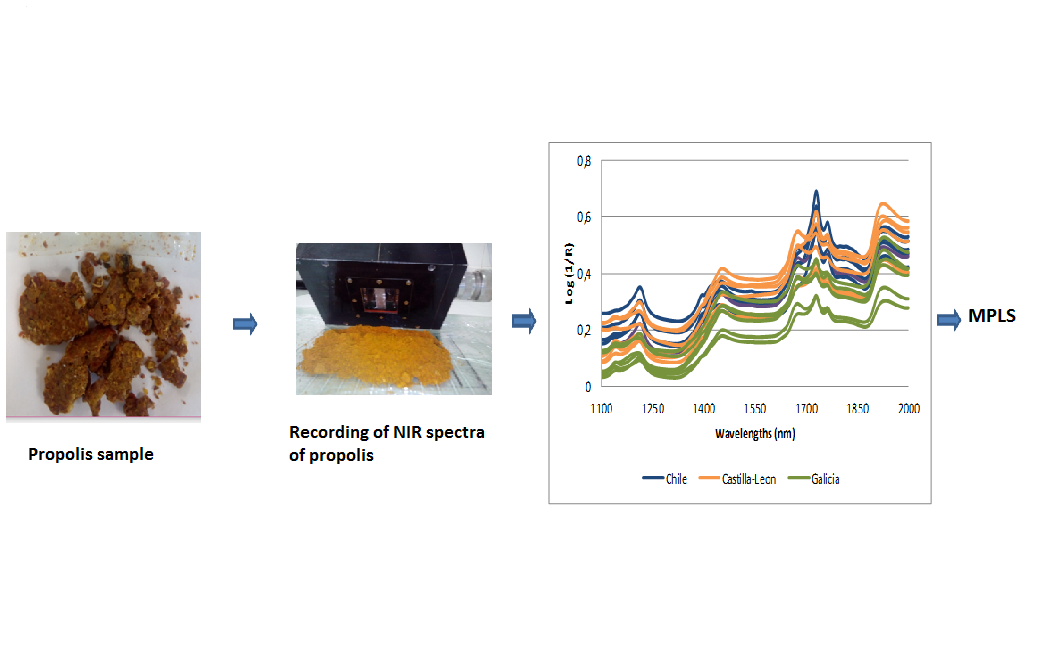
Propolis is a bee product widely used as a dietary supplement and included in sweets or baby foods due to its well-known antioxidant and nutritional properties that are directly correlated with its phenolic composition. For this reason, this study analysed the total contents of flavones and flavonols, flavanones and dihydroflavonols, and the antioxidant capacity by using the methods of ABTS and linoleic acid/β-carotene in 99 samples of propolis from Spain and Chile. A rapid method was developed for quantifying these parameters in raw propolis using near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy with an optical fibre probe of remote reflectance applied directly to the ground up sample. The models developed allow the determination of the total of flavones and flavonols (0-183 mg rutin/ g propolis), of the total of flavanones and dihydroflavonols (9-109 mg pinocembrin/ g propolis extract), and the antioxidant capacity by the ABTS method (0-3212 nmolesTrolox/ mg of propolis) and of linoleic acid/β-carotene (22-86% inhibition). The NIR spectroscopy models were applied in external validation to different samples of the calibration group, which led to the conclusion that the methods developed provide significantly identical data to the initial chemical data of reference.