Submitted:
26 January 2023
Posted:
27 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
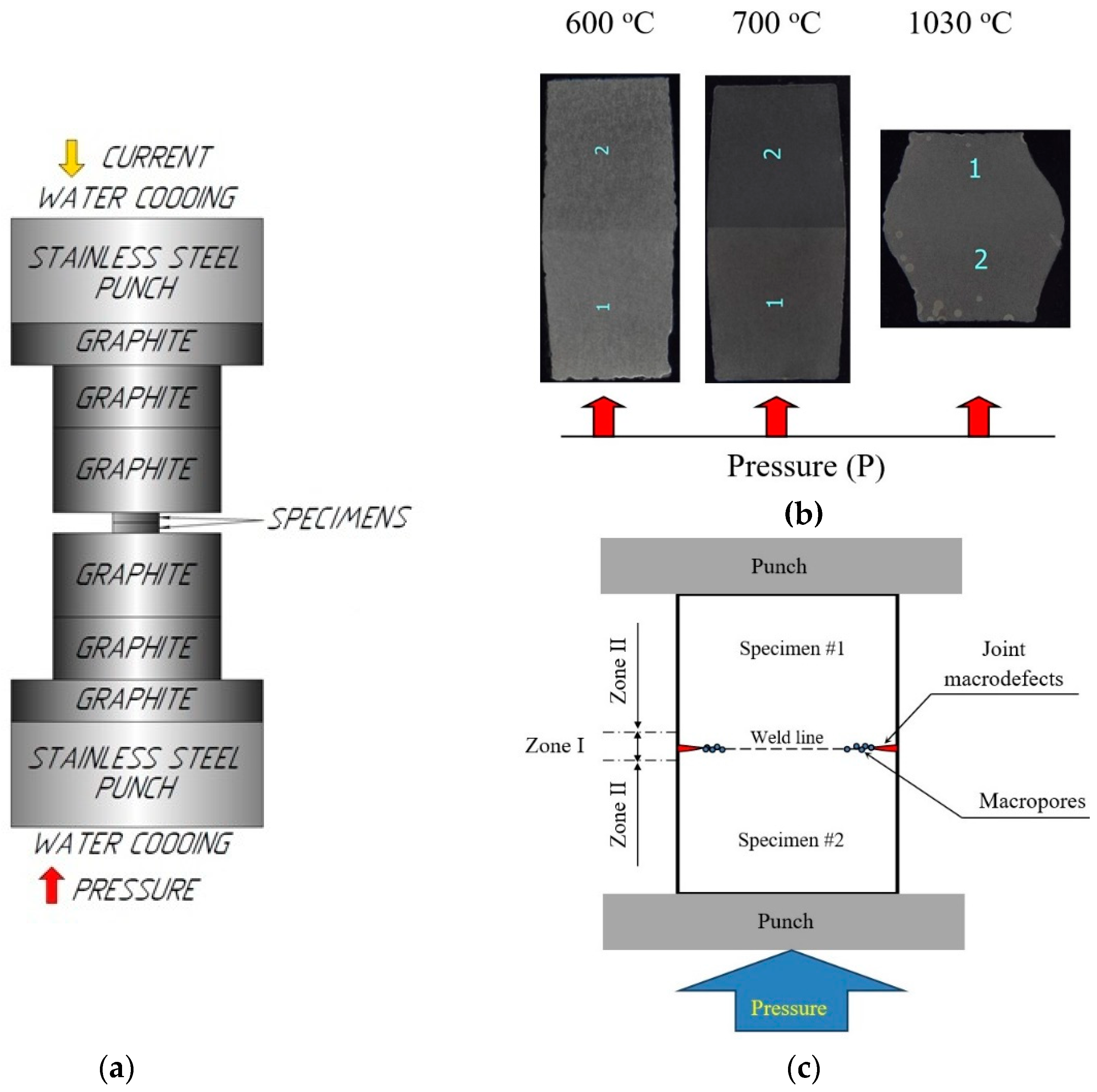
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
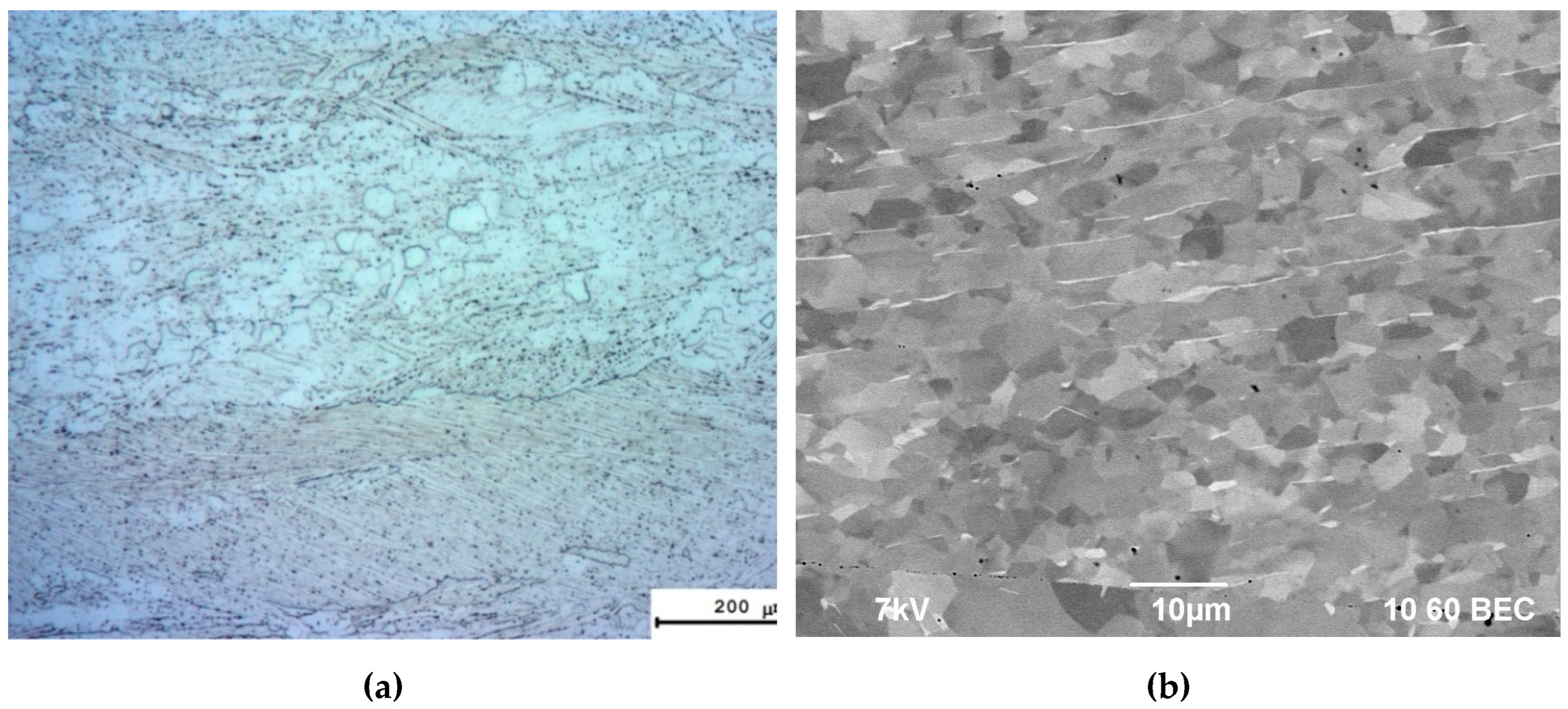
3.1. Microstructure and properties of the alloy in the initial state
