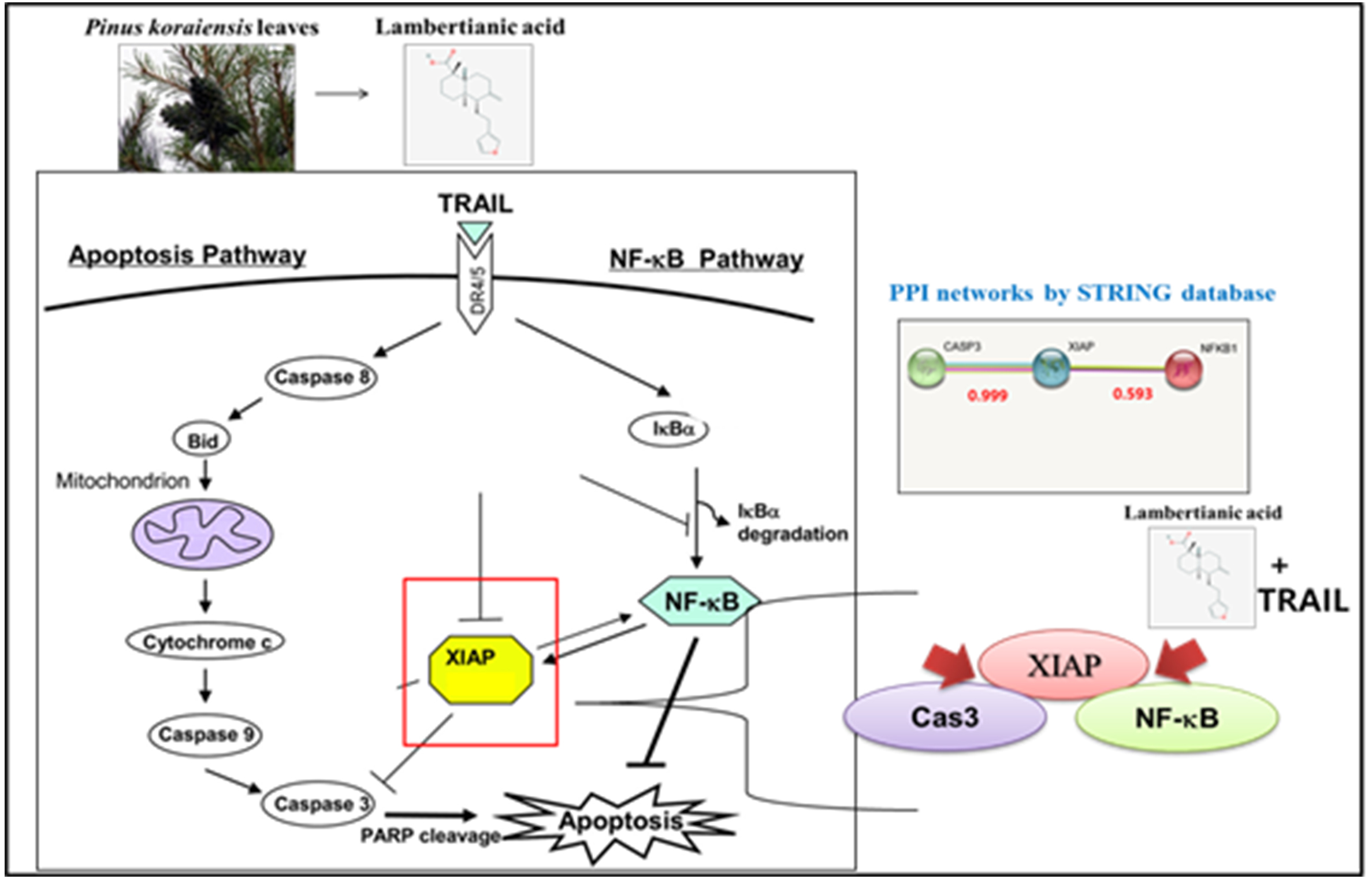
Lambertianic acid (LA) is a biologically active compound from the leaves of Pinus koraiensis. In the present study, apoptotic mechanisms of LA plus TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) were elucidated in non-small cell lung cancer cells (NSCLCs). Cytotoxicity assay, flow cytometry, immunoprecipitation and Western blotting were performed. Here, combined treatment of LA and TRAIL increased cytotoxicity, sub-G1 population and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and caspase3/8/9 in A549 and H1299 cells compared to LA or TRAIL alone. Furthermore, combined treatment of LA and TRAIL significantly decreased anti-apoptotic proteins such as B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), Fas-like inhibitor protein (FLIP) and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) and enhanced the activation of pro-apoptotic proteins Bid compared to LA or TRAIL alone. In addition, combined treatment of LA and TRAIL upregulated the expression of Death receptor 4 (DR4) and downregulated phosphorylation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (p-NF-B), inhibitory protein of kB family (p-IB) and FLIP in A549 and H1299 cells along with disrupted binding of XIAP with caspase3 or NF-B. Overall, these findings suggest that lambertianic acid enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis via inhibition of XIAP/NF-B in TRAIL resistant NSCLCs.