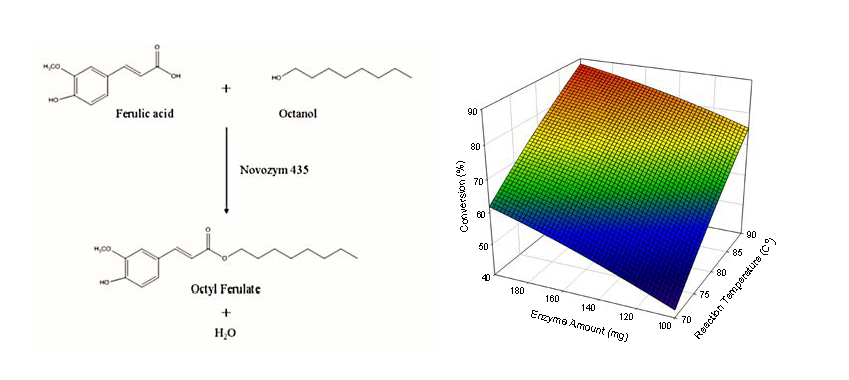
Ferulic acid esters have been suggested as a group of natural chemicals with sunscreen function. The study aimed to utilize an environment-friendly enzymatic method to produce octyl ferulate by esterification of ferulic acid with octanol. The Box-Behnken design with response surface methodology (RSM) was adopted to evaluate the effects of synthesis variables, including reaction temperature (70–90 °C), enzyme amount (1000–2000 PLU) and stir speed (50–150 rpm), on the molar conversion of octyl ferulate. According to the joint test, both the reaction temperature and enzyme amount had great impacts on the molar conversion. RSM-developed second-order polynomial equation further showed great ability on data-fitting. Based on ridge max analysis, the optimum parameters for the biocatalyzed reaction were: 72 h reaction time, 92.2 °C reaction temperature, 1831 PLU enzyme amount and 92.4 rpm stir speed, respectively. Finally, the molar conversion of octyl ferulate under optimum condition was verified to be 93.2 ± 1.5%. In conclusion, high yield of octyl ferulate synthesized by commercial immobilized lipase under elevated temperature conditions has been suggested, which our findings could broaden the utilization of the lipase and provide a biocatalytic approach, instead of the chemical method, for ferulic acid ester synthesis.