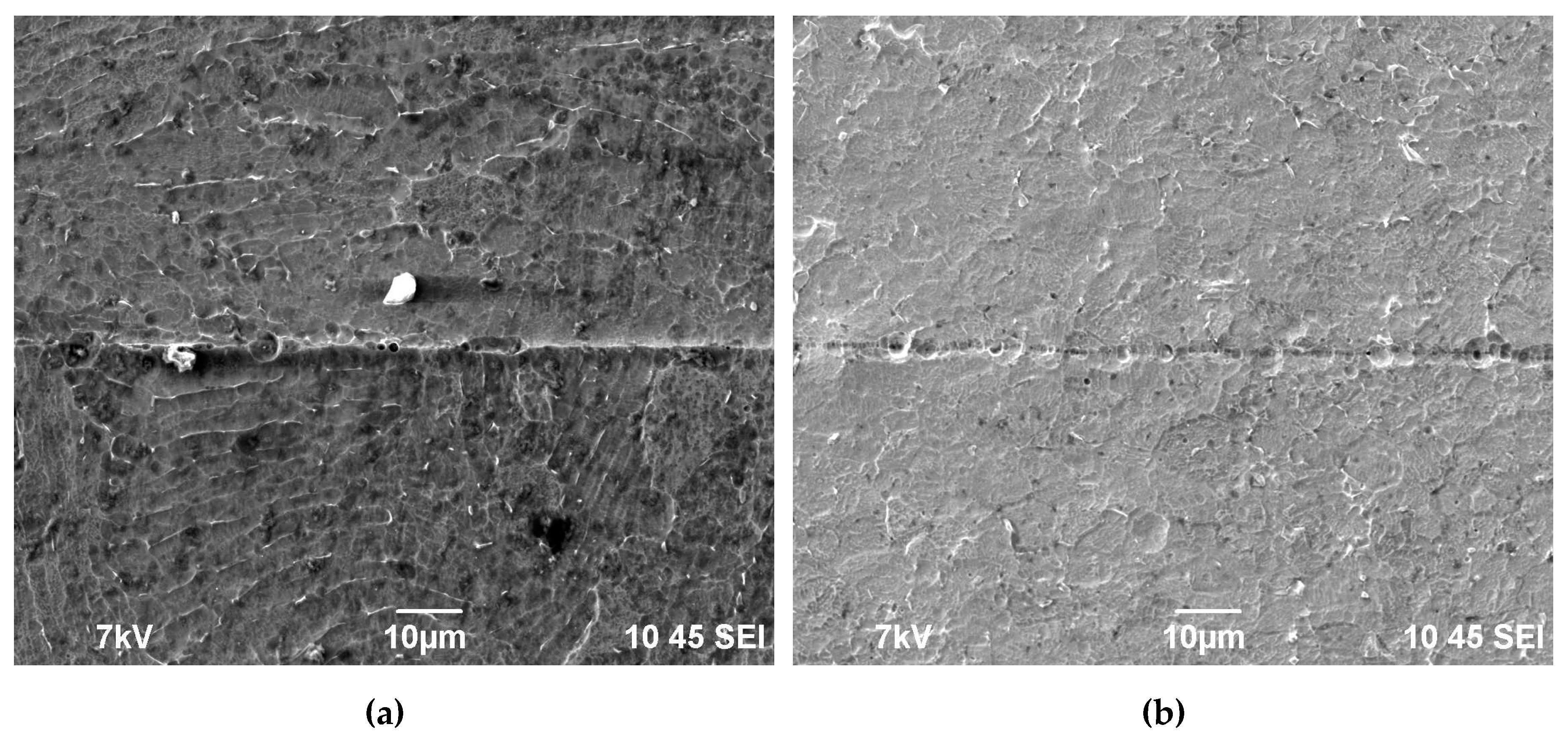
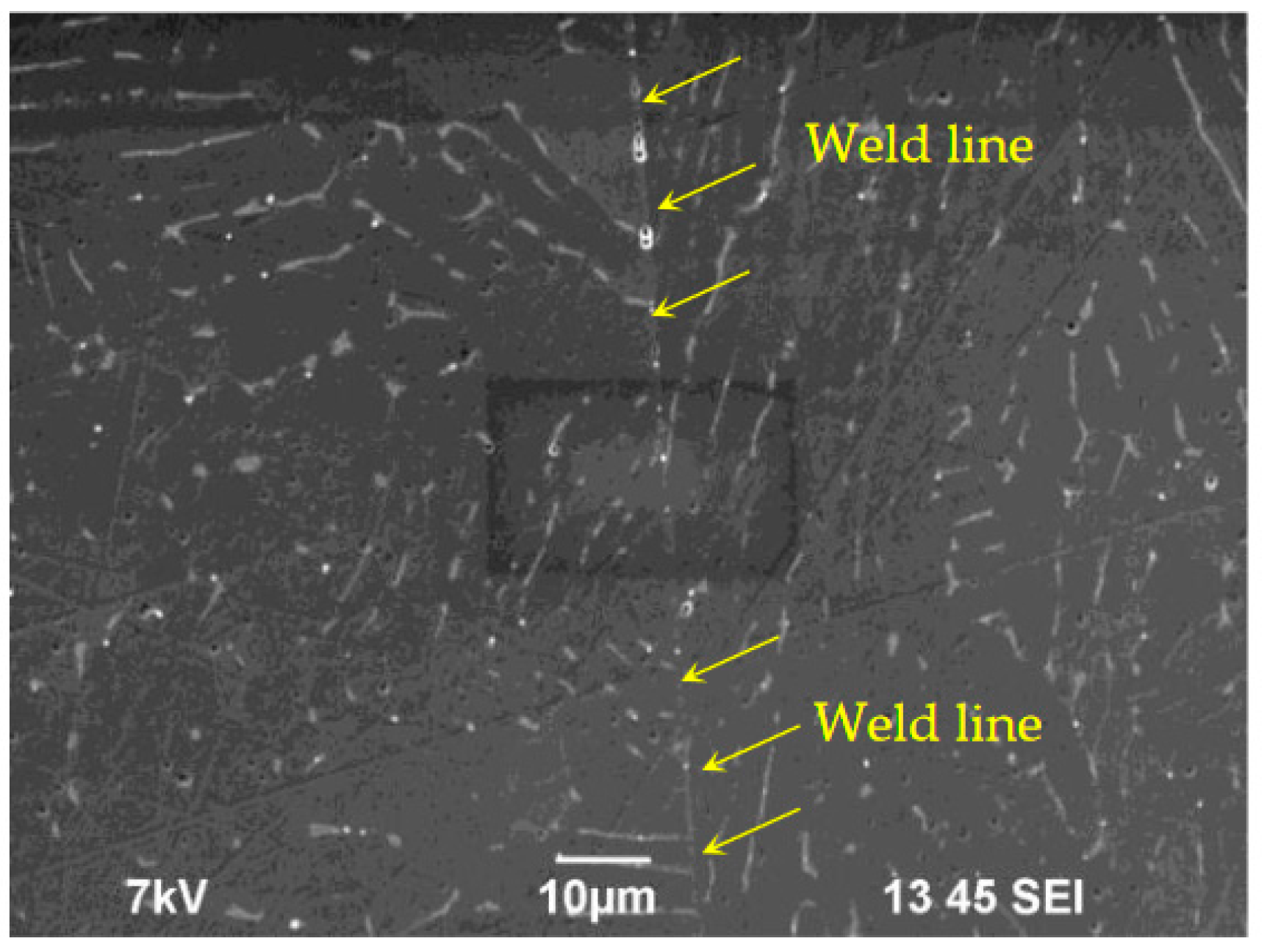
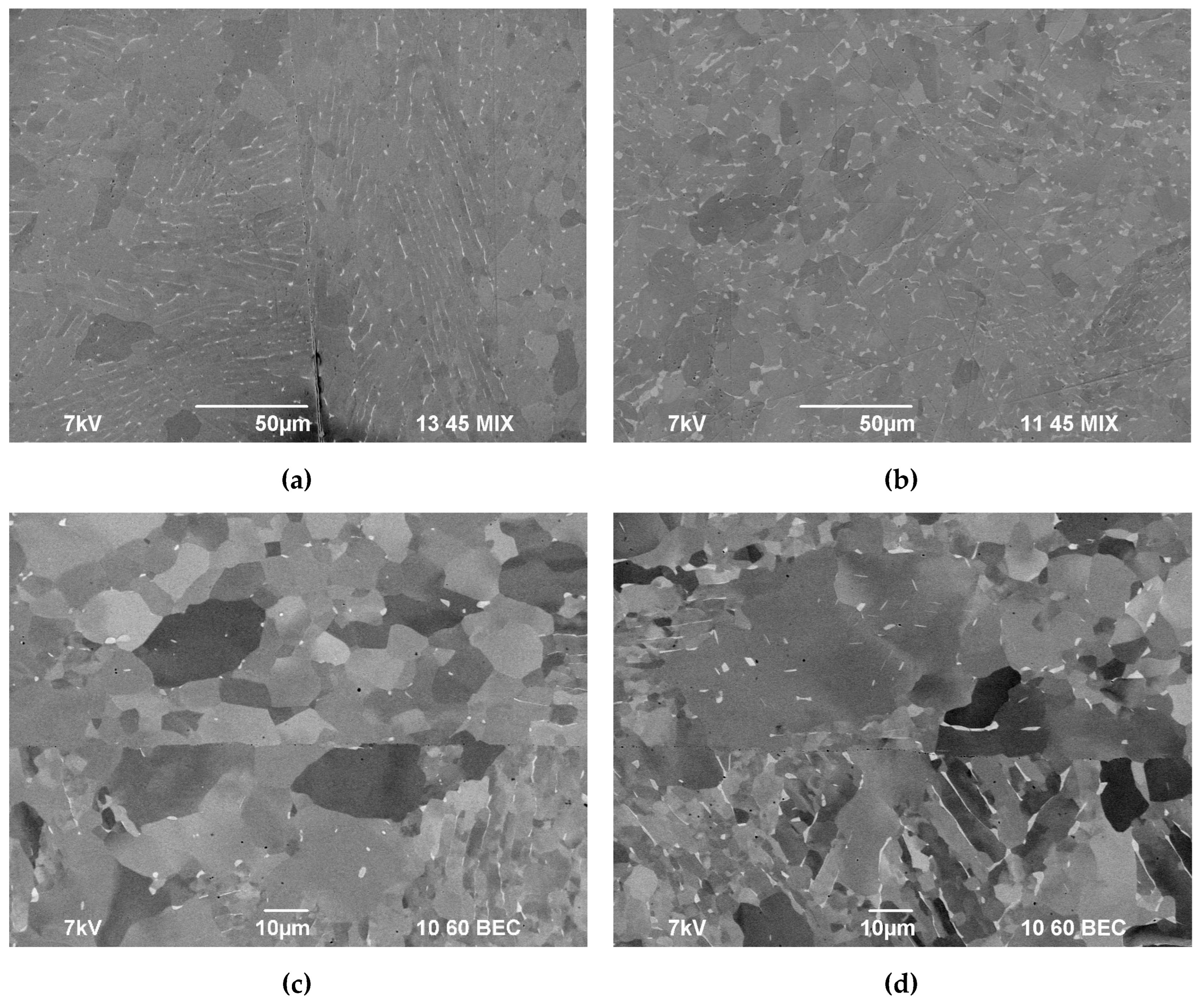
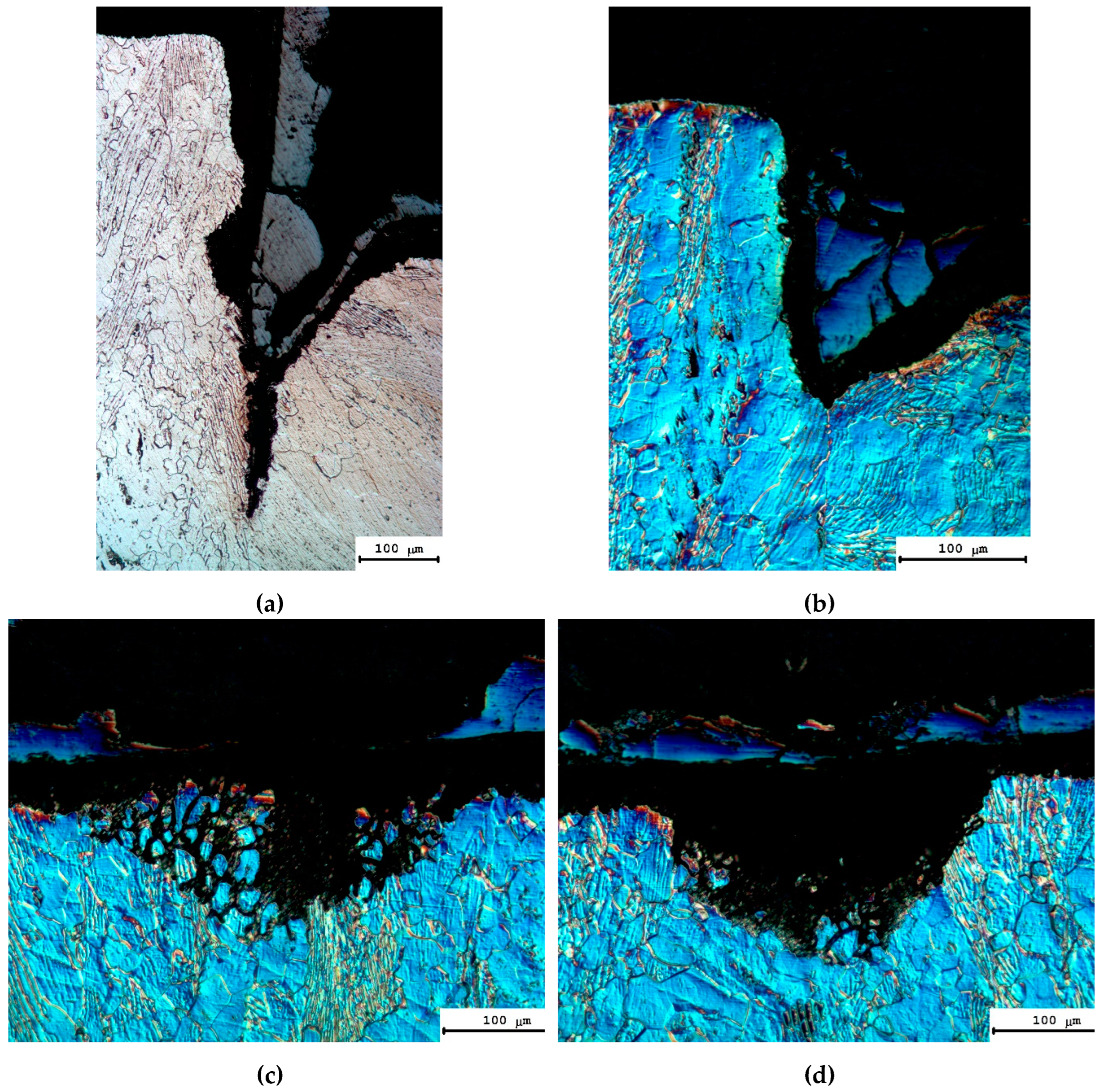
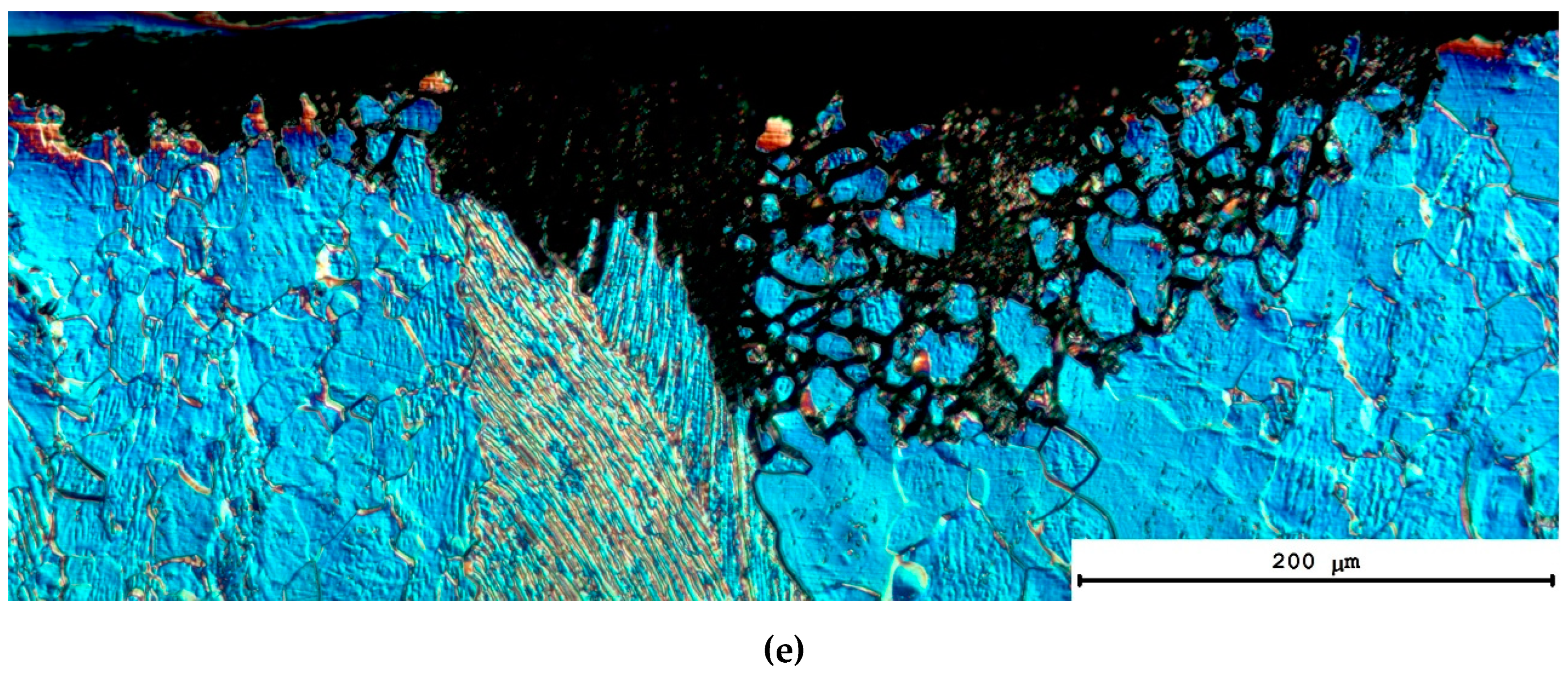
3.2. Macrostructure of the specimens after diffusion welding
