1. Introduction
The phenomenon of urban expansion and its consequential influence on the urban climate has garnered significant attention in recent years. However, amidst this extensive exploration of the topic, a pivotal inquiry remains conspicuously unanswered: the precise manner in which urban growth exerts its impact on the temperature dynamics of cities situated across diverse climatic regions and environmental circumstances, especially within arid desert locales. Of particular intrigue is the scenario unfolding in Iraq, where the population has experienced a rapid and dramatic surge. In the year 1985, the population of this nation stood at 15,555,800, yet by the year 2022, estimations indicated a remarkable ascent to 42,248,883, manifesting an annual growth rate of 2.5%. According to data provided by the Ministry of Planning, Baghdad, the capital city of Iraq and among its most densely inhabited regions, constitutes a substantial 23% of the nation's entire population (“mop.gov.iq” 2022).
Top of Form
The terrestrial landscape comprises an intricate amalgamation of various components, including vegetation, aqueous surfaces, impermeable materials, and exposed soils. The phenomenon of Land Surface Temperature (LST) exhibits spatiotemporal variations. The correlation between LST and Land Use Land Cover (LULC) has been well-established, elucidating that features such as water bodies, soil moisture, and vegetation tend to mitigate surface temperatures. However, in regions experiencing urban expansion, particularly in humid environments, there is a propensity for elevated surface temperatures. Conversely, in arid settings, urbanization may lead to a reduction in surface temperatures within urban areas compared to the surrounding dry regions, especially during daylight hours(Cai and Du 2009; Rasul, Balzter, and Smith 2015; Shigeta, Ohashi, and Tsukamoto 2009).
Remote sensing platforms, encompassing satellites, aircraft, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), serve as instrumental tools for the quantification of surface temperatures, often in conjunction with meteorological data (Watson 2012). In this array, the Landsat series holds a preeminent position, owing to its extensive historical data archive, cost-free accessibility, and optimal resolution for scrutinizing the intricacies of spatiotemporal variations in LST and its interplay with shifts in land use patterns (Rasul, Balzter, and Smith 2015; Xian et al. 2022).
Nonetheless, the impact of burgeoning urbanization on temperature fluctuations within cities situated in hot desert climates (classified as BWh), such as Baghdad, has received scant attention, with only a limited examination of a few aspects related to LST in such climatic regions. Consequently, the primary objective of this investigation was to delineate LULC alterations in Baghdad spanning the years from 1985 to 2021. To enhance the precision of our analysis, we harnessed advanced artificial intelligence methods, specifically the Random Forest algorithm, to classify LULC patterns from Landsat imagery. Additionally, the study aimed to meticulously evaluate the ramifications of LULC transformations on LST patterns and to discern the principal determinants governing surface temperature dynamics in this specific case study. To achieve these objectives, the research meticulously scrutinized Landsat imagery spanning the aforementioned temporal period, and systematically considered sixteen potential factors, including but not limited to the Dry Built-up Index (DBI), Dry Bare-soil Index (DBSI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI), Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index (NDLI), impervious surface extent, and population density.
The discoveries unearthed through this study make a substantial addition to the expanding compendium of research concerning the impact of urban expansion on urban climatology, with a particular focus on hot desert climates exemplified by Baghdad. Furthermore, the outcomes discern and elucidate the principal determinants regulating the surface temperature within the specified locale, encompassing factors such as vegetative cover and moisture levels. This informational corpus holds particular pertinence for governmental authorities and municipal administrations, as it empowers them to formulate strategies aimed at alleviating the ramifications of urbanization on local climate conditions, especially in the context of heatwaves and other extreme meteorological phenomena. Ultimately, these study findings wield profound ramifications for the effective administration of urban expansion within hot desert environments, thereby offering critical insights to guide policy initiatives geared towards fostering sustainable development.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Case study
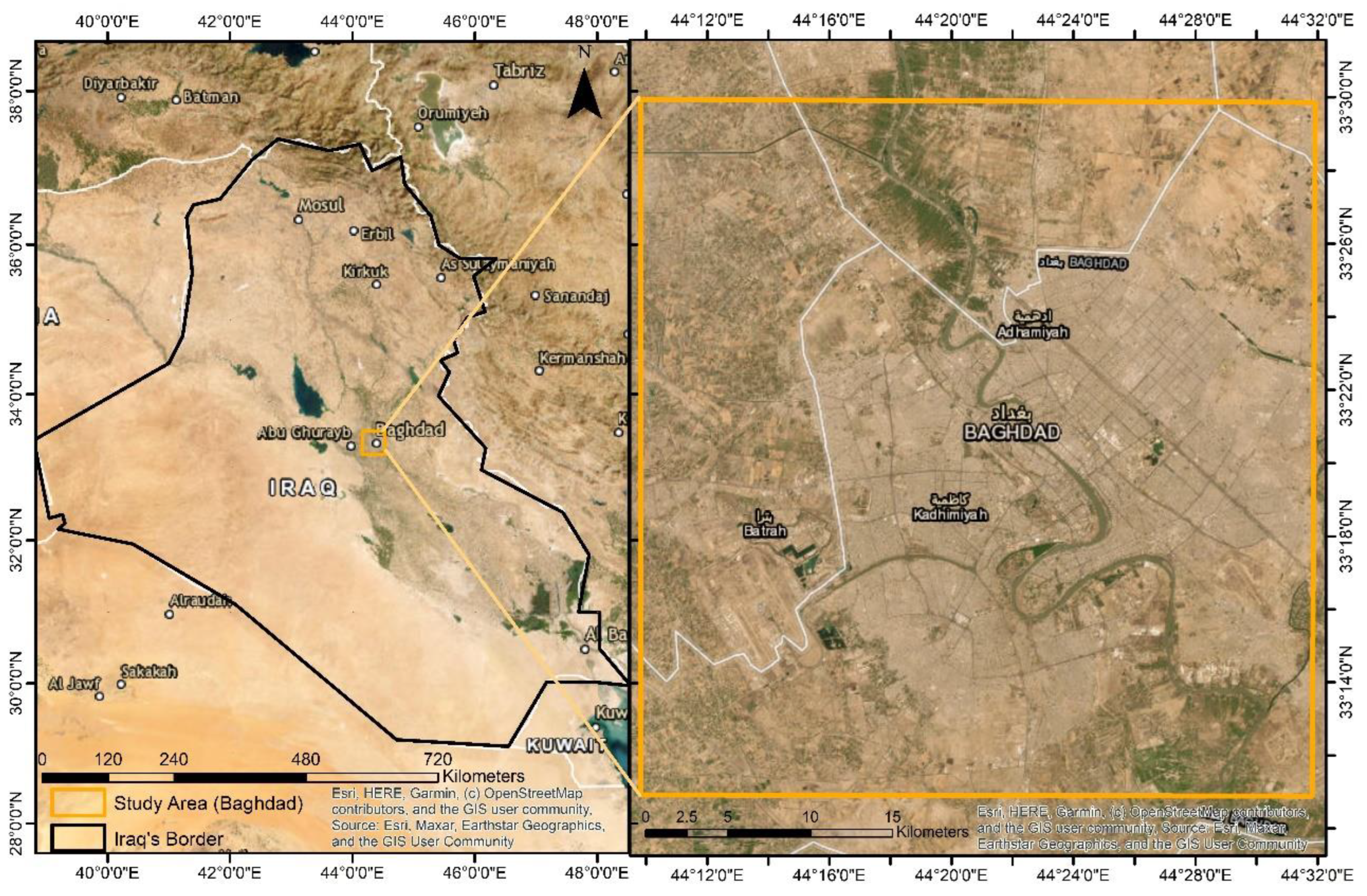
This investigation has chosen Baghdad city as its focal point, a metropolis positioned within the heartland of Iraq, serving as the nation's capital, most populous, and most densely inhabited urban center. This case study pertains to a quadrilateral expanse, lying within the geographical coordinates of 33° 10ʹ 38ʺ to 33° 30ʹ 10ʺ N latitude and 44° 09ʹ 26ʺ to 44° 32ʹ 07ʺ E longitude. This city spans both banks of the Tigris River, with Karkh on the west bank and Rusafa on the east bank, as visually depicted in
Figure 1. Furthermore, Baghdad is situated at varying elevations, ranging from 23 meters in the southern regions to approximately 48 meters above mean sea level in the northern areas (Ali and Ramahi 2020). Notably, this metropolis boasts a population of roughly 7.5 million inhabitants, encompassing an expansive territory of approximately 673 square kilometers, thereby manifesting a high population density and predominantly urban residential character (Ali and Ramahi 2020).
