Submitted:
07 July 2023
Posted:
10 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening for Bacteriophages
2.2. Isolation and Purification of Bacteriophages
2.3. TEM Imaging
2.4. One Step Growth Curve
2.5. Host Specificity
2.6. Temperature and pH Stability
2.7. In Vitro Time Kill Study
2.8. In Vivo Toxicity Study
2.9. In Vivo Infection
2.10. Genome Sequence and Analysis
2.11. E. coli Bacteriophage Host Receptor Prediction Using Machine Learning Based Multi Class Classifier
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Phage against XDR E. coli Strains
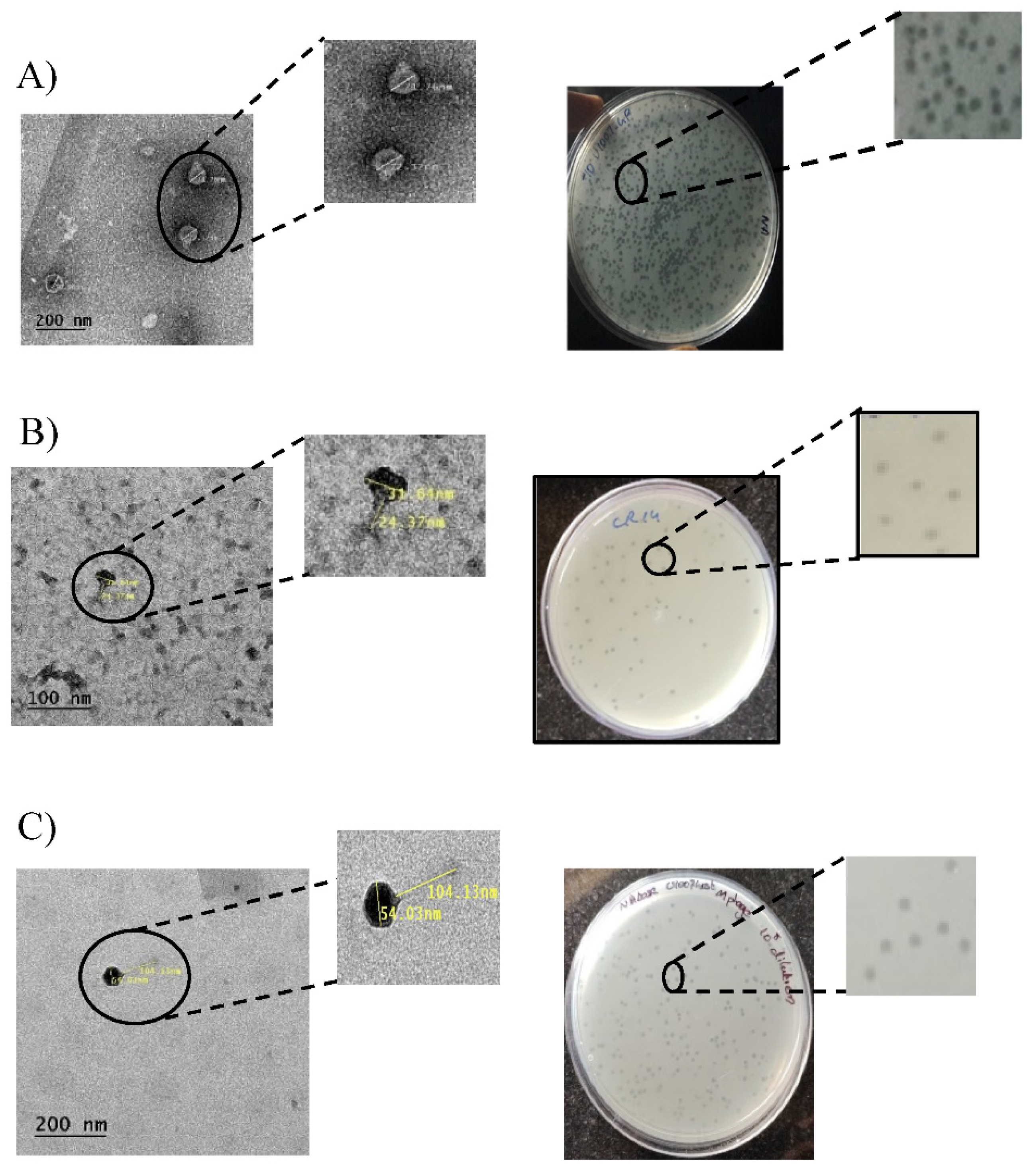
3.2. Isolation and Purification of U1G, CR and M Phages
3.3. TEM Imaging
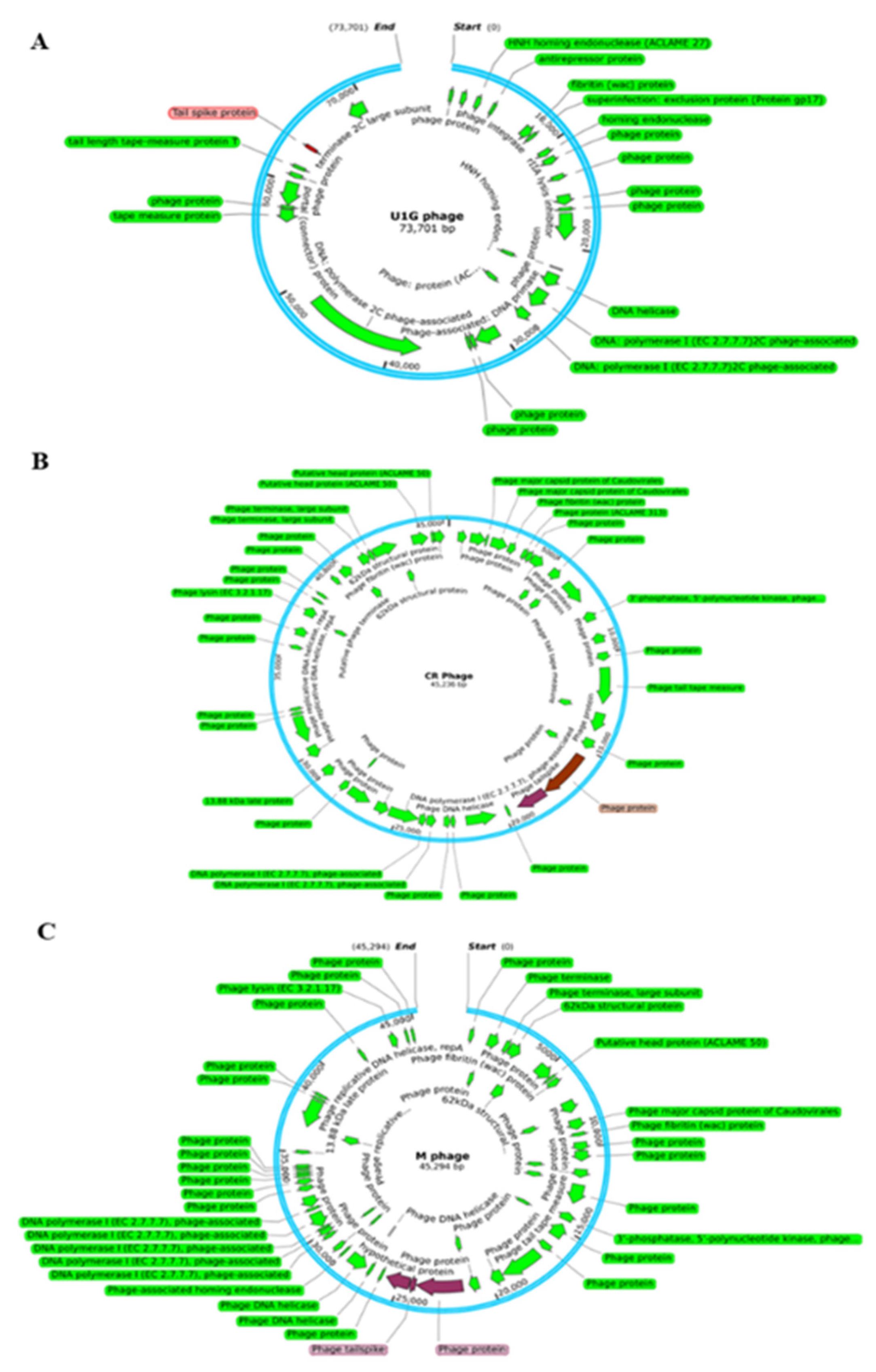
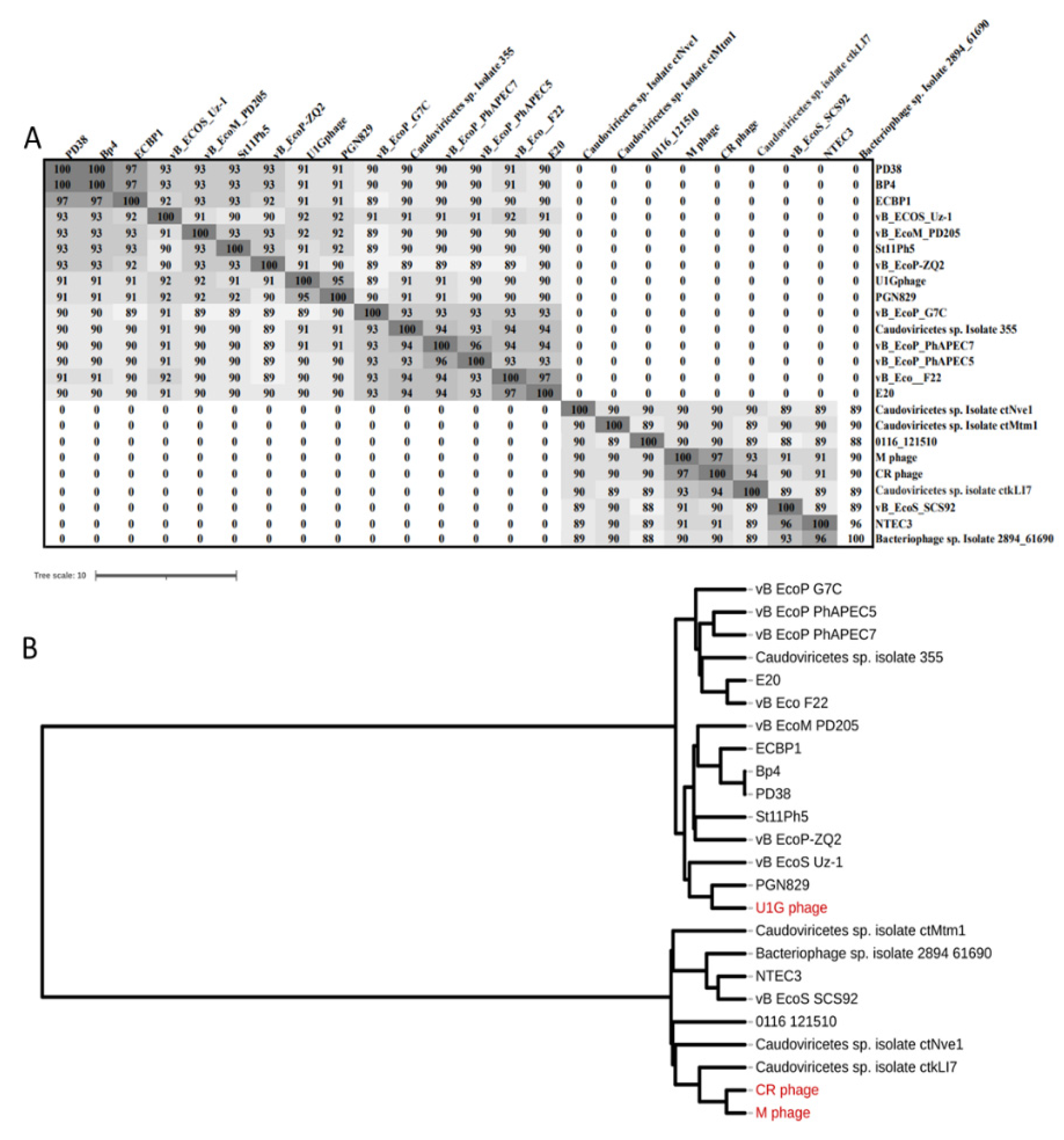
3.4. Genome Analysis
3.5. A multiclass-classification model for bacteriophage host-receptor prediction in E. coli:
