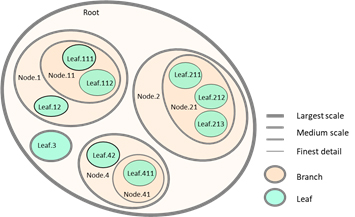
This work presents some characteristics of MoNet, a computerized platform for the modeling and visualization of complex systems. Emphasis is on the ideas that allowed the successful progressive development of this modeling platform, which goes along with the implementation of applications to the modeling of several studied systems. The platform has the capacity to represent different aspects of systems modeled at different observation scales. This tool offers advantages in the sense of favoring the perception of the phenomenon of the emergence of information, associated with changes of scale. Some criteria used for the construction of this modeling platform are included. The power of current computers has made practical representing graphic resources such as shapes, line thickness, overlaying-text tags, colors and transparencies, in the graphical modeling of systems made up of many elements. By visualizing diagrams conveniently designed to highlight contrasts, these modeling platforms allow the recognition of patterns that drive our understanding of systems and their structure. Graphs that reflect the benefits of the tool regarding the visualization of systems at different scales of observation are presented to illustrate the application of the platform.