Submitted:
25 February 2023
Posted:
28 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Norwegian cervical cancer screening settings during the study period
2.2. Study design
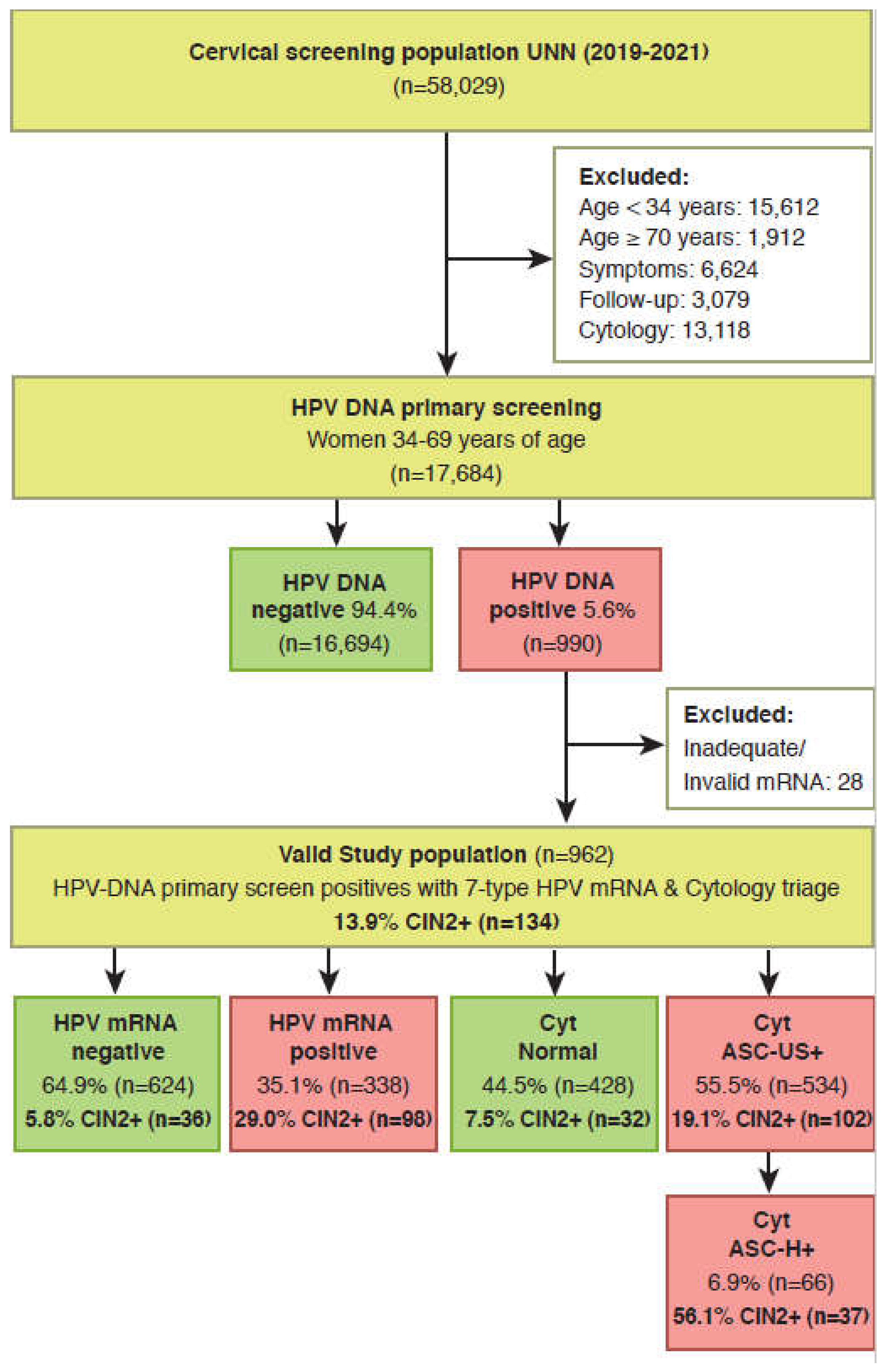
2.3. Selection of study population
2.4. Study outcomes
3. Results
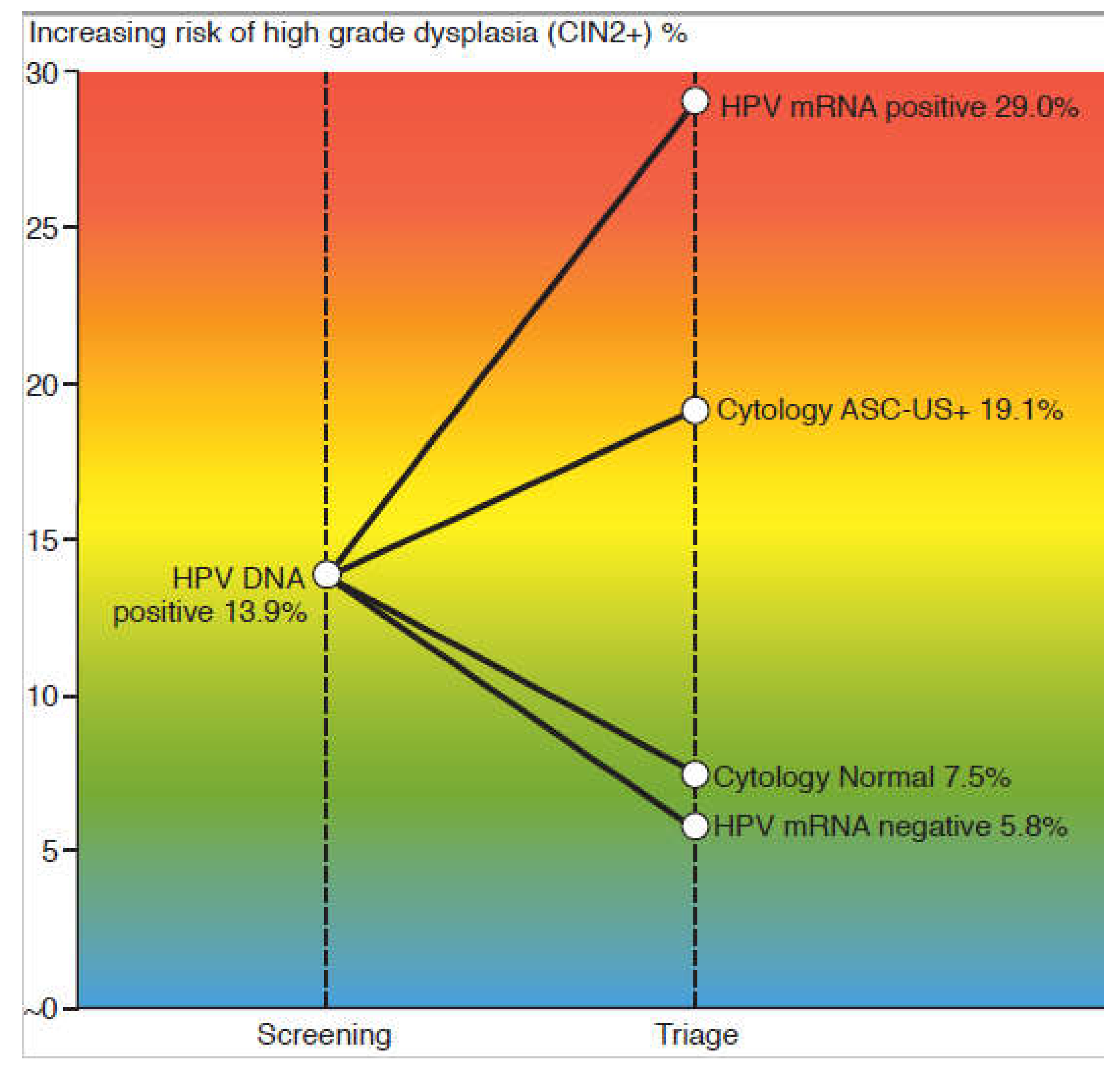
3.1. Test positivity rates and detection rate of CIN2+
3.2. Sensitivity, specificity and predictive values for CIN2+
3.3. Estimated number of colposcopies per CIN2+ detected
4. Discussion
Strengths and limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM, Bosch FX, Kummer JA, Shah KV, et al. Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J Pathol. 1999;189(1):12-9.
