Submitted:
05 January 2025
Posted:
06 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Background
i. Image Resizing and LLMs
ii. LLM-Related Work
iii. Image and Vision Generation Work
iv. Image Resizing and Seam Carving Research
III. Functionality
- LLM-Augmented Region Prioritization: LLMs analyze semantics or textual inputs to prioritize key regions, ensuring critical areas (e.g., faces, text) are preserved.
- LLM-Augmented Bicubic Interpolation: LLMs optimize bicubic interpolation for high-quality enlargements, adjusting parameters based on context or user input.
- LLM-Augmented LC Algorithm: LLMs adapt the LC algorithm by adjusting weights, ensuring the preservation of important image features during resizing.
- LLM-Augmented Canny Edge Detection: LLMs guide Canny edge detection to refine boundaries, enhancing clarity and accuracy based on contextual analysis.
- LLM-Augmented Hough Transformation: LLMs strengthen the Hough transformation, detecting structural lines and ensuring the preservation of geometric features.
- LLM-Augmented Absolute Energy Function: LLMs dynamically adjust energy maps to improve seam selection for more precise resizing.
- LLM-Augmented Dual Energy Model: LLMs refine energy functions, enhancing flexibility and ensuring effective seam carving across various use cases.
IV. LLM-Guided Region Prioritization
i. Semantic Importance Scoring by LLMs
- : Image embedding derived from input image I using a vision feature extractor.
- : Text embedding derived from optional user description D using a language transformer.
- g: A cross-modal scoring function combining and , implemented via attention mechanisms.
ii. Energy Map Adjustment
- : Gradients in x- and y-directions.
- : Semantic score indicating the importance of pixel .
