Submitted:
10 December 2024
Posted:
11 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
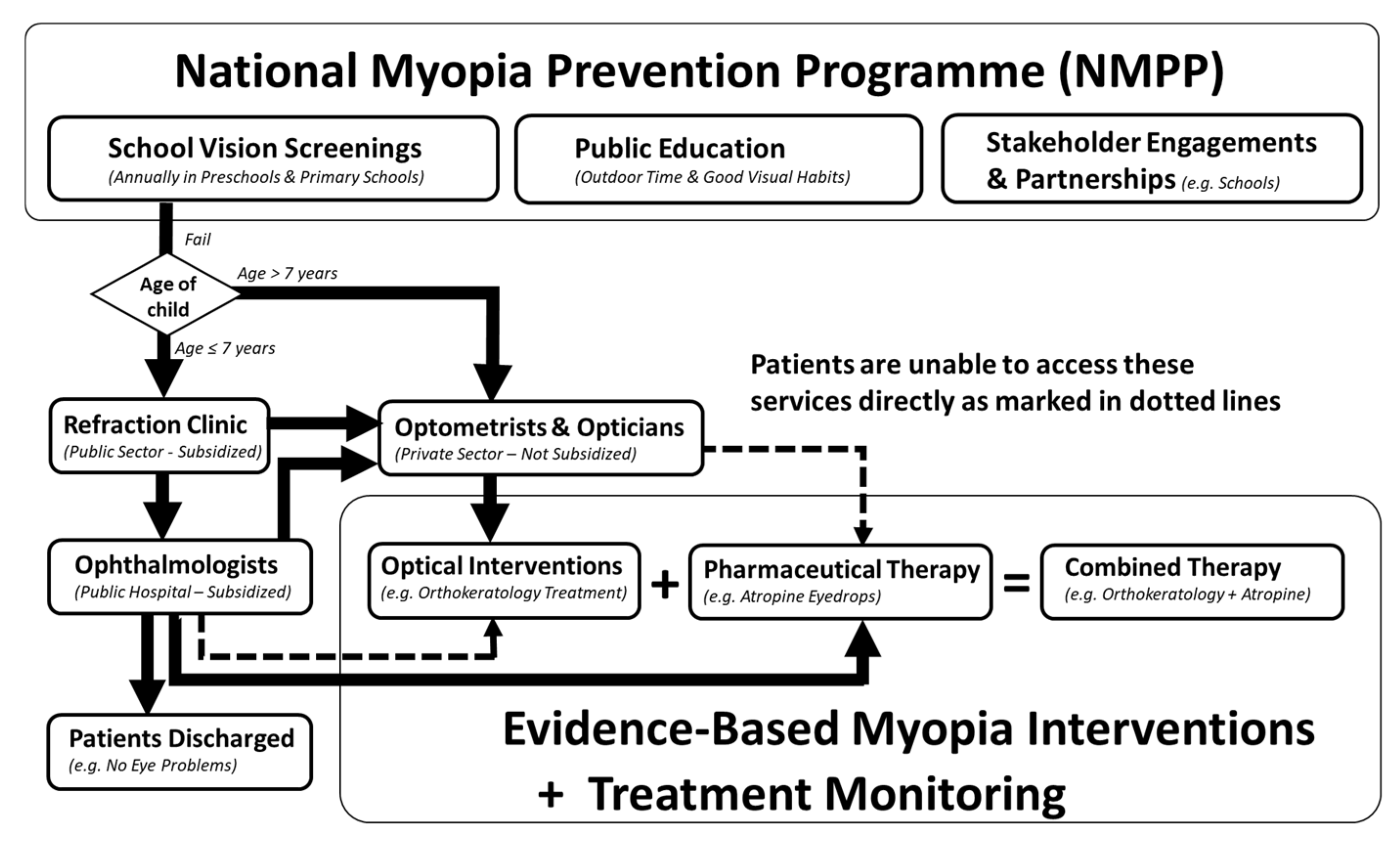
Current National Approach in Managing Childhood Myopia in Singapore
Evidence-Based Myopia Interventions
The Current Situation in Singapore
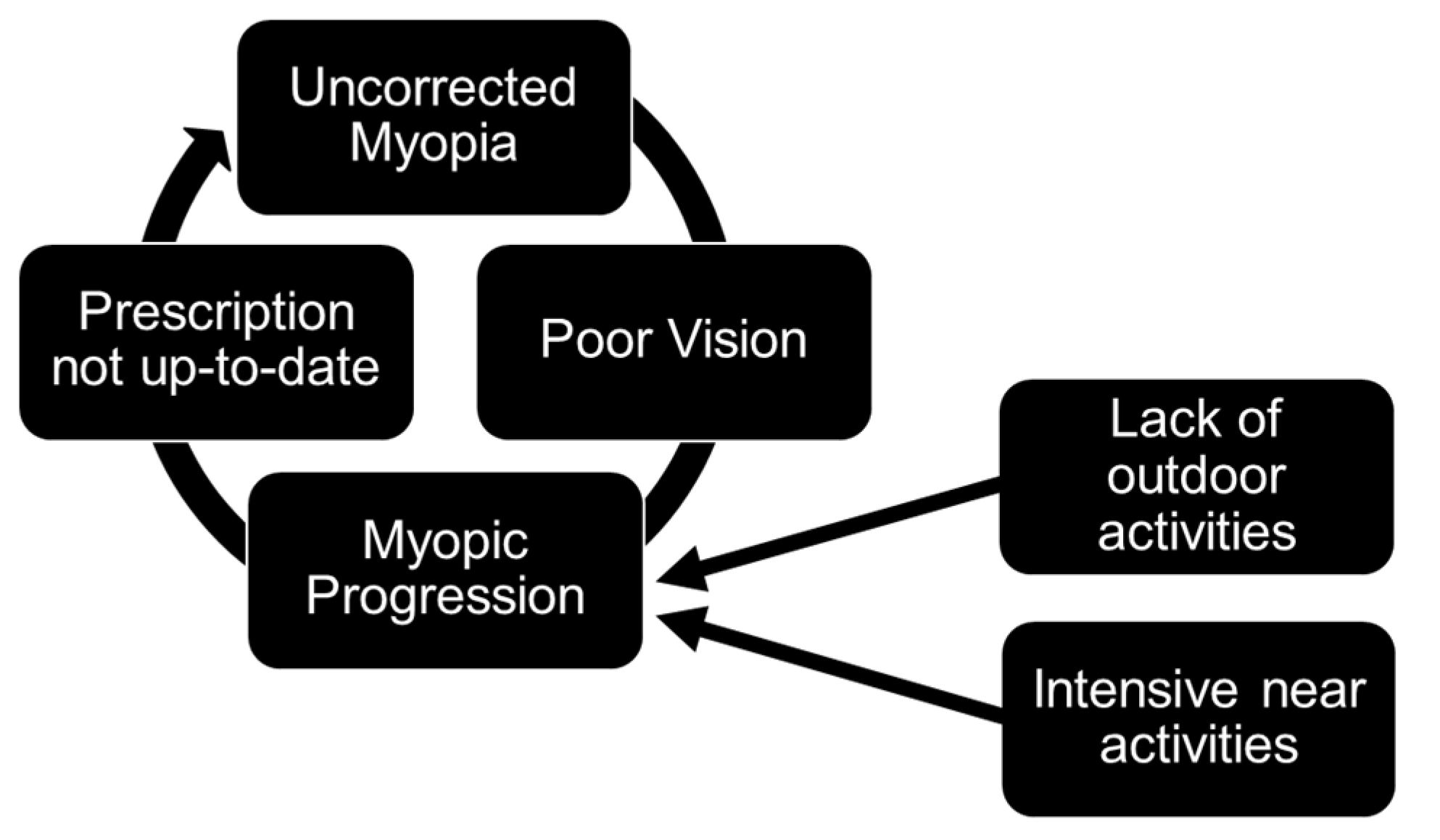
Barriers Affecting the Uptake of Evidence-Based Myopia Interventions in Singapore
Rationale of Pharmaceutical Prescribing Privileges for Optometrists
Aims and Objectives
Methods
Results
Public Health Impact of Pharmaceutical Prescribing Privileges for Optometrists
