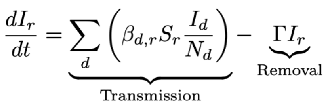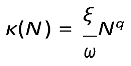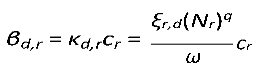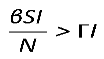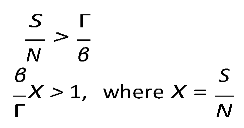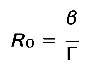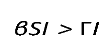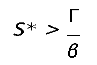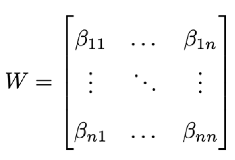1. Introduction
Most emerging pathogens in humans are directly transmitted viruses or bacteria that have crossed the species barrier, perhaps multiple times, likely facilitated by changes to the environment made by humans (Dobson and Foufopoulos, 2001; Smith et al., 2014). Recent demographic changes have led to increasing contact between humans and livestock with wildlife, providing new opportunities for disease spillover (Graham et al., 2008; Bar-On et al., 2018), and we are seeing a concomitant rise in disease outbreaks originating from wildlife (Daszak et al., 2000; Jones et al., 2008; Smith et al., 2014). However, predicting the establishment and onward transmission of a pathogen in a novel hosts requires information on the host behaviour and abundance, host and pathogen geographical overlap, host phylogeny and the pathogen’s mode of transmission (Pedersen et al., 2007; Keesing et al., 2010; Mollentze et al., 2020; Gougherty and Davies, 2022; Stewart Merrill et al., 2022).
In disease models, transmission describes the process by which an infected individual transmits a pathogen to an uninfected individual, and is a critical step in disease outbreak and spillover (Park et al., 2018). When interspecific transmission is sufficiently high, a pathogen may invade a novel host population (Daszak et al., 2000; Fenton and Pedersen, 2005; Wolfe et al., 2007). A key strategy for preventing spillover is to reduce transmission from the reservoir (a population of a single species that maintains the disease) to a susceptible, novel target population (Haydon et al., 2002). Understanding the process of transmission within and between species is thus an essential step for mitigating the risk of future disease emergence events.
Transmission is a complex, stepwise process, that is often hidden within a single parameter with opaque underlying assumptions. It is determined not only by the inherent behaviour of the pathogen, but also by the ecology of the host or vector, as pathogens rely on their host for reproduction (Rohani et al., 2003; Han et al., 2015). Properties of the host population that affect disease transmission include contact rates, population density, and individual birth and death rates. Disease parameters, such as recovery and transmission rates, are typically considered properties of the pathogen (Han et al., 2020), although they may better be described as the properties of the interaction between pathogen and host (Farrell and Davies, 2019). Because transmission integrates across many heterogeneities at different stages, including host contact rates and susceptibility (McCallum et al., 2017; Smith et al., 2009), the spread of a disease through a novel host population may be highly idiosyncratic, providing a challenge to simple disease models.
Here, we discuss the biology underlying models describing the transmission process. We synthesize assumptions of common transmission models, and how they affect the dynamics of the simple compartmental model of infectious disease spread (SIR, as we describe further below). While limited in epidemiological complexity, focusing on this subset of models allows us to easily expand to consider interspecific disease transmission, spillover and the much- debated disease-diversity relationship (Halliday and Rohr, 2019). We decompose the mathematical framework of transmission, and unify existing models with a general contact rate-function to examine how the biology of trans- mission and the mathematical assumptions in common models inform our understanding of the disease-diversity relationship. Using the well-studied multi-host bovine Tuberculosis disease system as illustration, we show how the choice of transmission model affects the projected disease dynamics, and thus the potential management decisions that follow.
2. The stages of transmission
Transmission is the transfer of infectious particles, or propagules, from an infected donor host, to a naive, receiving host. The transmission potential is dependent on a threshold propagule load within the donor host (Wilber et al., 2016; Blaser et al., 2014). As pathogen propagule particles often have to travel through space between leaving the donor host and establishing in the recipient host, the environment and the time a particle is free-roaming can play a role in transmission success (Tien and Earn, 2010). McCallum et al. (2017) deconstructed transmission into five discrete stages:
Stage 1: Dynamics of propagules within donor host.
Stage 2: Production of pathogen-infective stages in donor host.
Stage 3: Pathogen survival and growth in the environment (including the environment of an intermediate host).
Stage 4: Dose acquired by recipient host at exposure.
Stage 5: Pathogen load in the recipient host.
In Figure 1 we have graphically represented these stages of transmission for bovine Tuberculosis (bTB), Mycobacterium bovis, spilling over from its reservoir host (African buffalo, Syncerus caffer (Bengis and Erasmus, 1988)), to a novel host, (African elephant, Loxodonta africana) (Miller et al., 2021)). M. bovis is a bacterium that can infect nearly all mammals and is endemic in many areas in sub-Saharan Africa. Animals can become infected through inhalation, direct contact with mucous membranes, or by ingesting propagules through predation (although many more propagules are required for infection through ingestation than inhalation). The disease will initially establish in the respiratory tract, after which it can progress to the lymph nodes and create lesions (Spickler, 2019). As various transmission models have been developed for bTB, and given its widespread endemicity, it provides us with a useful case study.
Figure 1. Spillover of bovine Tuberculosis (bTB) from its reservoir, the African buffalo (Syncerus caffer ), to the African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana). Graphs in figure show an approximation of the stages of transmission as described by McCallum et al. (2017). Both direct and indirect (environmental) transmission modes are shown, typical for transmission of the bTB pathogen. In orange the progression of the mycobacterium is shown, in the lungs of both hosts, as well as in their dispersal propagules. The figure gives an empirical example of the complexity of a pathogen’s transmission cycle. Figure credit: Sylvia Herediaz, UBC Zoology.
Between the diferent stages of transmission, heterogeneities can arise and threshold-like behaviours may emerge. For example, nematode crowding within hosts causes an increased immune response, and saturates the relationship between transmission Stages 1 and 2, such that at high pathogen levels the production of the dispersal pathogen (nematode) life stage asymptotes (McCallum et al., 2017). Age of infection and host immunosuppressive capabilities can also have an effect on the production of pathogen infective stages (Stage 2). For example, people with sickle cell anaemia are more resistant to the malaria (Elguero et al., 2015), whereas in diseases such as cholera, high pathogen loads may increase the shedding of infectious particles.
In case of co-infection, within-host pathogen competition can additionally affect pathogen load and dispersal. For example, bTB infected African buffalo were found to have a lower pathogen load when coinfected with helminths (Ezenwa and Jolles, 2015). Such heterogeneities are not always well captured by conventional, linear frameworks of transmission (McCallum et al., 2017).
Some pathogens, including M. bovis, can survive in and be transmitted through the environment (Stage 3), which may contribute to interspecific transmission (Meunier et al., 2017; Palmer et al., 2004; Blackburn et al., 2019). The survival of pathogen propagules in the environment may then determine the subsequent received load, although donor and recipient host behaviour may moderate exposure. Some dispersal stages can persist outside hosts longer than others. For example, the decay rate of Mycobacteria is dependent on the temperature of the medium and likely also to light-exposure, and therefore differs among seasons (Fine et al., 2011; Barasona et al., 2017). Directly transmitted pathogens (e.g. rabies) are never exposed to the environment and thus skip Stage 3 of the transmission process. For such pathogens, the received pathogen load also depends on exposure (Stage 4), which is impacted by multiple factors including the relative density and immune competence of the donor host (Stage 2), the survival rate of the free-living pathogen (Stage 3) and, for trophically transmitted pathogens, the predation dynamics (e.g. Holling type II functional response). The final load that establishes in the recipient host (Stage 5) depends on the quantity of received particles, the recipient host immune response (which may depend on the species and its genotype (Parker et al., 2015)), and the presence of previously established pathogens (Ezenwa and Jolles, 2015).
3. Models of Transmission
The transmission of a pathogen is most commonly modelled using classic compartmental models (e.g., the
Susceptible-
Infected-
Recovered model) (Kermack and McKendrick, 1927; Anderson and May, 1982). To illustrate the variety of approaches to modelling disease transmission both within and between species, we begin with a simple SI model following the abundance of infections spread within a recipient (subscript
r) host population. This model captures classic expressions for intra-specific transmission in the case where the donor (subscript
d) and recipient species are the same, but allows for analogous expressions for models of inter-specific transmission. If
Sx is the number of susceptible hosts of species
x (
x = {
r, d} for recipient or donor host respectively) and
Ix is the number of infected hosts of species
x, the disease incidence in the recipient host is given by the following equation
Where t is time, Γ is the removal rate (recovery and mortality rates, combined), S and I are the number of susceptible and infected individuals, respectively, and the host population size is defined as N = S + I. Here, βd,r is a general transmission rate and describes the per-capita rate of new infections per unit time. This single constant, however, captures a wide range of possible complex dynamics and its value cannot be easily interpreted, particularly in the context of interspecific transmission. The summation in the transmission term captures the spillover (from donor to recipient), as well as chains of transmission between recipients, allowing us to see infections at different stages of disease emergence (Wolfe et al., 2007). The generalized transmission term of Eqn (1) is commonly used, and is usually referred to as Frequency-Dependent transmission (Begon et al., 2002). Here, we will show how this model can be considered as a general model from which we can derive the range of models seen in the disease ecology literature.
