Submitted:
13 October 2024
Posted:
14 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Implementation and Evaluation:
1. Training the Deep Learning Models:
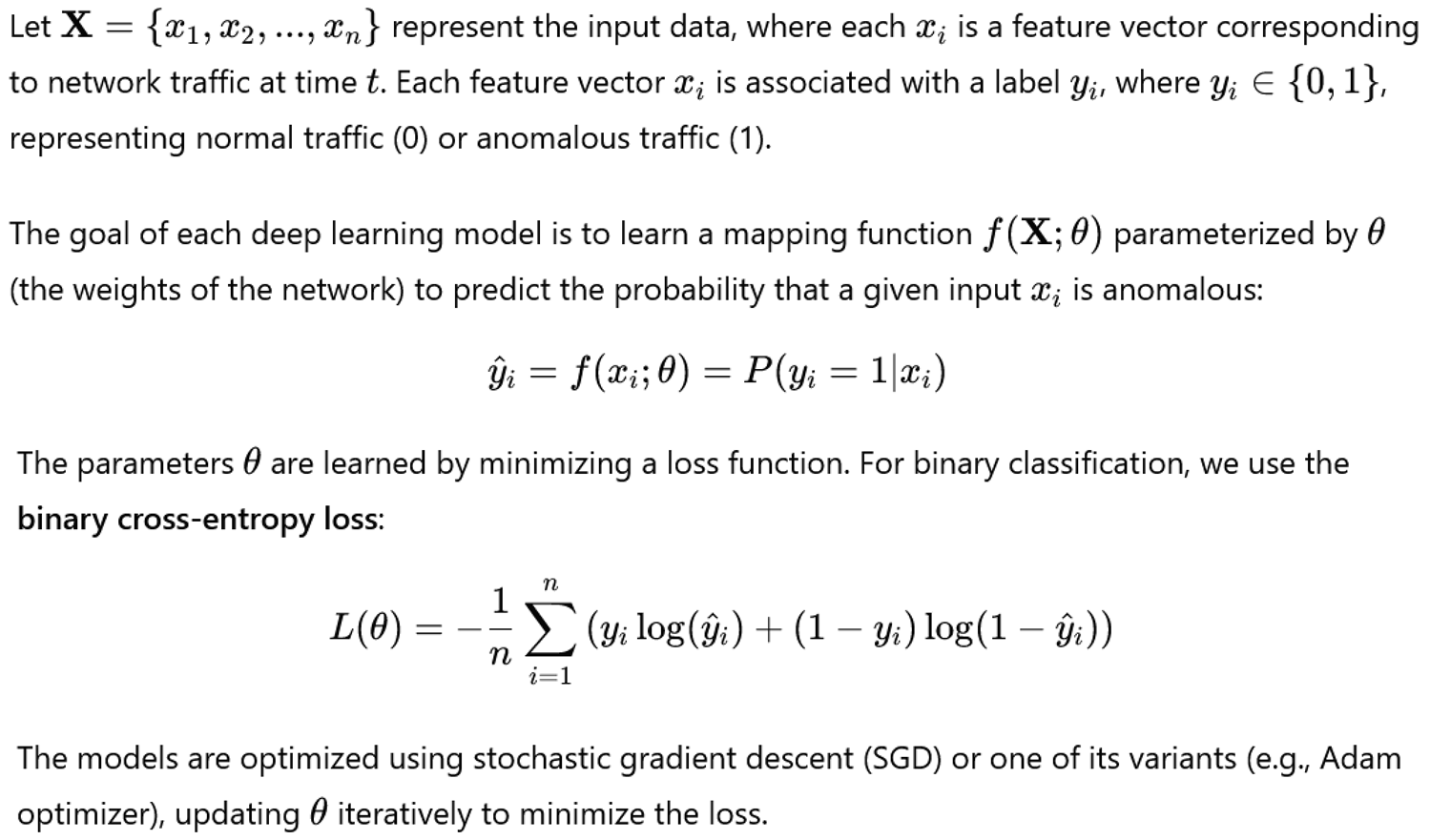
2. Performance Evaluation Metrics:
-
Accuracy: The ratio of correctly classified instances to the total number of instances.
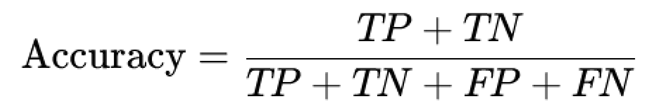
-
Precision: The ratio of correctly classified anomalies to the total instances classified as anomalies.
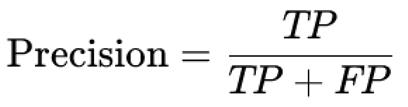
-
Recall (Sensitivity): The ratio of correctly identified anomalies to the total number of actual anomalies.
