Submitted:
04 January 2023
Posted:
04 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
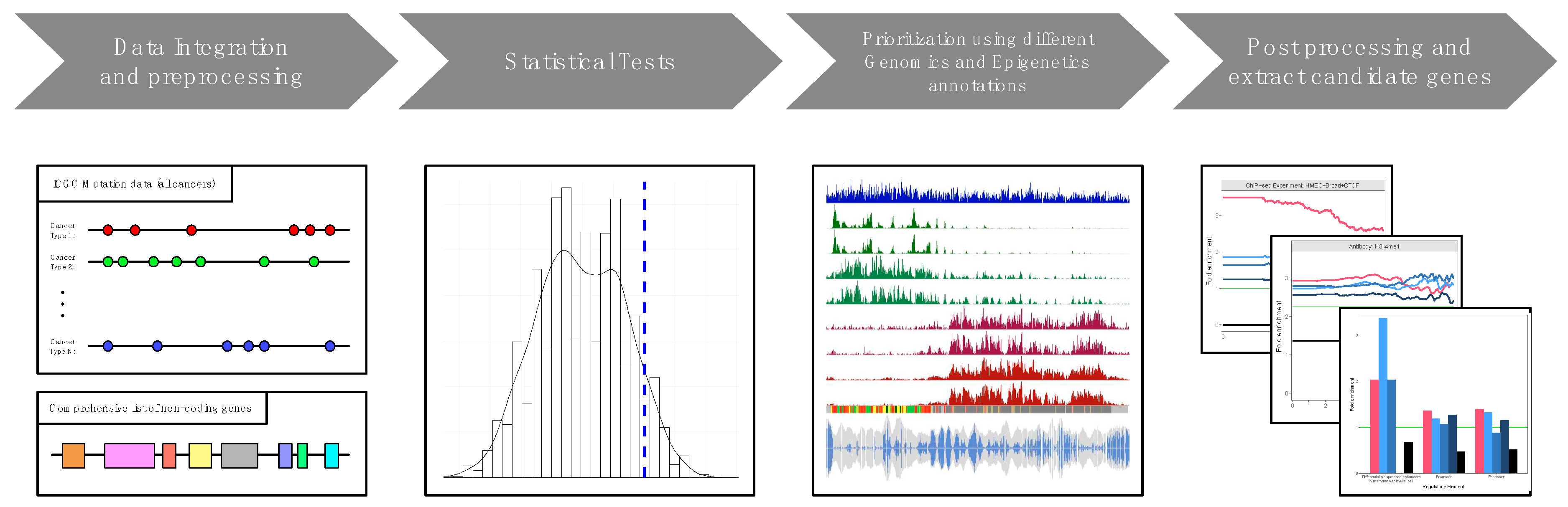
2. Implementation
Statistical framework
| #samples in that have a mutation in the region . | #samples in that do not have a mutation in the region . |
| #samples in all catalogs except that have a mutation in the region . | #samples in all catalogs except that do not have a mutation in the region . |
Annotations scheme
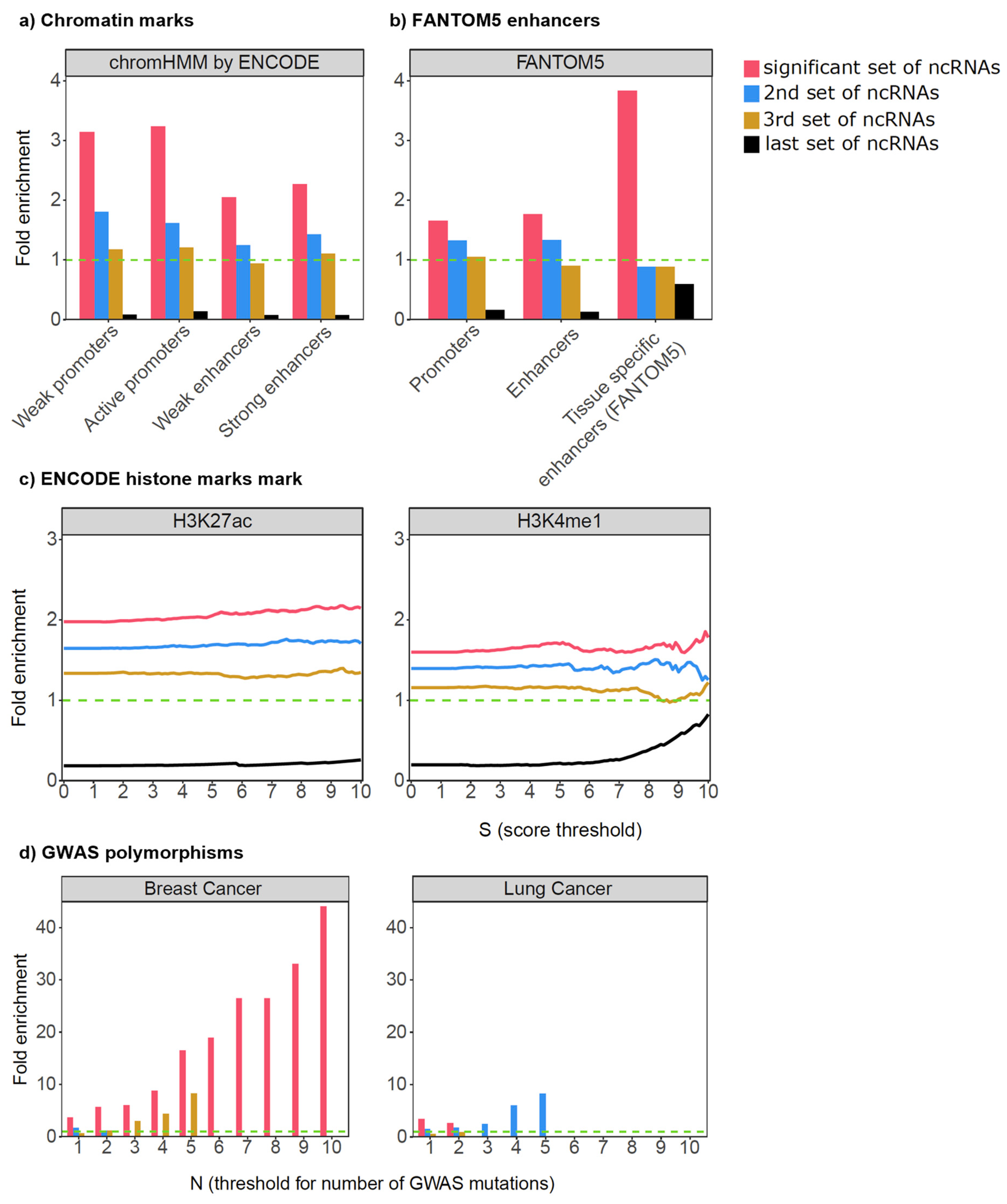
3. Application of SomaGene
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Availability and Implementation
Tool Availability
References
- Harrow J, Frankish A, Gonzalez JM, Tapanari E, Diekhans M, Kokocinski F, et al. GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Research. 2012;22(9):1760-74. [CrossRef]
- Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U, Sahu A, Hosono Y, et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nature Genetics. 2015;47:199. [CrossRef]
- Dashti H, Dehzangi, I., Bayati, M., Breen, J., Beheshti, A., Lovell, N. Integrative analysis of mutated genes and mutational processes reveals novel mutational biomarkers in colorectal cancer. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022;23(11):1-24. [CrossRef]
- Heidari R, Akbariqomi, M., Asgari, Y., Ebrahimi, D. A systematic review of long non-coding RNAs with a potential role in Breast Cancer. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research. 2021;787:108375. [CrossRef]
- Ghareyazi A, Mohseni, A., Dashti, H., Beheshti, A., Dehzangi, A., Rabiee, H. R. Whole-genome analysis of de novo somatic point mutations reveals novel mutational biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. Cancers. 2021;13(17):4376. [CrossRef]
- Bayati M, Rabiee, H. R., Mehrbod, M., Vafaee, F., Ebrahimi, D., Forrest, A. R. CANCERSIGN: a user-friendly and robust tool for identification and classification of mutational signatures and patterns in cancer genomes. Scientific reports. 2020;10(1):1-11. [CrossRef]
- Alinejad-Rokny H, Heng, J. I., & Forrest, A. R. Brain-enriched coding and long non-coding RNA genes are overrepresented in recurrent neurodevelopmental disorder CNVs. Cell Reports. 2020;33(4):108307. [CrossRef]
