Submitted:
14 September 2023
Posted:
15 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence collection
2.2. Nucleotide sequence alignment and analysis
2.3. Detection of regions with lower synonymous substitution rate
2.4. Protein sequence alignment and domain identification
2.5. Prediction of protein structural features
3. Results
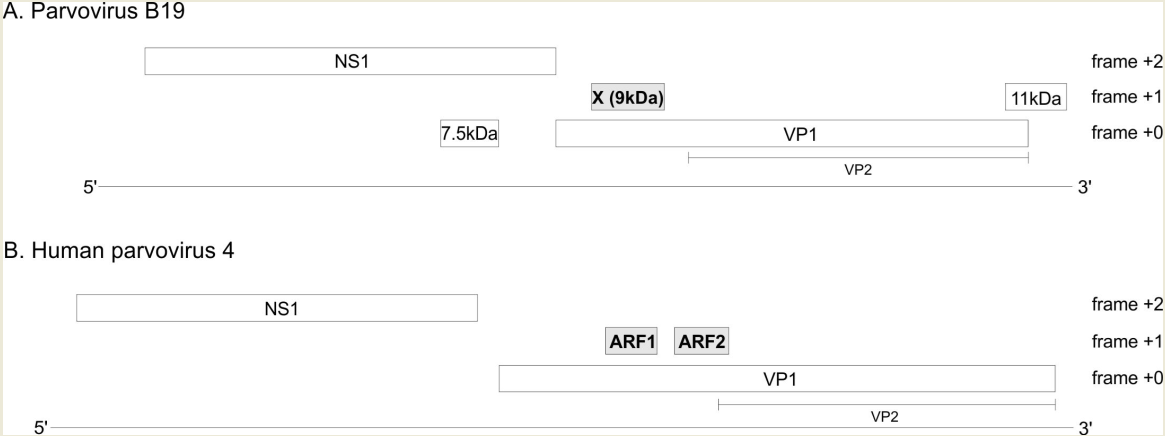
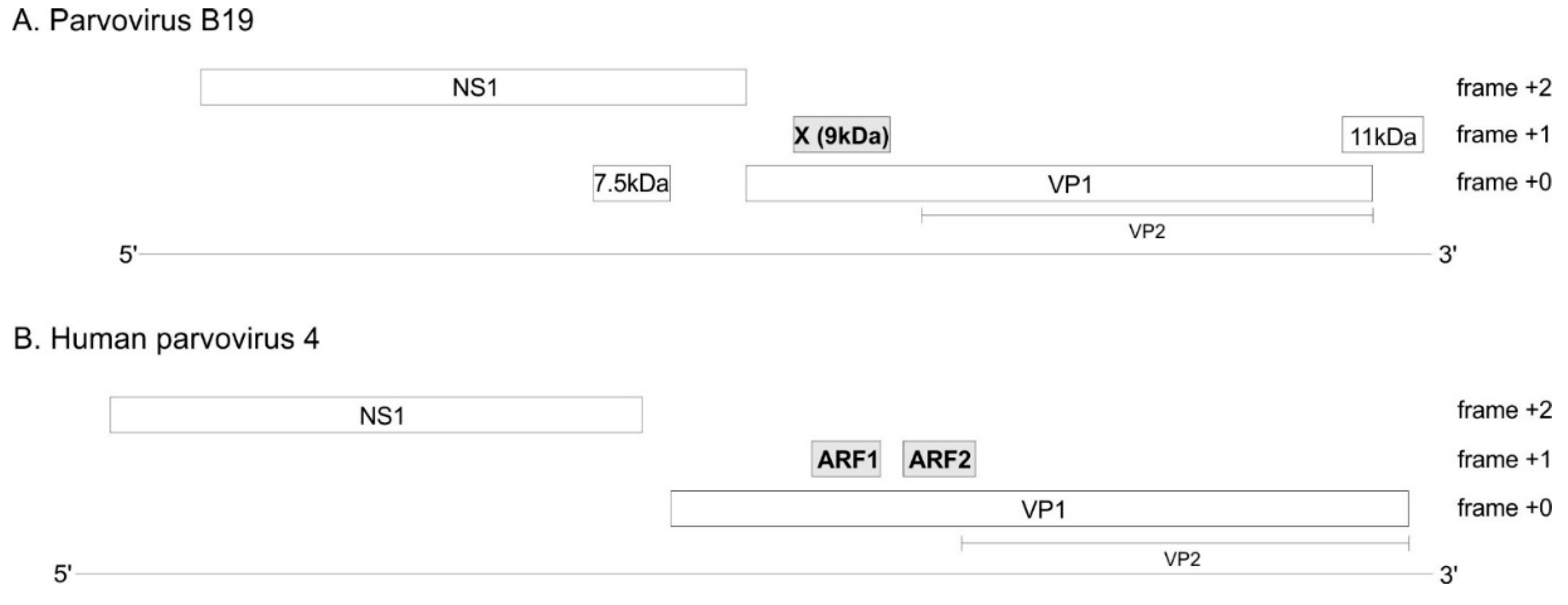
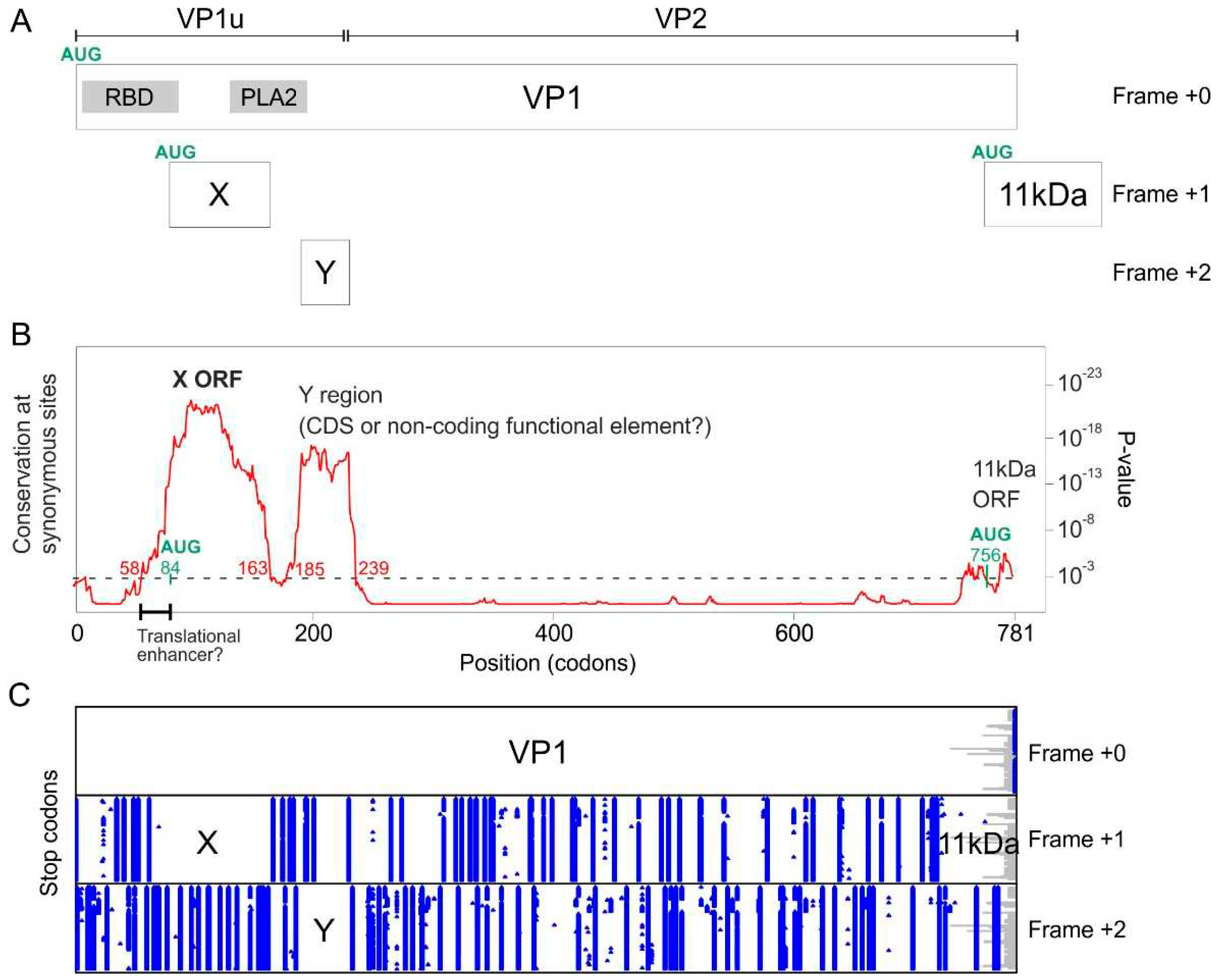
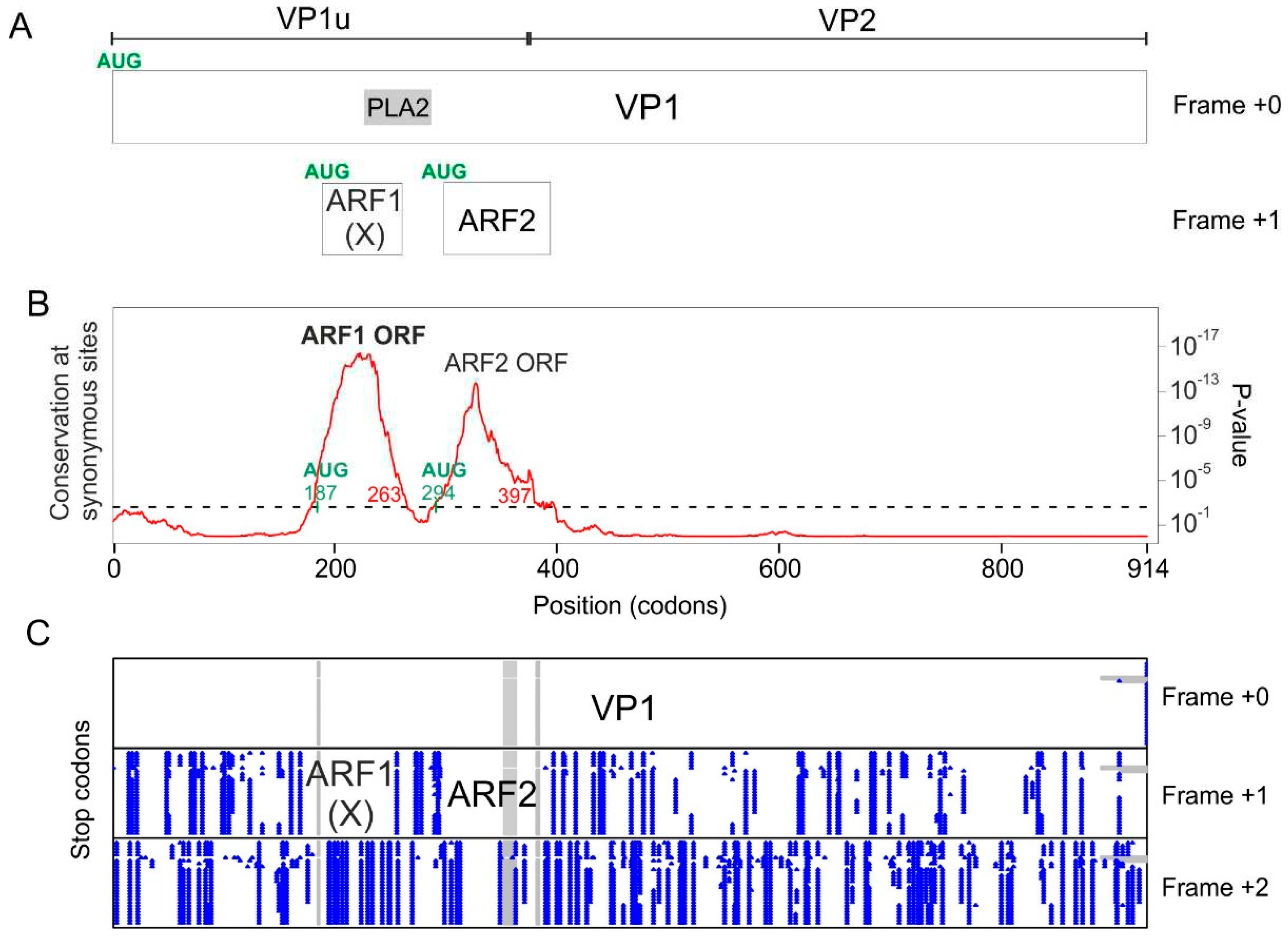
3.1. The VP1 gene of B19V contains 3 regions with significantly increased synonymous conservation, among which the X ORF
| Genus | Species | Common name(s) [Abbreviation] | Genbank genome accession number | Boundaries of the X ORF in the genome sequence (in nucleotides) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythroparvovirus | Primate erythroparvovirus 1 |
Parvovirus B19 [B19V] |
NC_000883 | 2874-3119 | |
| Erythroparvovirus | Primate erythroparvovirus 2 | Simian parvovirus | U26342.1 | 2718-2963 | |
| Erythroparvovirus | Primate erythroparvovirus 3 | Rhesus macaque parvovirus | AF221122.1 | 2841 | 3080 |
| Erythroparvovirus | Primate erythroparvovirus 4 |
Pig-tailed macaque parvovirus | AF221123.1 | 2563 | 2802 |