The criterion for a disease outbreak in this compartmental model, is described by the basic reproductive rate, R0, of the pathogen, the number of secondary infections arising from a single infected host in a fully susceptible host population. This quantity is also known as the lifetime reproductive success or fitness of the pathogen. Emergence of a disease in a population, or pathogen persistence in a community, will occur when R0 > 1. If R0 < 1, the pathogen will be lost from the host community, whereas an R0 = 1 represents an endemic disease. We provide the definition and derivation of R0 in assuming two commonly used transmission modes, where we show that β determines the intrinsic rate of increase of the pathogen.
The above model assumes hosts of a given species are identical and mixing among hosts is homogeneous. To include assumptions resulting in inter-host variation as described in transmission stages 1 and 2 of the previous section, the simple model in equation (1) can be extended by including additional discrete donor host classes (e.g., exposure, high-low risk classes) or continuous classes (e.g., age-dependent, activity, space). We will first consider a single-species model.
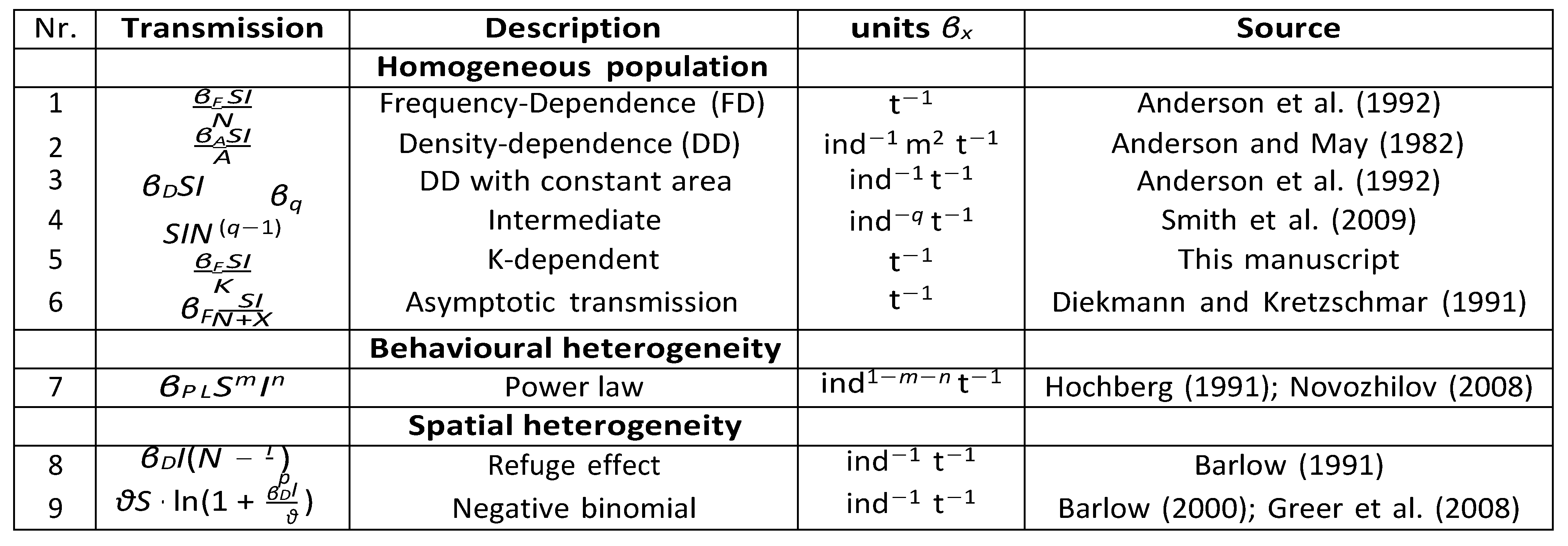
Following Keeling and Rohani (2011), we decompose the various commonly used transmission terms of single-species SI models, as summarized by McCallum et al. (2001) (
Table 1). We begin with the different relationships between susceptible and infected individuals for homogeneously and heterogeneously mixed populations (not including explicit contact networks), and examine how the contact rate between hosts determines the density- or frequency-dependent nature of transmission. Illustrating our framework in
Figure 2, we start with standard assumptions of homogeneity, where we decompose
β (left column), and then give some examples of heterogeneity (right column).
Table 2 sum- marizes the parameters that are used here and in the equations throughout this review.
3.1. Homogeneous mixing
In the simplest case, we can assume a homogeneous population in which all individuals are equally susceptible and interact with equal probability (
Figure 2, left column). There are various different options for modelling the interaction between
S,
I and
β (McCallum et al., 2001; Begon et al., 2002; Hoch et al., 2008). Here, we unify the contact rates into a general function, from which we can derive most transmission rate functions commonly used in the literature (
Table 1).
Decomposing the transmission rate, β
The rate of transmission is determined by the number of contacts an individual has per unit time, κ, and the prob- ability with which a contact leads to infection, c; transmission, β, in a homogeneous population is then simply a function of the contact rate and probability of successful transmission, β = −κ · ln(1 − c) (see Keeling and Rohani (2011) Box 2.1 for a derivation). We show how this can be simplified as β = κ · c in the appendix.
General contact rate
Pathogens can be transmitted directly via host-host contact or indirectly, via intermediate vectors. Some directly transmitted diseases are limited in their transmission, and contacts between infected and susceptible individuals may be independent of population size, which determines whether infection dynamics are density-dependent (DD) or frequency-dependent (FD). Here, we present a generalized version of this contact rate function that can be adapted to capture the spread of disease in a population assuming different contact structures (
Table 1).
Based on the definition
β =
κ ·
c from above, the general contact rate for a single-species model is:
Here, we can easily see how the transmission mode can determined by parameter q. Setting q = 1 returns DD dynamics, as the number of contacts increases linearly with the number of donor hosts, and setting q = 0 returns FD dynamics (Smith et al.,2009). ω portrays the biotic or abiotic asymptotic effects of the transmission, as it can include the carrying capacity of the host population or area in which hosts reside, on which we will elaborate below. If one wants to create heterogeneity in classes, the model can be extended through this parameter such that classes can have different biotic effects, for example with seperate ωS and ωI. Parameter ξ determines the per-capita contact rate, such that if transmission is FD, ξ represents solely the number of contacts and is the same across populations of different sizes. When transmission is DD, ξ represents the fraction of population contacted. This causes the units of β to differ between FD and DD (Table 1). We here provide a description of the units of β and the resulting implications for the order of magnitude of transmission. In Figure 3 we show how the general contact rate, Eqn (2), and its parameters can determine the commonly used transmission models 1.
Figure 3.
Flow chart showing how the contact rate function, κ(N ), determines the density- or frequency-dependent nature of the transmission term, which in turn determines the units of the transmission coefficient βx. The first 3 panels show a spectrum from fully DD to FD, determined by parameter q. The right panel shows a transmission function that can vary from DD to FD with population size.
To take a closer look into multi-host pathogen dynamics, we can easily extend the above transmission term and
The quantity
cr is the probability of infection of the recipient host given exposure. This captures stage 5 of trans- mission in
Section 2.
κd,r is a contact rate between donor and recipient hosts, which variously captures stages 3, and of transmission, above, and
ξr,d(
Nd)
q is the recipient-host per-capita contact rate. Below we will describe in more detail how parameter
q (0
< q <1) is involved in the determination of the transmission mode (Smith et al., 2009) , and variously impacts the unit of measurement of the per-capita contact rate
ξr,d.
3.1.1. Frequency-Dependence
When the transmission of a pathogen is limited by the number of possible interactions per time unit, we model the pathogen as Frequency-Dependent (FD). Common examples of FD transmission include sexually transmitted dis- eases for which transmission relies on the limited number of contacts or
transmission events between sexual partners. Here, the
proportion of the population each infected host interacts with per unit time,
ξ, is constant regardless of the total host population size,
N . Therefore, the contact rate (
κ) is constant per time unit, creating a transmission rate independent of host population density:
βF =
κ ·
c =
ξ ·
c, which returns the familiar FD transmission function shown in Row 1 of
Table 1. In this simple model, infections rise with the probability
the
proportion of infected hosts. We can find this model by setting
ω = 1 and
q = 0 in Eqn (2), see
Figure 3. Vectored diseases, such as Lyme’s disease, can also be approximated assuming FD dynamics, with transmission dependent on contact with an intermediate host. Here, the vector determines the speed of transmission, which may be limited by, for example, the number of meals the vector has per time unit. The FD transmission dynamic is shown in
Figure 4A and the equation and its derivation are provided in panel 3 of
Figure 3 and Appendix Eqn (2).