- Woodward KJ, Stampalia, J., Vanyai, H., Rijhumal, H., Potts, K., Taylor, F., ... & Heng, J. I. Atypical nested 22q11. 2 duplications between LCR 22B and LCR 22D are associated with neurodevelopmental phenotypes including autism spectrum disorder with incomplete penetrance. Molecular genetics & genomic medicine. 2019;7(2):e00507. [CrossRef]
- Poulton C, Baynam, G., Yates, C., Williams, S., Wright, H., ... & Heng, J. I. T. A review of structural brain abnormalities in Pallister-Killian syndrome. Molecular genetics & genomic medicine. 2018;6(1):92-8. [CrossRef]
- Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018;172(3):393-407. [CrossRef]
- Ørom UA, Derrien T, Beringer M, Gumireddy K, Gardini A, Bussotti G, et al. Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells. Cell. 2010;143(1):46-58. [CrossRef]
- Kim T-K, Hemberg M, Gray JM. Enhancer RNAs: a class of long noncoding RNAs synthesized at enhancers. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology. 2015;7(1):a018622. [CrossRef]
- Quinodoz S, Guttman M. Long noncoding RNAs: an emerging link between gene regulation and nuclear organization. Trends in cell biology. 2014;24(11):651-63. [CrossRef]
- Böhmdorfer G, Wierzbicki AT. Control of chromatin structure by long noncoding RNA. Trends in cell biology. 2015;25:623-32. [CrossRef]
- Alinejad-Rokny H, Ghavami Modegh, R., Rabiee, H. R., Ramezani Sarbandi, E., Rezaie, N., Tam, K. T., & Forrest, A. R. MaxHiC: A robust background correction model to identify biologically relevant chromatin interactions in Hi-C and capture Hi-C experiments. PLOS Computational Biology,. 2022;18(6):e1010241.
- Khakmardan S, Rezvani, M., Pouyan, A. A., Fateh, M. MHiC, an integrated user-friendly tool for the identification and visualization of significant interactions in Hi-C data. BMC genomics. 2020;21(1):1-10. [CrossRef]
- Rheinbay E, Parasuraman P, Grimsby J, Tiao G, Engreitz JM, Kim J, et al. Recurrent and functional regulatory mutations in breast cancer. Nature. 2017;547:55. [CrossRef]
- Weinhold N, Jacobsen A, Schultz N, Sander C, Lee W. Genome-wide analysis of noncoding regulatory mutations in cancer. Nature Genetics. 2014;46:1160. [CrossRef]
- Parhami P, Fateh, M., Rezvani, M. A comparison of deep neural network models for cluster cancer patients through somatic point mutations. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. 2022:1-16. [CrossRef]