Feasibility of Pharmaceutical Prescribing Privileges for Optometrists
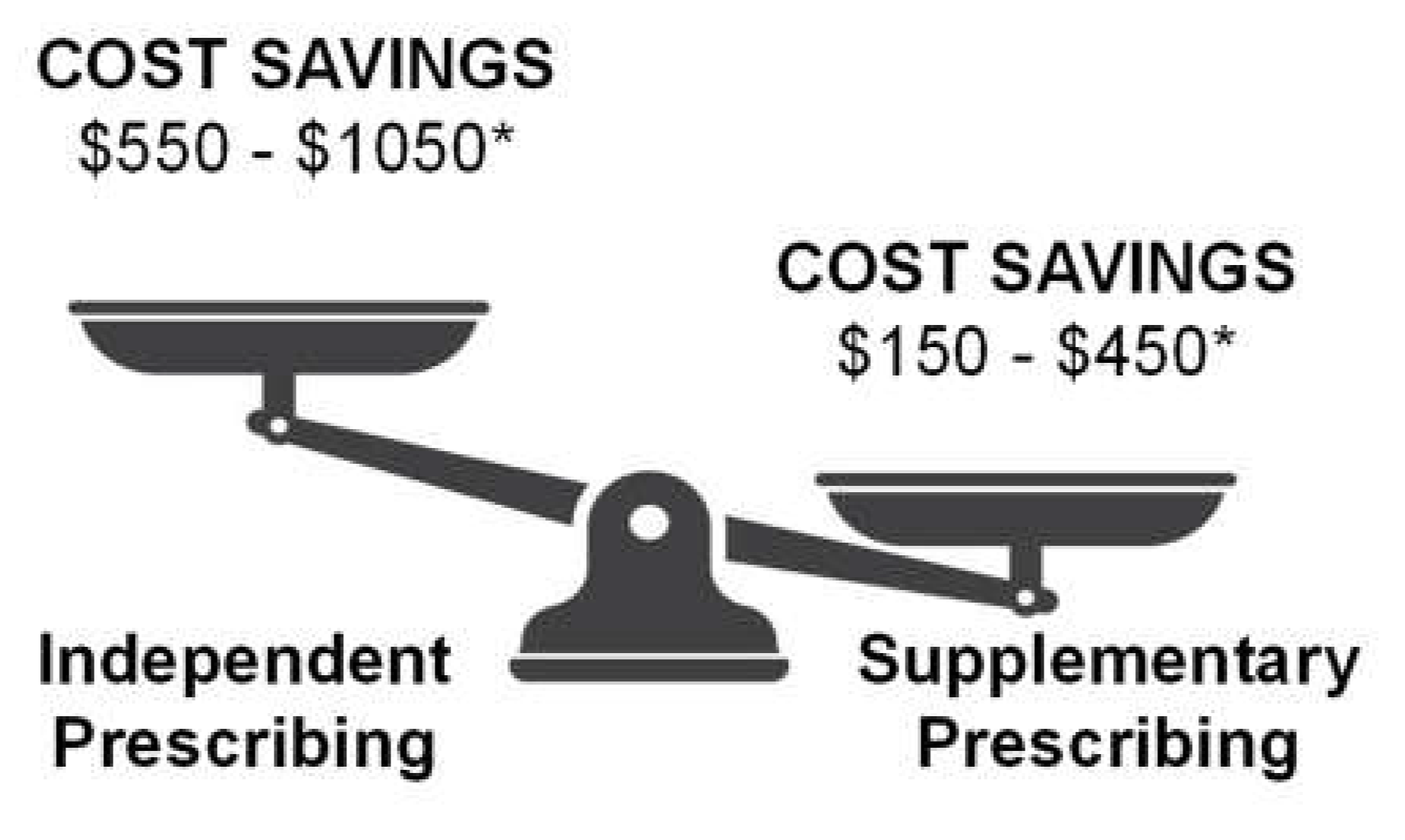
Economic Impact of Pharmaceutical Prescribing Privileges for Optometrists
Budgetary Impact, Disease Burden and Health Inequality
Discussion
Key Policy Solutions and Recommendations
Additional Recommendations and Considerations
Strengths, Limitations and Gaps in the Evidence
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix 1. Summary of the benefits and drawbacks of prescribing privileges for optometrists.