- Denny L. Cytological screening for cervical cancer prevention. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2012;26(2):189-96. [CrossRef]
- Ronco G, Dillner J, Elfstrom KM, Tunesi S, Snijders PJ, Arbyn M, et al. Efficacy of HPV-based screening for prevention of invasive cervical cancer: follow-up of four European randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9916):524-32. [CrossRef]
- Koliopoulos G, Nyaga VN, Santesso N, Bryant A, Martin-Hirsch PP, Mustafa RA, et al. Cytology versus HPV testing for cervical cancer screening in the general population. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;8:CD008587. [CrossRef]
- de Sanjose S, Brotons M, Pavon MA. The natural history of human papillomavirus infection. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2018;47:2-13. [CrossRef]
- zur HH. Papillomaviruses and cancer: from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(5):342-50. [CrossRef]
- Sroczynski G, Esteban E, Widschwendter A, Oberaigner W, Borena W, von Laer D, et al. Reducing overtreatment associated with overdiagnosis in cervical cancer screening-A model-based benefit-harm analysis for Austria. Int J Cancer. 2020;147(4):1131-42. [CrossRef]
- Cuschieri K, Ronco G, Lorincz A, Smith L, Ogilvie G, Mirabello L, et al. Eurogin roadmap 2017: Triage strategies for the management of HPV-positive women in cervical screening programs. Int J Cancer. 2018;143(4):735-45. [CrossRef]
- Sorbye SW, Suhrke P, Reva BW, Berland J, Maurseth RJ, Al-Shibli K. Accuracy of cervical cytology: comparison of diagnoses of 100 Pap smears read by four pathologists at three hospitals in Norway. BMC Clin Pathol. 2017;17:18. [CrossRef]
- Bonde JH, Sandri MT, Gary DS, Andrews JC. Clinical Utility of Human Papillomavirus Genotyping in Cervical Cancer Screening: A Systematic Review. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020 Jan;24(1):1-13. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbyn M, Tommasino M, Depuydt C, Dillner J. Are 20 human papillomavirus types causing cervical cancer? J Pathol. 2014;234(4):431-5. [CrossRef]
- Wentzensen N, Schiffman M, Palmer T, Arbyn M. Triage of HPV positive women in cervical cancer screening. J Clin Virol. 2016;76 Suppl 1:S49-S55. [CrossRef]
- Derbie A, Mekonnen D, Woldeamanuel Y, Van Ostade X, Abebe T. HPV E6/E7 mRNA test for the detection of high grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2+): a systematic review. Infect Agent Cancer. 2020;15:9. [CrossRef]
- Nayar R, Wilbur DC. The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology: A Historical Perspective. Acta Cytol. 2017;61(4-5):359-72. [CrossRef]
- Richart RM. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Pathol Annu. 1973;8:301-28. [CrossRef]
- Maver PJ, Poljak M. Primary HPV-based cervical cancer screening in Europe: implementation status, challenges, and future plans. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(5):579-83. [CrossRef]
- Hashim D, Engesaeter B, Baadstrand SG, Castle PE, Bjorge T, Trope A, et al. Real-world data on cervical cancer risk stratification by cytology and HPV genotype to inform the management of HPV-positive women in routine cervical screening. Br J Cancer. 2020;122(11):1715-23. [CrossRef]
- Sorbye SW, Fismen S, Gutteberg TJ, Mortensen ES, Skjeldestad FE. HPV mRNA is more specific than HPV DNA in triage of women with minor cervical lesions. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e112934. [CrossRef]
- Rijkaart DC, Berkhof J, van Kemenade FJ, Coupe VM, Hesselink AT, Rozendaal L, et al. Evaluation of 14 triage strategies for HPV DNA-positive women in population-based cervical screening. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(3):602-10. [CrossRef]
- Benevolo M, Vocaturo A, Caraceni D, French D, Rosini S, Zappacosta R, et al. Sensitivity, specificity, and clinical value of human papillomavirus (HPV) E6/E7 mRNA assay as a triage test for cervical cytology and HPV DNA test. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(7):2643-50. [CrossRef]
- Origoni M, Cristoforoni P, Carminati G, Stefani C, Costa S, Sandri MT, et al. E6/E7 mRNA testing for human papilloma virus-induced high-grade cervical intraepithelial disease (CIN2/CIN3): a promising perspective. Ecancermedicalscience. 2015;9:533. [CrossRef]
