart 2020, 106, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redinus, K.; Baek, J.H.; Yalamanoglu, A.; Shin, H.K.H.; Moldova, R.; Harral, J.W.; Swindle, D.; Pak, D.; Ferguson, S.K.; Nuss, R.; Hassell, K.; Nozik-Grayck, E.; Palmer, A.F.; Fini, M.A.; Karoor, V.; Stenmark, K.R.; Buehler, P.W.; Irwin, D.C. An Hb-mediated circulating macrophage contributing to pulmonary vascular remodeling in sickle cell disease. JCI Insight.
- Buehler, P.W.; Swindle, D.; Pak, D.I.; Fini, M.A.; Hassell, K.; Nuss, R.; Wilkerson, R.B.; D'Alessandro, A.; Irwin, D.C. Murine models of sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia demonstrate pulmonary hypertension with distinctive features. Pulm Circ 2021, 11, 20458940211055996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.L.; Champion, H.C.; Campbell-Lee, S.A.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Manci, E.A.; Diwan, B.A.; Schimel, D.M.; Cochard, A.E.; Wang, X.; Schechter, A.N.; Noguchi, C.T.; Gladwin, M.T. Hemolysis in sickle cell mice causes pulmonary hypertension due to global impairment in nitric oxide bioavailability. Blood 2007, 109, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Barst, R.J.; Castro, O.L.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Hillery, C.A.; Kato, G.J.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B.; Machado, R.; Morris, C.R.; Steinberg, M.H.; Vichinsky, E.P. Pulmonary hypertension and NO in sickle cell. Blood 2010, 116, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minneci, P.C.; Deans, K.J.; Zhi, H.; Yuen, P.S.; Star, R.A.; Banks, S.M.; Schechter, A.N.; Natanson, C.; Gladwin, M.T.; Solomon, S.B. Hemolysis-associated endothelial dysfunction mediated by accelerated NO inactivation by decompartmentalized oxyhemoglobin. J Clin Invest 2005, 115, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.R.; Kato, G.J.; Poljakovic, M.; Wang, X.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Sachdev, V.; Hazen, S.L.; Vichinsky, E.P.; Morris, S.M., Jr.; Gladwin, M.T. Dysregulated arginine metabolism, hemolysis-associated pulmonary hypertension, and mortality in sickle cell disease. JAMA 2005, 294, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, C.; Wang, X.; Tanus-Santos, J.; Hogg, N.; Cannon Rr Schechter, A.; MT, G. Cell-free hemoglobin limits nitric oxide bioavailability in sickle-cell disease. Nat Med 2002, 8, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.M.; Ferrige, A.G.; Moncada, S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 1987, 327, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Li, L.; Kitazawa, T. Cyclic GMP causes Ca2+ desensitization in vascular smooth muscle by activating the myosin light chain phosphatase. J Biol Chem 1997, 272, 5063–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, C.B.; Souza, L.E.; Leonardo, F.C.; Costa, F.T.; Werneck, C.C.; Covas, D.T.; Costa, F.F.; Conran, N. Acute hemolytic vascular inflammatory processes are prevented by nitric oxide replacement or a single dose of hydroxyurea. Blood 2015, 126, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, A.J.; Chang, S.S.; Park, C.; Lee, C.M.; Benza, R.L.; Passineau, M.J.; Ma, J.; Archer, D.R.; Sutliff, R.L.; Hart, C.M.; Kang, B.Y. PPARgamma increases HUWE1 to attenuate NF-kappaB/p65 and sickle cell disease with pulmonary hypertension. Blood Adv 2021, 5, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Shiva, S.; Ifedigbo, E.; Mathier, M.A.; Mollen, K.P.; Rao, J.; Bauer, P.M.; Choi, J.J.; Curtis, E.; Choi, A.M.; Gladwin, M.T. Nitrite potently inhibits hypoxic and inflammatory pulmonary arterial hypertension and smooth muscle proliferation via xanthine oxidoreductase-dependent nitric oxide generation. Circulation 2010, 121, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, K.C.; Durgin, B.G.; Schmidt, H.M.; Hahn, S.A.; Baust, J.J.; Bachman, T.; Vitturi, D.A.; Ghosh, S.