- : Weighting factor balancing pixel-based energy and semantic importance.
iii. Semantic Score Calculation with LLMs
- VisionEncoder: Extracts regional features from I (e.g., object locations, edges).
- TextEncoder: Encodes user-provided descriptions into contextual embeddings.
- Attention: Combines and to assign based on pixel relevance.
iv. Cumulative Energy Map Update
- : Left, right, and upward cost terms adjusted with .
- min: Ensures the optimal seam path minimizes distortion of high-priority regions.
V. LLM-Augmented Bicubic Interpolation
i. Traditional Bicubic Interpolation
ii. LLM-Augmented Interpolation
- : Semantic importance score for pixel , computed by the LLM.
- : Scalar factor controlling the influence of on the interpolation process.
iii. Semantic Importance Calculation
- I: Input image.
- D: Optional user-provided description specifying priorities (e.g., "preserve faces").
- : A function combining image embeddings and text embeddings through an attention mechanism:
iv. Cumulative Interpolation Update
VI. LLM-Augmented LC (Loyalty-Clarity) Policy
i. Global Contrast with Semantic Guidance
- scales the influence of semantic importance, computed by the LLM.
- represents the semantic weight of region r, also derived from the LLM.
- R is the set of semantically significant regions.
ii. Frequency-Based Contrast Refinement
- adjusts the frequency of region r based on the LLM’s analysis.
- weights the region according to its semantic importance.
iii. LLM Parameter Computation
- Image Embeddings : A vision encoder extracts pixel-level and global features:
- Text Embeddings : A text encoder processes user descriptions:
- Spatial Embeddings : Positional embeddings represent region-specific attributes:
- Semantic Weights : Attention mechanisms combine embeddings:
