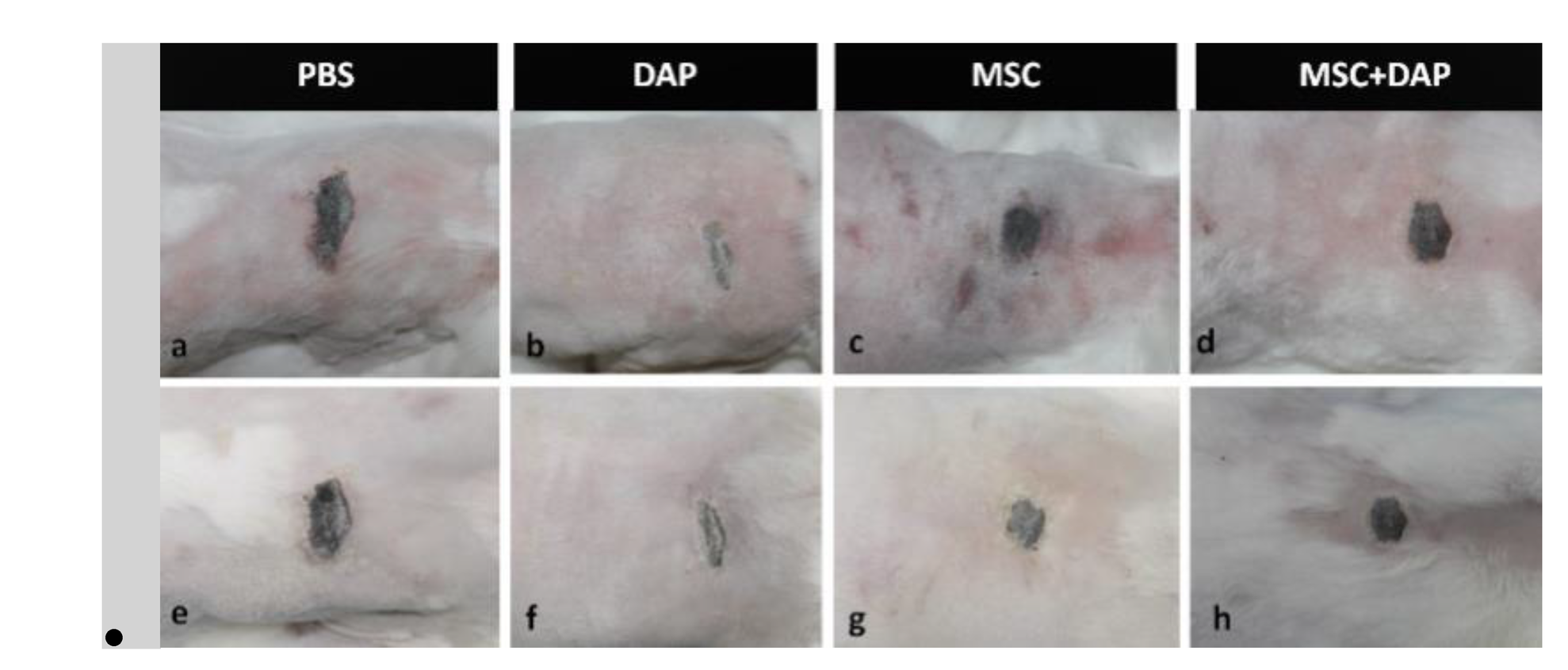
We studied the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), either alone or associated with dapsone (DAP) in the treatment of dermonecrotic wounds caused by Loxosceles laeta spider venom. Twenty-five male adult rabbits were distributed into five groups, of which four groups received an intradermal injection of 20 μg of L. laeta venom and only one received ultrapure water (negative control). After 4 hours, each group that received venom, was treated with MSC, DAP, MSC + DAP and Phosphate-buffered saline – PBS (positive control). Photographic records were made for analysis of the wound area evolution by morphometry. Twelve days after treatment, the skin samples around the lesion were removed for subsequent histological analysis. Concerning the rate of wound contraction, we observed that DAP showed the best percentage of contraction at day 3. In the treatments using MSCs, a negative value of wound contraction was observed for the isolated MSCs, as well as a lower contraction value for the association of the MSC + DAP when compared to PBS group. Histopathological analysis showed diminished tissue lesion and less intense inflammation in MSCs and DAP groups. This could indicated potential use of stem cells in regenerative therapies after loxoscelic accidents.