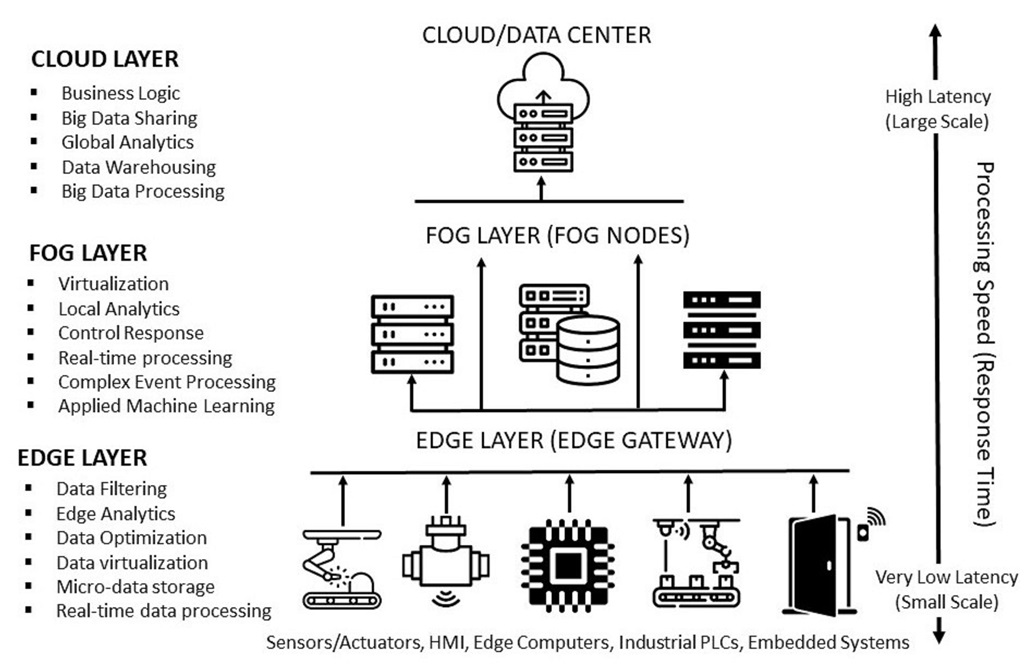
In a dynamic and rapidly changing world, customers’ often conflicting demands plus fluid economic requirements, often driven by geo-politics, have continued to evolve, out-striping the capability of existing production systems. With its inherent shortcomings, the traditional factory has proven to be incapable of addressing these modern-day manufacturing challenges. Recent advancements in Industry 4.0 have catalyzed the development of new manufacturing paradigms (or smart factory visions) under different monikers (e.g., Smart factory, Intelligent factory, Digital factory, Cloud-based factory etc.) would help fix these challenges. Due to a lack of consensus on a general nomenclature for these manufacturing paradigms, the term Future Factory (or Factory of the Future) is here used as a collective euphemism, without prejudice. The Future Factory constitutes a creative convergence of multiple technologies, techniques and capabilities that represent a significant change in current production capabilities, models, and practices. It is a data-driven manufacturing approach and system that harnesses intelligence from multiple information streams i.e., assets (including people), processes, and subsystems to help create new forms of production efficiency and flexibility. Serving both as a review monograph and reference companion, this paper details the meanings, characteristics, and technological underpinnings of the Future Factory. It also elucidates on the architectural models that guide the structured deployment of these modern factories with particular emphasis on three advanced communication technologies capable of speeding up advancements in the field. It not only highlights the relevance of communication between assets but also lays out mechanisms to achieve these interactions using the Administration shell. Finally, the paper also discusses the key enabling technologies that are typically embedded into bare bone factories to help improve their visibility, resilience, intelligence, and capacity, in addition to how these technologies are being deployed and to what effect. At the onset of the study, we were interested in developing a monograph which would serve as a comprehensive but concise review of general principles, fundamental concepts, major characteristics, key building blocks and implementation guidelines for the Future Factory within the overall context of the manufacturing ecosystem, in the age of Industry 4.0. Our hope is that this paper would enrich the extant literature on advanced manufacturing, help shape policy and research, and provide insights on how some of the identified pathways can be diffused into industry.