| Author of Articles | Publication Year |
Country (Geographical Region) |
Treatment Domains | Benefits / Drawbacks |
| Jindal, Abdulrasid, Mulholland, et al.[63] | 2024 | United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland) |
Cataract, glaucoma, paediatrics, low vision, external, urgent care clinic, medical retina, and contact lenses. | Hospital optometrists with independent prescribing qualifications had a higher number of advanced skills compared to those without. |
| Carmichael, Abdi, Balaskas, Costanza, and Blandford.[64] | 2022 | United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland) |
Glaucoma, cataract, and medial retina. | Additional training as part of independent prescribing for optometrists helps to reduce false-positive referrals and ease the strain at public hospitals. |
| Cottrell, North, Sheen, and Ryan.[92] | 2022 | United Kingdom (Wales) |
Glaucoma, anterior eye, dry eye, cataract, medical retina, and ocular motor balance. | Independent prescribing by optometrists during the 10-week COVID lockdown helped to reduce the burden on the hospital eye services. |
| Gunn, Creer, Bowen, et al.[66] | 2022 | United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland) |
Cornea, glaucoma, medical retina, cataract, diabetic eye disease, eye casualty, paediatrics, uveitis, neuro-ophthalmology, and laser surgery. | Hospital optometrists are often prescribing independently. A wide variety of clinical procedures or interventions are undertaken by hospital optometrists. A small number of hospital optometrists perform specific laser procedures, including selective laser trabeculoplasty. |
| MacIsaac, Naroo, and Rumney.[93] |
2022 | United Kingdom (England) |
Minor eye conditions include anterior eye, uvea, trauma, glaucoma, post-op inflammation, medical retina, and refractive errors. | With independent prescribing, more than 66% of patients from the hospital can be managed by optometrists in the community. |
| Ansari, Patel, and Harle.[65] | 2022 | United Kingdom (England) |
A variety of acute conditions from the emergency department | During the COVID lockdown, optometrists with independent prescribing privileges were able to safely and efficiently treat and manage the vast majority of urgent cases. |
| Jonuscheit, Geue, Laidlaw, et al.[84] | 2021 | United Kingdom (Scotland) |
Antibacterials, anti-inflammatories and dry eye treatments. | Optometrists in the community are contributing to lessening the burden in primary care. |
| Spillane, Courtenay, Chater, et al.[71] | 2021 | United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland) |
Glaucoma, anterior eye, and medical retina | Optometrists with therapeutics training were more confident in diagnosing and managing specific ocular conditions. Trained and experienced independent prescriber optometrists are able to make appropriate clinical decisions. Poor remuneration, fear of litigation and time/cost of training were barriers. |
| El-Abiary, Loffler, Young, et al.[85] | 2021 | United Kingdom (Scotland) |
Various conditions | With independent prescribing privileges, optometric referrals to public hospitals continued to rise. As age-related eye conditions become more prevalent, more patients require referral to public hospitals. |
| Todd, Bartlett, Thampy, et al. [72] | 2020 | United Kingdom (England) |
General ophthalmology, emergency, uveitis cornea, surgical/vitreo-retina, glaucoma, medical retina, neuro-ophthalmology and oculoplastics. | Clinical decision-making by optometrists with independent prescribing privileges are concordant with ophthalmologists. |
| Steward, MacLure, and George [59] | 2012 | United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland) |
Not reported | Independent prescribing is safe and appropriate. Patient acceptability and satisfaction of independent prescribing was high. |
| Courtenay, Carey, and Stenner [60] | 2012 | United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland) |
Not reported | The low use of supplementary prescribing due to the greater co-working requirement with a medical doctor. |
Appendix 2. Quality of evidence and data from the policy review and analysis on pharmaceutical prescribing privileges for optometrists based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Policy Analysis Framework.
References
- Flitcroft, D.I.; He, M.; Jonas, J.B.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Rahi, J.; Resnikoff, S.; Vitale, S.; Yannuzzi, L. IMI – Defining and Classifying Myopia: A Proposed Set of Standards for Clinical and Epidemiologic Studies. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2019, 60, M20–M30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, S.; Kocur, I.; Resnikoff, S.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.; He, M.; Holden, B.; Salomão, S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Jonas, J.; et al. The impact of myopia and high myopia. Report of the Joint World Health Organization-Brien Holden Vision Institute Global Scientific Meeting on Myopia; World Health Organisation: 2016.
- Dolgin, E. The myopia boom. Nature 2015, 519, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppiah, V.; Wong, L.; Tay, V.; Ge, X.; Kang, L.L. School-based programme to address childhood myopia in Singapore. Singapore Med J 2021, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, B.A.; Fricke, T.R.; Wilson, D.A.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Wong, T.Y.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Resnikoff, S.J.O. Global prevalence of myopia and high myopia and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050. 2016, 123, 1036–1042.