- Alinejad-Rokny H, Anwar, F., Waters, S. A., Davenport, M. P., & Ebrahimi, D. Source of CpG depletion in the HIV-1 genome. Molecular biology and evolution. 2016;33(12):3205-12. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi D, Davenport MP. Insights into the motif preference of APOBEC3 enzymes. PloS one. 2014;9(1):e87679. [CrossRef]
- Lloyd SB, Lichtfuss, M., Amarasena, T. H., Alcantara, S., De Rose, R., Tachedjian, G., ... & Kent, S. J. High fidelity simian immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase mutants have impaired replication in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 2016;492:1-10. [CrossRef]
- Gooneratne SL, Ebrahimi, D., Bohn, P. S., Wiseman, R. W., O'Connor, D. H., ... & Kent, S. J. Linking pig-tailed macaque major histocompatibility complex class I haplotypes and cytotoxic T lymphocyte escape mutations in simian immunodeficiency virus infection. Journal of virology. 2014;88(24):14310-25. [CrossRef]
- Andersson R, Gebhard C, Miguel-Escalada I, Hoof I, Bornholdt J, Boyd M, et al. An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature. 2014;507:455. [CrossRef]
- MacArthur J, Bowler E, Cerezo M, Gil L, Hall P, Hastings E, et al. The new NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies (GWAS Catalog). Nucleic acids research. 2017;45(D1):D896-D901. [CrossRef]
- Ernst J, Kellis M. Discovery and characterization of chromatin states for systematic annotation of the human genome. Nature Biotechnology. 2010;28:817. [CrossRef]
- Bernstein BE, Kamal M, Lindblad-Toh K, Bekiranov S, Bailey DK, Huebert DJ, et al. Genomic Maps and Comparative Analysis of Histone Modifications in Human and Mouse. Cell. 2005;120(2):169-81. [CrossRef]
- Sabo PJ, Hawrylycz M, Wallace JC, Humbert R, Yu M, Shafer A, et al. Discovery of functional noncoding elements by digital analysis of chromatin structure. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101(48):16837. [CrossRef]
- Rezaie N BM, Tahaei MS, Hamidi M, Khorasani S, Lovell NH, Breen J, Rabiee HR. Somatic point mutations are enriched in long non-coding RNAs with possible regulatory function in breast cancer. Communications Biology. 2022;5(1):1-13.