A particularly useful approximation of FD transmission can be obtained by using the carrying capacity (
K), instead of population size (
N), which we will refer to as
K-dependent transmission (Row 5, Table 1). We can replace
N with
K in any population for which it is assumed the host population is near demographic equilibrium, as for example in the host-parasite model by Gubbins et al. (2000), where in the absence of disease, the hosts approach carrying capacity. We can derive the contact rate for this function by setting
ω =
K and
q = 1 in Eqn (2). At low population densities, transmission follows traditional FD dynamics; however, transmission does not asymptote at higher population densities, but rather converges on DD dynamics, thus combining the behaviour of DD with the infection speed of FD. This reduces mathematical complexity by removing the dependence of the dynamics on a ratio of the state variables,
S and
I. We detail this dynamic in
Figure 4D. As
K can take the maximum size of
N, and therefore is considered of order
N (we explain the definition of
orders of the transmission term in), the units of
β are the same as in FD (Row 5,
Table 1).
3.1.2. Density-dependence
When the density of the population determines the spread of disease, the transmission of the pathogen is considered Density-Dependent (DD), and the higher the density of hosts, the higher pathogen prevalence. DD transmission is most appropriate when encounters between individuals are assumed to be brief (Begon et al., 2002; Smith et al., 2009), and is often referred to as (pseudo-) mass action. Here, the resulting number of interactions per host scales linearly with population density (N ), and pathogen spread is determined by the number if susceptible individuals each infected individual comes into contact with per unit time and unit area, ξ.
In DD models, the contact rate,
κ is dependent of the population size
N, such that the rate of contacts increases with increasing density of hosts, in contrast to FD, making
β a density-dependent rate. We can modify Eqn 2 by setting
q = 1 and
ω =
A, such that it includes the effect of population size (
N ), such that
κ(
N ) =
(see Appendix Eqn (3) and Panel 1 of
Figure 3). The derivation of the DD transmission model using this contact rate can be found in Appendix Eqn 4. Here,
ξ now represents a fraction of the population, and is thus of different order (See next section). The transmission term now shows the number of contact events increasing linearly with the density of hosts (Anderson and May, 1982; Antonovics, 2017). This brings us to Equations 2 and 3 in
Table 1, with infection simply dependent on the density of hosts. Frequently, area is simply considered a constant (Row 3 in
Table 1), as it is assumed that with constant area, an increase in number of individuals causes an increase in density (Kermack and McKendrick, 1927) (Appendix Eqn (5)).
The DD transmission model (
Figure 4B) fits well to directly transmitted diseases, such as the common cold or influenza, and it is commonly used for modeling wildlife diseases, including bTB (Ezenwa et al., 2010). The DD models are summarized in Panel 1 of
Figure 3 and their derivations are described in the SI.
Comparison FD and DD
Models assuming FD and DD vary importantly in their disease dynamics. For example, increasing city size decreased mean transmission, β, of measles during an outbreak in England (Bjørnstad et al., 2002), suggesting the per-capita transmission declined with increasing population size (βˆ = ) (Ferrari et al., 2011), as predicted by FD dynamics (βˆFD =). Because βˆ for DD transmission is independent of population size (βˆDD= β), we would not have predicted declining transmission under DD dynamics. Critically, under assumptions of FD, R0 remains constant across varying N, but under assumptions of DD, R0 increases with N (Ferrari et al., 2011), as a consequence, DD models predict a critical population density as an invasion threshold, which is not the case for FD (see in derivation of R0).
The assumptions of DD and FD dynamics are often violated when empirical data are examined, for example, as with phocine distemper virus in seals, for which βˆ was inversely related to population size (idiosyncratic to FD). Phocine distemper is assumed to be a directly transmitted virus, but was better modelled as FD (Swinton et al., 1999). Additionally, we know that contacts cannot indefinitely increase with population density, as is assumed in DD models (Smith et al., 2009). This shows the difficulty of choosing the right model for any one system.
The use of orders of magnitude in guiding transmission modelling
For both transmission and host removal (death and recovery) to be of importance in disease dynamics, their respective terms in Eqn. (1) need to be roughly the same size. Mathematically, this means that the terms are of the same order of magnitude with respect to the population size N (hereafter simply order) such that transmission and recovery events occur on roughly the same timescale. If this is not true, for example if transmission is of order N 2 while recovery is of order N , transmission will dominant and host recovery can be effectively ignored when modelling disease dynamics. For the examples provided in this paper we assume that the death and recovery-term (ΓN) has order N, hence the transmission term is most realistically also of order N ; this signifies that the addition of N individuals will increase transmission by an amount proportional to N . In contrast, if the transmission term were of order N 2 the addition of N individuals would result in an N 2 increase in transmission rate. This contrast plays out in the comparison of DD and FD dynamics.
When choosing a transmission model it is useful to consider the order of the transmission term and its implications for value and interpretation of the transmission rate
β. In FD,
β =
βF has the unit
t−1, so is independent of
N, and is of order 1 (
Table 1, Row 1). In DD,
β =
βD has to be of
order , meaning
βD is in units of
ind−1, as shown in
Table 1 rows 2 and 3. Hence the value of
β in these two models cannot be directly interchanged. If the units of
β are not adjusted appropriately, than it would appear that the transmission described by DD is an order of magnitude
N faster than in FD, as can be seen in
Figure 5. We therefore adjust the order of parameter
ξ, as described in the main text. In FD,
ξ is the number of contacts (constant over population size
N), whereas in DD,
ξ is the fraction of population (
) contacted and therefore an order lower. This brings the transmission terms for DD and FD back to the same order. For K-dependent transmission, replacing
N with
K does not change the order of the transmission term, and therefore the order remains the same as in FD. A summary of the units of
β can be found in
Table 1.
3.1.3. Intermediate FD-DD
It is rare to find a system that is truly FD or DD, and host contact behaviour (when homogeneous mixing is assumed) is often somewhere on the FD-DD continuum (Anderson et al., 1992; Smith et al., 2009; Ferrari et al., 2011). For example, it is unlikely that contact rates either increase indefinitely with
N, as is assumed under DD, or are com- pletely independent of density, as assumed in FD (McCallum et al., 2001). Therefore, Smith et al. (2009) designed a transmission model that could capture dynamics on this FD-DD continuum. We can show this model with pa- rameter
q of Eqn (2) (continuous and 0
< q <1), which now can be interpreted as the relative importance of a single added host within a population to the average contact rate. By allowing
q to vary, it is possible to capture seasonal dynamics, for example, cowpox in voles shifting towards FD dynamics in late summer and more DD dynamics in late winter, and variation with life stages, as in the phocine distemper virus outbreak in the Dutch Wadden Sea, where infection dynamics of less social juveniles and adult seals are better explained by FD, and subadults by DD (Klepac et al., 2009). Equations are shown in panel 2 of
Figure 3 and the derivation for transmission is in Appendix Eqn (9). Some examples of intermediate FD-DD dynamics are displayed in
Figure 4C.
Contact among individuals is also influenced by the area in which the individuals interact, which may be characterized by Michaelis-Menten-like dynamics, which are captured by the parameter ω. Because interaction behaviour can differ between the classes of individuals, S, I and R, we can additionally allow for heterogeneity in contact rate among these classes, and the transmission function can be extended such that classes can have different density limiting effects via the corresponding parameters ωS, ωI and ωR.
3.1.4. Asymptotic transmission
Some diseases are more likely to spread asymptotically, such that at low host densities contacts are directly proportional to host density (e.g., DD), but a maximum rate of contact is obtained at high host densities (e.g. due to spatial or social distribution) (Diekmann and Kretzschmar, 1991; McCallum et al., 2001). Including an additional term for the saturation of contacts at high population sizes, we can model these dynamics by allowing transmission to vary between DD and FD depending on the total population size (Antonovics, 2017). The equation for this contact function can be found in Appendix Eqn (10). Here, there is a shift from DD to FD with increasing
N (see Appendix for derivation of asymptotic contact rate and
Table 1, Row 6). Note that this transmission rate is equivalent to that for frequency dependent transmission,
βF, as they have similar units (and thus the transmission term is again of order
N ). We can therefore identify the critical level after which contacts start to saturate as
X =
N * (with 1
< X < ∞), the half saturation constant in Michealis-Menten kinetics. The lower
X, the higher the affinity of individual contacts and the quicker saturation of contacts is reached. In contrast to intermediate FD-DD transmission, where the shift arises through parameter
q and therefore is constant, here the shift from FD to DD is caused by increasing host density,
N, as shown in
Figure 3 (Panel 4).
Figure 4E shows the asymptotic transmission dynamics. Equations and derivations can be found in Appendix Eqn (9).
