1. Introduction
The susceptible-infected-recovered/removed (SIR) pandemics model developed originally by Kermack and McKendrick [
1] and refined by Kendall [
2] is the simplest, but still realistic compartment model where persons from a considered population are assigned to the three compartments
S (susceptible),
I (infectious) and
R (recovered/removed). The infection (
) and recovery (
) rates then regulate the transition probability between the compartment fractions. Later refinements of the SIR-model such as the SEIR [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12], SVEIR [
13,
14], SEIRD [
15], SIRD [
16,
17,
18], SIRS [
19,
20] and SIRV [
21,
22,
23,
24] have introduced additional compartments (for reviews see refs. [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]). The SIR-epidemic model provides a good explanation for the temporal evolution of Covid-19 waves from different mutants [
32,
33,
34].
An important key parameter of the SIR pandemics model is the ratio
of the recovery to infection rate. Existing analytical solutions to the SIR equations in the literature have adopted originally stationary values of
and
leading to the Kermack and McKendrick integral solution [
1]. Recently [
35,
36] this integral solution has been generalized to arbitrary time-dependent infection rates
assuming a stationary value of the ratio
so that the recovery rate has the same time dependence as the infection rate. A further generalization to slowly time-dependent ratios
is also possible [
37].
It is the purpose of the present manuscript to investigate for the first time a different approach. Instead of adopting different choices of the time dependence of the key parameter
and then solve the SIR equations as before we follow a different line of argument: in
Section 2 we express the ratio
in terms of the observable rate of new infections
and its corresponding cumulative fraction
. By adopting the earlier considered Gaussian evolution function [
38,
39,
40,
41] for the rate of new infections
we then calculate in
Section 3 the corresponding time dependence of the ratio
. If this required dependence of
agrees with the determination of the ratio
from monitored infection rates in different pandemic waves (
Section 4) it would prove the validity of the Gauss model for the time evolution of pandemic waves.
2. SIR model
2.1. Starting equations
The original SIR-equations read
obeying the sum constraint
at all times
after the start of the wave at time
with the initial consitions [
36]
where
is positive and usually very small,
. Very accurate analytical approximations [
42] of the solutions of the SIR-equations (1)–(
2) have been derived recently assuming a stationary value of the ratio
. In
Section 4 we also use the monitored data on the temporal evolution of pandemic waves in different countries to test the validity of the stationarity of
.
2.2. Key parameter
In terms of the reduced time
the SIR equations (1) read
as with the time-dependent ratio
Equation (
5a) provides
in terms of the rate of new infections
and the cumulative number of new infections
. In deriving Equation (
7) we have used that
. Likewise Equation (
5b) yields
where we inserted Equation (
7).
As an aside we note that the same relation (
8) results if we use Eqs. (
5c)–(
7) and the sum constraint (
2), i.e.
where in the last step we inserted Equation (
7).
In terms of the real time
and
Equation (
8) finally reads
in terms of the monitored cumulative rate of new infections
and the time-dependent infection rate
.
Multiplying Equation (
10) with
then provides
and for a stationary infection rate
, Eqs. (
10)–(
11) simplify to
and
respectively. In the case of stationary infection rate the entire real time dependence of the ratio
is attributed to a time-dependent recovery rate
.
We emphasize that Eqs. (
9)–(
13) hold for all reduced (
) and real (
t) times.
2.3. Limiting case
In practically all Covid-19 mutant waves the final cumulative fraction of infected persons is much less than unity, i.e.
. In the limit
we use the approximations
so that Eqs. (
10)–(
11) reduce to
and in case of stationary infection rates
The first Equation (
16) indicates that a small value of the stationary infection rate
provides a smaller value of the ratio
close to zero.
3. Condition for the validity of the Gaussian evolution
In this Section we adopt the Gaussian evolution for the rate of new infections [
40,
41]
The corresponding accumulative fraction of infections at any time then is given by
in terms of the error function.
denotes the final cumulative fraction of infections after infinite time
.