- Ito-Ohara, M.; Seko, Y.; Morita, H.; Imagawa, N.; Tokoro, T. Clinical course of newly developed or progressive patchy chorioretinal atrophy in pathological myopia. Ophthalmologica 1998, 212, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierro, L.; Camesasca, F.I.; Mischi, M.; Brancato, R. Peripheral retinal changes and axial myopia. Retina (Philadelphia, Pa.) 1992, 12, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.; Hourihan, F.; Sandbach, J.; Wang, J.J. The relationship between glaucoma and myopia: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, J.L.; Wong, T.Y.; Yeo, K.T. Trends in the pattern of blindness and major ocular diseases in Singapore and Asia. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore 1998, 27, 540–546. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, S.Y.L.; Foster, P.J. The Economic and Societal Impact of Myopia. In Updates on Myopia: A Clinical Perspective, Ang, M., Wong, T.Y., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp. 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gifford, K.L.; Richdale, K.; Kang, P.; Aller, T.A.; Lam, C.S.; Liu, Y.M.; Michaud, L.; Mulder, J.; Orr, J.B.; Rose, K.A.; et al. IMI - Clinical Management Guidelines Report. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2019, 60, M184–m203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.P.; Boon, M.Y. Electrodiagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Children with Refractive Amblyopia. Advances in Ophthalmology and Optometry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.P.; Luu, C.D.; Suttle, C.M.; Chia, A.; Boon, M.Y. Electrophysiological and Psychophysical Studies of Meridional Anisotropies in Children With and Without Astigmatism. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2019, 60, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.P. , Luu, C.D., Suttle, C.M., Chia, A., Boon, M.Y. Effect of stimulus orientation on visual function in children with refractive amblyopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2020, 61, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.P.; Luu, C.D.; Suttle, C.M.; Chia, A.; Boon, M.Y. Characterising the orientation-specific pattern-onset visual evoked potentials in children with bilateral refractive amblyopia and non-amblyopic controls. Documenta Ophthalmologica 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.P.; Luu, C.D.; Suttle, C.M.; Chia, A.; Boon, M.Y. The development of meridional anisotropies in neurotypical children with and without astigmatism: Electrophysiological and psychophysical findings. Vision Res 2024, 222, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, T.P. Dyslexia and vision: a review of current evidence and clinical interventions. Medical Grapevine Asia 2013, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pirindhavellie, G.-P.; Yong, A.C.; Mashige, K.P.; Naidoo, K.S.; Chan, V.F. The impact of spectacle correction on the well-being of children with vision impairment due to uncorrected refractive error: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannum, E.; Zhang, Y. Poverty and Proximate Barriers to Learning: Vision Deficiencies, Vision Correction and Educational Outcomes in Rural Northwest China. World development 2012, 40, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppenberger, L.S.; Sturm, V. The Role of Time Exposed to Outdoor Light for Myopia Prevalence and Progression: A Literature Review. Clin Ophthalmol 2020, 14, 1875–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sankaridurg, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Naduvilath, T.; He, M.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Morgan, I.G.; Xiong, S.; et al. Time Outdoors in Reducing Myopia: A School-Based Cluster Randomized Trial with Objective Monitoring of Outdoor Time and Light Intensity. Ophthalmology 2022, 129, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flitcroft, D.I.; Harb, E.N.; Wildsoet, C.F. The Spatial Frequency Content of Urban and Indoor Environments as a Potential Risk Factor for Myopia Development. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2020, 61, 42–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerial Statement on the Effectiveness of National Myopia Prevention Programme’s Strategies for Primary School Students. Notice Paper No. 2655 For the sitting of Parliament on 6 March 2024 2024 [cited 2024 29 Sept]; Available online:. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sg/news-highlights/details/effectiveness-of-national-myopia-prevention-programme-s-strategies-for-primary-school-students (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Chua, S.Y.; Sabanayagam, C.; Cheung, Y.B.; Chia, A.; Valenzuela, R.K.; Tan, D.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Saw, S.M. Age of onset of myopia predicts risk of high myopia in later childhood in myopic Singapore children. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2016, 36, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Naduvilath, T.; Zang, J.; Zou, H.; Zhu, J.; Lv, M.; He, X.; Xu, X. Time spent in outdoor activities in relation to myopia prevention and control: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Ophthalmol 2017, 95, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirani, M.; Tong, L.; Gazzard, G.; Zhang, X.; Chia, A.; Young, T.L.; Rose, K.A.; Mitchell, P.; Saw, S.M. Outdoor activity and myopia in Singapore teenage children. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2009, 93, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansah, J.P.; De Korne, D.; Bayer, S.; Pan, C.; Jayabaskar, T.; Matchar, D.B.; Lew, N.; Phua, A.; Koh, V.; Lamoureux, E.; et al. Future requirements for and supply of ophthalmologists for an aging population in Singapore. Human resources for health 2015, 13, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansah, J.P.; Koh, V.; de Korne, D.F.; Bayer, S.; Pan, C.; Thiyagarajan, J.; Matchar, D.B.; Lamoureux, E.; Quek, D. Projection of Eye Disease Burden in Singapore. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore 2018, 47, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, J.; Qu, C. Myopia prevention and control in children: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eye (Lond) 2023, 37, 3461–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, A.; Zhou, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Lim, E.W.; Spiegel, D.P.; et al. Spectacle Lenses With Aspherical Lenslets for Myopia Control vs Single-Vision Spectacle Lenses: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol 2022, 140, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Cai, C.; Ding, Q.; Dai, H. Efficacy and safety of atropine to control myopia progression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Ophthalmology 2020, 20, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yam, J.C.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Tang, S.M.; Li, F.F.; Kam, K.W.; Ko, S.T.; Yip, B.H.K.; Young, A.L.; et al. Three-Year Clinical Trial of Low-Concentration Atropine for Myopia Progression (LAMP) Study: Continued Versus Washout: Phase 3 Report. Ophthalmology 2022, 129, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, A.; Lu, Q.-S.; Tan, D.J.O. Five-year clinical trial on atropine for the treatment of myopia 2: myopia control with atropine 0. 01% eyedrops. 2016, 123, 391–399. [Google Scholar]
- Bullimore, M.A.; Ritchey, E.R.; Shah, S.; Leveziel, N.; Bourne, R.R.A.; Flitcroft, D.I. The Risks and Benefits of Myopia Control. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 1561–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.; Eisenberg, N.; Schulman, E.; Wang, F.M. Maximum atropine dose without clinical signs or symptoms. Optom Vis Sci 2013, 90, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanca, C.; Pang, C.P.; Grzybowski, A. Effectiveness of myopia control interventions: A systematic review of 12 randomized control trials published between 2019 and 2021. Frontiers in public health 2023, 11, 1125000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, J. The effect of 0.01% atropine and orthokeratology on ocular axial elongation for myopia children: A meta-analysis (a PRISMA-compliant article). Medicine 2022, 101, e29191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.N.; Tan, K.W. The synergistic efficacy and safety of combined low-concentration atropine and orthokeratology for slowing the progression of myopia: A meta-analysis. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2022, 42, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, R.K.M.; Hon, Y.; Law, T.K.; Wong, K.Y.Q.; To, C.H.; Shih, K.C.; Leung, C.K.S.; Tse, D.Y.Y. Combination effect of optical defocus and low dose atropine in myopia control: Study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. PLoS One 2024, 19, e0306050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Williams, B.T.; Qiu, K. Photobiomodulation therapy retarded axial length growth in children with myopia: evidence from a 12-month randomized controlled trial evidence. Scientific reports 2023, 13, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Bao, J.; Singh, N.; Drobe, B.; Chen, H. The Effects of Spatial Frequency on the Accommodative Responses of Myopic and Emmetropic Chinese Children. Translational Vision Science & Technology 2019, 8, 65–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, N.S.