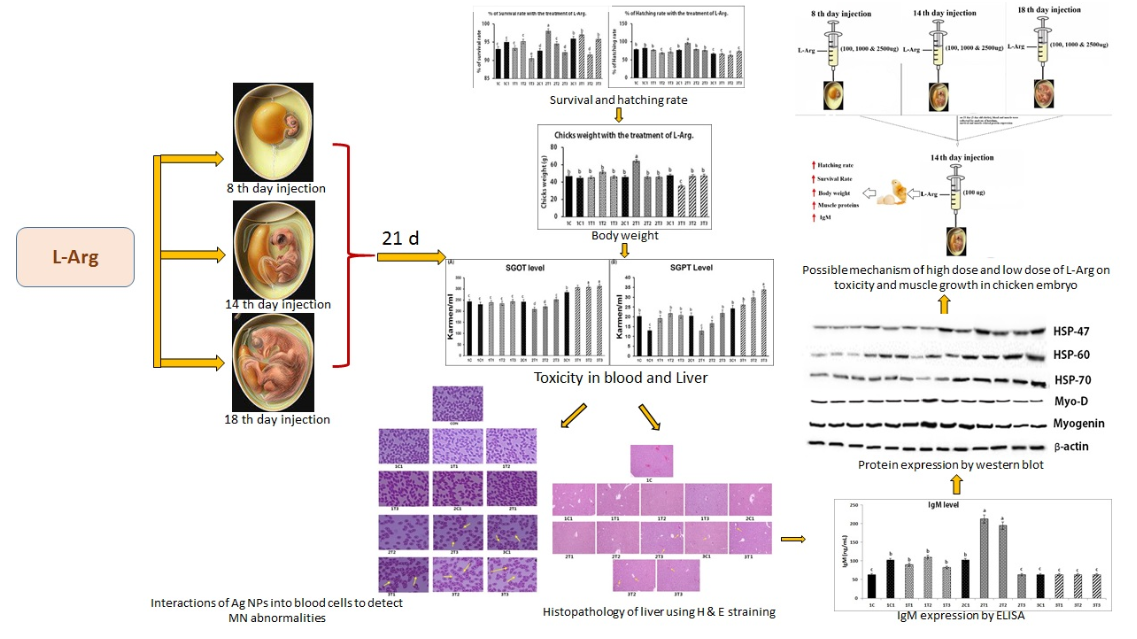
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of in ovo injection of L-arginine (L-Arg) into Ross broiler eggs at different embryonic developmental stages on their survival, hatchability, and body weight (BW). Additionally, we have analyzed the levels of serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT) and serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), protein expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs), also we have the determined micronuclei (MN) and nuclear abnormality (NA). Results showed that survival and hatching rates as well as body weight were increased on the 14th day incubation compared to 8th and 18th day incubation at lower concentration of L-Arg. Moreover, the levels of SGOT and SGPT were also significantly (P < 0.05) increased at 14th day incubation at the same concentration (100μg/μl/egg) of injection. In addition, IgM levels were increased on the 14th day incubation compared to other days. The protein expressions of HSP-47, HSP-60, and HSP-70 in the liver were significantly down-regulated whereas the expression of myogenin and MyoD were significantly up-regulated on the 14th day after incubation in treated with all different doses such as 100μg, 1000μg and 2500μg/μl/egg namely 3T1, 3T2 and 3T3 respectively. However, the treatment with low dose of L-Arg down-regulated expression levels of those proteins on the 14th day incubation. Histopathology of liver by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) straining showed that the majority of liver damage, specifically intracytoplasmic vacuoles, were observed in 3T1, 3T2, and 3T3. The minimum dose of 100 μg/ml/egg on the 14th day of incubation significantly prevented intracytoplasmic vacuole damages. These results demonstrate that in ovo administration of L-Arg at (100μg/μl/egg) may be an effective method to increase chick BW, hatch rate, increasing muscle growth related proteins and promote the immune response through increasing IgM on the 14th day of incubation period.