3.2. Heterogeneous mixing
A key challenge in modeling transmission is accurately capturing the inherent nature of host density and contact rates. Contact structure and animal behaviour can have a large impact on disease dynamics. For example, in models of bovine Tuberculosis for African buffalo, allowing for social groupings resulted in a departure from standard SIR disease dynamics (Cross et al., 2004, 2007). Failure to correctly represent contact structure can have significant implications for disease management. In the example of bTB in the European badger, culling intended to reduce number of infected individuals instead resulted in an increased contact rate (as aggregation increased in lower- density groups), and thus increased disease prevalence (Vicente et al., 2007). The epidemiological contact process, and the emergent relationship between host density and contact rate, can be modeled both explicitly, in the form of density-dependent or frequency-dependent compartmental models, and implicitly, for example, as a network or individual-based models (we describe some in Appendix section 2). The models described above assume individuals are homogeneous in their susceptibility, and that epidemiologically relevant contacts between hosts occur at random, known as the assumption of
random mixing. However, host behaviour can change the probability of encountering an infected individual and the geographic distribution and movement of hosts plays a significant role in modifying host contact rates (Pope et al., 2007; Vicente et al., 2007). This heterogeneity can affect the overall disease spread (Ferrari et al., 2011). We can recompose the transmission term in various ways to portray this heterogeneous mixing (
Figure 2, right column).
Behavioural heterogeneity
There are various approaches that allow us to include heterogeneity in behaviour of S and I, including network or individual-based models (Ferrari et al., 2011). Here, we review some simplified and commonly adopted formulations for our compartmental SIR model from Eqn (1).
3.2.1. Power-law transmission
Idiosyncratic behaviour or behaviour caused by infections can result in non-linear contact patterns between
S and
I individuals, departing from the linear assumptions of homogeneous mixing and mass-action dynamics of the common SIR model (Gubbins et al., 2000). The Power-law transmission function aims to encapsulate potential accelerating or decelerating responses that may be found in empirical systems by introducing
heterogeneity parameters m and
n. This transmission function simulates heterogeneous interactions between
S and
I individuals with accelerating and decelerating disease spread by raising
S and
I to the powers
m and
n, respectively (Hochberg, 1991), as shown in
Table 1, Row 7. These heterogeneity parameters determine how the densities
S and
I affect the
per capita transmission efficiency of the pathogen, such as the susceptibility (by
m) or the infectivity (by
n) of an individual (Hochberg, 1991; Novozhilov, 2008), and thus determine the speed of infection. When both parameters are unity, the model describes DD (with constant area).
There are many possible response types, as theoretically −∞
< m, n < ∞. For example, in plant-parasite interactions, the production of free-living pathogen stages, such as spores or other microparasites, may generate accelerating infection responses in plant communities (Gubbins et al., 2000). Here, we consider some biologically more relevant examples. Assuming
n = 1, when
m > 1, transmission accelerates, and new infections arise exponentially with linearly increasing number of susceptible individuals. When
n = 1 and
m < 1, rate of new infections decelerates.
Figure 4F shows the power law transmission dynamics with varying
n. We could find no real-world examples of exponents 0
< m <1, but it would represent a case when increasing
S decreases the rate of transmission (Novozhilov, 2008). Greer et al. (2008) found that the
Ambystoma tigrinum Virus (ATV) in its host (the Tiger Salamander,
Ambystoma tigrinum) was best described with a Power-law function with
m = 1 and
n = 0.255, suggesting that infection scales positively but non-linearly with
I. When
m < 0,
S is inversely related to transmission, and when
n <0,
I is inversely related to transmission. An example of the latter is seen in
Bacillus thuringiensis infections of
Plodia interpunctella moths, here, transmission requires cannibalism of infected individuals, and thus transmission increases with
S, and decrease with
I (Knell et al., 1996). In addition to capturing accelerating and decelerating behaviours, the power-law function can also represent scenarios where the infection risk is constant, and independent of the density of infected individuals, as is the case where there is constant re-inoculation of the disease from another species, for example, rabies virus from wild canines into domestic dogs (Rhodes et al., 1998; Mollentze et al., 2020). This could be modelled as
n = 0. By sampling from distributions of
m and
n, the power-law function can also approximate heterogeneity in transmission rates among
S and
I individuals (White et al., 2017).
Spatial heterogeneity
The assumption in SIR models of spatially homogeneous populations is also an obvious oversimplification of real population dynamics, especially for species exhibiting territoriality, sociality and other complex group or individual behaviours (Cross et al., 2004; Viana et al., 2014; White et al., 2017). A well-studied example of how species’ behaviour affects diseases dynamics, is the African Buffalo and bTB, where researchers claimed that
R0 was a bad predictor of disease outbreak potential due to the effect of fission-fusion dynamics portrayed by the host (Cross et al., 2004, 2005, 2007). Contact networks provide a useful approach to model more realistic population behaviour (Craft, 2015), but can rapidly become analytically intractable. We describe some network models in the Appendix
Section 2. Here, we illustrate how spatial heterogeneity in contacts can be included into our compartmental SIR models, making a few simplifying assumptions, and holding transmission rate,
β, constant.
3.2.2. Refuge effect
The refuge effect model includes the spatial aggregation of hosts, such that the transmission function incorporates host clustering (Barlow, 1991). In this model, the population is represented as consisting of patches with and without disease (Barlow, 1991; May and Anderson, 1984). The proportion of the total area that is occupied by diseased individuals,
p, represents how aggregated the disease is in space. If
p = 1, the diseased patch equals the total area (there is in fact no patch), and there is no aggregation of the disease. Then, the transmission term simplifies to
βDI(
N −
I) =
βDSI, DD dynamics. However, the more the disease is aggregated (the smaller
p), the lower the probability that an infectious individual will encounter a susceptible individual. The transmission term including this clustering is shown in Row 8 of Table 1. Assuming
N =
S +
I, so in this case a simple SI model excluding the R compartment, the number of susceptible individuals is
S =
Np −
I. With greater aggregation, transmission decreases, as individuals are now less homogeneously distributed. For
I =
pN, which is the maximum density of individuals in the diseased patch, transmission is 0.
Figure 4G shows these transmission dynamics for three different values of
p. One example of highly aggrevated disease prevalence is bTB in New Zealand possums (
Trichosurus vulpecula) (Barlow, 1991).
3.2.3. Negative binomial
The negative binomial model builds upon the Refuge effect (Barlow, 1991) and was also fit to model TB in possums, but with varying carrying capacities (different resource availability) among patches, allowing for increased contact rates by concentrating hosts (Civitello et al., 2018). Transmission now includes a heterogeneous mixing term,
θ (ind
−1 t
−1), which can take any value 0
< θ < ∞ (Barlow, 2000). This model assumes that the probability of infection is higher when a susceptible individual has an infected neighbor, and so infections are clustered in space. Small
θ corresponds to highly aggregated infections. As
θ decreases (
θ → 0), transmission decreases as the mean number of infected individuals encountered per susceptible individual is reduced. As
θ increases (
θ → ∞), aggregation is reduced, and transmission again simplifies to DD transmission. This transmission function is shown in Row 9 of
Table 1 and
Figure 4H.
3.3. Summary of transmission functions
There are multiple approaches for describing the spread of a pathogen through a host population, with contact rate the most important driver of disease dynamics. The most common division is between DD and FD dynamics, although various intermediate dynamics allow us to capture differences in the biology of the pathogen and the behaviour of the host. Wildlife diseases are almost always modeled assuming DD dynamics, regardless of the pathogen, as host behaviour, including local heterogeneities, is more likely to approximate mass-action dynamics at larger scales (McCallum, 2016; White et al., 2017). In contrast, local dynamics in human interactions commonly depart from assumptions of DD (people frequently form small contact networks), and might thus be better modelled using FD dynamics or, more realistically, with asymptotic transmission. However, many empirical studies have shown evidence of both FD and DD dynamics in the same system, with DD dynamics more often observed at low population densities, and FD dynamics more common at higher densities (Antonovics, 2017; Roberts and Heesterbeek, 2018). Unsurprisingly, more complex dynamics are also found in many disease systems. Individuals may vary in susceptibility and infectivity, as captured by the concept of superspreaders, which dramatically influences outbreak potential and disease dynamics (Lloyd-Smith et al., 2005). Similar concepts can be extended to super-movers, super-recipients, super-shedders, and super-susceptibles (Streicker et al., 2013; Craft, 2015; White et al., 2017). Additionally, hosts likely do not have a homogeneous contact structure, as these may be modified through networks or variation in population density. For example, in feline retrovirus, infrequent encounters at low host densities make contact rates close to constant (FD), at intermediate densities contact rate becomes proportional to density (DD), while at high densities there is a further increase in contact rate due to overlapping territories (Fromont et al., 1998). We elaborate on contact networks and describe some methods for quantifying transmission parameters in the Appendix. However, contacts in complex networks tend to homogenize over time (Cross et al., 2004). Therefore, over longer timescales, heterogeneity can average out, providing an opportunity to simplify otherwise complex models.
3.4. Derivation of pathogen net reproductive success, R0
To calculate
R0, we want to know when the pathogen can grow in the population. For
Frequency-Dependent transmission, we set
(from Eqn 1), which gives us:
Then, dividing by
I and rearranging we return:
When
S ~
N, fraction
X = 1, so assuming a fully susceptible population (which is the assumption in the definition of
R0), the disease will spread when is greater than unity:
For
density-dependent transmission, the definition of
R0 is the same, but has a different implementation. We again derive it from setting
: For DD transmission, we get:
As
R0 is by definition the number of secondary individuals that arise from a
single infected individual in a
fully susceptible population, we set
I = 1. Solving this for
S, we obtain:
By definition, for a disease to spread in a population, the product of the number of susceptibles (S) causing secondary infections (R0) must be greater than unity (R0S > 1), and thus R0 > . Therefore, in DD transmission, we define S∗ as a critical threshold host density for invasion of the pathogen, which does not exist in FD.
