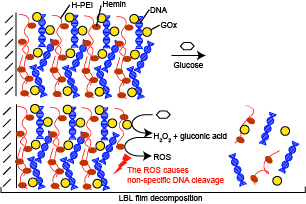
Glucose-sensitive films were prepared by the layer-by-layer (LbL) deposition of poly(ethyleneimine) (H-PEI) solution and DNA solution (containing glucose oxidase (GOx)). H-PEI/DNA+GOx multilayer films were constructed using electrostatic interactions. The (H-PEI/DNA+GOx)5 film was then partially decomposed by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The mechanism for the decomposition of the LbL film was considered to involve a more reactive oxygen species (ROS) that was formed by the reaction of hemin and H2O2, which then caused nonspecific DNA cleavage. GOx present in the LbL films reacts with glucose to generate hydrogen peroxide. Therefore, decomposition of the H-PEI/DNA+GOx)5 film was observed when the thin film was immersed in a glucose solution. A (H-PEI/DNA+GOx)5 film exposed to a glucose solution for periods of 24, 48 72, and 96 h indicated decomposition of the film increased with the time. The rate of LbL film decomposition increased with the glucose concentration. At pH and ionic strength close to physiological conditions, it was possible to slowly decompose the LbL film at a sub-millimolar glucose concentration.