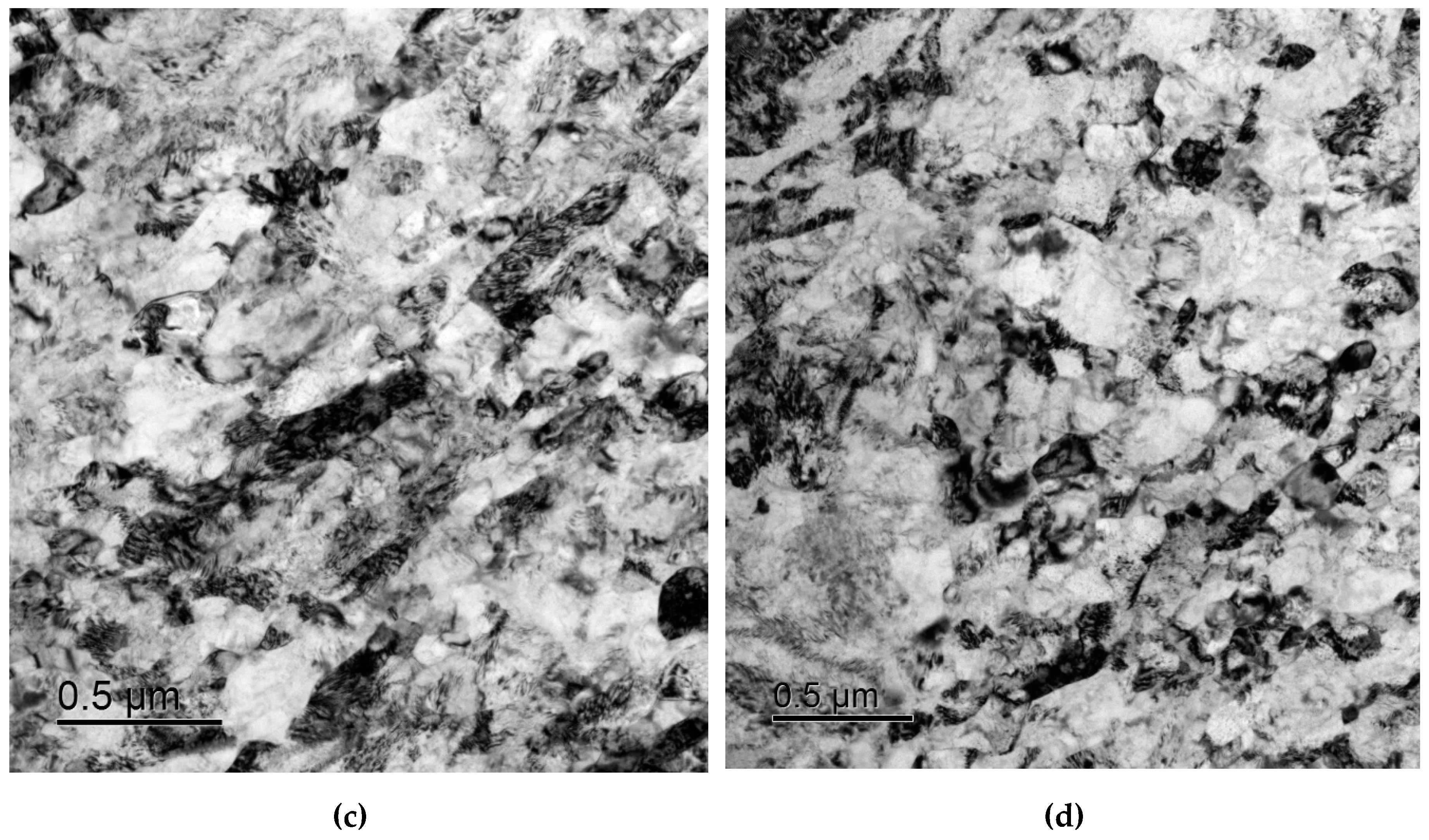
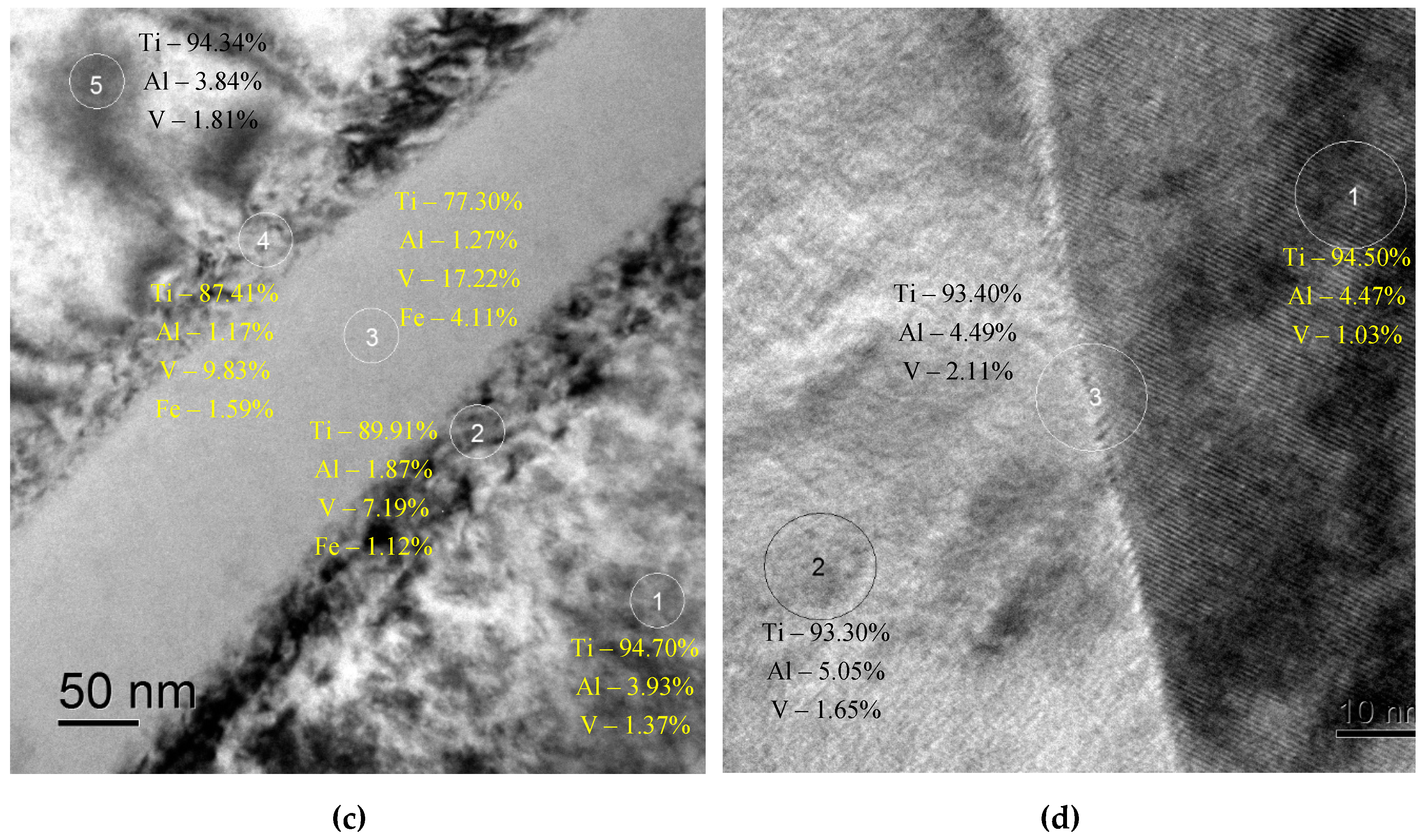
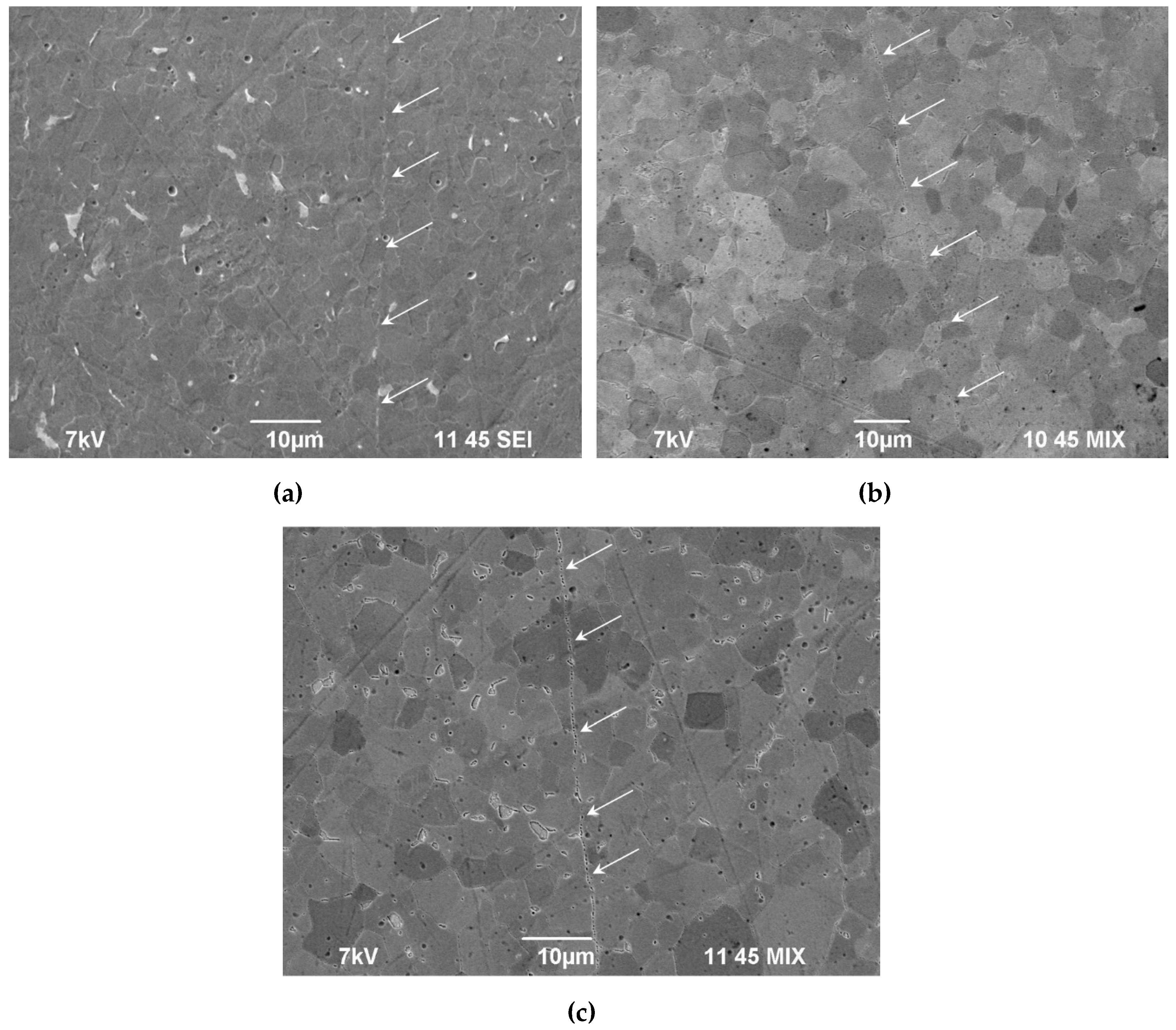
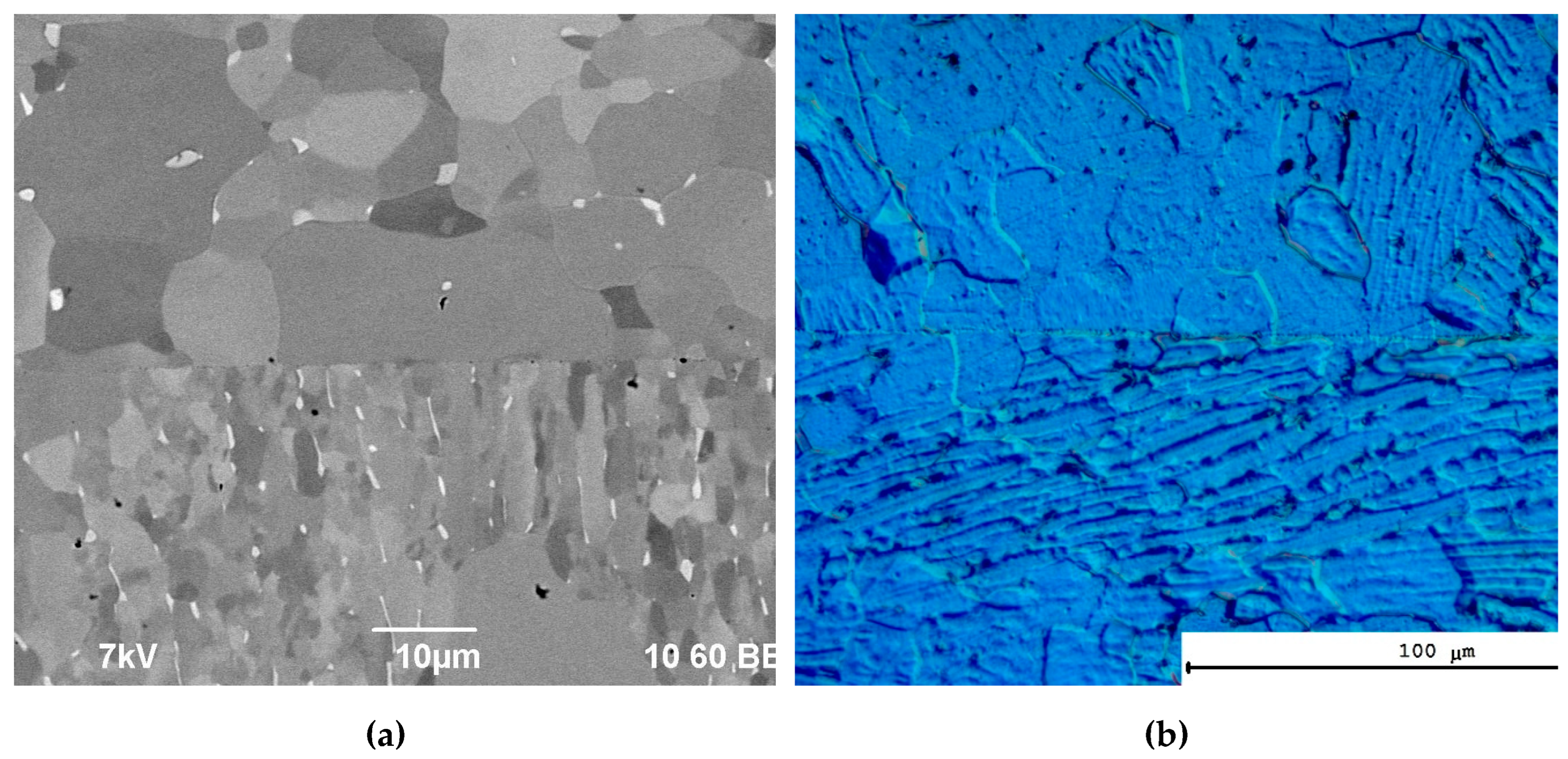
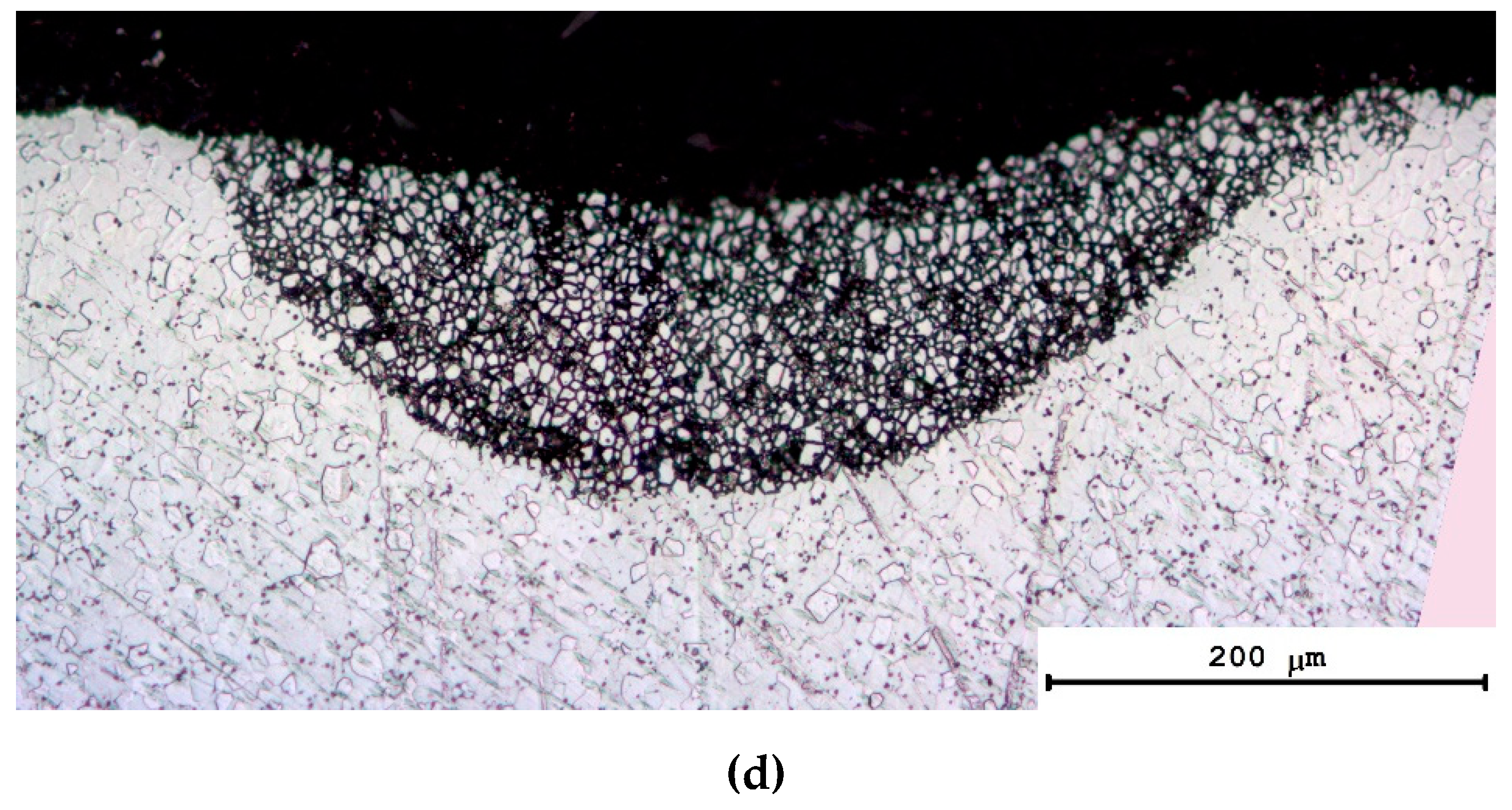
3.3. Microstructure of specimens after diffusion welding