- Physiological Validation of host OmpC as the receptor for U1G phage
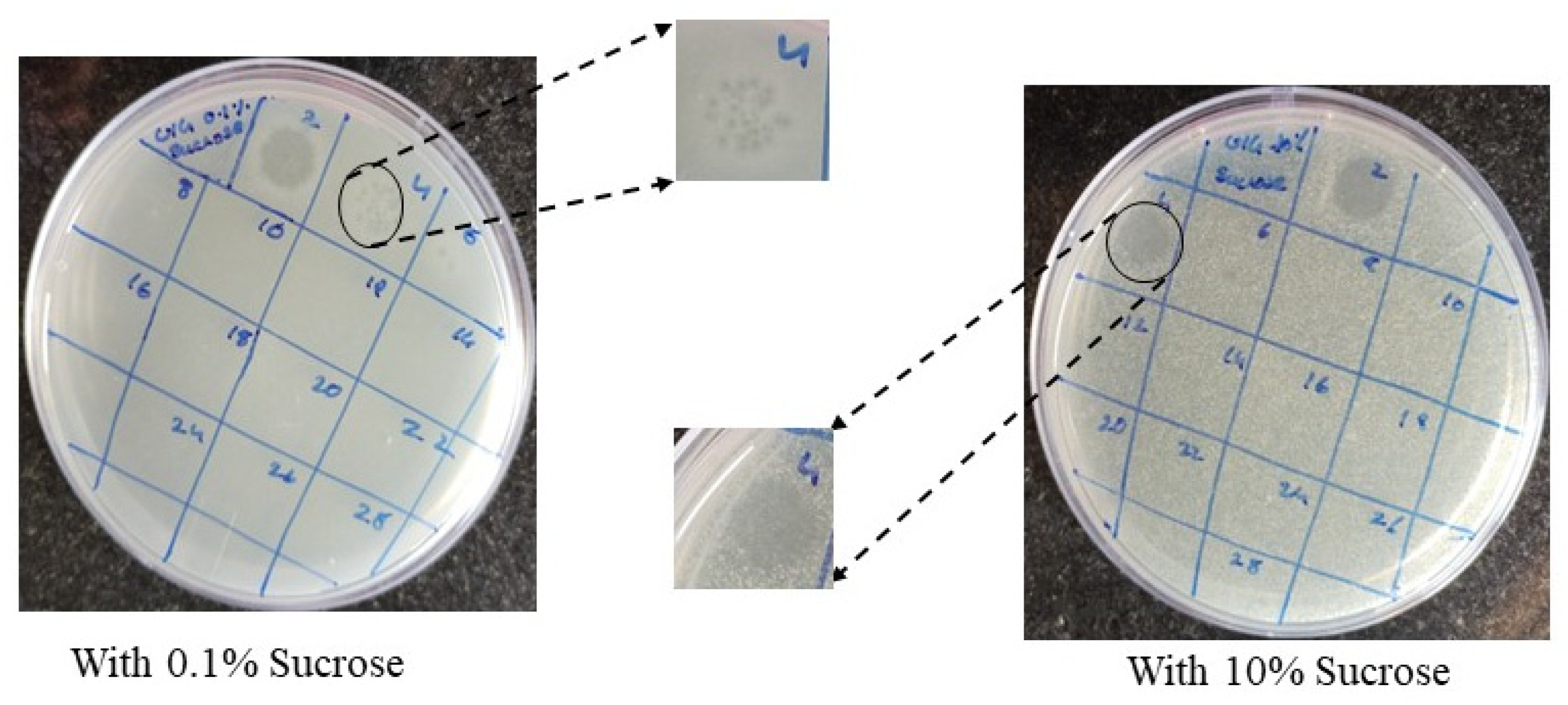
3.6. Burst Size, Latent Period and Host Specificity
3.7. pH and Temperature Sensitivity
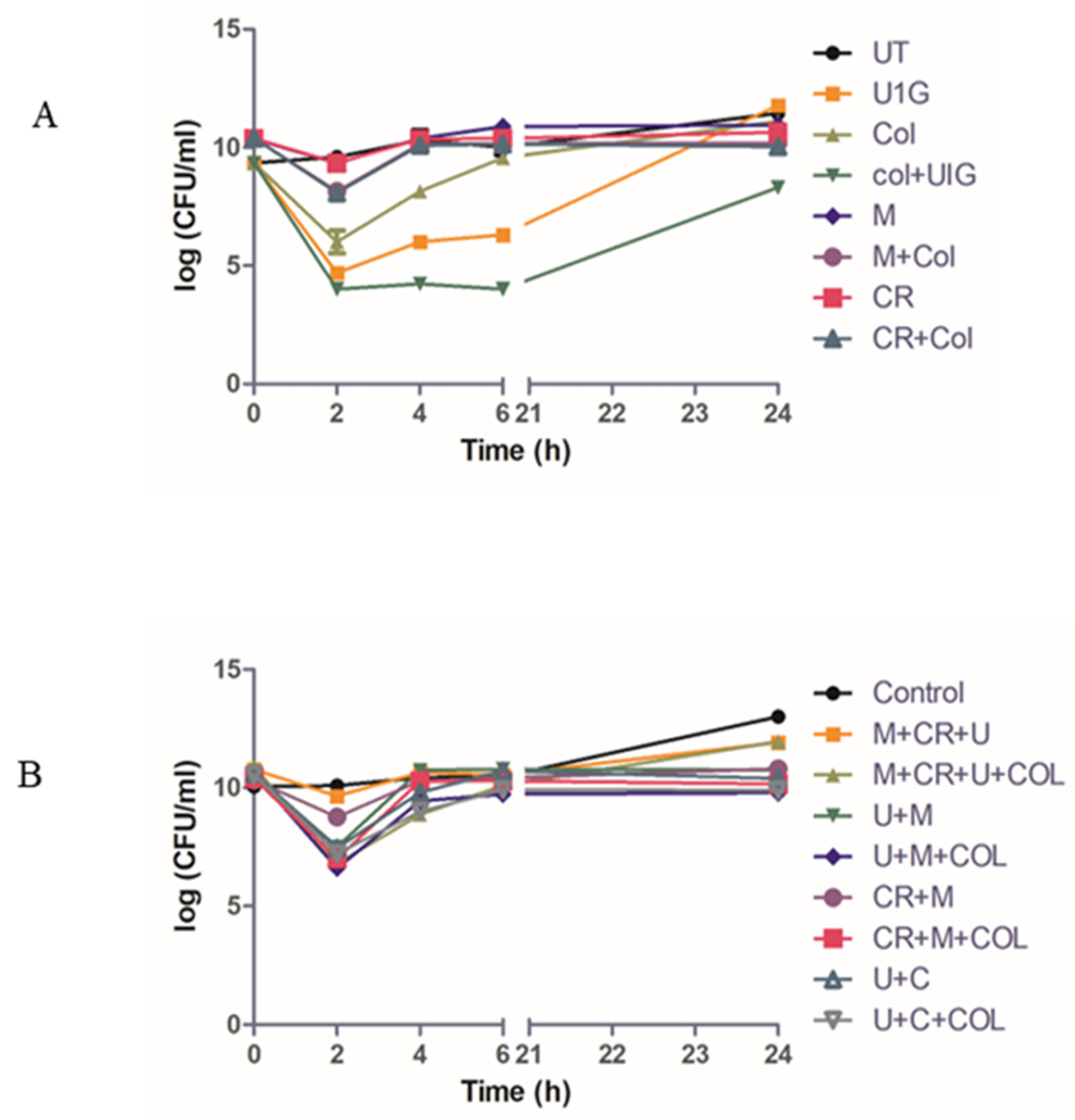
3.8. Time Kill Study
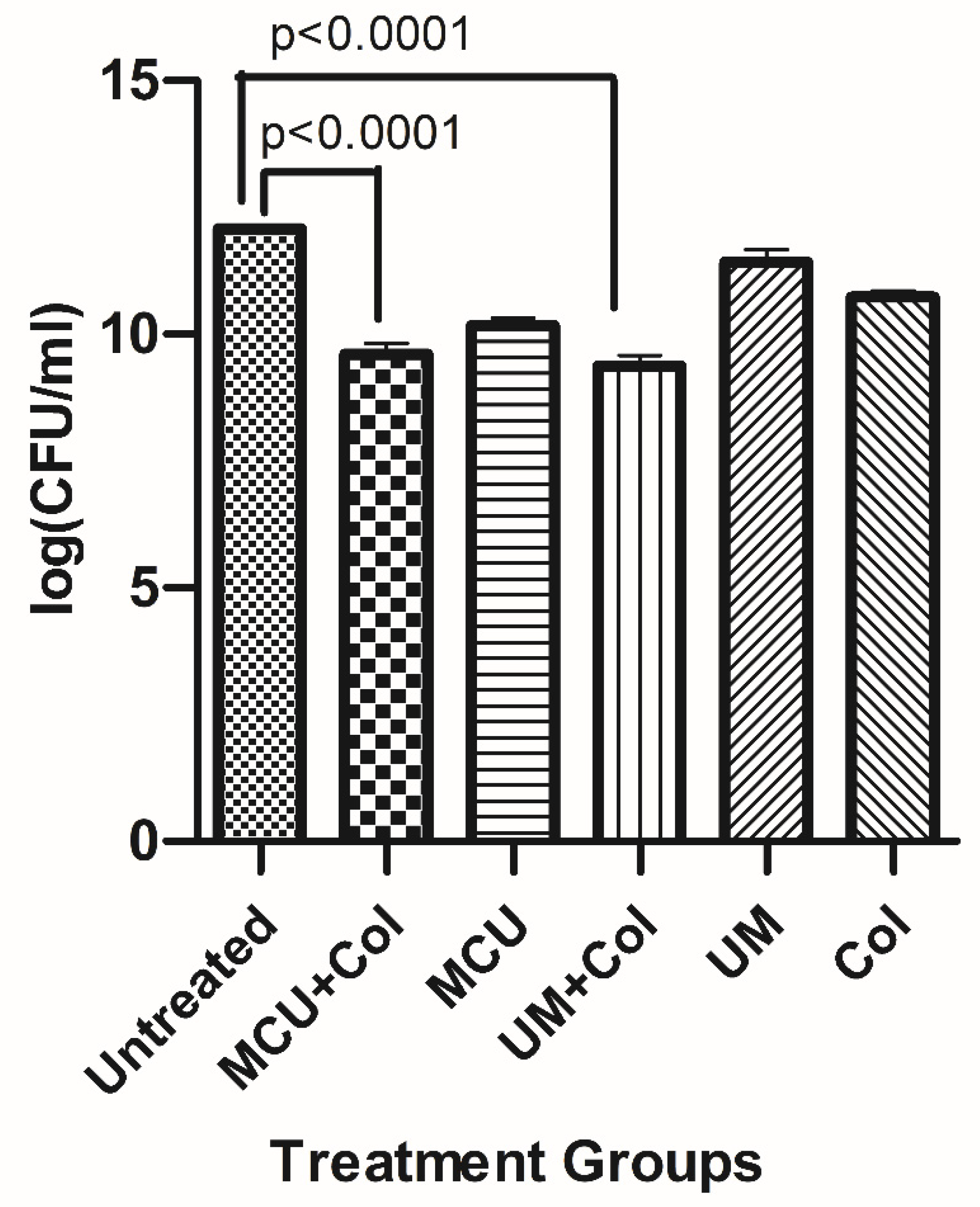
3.9. In Vivo Toxicity and Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romero-Calle, D.; Benevides, R.G.; Góes-Neto, A.; Billington, C. Bacteriophages as Alternatives to Antibiotics in Clinical Care. Antibiotics 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wang, G.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Li, R. Emergence and Transmission of Plasmid-Mediated Mobile Colistin Resistance Gene Mcr-10 in Humans and Companion Animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Majewski, P.; Gutowska, A.; Smith, D.G.E.; Hauschild, T.; Majewska, P.; Hryszko, T.; Gizycka, D.; Kedra, B.; Kochanowicz, J.; Glowiński, J.; et al. Plasmid Mediated Mcr-1.1 Colistin-Resistance in Clinical Extraintestinal Escherichia Coli Strains Isolated in Poland. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Voelker, R. FDA Approves Bacteriophage Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 638. [CrossRef]
- NIH No Title. 2020.
