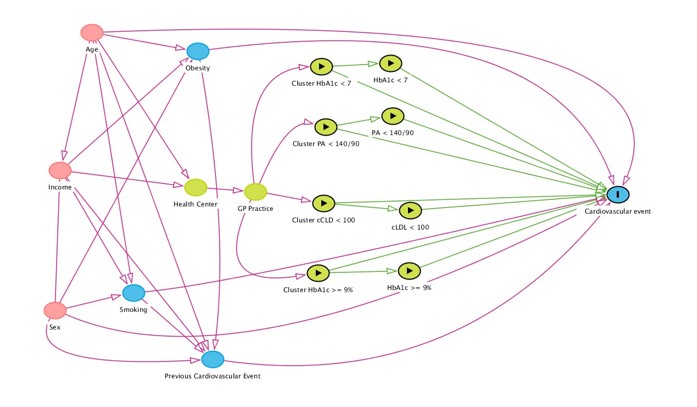
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity, mortality, and hospital admissions. There is variability in clinical practice. The objectives are to analyze the variability in the control of Blood Pressure (BP), HbA1c, and LDL-C in T2D patients and its influence on admissions due to cardiovascular events (CVE) Methods: We analyzed the electronic records in Primary Care Health centers in Navarra (Spain) and hospital admission for CVE. We follow 480637 people from 2012 to 2016. We calculated indicators of control of patients with T2D for each year, percentage with: HbA1c < 7%; HbA1c >= 9%; BP <140/90 mmHg; LDL-C <100 mg/dl. We used logistic and Cox regression. Results: Patients in the best control GP practices cluster are 2.5 times more likely to have HbA1c <7% [OR: 2.46 (95% CI: 2.29-3.64)]. Poor HbA1c control ≥ 9% is more likely in the worst control cluster [OR: 1.73 (95% CI:1.63-1.83)]. The probability of admission for CVE increases with age, being male, low income, obesity, history of CVE, having HbA1c ≥ 9%, and belonging to a GP practice in the cluster of HbA1C ≥ 9% worst control. In contrast, it decreases in patients with HbA1c <7%, BP<140/90 mmHg and LDL <100 mg/dl.