Baghdad boasts a scorching desert climate, officially designated as Köppen BWh, manifesting as chilly and moisture-laden in winter and swelteringly arid in summer, as reported by (Abdul-Hammed and Mahdi 2022). The city experiences an annual precipitation average of approximately 150 millimeters, with the majority of rainfall occurring between November and March. During January, the city registers a frigid mean minimum temperature of 3.8 degrees Celsius, while in July, it soars to a relatively mild 25.5 degrees Celsius. Moreover, Baghdad's typical maximum temperature reaches 15.5 degrees Celsius in January but skyrockets to a scorching 44 degrees Celsius in July, as per data from the National Climatic Center of Iraq (NCCI 2015).
The metropolis of Baghdad has witnessed profound transformations in its land utilization and land cover patterns throughout the past few decades. In the year 1985, the demographic count of this Iraqi capital stood at approximately three and a half million residents. Remarkably, by the time 2021 rolled around, the city's estimated populace had surged past the seven million mark, signifying a substantial uptick of 103%. This burgeoning urban expanse, along with consequential alterations in land utilization and land cover, exerts a pronounced influence on the localized climatic conditions within cities. It is this precise facet that constitutes the central axis of our research endeavor. Our study is crafted with the overarching goal of scrutinizing the ramifications of urban expansion on Baghdad's LST, while simultaneously delving into the primary determinants that govern the thermal characteristics of the urban landscape within the city.
2.2. Data
For the purpose of our analysis, we employed three Landsat images acquired during the dry season in the month of July. The initial image, Landsat 5, was taken on the 29th of July in the year 1985, whereas the subsequent image, Landsat 7, was captured on the 14th of July in the year 2000, just prior to the occurrence of a scan line error. The third image, Landsat 8, was acquired on the 23rd of July in the year 2021. We deliberately selected these particular months and acquisition dates to ensure that the images were procured under consistent conditions characterized by minimal cloud cover. These images were then subjected to processing and transformation into LULC as well as LST indices, utilizing the Google Earth Engine (GEE), a cloud-based remote sensing platform.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Estimation of Land Surface Temperature
The estimation of Land Surface Temperature (LST) for Landsat 5, 7, and 8 series in this study was carried out utilizing the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform, employing a code developed by (Ermida et al. 2020). All data employed in this research was resampled to a spatial resolution of 30 meters. To transform the original data into LST values, we applied the Statistical Mono-Window (SMW) algorithm (as defined in Equation 1). This algorithm conducted atmospheric correction on the Landsat thermal band series by leveraging atmospheric data available within the GEE platform, as well as re-analyses data sourced from the National Center for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) as described by (Kalnay et al. 1996).
While we corrected surface emissivity using Landsat Thermal Infrared (TIR) bare ground emissivity values, we also derived Fraction Vegetation Cover (FVC) values for the Landsat images from NDVI values using Equation 2, as proposed by (Wu et al. 2014). Additionally, we computed the emissivity of each pixel within the thermal band using Equation 3.
where
is the Top of Atmosphere (TOA) brightness temperature in the thermal channel, and
ε is the surface emissivity for the used channel. The algorithm coefficients
,
; and
are determined from linear regressions of radiative transfer simulations performed for 10 classes of Total Column Water Vapor (TCWV).
where
FVC is a fraction vegetation cover,
and
are the NDVI values of fully bare and completely vegetated pixels, respectively.
The value 0.004 represents the average emissivity value of bare land, while 0.986 corresponds to the average emissivity value of vegetated land.
The LST images were computed and retrieved onto a local computing device. Subsequently, the Normalized Ratio Scale (NRS) statistical approach, delineated in Equation 4 (as presented by (Rasul, Balzter, and Smith 2017)), was implemented using the R Programming language to standardize the LST variables collected across distinct time frames and in diverse climatic circumstances. This procedural step facilitated the comparability of LST values across disparate years.
Land Surface Temperature is a crucial factor in understanding the local climate of urban areas, and its accurate measurement is essential for assessing the impact of urban growth on the environment. In order to return LST values that are similar to the original values, a normalization process is necessary. This process involves multiplying the normalized LST values
by the results of Equation (5), which helps to ensure that the values remain consistent and accurate.
where is the mean LST of the original image and is the mean of the normalized LST image (from Equation (4)).
By standardizing LST values in this manner, scholars can attain a more refined comprehension of the intricate impact of urban expansion on the microclimate within a metropolis such as Baghdad. This becomes especially imperative in light of the expeditious urbanization occurring in the vicinity, coupled with the concomitant surge in population.
2.3.2. Image classification
Prior research has convincingly established the Random Forest (RF) algorithm as a preeminent choice for LULC classification, particularly within the context of Google Earth Engine (GEE), as exemplified by (Goldblatt et al. 2016). As a result, this current study prominently adopts the RF algorithm for the purpose of image classification, leveraging the formidable capabilities of the GEE environment. The key procedural stages encompass the acquisition of Landsat images spanning three distinct temporal epochs, the strategic allocation of testing and validation points, the subsequent generation of meticulously classified maps, and a rigorous evaluation of the accuracy associated with these resultant classified maps. This sophisticated AI-based approach enhances the precision and reliability of our LULC classification, aligning with the current state-of-the-art methodologies in remote sensing and geospatial analysis.
For the entirety of Landsat imagery utilized within this investigation, the RF algorithm is harnessed to categorize them into LULC classes. Given that Landsat imagery exhibits a spatial resolution of a mere 30 meters, these images are classified into four primary categories: aquatic bodies, vegetative elements (comprising grasslands, arboreal expanses, and agricultural plots), man-made structures (including buildings, roadways, and paved surfaces), and unvegetated terrains (comprising rocks, barren soil, and agricultural fields rendered dry during the summer season).
In the process of image classification, a total of 400 samples were meticulously chosen for each image, with an equitable distribution of 100 samples for each category. The selection of these samples was predicated upon a multi-faceted approach, encompassing the utilization of high-resolution satellite imagery from Maxar (with a resolution of 5 meters), the prior knowledge and expertise of the researcher, and an analysis of the spectral compositions of Landsat images, including both true and false color bands.
These selected samples were then segregated into two distinct categories, with 70% of them earmarked for the purpose of training the model, while the remaining 30% served as a crucial testing set for validation. Subsequent to a rigorous evaluation of the Random Forest (RF) classifier, it was determined that the optimal performance was achieved by employing an ensemble of 40 decision trees within the algorithm.
To further enhance the method's accuracy, various LULC indices, including NDVI, NDWI, DBI, and DBSI, were synergistically integrated with the original Landsat bands. Subsequently, the resulting values underwent normalization, transforming them into a standardized range between 0 and 1. The areas pertaining to each distinct category and their corresponding accuracy values were subsequently extracted. These classified images were then exported from GEE to Google Drive, followed by transfer to a local computer for the purpose of comprehensive analysis and visualization.
To ascertain the precision of the classified images, an evaluation of classifiers was conducted, encompassing metrics such as Overall Accuracy (OA), Kappa coefficient, Producer Accuracy, and User Accuracy. Overall Accuracy serves as an indicator of the comprehensive effectiveness of the methodology, and it is computed by dividing the total number of accurately classified samples by the total number of samples in the testing dataset. The Kappa coefficient, as defined by (Goldblatt, Rivera Ballesteros, and Burney 2017), gauges the extent of concurrence between the validation samples and the predicted values. In order to carry out this accuracy assessment, the Overall Accuracy (Equation 6) and Kappa (Equation 7) were derived through the utilization of the error matrix associated with the classified Landsat images.
= number of diagonal pixels (correctly classified)
N= total number of pixels.
= The attained OA or the actual percentage of classified land
= Probability of attaining a correct classification.
2.3.3. Land Use Land Cover variables
The research employed a diverse set of LULC variables sourced from the GEE platform. These encompassed a multitude of facets, such as Tree Canopy Cover (TCC), population density, Built-up Multitemporal, Degree of Urbanization, nighttime light intensity, elevation data, and the annual variation in impervious surfaces. Furthermore, a series of LULC indices were derived within GEE using the equations delineated in
Table 1. These indices include the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index (NDLI), Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), Dry Bare Soil Index (DBSI), Dry Built-up Index (DBI), Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI), and Normalized Soil Moisture Index (NSMI). Additionally, the study computed the topographic slope of the designated case study area by utilizing the "ee.Terrain.slope" function within GEE, considering the 4-connected neighbors of each pixel. Subsequently, the raster images representing these variables were downloaded to a local computer via Google Drive to facilitate further analysis.
2.3.4. Statistical analysis
The analysis encompassed the extraction of LULC variables and LST values from a dataset comprising 300 randomly selected samples. Stringent measures were employed to guarantee the faithful representation of diverse LULC categories and to investigate the interrelationship between these categories and LST. In this pursuit, pixels with diminished values were systematically excluded. Additionally, for the computation of the NDVI and EVI vegetation indices, pixels registering values equal to or less than 0.2 were deliberately omitted. Similarly, NDWI values associated with water bodies falling below the threshold of -0.2 were also deliberately disregarded (sentinel-hub 2019; sentinel-hub 2018).