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Cruickshank, F.E.; Allen, P.M.; Bandela, P.K.; Davies, L.N.; Hasebe, S.; Khanal, S.; Schmid, K.L.; Vera-Diaz, F.A.; et al. IMI Accommodation and Binocular Vision in Myopia Development and Progression. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2021, 62, 4–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Whayeb, Y.; Logan, N.S.; Weng, R. IMI-Global Trends in Myopia Management Attitudes and Strategies in Clinical Practice-2022 Update. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2023, 64, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, N.; Sadeghi, R.; Ehsaei, A.; Taghipour, A.; Hasanzadeh, S.; Zarifmahmoudi, L.; Heravian Shandiz, J. Under-correction or full correction of myopia? A meta-analysis. J Optom 2021, 14, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, N.S.; Wolffsohn, J.S. Role of un-correction, under-correction and over-correction of myopia as a strategy for slowing myopic progression. Clin Exp Optom 2020, 103, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P.P.; Yun, O.C.S.; Siow, K.; Saxena, N.; Heng, B.H.; Car, J.; Lockwood, C. Is there scope for expanding the optometrist's scope of practice in Singapore? - A survey of optometrists, opticians in Singapore. Contact lens & anterior eye : the journal of the British Contact Lens Association 2019, 42, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, R.; Huang, D.; Lin, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Prediction of premyopia and myopia in Chinese preschool children: a longitudinal cohort. BMC Ophthalmology 2021, 21, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tan, C.; Foo, L.L.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Bulloch, G.; Saw, S.M.; Li, J.; Morgan, I.; Guo, X.; et al. Development and Validation of a Model to Predict Who Will Develop Myopia in the Following Year as a Criterion to Define Premyopia. Asia-Pacific journal of ophthalmology (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2023, 12, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee PS, C.P. The Medical Profession and Pharmaceuticals: In-clinic Dispensing: Principles and Practice. Singapore Medical Association Publication 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Calossi, A.; Cho, P.; Gifford, K.; Jones, L.; Jones, D.; Guthrie, S.; Li, M.; Lipener, C.; Logan, N.S.; et al. Global trends in myopia management attitudes and strategies in clinical practice – 2019 Update. Contact Lens and Anterior Eye 2020, 43, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friel, S.; Collin, J.; Daube, M.; Depoux, A.; Freudenberg, N.; Gilmore, A.B.; Johns, P.; Laar, A.; Marten, R.; McKee, M.; et al. Commercial determinants of health: future directions. The Lancet 2023, 401, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optometrists and Opticians Act 2007 Singapore Statues: Singapore.
- Position Paper: The Sight Test: Refraction and Examinations of the Eye for the Purpose of Detecting Injury, Disease or Abnormality: The Public Health Case 2020, World Council of Optometry.
- Majithia, S.; Thakur, S. Differences in Optometry Practices Across the Globe. In Current Advances in Optometry, Shu, D., Singh, R.B., Ichhpujani, P., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, K.; Chen, J.; Ho, M.; Gammoh, Y.; Jansen, L.; DeSouza, N.; Lim, A.; Fitzpatrick, G.; Neuville, J. Advancing optometry education through global frameworks and international collaborations. Clinical and Experimental Optometry 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roving Optical Shop Within School Grounds As Part Of Enhanced Assistance Scheme For Needy Students With Myopia. Available online: https://www.hpb.gov.sg/newsroom/article/roving-optical-shop-within-school-grounds-as-part-of-enhanced-assistance-scheme-for-needy-students-with-myopia (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Naidoo, K.S.; Fricke, T.R.; Frick, K.D.; Jong, M.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Resnikoff, S.; Sankaridurg, P. Potential Lost Productivity Resulting from the Global Burden of Myopia: Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Modeling. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khee, G.Y.; Lim, P.S.; Chan, Y.L.; Lee, P.C. Collaborative Prescribing Practice in Managing Patients Post-Bariatric Surgery in a Tertiary Centre in Singapore. 2024, 12, 31. 12.
- Stewart, D.; MacLure, K.; George, J. Educating nonmedical prescribers. British journal of clinical pharmacology 2012, 74, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtenay, M.; Carey, N.; Stenner, K. An overiew of non medical prescribing across one strategic health authority: a questionnaire survey. BMC Health Services Research 2012, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, A.; Mason, J. Optometrist prescribing of therapeutic agents: findings of the AESOP survey. Health policy (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 2002, 60, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Li, F.J.; Sun, C.C.; Liao, L.L. Trajectories of myopia control and orthokeratology compliance among parents with myopic children. Contact lens & anterior eye : the journal of the British Contact Lens Association 2021, 44, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.; Abdulrasid, S.; Mulholland, P.J.; Anand, V.; Siriwardena, D. An evaluation of optometric advanced skills within a UK tertiary based setting. Eye 2024, 38, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, J.; Abdi, S.; Balaskas, K.; Costanza, E.; Blandford, A. The effectiveness of interventions for optometric referrals into the hospital eye service: A review. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2023, 43, 1510–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, E.; Patel, M.; Harle, D. Acute community ophthalmology services provided by independent prescribing optometrists supporting hospital eye services during the COVID-19 outbreak. J Optom 2022, 15, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, P.J.G.; Creer, R.C.; Bowen, M.; Tromans, C.; Jackson, A.J.; Tompkin, A.P.; Harper, R.A. Scope of practice of optometrists working in the UK Hospital Eye Service: Second national survey. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2022, 42, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumber, R.; Khoosal, D.; Gajebasia, N. Non-medical prescribing: audit, practice and views. Journal of psychiatric and mental health nursing 2012, 19, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eze, B.I.; Okoye, O.; Aguwa, E.N. Public's knowledge of the differences between ophthalmologists and optometrists: a critical issue in eye care service utilisation. Int J Ophthalmol 2016, 9, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violato, M.; Dakin, H.; Chakravarthy, U.; Reeves, B.C.; Peto, T.; Hogg, R.E.; Harding, S.P.; Scott, L.J.; Taylor, J.; Cappel-Porter, H.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of community versus hospital eye service follow-up for patients with quiescent treated age-related macular degeneration alongside the ECHoES randomised trial. BMJ open 2016, 6, e011121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banes, M.J.; Culham, L.E.; Bunce, C.; Xing, W.; Viswanathan, A.; Garway-Heath, D. Agreement between optometrists and ophthalmologists on clinical management decisions for patients with glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol 2006, 90, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillane, D.; Courtenay, M.; Chater, A.; Family, H.; Whitaker, A.; Acton, J.H. Factors influencing the prescribing behaviour of independent prescriber optometrists: a qualitative study using the Theoretical Domains Framework. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2021, 41, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.; Bartlett, H.; Thampy, R.; Dhawahir-Scala, F.; Wilson, H.; Tromans, C. Agreement in clinical decision-making between independent prescribing optometrists and consultant ophthalmologists in an emergency eye department. Eye (Lond) 2020, 34, 2284–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jampol, L.M.; Packer, S.; Mills, R.P.; Day, S.H.; Lichter, P.R.; Society, C.o.t.A.O. A Perspective on Commercial Relationships Between Ophthalmology and Industry. Archives of Ophthalmology 2009, 127, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical Highlights: New BAU Roster. EyeSight - A newsletter by EYE ACP, S: Ophthalmology and Visual Science Academic Clinical Programme.