The Gaussian evolution (
17) implies
In the general case of arbitrarily large
the full Equation (
12) yields for the Gauss evolution
In the limit
, as also indicated by the first Equation (
16), the last term in Equation (
20) is negligibly small providing in this limit
The full ratio (
20) and its approximation (
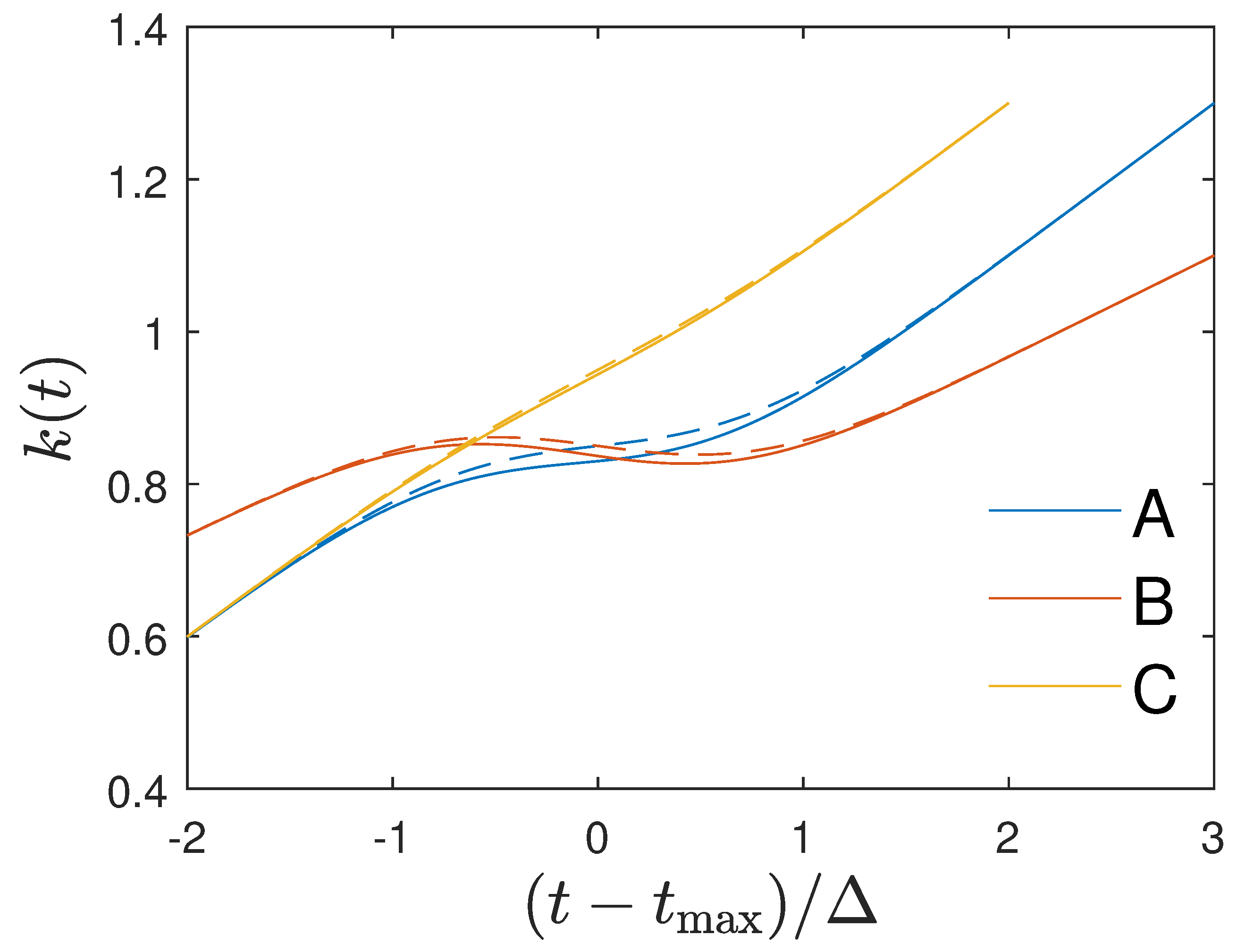
21) are shown in
Figure 1. One notices that the approximation (
21) agrees very well with the exact time variation (
20). Obviously
Figure 1 indicates three different regimes in time for the Gauss ratio:
- (i)
At early times the Gauss ratio increases linearly starting from ratio values less than unity.
- (ii)
At
times near maximum, i.e. close to
near the maximum of
, the Gauss ratio exhibits a dip which is more pronounced for smaller values of
which is also indicated by Equation (
21) as the third linear term is inversely proportional to
.
- (iii)
At late times beyond the Gauss ratio resumes its linear increase with time.
