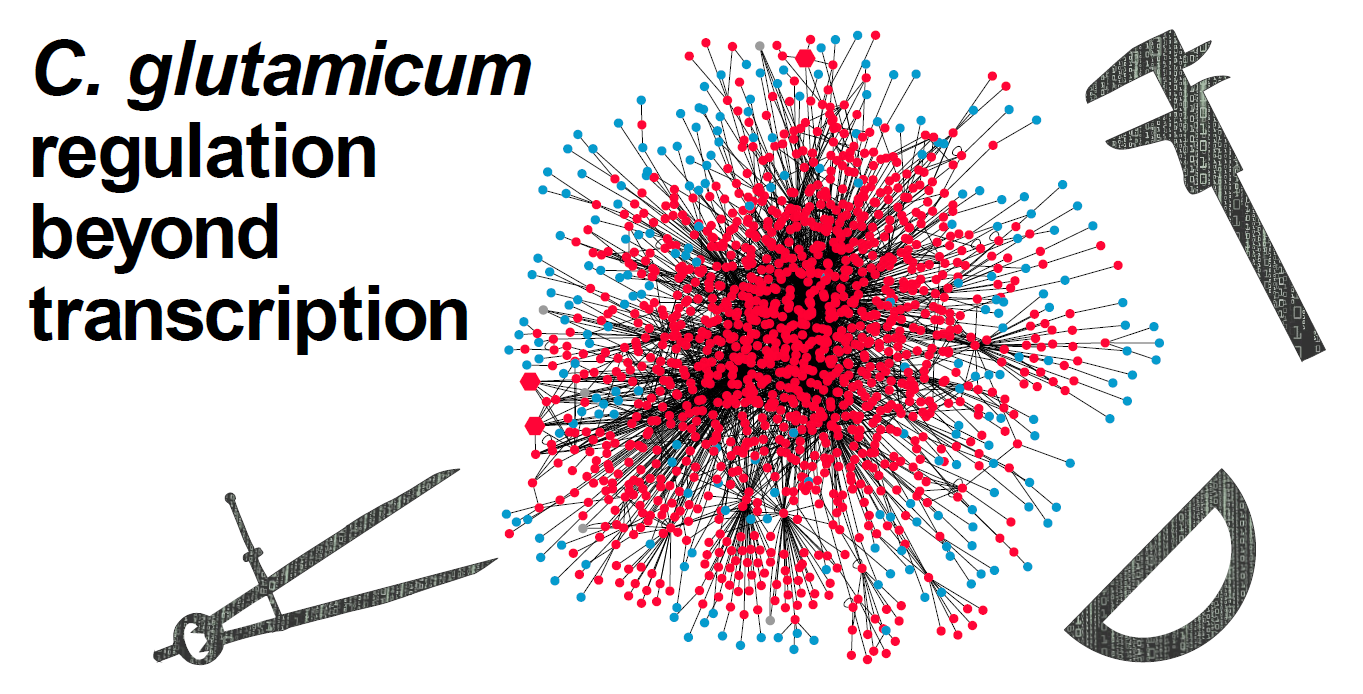
Corynebacterium glutamicum is a Gram-positive bacterium found in soil where the condition changes demand plasticity of the regulatory interactions, which study at the global scale has been challenged by the lack of data integration. Here, we update the manually-curated C. glutamicum transcriptional regulatory network, now including protein-protein interactions having a direct effect on gene transcription. The network model with regulations supported by any experimental evidence increased by 557 interactions regarding the previous (2018) version. 73 interactions supported by directed experiments were also included in a second model. We included 545 sRNA-mediated regulations in a third model with a total of 5164 interactions. We deposited the three network models in Abasy Atlas v2.4. We study the C. glutamicum regulatory structure by comparing it against the networks for more than 40 species, finding it to contrast in several global structural properties. We analyze the system-level components of the networks, finding that the inclusion of the sRNAs regulations changes their proportions, transferring part of the basal machinery to the modular class and increasing the number of modules while decreasing their size. Finally, we use strong networks of three model organisms to provide insights in future directions of the C. glutamicum network characterization.