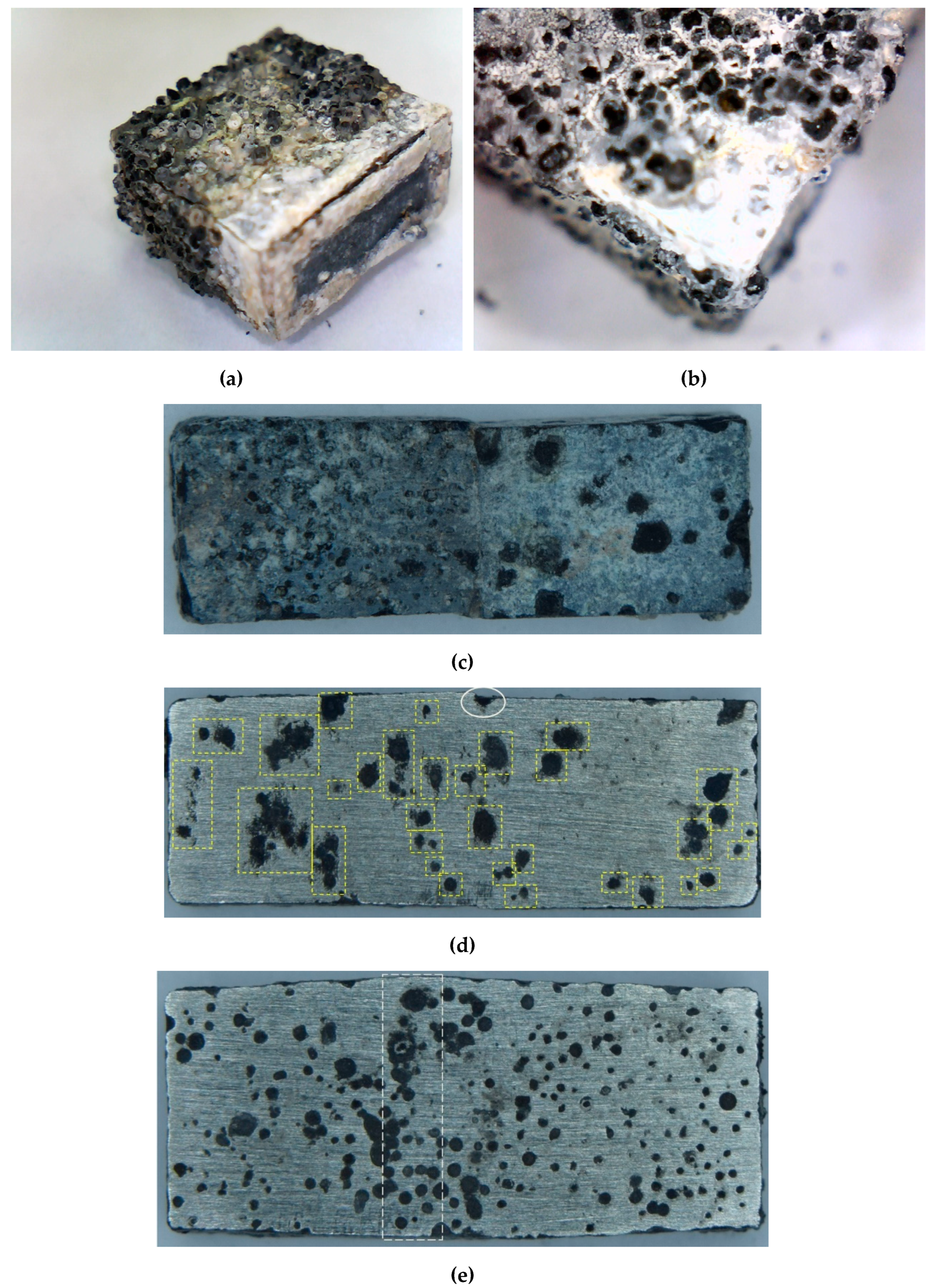
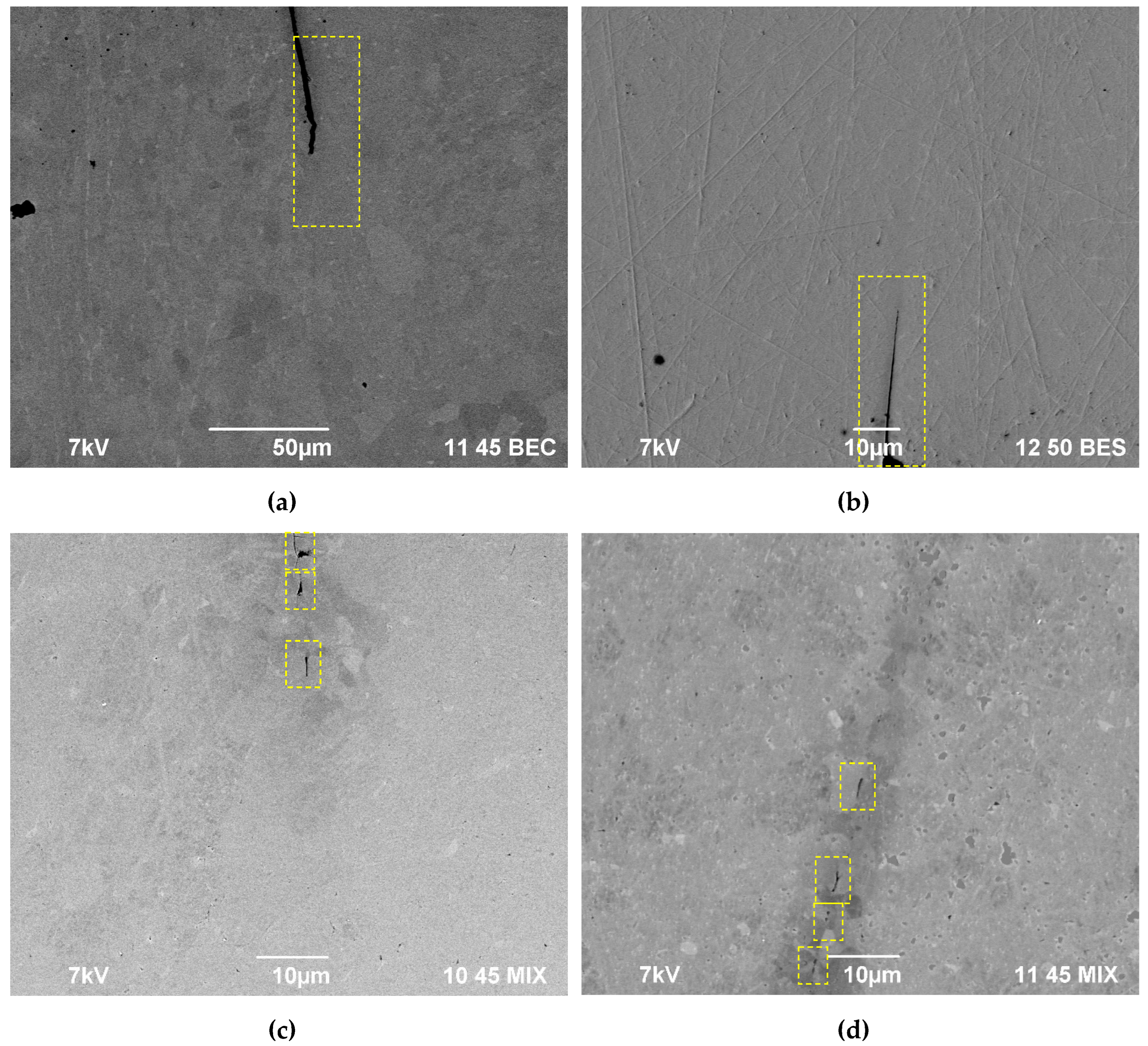
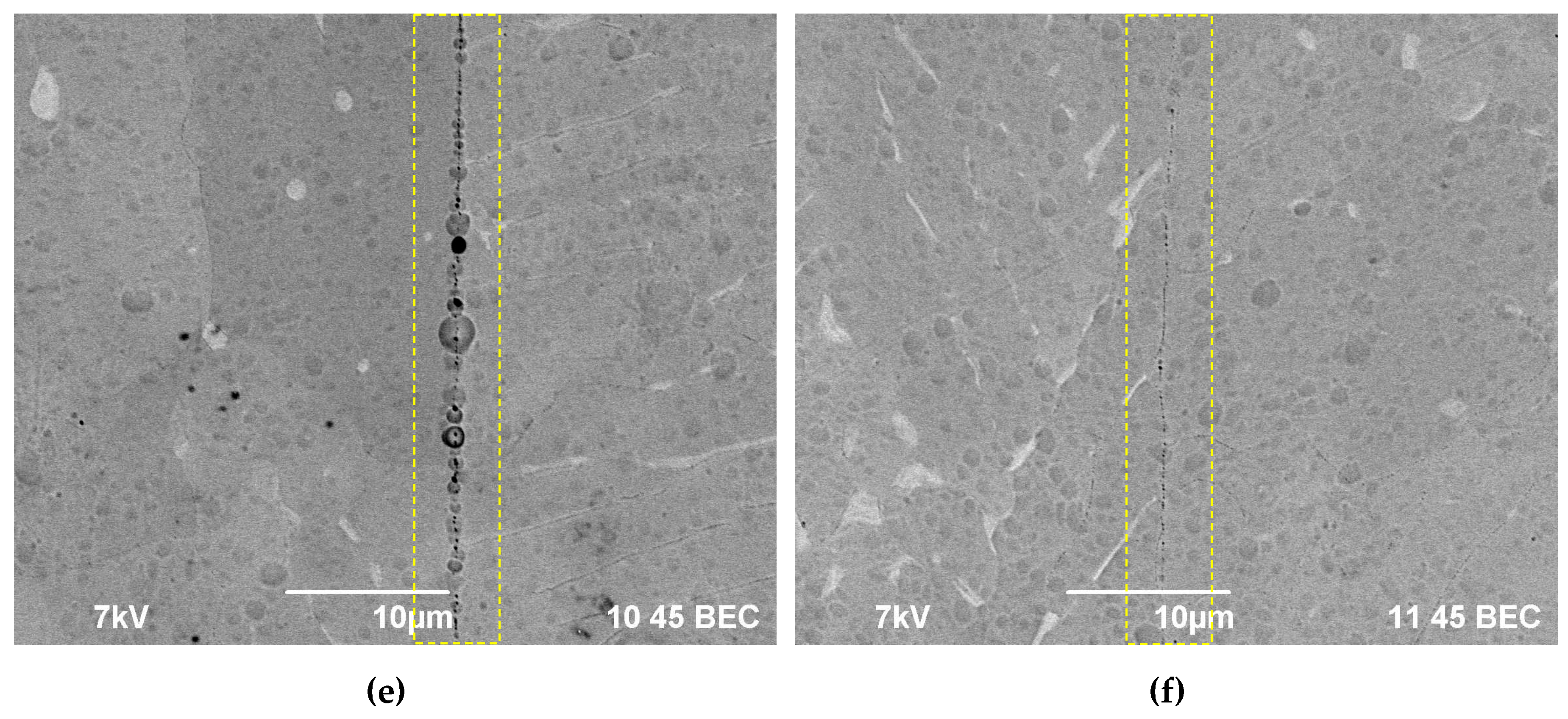
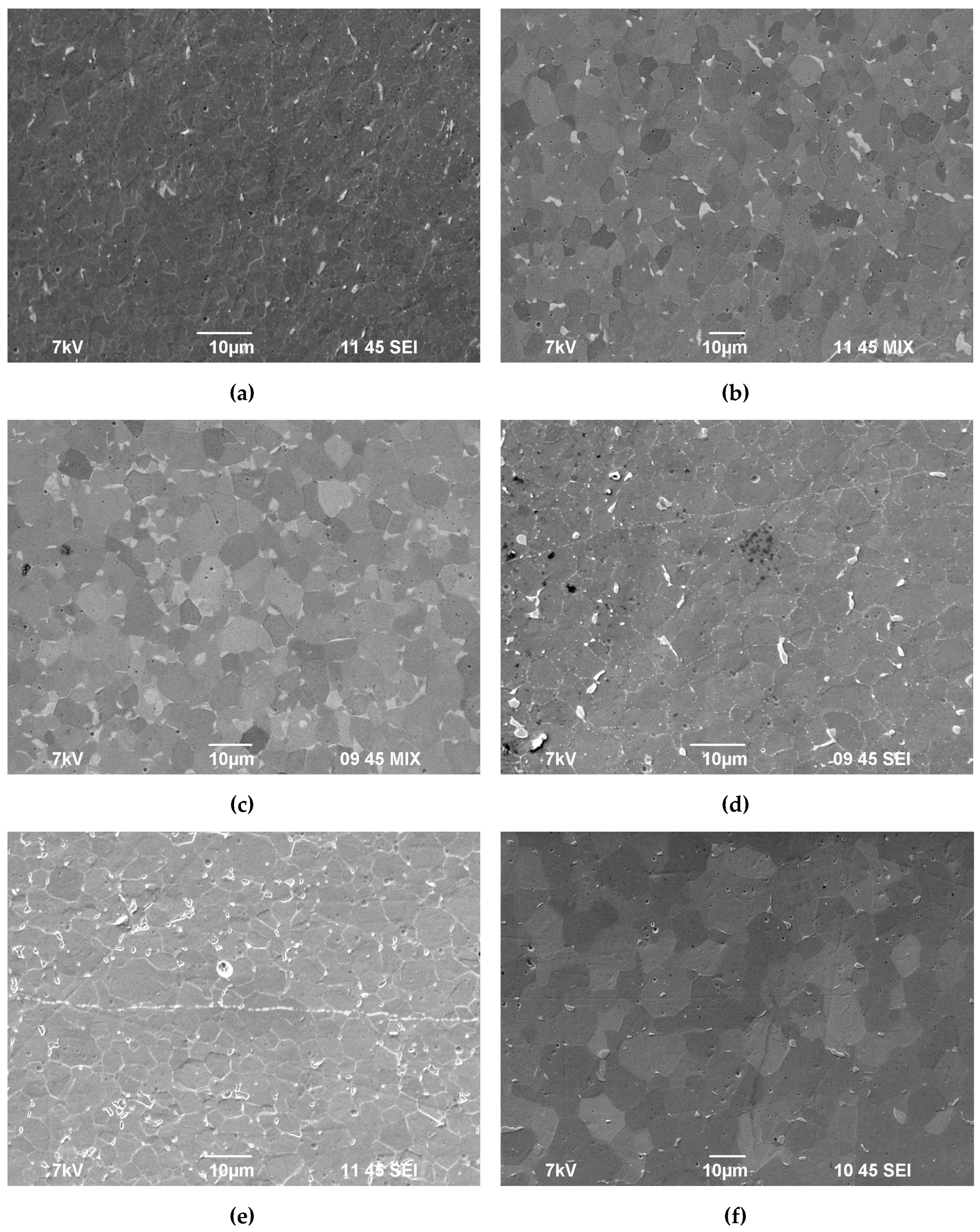
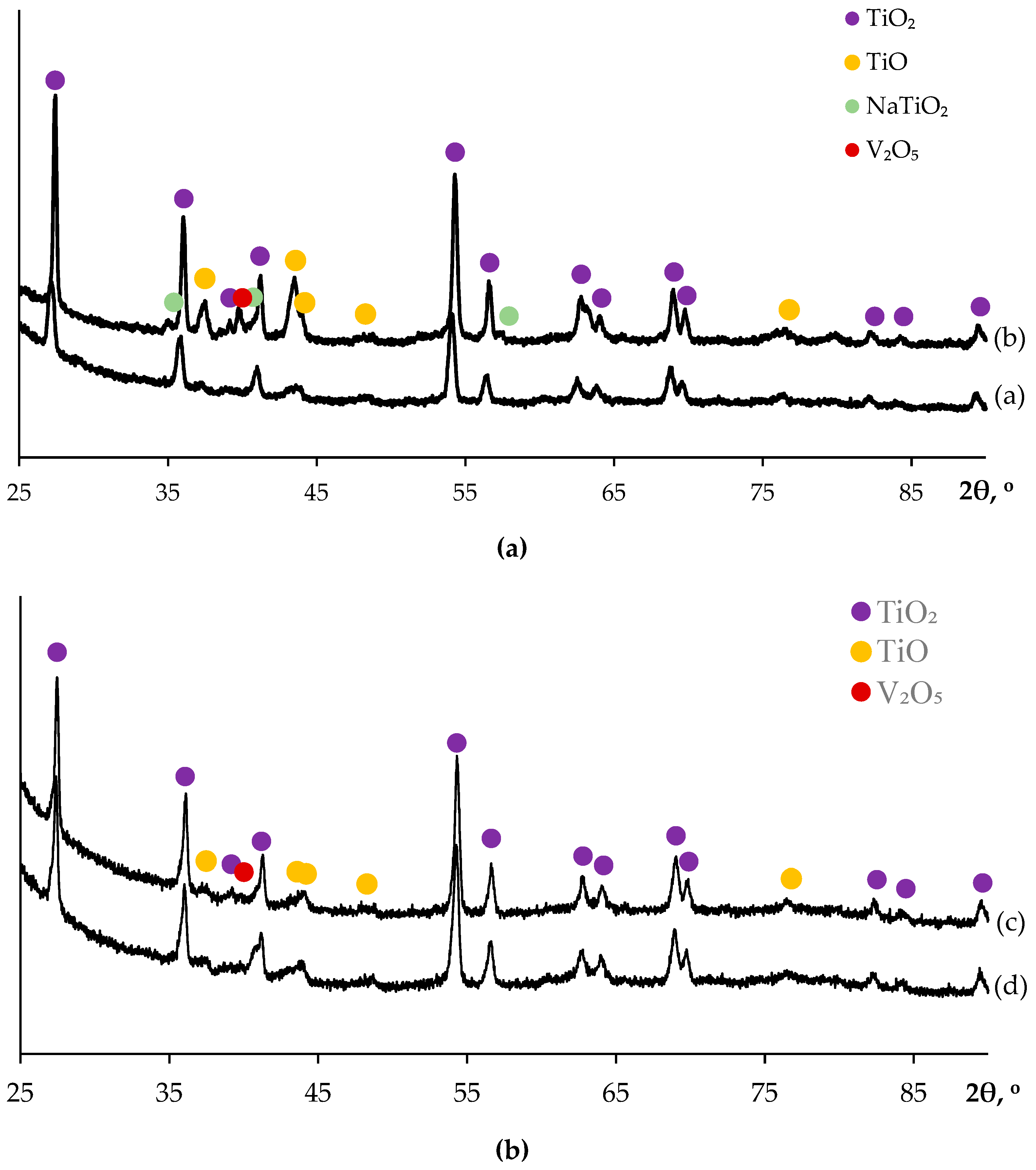
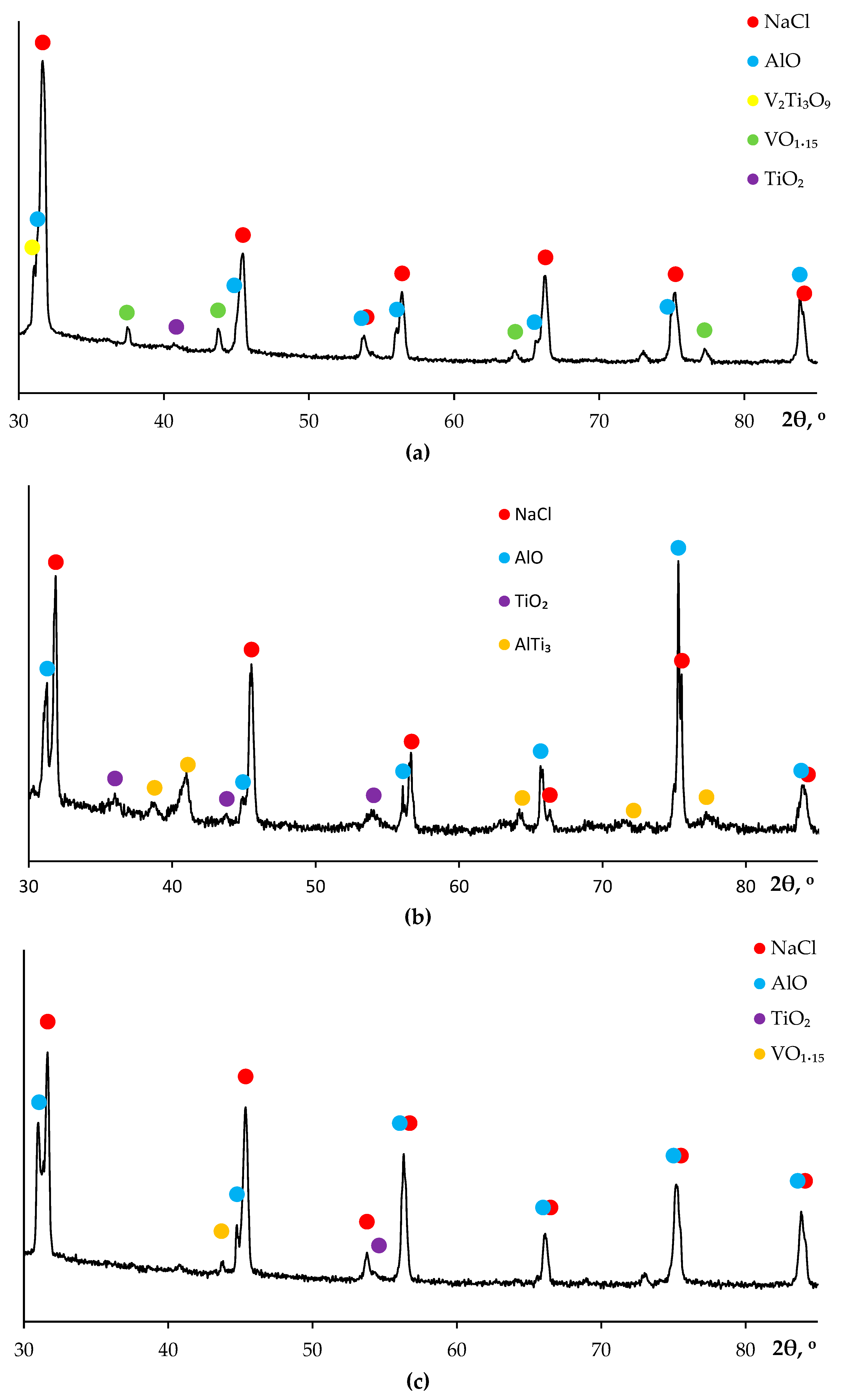
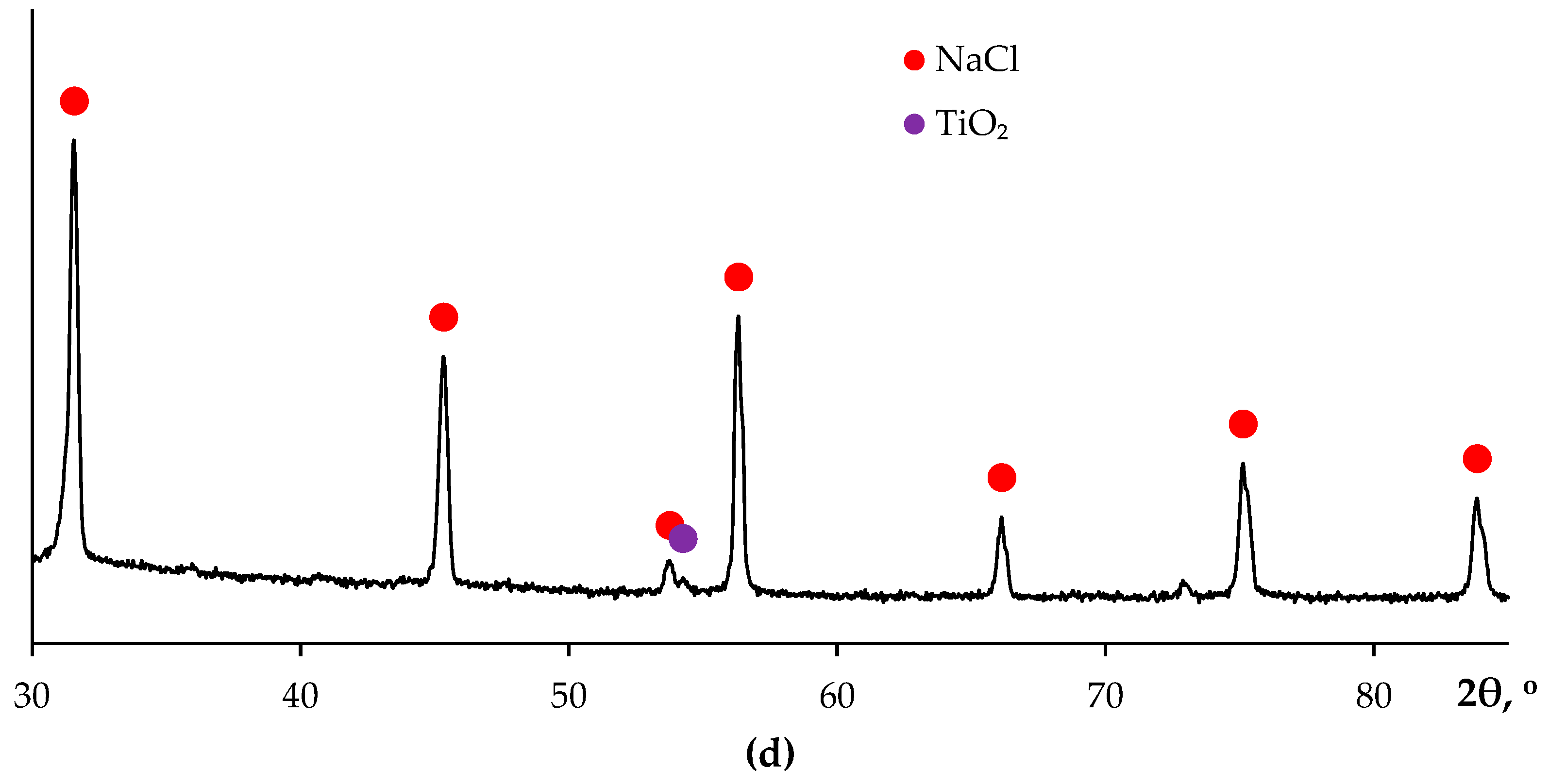