We conclude that for the time dependency (
20) of the ratio
the Gaussian evolution (
17) is an exact analytical solution of the SIR equations. Likewise, if the monitored differential and cumulative infection rates
and
inserted in Equation (
12) are well approximated by the Gaussian ratios (
20) and (
21) in all three distinct time regimes we can justify the use the Gaussian evolution (
17) as good approximations of the solutions of the SIR equations.
4. Determination of the ratio (12) from monitored infection rates of Covid-19 waves
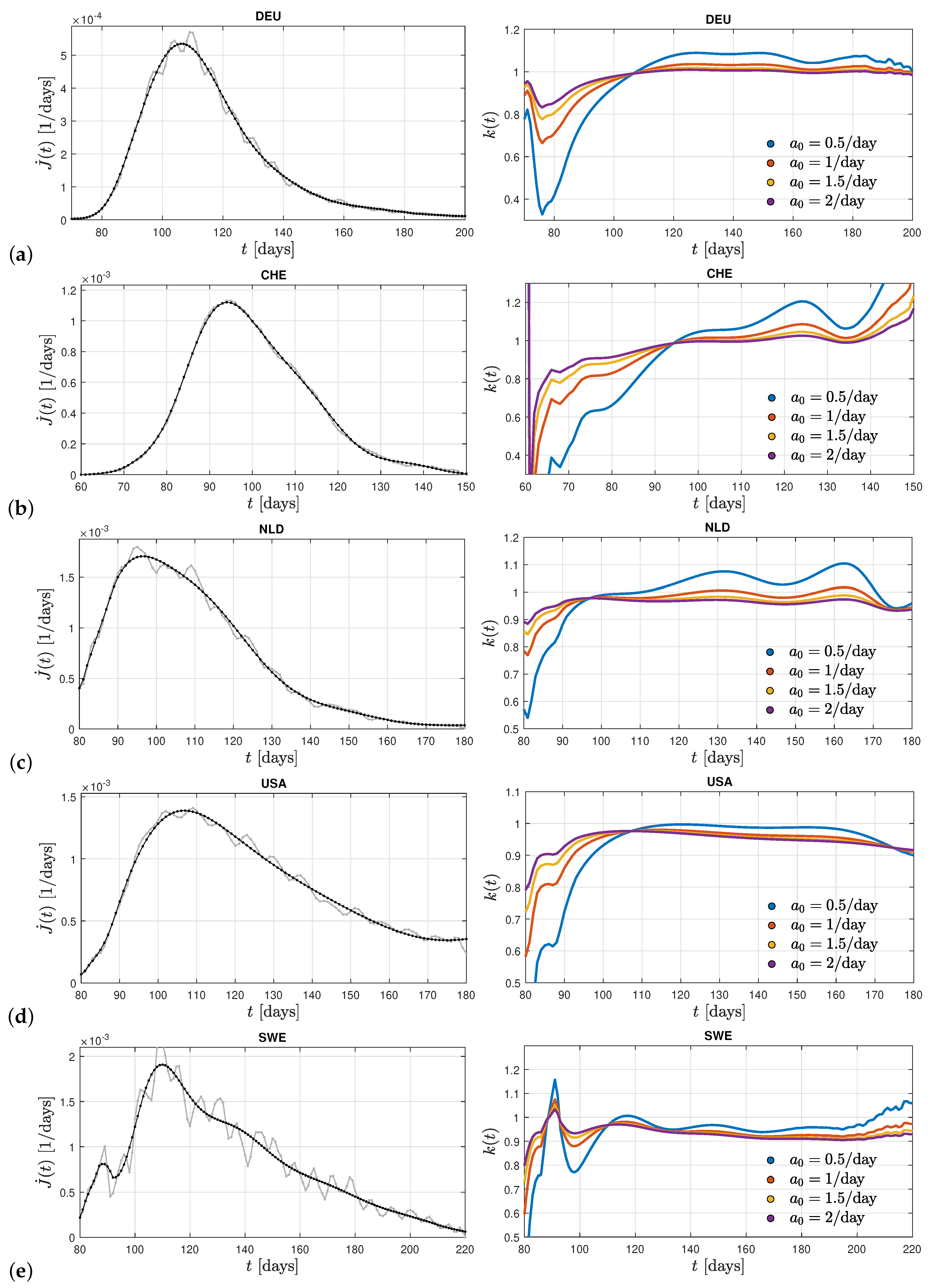
In
Figure 2 we show in the left panels the differential infection rate
in the five countries Germany, Switzerland, The Netherlands, United States, and Sweden inferred from the reported death rates adopting a fatality rate of 0.005. In each country the raw data (in grey) have been smoothed (black curves) in order to infer the second derivative
. More details on the considered Corona waves are given in the caption of
Figure 2. The respective right panels show the derived ratio
calculated from Equation (
16) for different values of the stationary infection rate
.