Statistical computations were executed using the R programming language. To evaluate the association between LST and the explanatory LULC variables, we employed univariate regression analysis based on Pearson's product-moment correlation coefficient ((Equation 8) (Zou, Tuncali, and Silverman 2003)). The significance of this relationship was ascertained through the utilization of Student's t-test ((Equation 9) (Obilor and Amadi 2018)).
A result approaching +1 signifies a robust positive correlation, whereas a value nearing -1 signifies a robust negative correlation. A value of zero indicates the absence of any discernible correlation between the variables. The formula employed to derive the t-value is as follows:
Here, r is the sample correlation coefficient and n is the number of cases.
3. Results
The primary objective of this research endeavor is to scrutinize the ramifications of urban sprawl on LST within cities situated in hot desert climates, exemplified by the case of Baghdad. Additionally, this investigation seeks to discern and elucidate the pivotal determinants that exert influence on the surface temperature of such urban locales. This section herein serves to expound upon the empirical findings concerning LST dynamics and the classification of LULC patterns, spanning the temporal spectrum from 1985 to 2021. Concurrently, it delves into the intricate spatial variations of 16 distinct LULC variables, meticulously considered within the ambit of this scholarly inquiry. Moreover, we shall proffer an exposition of the outcomes derived from the correlation analysis undertaken to unveil the interplay between these variables and the LST regime prevalent within the urban fabric of the city under scrutiny.
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations in Land Surface Temperature Across Baghdad: An In-Depth Analysis
Figure 2 (a-c) illustrates the spatial distribution of LST across the study area. The color-coded representation reveals that areas characterized by lower LST values, ranging from 300 to 320 Kelvin, are predominantly concentrated around water bodies, exemplified by the Tigris River, as well as vegetated regions located both to the north and south of the city, with a primary focus around the river. Additionally, lower LST values are evident in the built-up areas situated in the central parts of the city. Conversely, higher temperature zones, within the range of 325 to 350 Kelvin, are primarily co-located with bare soil and winter croplands that experience desiccation during the summer season. The highest temperature zone is situated in the northeastern region of the city, which corresponds to barren land and uncultivated croplands during the summertime.
In
Figure 2 (b and e), the temporal evolution of LST is presented, showcasing changes over the years. In the year 2000, an evident transformation from bare soil to built-up areas was observed, resulting in an increase in the prevalence of lower LST values. However, when analyzing satellite imagery captured in 2021, it is evident that LST values have experienced an overall rise in comparison to observations made in 1985 and 2000. This temperature increase is particularly pronounced in the northern sectors of the city, where LST values have reached as high as 350 Kelvin.
3.2. Temporal Analysis of Land Use and Land Cover Transformations in Baghdad: 1985-2021
In general, our classification methodology consistently demonstrated a high level of accuracy, ranging from 0.97 to 0.99, across all three categorized images (as summarized in
Table 2). The techniques employed in our study to enhance the precision of our approach yielded significant improvements. Specifically, the incorporation of LULC indices alongside the original Landsat bands, as well as an increase in the number of decision trees from 10 to 40 within the Random Forest algorithm, resulted in notable enhancements in both Kappa statistics and overall accuracy. Conversely, the process of normalizing values to a range between 0 and 1 did not exert a significant impact on accuracy levels. It is worth highlighting that all three classified images consistently exhibited total accuracy and Kappa values of 0.97 or higher, as detailed in
Table 2. The pinnacle of achievement was witnessed in the Landsat 8 image classification of 2000, where the total accuracy and Kappa reached an impressive 0.99.
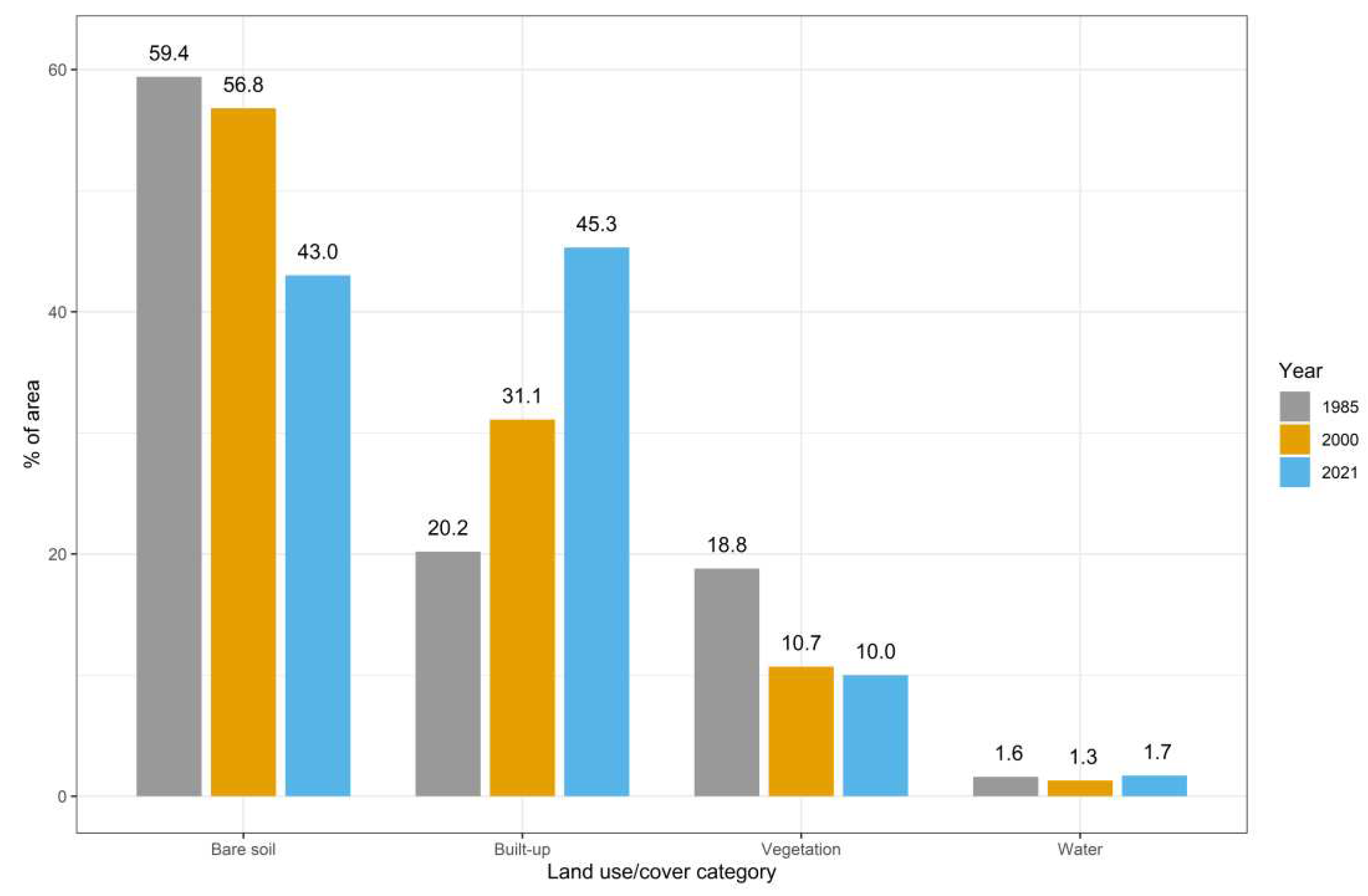
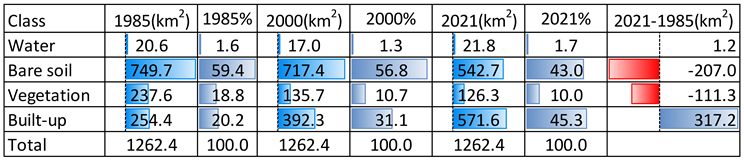
In the inaugural year of our study period, namely 1985, the predominant land use category within the designated region was that of bare soil, spanning an expanse of 749.7 square kilometers, constituting a substantial 59.4% of the total area. Subsequently, the built-up class secured the runner-up position, encompassing 20.2% of the territory, as illustrated in
Figure 3. The vegetated class, however, lagged behind in third place, covering a mere 18.8%, as documented in
Table 3 and
Figure 2 d:f.
Fast forward fifteen years to the year 2000, and we observe a persistence of bare soil as the dominant category, albeit with a slight reduction to 56.8% coverage, equivalent to 717.4 square kilometers. The built-up class maintained its second-place standing but underwent a substantial expansion from 254 to 392 square kilometers, marking a noteworthy shift from 20.2% to 31.1%. In contrast, the vegetated class dwindled from 18.8% to a mere 10.7%.