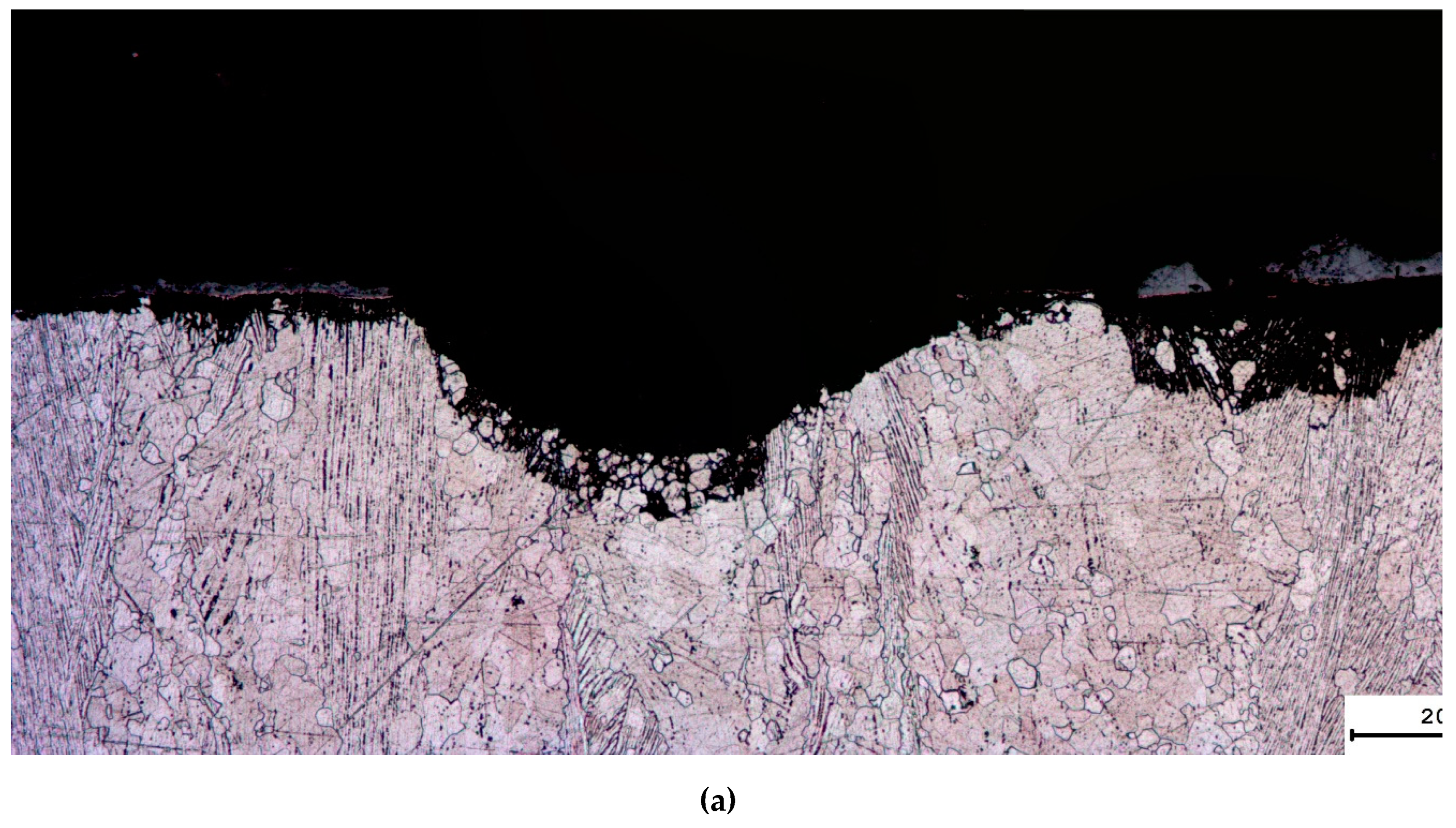
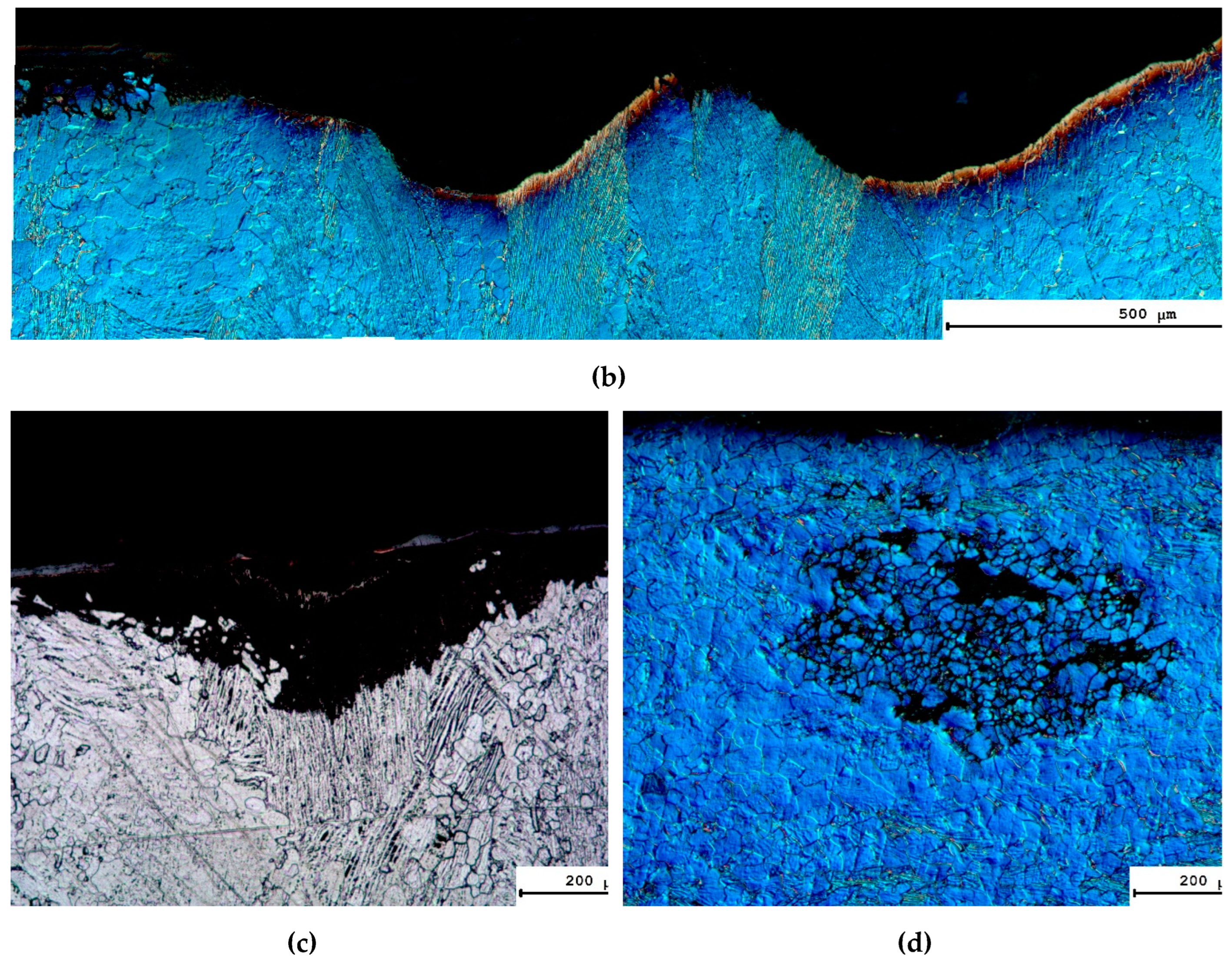
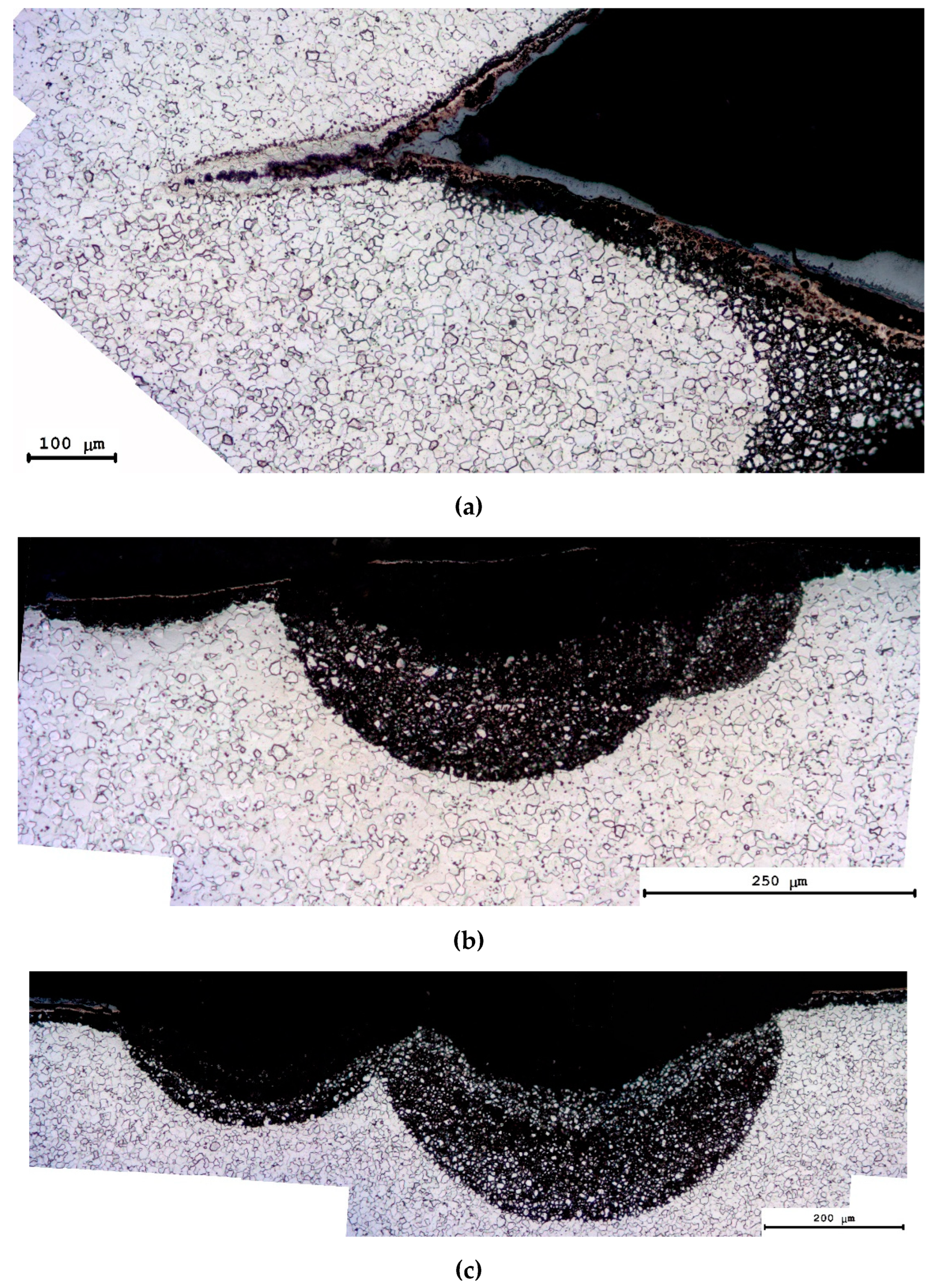
3.4. Hot salt corrosion test
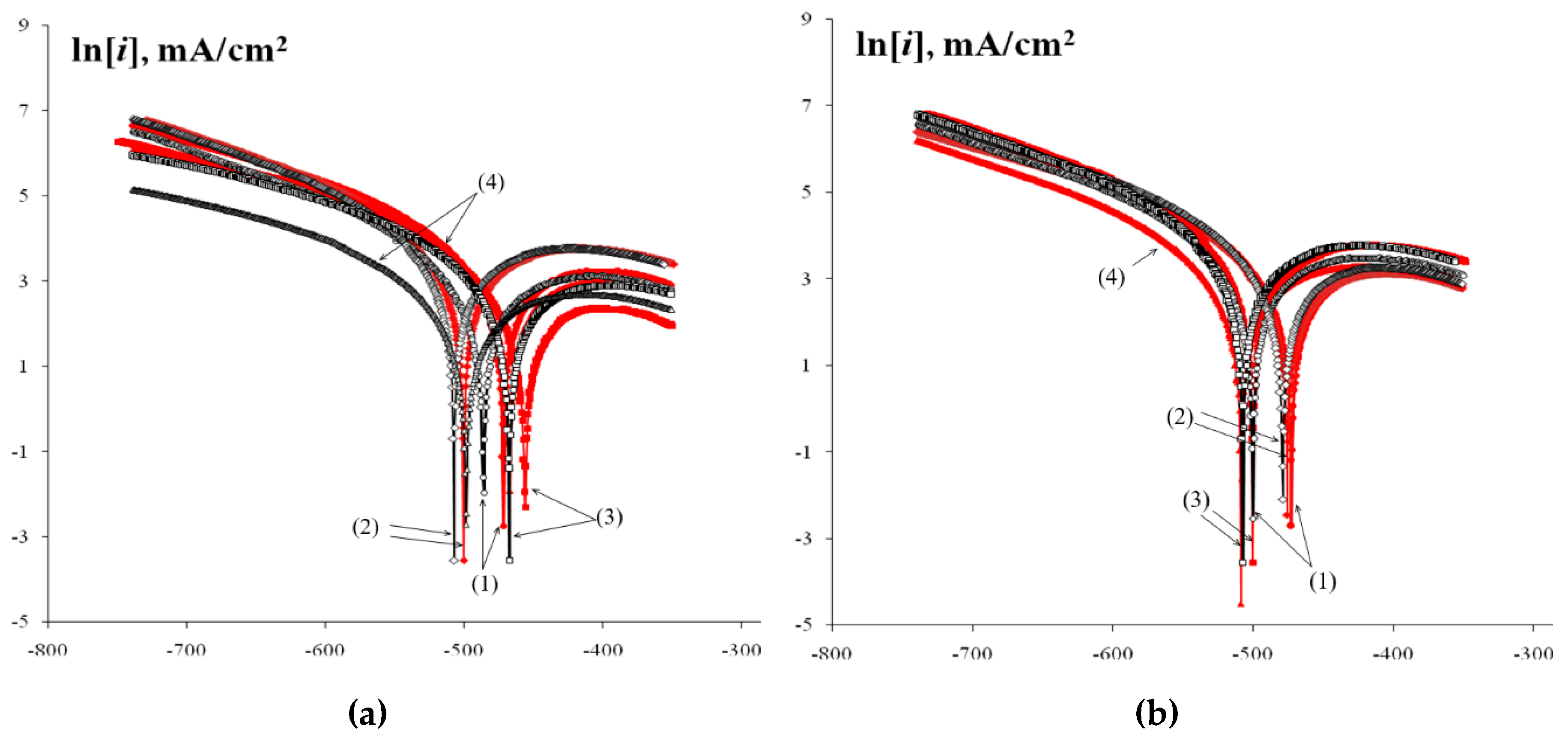
3.5. Electrochemical corrosion test
3.6. Microhardness test
4. Discussion
4.1. Corrosion resistance of welded joints. Crevice corrosion
4.2. Corrosion resistance of the metal. Pitting and intercrystalline corrosion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lütjering, G.; Williams, J.C. Titanium, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; p. 442.