The monitored infection rates exhibit one clear maximum during the selected time spans capturing a single wave. The corresponding inferred ratios
in these countries remarkably show more or less similar behaviors. In all cases, except Sweden, one notices a linear increase at early times below the first maximum of
before the ratios approach a nearly constant value close to unity at the time of the first maximum with small amplitude oscillations at later times. A resumed linear increase of the ratio at late times is not visible. Consequently, we may conclude that the Gaussian evolution (
17) provides a good approximation of the solutions of the SIR equations during early and peak times. It however fails at late times beyond the first maximum of the considered past corona waves in these five countries. This good agreement of the Gauss modeling at times prior the maximum in the monitored differential infection rates justifies a posteriori the earlier approaches [
38,
39,
40,
41]. Moreover, the almost constant values of the ratio
at times after the maximum time indicates that the analytical SIR-solutions [
35,
36] based on a constant ratio are well applicable at these times.
Common to all five examples shown in
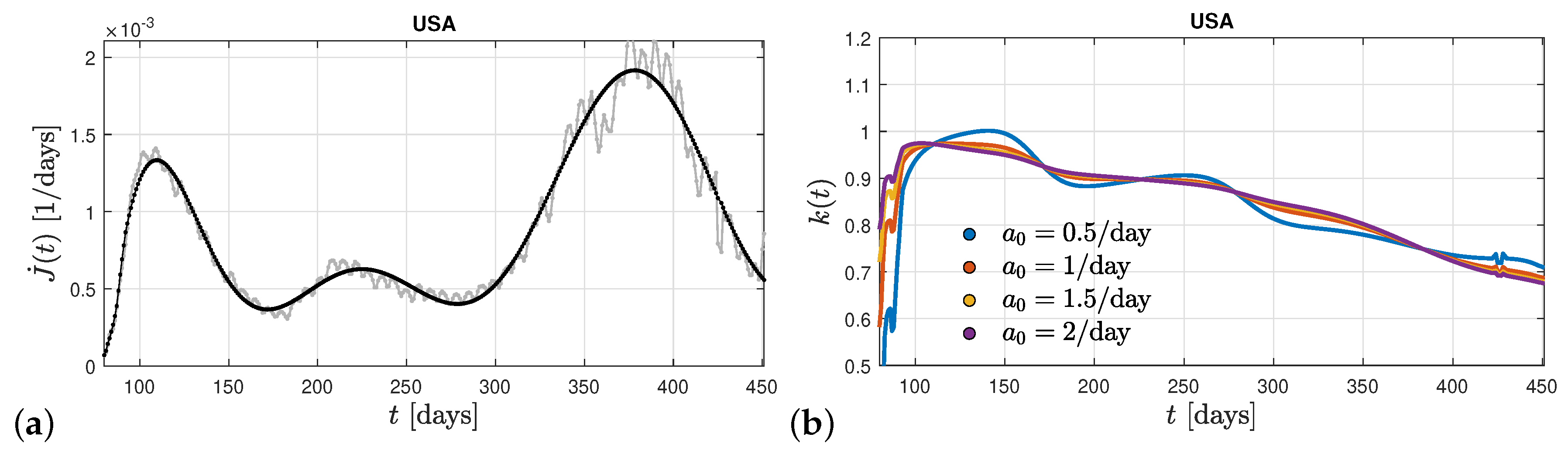
Figure 1 is that only one clear maximum in the differential rate of new infections is visible. In
Figure 3 we show the differential rate of new infections on a longer time scales in the United States. Here at least three maxima are exhibited so that the ratio
at late times deviates from its nearly constant value and decreases substantially with time. This clearly demonstrates that a decreasing ratio
to values considerably less than unity is responsible for leading to new maxima in the rate of new infections of the same mutant.
5. Summary and conclusions
The SIR-epidemic model provides a good explanation for the temporal evolution of Covid-19 waves from different mutants. An important key parameter of the SIR model is the ratio of the recovery to infection rate. Here, apparently for the first time, monitored differential infection rates of past Corona waves have been used to infer a posteriori the real time variation of this key parameter. By attributing its time dependence formally to a time dependent recovery rate the temporal evolution of the ratio is inferred for different values of the stationary infection rate .
