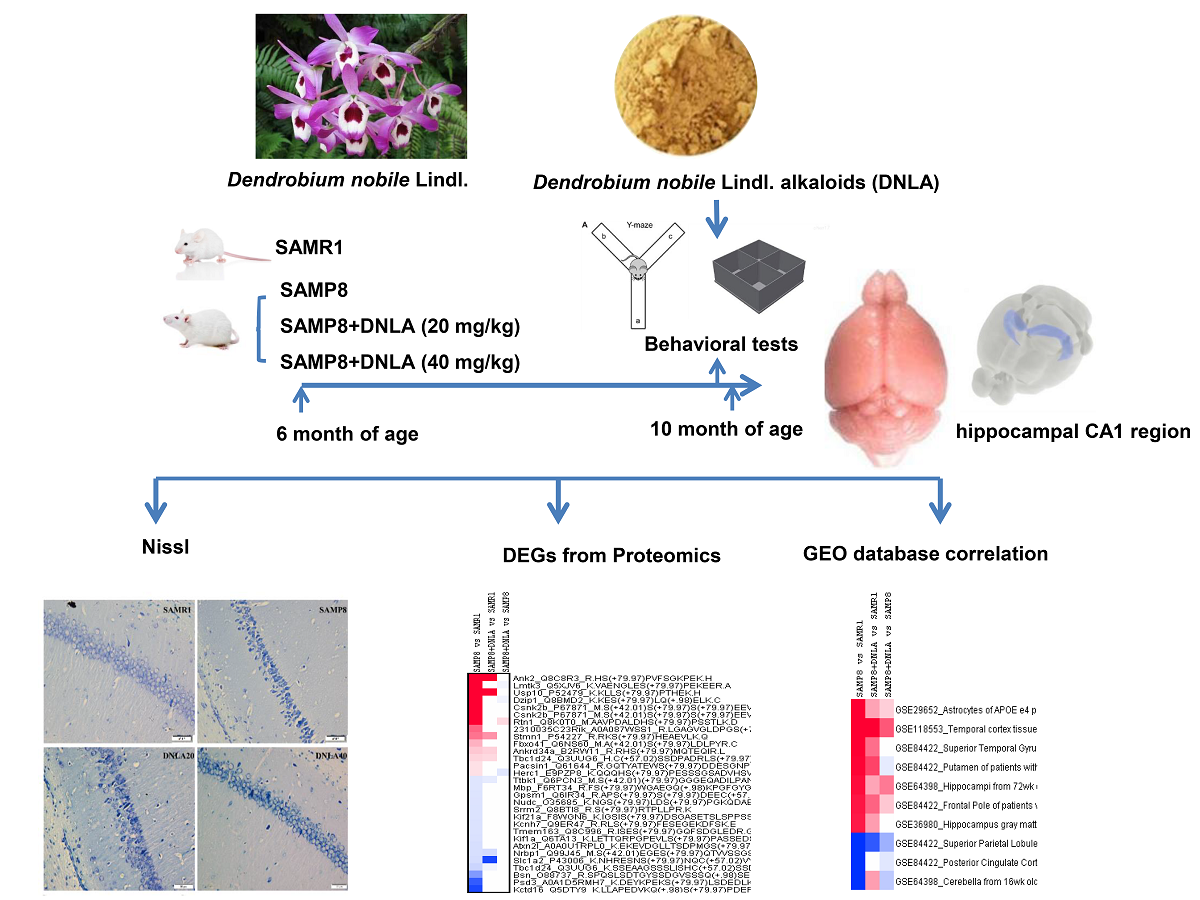
Senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) mice exhibit cognitive defects and neuron loss with aging, and are used to study anti-aging effects of Dendrobium nobile alkaloids (DNLA). SAMP8 mice were orally given DNLA from ages 6 to 10 months. At 10 months of age, behavioral tests and neuron damage were evaluated. Protein was extracted and subjected to phosphorylated proteomic analysis. The cognitive deficits and neuron loss in hippocampus and cortex of aged SAMP8 mice were improved by DNLA. Hippocampal proteomic analysis showed differentially expressed protein/genes in SAMP8 compared to age-matched senescence-accelerated resistant mice, including altered tubulin binding, microtubule binding, etc. via Gene Oncology. KEGG revealed endocytosis, mRNA surveillance, tight junction, protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, aldosterone synthesis and secretion, and glucagon signaling pathway changes. Upregulated protein/genes in the hippocampus of SAMP8 mice, such as Lmtk3, Usp10, Dzip1, Csnk2b, and Rtn1, were attenuated by DNLA; whereas downregulated protein/genes, such as Kctd16, Psd3, Bsn, Atxn2l, and Kif1a, were rescued by DNLA. The aberrant protein/gene expressions of SAMP8 mice were correlated with transcriptome changes of Alzheimer’s disease in the GEO database, and were attenuated by DNLA. Thus, DNLA improved cognitive dysfunction and ameliorated neuronal injury in aged SAMP8 mice, and attenuated aberrant protein/gene expressions.