- Tsai, W.Y.Y. , Husain, R., Lim, H.B., Yeo, W.L., Foo, F.C.Y., Ang, D.W.H. Reducing congestion and patient dwell time in SNEC by frontloading pre-consultation eye evaluation into the community (Poster). Singapore Healthcare Management.
- Zaidi, S.A. Planning in the health sector: for whom, by whom? Social science & medicine (1982) 1994, 39, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essex, R.; Kennedy, J.; Miller, D.; Jameson, J. A scoping review exploring the impact and negotiation of hierarchy in healthcare organisations. 2023, 30, e12571. [CrossRef]
- Low, K.X. , Lim, T.G., Wong, A., et. al. Implementation and evaluation of a collaborative patient review and medication prescribing model in the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Short Stay Ward for biologic administration (Poster). Value-based Healthcare Conference, Singapore.
- Barrett, C.; Loughman, J. Expanding the traditional role of optometry: Current practice patterns and attitudes to enhanced glaucoma services in Ireland. J Optom 2018, 11, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kea, B.; Sun, B.C. Consensus development for healthcare professionals. Internal and emergency medicine 2015, 10, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Burgess-Limerick, R.; Stapleton, F. What do clinical optometrists like about their job? Clin Exp Optom 2013, 96, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.C.; Gazzard, G.; Sim, E.L.; Tong, L.; Saw, S.M. Direct costs of myopia in Singapore. Eye (Lond) 2009, 23, 1086–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-F.; Pan, C.-W.; Chay, J.; Wong, T.Y.; Finkelstein, E.; Saw, S.-M. The Economic Cost of Myopia in Adults Aged Over 40 Years in Singapore. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2013, 54, 7532–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonuscheit, S.; Geue, C.; Laidlaw, R.; Fischbacher, C.; Melia, B.; Lewsey, J.; King, C. Towards transforming community eye care: an observational study and time-series analysis of optometrists' prescribing for eye disorders. Public health 2021, 196, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Abiary, M.; Loffler, G.; Young, D.; Strang, N.; Lockington, D. Assessing the effect of Independent Prescribing for community optometrists and referral rates to Hospital Eye Services in Scotland. Eye (Lond) 2021, 35, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.Y.; Boyd, M.; Wilson, G.; Hong, S.C. Photorefraction Screening Plus Atropine Treatment for Myopia is Cost-Effective: A Proof-of-Concept Markov Analysis. Clin Ophthalmol 2022, 16, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claxton, L.; Malcolm, B.; Taylor, M.; Haig, J.; Leteneux, C. Ranibizumab, verteporfin photodynamic therapy or observation for the treatment of myopic choroidal neovascularization: cost effectiveness in the UK. Drugs & aging 2014, 31, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bakal, J. THE VALUE COMPONENT OF EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE: The Cost-Utility of Photodynamic Therapy for Pathologic Myopia. Evidence-Based Ophthalmology 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Janowski, M.; Luo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, B.; Yang, G.; Liu, L. Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Atropine in Childhood Myopia: A Meta-analysisEfficacy and Adverse Effects of Atropine in Childhood MyopiaEfficacy and Adverse Effects of Atropine in Childhood Myopia. JAMA Ophthalmology 2017, 135, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congdon, N.G.; Patel, N.; Esteso, P.; Chikwembani, F.; Webber, F.; Msithini, R.B.; Ratcliffe, A. The association between refractive cutoffs for spectacle provision and visual improvement among school-aged children in South Africa. Br J Ophthalmol 2008, 92, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, M.G.; Nandy, A. Singapore's policy responses to ageing, inequality and poverty: An assessment. 2008, 61, 41–60. [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, P.; North, R.; Sheen, N.; Ryan, B. Optometry independent prescribing during COVID lockdown in Wales. 2022, 42, 1289–1303. [CrossRef]
- MacIsaac, J.C.; Naroo, S.A.; Rumney, N.J. Analysis of UK eye casualty presentations. Clin Exp Optom 2022, 105, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurjono, M.; Yoong, J.; Yap, P.; Wee, S.L.; Vrijhoef, H.M.J. Implementation of Integrated Care in Singapore: A Complex Adaptive System Perspective. International Journal of Integrated Care 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irtza, M.; Mahwish, R.; Mohamin, M.; Afzal, M.S.; Ali, M.Q.; Waqar, M.S. Non-compliance of Spectacle Wear in School-Going Children With Refractive Errors. Cureus 2024, 16, e52702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.-C.; Sun, C.-C.; Liao, L.-L. Compliance with orthokeratology care among parents of young children in Taiwan. Contact Lens and Anterior Eye 2021, 44, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, D.M.; Jethani, J. Compliance in usage of low-dose atropine for prevention of progression of myopia in Indian children. Indian journal of ophthalmology 2021, 69, 2230–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Ctori, I.; Shah, R.; Suttle, C.; Conway, M.L. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the agreement of non-cycloplegic and cycloplegic refraction in children. 2022, 42, 1276–1288. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Wei, S.F.; Li, S.M.; Hu, J.P.; Yang, X.H.; Cao, K.; Lin, C.X.; Du, J.L.; Guo, J.Y.; Li, H.; et al. Cycloplegic refraction by 1% cyclopentolate in young adults: is it the gold standard? The Anyang University Students Eye Study (AUSES). Br J Ophthalmol 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimouni, M.; Zoller, L.; Horowitz, J.; Wygnanski-Jaffe, T.; Morad, Y.; Mezer, E. Cycloplegic autorefraction in young adults: is it mandatory? Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology 2016, 254, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaridurg, P.; He, X.; Naduvilath, T.; Lv, M.; Ho, A.; Smith, E., 3rd; Erickson, P.; Zhu, J.; Zou, H.; Xu, X. Comparison of noncycloplegic and cycloplegic autorefraction in categorizing refractive error data in children. Acta Ophthalmol 2017, 95, e633–e640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, S. , Coombes, I. The right to prescribe: towards core prescribing competencies for all prescribers, in Australia Prescriber. 2011: Website: https://australianprescriber.tg.org.au/articles/the-right-to-prescribe-towardscore-prescribing-competencies-for-all-prescribers.html (Accessed on 27 Sept 2024).
