Submitted:
31 January 2023
Posted:
02 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Matrix Exopolysaccharides of P. aeruginosa biofilms
2.1. Psl and Pel
2.2. Alginate
3. Therapies
3.1. Matrix degrading enzymes
3.2. Other novel strategies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maisetta, G.; Grassi, L.; Esin, S.; Kaya, E.; Morelli, A.; Puppi, D.; Piras, M.; Chiellini, F.; Pifferi, M.; Batoni, G. Targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Sputum of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Patients with a Combinatorial Strategy Having Antibacterial and Anti-Virulence Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papi, A.; Bellettato, C.M.; Braccioni, F.; Romagnoli, M.; Casolari, P.; Caramori, G.; Fabbri, L.M.; Johnston, S.L. Infections and Airway Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Severe Exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, L.R.; Isabella, V.M.; Lewis, K. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms in Disease. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Hooper, D.C. Hospital-Acquired Infections Due to Gram-Negative Bacteria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltz, D.A.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Welsh, M.J. Origins of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoli, D.H.; Jones, C.J.; Wozniak, D.J. Bacterial Extracellular Polysaccharides in Biofilm Formation and Function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, J.C.; Ruseska, I.; Wright, J.B.; Costerton, J.W. Tobramycin Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cells Growing as a Biofilm on Urinary Catheter Material. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1985, 27, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thöming, J.G.; Häussler, S. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Is More Tolerant Under Biofilm Than Under Planktonic Growth Conditions: A Multi-Isolate Survey. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, B. Interactions between Neutrophils and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis. Pathogens 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.L.; Burns, J.L.; Ramsey, B.W. Pathophysiology and Management of Pulmonary Infections in Cystic Fibrosis. 2012, 168, 918–951. [CrossRef]
- Lund-Palau, H.; Turnbull, A.R.; Bush, A.; Bardin, E.; Cameron, L.; Soren, O.; Wierre-Gore, N.; Alton, E.W.F.W.; Bundy, J.G.; Connett, G.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Cystic Fibrosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2016, 10, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Barat, L.; Ciofu, O.; Kragh, K.N.; Pressler, T.; Johansen, U.; Motos, A.; Torres, A.; Hoiby, N. Phenotypic Shift in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Populations from Cystic Fibrosis Lungs after 2-Week Antipseudomonal Treatment. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antimicrobial Resistance: Risk Associated with Antibiotic Overuse and Initiatives to Reduce the Problem. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowat, E.; Paterson, S.; Fothergill, J.L.; Wright, E.A.; Ledson, M.J.; Walshaw, M.J.; Brockhurst, M.A.; Winstanley, C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Population Diversity and Turnover in Cystic Fibrosis Chronic Infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P.; Tulkens, P.M. Aminoglycosides: Nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Patient Registry: 2021 Annual Data Report. Bethesda, MD. 2022.
- Fainardi, V.; Neglia, C.; Muscarà, M.; Spaggiari, C.; Tornesello, M.; Grandinetti, R.; Argentiero, A.; Calderaro, A.; Esposito, S.; Pisi, G. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Children and Adolescents with Cystic Fibrosis. Children 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Montgomery, M. Dornase Alfa for Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunders, E.; Welch, M. Matrix Exopolysaccharides; the Sticky Side of Biofilm Formation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Conover, M.; Lu, H.; Parsek, M.R.; Bayles, K.; Wozniak, D.J. Assembly and Development of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Matrix. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Camper, A.K.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Costerton, J.W.; Davies, D.G. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Displays Multiple Phenotypes during Development as a Biofilm. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.; Falcone, M.; Molin, S.; Johansen, H.K. High-Resolution in Situ Transcriptomics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Unveils Genotype Independent Patho-Phenotypes in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs. Nat. Commun. 2018 91 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordes, A.; Grahl, N.; Koska, M.; Preusse, M.; Arce-Rodriguez, A.; Abraham, W.R.; Kaever, V.; Häussler, S. Establishment of an Induced Memory Response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa during Infection of a Eukaryotic Host. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2018–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, K.; Stoodley, P.; Goeres, D.M.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Burmølle, M.; Stewart, P.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. The Biofilm Life Cycle: Expanding the Conceptual Model of Biofilm Formation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022 2010 2022, 20, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Lu, H.; Sprinkle, A.; Parsek, M.R.; Wozniak, D.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Psl Is a Galactose- and Mannose-Rich Exopolysaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wozniak, D.J. Regulation of Biofilm Exopolysaccharide Biosynthesis and Degradation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 76, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, P.; Whitfield, G.B.; Hill, P.J.; Little, D.J.; Pestrak, M.J.; Robinson, H.; Wozniak, D.J.; Howell, P.L. Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Glycoside Hydrolase PslG Reveals That Its Levels Are Critical for Psl Polysaccharide Biosynthesis and Biofilm Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28374–28387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, M.S.; Sadovskaya, I.; Vinogradov, E.; Lu, H.; Sprinkle, A.B.; Richardson, S.H.; Ma, L.; Ralston, B.; Parsek, M.R.; Anderson, E.M.; et al. Genetic and Biochemical Analyses of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Psl Exopolysaccharide Reveal Overlapping Roles for Polysaccharide Synthesis Enzymes in Psl and LPS Production. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 73, 622–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Tseng, B.S.; Beckerman, B.; Jin, F.; Gibiansky, M.L.; Harrison, J.J.; Luijten, E.; Parsek, M.R.; Wong, G.C.L. Psl Trails Guide Exploration and Microcolony Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Nature 2013, 497, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Parsek, M.R.; Wozniak, D.J.; Ma, L.Z. A Spider Web Strategy of Type IV Pili-Mediated Migration to Build a Fibre-like Psl Polysaccharide Matrix in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2238–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.-G.; O’Toole, G.A. C-Di-GMP and Its Effects on Biofilm Formation and Dispersion: A Pseudomonas aeruginosa Review. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, Y.; Borlee, B.R.; O’Connor, J.R.; Hill, P.J.; Harwood, C.S.; Wozniak, D.J.; Parsek, M.R. Self-Produced Exopolysaccharide Is a Signal That Stimulates Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012, 109, 20632–20636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlee, B.R.; Goldman, A.D.; Murakami, K.; Samudrala, R.; Wozniak, D.J.; Parsek, M.R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Uses a Cyclic-Di-GMP-Regulated Adhesin to Reinforce the Biofilm Extracellular Matrix. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Mauff, F.; Razvi, E.; Reichhardt, C.; Sivarajah, P.; Parsek, M.R.; Howell, P.L.; Sheppard, D.C. The Pel Polysaccharide Is Predominantly Composed of a Dimeric Repeat of α-1,4 Linked Galactosamine and N-Acetylgalactosamine. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichhardt, C.; Jacobs, H.M.; Matwichuk, M.; Wong, C.; Wozniak, D.J.; Parsek, M.R. The Versatile Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Matrix Protein CdrA Promotes Aggregation through Different Extracellular Exopolysaccharide Interactions. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Yu, S.; Wozniak, D.J.; Ma, L.Z. The Exopolysaccharide Psl–EDNA Interaction Enables the Formation of a Biofilm Skeleton in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Byrd, M.S.; Sergeant, S.; Azad, A.K.; Parsek, M.R.; McPhail, L.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Wozniak, D.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Psl Polysaccharide Reduces Neutrophil Phagocytosis and the Oxidative Response by Limiting Complement-Mediated Opsonization. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, L.K.; Storek, K.M.; Ledvina, H.E.; Coulon, C.; Marmont, L.S.; Sadovskaya, I.; Secor, P.R.; Tseng, B.S.; Scian, M.; Filloux, A.; et al. Pel Is a Cationic Exopolysaccharide That Cross-Links Extracellular DNA in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015, 112, 11353–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.J.; Jackson, L.; CW Yau, Y.; Reichhardt, C.; Beaudoin, T.; Uwumarenogie, S.; Guttman, K.M.; Lynne Howell, P.; Parsek, M.R.; Hoffman, L.R.; et al. The Role of Psl in the Failure to Eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.J.; Yau, Y.C.W.; Park, S.; Eisha, S.; McDonald, N.; Parsek, M.R.; Howell, P.L.; Hoffman, L.R.; Nguyen, D.; DiGiandomenico, A.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aggregation and Psl Expression in Sputum Is Associated with Antibiotic Eradication Failure in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Sci. Reports 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.J.; Wozniaka, D.J. Psl Produced by Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Contributes to the Establishment of Biofilms and Immune Evasion. MBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, H.K.; Kwon, T.; Zlosnik, J.E.A.; Speert, D.P.; Marcotte, E.M.; Whiteley, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enhances Production of a Non-Alginate Exopolysaccharide during Long-Term Colonization of the Cystic Fibrosis Lung. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Parsek, M.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The Roles of Biofilm Matrix Polysaccharide Psl in Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.; Kolter, R. Genes Involved in Matrix Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 Biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, D.J.; Wyckoff, T.J.O.; Starkey, M.; Keyser, R.; Azadi, P.; O’Toole, G.A.; Parsek, M.R. Alginate Is Not a Significant Component of the Extracellular Polysaccharide Matrix of PA14 and PAO1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003, 100, 7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Mauff, F.; Razvi, E.; Reichhardt, C.; Sivarajah, P.; Parsek, M.R.; Howell, P.L.; Sheppard, D.C. The Pel Polysaccharide Is Predominantly Composed of a Dimeric Repeat of α-1,4 Linked Galactosamine and N-Acetylgalactosamine. Commun. Biol. 2022 51 2022, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Jackson, K.D.; Landry, R.M.; Parsek, M.R.; Wozniak, D.J. Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Conditional Psl Variants Reveals Roles for the Psl Polysaccharide in Adhesion and Maintaining Biofilm Structure Postattachment. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ulstrup, J.; Molin, S. Distinct Roles of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Development. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, K.M.; Gordon, V.D.; Murakami, K.; Borlee, B.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The Pel Polysaccharide Can Serve a Structural and Protective Role in the Biofilm Matrix of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog 2011, 7, 1001264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, L.K.; Dreifus, J.E.; Reichhardt, C.; Storek, K.M.; Secor, P.R.; Wozniak, D.J.; Hisert, K.B.; Parsek, M.R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Aggregates in Cystic Fibrosis Sputum Produce Exopolysaccharides That Likely Impede Current Therapies. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, K.M.; Irie, Y.; Tart, C.S.; Urbano, R.; Whitney, J.C.; Ryder, C.; Howell, P.L.; Wozniak, D.J.; Parsek, M.R. The Pel and Psl Polysaccharides Provide Pseudomonas aeruginosa Structural Redundancy within the Biofilm Matrix. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirisits, M.J.; Prost, L.; Starkey, M.; Parsek, M.R. Characterization of Colony Morphology Variants Isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häußler, S.; Ziegler, I.; Löttel, A.; Götz, F.V.; Rohde, M.; Wehmhöhner, D.; Saravanamuthu, S.; Tümmler, B.; Steinmetz, I. Highly Adherent Small-Colony Variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, G.L.; Krull, L.H. Characterization of the Exocellular Polysaccharides from Azotobacter Chroococcum. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 181, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fett, W.F.; Wijey, C.; Lifson, E.R. Occurrence of Alginate Gene Sequences among Members of the Pseudomonad RRNA Homology Groups I-IV. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 78, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacesa, P. Bacterial Alginate Biosynthesis - Recent Progress and Future Prospects. Microbiology 1998, 144, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, L.R.; Linker, A. Production and Characterization of the Slime Polysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1973, 116, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, L.C.; Pritchard, M.F.; Ferguson, E.L.; Powell, K.A.; Patel, S.U.; Rye, P.D.; Sakellakou, S.M.; Buurma, N.J.; Brilliant, C.D.; Copping, J.M.; et al. Targeted Disruption of the Extracellular Polymeric Network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Alginate Oligosaccharides. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2018, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govan, J.R.; Deretic, V. Microbial Pathogenesis in Cystic Fibrosis: Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia Cepacia. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 539–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Teitzel, G.M.; Balzer, G.J.; Heydorn, A.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Parsek, M.R. Alginate Overproduction Affects Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Structure and Function. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5395–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballmann, M.; Rabsch, P.; Von Der Hardt, H. Long-Term Follow up of Changes in FEV1 and Treatment Intensity during Pseudomonas aeruginosa Colonisation in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Thorax 1998, 53, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parad, R.B.; Gerard, C.J.; Zurakowski, D.; Nichols, D.P.; Pier, G.B. Pulmonary Outcome in Cystic Fibrosis Is Influenced Primarily by Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection and Immune Status and Only Modestly by Genotype. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R.L.; Mellis, C.M.; Petrovic, L. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is a Marker of Poor Survival in Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1992, 12, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVries, C.A.; Ohman, D.E. Mucoid-to-Nonmucoid Conversion in Alginate-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Often Results from Spontaneous Mutations in AlgT, Encoding a Putative Alternate Sigma Factor, and Shows Evidence for Autoregulation. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershberger, C.D.; Ye, R.W.; Parsek, M.R.; Xie, Z.D.; Chakrabarty, A.M. The AlgT (AlgU) Gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a Key Regulator Involved in Alginate Biosynthesis, Encodes an Alternative Sigma Factor (Sigma E). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995, 92, 7941–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, J.C.; Howell, P.L. Synthase-Dependent Exopolysaccharide Secretion in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, I.D.; Wang, Y.; Moradali, M.F.; Rehman, Z.U.; Rehm, B.H.A. Genetics and Regulation of Bacterial Alginate Production. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2997–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, R.C. Airway Surface Dehydration in Cystic Fibrosis: Pathogenesis and Therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2007, 58, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.W.; Schurr, M.J.; Mudd, M.H.; Govan, J.R.W.; Holloway, B.W.; Deretic, V. Mechanism of Conversion to Mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infecting Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1993, 90, 8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyczak, J.B.; Cannon, C.L.; Pier, G.B. Lung Infections Associated with Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 194–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvig, R.L.; Sommer, L.M.; Molin, S.; Johansen, H.K. Convergent Evolution and Adaptation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa within Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Nat. Genet. 2014 471 2014, 47, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troxler, R.B.; Hoover, W.C.; Britton, L.J.; Gerwin, A.M.; Rowe, S.M. CLEARANCE OF INITIAL MUCOID PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA IN PATIENTS WITH CYSTIC FIBROSIS. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2012, 47, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.S.; Van De Mortel, M.; Nielsen, L.; De Guzman, G.N.; Li, X.; Halverson, L.J. Alginate Production by Pseudomonas Putida Creates a Hydrated Microenvironment and Contributes to Biofilm Architecture and Stress Tolerance under Water-Limiting Conditions. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8290–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkawash, M.A.; Soothill, J.S.; Schiller, N.L. Alginate Lyase Enhances Antibiotic Killing of Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Biofilms. APMIS 2006, 114, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCaslin, C.A.; Petrusca, D.N.; Poirier, C.; Serban, K.A.; Anderson, G.G.; Petrache, I. Impact of Alginate-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa on Alveolar Macrophage Apoptotic Cell Clearance. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2015, 14, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N. Prospects for the Prevention and Control of Pseudomonal Infection in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Paediatr. Drugs 2000, 2, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, C. Early Infection and Progression of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2002, 34, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.L.; Emerson, J.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Burns, J.L.; McNamara, S.; Accurso, F.J.; Konstan, M.W.; Chatfield, B.A.; Retsch-Bogart, G.; Waltz, D.A.; et al. Duration of Treatment Effect after Tobramycin Solution for Inhalation in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2007, 42, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, S.Y.; Coakley, R.; Lau, G.W.; Lymar, S.V.; Gaston, B.; Karabulut, A.C.; Hennigan, R.F.; Hwang, S.H.; Buettner, G.; Schurr, M.J.; et al. Anaerobic Killing of Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Acidified Nitrite Derivatives under Cystic Fibrosis Airway Conditions. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Yin, H. Alginate Lyase: Review of Major Sources and Classification, Properties, Structure-Function Analysis and Applications. Bioengineered 2015, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Su, T.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, T.; Jin, Z.; Du, W.; Zhu, M.J.; Chua, S.L.; et al. PslG, a Self-Produced Glycosyl Hydrolase, Triggers Biofilm Disassembly by Disrupting Exopolysaccharide Matrix. Cell Res. 2015 2512 2015, 25, 1352–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmont, L.S.; Whitfield, G.B.; Rich, J.D.; Yip, P.; Giesbrecht, L.B.; Stremick, C.A.; Whitney, J.C.; Parsek, M.R.; Harrison, J.J.; Lynne Howell, P. PelA and PelB Proteins Form a Modification and Secretion Complex Essential for Pel Polysaccharide-Dependent Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 19411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colvin, K.M.; Alnabelseya, N.; Baker, P.; Whitney, J.C.; Lynne Howell, P.; Parsek, M.R. PelA Deacetylase Activity Is Required for Pel Polysaccharide Synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François Le Mauff, X.; Natalie Bamford, X.C.; Alnabelseya, N.; Zhang, Y.; Baker, P.; Robinson, H.; Codée, J.D.; Lynne Howell, P.; Sheppard, D.C.; Whitfield, C. Molecular Mechanism of Aspergillus Fumigatus Biofilm Disruption by Fungal and Bacterial Glycoside Hydrolases. J. Biol. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.; Hill, P.J.; Snarr, B.D.; Alnabelseya, N.; Pestrak, M.J.; Lee, M.J.; Jennings, L.K.; Tam, J.; Melnyk, R.A.; Parsek, M.R.; et al. Exopolysaccharide Biosynthetic Glycoside Hydrolases Can Be Utilized to Disrupt and Prevent Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snarr, B.D.; Baker, P.; Bamford, N.C.; Sato, Y.; Liu, H.; Lehoux, M.; Gravelat, F.N.; Ostapska, H.; Baistrocchi, S.R.; Cerone, R.P.; et al. Microbial Glycoside Hydrolases as Antibiofilm Agents with Cross-Kingdom Activity. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, J.; Zhai, C.; Ma, L.Z.; Gu, L.; Zhao, K. Effects of PslG on the Surface Movement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostapska, H.; Raju, D.; Corsini, R.; Lehoux, M.; Lacdao, I.; Gilbert, S.; Sivarajah, P.; Bamford, N.C.; Baker, P.; Gravelat, F.N.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of Recombinant Microbial Glycoside Hydrolases as Antibiofilm Agents in Acute Pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestrak, M.J.; Baker, P.; Dellos-Nolan, S.; Hill, P.J.; Passos da Silva, D.; Silver, H.; Lacdao, I.; Raju, D.; Parsek, M.R.; Wozniak, D.J.; et al. Treatment with the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Glycoside Hydrolase PslG Combats Wound Infection by Improving Antibiotic Efficacy and Host Innate Immune Activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, M.; Karakulska, J.; Sobolewski, P.; Kowalska, U.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Böttcher, D.