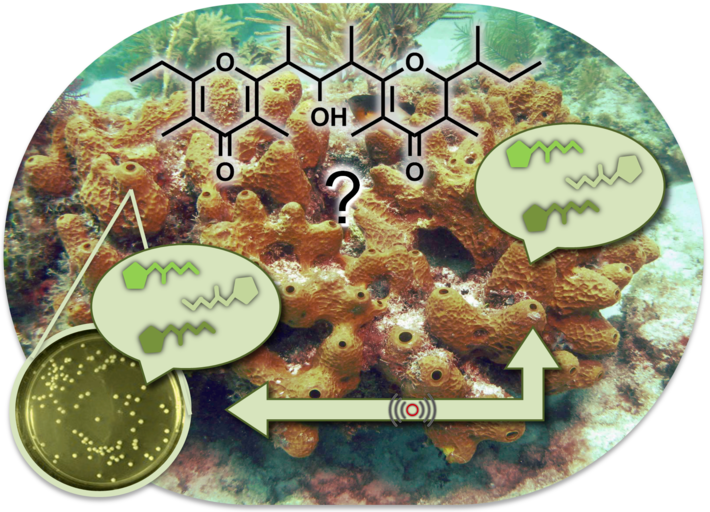
The organic extract of the Caribbean sponge Smenospongia aurea has been shown to contain an array of novel chlorinated secondary metabolites derived from a mixed PKS-NRPS biogenetic route, such as the smenamides. Here we report the presence of a biogenetically different compound, smenopyrone (1), a polypropionate containing two -pyrone rings. The structure of smenopyrone, including its relative and absolute stereochemistry, was determined by spectroscopic analysis (NMR, MS, ECD) supported by comparison with model compounds from the literature. Pyrone polypropionates are unprecedented in marine sponges, but are commonly found in marine mollusks, where their biosynthesis by symbiotic bacteria has been hypothesized and at least in one case demonstrated. As pyrones have recently been recognized as bacterial signaling molecules, we speculate that smenopyrone could mediate inter-kingdom chemical communication between S. aurea and its symbiotic bacteria.