Upon scrutinizing Landsat 8 classification data for July 2021, a noteworthy transformation occurred, with the built-up class ascending to the status of the most extensive land use category, encompassing 45.3% or 571.6 square kilometers of the region. Meanwhile, the coverage of bare soil dwindled to 43%, and the vegetated class experienced an even more pronounced contraction, reducing to a mere 10%. The water class exhibited only minor alterations during the course of our study.
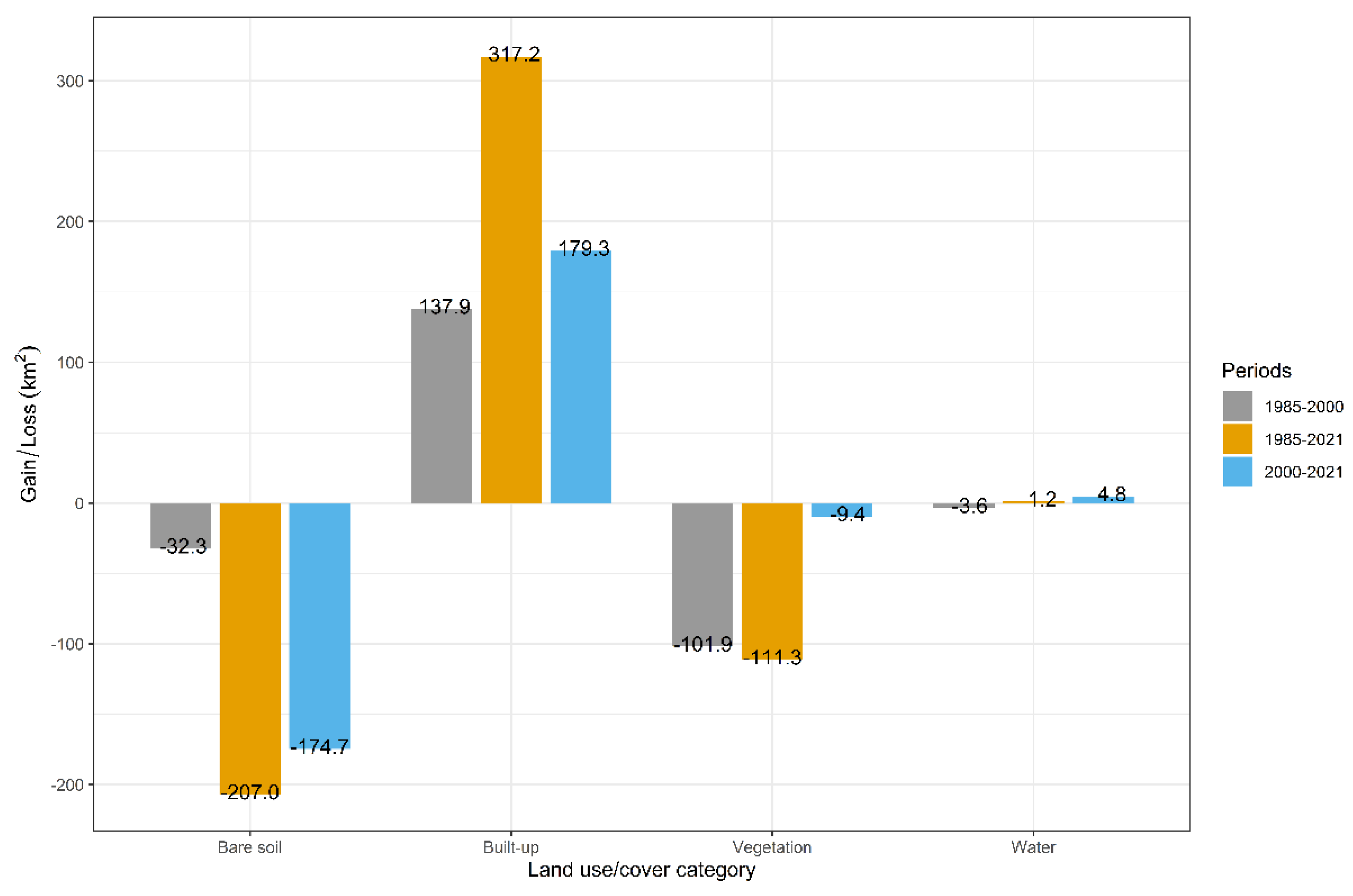
An examination of land use class areas between 1985 and 2021 reveals a staggering 124.7% surge, equivalent to 317 square kilometers, in the built-up area, whereas the coverage of bare soil and vegetation receded by 207 square kilometers (a 27.4% reduction) and 111.3 square kilometers (a 46.8% decline), respectively, as depicted in
Figure 4.
3.3. Disparities in Land Surface Temperature Among Land Use and Land Cover Categories
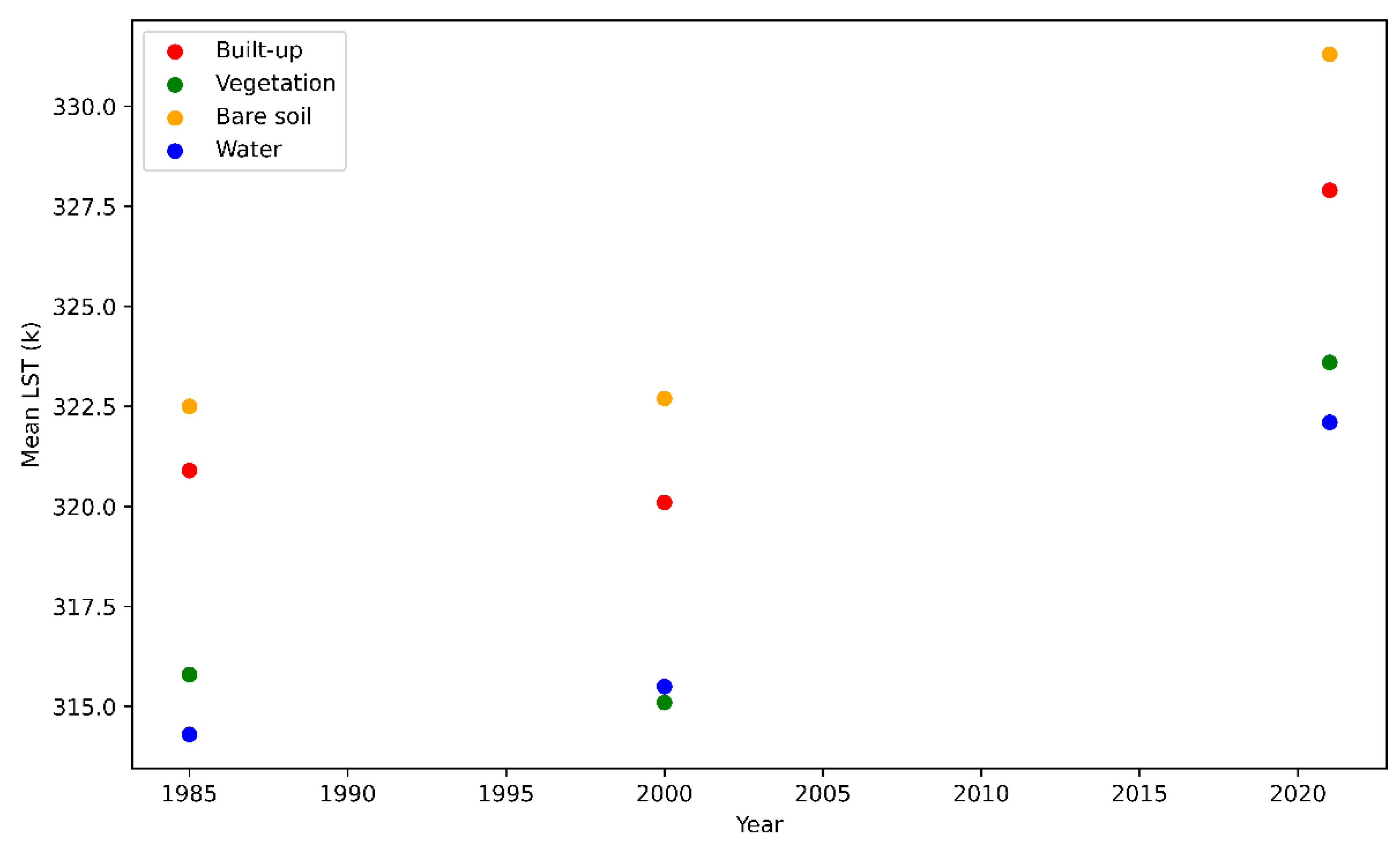
Across the expanse of the examined years, encompassing 1985, 2000, and 2021, it is discerned that the bare soil category consistently exhibited the most elevated LST values, standing at 322.5 K, 322.7 K, and 331.3 K for the respective years. Following closely behind in this thermal hierarchy, the built-up class registered LST values of 320.9 K, 320.1 K, and 327.9 K for the same temporal sequence. In stark contrast, both water bodies and vegetative areas displayed noticeably lower temperature readings, as depicted in
Figure 5. To elucidate the overarching trend, it is noteworthy that, as a sweeping generalization, the surface temperatures of all delineated classes exhibited an unequivocal ascent in 2021, outstripping their counterparts in both 1985 and 2000.