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Mora, A.L.; Gladwin, M.T.; Straub, A.C. Smooth muscle cytochrome b5 reductase 3 deficiency accelerates pulmonary hypertension development in sickle cell mice. Blood advances 2019, 3, 4104–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potoka, K.P.; Wood, K.C.; Baust, J.J.; Bueno, M.; Hahn, S.A.; Vanderpool, R.R.; Bachman, T.; Mallampalli, G.M.; Osei-Hwedieh, D.O.; Schrott, V.; Sun, B.; Bullock, G.C.; Becker-Pelster, E.M.; Wittwer, M.; Stampfuss, J.; Mathar, I.; Stasch, J.P.; Truebel, H.; Sandner, P.; Mora, A.L.; Straub, A.C.; Gladwin, M.T. Nitric Oxide-Independent Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation Improves Vascular Function and Cardiac Remodeling in Sickle Cell Disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2018, 58, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataga, K.I.; Moore, C.G.; Hillery, C.A.; Jones, S.; Whinna, H.C.; Strayhorn, D.; Sohier, C.; Hinderliter, A.; Parise, L.V.; Orringer, E.P. Coagulation activation and inflammation in sickle cell disease-associated pulmonary hypertension. Haematologica 2008, 93, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, J.; Holbert, K.; Czysz, K.; George, J.; Fernandes, C.; Fraidenburg, D.R. Hemin-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction and Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Chronic Hemolysis. Int J Mol Sci.
- Wang, X.; Mendelsohn, L.; Rogers, H.; Leitman, S.; Raghavachari, N.; Yang, Y.; Yau, Y.; Tallack, M.; Perkins, A.; Taylor, J.; Noguchi, C.; Kato, G. Heme-bound iron activates placenta growth factor in erythroid cells via erythroid Krüppel-like factor. Blood 124, 946–954. [CrossRef]
- Kapetanaki, M.G.; Gbotosho, O.T.; Sharma, D.; Weidert, F.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Kato, G.J. Free heme regulates placenta growth factor through NRF2-antioxidant response signaling. Free radical biology & medicine 2019, 143, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, V.K.; Zhang, S.; Malik, P.; Tahara, S.M. Placenta growth factor mediated gene regulation in sickle cell disease. Blood reviews 2018, 32, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, N.; Tailor, A.; Mendelsohn, L.; Wansapura, J.; Wang, X.; Higashimoto, T.; Pauciulo, M.W.; Gottliebson, W.; Kalra, V.K.; Nichols, W.C.; Kato, G.J.; Malik, P. High levels of placenta growth factor in sickle cell disease promote pulmonary hypertension. Blood 2010, 116, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, P.W.; Swindle, D.; Pak, D.I.; Ferguson, S.K.; Majka, S.M.; Karoor, V.; Moldovan, R.; Sintas, C.; Black, J.; Gentinetta, T.; Buzzi, R.M.; Vallelian, F.; Wassmer, A.; Edler, M.; Bain, J.; Schu, D.; Hassell, K.; Nuss, R.; Schaer, D.J.; Irwin, D.C. Hemopexin dosing improves cardiopulmonary dysfunction in murine sickle cell disease. Free radical biology & medicine 2021, 175, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Minniti, C.P.; Machado, R.F.; Coles, W.A.; Sachdev, V.; Gladwin, M.T.; Kato, G.J. Endothelin receptor antagonists for pulmonary hypertension in adult patients with sickle cell disease. British journal of haematology 2009, 147, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, N.A.; Conrey, A.; Lewis, D.; Mehari, A. Riociguat use in sickle cell related chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A case series. Pulm Circ 2018, 8, 2045894018791802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.F.; Martyr, S.; Kato, G.J.; Barst, R.J.; Anthi, A.; Robinson, M.R.; Hunter, L.; Coles, W.; Nichols, J.; Hunter, C.; Sachdev, V.; Castro, O.; Gladwin, M.T. Sildenafil therapy in patients with sickle cell disease and pulmonary hypertension. Br J Haematol 2005, 130, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer-Bour, C.; Ruhl, A.P.; Nouraie, S.M.; Emeh, R.O.; Ruopp, N.F.; Thein, S.L.; Weir, N.A.; Klings, E.S. Long-term tolerability of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors in pulmonary hypertension of sickle cell disease. Eur J Haematol 2021, 107, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.P.; Streiff, M.B.; Haywood, C., Jr.; Nelson, J.A.; Lanzkron, S. Venous thromboembolism in adults with sickle cell disease: a serious and under-recognized complication. Am J Med 2013, 126, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunson, A.; Lei, A.; Rosenberg, A.S.; White, R.H.; Keegan, T.; Wun, T. Increased incidence of VTE in sickle cell disease patients: risk factors, recurrence and impact on mortality. Br J Haematol 2017, 178, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, P.D.; Beemath, A.; Meyers, F.A.; Skaf, E.; Olson, R.E. Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in hospitalized patients with sickle cell disease. Am J Med 2006, 119, 897–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, R.P.; Streiff, M.B.; Haywood, C., Jr.; Segal, J.B.; Lanzkron, S. Venous thromboembolism incidence in the Cooperative Study of Sickle Cell Disease. J Thromb Haemost 2014, 12, 2010–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollamudi, J.; Sarvepalli, S.; Vadaparti Binf, A.; Alin, T.; Little, J.A.; Nayak, L. Venous Thromboembolism in Sickle Cell Disease is Associated with Neutrophilia. Hemoglobin 2021, 45, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisuwananukorn, A.; Raslan, R.; Zhang, X.; Shah, B.N.; Han, J.; Gowhari, M.; Molokie, R.E.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Saraf, S.L. Clinical, laboratory, and genetic risk factors for thrombosis in sickle cell disease. Blood Adv 2020, 4, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Stanek, J.; Creary, S.; Dunn, A.; O'Brien, S.H. Prevalence and risk factors for venous thromboembolism in children with sickle cell disease: an administrative database study. Blood Adv 2018, 2, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, R.; Silveira, A.A.; Conran, N. Red cell DAMPs and inflammation. Inflamm Res 2016, 65, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wandersee, N.J.; Guo, Y.; Jones, D.W.; Holzhauer, S.L.; Hanson, M.S.; Machogu, E.; Brousseau, D.C.; Hogg, N.; Densmore, J.C.; Kaul, S.; Hillery, C.A.; Pritchard, K.A., Jr. Sickle cell disease increases high mobility group box 1: a novel mechanism of inflammation. Blood 2014, 124, 3978–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, S.; Arora, T.; Wang, X.; Mendelsohn, L.; Nichols, J.; Allen, D.; Shet, A.S.; Combs, C.A.; Quezado, Z.M.N.; Thein, S.L. The platelet NLRP3 inflammasome is upregulated in sickle cell disease via HMGB1/TLR4 and Bruton tyrosine kinase. Blood advances 2018, 2, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, P.; Durco, F.; Miller-Ocuin, J.L.; Takedai, T.; Shankar, S.; Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Cui, X.; Sachdev, U.; Rath, D.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Gawaz, M.; Weber, A.N.; Vogel, S. The NLRP3 inflammasome and bruton's tyrosine kinase in platelets co-regulate platelet activation, aggregation, and in vitro thrombus formation. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2017, 483, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, J.D.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, J.; Milbauer, L.; Abdulla, F.; Alayash, A.I.; Smith, A.; Nath, K.A.; Hebbel, R.P.; Vercellotti, G.M. Heme triggers TLR4 signaling leading to endothelial cell activation and vaso-occlusion in murine sickle cell disease. Blood 2014, 123, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, C.; Ilich, A.; Sotiaux, A.; Sparkenbaugh, E.M.; Henderson, M.W.; Buczek, L.; Beckman, J.D.; Ellsworth, P.; Noubouossie, D.F.; Bhoopat, L.; Piegore, M.; Renoux, C.; Bergmeier, W.; Park, Y.; Ataga, K.I.; Cooley, B.; Wolberg, A.S.; Key, N.S.; Pawlinski, R. Red blood cells modulate structure and dynamics of venous clot formation in sickle cell disease. Blood 2019, 133, 2529–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beers, E.J.; Schaap, M.C.; Berckmans, R.J.; Nieuwland, R.; Sturk, A.; van Doormaal, F.F.; Meijers, J.C.; Biemond, B.J.; group, C.s. Circulating erythrocyte-derived microparticles are associated with coagulation activation in sickle cell disease. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1513–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vats, R.; Brzoska, T.; Bennewitz, M.F.; Jimenez, M.A.; Pradhan-Sundd, T.; Tutuncuoglu, E.; Jonassaint, J.; Gutierrez, E.; Watkins, S.C.; Shiva, S.; Scott, M.J.; Morelli, A.E.; Neal, M.D.; Kato, G.J.; Gladwin, M.T.; Sundd, P. Platelet Extracellular Vesicles Drive Inflammasome-IL-1beta-Dependent Lung Injury in Sickle Cell Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2020, 201, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.P.; Mackman, N. Tissue Factor: An Essential Mediator of Hemostasis and Trigger of Thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2018, 38, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubouossie, D.F.; Whelihan, M.F.; Yu, Y.B.; Sparkenbaugh, E.; Pawlinski, R.; Monroe, D.M.; Key, N.S. In vitro activation of coagulation by human neutrophil DNA and histone proteins but not neutrophil extracellular traps. Blood 2017, 129, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovey, A.; Kollander, R.; Shet, A.; Milbauer, L.C.; Choong, S.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Blazar, B.R.; Kelm, R.J.; Jr Hebbel, R.P. Endothelial cell expression of tissue factor in sickle mice is augmented by hypoxia/reoxygenation and inhibited by lovastatin. Blood 2004, 104, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Han, H.; Cruz, M.A.; Lopez, J.A.; Dong, J.F.; Guchhait, P. Haemoglobin blocks von Willebrand factor proteolysis by ADAMTS-13: a mechanism associated with sickle cell disease. Thromb Haemost 2009, 101, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnog, J.B.; Mac Gillavry, M.R.; van Zanten, A.P.; Meijers, J.C.; Rojer, R.A.; Duits, A.J.; ten Cate, H.; Brandjes, D.P. Protein C and S and inflammation in sickle cell disease. Am J Hematol 2004, 76, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelihan, M.F.; Lim, M.Y.; Mooberry, M.J.; Piegore, M.G.; Ilich, A.; Wogu, A.; Cai, J.; Monroe, D.M.; Ataga, K.I.; Mann, K.G.; Key, N.S. Thrombin generation and cell-dependent hypercoagulability in sickle cell disease. J Thromb Haemost 2016, 14, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavins, F.N.; Russell, J.; Senchenkova, E.L.; De Almeida Paula, L.; Damazo, A.S.; Esmon, C.T.; Kirchhofer, D.; Hebbel, R.P.; Granger, D.N. Mechanisms of enhanced thrombus formation in cerebral microvessels of mice expressing hemoglobin-S. Blood 2011, 117, 4125–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Massberg, S. Demystifying the prothrombotic role of NETs. Blood 2017, 129, 925–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.A.; Dampier, C.; Varlotta, L.; Allen, J.L. Airway hyperreactivity in children with sickle cell disease. J Pediatr 1997, 131, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendramini, E.C.; Vianna, E.O.; De Lucena Ethngulo, I.; De Castro, F.B.; Martinez, J.A.B.; Terra-Filho, J. Lung function and airway hyperresponsiveness in adult patients with sickle cell disease. Am J Med Sci 2006, 332, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Barron-Casella, E.A.; Strunk, R.C.; Hamilton, R.G.; Casella, J.F.; DeBaun, M.R. Elevation of IgE in children with sickle cell disease is associated with doctor diagnosis of asthma and increased morbidity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011, 127, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, J.J.; Horst, J.; Strunk, R.C.; White, F.V.; DeBaun, M.R. Death due to asthma in two adolescents with sickle cell disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiymo Mwa Mpollo, M.S.; Brandt, E.B.; Shanmukhappa, S.K.; Arumugam, P.I.; Tiwari, S.; Loberg, A.; Pillis, D.; Rizvi, T.; Lindsey, M.; Jonck, B.; Carmeliet, P.; Kalra, V.K.; Le Cras, T.D.; Ratner, N.; Wills-Karp, M.; Hershey, G.K.; Malik, P. Placenta growth factor augments airway hyperresponsiveness via leukotrienes and IL-13. The Journal of clinical investigation 2016, 126, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postma, D.S.; Kerstjens, H.A. Characteristics of airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998, 158, S187–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D.G.; Irvin, C.G. Mechanisms of airway hyper-responsiveness in asthma: the past, present and yet to come. Clin Exp Allergy 2015, 45, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills-Karp, M.; Luyimbazi, J.; Xu, X.; Schofield, B.; Neben, T.Y.; Karp, C.L.; Donaldson, D.D. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 1998, 282, 2258–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andemariam, B.; Adami, A.J.; Singh, A.; McNamara, J.T.; Secor, E.R.; Guernsey, L.A.; Thrall, R.S. The sickle cell mouse lung: proinflammatory and primed for allergic inflammation. Transl Res 2015, 166, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandedkar, S.D.; Feroah, T.R.; Hutchins, W.; Weihrauch, D.; Konduri, K.S.; Wang, J.; Strunk, R.C.; DeBaun, M.R.; Hillery, C.A.; Pritchard, K.A. Histopathology of experimentally induced asthma in a murine model of sickle cell disease. Blood 2008, 112, 2529–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niss, O.; Fleck, R.; Makue, F.; Alsaied, T.; Desai, P.; Towbin, J.A.; Malik, P.; Taylor, M.D.; Quinn, C.T. Association between diffuse myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction in sickle cell anemia. Blood 2017, 130, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niss, O.; Quinn, C.T.; Lane, A.; Daily, J.; Khoury, P.R.; Bakeer, N.; Kimball, T.R.; Towbin, J.A.; Malik, P.; Taylor, M.D. Cardiomyopathy With Restrictive Physiology in Sickle Cell Disease. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2016, 9, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muchtar, E.; Blauwet, L.A.; Gertz, M.A. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: Genetics, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Circ Res 2017, 121, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varat, M.A.; Adolph, R.J.; Fowler, N.O. Cardiovascular effects of anemia. American heart journal 1972, 83, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoudi, N.; Lionnet, F.; Redheuil, A.; Montalescot, G. Cardiovascular manifestations of sickle cell disease. Eur Heart J 2020, 41, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, T.N. Homage to James B. Herrick: a contemporary look at myocardial infarction and at sickle-cell heart disease: the 32nd Annual Herrick Lecture of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation 2000, 101, 1874–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbotosho, O.T.; Taylor, M.; Malik, P. Cardiac pathophysiology in sickle cell disease. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparkenbaugh, E.M.; Chantrathammachart, P.; Chandarajoti, K.; Mackman, N.; Key, N.S.; Pawlinski, R. Thrombin-independent contribution of tissue factor to inflammation and cardiac hypertrophy in a mouse model of sickle cell disease. Blood 2016, 127, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, P.I.; Mullins, E.S.; Shanmukhappa, S.K.; Monia, B.P.; Loberg, A.; Shaw, M.A.; Rizvi, T.; Wansapura, J.; Degen, J.L.; Malik, P. Genetic diminution of circulating prothrombin ameliorates multiorgan pathologies in sickle cell disease mice. Blood 2015, 126, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovey, A.; Lin, Y.; Browne, P.; Choong, S.; Wayner, E.; Hebbel, R.P. Circulating activated endothelial cells in sickle cell anemia. The New England journal of medicine 1997, 337, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, S.M.; De Moraes, J.A.; Bonnin, P.; Abbyad, P.; Le Jeune, S.; Lionnet, F.; Loufrani, L.; Grimaud, L.; Lambry, J.C.; Charue, D.; Kiger, L.; Renard, J.M.; Larroque, C.; Le Clesiau, H.; Tedgui, A.; Bruneval, P.; Barja-Fidalgo, C.; Alexandrou, A.; Tharaux, P.L.; Boulanger, C.M.; Blanc-Brude, O.P. Circulating cell membrane microparticles transfer heme to endothelial cells and trigger vasoocclusions in sickle cell disease. Blood 2015, 125, 3805–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelman, N.; Selvaraj, S.K.; Batra, S.; Luck, L.R.; Erdreich-Epstein, A.; Coates, T.D.; Kalra, V.K.; Malik, P. Placenta growth factor activates monocytes and correlates with sickle cell disease severity. Blood 2003, 102, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, S.K.; Giri, R.K.; Perelman, N.; Johnson, C.; Malik, P.; Kalra, V.K. Mechanism of monocyte activation and expression of proinflammatory