- NIH- Clinicaltrials No Title. 2020.
- Parfitt, T. Georgia: An Unlikely Stronghold for Bacteriophage Therapy. Lancet 2005, 365, 2166–2167. [CrossRef]
- Brives, C.; Pourraz, J. Phage Therapy as a Potential Solution in the Fight against AMR: Obstacles and Possible Futures. Palgrave Commun. 2020, 6, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Zaldastanishvili, E.; Leshkasheli, L.; Dadiani, M.; Nadareishvili, L.; Askilashvili, L.; Kvatadze, N.; Goderdzishvili, M.; Kutateladze, M.; Balarjishvili, N. Phage Therapy Experience at the Eliava Phage Therapy Center: Three Cases of Bacterial Persistence. Viruses 2021, 13, 1901. [CrossRef]
- Necel, A.; Bloch, S.; Nejman-Faleńczyk, B.; Grabski, M.; Topka, G.; Dydecka, A.; Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, K.; Grabowski, Ł.; Jurczak-Kurek, A.; Wołkowicz, T.; et al. Characterization of a Bacteriophage, VB_Eco4M-7, That Effectively Infects Many Escherichia Coli O157 Strains. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Cepko, L.C.S.; Garling, E.E.; Dinsdale, M.J.; Scott, W.P.; Bandy, L.; Nice, T.; Faber-Hammond, J.; Mellies, J.L. Myoviridae Phage PDX Kills Enteroaggregative Escherichia Coli without Human Microbiome Dysbiosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 309–323. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yin, B.; Yu, L.; Dang, M.; Guo, Z.; Yan, G.; Hu, D.; Gu, J.; Du, C.; Feng, X.; et al. Overexpression of AmpC Promotes Bacteriophage Lysis of Ampicillin-Resistant Escherichia Coli. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2973. [CrossRef]
- Valério, N.; Oliveira, C.; Jesus, V.; Branco, T.; Pereira, C.; Moreirinha, C.; Almeida, A. Effects of Single and Combined Use of Bacteriophages and Antibiotics to Inactivate Escherichia Coli. Virus Res. 2017, 240, 8–17. [CrossRef]
- Champagne, C.P.; Gardner, N. The Spot Test Method for the In-Plant Enumeration of Bacteriophages with Paired Cultures of Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Subsp. Bulgaricus and Streptococcus Salivarius Subsp. Thermophilus. Int. Dairy J. 1995, 5, 417–425. [CrossRef]
- Adams, M. Assay of Phages by the Agar Layer Method. In Bacteriophages; Interscience Publishers, 1959; pp. 450–451.
- Sulcius, S.; Staniulis, J.; Paškauskas, R. Morphology and Distribution of Phage-like Particles in a Eutrophic Boreal Lagoon. Oceanologia 2011, 53, 587–603. [CrossRef]
- Pajunen, M.; Kiljunen, S.; Skurnik, M. Bacteriophage PhiYeO3-12, Specific for Yersinia Enterocolitica Serotype O:3, Is Related to Coliphages T3 and T7. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5114–5120. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, C.; Chen, X.; Hu, L.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Lin, W.; Jiang, A.; Feng, R.; et al. Characterizing the Biology of Lytic Bacteriophage VB_EaeM_φEap-3 Infecting Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacter Aerogenes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 420. [CrossRef]
- Kering, K.K.; Zhang, X.; Nyaruaba, R.; Yu, J.; Wei, H. Application of Adaptive Evolution to Improve the Stability of Bacteriophages during Storage. Viruses 2020, 12, 423. [CrossRef]
- Anand, T.; Virmani, N.; Kumar, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Pavulraj, S.; Bera, B.C.; Vaid, R.K.; Ahlawat, U.; Tripathi, B.N. Phage Therapy for Treatment of Virulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae Infection in a Mouse Model. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 34–41. [CrossRef]
- Grillon, A.; Schramm, F.; Kleinberg, M.; Jehl, F. Comparative Activity of Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin and Moxifloxacin against Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia Assessed by Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations and Time-Kill Studies. PLoS One 2016, 11, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Strungaru, S.-A.; Huang, J.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Which Zebrafish Strains Are More Suitable to Perform Behavioral Studies? A Comprehensive Comparison by Phenomic Approach. Biology (Basel). 2020, 9, 200. [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Christena, L.R.; Subbarao, H.M.V.; Venkatasubramanian, U.; Thiagarajan, R.; Sivaramakrishnan, V.; Kasilingam, K.; Saisubramanian, N.; Ganesan, S.S. Identification of Benzochromene Derivatives as a Highly Specific NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitor to Mitigate the Drug Resistant Strains of s. Aureus†. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 30258–30267. [CrossRef]
- Neely, M.; Pfeifer, J.; Caparon, M. Streptococcus-Zebrafish Model of Bacterial Pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3904–3914. [CrossRef]
