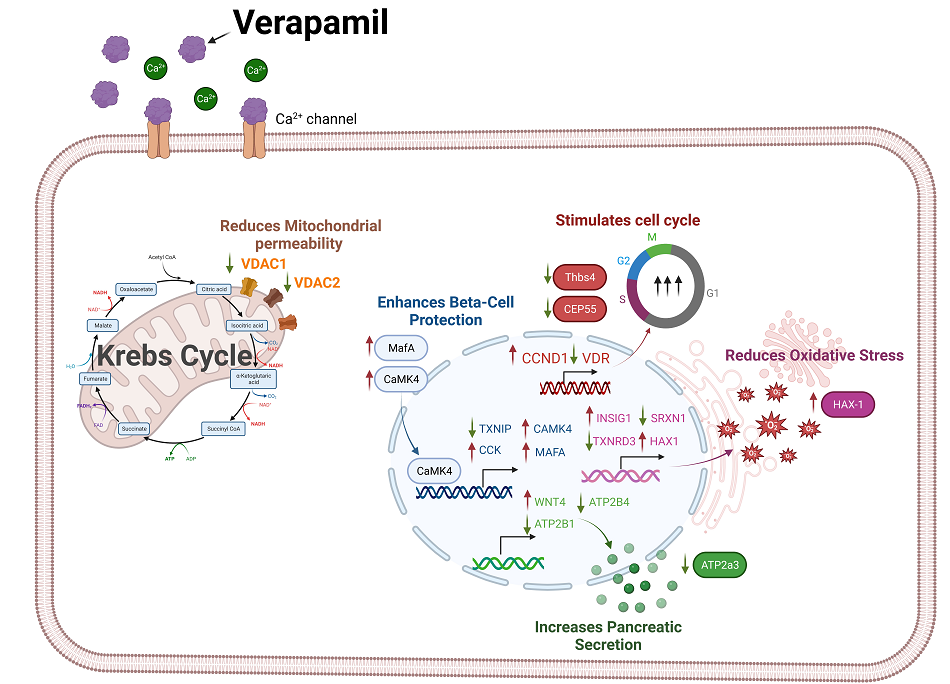
Unraveling Verapamil's Multidimensional Role in Diabetes Therapy: From β-Cell Regeneration to Cholecystokinin Induction
How to cite: Arefanian, H.; Al Madhoun, A.; Al-Rashed, F.; Alzaid, F.; Bahman, F.; Nizam, R.; Alhusayan, M.; John, S.E.; Jacob, S.; Williams, M.R.; Abu Khalaf, N.; Shenouda, S.; Joseph, S.; AlSaeed, H.; Kochumon, S.; Mohammad, A.; Koti, L.; Sindhu, S.; Abu-Farha, M.; Abubaker, J.; Thanaraj, T.A.; Ahmad, R.; Al-Mulla, F. Unraveling Verapamil's Multidimensional Role in Diabetes Therapy: From β-Cell Regeneration to Cholecystokinin Induction. Preprints 2024, 2024031681. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202403.1681.v1 Arefanian, H.; Al Madhoun, A.; Al-Rashed, F.; Alzaid, F.; Bahman, F.; Nizam, R.; Alhusayan, M.; John, S.E.; Jacob, S.; Williams, M.R.; Abu Khalaf, N.; Shenouda, S.; Joseph, S.; AlSaeed, H.; Kochumon, S.; Mohammad, A.; Koti, L.; Sindhu, S.; Abu-Farha, M.; Abubaker, J.; Thanaraj, T.A.; Ahmad, R.; Al-Mulla, F. Unraveling Verapamil's Multidimensional Role in Diabetes Therapy: From β-Cell Regeneration to Cholecystokinin Induction. Preprints 2024, 2024031681. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202403.1681.v1
Abstract
Keywords
Subject
Copyright: This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Comments (0)
We encourage comments and feedback from a broad range of readers. See criteria for comments and our Diversity statement.
Leave a public commentSend a private comment to the author(s)