cytochemokines by placenta growth factor. Blood 2003, 102, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antwi-Boasiako, C.; Donkor, E.S.; Sey, F.; Dzudzor, B.; Dankwah, G.B.; Otu, K.H.; Doku, A.; Dale, C.A.; Ekem, I. Levels of Soluble Endothelium Adhesion Molecules and Complications among Sickle Cell Disease Patients in Ghana. Diseases 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarray, S.; Saleh, L.R.; Lisa Saldanha, F.; Al-Habboubi, H.H.; Mahdi, N.; Almawi, W.Y. Serum IL-6, IL-10, and TNFalpha levels in pediatric sickle cell disease patients during vasoocclusive crisis and steady state condition. Cytokine 2015, 72, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbotosho, O.T.; Ghosh, S.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Lin, Y.; Weidert, F.; Bullock, G.C.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Kato, G.J. Cardiac expression of HMOX1 and PGF in sickle cell mice and haem-treated wild type mice dominates organ expression profiles via Nrf2 (Nfe2l2). British journal of haematology 2019, 187, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, A.; Puliyel, M.; Pepe, A.; Berdoukas, V.; Coates, T.D.; Wood, J.C. Cardiac iron overload in sickle-cell disease. American journal of hematology 2014, 89, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, A.H.J.; Benites, B.D.; Fertrin, K.Y. Myocardial Iron Overload in Sickle Cell Disease: A Rare But Potentially Fatal Complication of Transfusion. Transfus Med Rev 2019, 33, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparkenbaugh, E.; Pawlinski, R. Interplay between coagulation and vascular inflammation in sickle cell disease. British journal of haematology 2013, 162, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantrathammachart, P.; Mackman, N.; Sparkenbaugh, E.; Wang, J.G.; Parise, L.V.; Kirchhofer, D.; Key, N.S.; Pawlinski, R. Tissue factor promotes activation of coagulation and inflammation in a mouse model of sickle cell disease. Blood 2012, 120, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewerchin, M.; Carmeliet, P. PlGF: a multitasking cytokine with disease-restricted activity. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine.
- Carnevale, D.; Cifelli, G.; Mascio, G.; Madonna, M.; Sbroggio, M.; Perrino, C.; Persico, M.G.; Frati, G.; Lembo, G. Placental growth factor regulates cardiac inflammation through the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3/tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme axis: crucial role for adaptive cardiac remodeling during cardiac pressure overload. Circulation 2011, 124, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accornero, F.; van Berlo, J.H.; Benard, M.J.; Lorenz, J.N.; Carmeliet, P.; Molkentin, J.D. Placental growth factor regulates cardiac adaptation and hypertrophy through a paracrine mechanism. Circ Res 2011, 109, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwama, H.; Uemura, S.; Naya, N.; Imagawa, K.; Takemoto, Y.; Asai, O.; Onoue, K. Cardiac expression of placental growth factor predicts the improvement of chronic phase left ventricular function in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006, 47, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolakowski, S., Jr.; Berry, M.F.; Atluri, P.; Grand, T.; Fisher, O.; Moise, M.A.; Cohen, J.; Hsu, V.; Woo, Y.J. Placental growth factor provides a novel local angiogenic therapy for ischemic cardiomyopathy. Journal of cardiac surgery 2006, 21, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, M.; Uemura, S.; Takeda, Y.; Samejima, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Tsushima, H.; Hoshino, E.; Ueda, T.; Morimoto, K.; Okamoto, K.; Okada, S.; Onoue, K.; Okayama, S.; Kawata, H.; Kawakami, R.; Maruyama, N.; Akai, Y.; Iwano, M.; Shiiki, H.; Saito, Y. Placental Growth Factor as a Predictor of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with CKD from the NARA-CKD Study. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN 2015, 26, 2871–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbotosho, O.T.; Ghosh, S.; Kapetanaki, M.G.; Lin, Y.; Weidert, F.; Bullock, G.C.; Ofori-Acquah, S.F.; Kato, G.J. Cardiac expression of HMOX1 and PGF in sickle cell mice and haem-treated wild type mice dominates organ expression profiles via Nrf2 (Nfe2l2). British journal of haematology 2019, 187, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Sachdev, V. Cardiovascular abnormalities in sickle cell disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012, 59, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.C.; Kirkham, F.J.; Redline, S.; Rosen, C.L.; Yan, Y.; Roberts, I.; Gruenwald, J.; Marek, J.; DeBaun, M.R. Left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction in children with sickle cell disease are related to asleep and waking oxygen desaturation. Blood 2010, 116, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaied, T.; Niss, O.; Powell, A.W.; Fleck, R.J.; Cnota, J.F.; Chin, C.; Malik, P.; Quinn, C.T.; Taylor, M.D. Diastolic dysfunction is associated with exercise impairment in patients with sickle cell anemia. Pediatric blood & cancer 2018, 65, e27113. [Google Scholar]
- Sachdev, V.; Machado, R.F.; Shizukuda, Y.; Rao, Y.N.; Sidenko, S.; Ernst, I.; St Peter, M.; Coles, W.A.; Rosing, D.R.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Castro, O.; Kato, G.J.; Gladwin, M.T. Diastolic dysfunction is an independent risk factor for death in patients with sickle cell disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007, 49, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, V.; Kato, G.J.; Gibbs, J.S.; Barst, R.J.; Machado, R.F.; Nouraie, M.; Hassell, K.L.; Little, J.A.; Schraufnagel, D.E.; Krishnamurti, L.; Novelli, E.M.; Girgis, R.E.; Morris, C.R.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; Badesch, D.B.; Lanzkron, S.; Castro, O.L.; Taylor JGt Hannoush, H.; Goldsmith, J.C.; Gladwin, M.T.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Walk, P.I. Echocardiographic markers of elevated pulmonary pressure and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction are associated with exercise intolerance in adults and adolescents with homozygous sickle cell anemia in the United States and United Kingdom. Circulation 2011, 124, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.G. Cardiac Arrhythmias: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatments. Cell Biochem Biophys 2015, 73, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, R.M.; Tedrow, U.B.; Koplan, B.A.; Albert, C.M.; Epstein, L.M.; Sweeney, M.O.; Miller, A.L.; Michaud, G.F.; Stevenson, W.G. Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Lancet 2012, 380, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Bansod, S.; Patel, U. Nationwide prevalence and trends in acute cardiovascular events and in-hospital mortality among adult African Americans with sickle cell trait. Annals of hematology 2020, 99, 2207–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzhugh, C.D.; Lauder, N.; Jonassaint, J.C.; Telen, M.J.; Zhao, X.; Wright, E.C.; Gilliam, F.R.; De Castro, L.M. Cardiopulmonary complications leading to premature deaths in adult patients with sickle cell disease. American journal of hematology 2010, 85, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manci, E.A.; Culberson, D.E.; Yang, Y.M.; Gardner, T.M.; Powell, R.; Haynes, J., Jr.; Shah, A.K.; Mankad, V.N. Causes of death in sickle cell disease: an autopsy study. British journal of haematology 2003, 123, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbari, D.; Kple-Faget, P.; Kwagyan, J.; Rana, S.; Gordeuk, V.; Castro, O. Circumstances of death in adult sickle cell disease patients. Am J Hematol 2006, 81, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Fei, Y.D.; Kim, T.Y.; Xie, A.; Batai, K.; Greener, I.; Tang, H.; Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Juneman, E.; Indik, J.H.; Shi, G.; Christensen, J.; Gupta, G.; Hillery, C.; Kansal, M.M.; Parikh, D.S.; Zhou, T.; Yuan, J.X.; Kanthi, Y.; Bronk, P.; Koren, G.; Kittles, R.; Duarte, J.D.; Garcia, J.G.N.; Machado, R.F.; Dudley, S.C.; Choi, B.R.; Desai, A.A. IL-18 mediates sickle cell cardiomyopathy and ventricular arrhythmias. Blood 2021, 137, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.A.; Patel, A.R.; Ahmad, H.; Groth, J.V.; Thiruvoipati, T.; Turner, K.; Yodwut, C.; Czobor, P.; Artz, N.; Machado, R.F.; Garcia, J.G.N.; Lang, R.M. Mechanistic insights and characterization of sickle cell disease-associated cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2014, 7, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, T.N.; Riddick, L.; Massing, G.K. Sickle cells and sudden death: morphologic abnormalities of the cardiac conduction system. J Lab Clin Med 1994, 124, 507–520. [Google Scholar]
