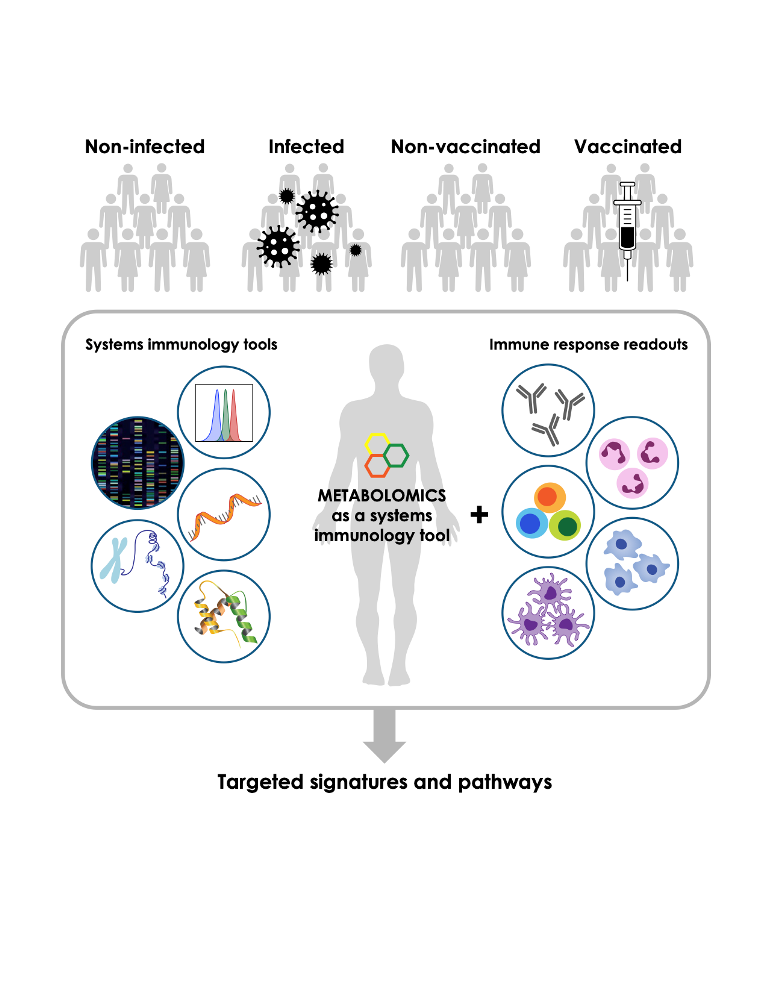
Approaches to identification of metabolites have progressed from early biochemical pathway evaluation to modern high dimensional metabolomics which is a powerful tool to identify and characterize biomarkers of health and disease. While traditionally considered relevant in the context of classic metabolic diseases, immunometabolism has emerged as an important area of study as leukocytes generate key metabolites important to innate and adaptive immunity. Herein we discuss the metabolomic signatures and pathways perturbed during infection as well as vaccination. For example, changes in lipid and amino acid pathways (e.g., tryptophan, serine, and threonine) have been noted during infection while carbohydrate and bile acid pathways have shift upon vaccination. Metabolomics holds substantial promise to provide fresh insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying host response to infection and vaccination, and its integration with other systems biology platforms will add further impact to our studies of health and disease.