Submitted:
17 June 2024
Posted:
18 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Presentation
2.2. Audiological Tests Methodology
2.3. Methodology of Intraoperative Hearing Monitoring
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
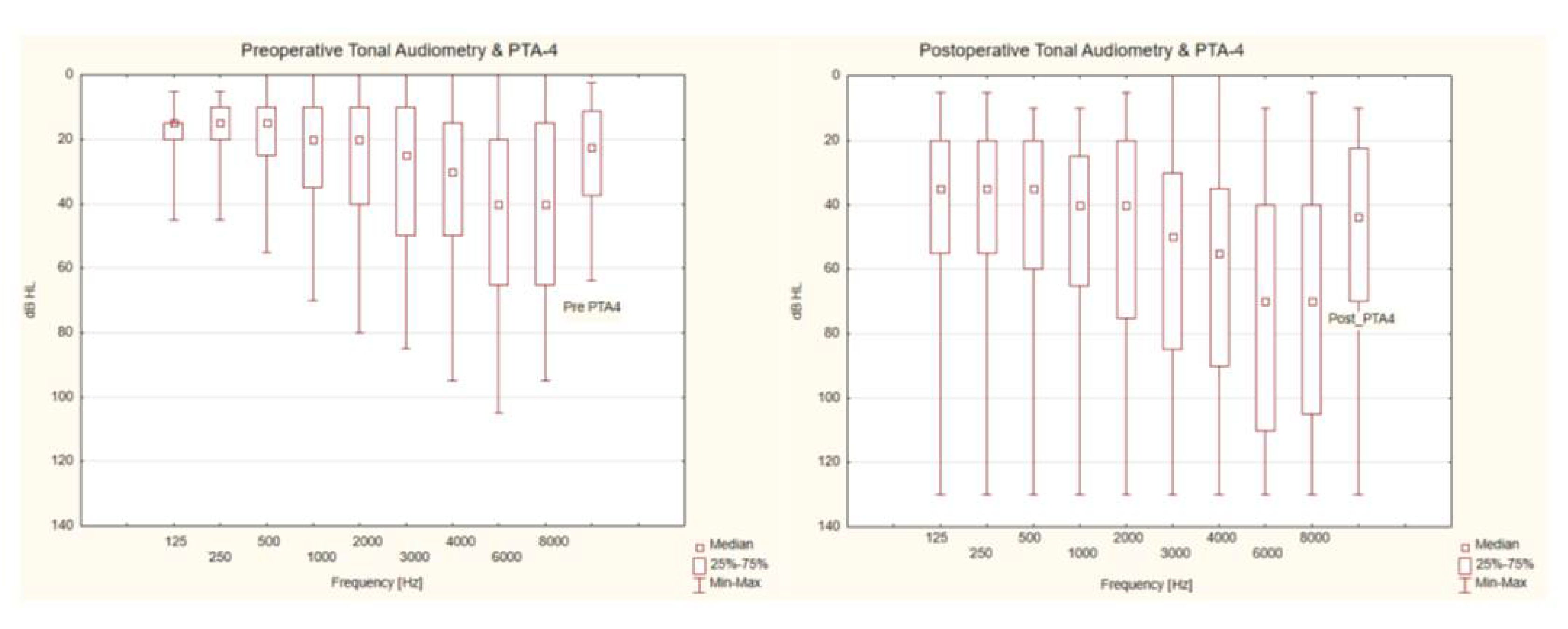
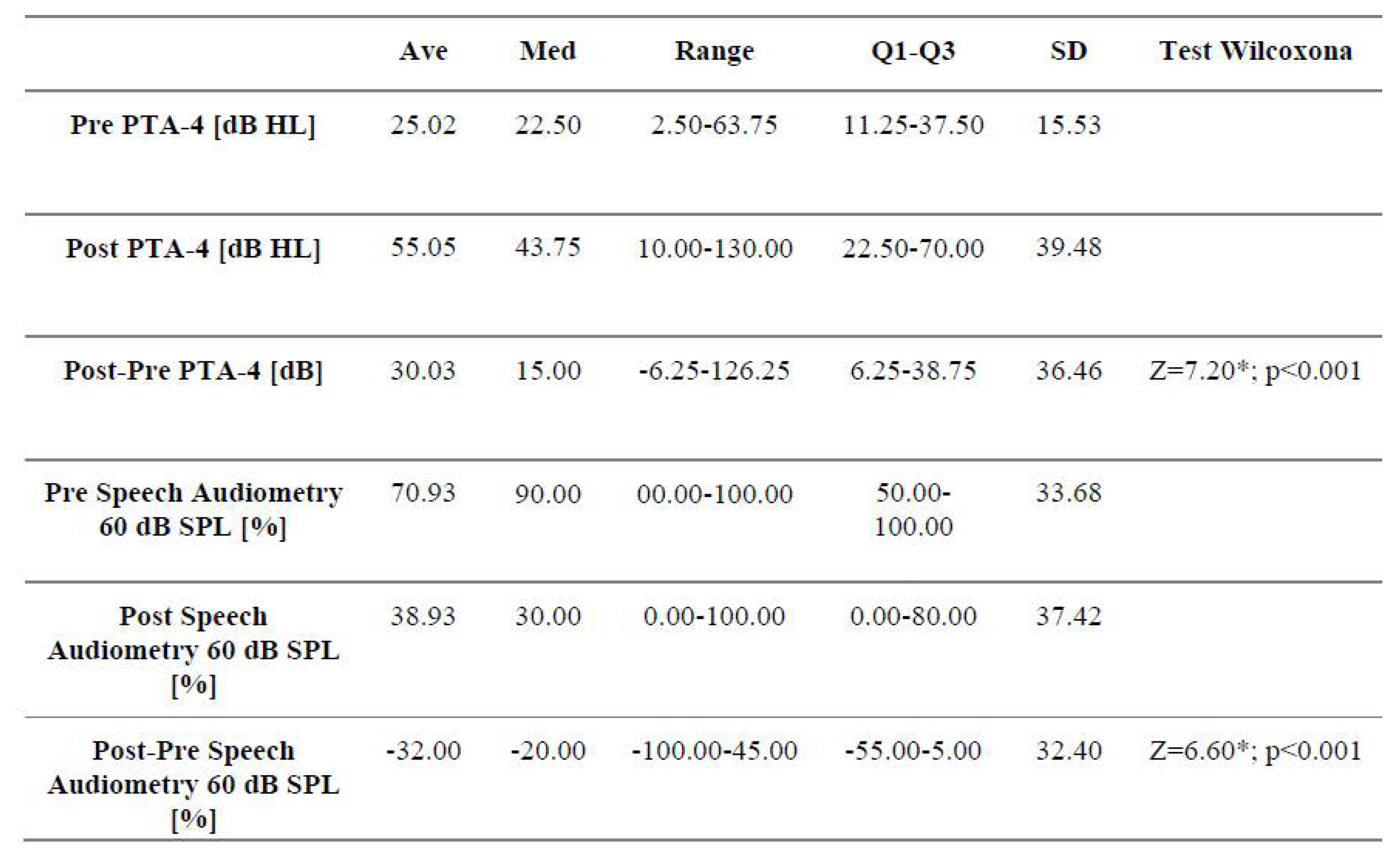
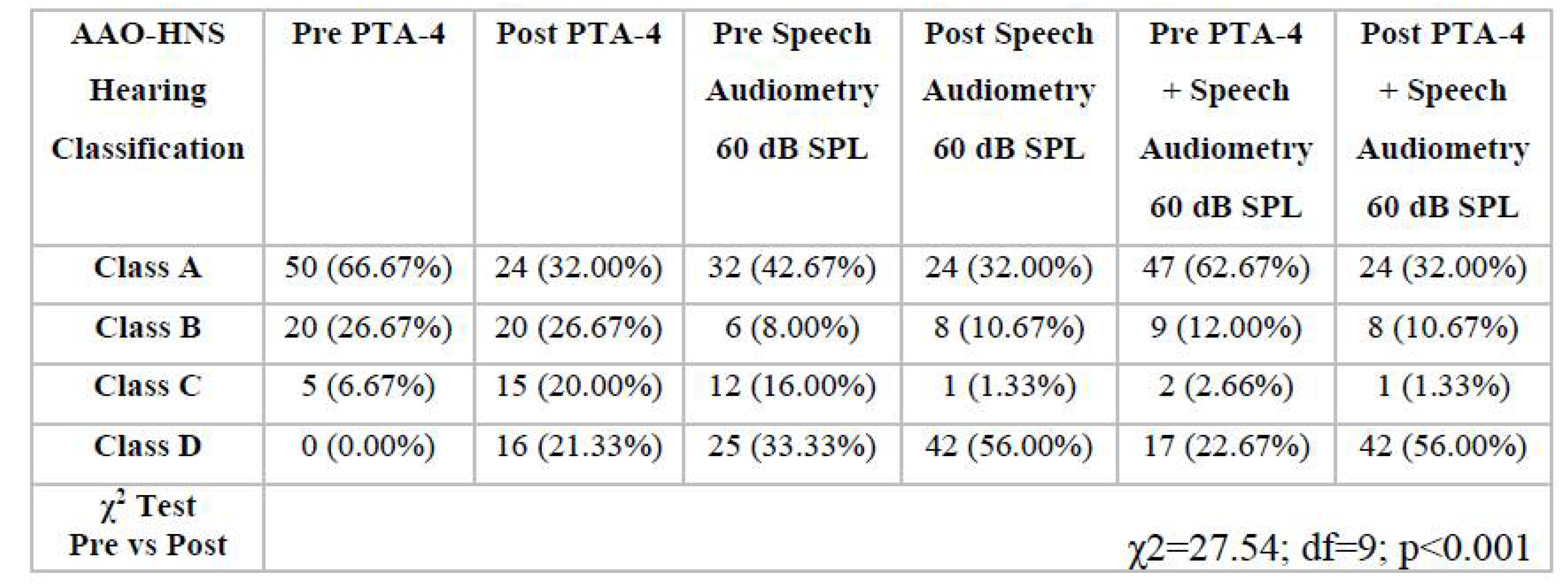
3.1. Analysis of Audiological Tests Before and After the Vestibular Schwannoma Removal