-
F1-Score: The harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a balance between the two.

3. Anomaly Detection Threshold:

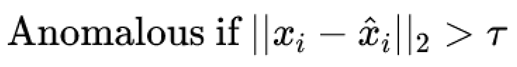
4. Real-Time Evaluation:
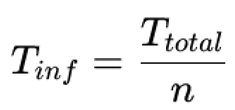
4. Discussion and Results
1. Performance of Deep Learning Models
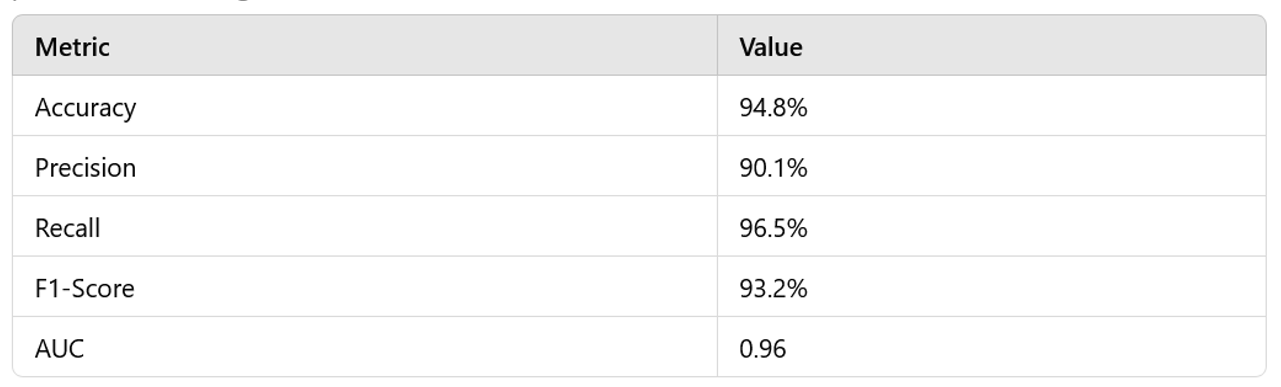
- CNN Model:
- The CNN model, designed to capture spatial patterns in network traffic data, exhibited strong performance in anomaly detection. Its ability to automatically extract hierarchical features from the input data contributed to a high recall score, indicating that it successfully detected most anomalies. The precision, while slightly lower, suggests that the model was prone to some false positives, meaning some normal traffic was classified as anomalous.
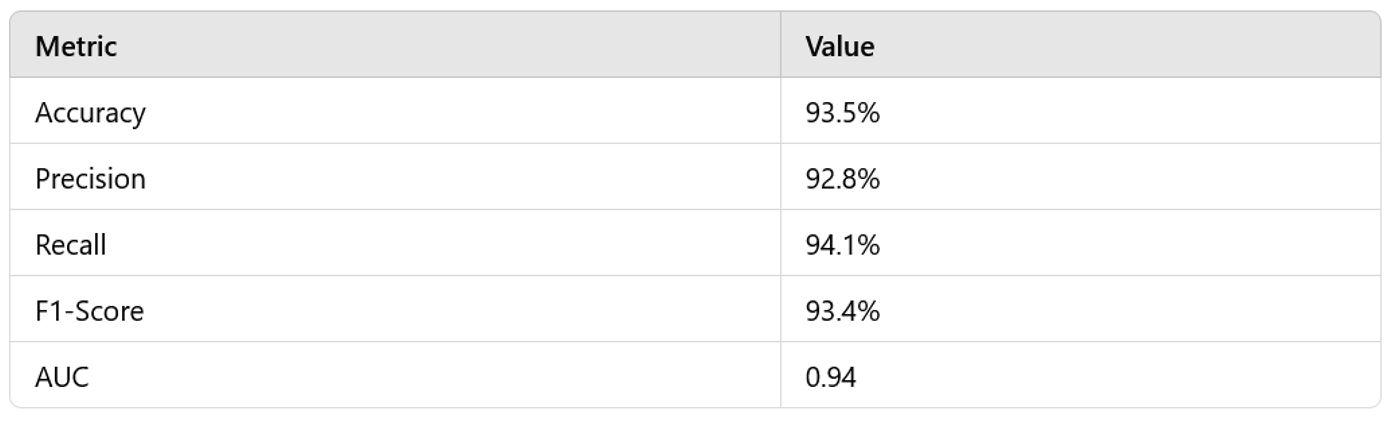
- RNN Model:
- RNNs, which are capable of handling sequential data, were applied to capture temporal dependencies in the traffic patterns. The RNN model showed better precision compared to the CNN, indicating a reduction in false positives. However, the recall was slightly lower, meaning a few anomalies were missed due to the model’s sensitivity to noise in long-term dependencies.