- Jafee, R.I.; Burte, H.M. (Eds.). Titanium Science and Technology. Springer: New York, US, 1973; p. 2739.
- Gorynin, I.V.; Chechulin, B.B. Titan in Mechanical Engineering. Mashinostroenie: Moscow, Russia, 1990; p. 400. (in Russian).
- Bilobrov, I.; Trachevsky, V. Approach to modify the properties of titanium alloys for use in nuclear industry. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 415, 222-225. [CrossRef]
- Oryshchenko, A.S.; Gorynin, I.V.; Leonov, V.P. et al. Marine titanium alloys: Present and future. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2015, 6, 571-579. [CrossRef]
- Leonov, V.P.; Gorynin, I.V.; Kudryavtsev, A.S. et al. Titanium alloys in steam turbine construction. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2015, 6, 580-590. [CrossRef]
- Gorynin, I.V. Titanium alloys for marine application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 1999, 263, 112-116. [CrossRef]
- Leonov, V.P.; Chudakov, E.V.; Malinkina, Y.Y. The influence of microadditives of ruthenium on the structure, corrosive-mechanical strength, and fractography of destruction of pseudo-alpha-titanium alloys. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2017, 8, 556-565. [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikov, O.A.; Nesterova, E.V.; Rybin, V.V.; Yarmolovich, I.I. Influence of neutron irradiation of deformability and fracture micromechanisms of titanium α-alloys. J. Nucl. Mater. 1999, 271-272, 472-477. [CrossRef]
- Malinkina, Y.Y.; Chudakov, E.V.; Leonov, V.P. The influence of ruthenium on structure, corrosion and mechanical properties, and fatigue characteristics of titanium α-alloys in corrosive environment. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2017, 8, 906-913. [CrossRef]
- Murashov, A.A.; Berendeyev, N.N.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Galaeva, E.A.; Chuvil’deev, V.N. Investigation of the process of fatigue and corrosion-fatigue destruction of pseudo-α titanium alloy. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2022, 13, 349-356. [CrossRef]
- Segal, V. Review: Modes and Processes of Severe Plastic Deformation. Materials 2018, 11, 1175. [CrossRef]
- Segal, V.M.; Beyerlein, I.J.; Tome, C.N.; Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Kopylov, V.I. Fundamentals and Engineering of Severe Plastic Deformation. Nova Science Publishers: New York, USA, 2010; p. 542.
- Gornakova, A.S.; Straumal, A.B.; Khodos, I.I. et al. Effect of composition, annealing temperature, and high pressure torsion on structure and hardness of Ti-V and Ti-V-Al alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 082522. [CrossRef]
- Straumal, B.B.; Kilmametov, A.R.; Ivanisenko, Y. et al. Diffusive and displacive phase transitions in Ti-Fe and Ti-Co alloys under high pressure torsion. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2281-2286. [CrossRef]
- Alkazraji, H.; El-Danaf, E.; Wolfmann, M.; Wagner, L. Enhanced fatigue strength of commercially pure Ti processed by rotary swaging. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 301837. [CrossRef]
- Pachla, W.; Kulczyk, M.; Prybysz, S. et al. Effect of severe plastic deformation realized by hydrostatic extrusion and rotary swaging on the properties of CP Ti grade 2. J. Mater. Process. Techn. 2015, 221, 255-268. [CrossRef]
- Zherebtsov, S.; Kudryavtsev, E.; Kostjuchenko, S. et al. Strength and ductility-related properties of ultrafine grained two-phase titanium alloy produced by warm multiaxial forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2012, 536, 190-196. [CrossRef]
- Zherebtsov, S.V.; Kudryavtsev, E.A.; Salishchev, G.A. et al. Microstructure evolution and mechanical behavior of ultrafine Ti-6Al-4V during low-temperature superplastic deformation. Acta Mater. 2016, 121, 152-163. [CrossRef]
- Czervinski, A.; Lapovok, R.; Tomus, D.; Estrin, Y.; Vinogradov, A. The influence of temporary hydrogenation on ECAP formability and low cycle fatigue life of CP titanium. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 2709-2715. [CrossRef]
- Estrin, Y.; Vinogradov, A. Fatigue behavior of light alloys with ultrafine grain structure produced by severe plastic deformation: An overview. Int. J. Fatigue 2010, 32, 898-907. [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.Yu.; Stolyarov, V.V.; Hashimoto, S.; Valiev, R.Z. Cyclic behavior of ultrafine-grain titanium processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2001, 318, 163-173. [CrossRef]
- Kral, P.; Dvorak, J.; Zherebtsov, S. et al. Effect of severe plastic deformation on creep behaviour of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 4789-4795. [CrossRef]
- Kral, P.; Dvorak, J.; Blum, W. et al. Creep study of mechanisms involved in low-temperature superplasticity of UFG Ti-6Al-4V processed by SPD. Mater. Charact. 2016, 116, 84-90. [CrossRef]
- Balyanov, A.; Kutnyakova, J.; Amirkhanova, N.A. et al. Corrosion resistance of ultrafine-grained Ti. Scr. Mat. 2004, 51, 225-229. [CrossRef]
- Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Kopylov, V.I.; Nokhrin, A.V. et al., Study of mechanical properties and corrosive resistance of ultrafine-grained α-titanium alloy Ti-5Al-2V. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 723, 354-367. [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, A.O.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V.; Kotov, A.D. et al. Superplastic deformation behavior of ultra-fine-grained Ti-1V-4Al-3Mo alloy: Constitutive modeling and processing map. Mater. Res. Expr. 2019, 6, 096584. [CrossRef]
- Raltson, K.; Birbilis, N. Effect of grain size on corrosion: A review. Corrosion 2010, 66, 0750051-07500513. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ma, A.; Jiang, J. et al. Simultaneously improving mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of pure Ti by continuous ECAP plus short-duration annealing. Mater. Charact. 2018, 138, 38-47. [CrossRef]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Imantalab, O.; Ansari, G. The role of grain refinement and film formation potential on the electrochemical behavior of commercial pure titanium in Hank’s physiological solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2017, 71, 827-834. [CrossRef]
- Chojnaka, A.; Kawalko, J.; Koscielny, H. et al. Corrosion anisotropy of titanium deformed by the hydrostatic extrusion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 987-994. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, W.J. Annealing effects on the corrosion resistance of ultrafine-grained pure titanium. Cor. Sci. 2014, 89, 331-337. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Yoo, S.J.; Ahn, J.W. et al. Ultrafine grained titanium sheets with high strength and high corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2011, 528, 8479-8485. [CrossRef]
- Gurao, N.P.; Manivasagam, G.; Govindaraj, P. et al. Effect of texture and grain size on bio-corrosion response of ultrafine-grained titanium. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 5602-5610. [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, A.V.; Il’in, A.P.; Lotkov, A.I. et al. Reactivity of submicrocrystalline titanium: I. Regulation of oxidation when heated in air. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 4 (2012) 5-12. (in Russian).
- Bozhko, P.V.; Korshunov, A.V.; Il’in, A.P. et al. Reactivity of submicrocrystalline titanium: II. Electrochemical properties and corrosion stability in sulfuric acid solutions. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2013, 4, 85-91. [CrossRef]
- Topol’s’kyi, V.P.; Petrychenko, I.K.; Akhonin, S.V.; Mishchenko, R.M. Weldability of T110 high-strength titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. 2008, 44, 413-417. [CrossRef]
- Lukoyanov, A.V. Formation of pores in the weld metal in automatic argon-shielded arc welding of titanium alloys. Welding Int. 2014, 28, 301-303. [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, P.; Jiang, P.; Liao, Z. The effect of constraint conditions on microstructure and properties of titanium alloy electron beam welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 721, 117-124. [CrossRef]
- Su, M.-L.; Li, J.-N.; Liu, K.-G. et al. Mechanical property and characterization of TA1 titanium alloy sheets welded by vacuum electron beam welding. Vacuum 2019, 159, 315-318. [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Friction-stir welding and processing of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Techn. 2018, 34, 58-72. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J. et al. Recent progress on control strategies for inherent issues in friction stir welding. Progr. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100706. [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.Yu.; Bychkov, V.M.; Selivanov, A.S. et al. Linear friction welding of two-phase titanium alloys VT6 and VT8-1. Welding Int. 2015, 29, 66-69. [CrossRef]
- Nasresfahani, A.R.; Soltanipur, A.R.; Farmanesh, K.; Ghasemi, A. The effect of friction stir welding on corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Mater. Eng. Performance. 2017, 26, 4311-4318. [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.; Dudina, D. Field-Assisted Sintering; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; p. 425. [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M. Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Method, Systems, and Applications. in Handbook of Advanced Ceramics, 2nd ed.; Somiya, S. Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK. 2013; p. 1149-1177. [CrossRef]
- Hulbert, D.M.; Anders, A.; Dudina, D.V. et al. The absence of plasma in “spark plasma sintering”. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 033305. [CrossRef]
- Ozerov, M.; Klimova, M.; Sokolovsky, V. et al. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti/TiB metal-matrix composite during isothermal multiaxial forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 770, 840-848. [CrossRef]
- Weston, N.S.; Derguti, F.; Tudball, A.; Jackson, M. Spark plasma sintering of commercial and development titanium alloys powders. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4860-4878. [CrossRef]
- Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Kopylov, V.I. et al. Spark plasma sintering for high-speed diffusion bonding of the ultrafine-grained near-α Ti-5Al-2V alloy with high strength and corrosion resistance for nuclear engineering. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 14926-14949. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Jiao, X. et al. Current-assisted diffusion bonding of extruded Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy by Spark Plasma Sintering: Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Engin. Performance. 2018, 27, 3035-3043. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. et al. Fast recrystallization and phase transformation in ECAP deformed Ti-6Al-4V alloy induced by pulsed electric current. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 786, 733-741. [CrossRef]
- Nokhrin, A.; Andreev, P.; Boldin, M.; Chuvil’deev, V.; Chegurov, M.; Smetanina, K.; Gryaznov, M.; Shotin, S.; Nazarov, A.; Shcherbak, G.; Murashov, A.; Nagicheva, G. Investigation of microstructure and corrosion resistance of Ti-Al-V titanium alloys obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering. Metals 2021, 11, 945. [CrossRef]
- Chevrot, Th. Pressure effects on the holt-salt stress-corrosion cracking of titanium alloys. PhD Thesis. Cranfield University. School of Industrial and Manufacturing Science, Bedford, UK, 1994. https://dspace.lib.cranfield.ac.uk/handle/1826/7745.
- Sinigaglia, D.; Taccani, G.; Vicentini, B. Hot-salt-stress-corrosion cracking of titanium alloys. Cor. Sci. 1998, 18, 781-796. [CrossRef]
- Pustode, M.D.; Raja, V.S.; Paulose, N. The stress-corrosion cracking suspeptibility of near-α titanium alloy IMI 834 in presence of hot salt. Cor. Sci. 2014, 82, 191-196. [CrossRef]
- Ciszaka, C.; Popa, I.; Brossard, J.-M. et al. NaCl induced corrosion of Ti-6Al-4V alloy at high temperature. Cor. Sci. 2016, 110, 91-104. [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.R.; Hall, J.A. Hat salt corrosion cracking of titanium alloys: An improved model for the mechanism. Corrosion 1977, 33, 252-257. [CrossRef]
- Pustode, M.D.; Raja, V.S. Hot salt stress corrosion cracking behavior of Ti-6242S alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 6081-6089. [CrossRef]
- Pustode, M.D.; Raja, V.S.; Dewangan, B.; Paulose, N. Effect of long term exposure and hydrogen effects on HSSCC behaviour of titanium alloy IMI 834. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 841-847. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Lindley, T.C.; Dye, D.; Saunders, E.A. The mechanisms of hot salt stress corrosion cracking in titanium alloy Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo. Cor. Sci. 2018, 134, 169-178. [CrossRef]
- Pyshmintsev, I.Yu.; Kosmatskii, Ya.I.; Filyaeva, E.A. et al. Alloy Ti-3Al-2.5V hot-extruded pipe metal structure and properties. Metallurgist 2018, 62, 374-379. [CrossRef]
- Illarionov, A.G.; Kostamatskii, Ya.I.; Filyaeva, E.A. et al. Experimental determination of temperature parameters for evaluating the possibility of manufacturing alloy Ti-3Al-2.5V hot-extruded tubes. Metallurgist 2017, 60, 983-988. [CrossRef]
- Illarionov, A.G.; Vodolazskiy, F.V.; Barannikova, N.A. et al. Influence of phase composition on thermal expansion of Ti-0.4Al, Ti-2.2Al-2.5Zr and Ti-3Al-2.5V alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 158049. [CrossRef]
- Bykh, O.; Bakhmetev, A.; Sandler, N. et al. Hot-salt corrosion of alloys PT-7M, 42XHM, Inconel 690 and Incoloy 800. Applied Solid State Chemistry 2019, 1, 23-31. [CrossRef]
- Andreev, P.V.; Gudz, D.A.; Smetanina, K.E. Surface treatment of titanium alloys for the X-ray diffraction study. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2315, 03001. [CrossRef]
- Chuvil’deev, V.N.; Kopylov, V.I.; Nokhrin, A.V. et al. Effect of severe plastic deformation realized by rotary swaging on the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of near-α-titanium alloy Ti-2.5Al-2.6Zr. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 785, 1233-1244. [CrossRef]
- Tomashov, N.D.; Chernova, G.P. Theory of corrosion and corrosion-resistant structural alloys. Metallurgiya: Moscow, Russia, 1986; 358 p. (in Russian).