3.4. Geospatial Patterns of Land Cover Variables
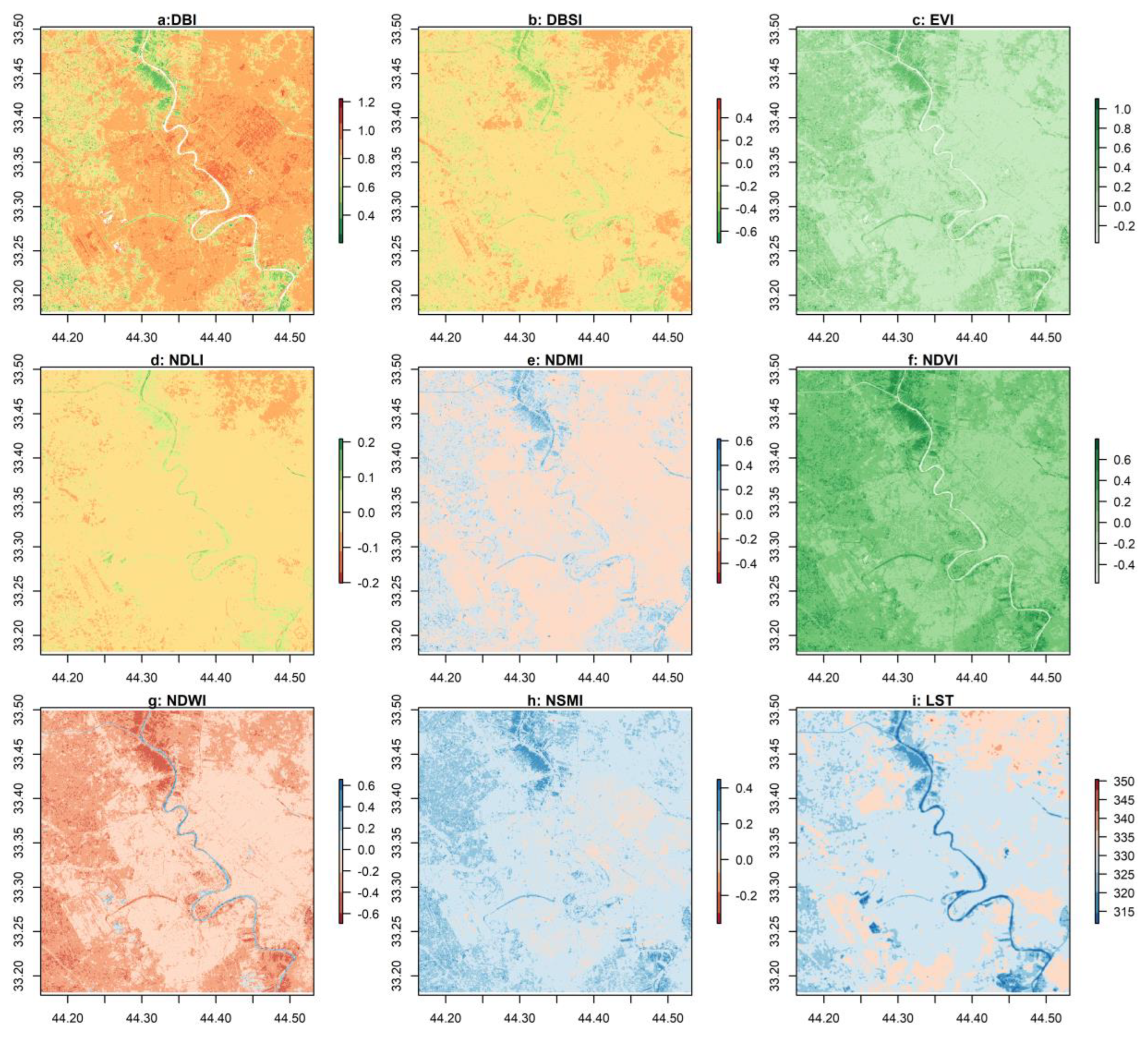
Areas with a DBI exceeding 0.8 are categorized as extensive built-up zones, encompassing the majority of the 2021 study area. In contrast, areas exhibiting a DBI exceeding 1 are classified as highly built-up regions, primarily concentrated within specific polygons situated to the right of the Tigris River (as illustrated in
Figure 6:a). Surrounding these built-up regions, there are expanses of bare soil, identifiable by their brown coloration and a BDSI reading of 0.2 or higher, notably concentrated in the upper-right corner of the study area (depicted in
Figure 6:b).
Analysis of the NDVI and EVI in
Figure 6:c and
Figure 6:f, respectively, indicates that densely vegetated regions, characterized by an NDVI exceeding 0.4, are predominantly situated in the northern part of the city, particularly in proximity to the Tigris River. The second-highest concentration of vegetation is found in the lower-right section of the study area, with a separate pocket of vegetation located in the western part of Baghdad. These regions exhibiting elevated vegetation indices correspond to lower surface temperatures, denoted by dark blue hues in Image 6:i.
Conversely, regions displaying very low NDLI values correlate with the bare soil areas in the upper-right quadrant (depicted in brown). In contrast, NDLI values surpassing 0.1 are associated with bodies of water and vegetated areas encircling the Tigris River (as observed in
Figure 6:d). Notably, an NDLI value exceeding 0.2 clearly delineates the course of the Tigris River from the upper to lower bounds of the area, with additional water bodies located in the western section of the study area (illustrated in
Figure 6:g). This heightened NDWI is concomitant with relatively lower surface temperatures, as depicted in
Figure 6:i.
Moisture content in the city exhibits a distinct spatial distribution, with low moisture levels prevalent in the built-up and bare soil regions, while elevated moisture content predominates in the northern and lower-right sectors, corresponding to the vegetated areas. Furthermore, isolated pockets of high moisture content are discernible in the western part of the area. These areas characterized by heightened moisture content contribute to a reduction in surface temperature, as evidenced in
Figure 6:i.
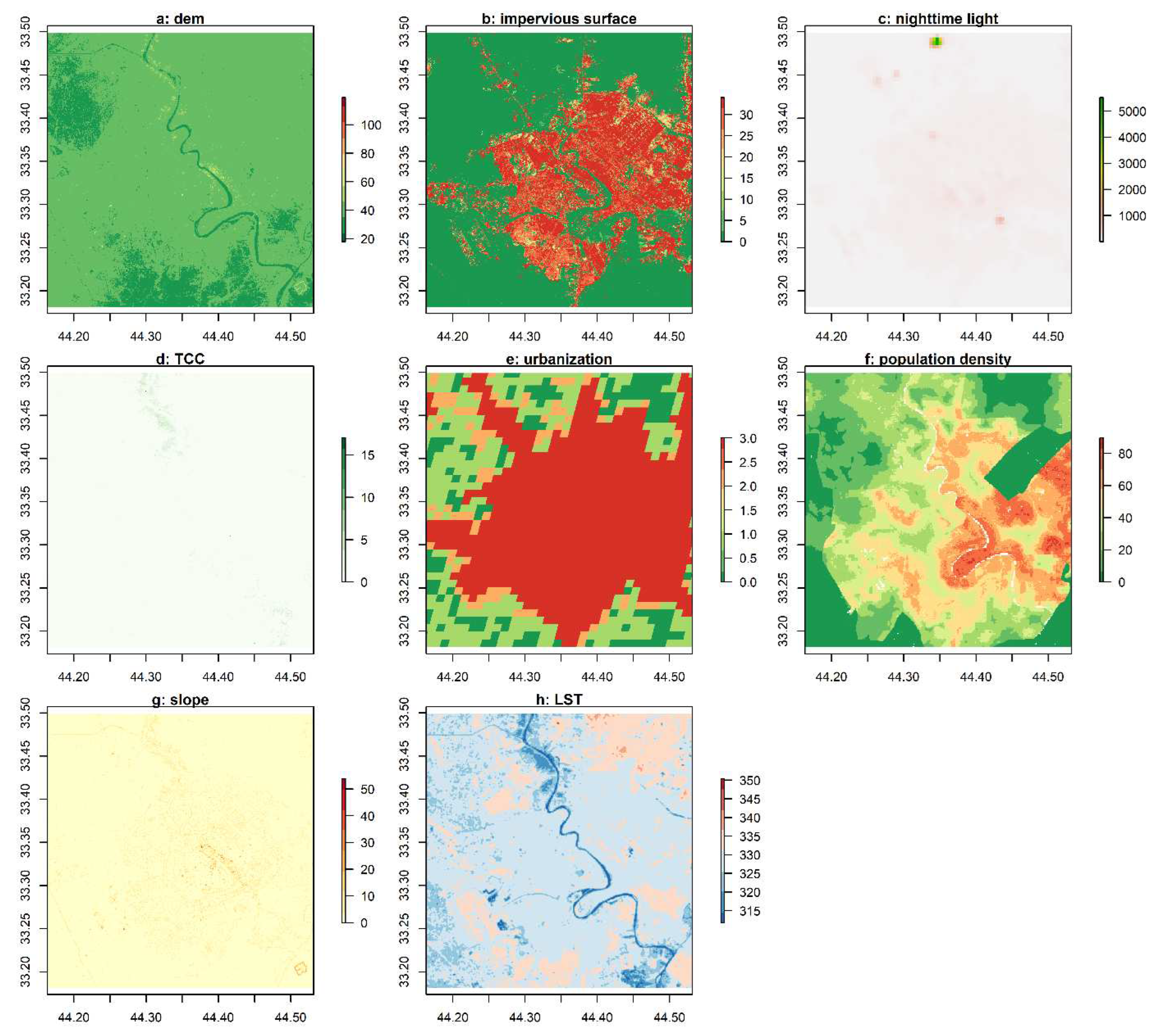
Turning attention to
Figure 7:a, it unveils the elevation profile of the study area, revealing low-lying regions (approximately 20 meters) in the southern and northwestern extremities. Impervious surfaces, identified by values of 30 or higher (indicated by a brown color palette), signify the built-up zones, while the surrounding cityscape exhibits lower impervious values in shades of green. The densely impervious regions correlate with moderate surface temperatures, represented by light blue shades in
Figure 7:h.