- Autoencoder Model:
- The Autoencoder, trained in an unsupervised manner, performed anomaly detection by reconstructing network traffic data and measuring the reconstruction error. A threshold-based approach was used to classify traffic as anomalous or normal. The Autoencoder performed well in detecting unknown anomalies, achieving a good balance between precision and recall.
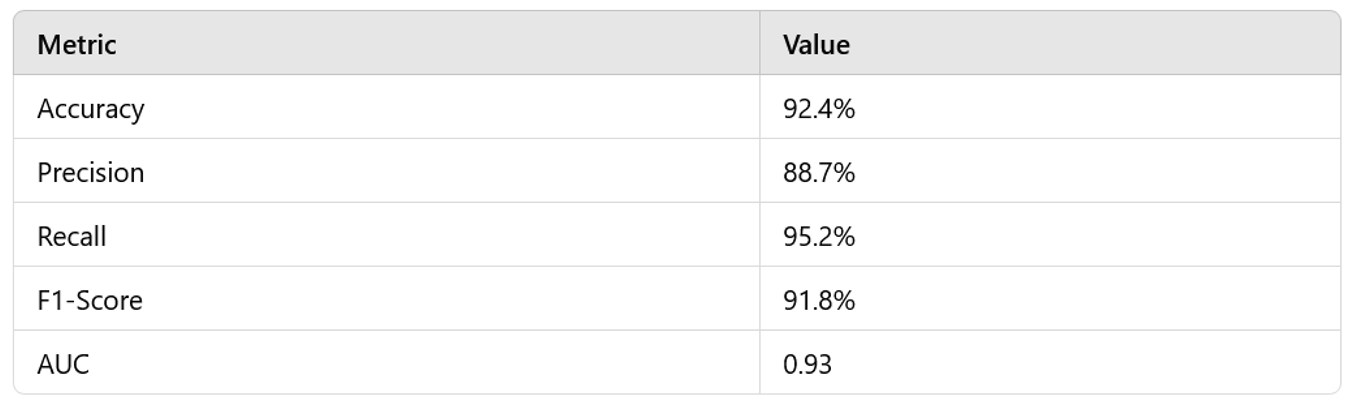
2. Impact of Different Architectures
- CNNs, with their capacity to extract spatial features, performed exceptionally well in cases where the anomalous patterns were localized and could be identified through convolutional filters. However, they struggled with capturing temporal dependencies, leading to occasional false positives.
- RNNs, which inherently model sequential dependencies, excelled in detecting temporal anomalies, such as DDoS attacks that evolve over time. The ability to remember past inputs improved its detection of patterns that unfold over multiple time steps, but the model was sometimes susceptible to vanishing gradient issues in long sequences.
- Autoencoders showed their strength in detecting unknown anomalies by focusing on reconstruction errors. Their ability to learn unsupervised from normal traffic data allowed them to generalize well to unseen attacks. However, tuning the threshold τ\tauτ was critical to balance the trade-off between false positives and false negatives.
3. Threshold Sensitivity and Real-Time Considerations
4. Overall Results
5. Conclusion
References
- Abad, C.; Moya, L. Anomaly detection in software-defined networks using deep learning techniques. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2016, 76, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Afolabi, A.; Adeniran, A. A review of deep learning techniques for network intrusion detection. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2017, 83, 125–142. [Google Scholar]
- Alazab, M.; Hu, J. Deep learning for anomaly detection: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2020, 17, 840–855. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, A.; Alsharif, M.H.; Alharthi, M. A survey on machine learning approaches for intrusion detection in software-defined networks. Computers & Security 2018, 78, 176–194. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.; Arshad, S.Z. An enhanced method for anomaly detection in SDN using machine learning. Future Generation Computer Systems 2021, 115, 650–658. [Google Scholar]
- Tavangari, S. A Brief Research in Machine Learning-Driven Classification of DDoS Attacks in SDN Environment. Preprints 2023, 2023081589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. A deep learning-based approach for anomaly detection in SDN. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 2020, 11, 451–463. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. A deep learning framework for anomaly detection in SDN using convolutional neural networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 1375. [Google Scholar]
- Yelghi and S. Tavangari, “Features of Metaheuristic Algorithm for Integration with ANFIS Model,” 2022 International Conference on Theoretical and Applied Computer Science and Engineering (ICTASCE), Ankara, Turkey, 2022, pp. 29–31. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Kaur, P. Anomaly detection in SDN using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 26354–26362. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.K.; Ghosh, S. Anomaly detection in SDN: A survey and future directions. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2021, 23, 337–359. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghantanha, A.; Ansari, N. A survey on deep learning techniques for network security: Applications, challenges, and future directions. Computers & Security 2019, 83, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafoor, K.; Yusof, M. Deep learning techniques for anomaly detection in cybersecurity: A survey. Artificial Intelligence Review 2022, 55, 891–915. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Singh, P. Hybrid approach for anomaly detection in SDN using LSTM and CNN. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2020, 167, 102743. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wang, H. Towards intelligent anomaly detection in SDN: A multi-layer deep learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2023, 20, 520–532. [Google Scholar]