For
multiple species, we can calculate the
R0 for the whole community using a Next Generation Matrix calculation (Diekmann et al., 1990; Dobson, 2004; Diekmann et al., 2010). Here, transmission data from species
j to
i,
βij is summarized in the
Who-acquired-infection-from-who matrix
W:
According to Next-Generation calculation (Diekmann et al., 1990), matrix W can be used to form a new matrix, R, including the removal rates, as in the single-dimensional calculations above. Then, the maximum eigenvalue of matrix R will be the Community R0, or R0,total. For a detailed derivation see Dobson (2004).
4. Ecology of transmission
Host community structure can both affect and be affected by pathogen dynamics. It is common for pathogens to infect multiple host species (Woolhouse et al., 2001), and this can significantly alter disease dynamics. In multi- host systems, transmission is determined by multiple shedding hosts, each of which can contribute differently to disease prevalence, depending on their inter- and intraspecific ecological interactions (Haydon et al., 2002; Streicker et al., 2013; Fenton et al., 2015). This complicates models and how we estimate transmission, which may be asymmetric among hosts, with some hosts acting as pathogen reservoirs, others as sinks, and pathogens may express different life-history syndromes in different hosts (Haydon et al., 2002; Gandon, 2004). In this section, we describe how transmission can be defined in such systems and how host diversity in multi-host systems can impact disease dynamics The well-known disease-diversity relationship is a highly-disputed concept in disease-ecology.
4.1. Host community effects on pathogen prevalence
The
dilution effect suggests a higher diversity of hosts reduces the probability of a pathogen infecting a new host, for example directly, by reducing encounters, and therefore transmission between hosts or indirectly, by changing total host abundance (Keesing et al., 2006, 2010) (
Table 3). One well-modelled example of encounter reduction (also known as
frequency-dependent dilution) is provided by Rudolf and Antonovics (2005) in FD systems; here, a host is rescued from pathogen mediated-extinction by a second host that is infected by the same disease (
apparent mutualism). The secondary host is assumed less competent, and therefore functions as a buffer, reducing further disease spread by replacing contacts (and therefore transmission events) with the original host, effectively reducing frequency of contacts between competent hosts. Lyme disease is a frequently cited empirical example of the dilution effect, where diversity of vertebrate hosts decreases the risk of spillover to humans. The bacterial pathogen (
Borrelia burgdorferi ) is vectored by the black legged tick (
Ixodes scapularis), and uses the white footed mouse (
Peromyscus leucopus) as a primary host. Prevalence of
B. burgdorferi decreases when a secondary, less competent host, the eastern chipmunk (
Tamias striatus), increases in density (Keesing et al., 2006). Several other systems have provided evidence for dilution effects, including bTB in sub-Saharan Africa, which may be reduced at higher mammal density (Huang et al., 2013, 2014). A summary of diseases with dilution effect can be found in Keesing et al. (2010).
In contrast to dilution, the
amplification effect suggests that higher host diversity increases disease prevalence. This can be
directly, via elevating contact rates by increasing total host density (Rudolf and Antonovics, 2005) or by the addition of a highly competent, super-spreader host (a phenomenon parallel to
the selection effect in biodiversity science (Loreau and Hector, 2001)), or
indirectly by changing host densities through competition (Holt and Bonsall, 2017) (
Table 3). For example, higher amphibian diversity is thought to have increased Chytrid disease (
Ba- trachochytrium dendrobatidis) prevalence in some species of frogs, as highly competent (amplifying) hosts are more abundant in species-rich habitats (Ostfeld and Keesing, 2012). The amplification effect may also arise in vectored diseases (often modelled as FD) if increased diversity supports more competent host species (Ostfeld and Keesing, 2000).
In all cases of amplification or dilution (
Table 3), it is assumed that the pathogen is a generalist and that hosts differ in competence (except for direct amplification in DD systems, which assumes contacts are additive and there is no limit to contacts per time unit). In FD, amplification depends on host
identity and, by extension, host competence. Under strict assumptions of DD, amplification will always occur, as contacts increase with host density, and contacts are always additive and never substitutive (Dobson, 2004; Rudolf and Antonovics, 2005). Increasing the number of hosts simply increases encounter rates between
S and
I individuals, and will therefore always amplify the disease, regardless of the competence of the hosts. In contrast, the direct effect of diversity in FD transmission, assuming a constant number of contacts per time unit and varying competence, are mixed. The addition of a less competent host will always have a diluting effect, whereas the addition of a highly competent host may have an amplifying effect. Predicting the
indirect effects of diversity is more challenging. Changes in prevalence will reflect how communities are altered by the introduction of novel host species (Ostfeld and Keesing, 2000). Community evenness is a particularly important dimension in multi-host systems, as the relative dominance of the most competent host will largely determine disease dynamics (Ostfeld and Keesing, 2000; Sintayehu et al., 2017). For example, dilution can occur indirectly in Lyme’s disease when the alternative host reduces the density of the main reservoir through competition (Ogden and Tsao, 2009). Because host contacts likely saturate at higher densities (Antonovics, 2017), as density increases disease dynamics may switch from DD to FD dynamics (c.f. asymptotic transmission), and in general we might predict dilution effects to be more common at higher densities.
4.2. Pathogen effects on host community
While we expect a pathogen’s persistence to be influenced by the abundance of its hosts, host abundance might also be influenced by the pathogen. Most obviously, a pathogen can suppress host abundance directly through disease induced mortality. In multi-host systems, pathogen sharing among hosts can result in apparent competition (Holt and Pickering, 1985). For example, a reservoir host may indirectly suppress the density of a spillover host by acting as a source of infection, and if the reservoir host has a better adapted immune system to the pathogen, it can reduce the density of the spillover host via pathogen induced mortality. One example of apparent competition is provided by the spillover of the vector-transmitted Barley Yellow Dwarf virus (genus Luteovirus) from wild oats (Avena fatua), which reduced the abundance of the spillover host species, Setaria, allowing the wild oat to maintain ecological dominance (Power and Mitchell, 2004). Although disease dynamics may appear similar, and feedback into dilution or amplification effects, apparent competition describes the effect of pathogen prevalence on hosts, whereas, dilution and amplification describe the effects of host diversity on pathogen prevalence. Apparent competition is typically only a property of DD systems, but may be possible in FD systems if the pathogen is not directly diluted by a less susceptible, spillover host(s).
Apparent mutualism can occur in FD systems when hosts have equal competence. In this case, the introduction of a novel host can reduce the disease prevalence in the original host by replacing contacts. There is no ’competition’ as all hosts are equally affected by the pathogen (Holt and Bonsall, 2017), and all hosts benefit from additional hosts. Apparent mutualism differs from dilution, as dilution assumes difference in host competence, while apparent mutualism assumes hosts are identical in their competence.
In summary, under assumptions of DD dynamics, increasing diversity results in amplification, irrespective of differences in host competence, assuming each host adds to overall disease transmission. Under assumptions of FD dynamics, increasing host diversity can result in apparent mutualism when hosts are equal in their competence, and dilution can occur when hosts have unequal competence. However, apparent competition is possible under both FD and DD dynamics if hosts vary in competence and one host experiences lower pathogen related mortality, for example, through having a superior immune system.
4.3. The role of community structure in interspecific transmission
Changing host community structure alters intraspecific and interspecific contact rates, and thus disease dynamics. The interspecific transmission rate determines the effect of species richness on the outbreak potential, R0, with disease competence determining whether a host acts as an amplifier or a diluter, and the persistence of a disease in multiple hosts is determined by the interspecific and intraspecific transmission dynamics (section 4.1). For example, jackals (Canis adustus) need to be frequently reinoculated by rabies virus from domestic dogs to support an infection in the population (Rhodes et al., 1998; Keesing et al., 2006) as their intraspecific transmission is too low to sustain endemic prevalence, and thus jackals are more likely a diluter than an amplifier of rabies. There are many approximations for interspecific transmission, focusing on the ecology of hosts or the co-evolution of pathogens and hosts, for example using matching-allele and gene-for-gene models (Poullain and Nuismer, 2012). In this section we consider some approaches that we think may be most promising for addressing questions on the disease-diversity relationship.
Interspecific transmission can be modeled in a WAIFW-matrix (Who Acquired Infection From Who), an n by n - matrix showing the transmission between species in an n-species system, where intraspecific transmission can be found on the diagonal, and interspecific transmission on the off-diagonals (Dobson and Foufopoulos, 2001; Diekmann et al., 2010). This is shown in Eqn (f) in the last paragraph of this section. Transmission is defined as βi,j, where i is the receiving host and j the donating host (j infects i). This matrix can be used to form the Next Generation Matrix which calculates the community R0 (see final paragraph of this section), and determines the overall disease prevalence in the system, as well as the contributions of each individual host (Diekmann et al., 2010). One way to estimate the interspecific transmission rate is to take the average of the intraspecific transmission rates, using a scaling parameter to account for differences in transmission potential between species i and j (Dobson, 2004). This scaling parameter can determine the magnitude of diluting and amplifying behaviour of each host species in the system. Alternatively, one can parameterize the probability of successful transmission, c, per host species-pair, assuming that disease competence, and therefore transmission, is dependent on the donating and receiving host species’ identities (Stewart Merrill et al., 2022), and can be asymmetrical.