| Erythroparvovirus | Rodent erythroparvovirus 1 | Chipmunk parvovirus | GQ200736.1 | 3031 | 3228 |
| Erythroparvovirus | Seal parvovirus | Seal parvovirus | KF373759.1 | 2789 | 3100 |
| Erythroparvovirus (*) |
Ungulate erythroparvovirus 1 | Bovine parvovirus 3 [bPARV3] | NC_037053 | 2627-2926 | |
| Tetraparvovirus | Chiropteran tetraparvovirus 1 | Eidolon helvum parvovirus | NC_016744.1 | 2829-3062 | |
| Tetraparvovirus | Primate tetraparvovirus 1 |
Human parvovirus 4 [PARV4] |
NC_007018.1 | 2937-3140 | |
| Tetraparvovirus | Ungulate tetraparvovirus 1 | Bovine hokovirus 1 |
NC_028136 | 2857-3111 | |
| Tetraparvovirus | Ungulate tetraparvovirus 2 | Porcine hokovirus | EU200677.1 | 2808 | 3062 |
| Tetraparvovirus | Ungulate tetraparvovirus 5 | Deer tetraparvovirus | NC_031670.1 | 2766-3020 | |
| Tetraparvovirus (*) | Ungulate tetraparvovirus 3 | Porcine parvovirus 2 [pPARV2]; Porcine cnvirus; Parvovirus YX | NC_035180 | No X ORF; boundaries of the Z ORF are 2817-3098 | |
| Tetraparvovirus | Ungulate tetraparvovirus 4 | Ovine hokovirus | JF504699.1 | 2855-3112 | |
| Tetraparvovirus | - | Opossum parvovirus | MG745671.1 | 2862-3092 | |
| Tetraparvovirus | - | Rodent parvovirus | MG745669.1 | 2960-3217 | |