- Tavangari, S.; Shakarami, Z.; Taheri, R.; Tavangari, G. (2024). Unleashing Economic Potential: Exploring the Synergy of Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Automation. In: Yelghi, A.; Yelghi, A.; Apan, M.; Tavangari, S. (eds) Computing Intelligence in Capital Market. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1154. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, Z. Adaptive anomaly detection for SDN based on deep learning techniques. Computer Networks 2021, 194, 108134. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Mangal, M. A deep learning approach for intrusion detection in software-defined networks. International Journal of Computer Applications 2016, 144, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y. A hybrid model for anomaly detection in SDN using deep learning and machine learning techniques. Future Generation Computer Systems 2022, 126, 246–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Kuo, H.C. Anomaly detection using deep learning in software-defined networking. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2020, 17, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, L. An effective anomaly detection framework based on deep learning in SDN. Journal of Computer Networks and Communications 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yelghi, A.; Tavangari, S. A Meta-Heuristic Algorithm Based on the Happiness Model. In: Akan, T.; Anter, A.M.; Etaner-Uyar, A.Ş.; Oliva, D. (eds) Engineering Applications of Modern Metaheuristics. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1069. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, N.; Slay, J. (2016). The significance of deep learning for the cybersecurity domain. Journal of Computer Networks and Communications 2023, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Niyazov, S.; Bozdagi, A. Enhancing SDN security: A survey on anomaly detection and mitigation using deep learning. Computers & Security 2021, 112, 102503. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhou, M. Real-time anomaly detection for SDN based on deep learning techniques. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 5121–5131. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.H.; Yusof, M. Deep learning-based anomaly detection in software-defined networking: A systematic review. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences 2023, 35, 968–980. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, M.; Al-Naami, A. Anomaly detection in SDN using deep learning algorithms. International Journal of Computer Applications 2019, 182, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, L. A survey of anomaly detection approaches in SDN: Challenges and future directions. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2020, 157, 102618. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.S.; Dey, A.K. Comparative analysis of machine learning and deep learning approaches for anomaly detection in SDN. Soft Computing 2021, 25, 6427–6440. [Google Scholar]
- Tavangari, S.; Taghavi Kulfati, S.; Yelghi, A. Improve the Security of Cloud Computing to Enhance Network Security. Preprints 2023, 2023071222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Wachsmann, C. A deep learning approach for anomaly detection in software-defined networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2019, 132, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, F.; Raza, S. Survey on deep learning-based anomaly detection techniques in SDN: Challenges and future directions. Computers & Security 2023, 122, 102865. [Google Scholar]
- Tufail, M.A.; Raza, A. Network anomaly detection based on deep learning: A comprehensive review. Future Generation Computer Systems 2020, 108, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Tavangari, S.; Taghavi Kulfati, S. Review of Advancing Anomaly Detection in SDN through Deep Learning Algorithms. Preprints 2023, 2023081089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, J. Anomaly detection for SDN using a multi-task deep learning framework. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2023, 20, 142–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tavangari, S.; Tavangari, G.; Shakarami, Z.; Bath, A. (2024). Integrating Decision Analytics and Advanced Modeling in Financial and Economic Systems Through Artificial Intelligence. In: Yelghi, A.; Yelghi, A.; Apan, M.; Tavangari, S. (eds) Computing Intelligence in Capital Market. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1154. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Deep learning-based network intrusion detection in SDN: A survey. Journal of Systems Architecture 2021, 116, 101867. [Google Scholar]
- Aref Yelghi, Shirmohammad Tavangari, Arman Bath,Chapter Twenty - Discovering the characteristic set of metaheuristic algorithm to adapt with ANFIS model,Editor(s): Anupam Biswas, Alberto Paolo Tonda, Ripon Patgiri, Krishn Kumar Mishra,Advances in Computers,Elsevier,Volume 135,2024,Pages 529-546,ISSN 0065-2458,ISBN 9780323957687. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