- Frequency Adjustment : The LLM refines the frequency distribution:
- Scaling Factor : A sigmoid function ensures :
iv. Contrast-Based Resizing Decision

VII. LLM-Augmented Canny Line Detection
i. Gaussian Filtering
- : Semantic importance score for region r.
- : Scaling factor for the semantic influence.
ii. Gradient Calculation
iii. LLM Semantic Parameter Calculation
iv. Edge Refinement
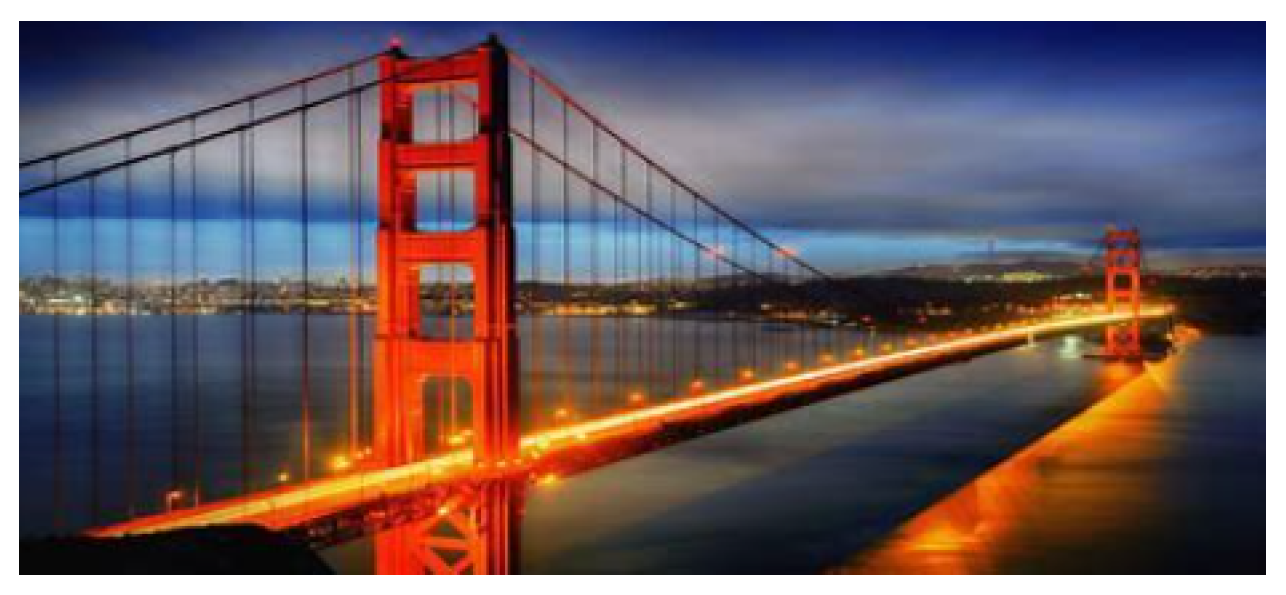

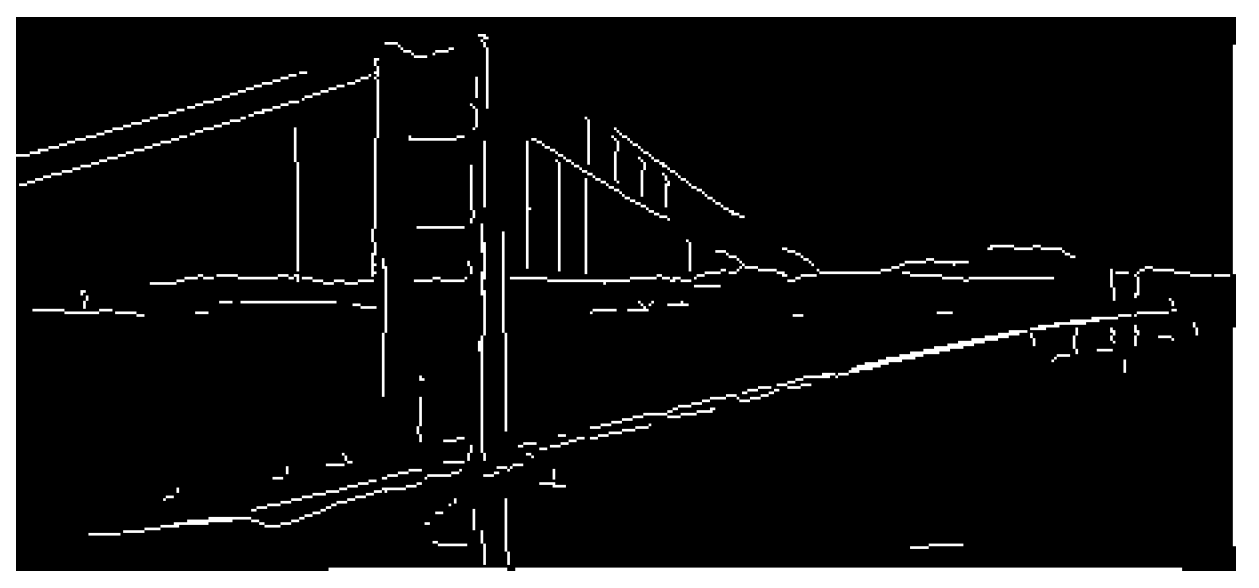
VIII. LLM-Augmented Hough Transformation
i. Mathematical Formulation
- : Accumulator value for the line parameterized by .
- : Semantic importance score computed for pixel .
ii. Semantic Score Calculation
iii. LLM-Augmented Hough Transformation Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 LLM-Augmented Hough Transformation |
|
Require: : Input image I, optional description D. Ensure: : Detected lines with semantic weighting.
|
iv. Threshold Adaptation
- : Adaptive threshold for .
- : Average semantic score for lines contributing to .
- : Scaling factor controlling semantic influence.
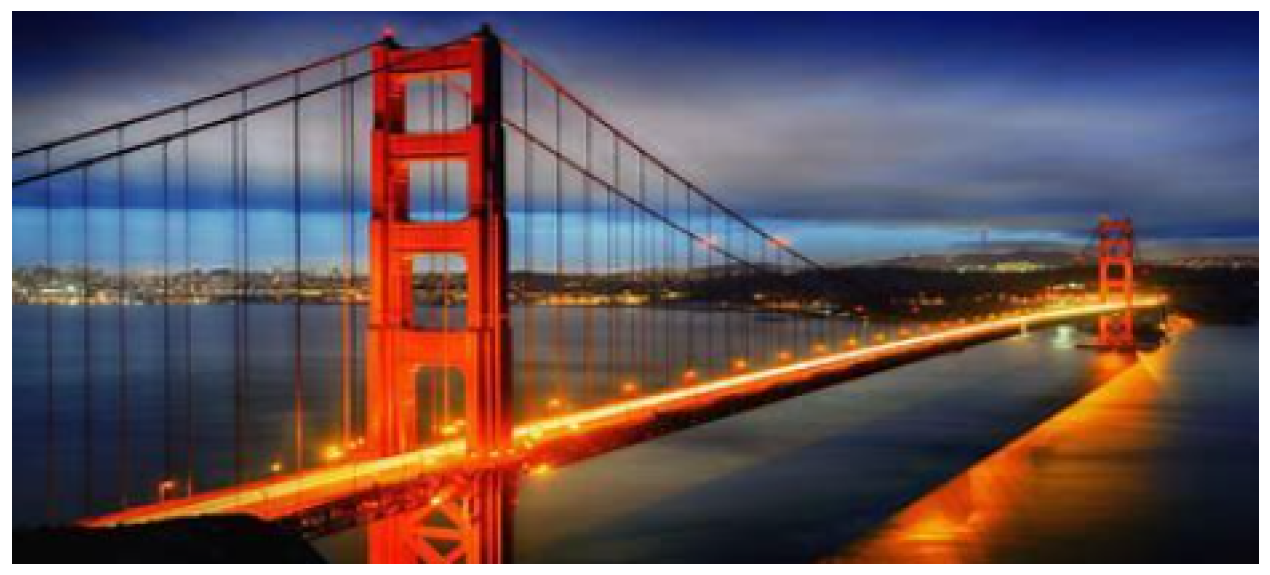
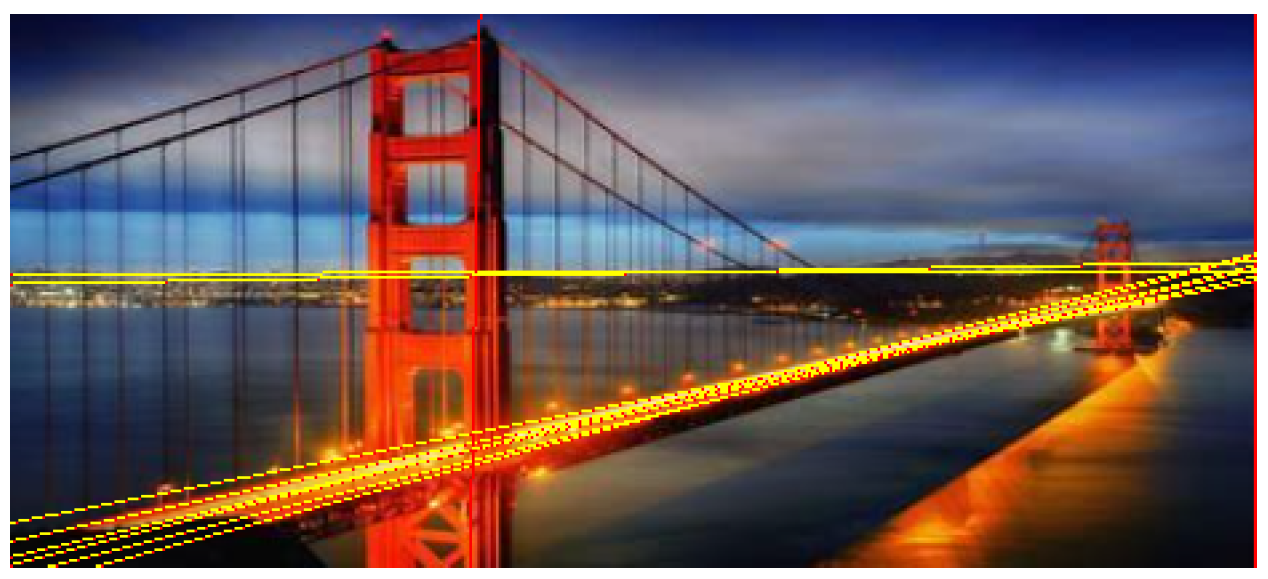


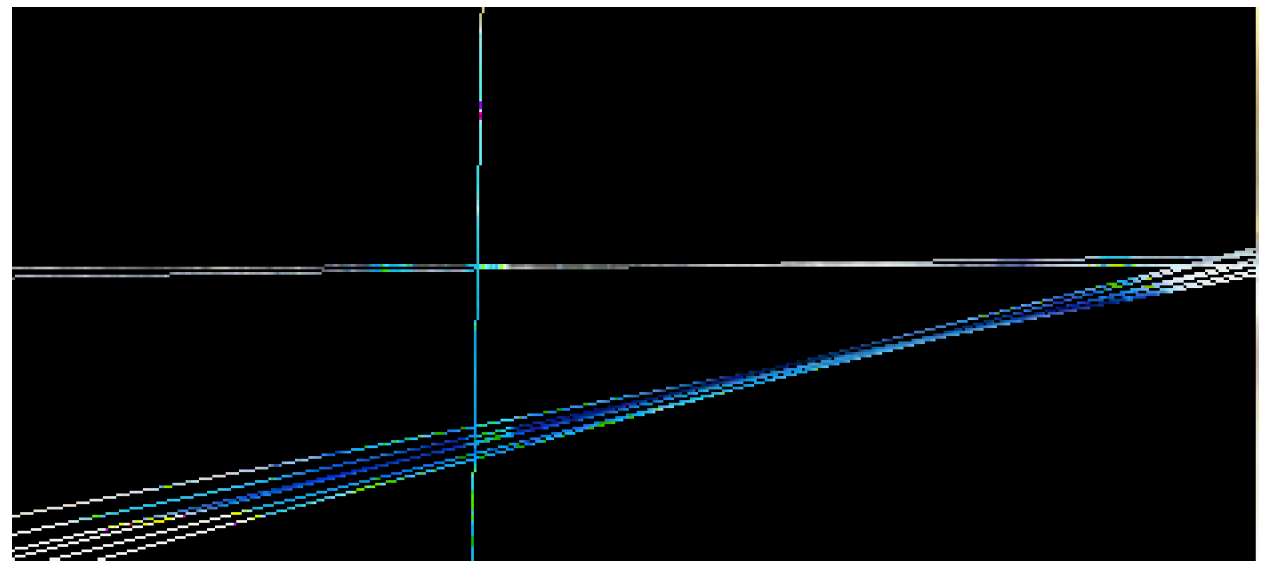
IX. LLM-Augmented Absolute Energy Equation
i. Semantic Weighting
ii. Gradient Refinement
iii. Cumulative Energy Update
X. LLM-Augmented Dual Gradient Energy Equation
i. Numerical Differentiation with LLM Adjustments
ii. Gradient Approximation with Adaptive Refinements
iii. Energy Calculation with LLM Refinements
XI. Result Evaluation
i. Evaluation Metrics
- Semantic Preservation (): Measures the alignment of detected features or preserved regions with semantically significant areas, as defined by the LLM:where is the semantic importance score for feature i.
