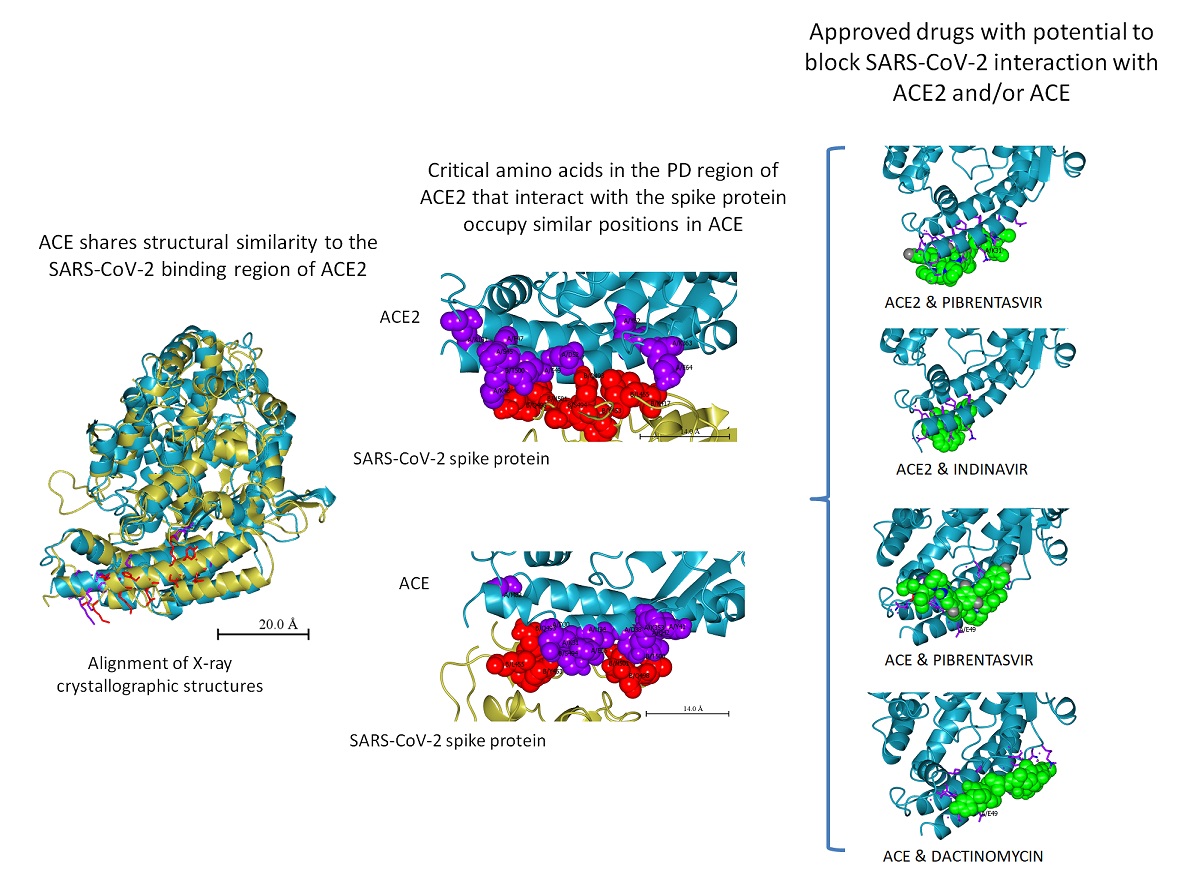
Background: Respiratory transmission is the primary route of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the known receptor of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein for entry into human cells. A recent study reported absent to low ACE2 promoter activity in a variety of human lung epithelial cell samples. Three bioprojects (PRJEB4337, PRJNA270632 and PRJNA280600) invariably found abundant expression of ACE in human lungs compared to very low expression of ACE2. Methods: In silico tools were applied to assess potential interaction of SARS-CoV-2 surface spike protein with human ACE as well as predict the drugs that may block SARS-CoV-2 interaction with host receptor. Results: Although it is not obvious from the primary sequence alignment of ACE2 and its homolog ACE (also known as ACE1), comparison of X-ray crystallographic structures show striking similarity in the regions of these proteins which is known (for ACE2) to interact with the receptor binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Critical amino acids that mediate interaction with the viral spike protein in ACE2 are organized in the same order in ACE. In silico analyses predicts comparable interaction of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with ACE2 and ACE. In addition, this study predicts and selects already approved drugs from a list of 1263, which may interfere with the binding of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein to ACE2 and/or ACE.