| Virus name | Region | Boundaries of the region with lower synonymous codon variability in the VP1 CDS | Boundaries of the corresponding ORF in the VP1 CDS |
|---|---|---|---|
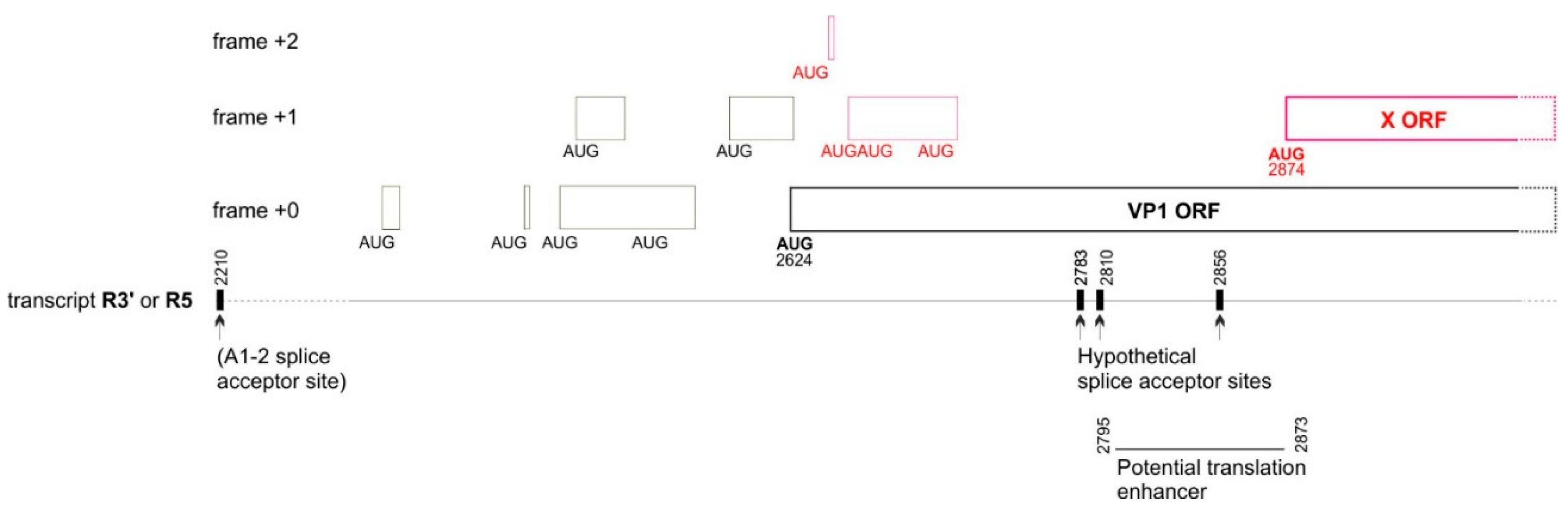
| Parvovirus B19 | X ORF | Codons 58-163 (nucleotides 172-489) |
Codons 84-166 (Nucleotides 251-496) |
| Parvovirus B19 | Y region(*) | Codons 185-239 (nucleotides 553-715) |
Codons 185-230(*) (nucleotides 553-688) |
| Human parvovirus 4 | ARF1 ORF (=X ORF) |
Codons 180-263 (nucleotides 538-789) |
Codons 187-255 (nucleotides 560-763) |
| Human parvovirus 4 | ARF2 ORF | Codons 294-397 (nucleotides 880-1189) |
Codons 295-379 (nucleotides 884-1135) |
| Bovine parvovirus 3 | X-like ORF | Codons 205-306 (nucleotides 614-916) |
Codons 215-315 (nucleotides 644-943) |
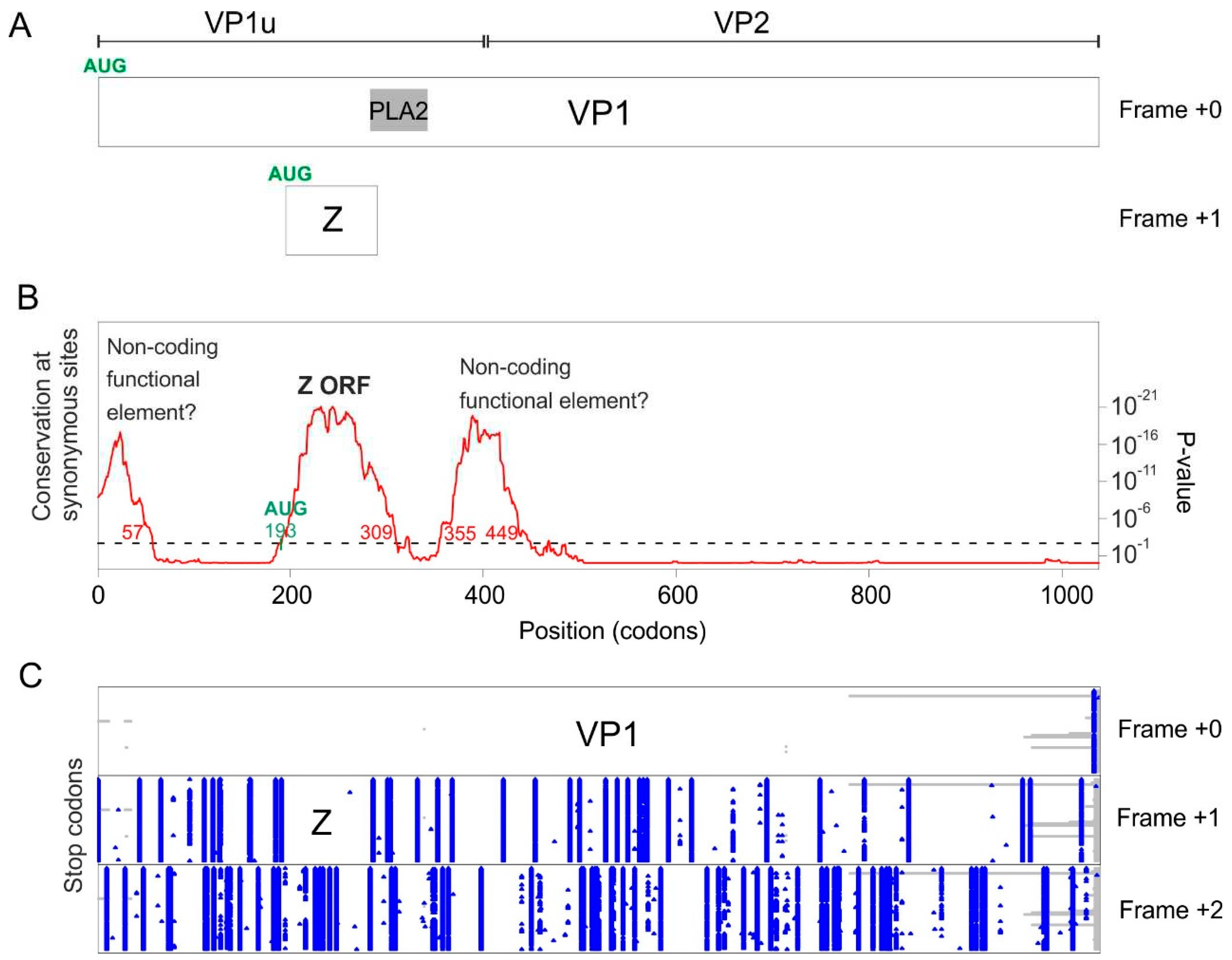
| Porcine parvovirus 2 | Z ORF | Codons 193-309 (nucleotides 577-927) |
Codons 193-285 (nucleotides 578-854) |
3.2. The VP1 gene of PARV4 contains 2 regions with significantly reduced synonymous variability, corresponding to ARF1 and ARF2
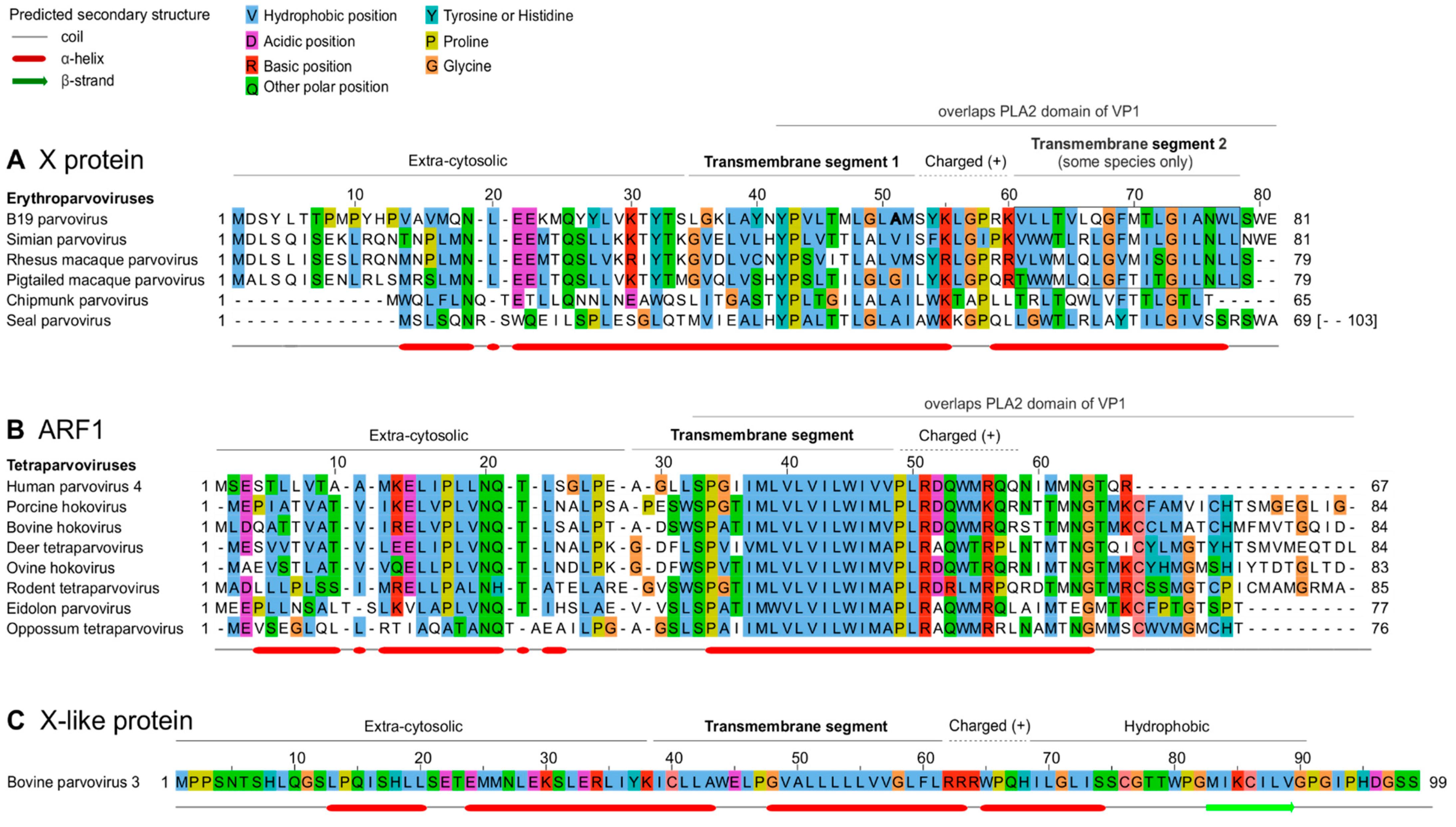
3.3. The X protein and ARF1 are homologous
3.3.1. The B19V X protein and PARV4 ARF1 protein have similar predicted features, in particular a central transmembrane segment
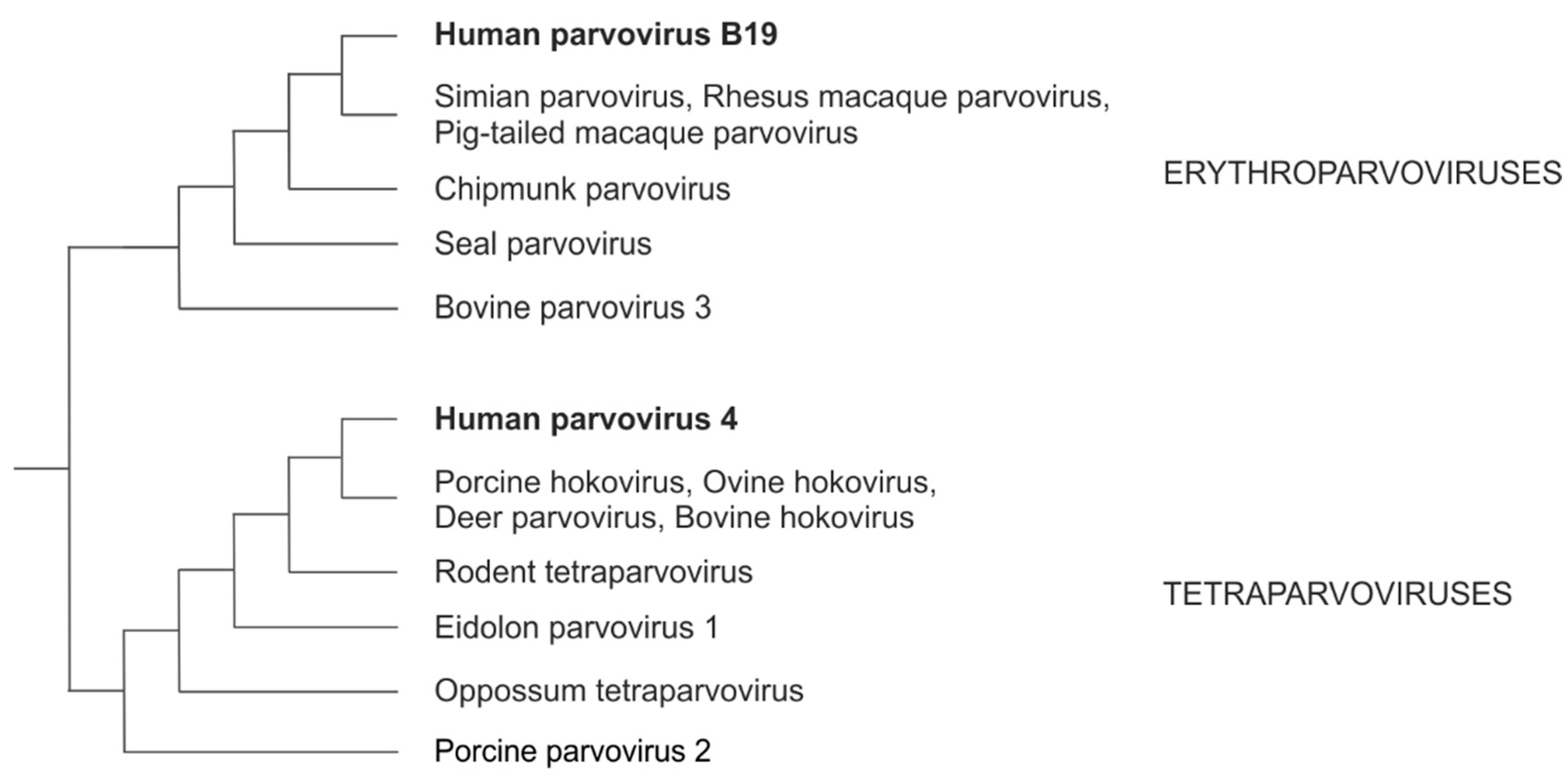