- Visual Quality (): Evaluates the perceptual quality of resized images using metrics such as PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio) and SSIM (Structural Similarity Index):
- Computational Efficiency (): Measures the average runtime per image:
ii. Results and Discussion
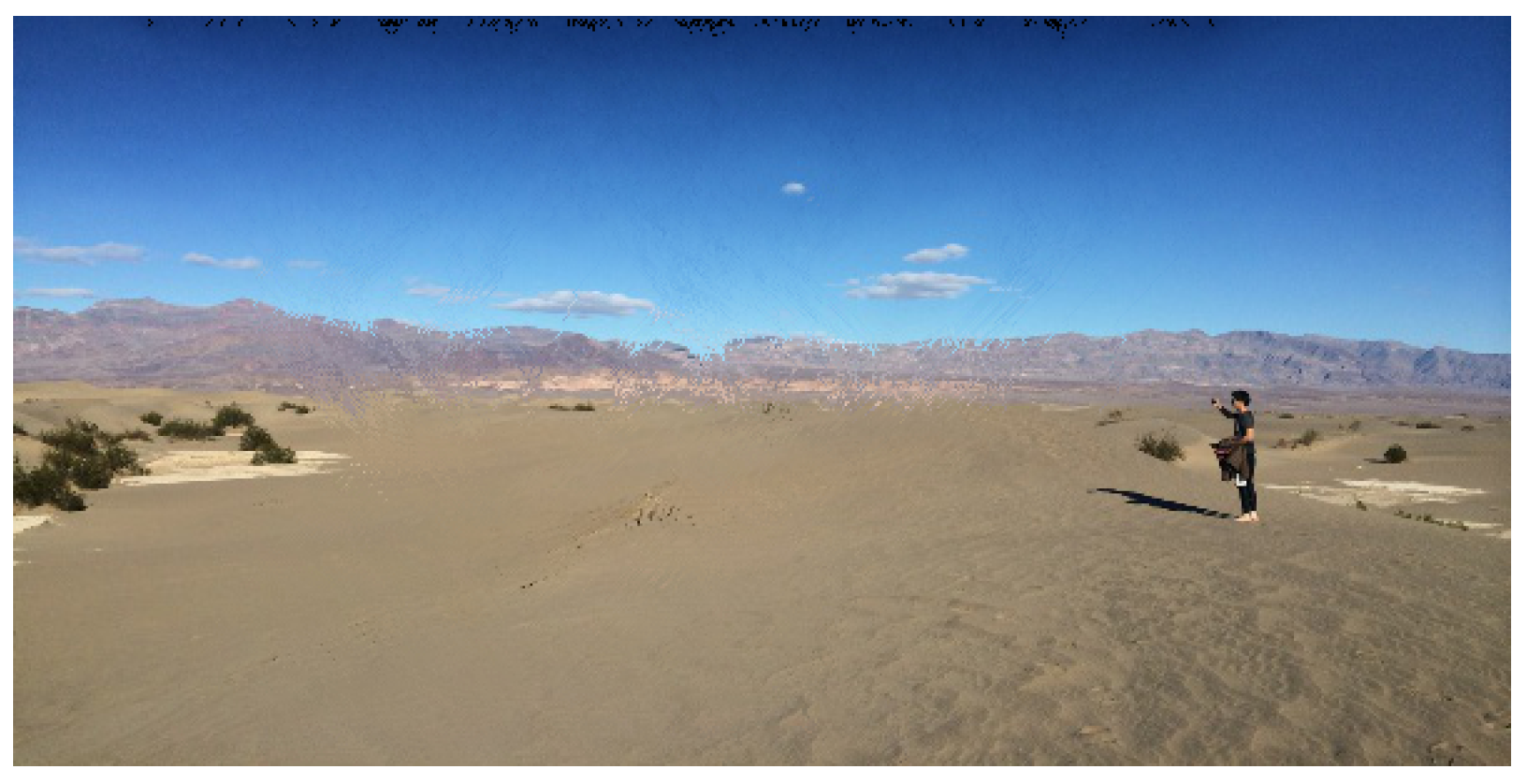
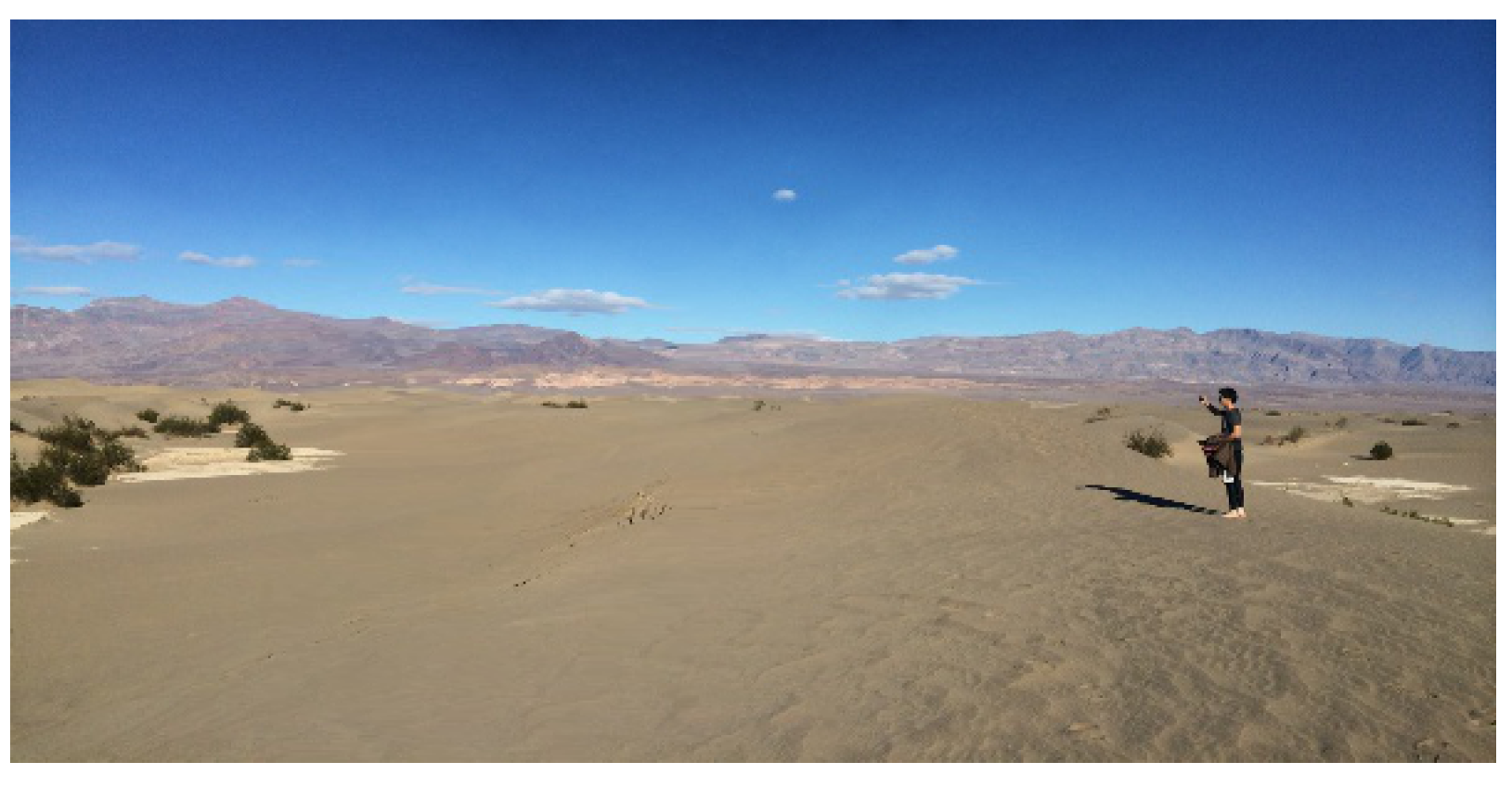
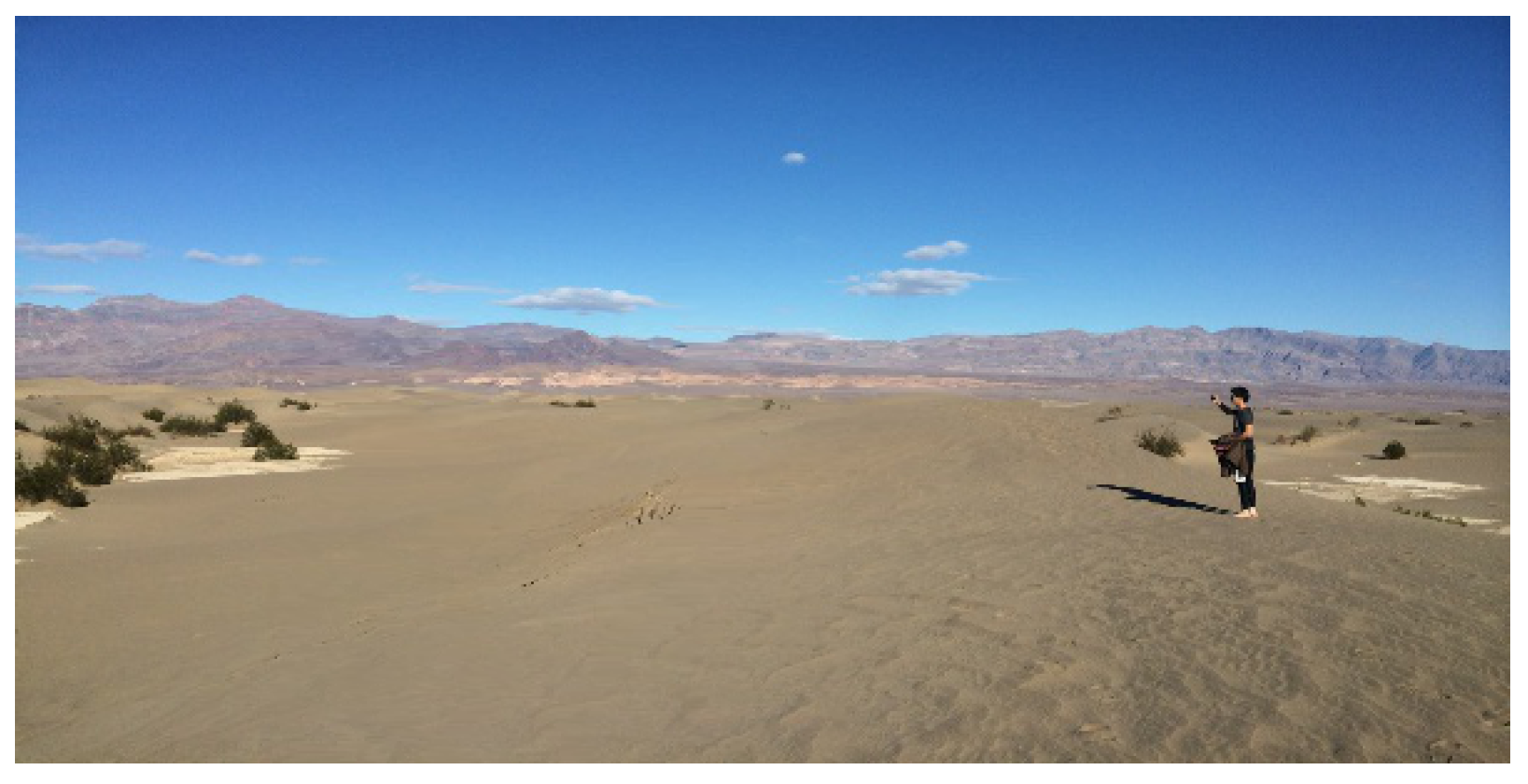