The highest intensity of nocturnal lighting is concentrated in the northern portion of the study area, as showcased in
Figure 7:c. Notably,
Figure 4:d illustrates that a relatively small section in the northern part of the study area features high trees with a canopy cover value of approximately 5. Pixels denoted with the highest level of urbanization (value 3) are rendered in a deep red hue and encompass the majority of the study area, as depicted in
Figure 7:e. Rural expanses are demarcated in green in the north, south, and west regions. Densely populated areas within the city, characterized by exceeding 60 inhabitants, adopt a brown hue and are primarily concentrated in the eastern sector, enveloping the Tigris River. Sparsely populated areas encircle the urban core, as exemplified in
Figure 7:f. Lastly,
Figure 7:g provides insights into the slope characteristics of the study area, revealing that areas with steep slopes (less than 30 meters) are primarily situated in the central portion of the study zone.
3.5. Statistical Analysis of the Correlation Between Independent Variables and Land Surface Temperature
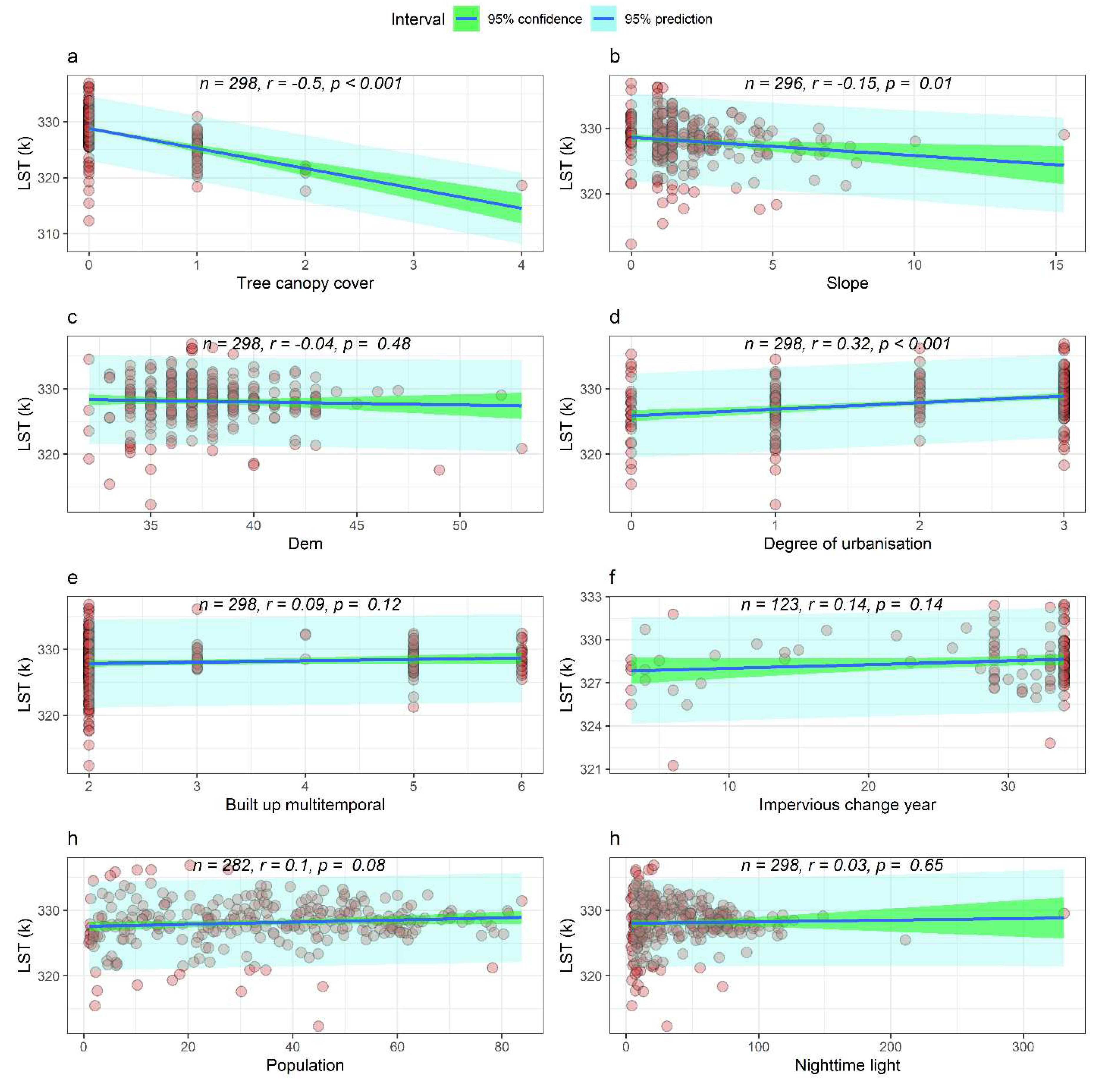
The statistical analysis conducted within this study has unveiled a robust and statistically significant inverse relationship between LST and various environmental variables. To be specific, the analysis has revealed a pronounced negative correlation between LST and several indices, namely, NDMI, NDVI, EVI, NDLI, NDWI, and TCC, as visually depicted in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9. Conversely, a substantial and statistically significant positive correlation has been identified between LST and two factors: the DBSI and the DBI.
Furthermore, the analysis has uncovered a moderately positive correlation between LST and the level of urbanization, denoted as the degree of urbanization (r = 0.32). In contrast, a moderate negative correlation has been ascertained with the NSMI (r = -0.49). Conversely, a relatively weak negative correlation has been discerned between LST and slope (r = -0.15).
In addition, the statistical examination has not yielded any discernible associations or statistically significant relationships between LST and other variables, including population density, multi-temporal built-up areas, impervious change over the years, nighttime illumination, and DEM, as illustrated in
Figure 9.
Taken together, these findings put forward the proposition that urbanization, vegetative coverage, soil moisture levels, and land usage patterns wield substantial influence over LST within the study region. The positive correlation between LST and DBSI, as well as DBI, may be attributed to the elevated thermal conductivity characteristics observed in built-up regions. Conversely, the negative correlation between LST and various vegetation indices (NDMI, NDVI, EVI, NDLI, and NDWI) underscores the cooling effect associated with vegetative cover and underscores the significance of urban green infrastructure in mitigating the urban heat island effect.
4. Discussion
The research findings indicate that the most intense heat in the Baghdad region is concentrated in the northeastern quadrant, characterized by exposed soil, and the LULC classification displayed a remarkable accuracy level of 0.97 or higher. Over the course of the study period, there was a substantial transformation in the primary land use categories, with urban development expanding by an astonishing 124.7%, while vegetative cover experienced a significant decline of 46.8%. Regarding variations in LST among land use categories, bare soil exhibited the highest recorded surface temperature, closely followed by urban built-up areas. Conversely, areas with vegetation and bodies of water registered lower surface temperatures, primarily concentrated along the Tigris River and its surrounding areas, spanning from the northwest to the southeast of the study zone.
Statistical analysis elucidated the relationship between surface temperature and potential factors, revealing that moisture content (NDMI), vegetative cover (NDVI, EVI, and TCC), and latent heat (NDLI) were the predominant factors contributing to decreased surface temperatures. Conversely, a strong positive correlation was observed between LST and indices related to bare soil (DBSI) and urban development (DBI).