- Nalley, C. Prescribe Oral Meds Like a Pro, in Review of Optometry. 2022: Website: https://www.reviewofoptometry.com/article/prescribe-oral-meds-like-a-pro (Accessed on 27 Sept 2024).
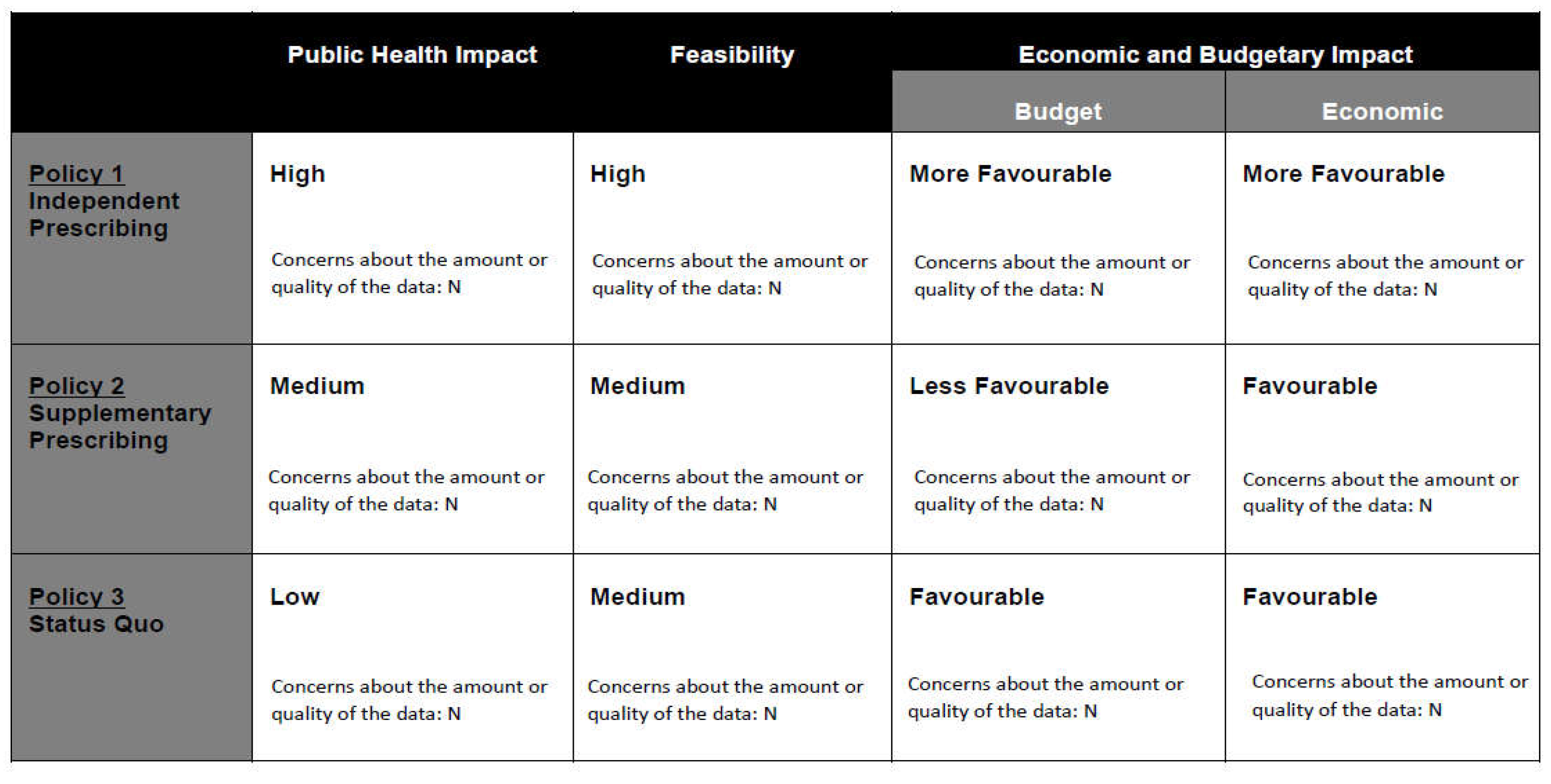
|
Policy 1 Independent Prescribing |
Policy 2 Supplementary Prescribing |
Policy 3 Status Quo |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Public Health Impact |
(1) Increases access and reduces barriers by streamline treatment processes so that all tests can be completed within one visit; reduces wait time and inconvenience. (2) Children with myopia are at risk; high prevalence in Singapore (3) Likely to reduce health disparity due to lower treatment costs. (4) Evidence is strong concerning myopia control. |
(1) Increases access and reduces barriers by streamline treatment processes so that all tests can be completed within one visit; reduces wait time and inconvenience. (2) Children with myopia are at risk; high prevalence in Singapore (3) Likely to reduce health disparity due to lower treatment costs. (4) Evidence is strong concerning myopia control. |
(1) Delayed interventions due to barriers, (2) Children are not getting the most effective myopia control approaches. (3) Health disparity as a result of high treatment costs. (4) Strong evidence showing barriers to treatment. |
| Feasibility |
Political (1) Pushback from ophthalmologists due to traditional mindset and vested interests. (2) Consumers may support lower cost treatment if it is made available (3) Patients may perceive service is poorer from optometrists (4) Substantial cost-savings to patient and substantially reduces healthcare costs. |
Political 1) Ophthalmologists are more likely to agree with co-management due to shared fee structure. (2) Consumers may support as it may add an extra layer of safety in the prescribing. (3) Patients may be confused if tests need to be repeated. (4) Moderate cost-saving and has little impact on healthcare costs |