3.3.2. The X protein of erythroparvoviruses and the ARF1 protein of tetraparvoviruses are homologous
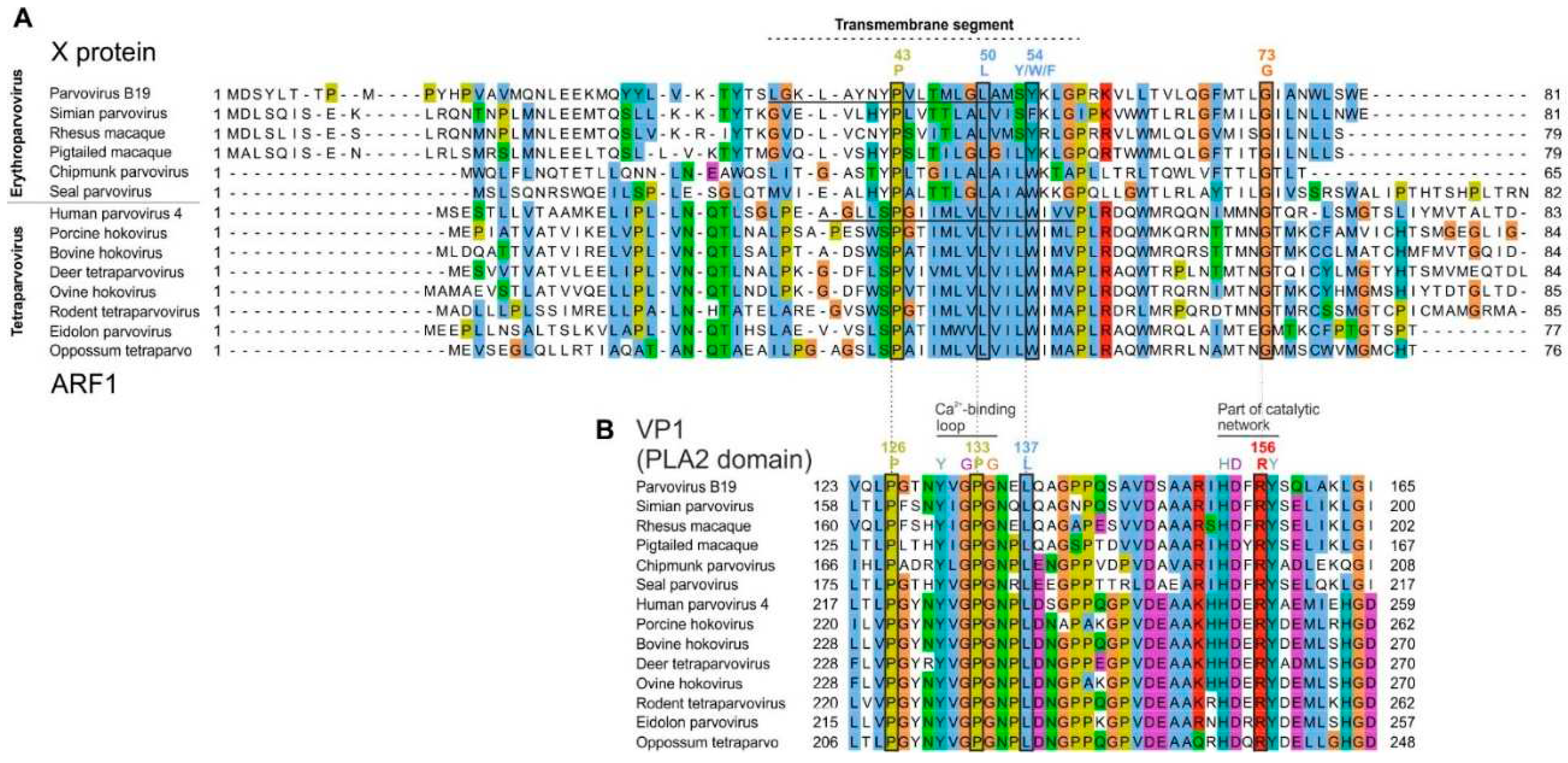
3.3.3. Conserved features of the X protein mostly but not exclusively correspond to conserved motifs of the PLA2 domain of VP1
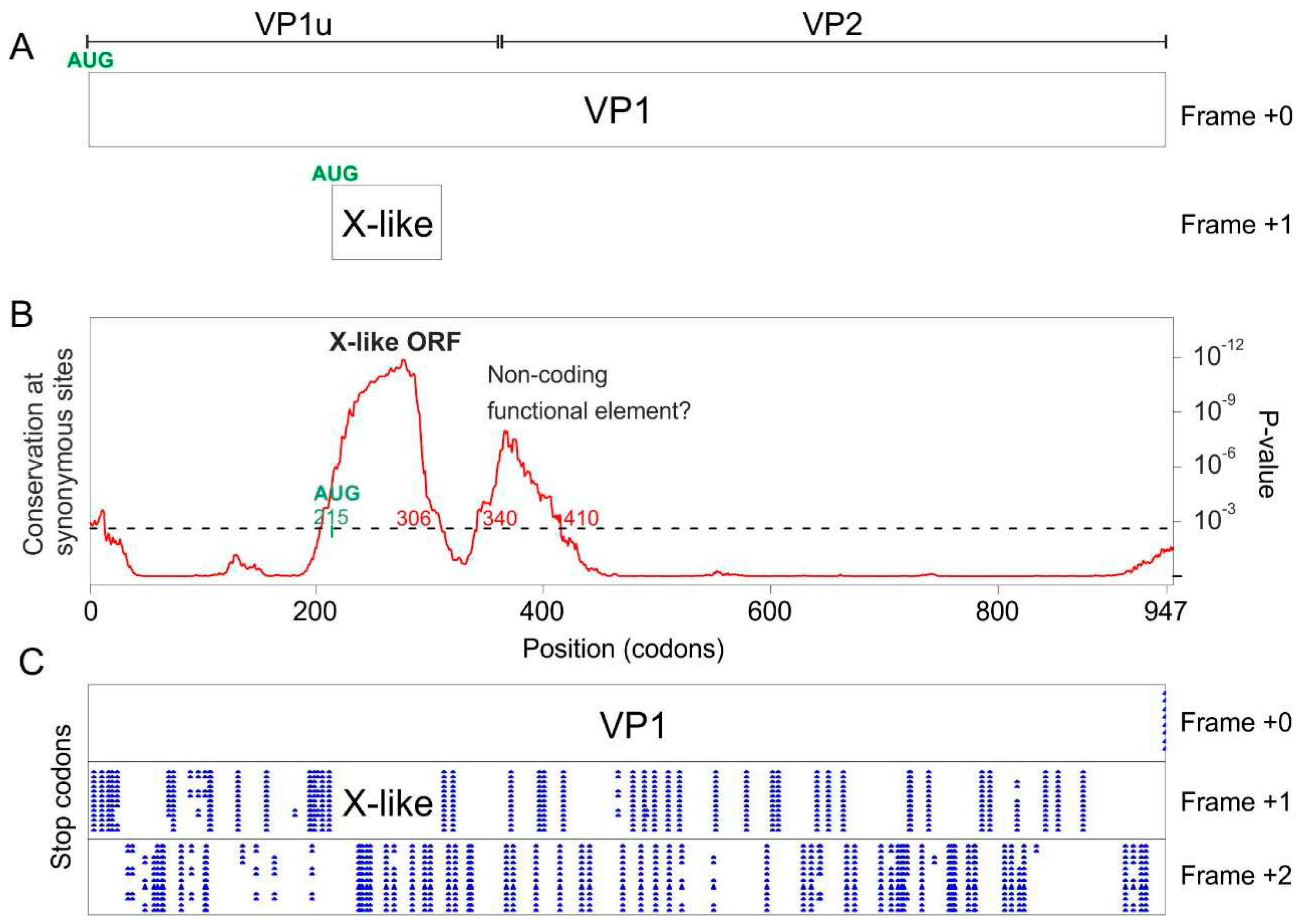
3.4. The VP1 gene of Bovine parvovirus 3 and porcine parvovirus 2 differs from that of other erythro- and tetraparvoviruses
3.4.1. Bovine parvovirus 3 VP1 gene encodes an X-like ORF, despite not encoding a PLA2 domain
3.4.2. Porcine parvovirus 2 does not encode an X ORF, but encodes a “Z ORF” overlapping VP1
4. Discussion
4.1. Sequence analyses provide compelling evidence that the X protein must be expressed and have a crucial function
4.1.1. The X protein could be translated either by a non-conventional mechanism or from an overlooked mRNA
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruber AR, Neubock R, Hofacker IL, Washietl S. The RNAz web server: prediction of thermodynamically stable and evolutionarily conserved RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Research. 2007, 35, W335–W338. [CrossRef]
- Washietl S, L. Hofacker I. Identifying Structural Noncoding RNAs Using RNAz. In: Baxevanis AD, Davison DB, Page RDM, Petsko GA, Stein LD, Stormo GD, editors. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2007. p. bi1207s19. [CrossRef]