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Drozd, R. Glycoside Hydrolase (PelAh) Immobilization Prevents Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Formation on Cellulose-Based Wound Dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorn, C.R.; Raju, D.; Lacdao, I.; Gilbert, S.; Sivarajah, P.; Howell, P.L.; Prestidge, C.A.; Thomas, N. Protective Liquid Crystal Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of PslG: A Biofilm Dispersing Enzyme. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 2102–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; He, J.; Li, N.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.; Gu, L. A Rational Designed PslG With Normal Biofilm Hydrolysis and Enhanced Resistance to Trypsin-Like Protease Digestion. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asker, D.; Awad, T.S.; Raju, D.; Sanchez, H.; Lacdao, I.; Gilbert, S.; Sivarajah, P.; Andes, D.R.; Sheppard, D.C.; Howell, P.L.; et al. Preventing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms on Indwelling Catheters by Surface-Bound Enzymes. ACS Appl. bio Mater. 2021, 4, 8248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, A.S.; Park, S.; Ramos, M.C.; Nast, C.C.; Eftekhar, F.; Schiller, N.L. Effects of Alginase on the Natural History and Antibiotic Therapy of Experimental Endocarditis Caused by Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 3979–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daboor, S.M.; Rohde, J.R.; Cheng, Z. Disruption of the Extracellular Polymeric Network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms by Alginate Lyase Enhances Pathogen Eradication by Antibiotics. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, M.; Suntres, Z.E.; Omri, A. Importance of DNase and Alginate Lyase for Enhancing Free and Liposome Encapsulated Aminoglycoside Activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspe, M.; Jensen, L.; Melegrito, J.; Sun, M. The Role of Alginate and Extracellular DNA in Biofilm-Meditated Pseudomonas aeruginosa Gentamicin Resistance. J. Exp. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 16, 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Eftekhar, F.; Speert, D.P. Alginase Treatment of Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enhances Phagocytosis by Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, B.E.; Ertesvåg, H.; Beyenal, H.; Lewandowski, Z. Resistance of Biofilms Containing Alginate-producing Bacteria to Disintegration by an Alginate Degrading Enzyme (Algl). Biofouling 2009, 17, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamppa, J.W.; Griswold, K.E. Alginate Lyase Exhibits Catalysis-Independent Biofilm Dispersion and Antibiotic Synergy. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Sunsunwal, S.; Gautam, V.; Singh, M.; Ramya, T.N.C. Biofilm Inhibitory Effect of Alginate Lyases on Mucoid P. Aeruginosa from a Cystic Fibrosis Patient. Biochem. Biophys. reports 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamppa, J.W.; Ackerman, M.E.; Lai, J.I.; Scanlon, T.C.; Griswold, K.E. Genetically Engineered Alginate Lyase-PEG Conjugates Exhibit Enhanced Function and Reduced Immunoreactivity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 17042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.K.; Tripathi, M.; Pandey, N.; Agrawal, A.K.; Gade, S.; Anjum, M.M.; Tilak, R.; Singh, S. Alginate Lyase Immobilized Chitosan Nanoparticles of Ciprofloxacin for the Improved Antimicrobial Activity against the Biofilm Associated Mucoid P. Aeruginosa Infection in Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 563, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latka, A.; Maciejewska, B.; Majkowska-Skrobek, G.; Briers, Y.; Drulis-Kawa, Z. Bacteriophage-Encoded Virion-Associated Enzymes to Overcome the Carbohydrate Barriers during the Infection Process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.W. Polysaccharide Lyases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 16, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanlon, G.W.; Denyer, S.P.; Olliff, C.J.; Ibrahim, L.J. Reduction in Exopolysaccharide Viscosity as an Aid to Bacteriophage Penetration through Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glonti, T.; Chanishvili, N.; Taylor, P.W. Bacteriophage-Derived Enzyme That Depolymerizes the Alginic Acid Capsule Associated with Cystic Fibrosis Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; He, T.; Gao, S.; Xing, S.; Huang, Y.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X.; Yu, W.; et al. Identification of a Lytic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Phage Depolymerase and Its Anti-Biofilm Effect and Bactericidal Contribution to Serum. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ph 1/2 Study Evaluating Safety and Tolerability of Inhaled AP-PA02 in Subjects With Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infections and Cystic Fibrosis. Available online: Https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Ct2/Show/NCT04596319. (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- CYstic Fibrosis BacterioPHage Study at Yale (CYPHY). Available online: Https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Ct2/Show/NCT04684641. (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Nebulized Bacteriophage Therapy in Cystic Fibrosis Patients With Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pulmonary Infection. Available online: Https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Ct2/Show/NCT05010577. (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- A Phase 1b/2 Trial of the Safety and Microbiological Activity of Bacteriophage Therapy in Cystic Fibrosis Subjects Colonized With Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Available online: Https://Clinicaltrials.Gov/Ct2/Show/NCT05453578. (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Khan, S.; Tøndervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Klinkenberg, G.; Emanuel, C.; Onsøyen, E.; Myrvold, R.; Howe, R.A.; Walsh, T.R.; Hill, K.E.; et al. Overcoming Drug Resistance with Alginate Oligosaccharides Able To Potentiate the Action of Selected Antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, M.F.; Powell, L.C.; Menzies, G.E.; Lewis, P.D.; Hawkins, K.; Wright, C.; Doull, I.; Walsh, T.R.; Onsøyen, E.; Dessen, A.; et al. A New Class of Safe Oligosaccharide Polymer Therapy To Modify the Mucus Barrier of Chronic Respiratory Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokniene, J.; Varache, M.; Rye, P.D.; Hill, K.E.; Thomas, D.W.; Ferguson, E.L. Alginate Oligosaccharides Enhance Diffusion and Activity of Colistin in a Mucin-Rich Environment. Sci. Reports 2022 121 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengzhuang, W.; Song, Z.; Ciofu, O.; Onsøyen, E.; Rye, P.D.; Høiby, N. OligoG CF-5/20 Disruption of Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm in a Murine Lung Infection Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2620–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, M.F.; Powell, L.C.; Jack, A.A.; Powell, K.; Beck, K.; Florance, H.; Forton, J.; Rye, P.D.; Dessen, A.; Hill, K.E.; et al. A Low-Molecular-Weight Alginate Oligosaccharide Disrupts Pseudomonal Microcolony Formation and Enhances Antibiotic Effectiveness. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokniene, J.; Powell, L.C.; Aarstad, O.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Rye, P.D.; Hill, K.E.; Thomas, D.W.; Ferguson, E.L. Bi-Functional Alginate Oligosaccharide–Polymyxin Conjugates for Improved Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections. Pharm. 2020, Vol. 12, Page 1080 2020, 12, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahonen, M.J.R.; Dorrier, J.M.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Antibiofilm Efficacy of Nitric Oxide-Releasing Alginates against Cystic Fibrosis Bacterial Pathogens. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koningsbruggen-Rietschel, S. van; Davies, J.C.; Pressler, T.; Fischer, R.; MacGregor, G.; Donaldson, S.H.; Smerud, K.; Meland, N.; Mortensen, J.; Fosbøl, M.Ø.; et al. Inhaled Dry Powder Alginate Oligosaccharide in Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Phase 2b Study. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00132–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Pivotal Phase IIb Clinical Trial of Inhaled Alginate Oligosaccharide (OligoG) for Cystic Fibrosis. Available online: Https://Cordis.Europa.Eu/Project/Id/755234. (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Christensen, B.E.; Ertesvag, H.; Haluk, B.; Lewandowski, Z. Biofouling Resistance of Biofilms Containing Alginate-Producing Bacteria to Disintegration by an Alginate Degrading Enzyme (Algl). 2001. [CrossRef]