- Tavadze, F.N.; Mandzhgaladze, S.N. Corrosion resistance of titanium alloys. Metallurgiya: Moscow, Russia, 1969; 208 p. (in Russian).
- Tomashov, N.D. Titanium and Titanium-based corrosion-resistance alloys. Metallurgiya: Moscow, Russia, 1985; 80 p. (in Russian).
- Ratochka, I.V.; Lykova, O.N.; Naydenkin, E.V. Influence of low-temperature annealing time on the evolution of the structure and mechanical properties of a titanium Ti-Al-V alloy in the submicrocrystalline state. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 2015, 116, 302-308. [CrossRef]
- Ratochka, I.; Lykova, O.; Mishin, I.; Naydenkin, E. Superplastic deformation behavior of Ti-4Al-2V alloy governed by its structure and precipitation phase evolution. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 577-582. [CrossRef]
- Sherbinin, V.F.; Leonov, V.P.; Malinkina, Yu.Yu. Increase in corrosion resistance of titanium alloy in concentrated aqueous solutions of chlorides at high temperatures. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2013, 4, 537-541. [CrossRef]
- Bokhonov, B.; Ukhina, A.; Dudina, D. et al. Carbon uptake during Spark Plasma Sintering: investigation through the analysis of the carbide “footprint” in a Ni-W alloy. RSC Advances 2015, 5, 80228-80237. [CrossRef]
- Dudina, D.V.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Ukhina, A.V. et al. Reactivity of materials towards carbon of graphite foil during Spark Plasma Sintering: A case study using Ni-W powders. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 62-67. [CrossRef]
- Gornakova, A.S.; Straumal, B.B.; Prokofiev, S.I. Coarsening of (αTi) + (βTi) microstructure in the Ti-Al-V alloy at constant temperature. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1800510. [CrossRef]
- Gornakova, A.S.; Prokofjev, S.I. Energetics of intergranular and Interphase boundaries in Ti-6Al-4V alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 9225-9236. [CrossRef]
- Hein, K.; Buhrig, E. (Eds.) Kristallisationaus Schmelzen; VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie: E. Leipzig, Germany, 1983; 356 p. (in Germany).
- Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y. et al. Influence of thermal treatment on element partitioning in α+β titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 791, 575-585. [CrossRef]
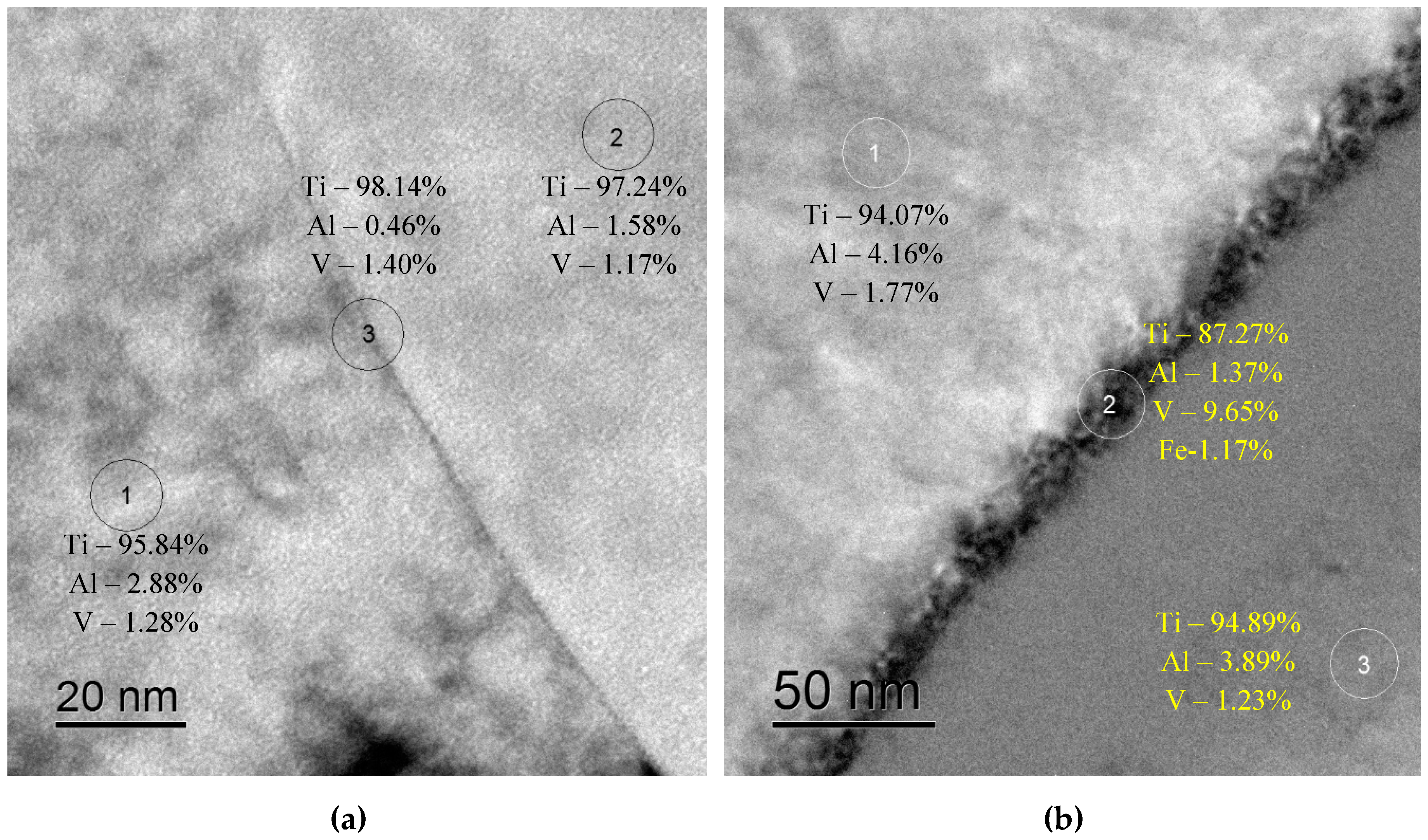


| Contents of alloying elements, wt.% | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Al | V | Zr | Fe | Si | O | N | C | H | |
| Tested alloy | Balance | 4.73 | 1.88 | 0.019 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.042 | 0.01 | 0.0024 | 0.004 |
| Russian standard GOST 19807-91 | Balance | 3.5-5.0 | 1.2-2.5 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.006 |
| No. | Welding regime | Coarse-grained alloy | UFG alloy | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Т, oC |
Vh, oC/min |
t, min |
Р, MPa |
dα, µm |
dβ, µm |
Weld porosity (Zone II) | Hv, GPa | dα, µm |
dβ, µm |
Weld porosity (Zone II) | Hv, GPa | |||
| Weld | Alloy | Weld | Alloy | |||||||||||
| 0 | State before welding | 10-100 | 3-15 | - | - | 2.0-2.1 | 0.5 | - | - | - | 3.1-3.2 | |||
| 1 | 600 | 100 | 10 | 50 | ~16 | 3.2 | High | 2.5 | 2.4-2.5 | 4.8 | 2.4 | High | 3.0 | 3.0-3.1 |
| 2 | 700 | ~17 | 3.0 | Medium | 2.5 | 2.5-2.6 | 5.9 | 3.0 | Low | 2.8 | 2.8-2.9 | |||
| 3 | 800 | ~18-19 | 5.1 | Medium | 2.3 | 2.3-2.4 | 6.9 | 3.3 | Medium | 3.2 | 3.2 | |||
| 4 | 1030 | ~12 | - | Low | 2.5 | 2.4 | - | - | - | |||||
| 1142 | - | - | - | - | - | 5.2 | Low | 2.6 | 2.6-2.7 | |||||
| 5 | 700 | 10 | 10 | 50 | ~16-18 | 5.0 | Low | 2.6 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 3.1 | High | 2.5 | 2.5-2.6 |
| 6 | 50 | ~17-18 | 3.5 | Medium | 2.6 | 2.4-2.3 | 5.5 | 3.3 | Medium | 2.7 | 2.8-2.9 | |||
| 7 | 100 | ~18-19 | 3.0 | Medium | 2.4 | 2.5 | 5.9 | 3.0 | Low | 2.7 | 2.7-2.9 | |||
| 8 | 350 | ~18 | 3.0 | High | 2.4 | 2.5 | 3.8 | 3.3 | Low | 2.9 | 3.0-3.1 | |||
| 9 | 700 | 100 | 10 | 50 | ~18-19 | 3.5 | Medium | 2.5 | 2.4-2.6 | 5.9 | 3.3 | Low | 2.7 | 2.8-2.9 |
| 10 | 70 | ~15 | 3.2 | High | 2.7 | 2.6-2.7 | 5.3 | 2.6 | High | 2.7 | 2.9-3.0 | |||
| 11 | 100 | ~10 | 2.9 | High | 2.7 | 2.5-2.6 | 4.9 | 2.5 | High | 2.7 | 3.0-3.1 | |||
| 12 | 700 | 100 | 0 | 50 | ~18-19 | 3.5 | High | 2.5 | 2.5-2.6 | 4.7 | 2.0 | High | 2.9 | 2.9-3.1 |
| 13 | 10 | ~18-19 | 3.0 | Medium | 2.4 | 2.4-2.5 | 5.9 | 3.3 | Medium | 2.7 | 2.8-2.9 | |||
| 14 | 50 | ~16-17 | 2.0 | Medium | 2.3 | 2.3-2.6 | 9.1 | 3.5 | Low | 2.6 | 2.8 | |||
| 15 | 90 | ~12-13 | 2.0 | Medium | 2.4 | 2.4-2.6 | 9.3 | 3.5 | Low | 2.5 | 2.5-2.6 | |||
| No. | Welding regime | Coarse-grained alloy | UFG alloy | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Т, oC |
Vh, oC/min |
t, min |
Р, MPa |
HSC test | Tafel test | HSC test | Tafel test | |||||||||
| HSC character 1 |
hmax, μm |
hav, μm |
icorr, mА/cm2 |
Ecorr, mV |
HSC character 1 |
hmax, μm |
hav, μm |
icorr, mА/cm2 |
Ecorr, mV |
|||||||
| Zone I |
Zone II |
Zone I |
Zone II |
|||||||||||||
| 0 | State before welding | ICC | ~600 | ~400 | ICC | ~150 | ~100 | |||||||||
| 1 | 600 | 100 | 10 | 50 | C | P, ICC | 223 | 162 ± 43 | 1.21 | -471 | C | P, ICC | 188 | 124 ± 34 | 1.03 | -486 |
| 2 | 700 | C | P, ICC | 235 | 231 ± 39 | 1.69 | -500 | - | P, ICC | 420 | 273 ± 62 | 0.92 | -507 | |||
| 3 | 800 | C | P | 280 | 265 ± 48 | 1.30 | -456 | C | P, ICC | 400 | 285 ± 59 | 0.66 | -468 | |||
| 4 | 1030 | - | P | 358 | 184 ± 35 | 1.74 | -467 | |||||||||
| 1142 | C | P, ICC | 557 | 211 ± 45 | 0.82 | -499 | ||||||||||
| 5 | 700 | 10 | 10 | 50 | - | P, ICC | 238 | 182 ± 45 | 1.12 | -473 | - | P | 171 | 132 ± 24 | 0.66 | -500 |
| 6 | 50 | C | P, ICC | 235 | 231 ± 39 | 1.51 | -476 | - | P, ICC | 442 | 304 ± 51 | 1.32 | -479 | |||
| 7 | 100 | C | P, ICC | 358 | 185 ± 75 | 1.69 | -500 | - | P, ICC | 420 | 273 ± 42 | 0.92 | -507 | |||
| 8 | 350 | C | P, ICC | 444 | 220 ± 92 | 0.99 | -509 | - | P, ICC | 451 | 189 ± 36 | 0.16 | -180 | |||
| 9 | 700 | 100 | 10 | 50 | C | P, ICC | 290 | 215 ± 49 | 0.66 | -470 | - | P, ICC | 430 | 280 ± 30 | 0.92 | -507 |
| 10 | 70 | C | P, ICC | 132 | 108 ± 21 | 0.69 | -495 | - | P | 138 | 113 ± 28 | 1.09 | -502 | |||
| 11 | 100 | C | P, ICC | 246 | 178 ± 77 | 1.04 | -495 | - | P | 163 | 93 ± 40 | 1.12 | -494 | |||
| 12 | 700 | 100 | 0 | 50 | C | P, ICC | 390 | 211 ± 82 | 1.24 | -475 | C | P, ICC | 385 | 249 ± 58 | 1.77 | -507 |
| 13 | 10 | C | P, ICC | 358 | 184 ± 75 | 1.62 | -486 | - | P, ICC | 358 | 284 ± 55 | 0.92 | -507 | |||
| 14 | 50 | C | P, ICC | 354 | 191 ± 67 | 1.27 | -452 | - | P, ICC | 495 | 237 ± 40 | 1.24 | -498 | |||
| 15 | 90 | C | P, ICC | 163 | 125 ± 62 | - | - | P, ICC | 512 | 297 ± 47 | 1.20 | -488 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).