- Söderlund-Venermo, M. Emerging Human Parvoviruses: The Rocky Road to Fame. Annu Rev Virol. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasan S, Agbandje-McKenna M, Parrish CR. Parvovirus Family Conundrum: What Makes a Killer? Annu Rev Virol. 2015, 2, 425–450. [CrossRef]
- Cotmore SF, Tattersall P. Parvoviruses: Small Does Not Mean Simple. Annu Rev Virol. 2014, 1, 517–537. [CrossRef]
- Ganaie SS, Qiu J. Recent Advances in Replication and Infection of Human Parvovirus B19. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018, 8, 166. [CrossRef]
- Matthews PC, Sharp C, Simmonds P, Klenerman P. Human parvovirus 4 ‘PARV4′ remains elusive despite a decade of study. F1000Res. 2017, 6, 82. [CrossRef]
- Luo W, Astell CR. A Novel Protein Encoded by Small RNAs of Parvovirus B19. Virology. 1993, 195, 448–455. [CrossRef]
- St Amand J, Beard C, Humphries K, Astell CR. Analysis of splice junctions and in vitro and in vivo translation potential of the small, abundant B19 parvovirus RNAs. Virology. 1991, 183, 133–142. [CrossRef]
- St Amand J, Astell CR. Identification and characterization of a family of 11-kDa proteins encoded by the human parvovirus B19. Virology. 1993, 192, 121–131. [CrossRef]