- Boulé, J.; Sholberg, P.L.; Lehman, S.M.; O’Gorman, D.T.; Svircev, A.M. Isolation and Characterization of Eight Bacteriophages Infecting Erwinia Amylovora and Their Potential as Biological Control Agents in British Columbia, Canada. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 33, 308–317. [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and Accurate Long-Read Assembly via Adaptive k-Mer Weighting and Repeat Separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, gr.215087.116. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 75. [CrossRef]
- M, J.; I, Z.; Y, R.; Y, M.; S, M.; TL, M. NCBI BLAST: A Better Web Interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36. [CrossRef]
- PP, C.; TM, L. TRNAscan-SE: Searching for TRNA Genes in Genomic Sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1962, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHAST, PHASTER and PHASTEST: Tools for Finding Prophage in Bacterial Genomes. Brief. Bioinform. 2017. [CrossRef]
- LM, R.-R.; KT, K. The Enveomics Collection: A Toolbox for Specialized Analyses of Microbial Genomes and Metagenomes. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M. V. Identification of Acquired Antimicrobial Resistance Genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-Time Whole-Genome Sequencing for Routine Typing, Surveillance, and Outbreak Detection of Verotoxigenic Escherichia Coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [CrossRef]
- Boeckaerts, D.; Stock, M.; Criel, B.; Gerstmans, H.; De Baets, B.; Briers, Y. Predicting Bacteriophage Hosts Based on Sequences of Annotated Receptor-Binding Proteins. Sci. Reports 2021 111 2021, 11, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Bertozzi Silva, J.; Storms, Z.; Sauvageau, D. Host Receptors for Bacteriophage Adsorption. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Rothenberg, E. Interaction of Bacteriophage λ with Its E. Coli Receptor, LamB. Viruses 2012, 4, 3162. [CrossRef]
- Sandulache, R.; Prehm, P.; Kamp, D. Cell Wall Receptor for Bacteriophage Mu G(+). J. Bacteriol. 1984, 160, 299. [CrossRef]
- Blagus, R.; Lusa, L. SMOTE for High-Dimensional Class-Imbalanced Data. BMC Bioinformatics 2013, 14, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa FABIANPEDREGOSA, F.; Michel, V.; Grisel OLIVIERGRISEL, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Vanderplas, J.; Cournapeau, D.; Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python Gaël Varoquaux Bertrand Thirion Vincent Dubourg Alexandre Passos PEDREGOSA, VAROQUAUX, GRAMFORT ET AL. Matthieu Perrot. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830.
- Sundaramoorthy, N.S.; Mohan, H.M.; Subramaniam, S.; Raman, T.; Selva Ganesan, S.; Sivasubamanian, A.; Nagarajan, S. Ursolic Acid Inhibits Colistin Efflux and Curtails Colistin Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. AMB Express 2019, 9, 27. [CrossRef]
- J, W.; D, T.; AD, M.; P, M.; AM, K.; EM, A. From Orphan Phage to a Proposed New Family-the Diversity of N4-Like Viruses. Antibiot. (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 9, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Puente, J.L.; Verdugo-Rodríguez, A.; Calva, E. Expression of Salmonella Typhi and Escherichia Coli OmpC Is Influenced Differently by Medium Osmolarity; Dependence on Escherichia Coli OmpR. Mol. Microbiol. 1991, 5, 1205–1210. [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Machida, K.; Arikado, E.; Saito, H.; Kakegawa, T.; Kobayashi, H. Expression of Outer Membrane Proteins in Escherichia Coli Growing at Acid PH. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 943–947. [CrossRef]
- Mead, A.; Toutain, P.-L.; Richez, P.; Pelligand, L. Quantitative Pharmacodynamic Characterization of Resistance versus Heteroresistance of Colistin in E. Coli Using a Semimechanistic Modeling of Killing Curves. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, L.; He, Y.; Yu, W.; Fu, S.; Ni, W.; Gao, Z. Heteroresistance Is Associated With in Vitro Regrowth During Colistin Treatment in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.M.; Koskella, B.; Lin, H.C. Phage Therapy: An Alternative to Antibiotics in the Age of Multi-Drug Resistance. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 8, 162. [CrossRef]
- Dublanchet, A.; Bourne, S. The Epic of Phage Therapy. In Proceedings of the Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology; Hindawi Limited, 2007; Vol. 18, pp. 15–18. [CrossRef]
- Chanishvili, N. Phage Therapy-History from Twort and d’Herelle Through Soviet Experience to Current Approaches. In Advances in Virus Research; Academic Press Inc., 2012; Vol. 83, pp. 3–40. [CrossRef]
- WHO No Title.