Political 1) Ophthalmologists tend to favour status quo due to vested interests. (2) Consumers may worry that optometrists are not well trained to prescribe medications. (3) Patients may lack understanding on myopia control (4) Costs are high due to multiple separate visits to both optometrist and ophthalmologists |
|
Operational (1) Legislation and regulatory changes may be necessary (2) Two years to be enacted, implemented and enforced. (3) Uptake is likely and is scalable. |
Operational (1) Legislation and regulatory changes may be necessary (2) Unpredictable due to contractual agreements and commercial interests. (3) Not likely to be sustainable due to possible contractual disagreements. |
Operational (1) Legislation and regulatory changes not required (2) Not applicable. (3) Not likely to improve public access to treatment. |
|
|
Economic and Budgetary Impact |
Budget (1) Minimal costs required |
Budget (1) Moderate costs required for system level changes |
Budget (1) No impact |
|
Economic (1) Substantial cost-savings to patients (2) Potentially reduce healthcare cost and disease burden due to reduced prevalence of myopia and healthcare costs. (3) Good evidence showing that myopia control can work; data gap in some areas. |
Economic (1) Moderate cost-savings to patients (2) Unlikely to reduce healthcare cost and disease burden (3) Good evidence showing that myopia control can work; data gap in some areas. |
Economic (1) High treatment costs which is entirely out-of-pocket (2) Healthcare costs of myopia is high in Singapore (3) Evidence shows barriers are significantly hindering treatment uptake. |
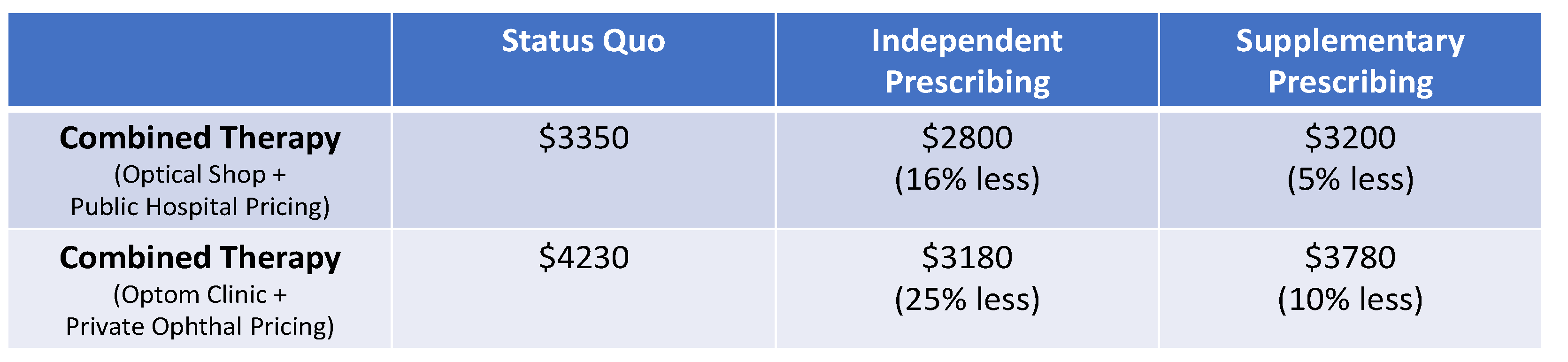
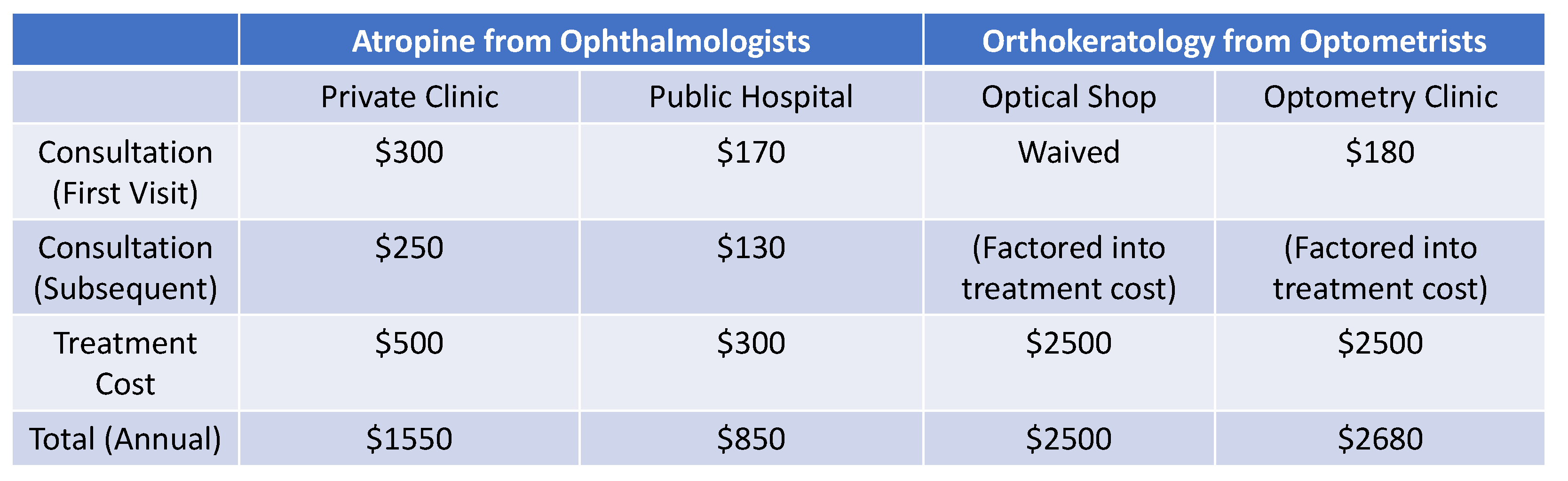
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




