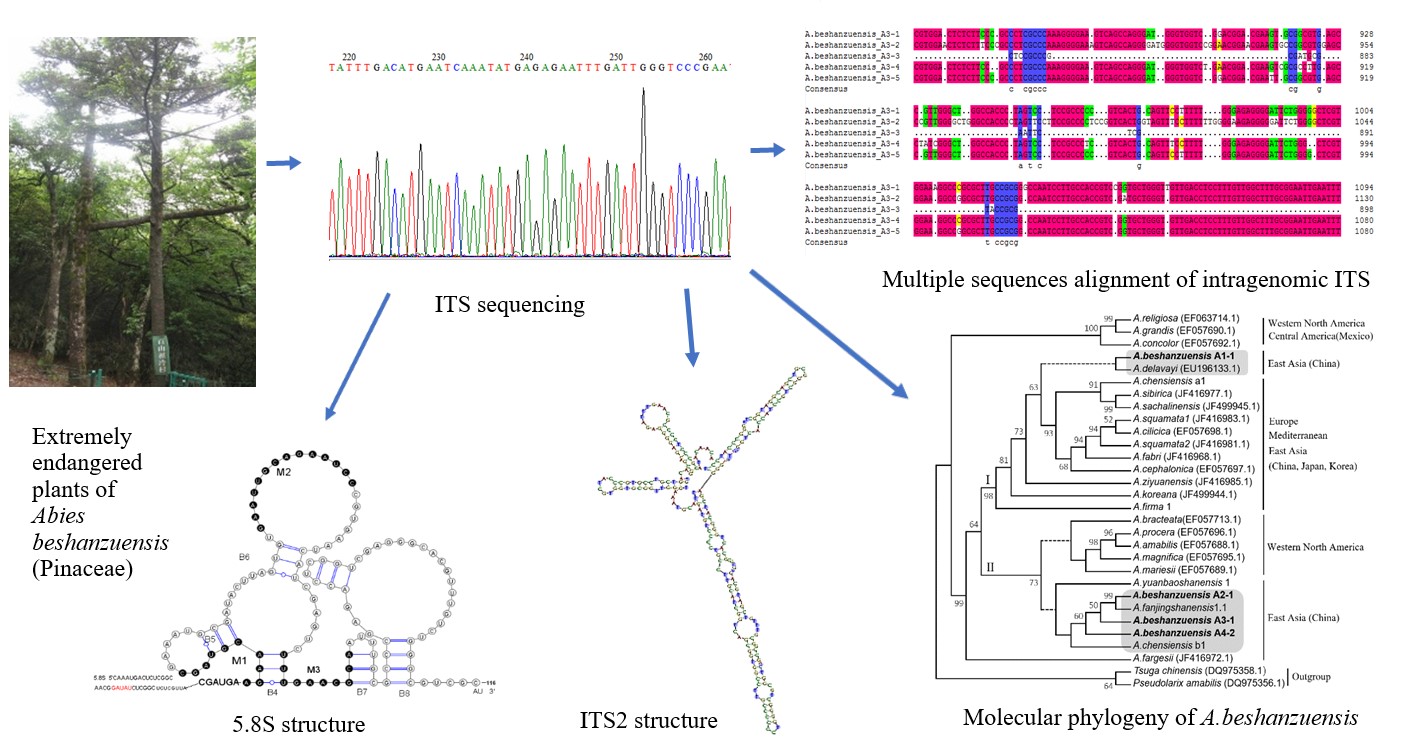
Abies beshanzuensis, an extremely endangered species, attracts serious concerns on genetic diversity recovery and population protection. However, little genetic information was known about it till now. In this study, intra-/intergenomic ITS variation, secondary structure, and molecular phylogeny of A.beshanzuensis were determined by nrDNA-ITS marker, and results indicated that, ITS region featured rich polymorphism in ITS1 and highly conservative in 5.8S/ITS2 among intra-/inter-genome, implying rich genetic diversities and the occurrence of non-concerted evolution in ITS region. Predicated 5.8S structure possessed Helices-Loops with 3 motifs (M1/M2/M3) and 5 helices B4-B8, and ITS2 could form conservative Clover-like structure with 5 ribotypes, manifesting genetically structural generalities and individualities. Thirteen ITS pseudogenes were also identified from 76 samples (or clones). Molecular phylogeny revealed that, A.beshanzuensis shared genetically closer relationships with A.fanjingshanensis, A.chensiensis, A.yuanbaoshanensis among genus Abies. The available original data provided rich genetic information on ITS sequence, structure and molecular phylogeny of A.beshanzuensis, which not only updated the databases of ITS sequences as well as secondary structures essential for phylogenetic reference and DNA barcoding analyses, but also contributed to deep exploration of population diversities, origin and evolution as well theoretical direction for population recovery and protection of A.beshanzuensis.