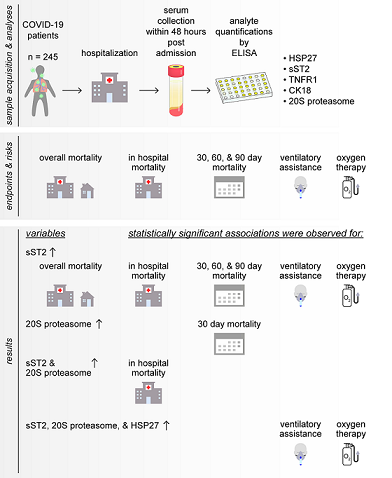
Although, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus – 2 (SARS-CoV 2) represents one of the biggest challenges in the world today, the exact immunopathogenic mechanism that leads to severe or critical Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has remained incompletely understood. Several studies have indicated that high systemic plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines result in the so-called “cytokine storm”, with subsequent development of microthrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and multiorgan-failure. Therefore, we reasoned that elevated inflammatory cytokine might act as prognostic factors. Here, we analyzed 245 serum samples of patients with COVID-19, collected at hospital admission. We assessed the levels of heat shock protein 27 (HSP27), soluble suppressor of tumorigenicity- 2 (sST2), caspase cleaved cytokeratin 18 (cCK18), 20S proteasome, and tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR-1) and explored their associations with overall-, 30-, 60-, 90-day- and in-hospital mortality. Moreover, we investigated their association with the risk of ventilation. We demonstrated that increased serum sST2 was uni- and multivariably associated with all endpoints. However, we also identified 20S proteasome as independent prognostic factor for in-hospital mortality. Furthermore, elevated HSP27, sST2, and 20S proteasome levels at hospital admission were univariably associated with higher risk of invasive ventilation. These findings could help to identify high-risk patients early in the course of COVID-19.