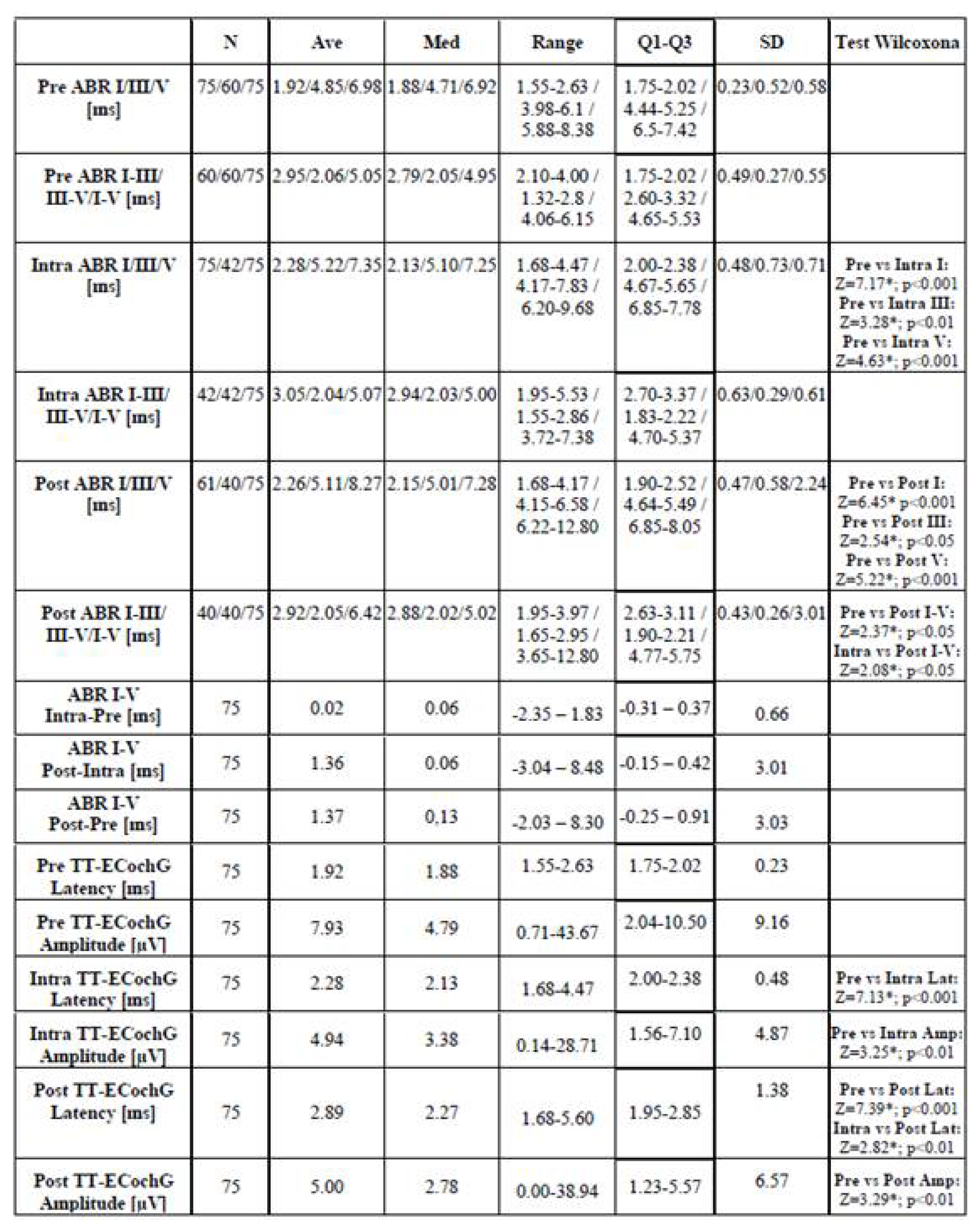
3.2. Characteristics of Electrophysiological Tests
3.2.1. Auditory Brainstem Responses – ABR
3.2.2. Transtympanic Electrocochleography
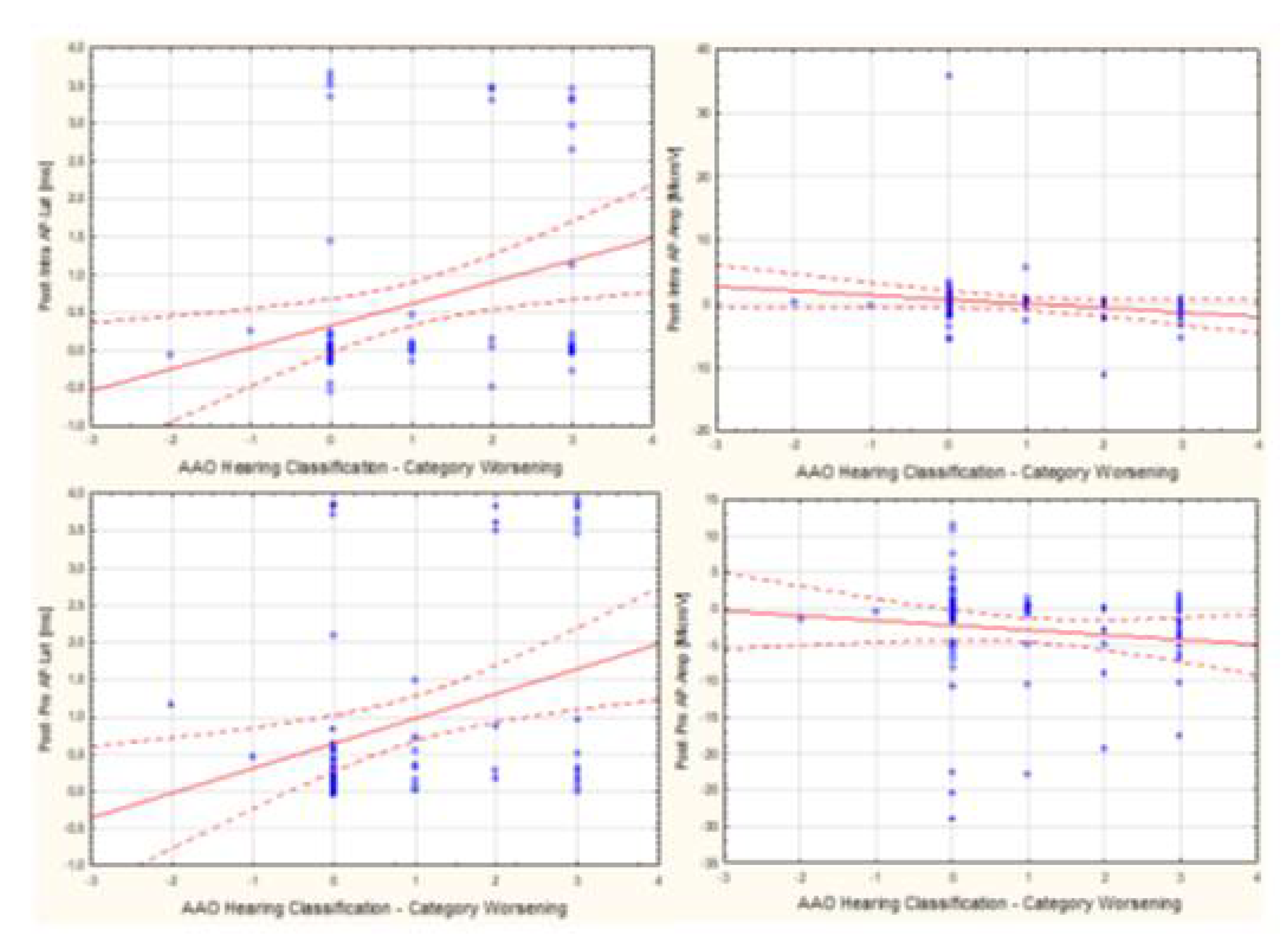
