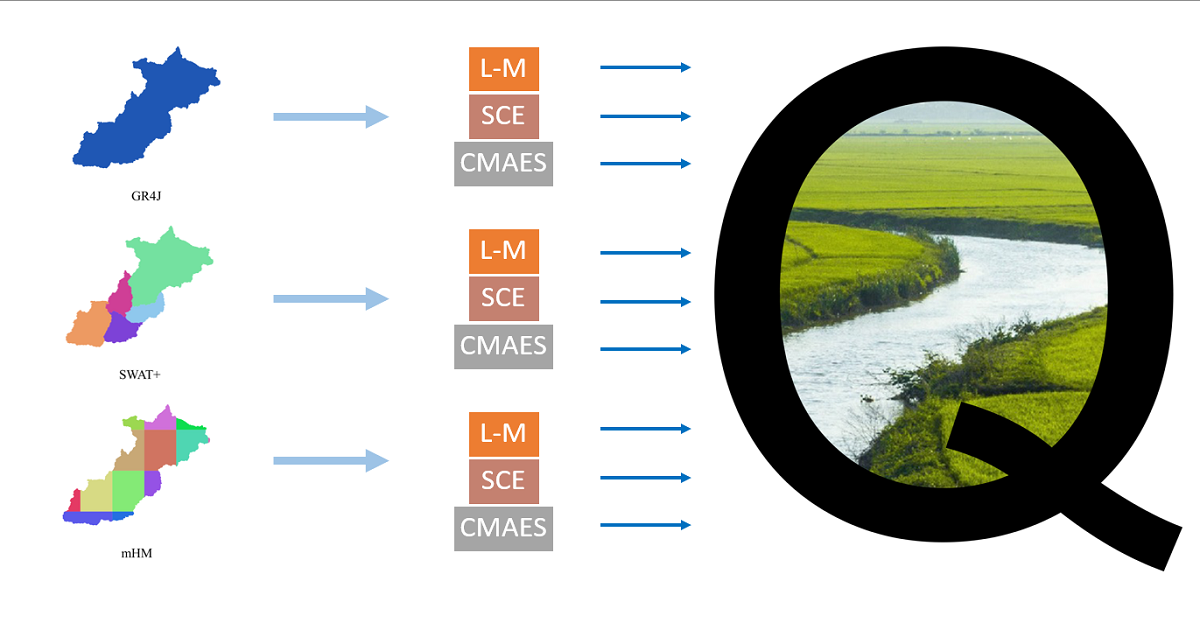
In this study, Acısu Basin, which is upper side of one of the most important basins (Gediz) in Türkiye, was modelled using three types of hydrological models and three different calibration algorithms. Lumped (GR4J), semi-distributed (SWAT+), and fully distributed (mHM) hydrological models were built and integrated with Parameter Estimation Tool (PEST) which is a model independent calibration tool including various algorithms. Levenberg Marquardt (L-M), Shuffled Complex Evolution (SCE), and Covariance Matrix Adoption Evolution Strategy (CMA-ES) were selected as calibration algorithms. Calibration period was 1991-2000, and validation results were obtained for 2002-2005. The effect of model structure and calibration algorithm selection on discharge simulation was evaluated via comparison of 9 different model-algorithm combinations. Results have shown that mHM and CMA-ES combination showed the best discharge simulation performance according to NSE values (calibration: 0.67, validation: 0.60). Although statistically the model results were classified as acceptable, the pattern comparison of discharge value shows that all of the models miss the peak values in significant amounts. This problem may be related to the interventions made in 2000-2001 years interval and possible to overcome by changing the calibration and validation periods, increasing the number of iterations or using the naturalized gauge data.