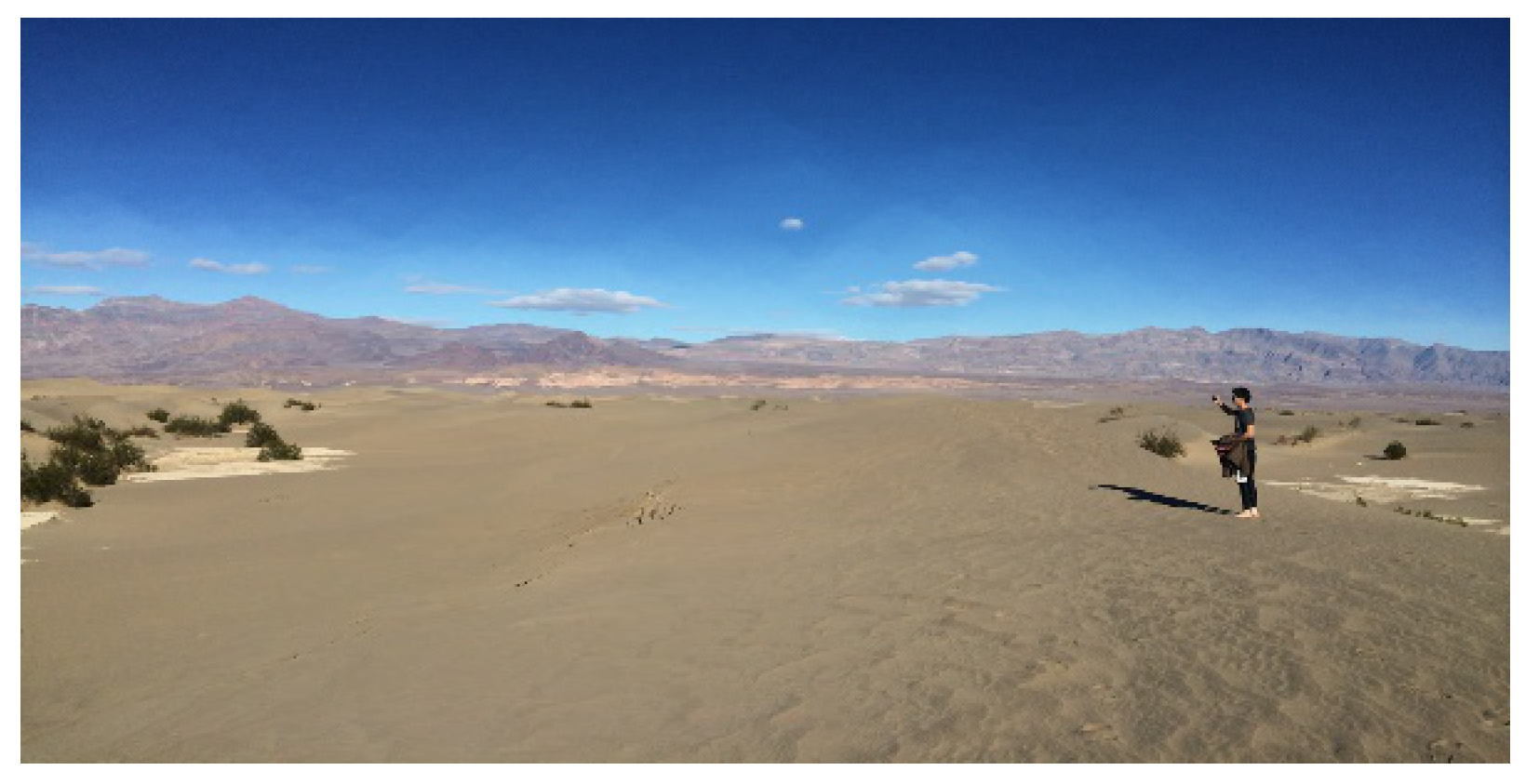
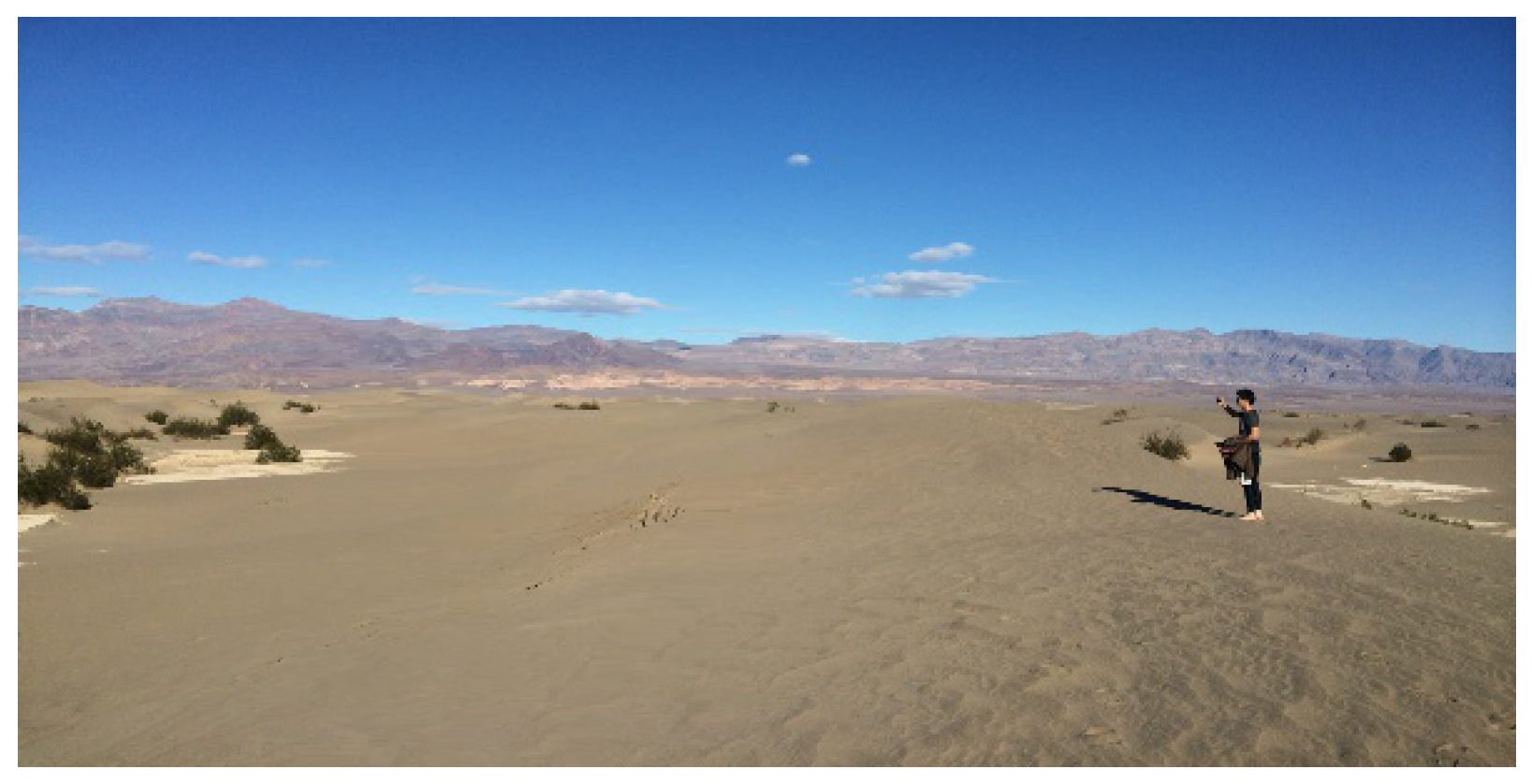
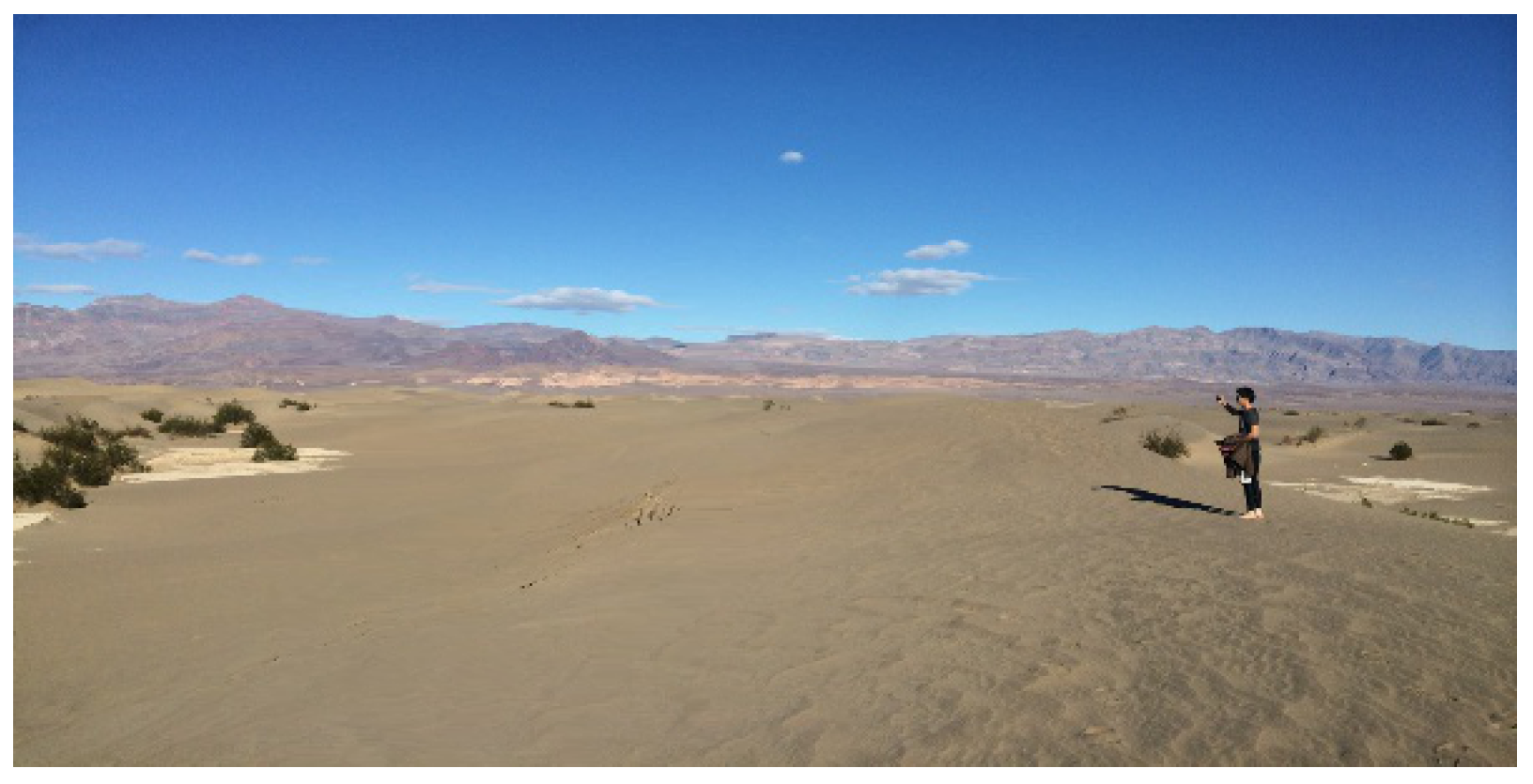
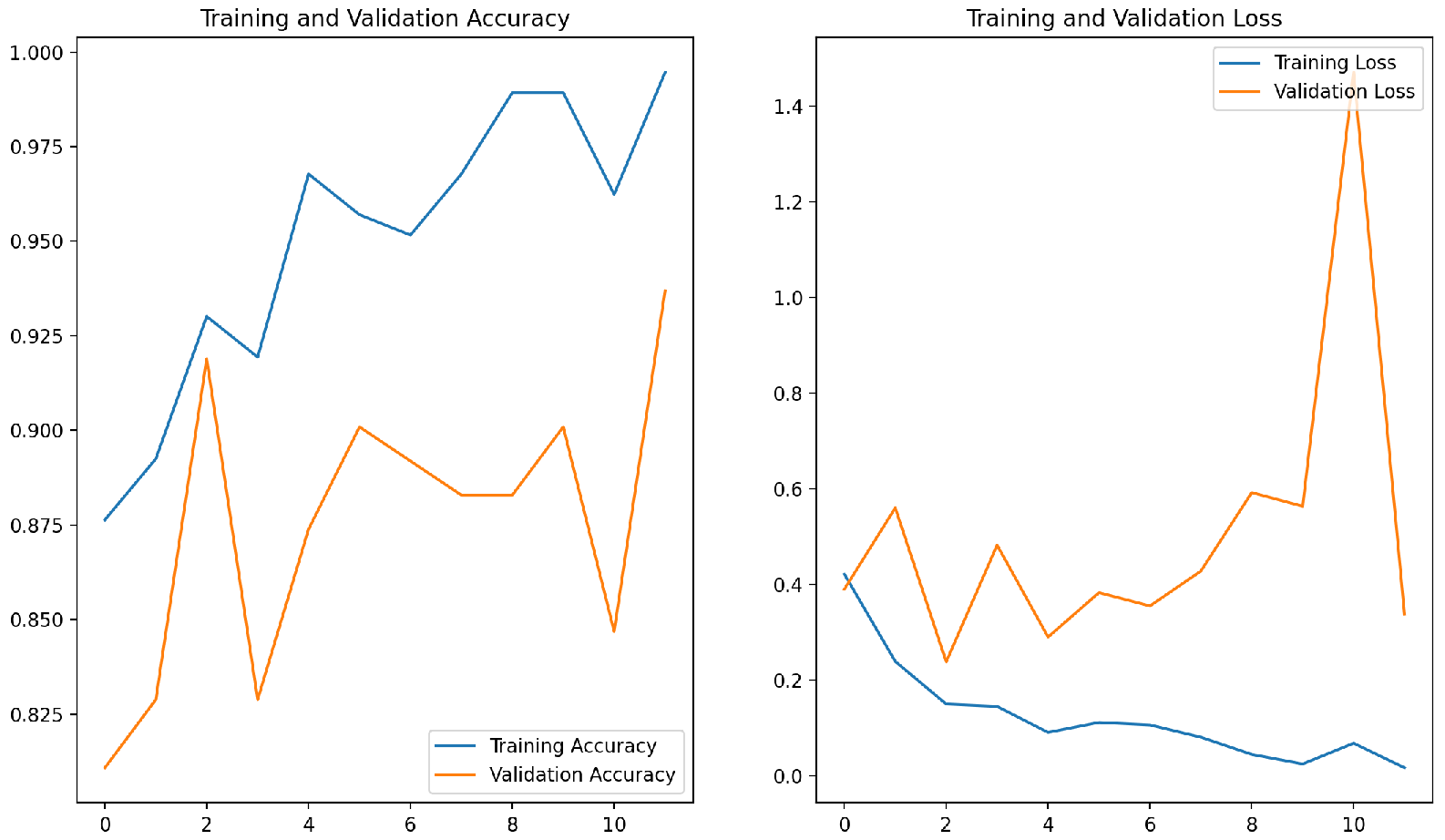






iii. Conclusion
References
- Xingyuan Bu, Yuwei Wu, Zhi Gao, and Yunde Jia. Deep convolutional network with locality and sparsity constraints for texture classification. Pattern Recognition, 91:34–46, 2019.