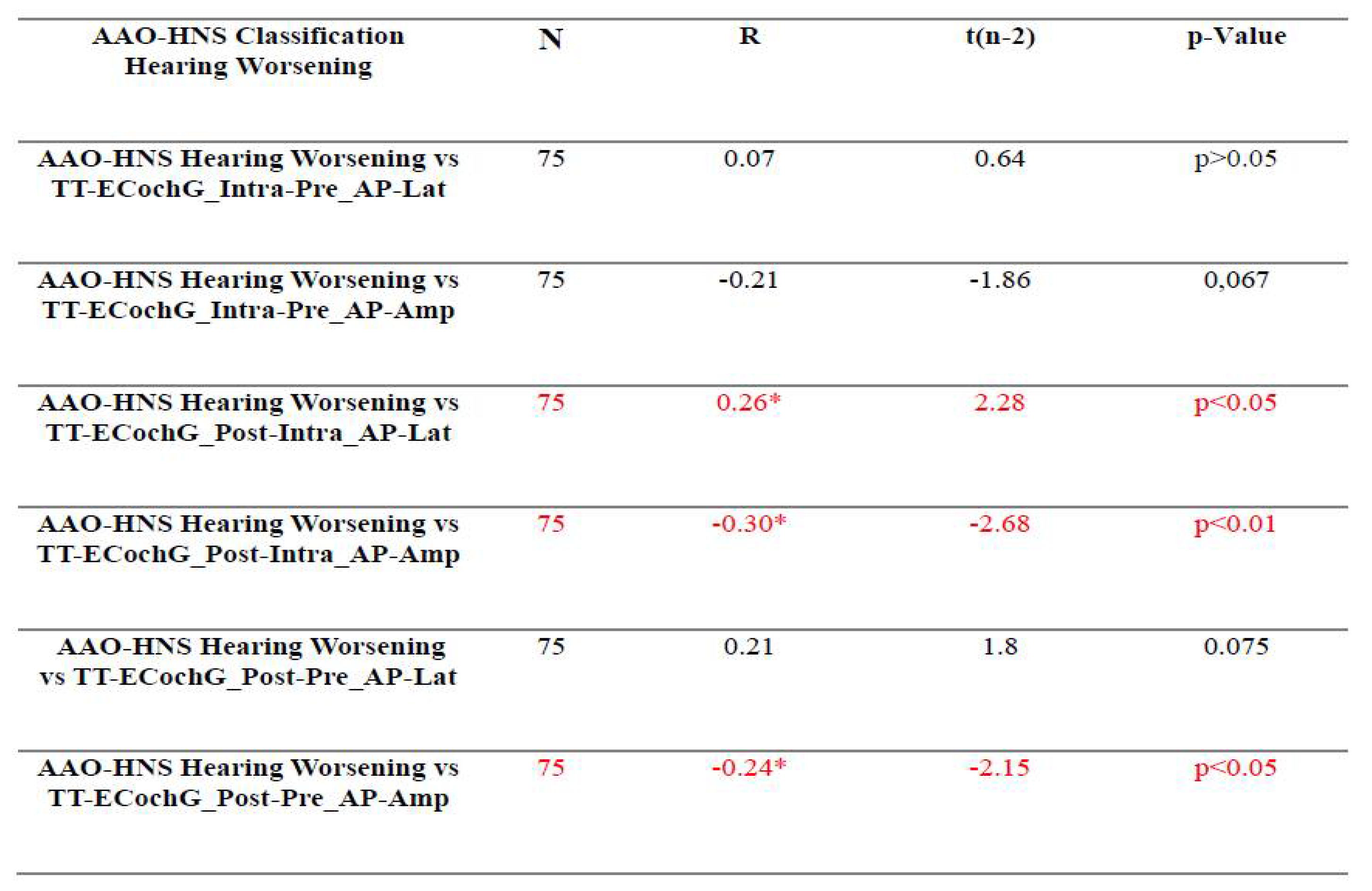
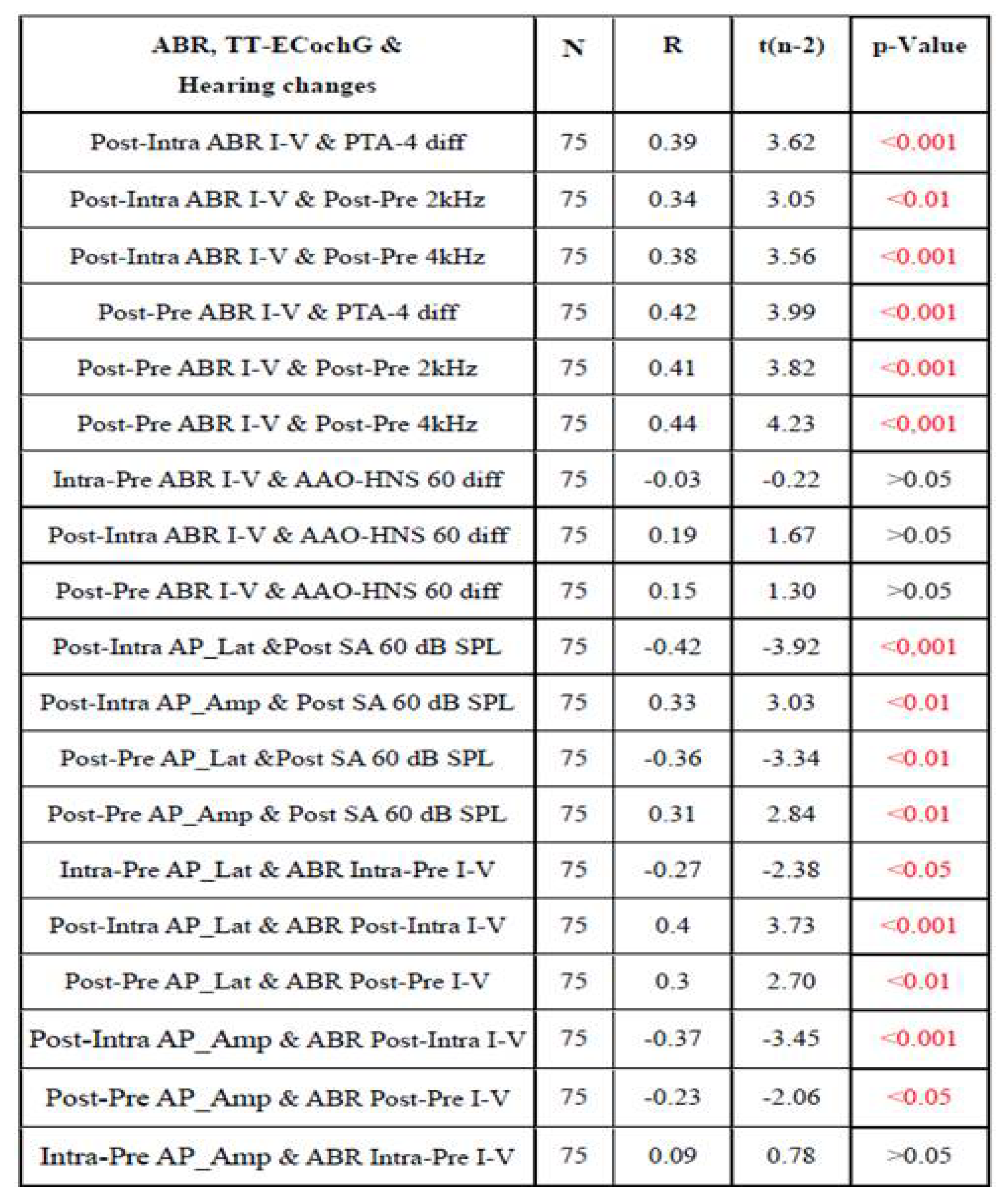
3.3. Assessment of the Relationship Between Audiological Tests and Electrophysiological Tests Used For Intraoperative Hearing Monitoring