- Westre B, Giske A, Guttormsen H, Sorbye SW, Skjeldestad FE. 5-type HPV mRNA versus 14-type HPV DNA test: test performance, over-diagnosis and overtreatment in triage of women with minor cervical lesions. BMC Clin Pathol. 2016;16:9. [CrossRef]
- Sorbye SW, Fismen S, Gutteberg T, Mortensen ES. Triage of women with minor cervical lesions: data suggesting a "test and treat" approach for HPV E6/E7 mRNA testing. PLoS One. 2010;5(9):e12724. [CrossRef]
- Aranda Flores CE, Gomez Gutierrez G, Ortiz Leon JM, Cruz Rodriguez D, Sorbye SW. Self-collected versus clinician-collected cervical samples for the detection of HPV infections by 14-type DNA and 7-type mRNA tests. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21(1):504. [CrossRef]
- Giorgi Rossi P, Fortunato C, Barbarino P, Boveri S, Caroli S, Del Mistro A, et al. Self-sampling to increase participation in cervical cancer screening: an RCT comparing home mailing, distribution in pharmacies, and recall letter. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(4):667-75. [CrossRef]
- Kombe Kombe AJ, Li B, Zahid A, Mengist HM, Bounda GA, Zhou Y, et al. Epidemiology and Burden of Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases, Molecular Pathogenesis, and Vaccine Evaluation. Front Public Health. 2020;8:552028. [CrossRef]
- Castle PE, Glass AG, Rush BB, Scott DR, Wentzensen N, Gage JC, et al. Clinical human papillomavirus detection forecasts cervical cancer risk in women over 18 years of follow-up. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(25):3044-50. [CrossRef]
- Stoler MH, Baker E, Boyle S, Aslam S, Ridder R, Huh WK, et al. Approaches to triage optimization in HPV primary screening: Extended genotyping and p16/Ki-67 dual-stained cytology-Retrospective insights from ATHENA. Int J Cancer. 2020;146(9):2599-607. [CrossRef]
- Demarco M, Egemen D, Raine-Bennett TR, Cheung LC, Befano B, Poitras NE, et al. A Study of Partial Human Papillomavirus Genotyping in Support of the 2019 ASCCP Risk-Based Management Consensus Guidelines. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24(2):144-7. [CrossRef]
- So KA, Lee IH, Lee KH, Hong SR, Kim YJ, Seo HH, Kim TJ. Human papillomavirus genotype-specific risk in cervical carcinogenesis. J Gynecol Oncol. 2019 Jul;30(4):e52. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjær SK, Frederiksen K, Munk C, Iftner T. Long-term absolute risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 or worse following human papillomavirus infection: role of persistence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010 Oct 6;102(19):1478-88. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan P, Howell-Jones R, Li N, Bruni L, de Sanjosé S, Franceschi S, Clifford GM. Human papillomavirus types in 115,789 HPV-positive women: a meta-analysis from cervical infection to cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012 Nov 15;131(10):2349-59. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzick J, Cadman L, Mesher D, Austin J, Ashdown-Barr L, Ho L, et al. Comparing the performance of six human papillomavirus tests in a screening population. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(4):908-13. [CrossRef]
- Engesaeter B, van Diermen Hidle B, Hansen M, Moltu P, Staby KM, Borchgrevink-Persen S, et al. Quality assurance of human papillomavirus (HPV) testing in the implementation of HPV primary screening in Norway: an inter-laboratory reproducibility study. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16(1):698. [CrossRef]
| Triage strategies | TP | TN | FP | FN | SE % | SP % | AU* % | PPV % | 95% CI (PPV) | NPV % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytology ASC-US+ | 102 | 396 | 432 | 32 | 76.1 | 47.8 | 62.0 | 19.1 | 15.8 - 22.4 | 92.5 |
| Cytology ASC-H+ | 37 | 799 | 29 | 97 | 27.6 | 96.5 | 62.1 | 56.1 | 44.1 - 68.0 | 89.2 |
| HPV mRNA 16,18,31,33,45+ | 86 | 646 | 182 | 48 | 64.2 | 78.0 | 71.1 | 32.1 | 26.5 - 37.7 | 93.1 |
| HPV mRNA 16,18,31,33,45,52,58+ | 98 | 588 | 240 | 36 | 73.1 | 71.0 | 72.1 | 29.0 | 24.2 - 33.8 | 94.2 |
| Triage strategies | Triage positives (%) | No. of CIN2+ (1) | No. of colposcopies (2) | Colposcopies/CIN2+ (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytology ASC-US+ | 55.5 | 102 | 534 | 5.2 |
| Cytology ASC-H+ | 6.9 | 37 | 66 | 1.8 |
| HPV mRNA 16,18,31,33,45+ | 27.9 | 86 | 268 | 3.1 |
| HPV mRNA 16,18,31,33,45,52,58+ | 35.1 | 98 | 338 | 3.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