- Bondy-Denomy, J.; Qian, J.; Westra, E.R.; Buckling, A.; Guttman, D.S.; Davidson, A.R.; Maxwell, K.L. Prophages Mediate Defense against Phage Infection through Diverse Mechanisms. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2854–2866. [CrossRef]
- Sundaramoorthy, N.S.; Thothathri, S.; Bhaskaran, M.; GaneshPrasad, A.K.; Nagarajan, S. Phages from Ganges River Curtail in Vitro Biofilms and Planktonic Growth of Drug Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae in a Zebrafish Infection Model. AMB Express 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Dimri, A.; Awasthi, C.; Uniyal, S.; Nautiyal, A.; Singh, K.P. Isolation and Characterization of Coliform Bacteria and Bacteriophages from Ganga River in Northern Himalayan Regions. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1582–1592. [CrossRef]
- Manohar, P.; Tamhankar, A.J.; Lundborg, C.S.; Nachimuthu, R. Therapeutic Characterization and Efficacy of Bacteriophage Cocktails Infecting Escherichia Coli, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, and Enterobacter Species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 574. [CrossRef]
- Khairnar, K. Ganges: Special at Its Origin. J. Biol. Res. 2016, 23, 16. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Yadav, B.; Tyagi, R.D. Microbiology of Hospital Wastewater. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 103–148.
- Boyer, M.; Wisniewski-Dyé, F.; Combrisson, J.; Bally, R.; Duponnois, R.; Costechareyre, D. Nettle Manure: An Unsuspected Source of Bacteriophages Active against Various Phytopathogenic Bacteria. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1099–1110. [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T.; Herschler, T.D.; Stopar, D. Bacteriophage Latent-Period Evolution as a Response to Resource Availability. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4233–4241. [CrossRef]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.-M. Mechanisms of Polymyxin Resistance: Acquired and Intrinsic Resistance in Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 643. [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Chen, A.I.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Egan, M.; Yang, X.; Kan, B.; Wang, H.; Goulian, M.; Zhu, J. Colistin Resistance-Mediated Bacterial Surface Modification Sensitizes Phage Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63. [CrossRef]
- Versoza, C.J.; Pfeifer, S.P. Computational Prediction of Bacteriophage Host Ranges. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 149. [CrossRef]
- Qimron, U.; Marintcheva, B.; Tabor, S.; Richardson, C.C. Genomewide Screens for Escherichia Coli Genes Affecting Growth of T7 Bacteriophage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2006, 103, 19039–19044. [CrossRef]
- Darcan, Cihan & Ozkanca, Resit & Dil, Ö. The Role of RpoS, H-NS and AcP on the PH-Dependent OmpC and OmpF Porin Expressions of Escherichia Coli at Different PH. African J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1845-1854.
- Heyde, M.; Portalier, R. Regulation of Major Outer Membrane Porin Proteins of Escherichia Coli K 12 by PH. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1987, 208, 511–517. [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T. Bacteriophage Secondary Infection. Virol. Sin. 2015, 30, 3–10. [CrossRef]
- M, A.-Z.; M, W.; EK, C.; AF, G.; RE, S.; K, A.; A, A.; C, E.; C, M.; S, M.; et al. Identification of Novel Bacteriophages with Therapeutic Potential That Target Enterococcus Faecalis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87. [CrossRef]
- Cafora, M.; Deflorian, G.; Forti, F.; Ferrari, L.; Binelli, G.; Briani, F.; Ghisotti, D.; Pistocchi, A. Phage Therapy against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infections in a Cystic Fibrosis Zebrafish Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- M, E.; M, D.Z.; HJ, S. Application of Phage Therapy: Synergistic Effect of Phage EcSw (ΦEcSw) and Antibiotic Combination towards Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia Coli. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2809–2817. [CrossRef]
- Comeau, A.M.; Tétart, F.; Trojet, S.N.; Prère, M.-F.; Krisch, H.M. Phage-Antibiotic Synergy (PAS): β-Lactam and Quinolone Antibiotics Stimulate Virulent Phage Growth. PLoS One 2007, 2, e799. [CrossRef]
- North, O.I.; Brown, E.D. Phage–Antibiotic Combinations: A Promising Approach to Constrain Resistance Evolution in Bacteria. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1496, 23–34. [CrossRef]
- Maltas, J.; Wood, K.B. Pervasive and Diverse Collateral Sensitivity Profiles Inform Optimal Strategies to Limit Antibiotic Resistance. PLOS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000515. [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, T.L.; Jansen, M.; Horz, H.-P. Fighting Pathogenic Bacteria on Two Fronts: Phages and Antibiotics as Combined Strategy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
| All features | ANOVA Feature Selected Dataset | L2 Regularization Feature Selected Dataset | |||||||
| Performance Score | RF | DT | LR | RF | DT | LR | RF | DT | LR |
| Precision | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.78 |
| Recall | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.66 | 0.77 |
| Accuracy | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.79 | 0.66 | 0.77 |
| F-1 Score | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.63 | 0.75 |
| MCC | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.76 |
|
Phage |
RBP |
Predicted Receptors | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Features | ANOVA | L2 Regularization | ||
| U1G phage | Phage tail spike protein (107 aa) |
LPS O antigen | LPS O antigen | OmpC or LamB |
| CR phage | Phage protein (828 aa) | FhuA | FhuA | OmpC |
| M phage | Phage protein (852 aa) | OmpC or LamB | FhuA and TonB | OmpF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