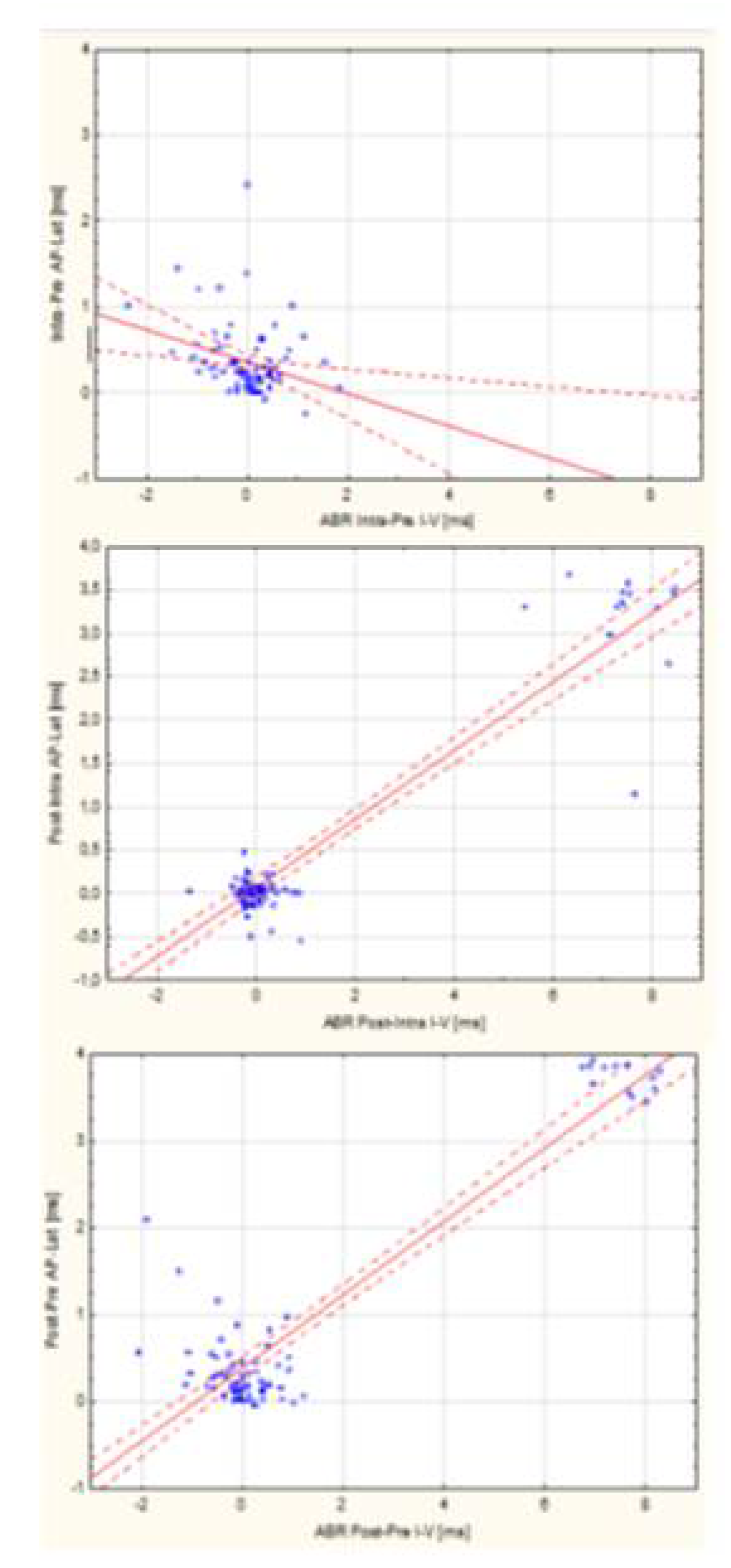
3.4. Assessment of the Relationship Between ABR and TT-ECochG During Intraoperative Hear-ing Monitoring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Acknowledgments
References
- Brackmann, D.; Arriaga, M. ; Differential diagnosis of neoplasmas of the posterior fossa. In Cummings Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, Ear and cranial base. Publisher: Mosby; 1993; Volume 4, pp. 3271–3291.