- Dashti H, Dehzangi, A., Bayati, M., Breen, J., Lovell, N., Ebrahimi, D. Integrative analysis of mutated genes and mutational processes reveals seven colorectal cancer subtypes. bioRxiv. 2020;2020.
- Javanmard R, JeddiSaravi, K. Proposed a new method for rules extraction using artificial neural network and artificial immune system in cancer diagnosis. Journal of Bionanoscience. 2013;7(6):665-72. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi MR, Akbarzadeh, H., Parvin, H., Nejatian, S., Rezaie, V. Consensus function based on cluster-wise two level clustering. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2021;54(1):639-65. [CrossRef]
- Niu H, Khozouie, N., Parvin, H., Beheshti, A., & Mahmoudi, M. R. An ensemble of locally reliable cluster solutions. Applied Sciences. 2020;10(5):1891. [CrossRef]
- Rajaei P, Jahanian, K. H., Beheshti, A., Band, S. S., Dehzangi, A. VIRMOTIF: A user-friendly tool for viral sequence analysis. Genes. 2021;12(2):186. [CrossRef]
- Shamshirband S, Fathi, M., Dehzangi, A., Chronopoulos, A. T., A review on deep learning approaches in healthcare systems: Taxonomies, challenges, and open issues. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2021;113:103627. [CrossRef]
- Alinejad-Rokny H, Sadroddiny, E., & Scaria, V. Machine learning and data mining techniques for medical complex data analysis. Neurocomputing. 2018;276(1). [CrossRef]
- Alinejad-Rokny H, Pourshaban, H., Orimi, A. G., & Baboli, M. M. Network motifs detection strategies and using for bioinformatic networks. Journal of Bionanoscience. 2014;8(5):353-9. [CrossRef]
- Parvin H, & Parvin, S. A classifier ensemble of binary classifier ensembles. International Journal of Learning Management Systems. 2013;1(2):37-47. [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili L, Behrouz Minaei-Bidgoli, and Mahdi Nasiri. Hybrid recommender system for joining virtual communities. Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology. 2012;4(5):500-9.
- Hosseinpoor M, Parvin, H., Nejatian, S., Rezaie, V., Bagherifard, K., Dehzangi, A. Proposing a novel community detection approach to identify cointeracting genomic regions. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering. 2020;17(3):2193-217. [CrossRef]
- Alinejad-Rokny H. Proposing on Optimized Homolographic Motif Mining Strategy Based on Parallel Computing for Complex Biological Networks. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics. 2016;6(2):416-24. [CrossRef]
- Parvin H, Seyedaghaee, N., & Parvin, S. A heuristic scalable classifier ensemble of binary classifier ensembles. Journal of Bioinformatics and Intelligent Control. 2012;1(2):163-70. [CrossRef]
- Parvin H, Helmi H, Minaei B, Shirgahi H. Linkage learning based on differences in local optimums of building blocks with one optima. International Journal of Physical Sciences. 2011;6(14):3419-25.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