- Zhi N, Mills IP, Lu J, Wong S, Filippone C, Brown KE. Molecular and functional analyses of a human parvovirus B19 infectious clone demonstrates essential roles for NS1, VP1, and the 11-kilodalton protein in virus replication and infectivity. J Virol. 2006, 80, 5941–5950. [CrossRef]
- Simmonds P, Douglas J, Bestetti G, Longhi E, Antinori S, Parravicini C, et al. A third genotype of the human parvovirus PARV4 in sub-Saharan Africa. J Gen Virol. 2008, 89, 2299–2302. [CrossRef]
- Pavesi A, Vianelli A, Chirico N, Bao Y, Blinkova O, Belshaw R, et al. Overlapping genes and the proteins they encode differ significantly in their sequence composition from non-overlapping genes. PLoS ONE. 2018, 13, e0202513. [CrossRef]
- Pavesi, A. Computational methods for inferring location and genealogy of overlapping genes in virus genomes: approaches and applications. Current Opinion in Virology. 2022, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth AE, Brown CM. Detecting overlapping coding sequences with pairwise alignments. Bioinformatics. 2005, 21, 282–292. [CrossRef]
- Sabath N, Landan G, Graur D. A method for the simultaneous estimation of selection intensities in overlapping genes. PLoS ONE. 2008, 3, e3996. [CrossRef]
- Norja P, Eis-Hübinger AM, Söderlund-Venermo M, Hedman K, Simmonds P. Rapid sequence change and geographical spread of human parvovirus B19: comparison of B19 virus evolution in acute and persistent infections. J Virol. 2008, 82, 6427–6433. [CrossRef]
- Firth, AE. Mapping overlapping functional elements embedded within the protein-coding regions of RNA viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12425–12439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung BY-W, Miller WA, Atkins JF, Firth AE. An overlapping essential gene in the Potyviridae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008, 105, 5897–5902. [CrossRef]
- Jagger BW, Wise HM, Kash JC, Walters K-A, Wills NM, Xiao Y-L, et al. An overlapping protein-coding region in influenza A virus segment 3 modulates the host response. Science. 2012, 337, 199–204. [CrossRef]
- Ratinier M, Caporale M, Golder M, Franzoni G, Allan K, Nunes SF, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel non-structural protein of bluetongue virus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002477. [CrossRef]
- Zádori Z, Szelei J, Lacoste MC, Li Y, Gariépy S, Raymond P, et al. A viral phospholipase A2 is required for parvovirus infectivity. Dev Cell. 2001, 1, 291–302.
