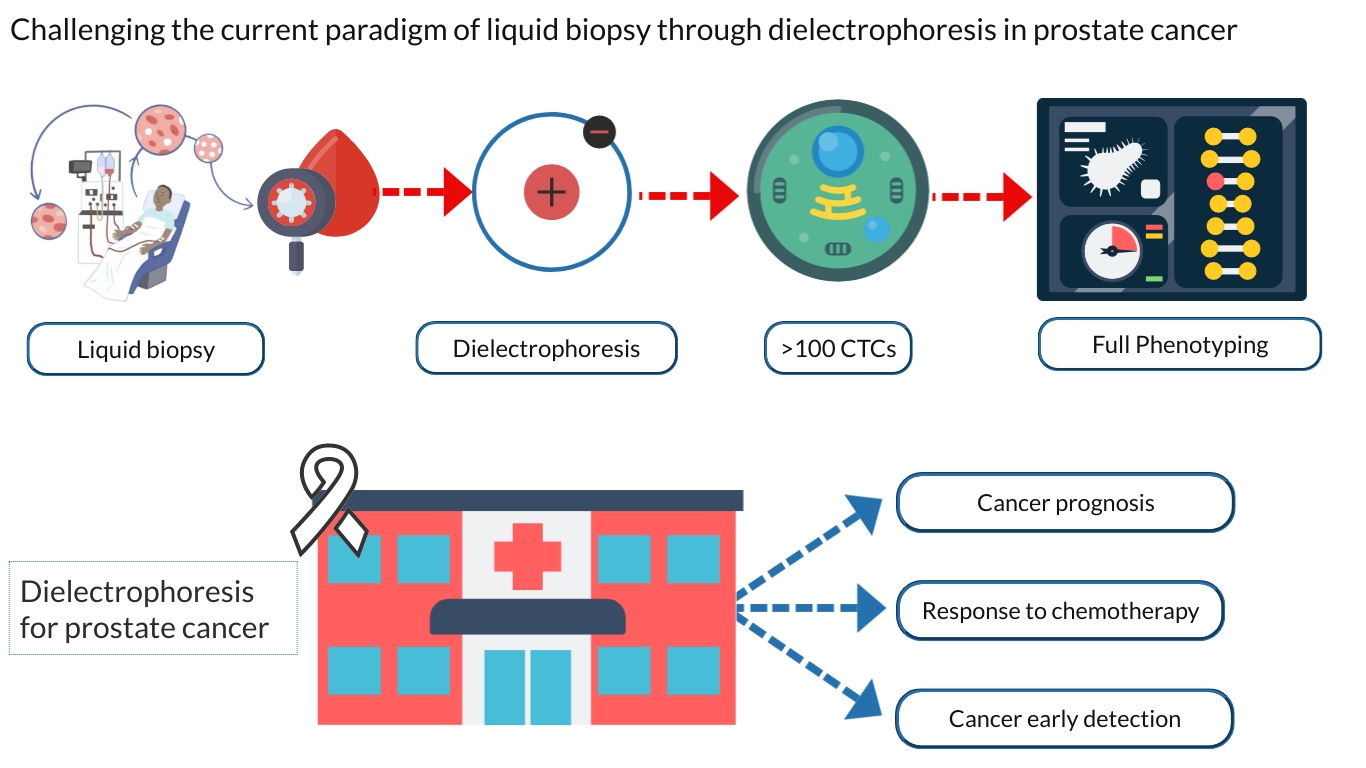
Liquid biopsy via isolation of circulating tumour cells (CTCs) represents a promising diagnostic tool capable of supplementing state-of-the-art for prostate cancer (PC) prognosis. Unfortunately, most of CTC technologies, such as AdnaTest or Cellsearch, critically rely on the Epithelial-Cell-Adhesion-Molecule (EpCAM) marker, limiting the possibility of detecting stem-like cells (CSCs) and mesenchymal-like cells (EMT-CTCs) that are present during PC progression. In this tontext, dielectrophoresis (DEP) is an epCAM independent, label-free, enrichment system, separating rare cells simply on the basis of their specific electrical properties. As compared to other technollgies, DEP represents a superior technique in terms of running costs, cells yield and specificity, but due to its higher complexity, requires still further technical as well as clinical development. Interestingly, DEP can be improved by the use of microfluid, nanostructured materials and fluoroimaging in order to increase its potential applications. In the context of PC, the utility of DEP can be translated in its capacity to detect CTC in the bloodstream in their epithelial, mesenchymal, or epithelial-mesenchymal phenotypes, which should be taken into account when choosing CTC enrichment and analysis methods for PC prognosis and early diagnosis.