A similar approach can also be applied to contact rates, κ, if one wants to define c separately for individual host species (or species pairs), rather than the community average (Anguelov et al., 2014). However, there can be asymmetrical transmission between hosts, for example Blancou and Aubert (1997) suggest that for a fox with rabies to infect a dog or cat, requires a million times more virus particles than would be necessary to infect another fox (Ostfeld et al., 2008). Such asymmetries may be overlooked when simply averaging intraspecific transmission rates.
5. Future directions
Defining the shape of the transmission function between hosts is challenging, and seemingly small differences can have dramatic effects on predictions in multi-species models (Dobson, 2004). Accelerating rates of biodiversity loss and habitat degradation worldwide, have been accompanied by increasing disease outbreaks in wildlife, domestic animals and human populations, generating an urgent need for studies on how biodiversity and environmental carrying capacity of wild species may modify pathogen transmission rates. Habitat fragmentation and a decrease in the carrying capacity of an ecosystem can both affect transmission dynamics (Childs et al., 2007; Lafferty and Holt, 2003) with increased interspecific transmission observed at the interface between natural and converted landscapes (Wolfe et al., 2005; Faust et al., 2018; Goldberg et al., 2008).
As most hosts and pathogens exist within multi-host systems, we need to better understand how transmission affects disease outbreaks in such systems. The next-generation matrix (Diekmann et al., 2010), which allows us to calculate the community R0 and each host’s relative contribution, is a useful framework for modelling the dynamics of multi- host pathogens and disease maintenance in the reservoir. However, the complexity in quantifying transmission, with asymmetries in interspecific rates and between reservoir and novel hosts following spillover events (Wolfe et al., 2007; Auld et al., 2017), can make the application of such models fraught. Additional challenges include accounting for spatial heterogeneity and contact structure, although over longer timescales transmission dynamics may appear more homogeneous (Cross et al., 2004). However, as pathogen sharing is affected by the overlapping geographical ranges of hosts (Davies and Pedersen, 2008), investigating the effect of local versus global dynamics remains important.
It is also becoming increasingly clear that the evolutionary relationship between species plays a role in disease trans- mission, with strong evidence of phylogenetic signal in the likelihood of pathogen sharing among hosts (Davies and Pedersen, 2008; Farrell et al., 2019; Streicker et al., 2019; Olival et al., 2017). It is likely, for example, that similarity in the immune defenses of closely related species due to the evolutionary conservation of the cellular, immunological, or metabolic traits, favours pathogen exchange between them (Kuiken et al., 2006; Streicker et al., 2010). Similar phylogenetic signature in pest and pathogen sharing is observed in plants (Gilbert and Webb, 2007; Gilbert et al., 2012; Parker et al., 2015; Ssebuliba and Davies, 2021), and phylogeny is also suggested to be a strong predictor of pathogen impact, with declining severity of the effect of the disease with increasing evolutionary distance between hosts (Gilbert et al., 2015; Gougherty and Davies, 2021). So, understanding the phylogenetic structure of host communities may help us determine the probability of interspecific transmission and predict novel host shifts (Poullain and Nuismer, 2012; Parker et al., 2015).
6. Conclusion
Transmission mode mediates the effect of biodiversity on disease burden, careful consideration of the design of transmission model is thus central to disease ecology.
By decomposing the transmission model into its separate parameters, we show how each captures different aspects of the outbreak process within and between species.
We present a general contact rate function that can aid modellers in selecting a transmission model that best fits their system.
We highlight that density dependent transmission will always lead to disease amplification, as it assumes indefinitely increasing contacts, whereas frequency dependent transmission can lead to disease dilution.
At higher population densities, assumptions of increasing contacts are unlikely to hold, and thus disease dilution effects may arise at high population densities for pathogens which are density dependent at low population densities.
Future work in disease ecology should focus on how the composition of host communities determines the prevalence, maintenance and onward transmission of diseases, and the likelihood of novel pathogen emergence via host shifts. Accurately defining the transmission process will be a critical first step.
References
- Anderson, R. M. and May, R. M. (1982). Coevolution of Hosts and Parasites. Parasitology, 85(2):411–426.
- Anderson, R. M., May, R. M., and Ng, T. W. (1992). A ge-dependent choice of sexual partners and the transm ission dynam ics of H IV in S ub -S ah aran Africa. pages 135–155.
- Anguelov, R., Garba, S. M., and Usaini, S. (2014). Backward bifurcation analysis of epidemiological model with partial immunity. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 68(9):931–940.
- Antonovics, J. (2017). Transmission dynamics: Critical questions and challenges. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 372(1719).
- Auld, S. K., Searle, C. L., and Duffy, M. A. (2017). Parasite transmission in a natural multihost-multiparasite community. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 372(1719):1–10.
- Bar-On, Y. M., Phillips, R., and Milo, R. (2018). The biomass distribution on Earth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(25):6506–6511.
- Barasona, J. A., Vicente, J., D´ıez-Delgado, I., Aznar, J., Gort´azar, C., and Torres, M. J. (2017). Environmental presence of mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in aggregation points at the wildlife/livestock interface. Trans- boundary and emerging diseases, 64(4):1148–1158.
- Barlow, N. D. (1991). A spatially aggregated disease/host model for bovine tb in new zealand possum populations.
-
Journal of applied ecology, pages 777–793.
- Barlow, N. D. (2000). Non-linear transmission and simple models for bovine tuberculosis. Journal of Animal Ecology, 69(4):703–713.
- Begon, M., Bennett, M., Bowers, R. G., French, N. P., Hazel, S. M., and Turner, J. (2002). A clarification of transmission terms in host-microparasite models: Numbers, densities and areas. Epidemiology and Infection, 129(1):147–153.
- Bengis, R. and Erasmus, J. (1988). Wildlife diseases in south africa: a review. Revue Scientifique et Technique de l’OIE.
- Bjørnstad, O. N., Finkenst¨adt, B. F., and Grenfell, B. T. (2002). Dynamics of measles epidemics: estimating scaling of transmission rates using a time series sir model. Ecological monographs, 72(2):169–184.
- Blackburn, J. K., Ganz, H. H., Ponciano, J. M., Turner, W. C., Ryan, S. J., Kamath, P., Cizauskas, C., Kausrud, K., Holt, R. D., Stenseth, N. C., et al. (2019). Modeling r0 for pathogens with environmental transmission: animal movements, pathogen populations, and local infectious zones. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(6):954.
- Blancou, J. and Aubert, M. (1997). Transmission of rabies virus: importance of the species barrier. Bulletin de L’academie Nationale de Medecine, 181(2):301–11.
- Blaser, N., Wettstein, C., Estill, J., Vizcaya, L. S., Wandeler, G., Egger, M., and Keiser, O. (2014). Impact of viral load and the duration of primary infection on hiv transmission: systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS (London, England), 28(7):1021.
- Childs, J. E., Mackenzie, J. S., and Richt, J. A. (2007). Wildlife and emerging zoonotic diseases: the biology, circumstances and consequences of cross-species transmission, volume 315. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Civitello, D. J., Allman, B. E., Morozumi, C., and Rohr, J. R. (2018). Assessing the direct and indirect effects of food provisioning and nutrient enrichment on wildlife infectious disease dynamics. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 373(1745).
- Craft, M. E. (2015). Infectious disease transmission and contact networks in wildlife and livestock. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 370(1669).
- Cross, P. C., Johnson, P. L., Lloyd-Smith, J. O., and Getz, W. M. (2007). Utility of R0 as a predictor of disease invasion in structured populations. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 4(13):315–324.
- Cross, P. C., Lloyd-Smith, J. O., Bowers, J. A., Hay, C. T., Hofmeyr, M., and Getz, W. M. (2004). Integrating association data and disease dynamics in a social ungulate: Bovine tuberculosis in African buffalo in the Kruger National Park. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 41(6):879–892.
- Cross, P. C., Lloyd-Smith, J. O., and Getz, W. M. (2005). Disentangling association patterns in fission-fusion societies using African buffalo as an example. Animal Behaviour, 69(2):499–506.
- Daszak, P., Cunningham, A. A., and Hyatt, A. D. (2000). Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife - Threats to biodiversity and human health. Science, 287(5452):443–449.
- Davies, T. J. and Pedersen, A. B. (2008). Phylogeny and geography predict pathogen community similarity in wild primates and humans. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 275(1643):1695–1701.
- Diekmann, O., Heesterbeek, J., and Roberts, M. G. (2010). The construction of next-generation matrices for com- partmental epidemic models. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 7(47):873–885.