- A. Chaurasia and E. Culurciello. Linknet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.03718, 2017. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.03718.
- Han-Cheng Dan, Zhetao Huang, Bingjie Lu, and Mengyu Li. Image-driven prediction system: Automatic extraction of aggregate gradation of pavement core samples integrating deep learning and interactive image processing framework. Construction and Building Materials, 453:139056, 2024.
- A. et al. Dosovitskiy. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2021. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929.
- Roderick Frankovich. Enhanced seam carving: Energy gradient functionals and resizing control. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pages 2157–2160, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Fusen Guo, Huadong Mo, Jianzhang Wu, Lei Pan, Hailing Zhou, Zhibo Zhang, Lin Li, and Fengling Huang. A hybrid stacking model for enhanced short-term load forecasting. Electronics, 13(14):2719, 2024.
- Yue Guo, Shiqi Chen, Ronghui Zhan, Wei Wang, and Jun Zhang. Lmsd-yolo: A lightweight yolo algorithm for multi-scale sar ship detection. Remote Sensing, 14(19):4801, 2022.
- S. Han, J. Pool, J. Tran, and W. J. Dally. Deep compression: Compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and huffman coding. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2016. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/1510.00149.
- J. Ho, A. Jain, and P. Abbeel. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), pages 6840–6851, 2020. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239.
- Zhuohuan Hu, Fu Lei, Yuxin Fan, Zong Ke, Ge Shi, and Zichao Li. Research on financial multi-asset portfolio risk prediction model based on convolutional neural networks and image processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.03618, 2024.
- Zong Ke and Yuchen Yin. Tail risk alert based on conditional autoregressive var by regression quantiles and machine learning algorithms. arXiv.org, 2024. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.06193.
- Holger Kiess. Improved edge preservation in seam carving for image resizing. Computer Graphics Forum, 33(2):421–429, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Zhixin Lai, Jing Wu, Suiyao Chen, Yucheng Zhou, and Naira Hovakimyan. Residual-based language models are free boosters for biomedical imaging. 2024. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.17343, https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.17343.
- H. et al. Li. Densefuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 30:300–312, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3059619. [CrossRef]
- Keqin Li, Jin Wang, Xubo Wu, Xirui Peng, Runmian Chang, Xiaoyu Deng, Yiwen Kang, Yue Yang, Fanghao Ni, and Bo Hong. Optimizing automated picking systems in warehouse robots using machine learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.16633, 2024.
- Sicheng Li, Keqiang Sun, Zhixin Lai, Xiaoshi Wu, Feng Qiu, Haoran Xie, Kazunori Miyata, and Hongsheng Li. Ecnet: Effective controllable text-to-image diffusion models. 2024. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.18417, arXiv:2403.18417.
- Dong Liu. Contemporary model compression on large language models inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.01990, 2024.
- Dong Liu. Mt2st: Adaptive multi-task to single-task learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.18038, 2024.
- Dong Liu, Meng Jiang, and Kaiser Pister. Llmeasyquant–an easy to use toolkit for llm quantization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.19657, 2024.
- Dong Liu, Roger Waleffe, Meng Jiang, and Shivaram Venkataraman. Graphsnapshot: Graph machine learning acceleration with fast storage and retrieval. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.17918, 2024.
- Junran Peng, Xingyuan Bu, Ming Sun, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Tieniu Tan, and Junjie Yan. Large-scale object detection in the wild from imbalanced multi-labels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 9709–9718, 2020.
- Meta AI Research. Efficientsam: Fast segmentation everything model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.00860, 2024. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.00860.
- Z. et al. Wang. Controlnet: Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.05543, 2023. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543.
- Chunya Wu, Zhuoyu Yu, and Dexuan Song. Window views psychological effects on indoor thermal perception: A comparison experiment based on virtual reality environments. E3S Web of Conferences, 546:02003, 2024. URL. [CrossRef]
- Wenjun Wu. Alphanetv4: Alpha mining model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.04409, 2024.
- Ao Xiang, Zongqing Qi, Han Wang, Qin Yang, and Danqing Ma. A multimodal fusion network for student emotion recognition based on transformer and tensor product. 2024. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.08511, arXiv:2403.08511.
- Jun Xiang, Jun Chen, and Yanchao Liu. Hybrid multiscale search for dynamic planning of multi-agent drone traffic. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 46(10):1963–1974, 2023.
- Wangjiaxuan Xin, Kanlun Wang, Zhe Fu, and Lina Zhou. Let community rules be reflected in online content moderation. 2024. URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.12035, arXiv:2408.12035.
- Wei Zhang, Changxu Wu, and Xiang Li. Comparison of image resizing techniques: A case study of seam carving vs. traditional resizing methods. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 29:149–158, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2015.05.010. [CrossRef]
- Zhibo Zhang, Pengfei Li, Ahmed Y Al Hammadi, Fusen Guo, Ernesto Damiani, and Chan Yeob Yeun. Reputation-based federated learning defense to mitigate threats in eeg signal classification. In 2024 16th International Conference on Computer and Automation Engineering (ICCAE), pages 173–180. IEEE, 2024.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