In previous studies, it was established that regions dominated by non-urban land with abundant vegetation tend to exhibit higher LST values (Xian et al. 2022). However, the findings in Baghdad reveal an interesting contrast: during the morning, coinciding with the Landsat satellite pass, bare soil exhibited higher surface temperatures than urban areas. This outcome aligns with observations in arid landscapes (Frey et al. 2005; Li, Mo, and Dai 2011; Rasul, Balzter, and Smith 2015) but diverges from other research (Amiri et al. 2009; Carlson and Arthur 2000; Owen, Carlson, and Gillies 1998).
In this study, the implementation of advanced techniques significantly enhanced the accuracy of supervised classification, particularly through the integration of LULC indices with the original satellite image bands. This augmentation led to improvements in both kappa and overall accuracy, facilitating the classifier's ability to distinguish between land use categories. Throughout the study period, the Baghdad region underwent rapid land use transformations. In 1985, bare soil and non-vegetated croplands dominated the area during the summer, whereas by 2021, the built-up urban class had become predominant. Additionally, vegetated regions dwindled during the study timeframe. These swift land use alterations signify a fundamental shift in the land's capacity to absorb and emit heat during the day and night. The proliferation of impermeable materials in the newly urbanized areas contributes to groundwater recharge and escalates the risk of flash floods during intense winter precipitation events.
Our findings unequivocally establish that bare soil areas consistently recorded higher surface temperatures compared to the three primary land use categories—urban development, vegetative cover, and water bodies. The substitution of vegetative areas with urban development materials engenders an increase in surface temperature in Baghdad. Conversely, the replacement of bare soils with urban development translates to a reduction in surface temperature during summer daytime. Moreover, vegetation and moisture indices exhibit a robust inverse relationship with surface temperature. Consequently, augmenting vegetation such as parks within the city and promoting the presence of moisture and water bodies emerges as a promising strategy for policymakers to mitigate elevated temperatures in Baghdad and analogous cities situated in hot desert climates.
We recommend that future research delves into the intricate relationship between LST and LULC dynamics in Baghdad, as well as similar urban locales, utilizing both daytime and nighttime data and inter-seasonal imagery. In our investigation, we harnessed a comprehensive array of potential LULC factors, primarily sourced from satellite imagery, providing a distinct advantage in encompassing a vast spatial extent. However, it is imperative to acknowledge that this study exclusively concentrated on the impact of land use and land cover changes on land surface temperature and did not factor in other variables such as atmospheric conditions and anthropogenic heat sources, which may also contribute to localized climate variations within the study area.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this research was undertaken with the overarching objective of investigating the implications of urban expansion on land surface temperature in cities situated within hot desert climates, with a specific focus on Baghdad, a prominent metropolis in the Middle East. A comprehensive analysis was conducted utilizing Landsat imagery spanning the temporal spectrum from 1985 to 2021. This analysis incorporated the application of advanced artificial intelligence techniques, notably the Random Forest method, for LULC classification. Additionally, sixteen potential contributing factors were examined to assess variations in land usage and their consequential impact on the city's temperature regime.
The findings revealed a noteworthy 46.8% reduction in vegetated areas and a simultaneous increase of 124.7% in urbanized spaces during the study's duration. During the scorching daytime hours of summer, bare soil exhibited the highest land surface temperatures, closely followed by the built-up urban environment. In stark contrast, water bodies displayed the lowest land surface temperatures, with vegetated regions marginally warmer. Furthermore, the investigation of vegetation and moisture indices unveiled a robust inverse relationship with surface temperature, reaffirming the critical role of vegetation in mitigating temperature fluctuations induced by urbanization.
The significance of this research extends to its integration of cutting-edge artificial intelligence techniques, particularly the Random Forest algorithm, which enhances the accuracy and precision of LULC classification. This research not only provides valuable insights to policymakers but also underscores the urgency of implementing mitigation measures to counteract the adverse consequences of urbanization on localized climate dynamics. Equipped with the knowledge derived from this study, policymakers can make informed decisions regarding future urban development, thereby ameliorating the adverse effects of climate change. In essence, this study represents a comprehensive exploration of the intricate interplay between urban growth, land surface temperature, and the advanced application of AI methods, emphasizing the indispensable role of sustainable urban planning in mitigating the detrimental impacts of urbanization on local desert climates.
Author Contributions
Azad Rasul; conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, review and editing.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
not applicable.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
not applicable.
References
- Abdul-Hammed, A.N.; Mahdi, A.S. Monitoring Vegetation Area in Baghdad Using Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. Iraqi J. Sci. 2022, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.K.M.; Al Ramahi, F.K.M. A study of the Effect of Urbanization on Annual Evaporation Rates in Baghdad City Using Remote Sensing. Iraqi J. Sci. 2020, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Weng, Q.; Alimohammadi, A.; Alavipanah, S.K. Spatial–temporal dynamics of land surface temperature in relation to fractional vegetation cover and land use/cover in the Tabriz urban area, Iran. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2606–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Du, M. 2009. Relationship between Thermal Inertia and Urban Heat Sink in Beijing Derived from Satellite Images. In 2009 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, 1–5. IEEE.
- Carlson, T.N.; Traci Arthur, S. The impact of land use — land cover changes due to urbanization on surface microclimate and hydrology: a satellite perspective. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2000, 25, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermida, S.L.; Soares, P.; Mantas, V.; Göttsche, F.-M.; Trigo, I.F. Google Earth Engine Open-Source Code for Land Surface Temperature Estimation from the Landsat Series. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, Corinne M., Gergely Rigo, Eberhard Parlow, and A. Marçal. 2005. “The Cooling Effect of Cities in a Hot and Dry Environment.” In Global Developments in Environmental Earth Observation from Space, Proceedings of the 25th Annual Symposium of the European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories, Porto, Portugal, 6–11.
- Goldblatt, R.; Ballesteros, A.R.; Burney, J. High Spatial Resolution Visual Band Imagery Outperforms Medium Resolution Spectral Imagery for Ecosystem Assessment in the Semi-Arid Brazilian Sertão. Remote. Sens. 2017, 9, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; You, W.; Hanson, G.; Khandelwal, A.K. Detecting the Boundaries of Urban Areas in India: A Dataset for Pixel-Based Image Classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubrock, S.-N.; Chabrillat, S.; Lemmnitz, C.; Kaufmann, H. Surface soil moisture quantification models from reflectance data under field conditions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.R.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, Eugenia, Masao Kanamitsu, Robert Kistler, William Collins, Dennis Deaven, Lev Gandin, Mark Iredell, Suranjana Saha, Glenn White, and John Woollen. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 13. Li, Shaoqing, Hongwei Mo, and Yaling Dai. 2011. “Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Urban Cool Island Intensity and Its Eco-Environmental Response in Chang-Zhu-Tan Urban Agglomeration.” Communications in Information Science and Management Engineering 1 (9). World Academic Publishing LTD.
- Liou, Y.-A.; Le, M.S.; Chien, H. Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index for Remote Sensing of Land Surface Energy Fluxes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2018, 57, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “mop.gov.iq.” 2022. https://mop.gov.iq/archives/8252.
- NCCI. 2015. “Baghdad Governorate Profile.”. https://www.ncciraq.org/images/infobygov/NCCI_Baghdad_Governorate_Profile.pdf.
- Obilor, Esezi Isaac, and Eric Chikweru Amadi. Test for Significance of Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient. International Journal of Innovative Mathematics, Statistics & Energy Policies 2018, 6, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, T.W.; Carlson, T.N.; Gillies, R.R. An assessment of satellite remotely-sensed land cover parameters in quantitatively describing the climatic effect of urbanization. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 1998, 19, 1663–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Balzter, H.; Ibrahim, G.R.F.; Hameed, H.M.; Wheeler, J.; Adamu, B.; Ibrahim, S.; Najmaddin, P.M. Applying Built-Up and Bare-Soil Indices from Landsat 8 to Cities in Dry Climates. Land 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Balzter, H.; Smith, C. Spatial variation of the daytime Surface Urban Cool Island during the dry season in Erbil, Iraqi Kurdistan, from Landsat 8. Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Balzter, H.; Smith, C. Applying a normalized ratio scale technique to assess influences of urban expansion on land surface temperature of the semi-arid city of Erbil. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2017, 38, 3960–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J. W., R. H. Hass, J. A. Schell, and D. W. Deering. 1973. “Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. Third Earth Resources Technology Satellite (ERTS) Symposium, 1, 309-317.”.
- sentinel-hub. 2018. “NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index).” Sentinel-Hub.Com. https://www.sentinel-hub.com/eoproducts/ndvi-normalized-difference-vegetation-index.