- Bakeer, N.; James, J.; Roy, S.; Wansapura, J.; Shanmukhappa, S.K.; Lorenz, J.N.; Osinska, H.; Backer, K.; Huby, A.C.; Shrestha, A.; Niss, O.; Fleck, R.; Quinn, C.T.; Taylor, M.D.; Purevjav, E.; Aronow, B.J.; Towbin, J.A.; Malik, P. Sickle cell anemia mice develop a unique cardiomyopathy with restrictive physiology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016, 113, E5182–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niss, O.; Detterich, J.; Wood, J.C.; Coates, T.D.; Malik, P.; Taylor, M.D.; Quinn, C.T. Early initiation of disease-modifying therapy can impede or prevent diffuse myocardial fibrosis in sickle cell anemia. Blood 2022, 140, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, O.S. Sickle cell anemia as an inflammatory disease. The Journal of clinical investigation 2000, 106, 337–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belcher, J.D.; Marker, P.H.; Weber, J.P.; Hebbel, R.P.; Vercellotti, G.M. Activated monocytes in sickle cell disease: potential role in the activation of vascular endothelium and vaso-occlusion. Blood 2000, 96, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathare, A.; Al Kindi, S.; Alnaqdy, A.A.; Daar, S.; Knox-Macaulay, H.; Dennison, D. Cytokine profile of sickle cell disease in Oman. American journal of hematology 2004, 77, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Nakamura, S.; Saito, Y.; Kosugi, M.; Magata, Y. What can be seen by 18F-FDG PET in atherosclerosis imaging? The effect of foam cell formation on 18F-FDG uptake to macrophages in vitro. J Nucl Med 2012, 53, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Friera, L.; Fuster, V.; Lopez-Melgar, B.; Oliva, B.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, J.; Macias, A.; Perez-Asenjo, B.; Zamudio, D.; Alonso-Farto, J.C.; Espana, S.; Mendiguren, J.; Bueno, H.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Ibanez, B.; Fernandez-Ortiz, A.; Sanz, J. Vascular Inflammation in Subclinical Atherosclerosis Detected by Hybrid PET/MRI. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019, 73, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Disease complication | Major contributors | Potential novel treatments that may target major inflammatory/anti-inflammatory pathways | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS) | Free heme, heme oxygenase (HMOX-1), neutrophils and platelet interactions, p-selectin | Glyco-protein Ibalpha inhibitor (CCP-224) [24] D3T (3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione) [37] Hemopexin [38] |
Anea [24], Jimenez [25], Ghosh [26], Bean [36], Ghosh [37], Ghosh [38], Alishlash [39] |
| 2. Pulmonary hypertension | Endothelial dysfunction, hemolysis, decreased NO, increased placenta growth factor (PIGF), PPAR alpha and PPAR gamma | Hemopexin [38] BAY 54-654455 |
Jang [53], Wood [55], Gonzales [58], Hsu [47], Morris [50] Perelman [109], Selvaraj [110], Potoka [56], Buehler [63] |
| 3. Pulmonary thrombosis | NETs, DAMPs, tissue factor upregulation, lower protein S and C endothelial dysfunction | Anti-TF antibody | Sparkenbaugh [105] Whelihan [85] Faes [77] Solovey [82] |
| 4. Cardiac hypertrophy | ROS, endothelial dysfunction, hemolysis, hypercoagulation, PIGF, IL-6, heme, | Rivaroxaban [104] | Sparkenbaugh [104] Bakeer [137] Gbotosho [16] Menon [14] Arumugam [106] |
| 5. Diastolic dysfunction and cardiac arrhythmia | IL-18, FUCA-2 | Anti-IL-18 binding protein [133] | Duarte [11] Gupta [134] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