- Diekmann, O., Heesterbeek, J. A. P., and Metz, J. A. (1990). On the definition and the computation of the basic reproduction ratio r 0 in models for infectious diseases in heterogeneous populations. Journal of mathematical biology, 28(4):365–382.
- Diekmann, O. and Kretzschmar, M. (1991). Patterns in the effects of infectious diseases on population growth. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 29(6):539–570.
- Dobson, A. (2004). Population Dynamics of Pathogens with Multiple Host Species. 164(november).
- Dobson, A. and Foufopoulos, J. (2001). Emerging infectious pathogens of wildlife. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 356(1411):1001–1012.
- Elguero, E., D´elicat-Loembet, L. M., Rougeron, V., Arnathau, C., Roche, B., Becquart, P., Gonzalez, J.-P., Nkoghe, D., Sica, L., Leroy, E. M., et al. (2015). Malaria continues to select for sickle cell trait in central africa. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(22):7051–7054.
- Ezenwa, V. O., Etienne, R. S., Luikart, G., Beja-Pereira, A., and Jolles, A. E. (2010). Hidden consequences of living in a wormy world: Nematode-induced immune suppression facilitates tuberculosis invasion in African buffalo. American Naturalist, 176(5):613–624.
- Ezenwa, V. O. and Jolles, A. E. (2015). Opposite effects of anthelmintic treatment on microbial infection at individual versus population scales. Science, 347(6218):175–177.
- Farrell, M. J. and Davies, T. J. (2019). Disease mortality in domesticated animals is predicted by host evolutionary relationships. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(16):7911–7915.
- Farrell, M. J., Govender, D., Hajibabaei, M., Van Der Bank, M., and Davies, T. J. (2019). Bacterial diversity in the waterholes of the Kruger National Park: An eDNA metabarcoding approach. Genome, 62(3):229–242.
- Faust, C. L., McCallum, H. I., Bloomfield, L. S., Gottdenker, N. L., Gillespie, T. R., Torney, C. J., Dobson, A. P., and Plowright, R. K. (2018). Pathogen spillover during land conversion. Ecology Letters, 21(4):471–483.
- Fenton, A. and Pedersen, A. B. (2005). Community epidemiology framework for classifying disease threats. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 11(12):1815–1821.
- Fenton, A., Streicker, D. G., Petchey, O. L., and Pedersen, A. B. (2015). Are all hosts created equal? Partitioning host species contributions to parasite persistence in multihost communities. American Naturalist, 186(5):610–622.
- Ferrari, M. J., Perkins, S. E., Pomeroy, L. W., and Bjrnstad, O. N. (2011). Pathogens, social networks, and the paradox of transmission scaling. Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Diseases, 2011.
- Fine, A. E., Bolin, C. A., Gardiner, J. C., and Kaneene, J. B. (2011). A study of the persistence of mycobacterium bovis in the environment under natural weather conditions in Michigan, USA. Veterinary Medicine International, 2011.
- Fromont, E., Pontier, D., and Langlais, M. (1998). Dynamics of a feline retrovirus (FeLV) in host populations with variable spatial structure. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 265(1401):1097–1104.
- Gandon, S. (2004). Evolution of multihost parasites. Evolution, 58(3):455–469.
- Gilbert, G. S., Briggs, H. M., and Magarey, R. (2015). The impact of plant enemies shows a phylogenetic signal.
-
PLoS ONE, 10(4):1–11.
- Gilbert, G. S., Magarey, R., Suiter, K., and Webb, C. O. (2012). Evolutionary tools for phytosanitary risk analysis: Phylogenetic signal as a predictor of host range of plant pests and pathogens. Evolutionary Applications, 5(8):869– 878.
- Gilbert, G. S. and Webb, C. O. (2007). Phylogenetic signal in plant pathogen–host range. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(12):4979–4983.
- Goldberg, T. L., Gillespie, T. R., Rwego, I. B., Estoff, E. L., and Chapman, C. A. (2008). Forest fragmentation as cause of bacterial transmission among nonhuman primates, humans, and livestock, uganda. Emerging infectious diseases, 14(9):1375.
- Gougherty, A. V. and Davies, T. J. (2021). Towards a phylogenetic ecology of plant pests and pathogens. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 376(1837):20200359.
- Gougherty, A. V. and Davies, T. J. (2022). Host phylogenetic diversity predicts the global extent and composition of tree pests. Ecology Letters, 25(1):101–112.
- Graham, J. P., Leibler, J. H., Price, L. B., Otte, J. M., Pfeiffer, D. U., Tiensin, T., and Silbergeld, E. K. (2008). The animal-human interface and infectious disease in industrial food animal production: Rethinking biosecurity and biocontainment. Public Health Reports, 123(3):282–299.
- Greer, A. L., Briggs, C. J., and Collins, J. P. (2008). Testing a key assumption of host-pathogen theory: Density and disease transmission. Oikos, 117(11):1667–1673.
- Gubbins, S., Gilligan, C. A., and Kleczkowski, A. (2000). Population dynamics of plant-parasite interactions: Thresh- olds for invasion. Theoretical Population Biology, 57(3):219–233.
- Halliday, F. W. and Rohr, J. R. (2019). Measuring the shape of the biodiversity-disease relationship across systems reveals new findings and key gaps. Nature Communications, 10(1):1–10.
- Han, B. A., O’Regan, S. M., Paul Schmidt, J., and Drake, J. M. (2020). Integrating data mining and transmission theory in the ecology of infectious diseases. Ecology Letters, 23(8):1178–1188.
- Han, B. A., Park, A. W., Jolles, A. E., and Altizer, S. (2015). Infectious disease transmission and behavioural allometry in wild mammals. Journal of Animal Ecology, 84(3):637–646.
- Haydon, D. T., Cleaveland, S., Taylor, L. H., and Laurenson, M. K. (2002). Identifying reservoirs of infection: A conceptual and practical challenge. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 8(12):1468–1473.
- Hoch, T., Fourichon, C., Viet, A. F., and Seegers, H. (2008). Influence of the transmission function on a simulated pathogen spread within a population. Epidemiology and Infection, 136(10):1374–1382.
- Hochberg, M. E. (1991). Non-linear transmission rates and the dynamics of infectious disease. Journal of theoretical biology, 153(3):301–321.
- Holt, R. D. and Bonsall, M. B. (2017). Apparent Competition. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 48:447–471.
- Holt, R. D. and Pickering, J. (1985). Infectious Disease and Species Coexistence : A Model of Lotka-Volterra Form Author ( s ): Robert D. Holt and John Pickering Source : The American Naturalist, Vol. 126, No. 2 ( Aug., 1985 ), pp. 196-211 Published by : The University of Chicago Press. The American naturalist, 126(2):196–211.
- Huang, Z. Y., de Boer, W. F., Van Langevelde, F., Xu, C., Ben Jebara, K., Berlingieri, F., and Prins, H. H. (2013). Dilution effect in bovine tuberculosis: Risk factors for regional disease occurrence in Africa. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 280(1765):1–7.
- Huang, Z. Y., Xu, C., Van Langevelde, F., Prins, H. H., Ben Jebara, K., and De Boer, W. F. (2014). Dilution effect and identity effect by wildlife in the persistence and recurrence of bovine tuberculosis. Parasitology, 141(7):981–987.
- Jones, K. E., Patel, N. G., Levy, M. A., Storeygard, A., Balk, D., Gittleman, J. L., and Daszak, P. (2008). Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature, 451(7181):990–993.
- Keeling, M. J. and Rohani, P. (2011). Modeling infectious diseases in humans and animals. Princeton university press.
- Keesing, F., Belden, L. K., Daszak, P., Dobson, A., Harvell, C. D., Holt, R. D., Hudson, P., Jolles, A., Jones, K. E., Mitchell, C. E., Myers, S. S., Bogich, T., and Ostfeld, R. S. (2010). Impacts of biodiversity on the emergence and transmission of infectious diseases. Nature, 468(7324):647–652.
- Keesing, F., Holt, R. D., and Ostfeld, R. S. (2006). Effects of species diversity on disease risk. Ecology Letters, 9(4):485–498.
- Kermack, W. O. and McKendrick, A. G. (1927). A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proceedings of the royal society of london. Series A, Containing papers of a mathematical and physical character, 115(772):700– 721.
- Klepac, P., Pomeroy, L. W., Bjørnstad, O. N., Kuiken, T., Osterhaus, A. D., and Rijks, J. M. (2009). Stage-structured transmission of phocine distemper virus in the dutch 2002 outbreak. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 276(1666):2469–2476.
- Knell, R. J., Begon, M., and Thompson, D. J. (1996). Transmission dynamics of bacillus thuringiensis infecting plodia interpunctella: a test of the mass action assumption with an insect pathogen. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 263(1366):75–81.
- Kuiken, T., Holmes, E. C., McCauley, J., Rimmelzwaan, G. F., Williams, C. S., and Grenfell, B. T. (2006). Host species barriers to influenza virus infections. Science, 312(5772):394–397.
- Lafferty, K. D. and Holt, R. D. (2003). How should environmental stress affect the population dynamics of disease?