- sentinel-hub. 2019. “EVI (Enhanced Vegetation Index).”. https://www.sentinel-hub.com/eoproducts/evi-enhanced-vegetation-index-0.
- Shigeta, Yoshinori, Yukitaka Ohashi, and Osamu Tsukamoto. 2009. “Urban Cool Island in Daytime-Analysis by Using Thermal Image and Air Temperature Measurements.” In The Seventh International Conference on Urban Climate. Vol. 29.
- Watson, Charles. 2012. Analysis of Urban Heat Island Climates along the I-85/I-40 Corridor in Central North Carolina. The University of North Carolina at Greensboro.
- Wilson, E.H.; Sader, S.A. Detection of forest harvest type using multiple dates of Landsat TM imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, T.; Tang, B.; Zhao, W.; Jia, K. Evaluation of Spatiotemporal Variations of Global Fractional Vegetation Cover Based on GIMMS NDVI Data from 1982 to 2011. Remote. Sens. 2014, 6, 4217–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Q.; Auch, R.; Gallo, K.; Wu, Z.; Kolian, M. Monitoring and characterizing multi-decadal variations of urban thermal condition using time-series thermal remote sensing and dynamic land cover data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2021, 269, 112803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Kelly H., Kemal Tuncali, and Stuart G. Silverman. Correlation and Simple Linear Regression. Radiology 2003, 227, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Geographical Reference Point for the Case Study (Baghdad).
Figure 1.
Geographical Reference Point for the Case Study (Baghdad).
Figure 2.
Depicts the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Surface Temperature (LST) and Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Classification Across the Period 1985-2021. Panel a: 1985 LST, Panel b: 2000 LST, Panel c: 2021 LST; Panels d, e, and f: LULC Classifications for 1985, 2000, and 2021, respectively. Color Coding: Blue for Water, Yellow for Bare Soil, Green for Vegetation, and Red for Built-Up Areas.
Figure 2.
Depicts the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Surface Temperature (LST) and Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Classification Across the Period 1985-2021. Panel a: 1985 LST, Panel b: 2000 LST, Panel c: 2021 LST; Panels d, e, and f: LULC Classifications for 1985, 2000, and 2021, respectively. Color Coding: Blue for Water, Yellow for Bare Soil, Green for Vegetation, and Red for Built-Up Areas.
Figure 3.
Temporal Dynamics of Land Use and Land Cover Classes in Baghdad City (1985-2021).
Figure 3.
Temporal Dynamics of Land Use and Land Cover Classes in Baghdad City (1985-2021).
Figure 4.
Illustrates the change in land use and land cover (LULC) of Baghdad city between different time periods, indicating the gain or loss (in km2) for each LULC class.
Figure 4.
Illustrates the change in land use and land cover (LULC) of Baghdad city between different time periods, indicating the gain or loss (in km2) for each LULC class.
Figure 5.
Illustrates Disparities in Mean Land Surface Temperature (LST) Across Varied Land Cover Types in Baghdad for the Years 1985, 2000, and 2021.
Figure 5.
Illustrates Disparities in Mean Land Surface Temperature (LST) Across Varied Land Cover Types in Baghdad for the Years 1985, 2000, and 2021.
Figure 6.
Illustrates the spatial variation of land cover variables and Land Surface Temperature (LST). Panels a through i show the distribution of various land cover indices, including Dry Built-up Index (DBI), Dry Bare-soil Index (DBSI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index (NDLI), Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI), Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), Normalized Soil Moisture Index (NSMI), and LST (K).
Figure 6.
Illustrates the spatial variation of land cover variables and Land Surface Temperature (LST). Panels a through i show the distribution of various land cover indices, including Dry Built-up Index (DBI), Dry Bare-soil Index (DBSI), Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index (NDLI), Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI), Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), Normalized Soil Moisture Index (NSMI), and LST (K).
Figure 7.
Spatial variation of land cover variables and Land Surface Temperature (LST), a: digital elevation model (dem m), b: impervious surface, c: nighttime light, d: Tree Canopy Cover (TCC), e: degree of urbanisation, f: population density, g: slope, h: LST (K).
Figure 7.
Spatial variation of land cover variables and Land Surface Temperature (LST), a: digital elevation model (dem m), b: impervious surface, c: nighttime light, d: Tree Canopy Cover (TCC), e: degree of urbanisation, f: population density, g: slope, h: LST (K).
Figure 8.
The Correlation Between Key Factors and Land Surface Temperature (LST) in the Year 2021, Featuring: a) Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI), b) Normalized Soil Moisture Index (NSMI), c) Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), d) Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), e) Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), f) Dry Bare-soil Index (DBSI), g) Dry Built-up Index (DBI), and h) Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index (NDLI).
Figure 8.
The Correlation Between Key Factors and Land Surface Temperature (LST) in the Year 2021, Featuring: a) Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI), b) Normalized Soil Moisture Index (NSMI), c) Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), d) Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), e) Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), f) Dry Bare-soil Index (DBSI), g) Dry Built-up Index (DBI), and h) Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index (NDLI).
Figure 9.
Correlation Analysis of Key Variables with 2021 Land Surface Temperature (LST), Including: a) Tree Canopy Cover (TCC), b) Slope, c) Digital Elevation Model (DEM), d) Degree of Urbanization, e) Multi-Temporal Built-Up Areas, f) Impervious Change Over Time, g) Population Density, and h) Nocturnal Illumination.
Figure 9.
Correlation Analysis of Key Variables with 2021 Land Surface Temperature (LST), Including: a) Tree Canopy Cover (TCC), b) Slope, c) Digital Elevation Model (DEM), d) Degree of Urbanization, e) Multi-Temporal Built-Up Areas, f) Impervious Change Over Time, g) Population Density, and h) Nocturnal Illumination.
Table 1.
Detailed mathematical formulas for the calculated indices in the study.
Table 1.
Detailed mathematical formulas for the calculated indices in the study.
| Index |
Equation |
Reference |
| Enhanced Vegetation Index |
|
(Jiang et al. 2008) |
| Normalized Different Vegetation Index |
|
(Rouse et al. 1973) |
| Normalized Different Water Index |
|
(McFeeters 1996) |
| Normalized Difference Latent Heat Index |
|
(Liou, Le, and Chien 2018) |
| Dry Built-up Index |
|
(Rasul et al. 2018) |
| Dry Bare-soil Index |
|
(Rasul et al. 2018) |
| Normalized Difference Moisture Index |
|
(Wilson and Sader 2002) |
| Normalized Soil Moisture Index |
|
(Haubrock et al. 2008) |
Table 2.
Accuracy Assessment of LULC Classification Based on Random Forest Algorithm.
Table 2.
Accuracy Assessment of LULC Classification Based on Random Forest Algorithm.
| Year 1985 |
Water |
Bare Soil |
Vegetation |
Built-up |
Total |
User's Accuracy |
Overall Accuracy |
0.98 |
| Water |
33 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
33 |
100 |
Kappa |
0.97 |
| Bare Soil |
0 |
31 |
0 |
2 |
33 |
93.9 |
|
|
| Vegetation |
0 |
0 |
24 |
0 |
24 |
100 |
|
|
| Built-up |
0 |
1 |
0 |
34 |
35 |
97.1 |
|
|
| Total |
33 |
32 |
24 |
36 |
|
|
|
|
| Producer's Accuracy |
100 |
96.9 |
100.0 |
94.4 |
|
|
|
|
| Year 2000 |
Water |
Bare Soil |
Vegetation |
Built-up |
Total |
User's Accuracy |
Overall Accuracy |
0.99 |
| Water |
26 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
26 |
100 |
Kappa |
0.99 |
| Bare Soil |
0 |
31 |
0 |
1 |
32 |
96.9 |
|
|
| Vegetation |
0 |
0 |
32 |
0 |
32 |
100 |
|
|
| Built-up |
0 |
0 |
0 |
23 |
23 |
100.0 |
|
|
| Total |
26 |
31 |
32 |
24 |
|
|
|
|
| Producer's Accuracy |
100 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
95.8 |
|
|
|
|
| Year 2021 |
Water |
Bare Soil |
Vegetation |
Built-up |
Total |
User's Accuracy |
Overall Accuracy |
0.98 |
| Water |
35 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
35 |
100 |
Kappa |
0.97 |
| Bare Soil |
0 |
24 |
0 |
0 |
24 |
100 |
|
|
| Vegetation |
0 |
0 |
29 |
0 |
29 |
100 |
|
|
| Built-up |
0 |
3 |
0 |
36 |
39 |
92.3 |
|
|
| Total |
35 |
27 |
29 |
36 |
|
|
|
|
| Producer's Accuracy |
100 |
88.9 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
|
|
Table 3.
Illustrates Land Cover Class Areas and Their Transformations from 1985 to 2021, Utilizing Landsat Imagery.
Table 3.
Illustrates Land Cover Class Areas and Their Transformations from 1985 to 2021, Utilizing Landsat Imagery.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).