- Dorsch S, Liebisch G, Kaufmann B, von Landenberg P, Hoffmann JH, Drobnik W, et al. The VP1 unique region of parvovirus B19 and its constituent phospholipase A2-like activity. J Virol. 2002, 76, 2014–2018. [CrossRef]
- Campbell MA, Loncar S, Kotin RM, Gifford RJ. Comparative analysis reveals the long-term coevolutionary history of parvoviruses and vertebrates. Quental TB, editor. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001867. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Gribskov M. IRESpy: an XGBoost model for prediction of internal ribosome entry sites. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019, 20, 409. [CrossRef]
- McNair K, Salamon P, Edwards RA, Segall AM. PRFect: A tool to predict programmed ribosomal frameshifts in prokaryotic and viral genomes. Res Sq. 2023; rs.3.rs-2997217. [CrossRef]
- Atkins JF, Loughran G, Bhatt PR, Firth AE, Baranov PV. Ribosomal frameshifting and transcriptional slippage: From genetic steganography and cryptography to adventitious use. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7007–7078. [CrossRef]
- Leisi R, Di Tommaso C, Kempf C, Ros C. The Receptor-Binding Domain in the VP1u Region of Parvovirus B19. Viruses. 2016, 8, 61. [CrossRef]
- Baker JA, Wong W-C, Eisenhaber B, Warwicker J, Eisenhaber F. Charged residues next to transmembrane regions revisited: “Positive-inside rule” is complemented by the “negative inside depletion/outside enrichment rule.” BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 66. [CrossRef]
- Wong W-C, Maurer-Stroh S, Eisenhaber F. Not all transmembrane helices are born equal: Towards the extension of the sequence homology concept to membrane proteins. Biol Direct. 2011, 6, 57. [CrossRef]
- Abascal F, Zardoya R, Telford MJ. TranslatorX: multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W7–13. [CrossRef]
- Lo MK, Søgaard TM, Karlin DG. Evolution and structural organization of the C proteins of paramyxovirinae. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e90003. [CrossRef]
- Söding J, Biegert A, Lupas AN. The HHpred interactive server for protein homology detection and structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W244–248. [CrossRef]
- Allander T, Emerson SU, Engle RE, Purcell RH, Bukh J. A virus discovery method incorporating DNase treatment and its application to the identification of two bovine parvovirus species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001, 98, 11609–11614. [CrossRef]
- Wang F, Wei Y, Zhu C, Huang X, Xu Y, Yu L, et al. Novel parvovirus sublineage in the family of Parvoviridae. Virus Genes. 2010, 41, 305–308. [CrossRef]
- Shade RO, Blundell MC, Cotmore SF, Tattersall P, Astell CR. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human parvovirus B19 isolated from the serum of a child during aplastic crisis. J Virol. 1986, 58, 921–936.
- Filippone C, Zhi N, Wong S, Lu J, Kajigaya S, Gallinella G, et al. VP1u phospholipase activity is critical for infectivity of full-length parvovirus B19 genomic clones. Virology. 2008, 374, 444–452. [CrossRef]
- Hernández G, Osnaya VG, Pérez-Martínez X. Conservation and Variability of the AUG Initiation Codon Context in Eukaryotes. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2019; S096800041930146X. [CrossRef]
- Firth AE, Brierley I. Non-canonical translation in RNA viruses. Journal of General Virology. 2012, 93, 1385–1409. [CrossRef]
- Gupta A, Bansal M. RNA-mediated translation regulation in viral genomes: computational advances in the recognition of sequences and structures. Briefings in Bioinformatics. 2019; bbz054. [CrossRef]
- Ozawa K, Ayub J, Young N. Translational regulation of B19 parvovirus capsid protein production by multiple upstream AUG triplets. J Biol Chem. 1988, 263, 10922–10926.
- Baralle M, Baralle FE. The splicing code. Biosystems. 2018, 164, 39–48. [CrossRef]
- Rancurel C, Khosravi M, Dunker AK, Romero PR, Karlin D. Overlapping genes produce proteins with unusual sequence properties and offer insight into de novo protein creation. J Virol. 2009, 83, 10719–10736. [CrossRef]
- Keese PK, Gibbs A. Origins of genes: “big bang” or continuous creation? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992, 89, 9489–9493. [CrossRef]
- Sabath N, Wagner A, Karlin D. Evolution of viral proteins originated de novo by overprinting. Mol Biol Evol. 2012, 29, 3767–3780. [CrossRef]
- Pavesi A, Magiorkinis G, Karlin DG. Viral proteins originated de novo by overprinting can be identified by codon usage: application to the “gene nursery” of Deltaretroviruses. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013, 9, e1003162. [CrossRef]
- Schaloske RH, Dennis EA. The phospholipase A2 superfamily and its group numbering system. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)–Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 2006, 1761, 1246–1259. [CrossRef]
- Zádori Z, Szelei J, Tijssen P. SAT: a late NS protein of porcine parvovirus. J Virol. 2005, 79, 13129–13138. [CrossRef]
- Sealfon RS, Lin MF, Jungreis I, Wolf MY, Kellis M, Sabeti PC. FRESCo: finding regions of excess synonymous constraint in diverse viruses. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 38. [CrossRef]
- Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DMA, Clamp M, Barton GJ. Jalview Version 2--a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics. 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [CrossRef]
- Procter JB, Thompson J, Letunic I, Creevey C, Jossinet F, Barton GJ. Visualization of multiple alignments, phylogenies and gene family evolution. Nat Methods. 2010, 7, S16–25. [CrossRef]
- Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, et al. Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W465–469. [CrossRef]
- Katoh K, Frith MC. Adding unaligned sequences into an existing alignment using MAFFT and LAST. Bioinformatics. 2012, 28, 3144–3146. [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski LP, Bujnicki JM. MetaDisorder: a meta-server for the prediction of intrinsic disorder in proteins. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012, 13, 111. [CrossRef]
- Ferron F, Longhi S, Canard B, Karlin D. A practical overview of protein disorder prediction methods. Proteins. 2006, 65, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Ludwiczak J, Winski A, Szczepaniak K, Alva V, Dunin-Horkawicz S. DeepCoil-a fast and accurate prediction of coiled-coil domains in protein sequences. Bioinformatics. 2019, 35, 2790–2795. [CrossRef]
- Kuchibhatla DB, Sherman WA, Chung BYW, Cook S, Schneider G, Eisenhaber B, et al. Powerful sequence similarity search methods and in-depth manual analyses can identify remote homologs in many apparently “orphan” viral proteins. J Virol. 2014, 88, 10–20. [CrossRef]
- Dobson L, Reményi I, Tusnády GE. CCTOP: a Consensus Constrained TOPology prediction web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W408–412. [CrossRef]
- Floden EW, Tommaso PD, Chatzou M, Magis C, Notredame C, Chang J-M. PSI/TM-Coffee: a web server for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignments of regular and transmembrane proteins using homology extension on reduced databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W339–343. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