-
Ecology Letters, 6(7):654–664.
- Lloyd-Smith, J. O., Schreiber, S. J., Kopp, P. E., and Getz, W. M. (2005). Superspreading and the effect of individual variation on disease emergence. Nature, 438(7066):355–359.
- Loreau, M. and Hector, A. (2001). Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature, 412(6842):72–76.
- May, R. M. and Anderson, R. M. (1984). Spatial heterogeneity and the design of immunization programs. Mathe- matical Biosciences, 72(1):83–111.
- McCallum, H. (2016). Models for managing wildlife disease. Parasitology, 143(7):805–820.
- McCallum, H., Barlow, N., and Hone, J. (2001). How should pathogen transmission be modelled? Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 16(6):295–300.
- McCallum, H., Fenton, A., Hudson, P. J., Lee, B., Levick, B., Norman, R., Perkins, S. E., Viney, M., Wilson, A. J., and Lello, J. (2017). Breaking beta: Deconstructing the parasite transmission function. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 372(1719).
- Meunier, N. V., Sebulime, P., White, R. G., and Kock, R. (2017). Wildlife-livestock interactions and risk areas for cross-species spread of bovine tuberculosis. Onderstepoort Journal of Veterinary Research, 84(1):1–10.
- Miller, M. A., Kerr, T. J., de Waal, C. R., Goosen, W. J., Streicher, E. M., Hausler, G., Rossouw, L., Manamela, T., van Schalkwyk, L., Kleynhans, L., et al. (2021). Mycobacterium bovis infection in free-ranging african elephants. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 27(3):990.
- Mollentze, N., Streicker, D. G., Murcia, P. R., Hampson, K., and Biek, R. (2020). Virulence mismatches in index hosts shape the outcomes of cross-species transmission. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(46):28859–28866.
- Novozhilov, A. S. (2008). Heterogeneous Susceptibles-Infectives model: Mechanistic derivation of the power law transmission function. pages 1–14.
- Ogden, N. H. and Tsao, J. I. (2009). Biodiversity and Lyme disease: Dilution or amplification? Epidemics, 1(3):196– 206.
- Olival, K. J., Hosseini, P. R., Zambrana-Torrelio, C., Ross, N., Bogich, T. L., and Daszak, P. (2017). Host and viral traits predict zoonotic spillover from mammals. Nature, 546(7660):646–650.
- Ostfeld, R. S. and Keesing, F. (2000). Biodiversity series: the function of biodiversity in the ecology of vector-borne zoonotic diseases. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 78(12):2061–2078.
- Ostfeld, R. S. and Keesing, F. (2012). Effects of host diversity on infectious disease. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 43:157–182.
- Ostfeld, R. S., Keesing, F., and Eviner, V. T. (2008). Infectious disease ecology: effects of ecosystems on disease and of disease on ecosystems. Princeton University Press.
- Palmer, M. V., Waters, W. R., and Whipple, D. L. (2004). Investigation of the transmission of mycobacterium bovis from deer to cattle through indirect contact. American journal of veterinary research, 65(11):1483–1489.
- Park, A. W., Farrell, M. J., Schmidt, J. P., Huang, S., Dallas, T. A., Pappalardo, P., Drake, J. M., Stephens, P. R., Poulin, R., Nunn, C. L., and Davies, T. J. (2018). Characterizing the phylogenetic specialism-generalism spectrum of mammal parasites. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 285(1874).
- Parker, I. M., Saunders, M., Bontrager, M., Weitz, A. P., Hendricks, R., Magarey, R., Suiter, K., and Gilbert, G. S. (2015). Phylogenetic structure and host abundance drive disease pressure in communities. Nature, 520(7548):542– 544.
- Pedersen, A. B., Jones, K. E., Nunn, C. L., and Altizer, S. (2007). Infectious diseases and extinction risk in wild mammals. Conservation Biology, 21(5):1269–1279.
- Pope, L. C., Butlin, R. K., Wilson, G. J., Woodroffe, R., Erven, K., Conyers, C. M., Franklin, T., Delahay, R. J., Cheeseman, C. L., and Burke, T. (2007). Genetic evidence that culling increases badger movement: implications for the spread of bovine tuberculosis. Molecular Ecology, 16(23):4919–4929.
- Poullain, V. and Nuismer, S. L. (2012). Infection genetics and the likelihood of host shifts in coevolving host-parasite interactions. American Naturalist, 180(5):618–628.
- Power, A. G. and Mitchell, C. E. (2004). Pathogen spillover in disease epidemics. the american naturalist, 164(S5):S79–S89.
- Rhodes, C. J., Atkinson, R. P. D., Anderson, R. M., and Macdonald, D. W. (1998). Rabies in Zimbabwe : reservoir dogs and the implications for disease control. (November 1996).
- Roberts, M. G. and Heesterbeek, J. A. (2018). Quantifying the dilution effect for models in ecological epidemiology.
-
Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 15(140).
- Rohani, P., Green, C. J., Mantilla-Beniers, N. B., and Grenfell, B. T. (2003). Ecological interference between fatal diseases. Nature, 422(6934):885–888.
- Rudolf, V. H. and Antonovics, J. (2005). Species coexistence and pathogens with frequency-dependent transmission.
-
American Naturalist, 166(1):112–118.
- Sintayehu, D. W., Heitk¨onig, I. M., Prins, H. H., Tessema, Z. K., and De Boer, W. F. (2017). Effect of host diversity and species assemblage composition on bovine tuberculosis (bTB) risk in Ethiopian cattle. Parasitology, 144(6):783–792.
- Smith, K. F., Goldberg, M., Rosenthal, S., Carlson, L., Chen, J., Chen, C., and Ramachandran, S. (2014). Global rise in human infectious disease outbreaks. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 11(101):1–6.
- Smith, M. J., Telfer, S., Kallio, E. R., Burthe, S., Cook, A. R., Lambin, X., and Begon, M. (2009). Host-pathogen time series data in wildlife support a transmission function between density and frequency dependence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(19):7905–7909.
- Spickler, A. R. (2019). Zoonotic Tuberculosis in Mammals, including Bovine and Caprine Tuberculosis. pages 1–20.
- Ssebuliba, E. and Davies, T. J. (2021). Assessing the phylogenetic host breadth of millet pathogens and its implication for disease spillover. Ecological Solutions and Evidence, 2(1):1–11.
- Stewart Merrill, T. E., Calhoun, D. M., and Johnson, P. T. (2022). Beyond single host, single parasite interactions: Quantifying competence for complete multi-host, multi-parasite communities. Functional Ecology, 36(8):1845– 1857.
- Streicker, D. G., Fallas Gonz´alez, S. L., Luconi, G., Barrientos, R. G., and Leon, B. (2019). Phylodynamics reveals extinction–recolonization dynamics underpin apparently endemic vampire bat rabies in Costa Rica. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 286(1912).
- Streicker, D. G., Fenton, A., and Pedersen, A. B. (2013). Differential sources of host species heterogeneity influence the transmission and control of multihost parasites. Ecology Letters, 16(8):975–984.
- Streicker, D. G., Turmelle, A. S., Vonhof, M. J., Kuzmin, I. V., McCracken, G. F., and Rupprecht, C. E. (2010). Host phylogeny constrains cross-species emergence and establishment of rabies virus in bats. Science, 329(5992):676–679.
- Swinton, J., Gilligan, C. A., Harwood, J., and Hall, A. (1999). Scaling of phocine distemper virus transmission with harbour seal community size. Ecologie, 30(4):231.
- Tien, J. H. and Earn, D. J. (2010). Multiple transmission pathways and disease dynamics in a waterborne pathogen model. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 72(6):1506–1533.
- Viana, M., Mancy, R., Biek, R., Cleaveland, S., Cross, P. C., Lloyd-Smith, J. O., and Haydon, D. T. (2014). Assembling evidence for identifying reservoirs of infection. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 29(5):270–279.
- Vicente, J., Delahay, R. J., Walker, N. J., and Cheeseman, C. L. (2007). Social organization and movement influence the incidence of bovine tuberculosis in an undisturbed high-density badger Meles meles population. Journal of Animal Ecology, 76(2):348–360.
- White, L. A., Forester, J. D., and Craft, M. E. (2017). Using contact networks to explore mechanisms of parasite transmission in wildlife. Biological Reviews, 92(1):389–409.
- Wilber, M. Q., Langwig, K. E., Kilpatrick, A. M., McCallum, H. I., and Briggs, C. J. (2016). Integral Projection Models for host–parasite systems with an application to amphibian chytrid fungus. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7(10):1182–1194.
- Wolfe, N. D., Daszak, P., Kilpatrick, A. M., and Burke, D. S. (2005). Bushmeat hunting, deforestation, and prediction of zoonotic disease. Emerging infectious diseases, 11(12):1822.
- Wolfe, N. D., Dunavan, C. P., and Diamond, J. (2007). Origins of major human infectious diseases. Nature, 447(7142):279–283.
- Woolhouse, M. E., Taylor, L. H., and Haydon, D. T. (2001). Population biology of multihost pathogens. Science, 292(5519):1109–1112.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).