For past corona waves in five different countries it is found that the ratio exhibits a linear increase at early times below the first maximum of the differential infection rate before the ratio approaches a nearly constant value close to unity at the time of the first maximum with small amplitude oscillations at later times.
The observed time dependencies at early times and at times near the first maximum agree favorably well with the behavior of the calculated ratio for the Gaussian evolution for the rate of new infections, although the predicted linear increase of the Gauss ratio at late times is not observed.
Likewise, the near constancy of the ratio at times after the maximum time indicates that earlier analytical solutions of the SIR equations for constant ratios are well justified.
On longer time intervals more than one maximum in the differential rate of new infections indicate the presence of several maxima which can be explained by a decrease of the ratio at times after the first maximum to values considerably less than unity. This decrease then is responsible for causing new maxima in the rate of new infections of the same mutant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S.; methodology, R.S., M.K.; software, M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.; writing—review and editing, R.S., M.K.; visualization, M.K.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw, real-time data used in this study has been retrieved from [
43].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. A 1927, 115, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, D.G. Deterministic and stochastic epidemics in closed populations. Proc. Third Berkeley Symp. on Math. Statist. and Prob. 1956, 4, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annas, S.; Pratama, M.I.; Rifandi, M.; Sanusi, W.; Side, S. Stability analysis and numerical simulation of SEIR model for pandemic Covid-19 spread in Indonesia. Chaos Solit. Fract. 2020, 139, 110072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hua, L.; Yuan, J.; He, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jia, Q.; Zhao, C.; et al. The effectiveness of quarantine of Wuhan city against the Corona Virus Disease 2019 (Covid-19): A well-mixed SEIR model analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, K.; Wong, S.S.; Liang, W.; Zanin, M.; Liu, P.; Cao, X.; Gao, Z.; Mai, Z.; et al. Modified SEIR and AI prediction of the epidemics trend of Covid-19 in China under public health interventions. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 165+. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Peng, Y.; Sun, K. SEIR modeling of the Covid-19 and its dynamics. Nonlin. Dyn. 2020, 101, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezapour, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Samei, M.E. SEIR epidemic model for Covid-19 transmission by Caputo derivative of fractional order. Adv. Diff. Eqs. 2020, 2020, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghostine, R.; Gharamti, M.; Hassrouny, S.; Hoteit, I. An Extended SEIR Model with Vaccination for Forecasting the Covid-19 Pandemic in Saudi Arabia Using an Ensemble Kalman Filter. Math. 2021, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, D.; Herkenhoff, K.; Huang, C.; Mongey, S. Testing and reopening in an SEIR model. Rev. Econ. Dyn. 2022, 43, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbert, R.; Rabe, M.M.; Kliegl, R.; Reich, S. Sequential Data Assimilation of the Stochastic SEIR Epidemic Model for Regional Covid-19 Dynamics. Bull. Math. Biol. 2021, 83, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentout, S.; Chen, Y.; Djilali, S. Global Dynamics of an SEIR Model with Two Age Structures and a Nonlinear Incidence. Acta Appl. Math. 2021, 171, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcione, J.M.; Santos, J.E.; Bagaini, C.; Ba, J. A Simulation of a Covid-19 Epidemic Based on a Deterministic SEIR Model. Front. Publ. Health 2020, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabti, A.; Ghanbari, B. Global stability analysis of a fractional SVEIR epidemic model. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2021, 44, 8577–8597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.; Rodo, X. A modified SEIR model to predict the Covid-19 outbreak in Spain and Italy: Simulating control scenarios and multi-scale epidemics. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, I. Identification and estimation of the SEIRD epidemic model for Covid-19. J. Econom. 2021, 220, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanshahi, H.; Munoz-Pacheco, J.M.; Bekiros, S.; Alotaibi, N.D. A fractional-order SIRD model with time-dependent memory indexes for encompassing the multi-fractional characteristics of the Covid-19. Chaos Solit. Fract. 2021, 143, 110632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, K.S.; Ahmad, S.; Ullah, A.; Shah, K.; Alrabaiah, H.; Arfan, M. Mathematical analysis of SIRD model of Covid-19 with Caputo fractional derivative based on real data. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faruk, O.; Kar, S. A Data Driven Analysis and Forecast of Covid-19 Dynamics during the Third Wave Using SIRD Model in Bangladesh. Covid 2021, 1, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, S.P.; Pitchaimani, M. Ergodic stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic SIRS epidemic model with logistic growth and nonlinear incidence. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 377, 125143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yuan, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C. Global dynamics of an SIRS model with demographics and transfer from infectious to susceptible on heterogeneous networks. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 5729–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, N.A.; Ozer, T. On exact integrability of a Covid-19 model: SIRV. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifhat, R.; Teng, Z.; Wang, C. Extinction and persistence of a stochastic SIRV epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate. Adv. Diff. Eqs. 2021, 2021, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameen, I.; Baleanu, D.; Ali, H.M. An efficient algorithm for solving the fractional optimal control of SIRV epidemic model with a combination of vaccination and treatment. Chaos Solit. Fract. 2020, 137, 109892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, M.O.; Ogunmiloro, O.M.; Akinwumi, C.T.; Raji, R.A. Mathematical Modeling and Stability Analysis of a SIRV Epidemic Model with Non-linear Force of Infection and Treatment. Commun. Math. Appl. 2019, 10, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, M.J.; Rohani, P. Modeling Infectious Diseases in Humans and Animals; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E., E. Covid-19 and Sars-Cov-2, Modeling the present, looking at the future. Phys. Rep. 2020, 869, 1. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, L.; Rodo, X. The end of social confinement and Covid-19 re-emergence risk. Nat. Human Behav. 2020, 4, 746+. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, I.F.; Becker, A.D.; Grenfell, B.T.; Metcalf, C.J.E. Disease and healthcare burden of Covid-19 in the United States. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, Jr., R.C.; Barber, R.M.; Collins, J.K.; Zheng, P.; Adolph, C.; Albright, J.; Antony, C.M.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Bachmeier, S.D.; Bang-Jensen, B.; et al. Modeling Covid-19 scenarios for the United States. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 94+. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linka, K.; Peirlinck, M.; Sahli Costabal, F.; Kuhl, E. Outbreak dynamics of Covid-19 in Europe and the effect of travel restrictions. Comp. Meth. Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 23, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filindassi, V.; Pedrini, C.; Sabadini, C.; Duradoni, M.; Guazzini, A. Impact of Covid-19 First Wave on Psychological and Psychosocial Dimensions: A Systematic Review. Covid 2022, 2, 273–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikov, E.B. Estimation of Covid-19 dynamics “on a back-of-envelope?: Does the simplest SIR model provide quantitative parameters and predictions? Chaos Solit. Fract. 2020, 135, 109841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, I.; Mondal, A.; Antonopoulos, C.G. A SIR model assumption for the spread of Covid-19 in different communities. Chaos Solit. Fract. 2020, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hespanha, J.P.; Chinchilla, R.; Costa, R.R.; Erdal, M.K.; Yang, G. Forecasting Covid-19 cases based on a parameter-varying stochastic SIR model. Annu. Rev. Control 2021, 51, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, M.; Schlickeiser, R. Analytical solution of the SIR-model for the temporal evolution of epidemics. Part A: Time-independent reproduction factor. J. Phys. A 2020, 53, 505601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Kröger, M. Analytical solution of the SIR-model for the temporal evolution of epidemics: Part B. Semi-time case. J. Phys. A 2021, 54, 175601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, M.; Schlickeiser, R. SIR-solution for slowly time-dependent ratio between recovery and infection rates. Physics 2022, 4, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciufolini, I.; Paolozzi, A. Mathematical prediction of the time evolution of the Covid-19 pandemic in Italy by a Gauss error function and Monte Carlo simulations. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lixiang, L.; Yang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Meng, C.; Huang, J.; Meng, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Peng, J. Propagation analysis and prediction of the Covid-19. Infect. Disease Model. 2020, 5, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlickeiser, R.; Schlickeiser, F. A gaussian model for the time development of the Sars-Cov-2 corona pandemic disease. Prrdictions for Germany made on March 30. Physics 2020, 2, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüttler, J.; Schlickeiser, R.; Schlickeiser, F.; Kröger, M. Covid-19 predictions using a Gauss model, based on data from April 2. Physics 2020, 2, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, M.; Schlickeiser, R. Verification of the accuracy of the SIR model in forecasting based on the improved SIR model with a constant ratio of recovery to infection rate by comparing with monitored second wave data. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 211379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track Covid-19 in real time. Lancet 2020, 5, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).