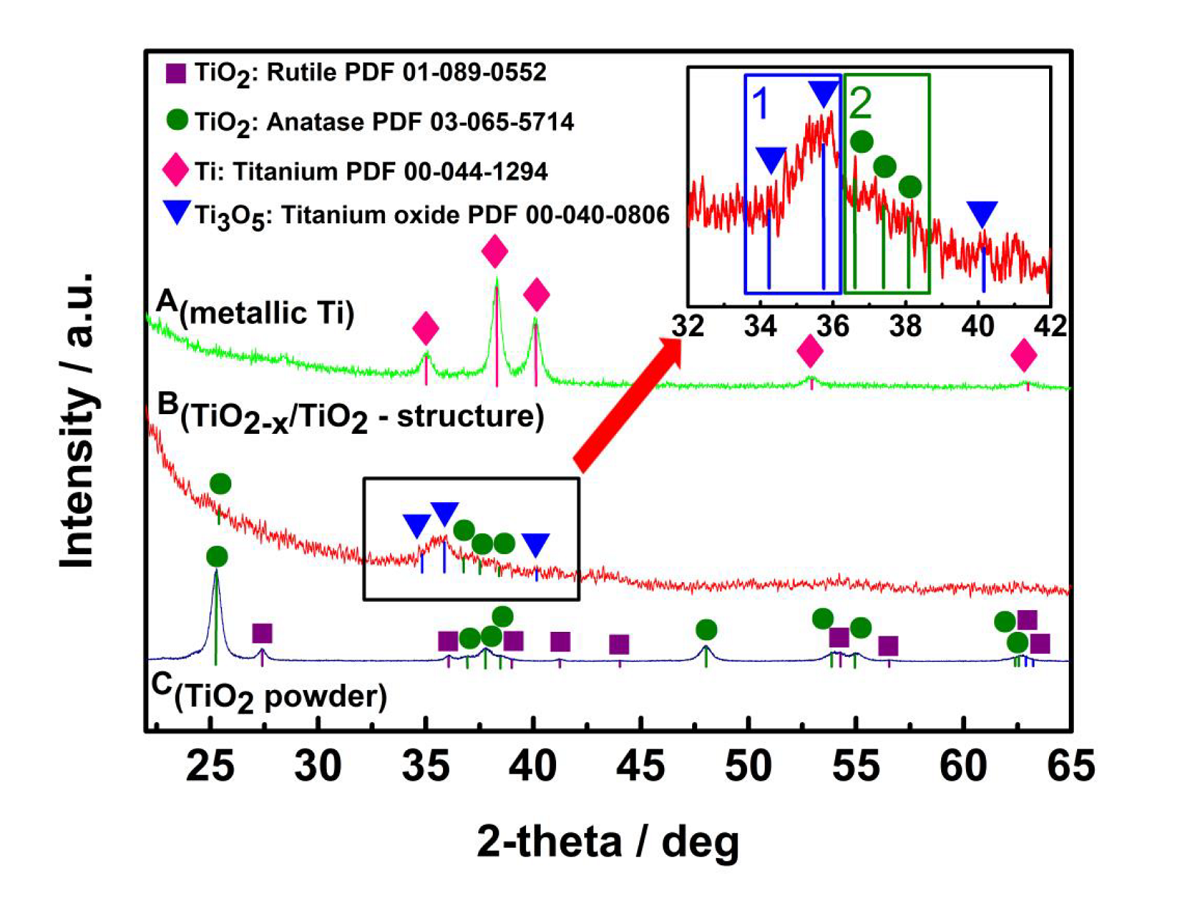
In this research we are reporting gas sensing properties of TiO2-x/TiO2-based hetero-structure, which was ‘self-heated’ by current that at constant potential passed through the structure. Amperometric measurements were applied for the evaluation of sensor response towards ethanol, methanol, n-propanol and acetone gases/vapors. The sensitivity towards these gases was based on electrical resistance changes, which were determined by amperometric measurements of current at fixed voltage applied between Pt-based contacts/electrodes deposited on TiO2-x/TiO2-based layer. XRD analysis revealed the formation of TiO2-x/TiO2-based hetero-structure, which is mainly based on Ti3O5/TiO2 formed during hydro-thermal oxidation based sensing layer preparation process. Additionally, photoluminescence and time-resolved photoluminescence decay kinetics based signals of this sensing structure revealed the presence of TiO2 mainly in the anatase phase in the TiO2-x/TiO2-based hetero-structure, which was formed at 400°C annealing temperature. The evaluation of TiO2-x/TiO2-based gas sensing layer was performed at several different temperatures (25°C, 72°C, 150°C, 180°C) and at these temperatures different sensitivity to aforementioned gaseous materials was determined.