- Żurek, M.; Wojciechowski, T.; Niemczyk, K. Nationwide clinico-epidemiological treatment analysis of adult patients with tumors of cerebellopontine angle and internal acoustic meatus in Poland during 2011–2020. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Shudifat, A.R.; Kahlon, B.; Höglund, P.; Soliman, A.Y.; Lindskog, K.; Peter Siesjo, P. Age, gender and tumour size predict work capacity after surgical treatment of vestibular schwannomas. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2014, 85, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldridge, R.; Parry, D. Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma). Consensus development conference. Neurosurgery. 1992, 30, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arthurs, B.J.; Fairbanks, R.K.; Demakas, J.J.; Lamoreaux, W.T.; Giddings, N.A.; Mackay, A.R.; Cooke, B.S.; Elaimy, A.L.; Lee, Ch.M. A review of treatment modalities for vestibular schwannoma. Neurosurg Rev. 2011, 34, 265–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Thakker, A.; Gupta, K.K. Vestibular Schwannoma: What We Know and Where We are Heading. Head and Neck Pathology 2020, 14, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldbrunner, R.; Weller, M.; Regis, J.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Stavrinou, P.; Reuss, D.; Evans, G. , Florence Lefranc.; Kita Sallabanda et al. EANO guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of vestibular schwannoma. Neuro Oncol 2020, 22, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colletti, V.; Fiorino, F.G.; Mocella, S.; Policante, Z. ECochG, CNAP and ABR monitoring during vestibular Schwannoma surgery. Audiology. 1998, 37, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlake, H.P.; Milewski, C.; Goldbrunner, R.H.; et al. Combined intra-operative monitoring of hearing by means of auditory brainstem responses (ABR) and transtympanic electrocochleography (ECochG) during surgery of intra- and extrameatal acoustic neurinomas. Acta Neurochir. 2001, 143, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, C.; Mastrodimos, B.; Cueva, R.A. A comparison of direct eighth nerve monitoring and auditory brainstem response in hearing preservation surgery for vestibular schwannoma. Otol Neurotol. 2004, 25, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, KF.; Hryciuk, A.; Morawski, R.; Niemczyk, K. Wstęp do elektrofizjologii klinicznej obwodowej części narządu słuchu. Pol Otorhino Rev. 2012, 1, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobożny, I.; Morawski, K.; Pierchała, K.; Bartoszewicz, R.; Niemczyk, K. Prognostic value of ABR-ECochG intraoperative morphology changes in term of hearing preservation in patients with vestibular schwannoma. Pol Otorhino Rev. 2016, 5, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Battista, R.A.; Wiet, R.J.; Paauwe, L. Evaluation of three intraoperative auditory monitoring techniques in acoustic neuroma surgery. Am J Otol. 2000, 21, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, A.R.; Jannetta, P.J. Compound action potentials recorded intracranially from the auditory nerve in man. Exp Neurol. 1981, 74, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, A.R.; Jannetta, P.; Moller, M.B. Intracranially recorded auditory nerve response in man. New interpretations of BSER. Arch Otolaryngol. 1982, 108, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakami, I.; Yoshinori, H.; Saeki, N.; Wada, M.; Oka, N. Hearing preservation and intraoperative auditory brainstem response and cochlear nerve compound action potential monitoring in the removal of small acoustic neurinoma via the retrosigmoid approach. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009, 80, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, A.S.; Downes, A.E. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring in vestibular schwannoma surgery: advances and clinical implications. Neurosurg Focus 2009, 27, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.; Nagasawa, D.T.; Fong, B.M.; Trang, A.; Quinto n Gopen, Parsa, A. Yang, I. Intraoperative neuromonitoring techniques in the surgical management of acoustic neuromas. Neurosurg Focus 2012, 33, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, K.; Kohno, M. Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery. No Shinkei Geka 2023, 51, 490–499. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, H.; McDaniel, A.; Norrell, H.; Haberkamp, T. Hearing preservation after acoustic neuroma surgery with intraoperative direct eighth cranial nerve monitoring: Part II. A classification of results. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986, 95(3 Pt 1) Pt 1, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobożny, I.; Lachowska, M.; Bartoszewicz, R.; Niemczyk, K. Detailed insight into transtympanic electrocochleography (TT-ECochG) and direct cochlear nerve action potential (CNAP) for intraoperative hearing monitoring in patients with vestibular schwannoma – methodology of measurements and interpretation of results. Otolaryngol Pol 2020, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobożny, I.; Morawski, K.; Pierchała, K.; Bartoszewicz, R.; Niemczyk, K. Prognostic value of ABR-ECochG intraoperative morphology changes in term of hearing preservation in patients with vestibular schwannoma. Pol Otorhino Rev. 2016, 5, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.Q.; Sullivan, C.; Kung, R.W.; Asklof, M.; Hansen, M.R.; Gantz, B.J. How Well Does Intraoperative Audiologic Monitoring Predict Hearing Outcome During Middle Fossa Vestibular Schwannoma Resection? Otology & Neurotology 2018, 39, 908–915. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Al-Shaar, H.; Abunimer, A.M.; Whit, T.G.; Dehdashti, A.R. Hearing preservation after removal of small vestibular schwannomas: the role of ABR neuromonitoring. Acta Neurochirurgica 2019, 161, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliba, J.; Friedman, R.A.; Cueva, R.A. Hearing Preservation in Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery. J Neurol Surg B 2019, 80, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosty, J.A.; Stevens, S.M.; Gozal, Y. M,; DiNapoli, Aatel V.; et al. Middle Fossa Approach for Resection of Vestibular Schwannomas: A Decade of Experience. Middle Fossa Approach for Resection of Vestibular Schwannomas: A Decade of Experience. Operative Neurosurgery 2019, 16, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberson, J.; Senne, A.; Brackmann, D.; Hitselberger, W.E.; Saunders, J. Direct cochlear nerve action potentials as an aid to hearing preservation in middle fossa acoustic neuroma resection. Am J Otol. 1996, 17, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colletti, V.; Bricolo, A.; Fiorino, F.G.; Bruni, L. Changes in directly recorded cochlear nerve compound action potentials during acoustic tumor surgery. Skull Base Surg. 1994, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueva, R.A.; Morris, G.F.; Prioleau, G.R. Direct cochlear nerve monitoring: first report on a new atraumatic, self-retaining electrode. Am J Otol. 1998, 19, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aihara, N.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Cochlear nerve action potential monitoring with the microdissector in vestibular schwannoma surgery. Skull Base. 2009, 19, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Kojima, A.; Terao, S.; Nagai, M.; Kusaka, G.; Naritaka, H. Cochlear Nerve Action Potential Monitoring for Preserving Function of an Unseen Cochlear Nerve in Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery. World Neurosurg, 1: 106, 2017; 106:1057, e1051–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Hochet, B.; Daoudi, H.; Lefevre, E.; Nguyen, Y.; Bernat, I.; Sterkers, O.; Lahlou, G. and Michel Kalamarides. Monitoring Cochlear Nerve Action Potential for Hearing Preservation in Medium/Large Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery: Tips and Pitfalls. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koos, W.T.; Day, J.D.; Matula, C.; Levy, D.I. Neurotopographic considerations in the microsurgical treatment of small acoustic neurinomas. J Neurosurg. 1998, 88, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthies, C.; Samii, M. Management of vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): the value of neurophysiology for evaluation and prediction of auditory function in 420 cases. Neurosurgery. 1997, 40, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium: Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of hearing preservation in acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 179–180. [CrossRef]
- Silk, P.S.; Lane, J.I.; Driscoll, C.L. Surgical approaches to vestibular schwannomas: what the radiologist needs to know. Radiographics. 2009, 29, 1955–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larjavaara, S.; Feychting, M.; Sankila, R.; Johansen, S.; Klaeboe, L.; Schüz, Auvinen, A. Incidence trends of vestibular schwannomas in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden in 1987–2007. Br J Cancer. 2011, 105, 1069–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanidis, K.; Stepanidis, K.; Kessel, M.; Caye-Thomasen, P.; Sven-Eric. Stangerup Socio-demographic distribution of vestibular schwannomas in Denmark. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014, 134, 551–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N. L.B. Thai et al. 2022.
- Zanoletti, E.; Concheri, S.; Tealdo, G. , Cazzador, D.; Denaro L.; d’Avella, D.; Mazzoni A. Early surgery and definitive cure in small sporadic vestibular schwannoma. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2022, 42, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, G.; Robertson, J.H. Hearing preservation in unilateral acoustic neuroma surgery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1988, 97, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concheri, S.; Deretti, A.; Tealdo, G.; Zanoletti, E. Prognostic Factors for Hearing Preservation Surgery in Small Vestibular Schwannoma. Audiol Res. 2023, 13, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancey, K.; Barnett, SL.; Kutz, W.; Isaacson, B.; Wardak, Z.; Micke, B.; Hunter, J.B. Hearing Preservation After Intervention in Vestibular Schwannoma. Otology & Neurotology 2022, 43, e846–e855. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, Ch.M.; Mannarelli, G.; Koehler, L.; Telian, S.T. Intraoperative Auditory Brainstem Response Results Predict Delayed Sensorineural Hearing Loss After Middle Cranial Fossa Resection of Vestibular Schwannoma. Otol Neurotol 2021, 42, e771–e778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankekar, G.; Holmes, S. Hearing Rehabilitation in Vestibular Schwannoma. Audiol. Res. 2023, 13, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, E.X.; Carlson, M.L.; Neff, B.A.; et al. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines on Intraoperative Cranial Nerve Monitoring in Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery. Neurosurgery 2018, 82, E44–E46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