- Ostapska, H.; Raju, D.; Corsini, R.; Lehoux, M.; Lacdao, I.; Gilbert, S.; Sivarajah, P.; Bamford, N.C.; Baker, P.; Gravelat, F.N.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of Recombinant Microbial Glycoside Hydrolases as Antibiofilm Agents in Acute Pulmonary Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiPuma, J.J. The Sense and Nonsense of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11 (Suppl. S2), S46–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, V.; Ratjen, F. Standard versus Biofilm Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing to Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Waters, V.; Jahnke, N.; Ratjen, F. Standard versus Biofilm Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing to Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S.; Nair, H.A.S.; Lee, K.W.K.; Ong, J.; Goh, J.Q.J.; Kjelleberg, S.; Rice, S.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Exopolysaccharides Are Important for Mixed Species Biofilm Community Development and Stress Tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudoin, T.; Yau, Y.C.W.; Stapleton, P.J.; Gong, Y.; Wang, P.W.; Guttman, D.S.; Waters, V. Staphylococcus Aureus Interaction with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilm Enhances Tobramycin Resistance. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, N.; Ramirez Millan, M.; Caldara, M.; Rusconi, R.; Tarasova, Y.; Stocker, R.; Ribbeck, K. The Extracellular Matrix Component Psl Provides Fast-Acting Antibiotic Defense in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. PLOS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, S.C.; Kundukad, B.; Seviour, T.; Van der Maarel, J.R.C.; Yang, L.; Rice, S.A.; Doyle, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Dynamic Remodeling of Microbial Biofilms by Functionally Distinct Exopolysaccharides. MBio 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoli, D.H.; Whitfield, G.B.; Kitao, T.; Ivey, M.L.; Davis, M.R.; Grahl, N.; Hogan, D.A.; Rahme, L.G.; Howell, P.L.; O’Toole, G.A.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alginate Overproduction Promotes Coexistence with Staphylococcus Aureus in a Model of Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Infection. MBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattoraj, S.S.; Murthy, R.; Ganesan, S.; Goldberg, J.B.; Zhao, Y.; Hershenson, M.B.; Sajjan, U.S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alginate Promotes Burkholderia Cenocepacia Persistence in Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Knockout Mice. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salsgiver, E.L.; Fink, A.K.; Knapp, E.A.; LiPuma, J.J.; Olivier, K.N.; Marshall, B.C.; Saiman, L. Changing Epidemiology of the Respiratory Bacteriology of Patients With Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 2016, 149, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBennett, K.A.; Davis, P.B.; Konstan, M.W. Increasing Life Expectancy in Cystic Fibrosis: Advances and Challenges. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57 (Suppl. S1), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reznikov, L.R.; Abou Alaiwa, M.H.; Dohrn, C.L.; Gansemer, N.D.; Diekema, D.J.; Stoltz, D.A.; Welsh, M.J. Antibacterial Properties of The Cftr Potentiator Ivacaftor. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, J.E.; Dubois, A.V.; Ingram, R.J.; Weldon, S.; Taggart, C.C.; Elborn, J.S.; Tunney, M.M. Activity of Innate Antimicrobial Peptides and Ivacaftor against Clinical Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Pathogens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.Y.; Lim, D.J.; Mackey, C.; Skinner, D.; Zhang, S.; McCormick, J.; Woodworth, B.A. Ivacaftor, a Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Potentiator, Enhances Ciprofloxacin Activity Against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2019, 33, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, R.V.E.; Su, V.C.H.; Quon, B.S. Real-World Safety of CFTR Modulators in the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisert, K.B.; Heltshe, S.L.; Pope, C.; Jorth, P.; Wu, X.; Edwards, R.M.; Radey, M.; Accurso, F.J.; Wolter, D.J.; Cooke, G.; et al. Restoring Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Function Reduces Airway Bacteria and Inflammation in People with Cystic Fibrosis and Chronic Lung Infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durfey, S.L.; Pipavath, S.; Li, A.; Vo, A.T.; Ratjen, A.; Carter, S.; Morgan, S.J.; Radey, M.C.; Grogan, B.; Salipante, S.J.; et al. Combining Ivacaftor and Intensive Antibiotics Achieves Limited Clearance of Cystic Fibrosis Infections. MBio 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
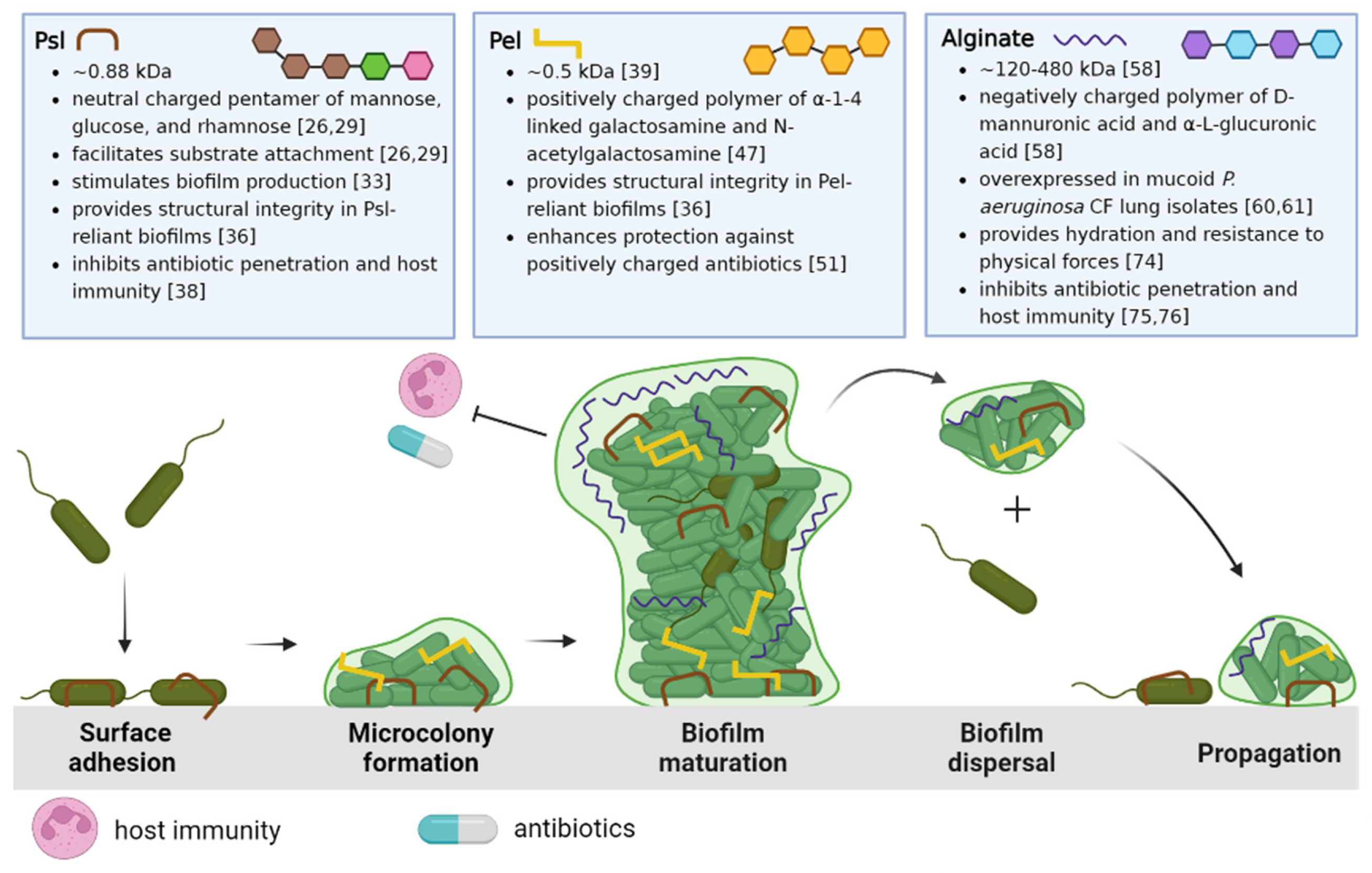
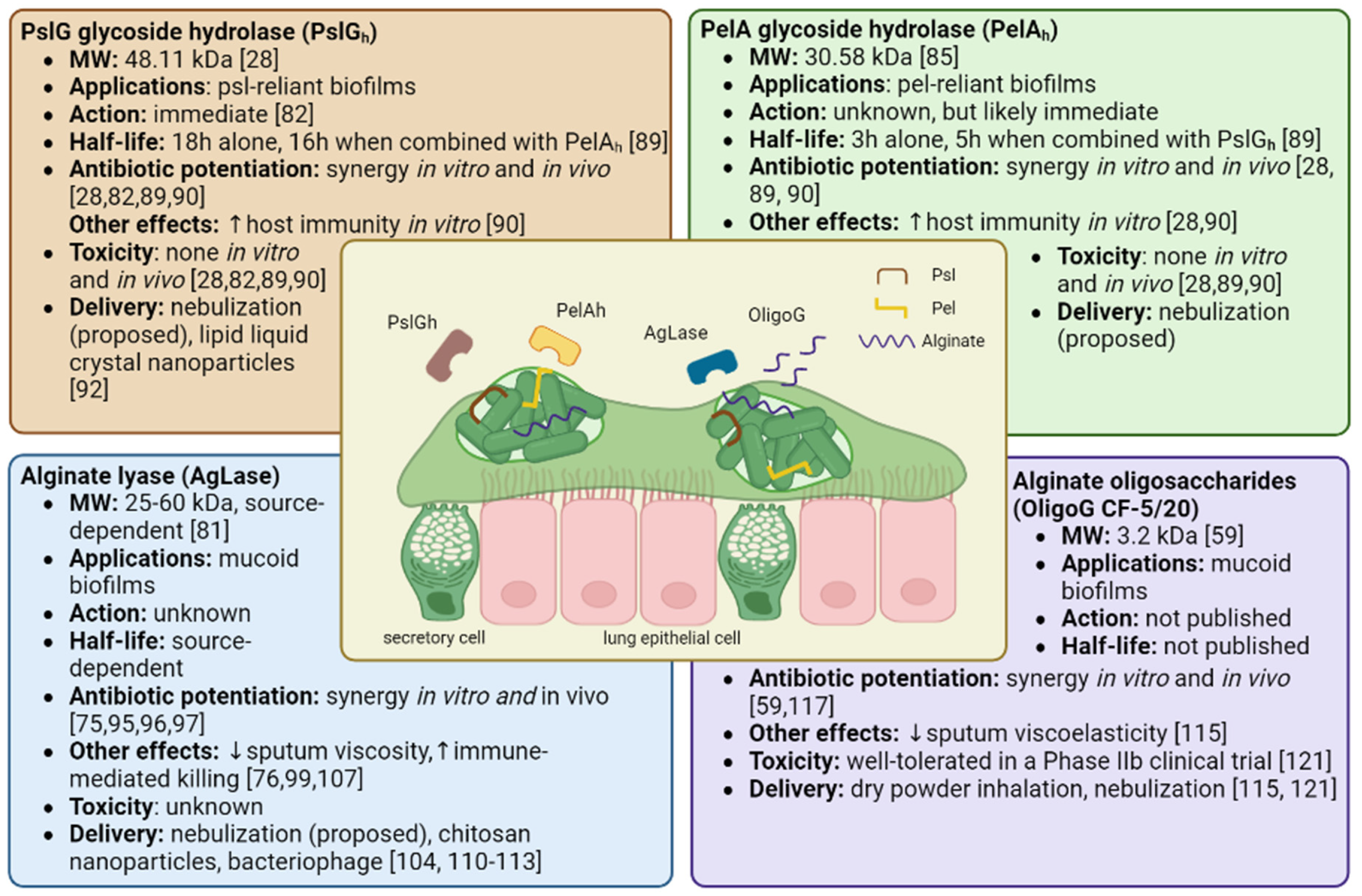
| Product | Therapeutic Challenges and Considerations |
|---|---|
| PslG glycoside hydrolase (PslGh) |
|
| PelA glycoside hydrolase (PelAh) |
|
| Alginate Lyase (AgLase) |
|
|
Alginate Oligosaccharide (OligoG, CF-5/20) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




