1. Introduction
As SARS-CoV-2 is allowed to spread among human populations, genetic changes occur and accumulate in the circulating virus, resulting in numerous variants since July, 2020. The newly dominant Omicron JN.1 variant has 26 amino acid mutations in its Spike protein ACE2 receptor binding domain (RBD) [
1]. According to an estimate made by the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on March 2, 2024, more than 92% of the SARS-CoV-2 isolates were those of the JN.1 variant [
2], rising from <0.1% in the end of October 2023 in the United States [
3]. Such a rapid takeover by a newly introduced variant among a highly COVID-19 vaccinated population suggested that the JN.1 variant may be a highly immune-evading variant compared with other Omicron variants. However, based on one serum neutralization study conducted in September 2023 in Germany, the JN.1 variant was not associated with further reduced serological protection beyond prior Omicron variants [
4]. On the other hand, more recent studies based on breakthrough infections have shown that JN.1 displayed significantly enhanced immune escape and suggested that JN.1 is one of the most immune-evading variants to-date due to its acquisition of L455S mutation in the RBD [
5,
6].
Recently, CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices analyzed a group of tests performed at two pharmacy chains on COVID-19 patients 60–119 days after receiving updated monovalent XBB.1.5 COVID-19 vaccines, using the reverse transcription-qPCR TaqPath COVID-19 Combo Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) as the testing method to define JN.1 infection [
7]. The results showed that 49% (95% CI = 19%–68%) of the 679 positive tests exhibited S-gene target failure (SGTF) as the proxy indicator of JN.1 infection, and 60% (95% CI = 35%–75%) of the positive tests exhibited S-gene target presence (SGTP) as the proxy indicator of non-JN.1 infection, suggesting that there is substantial vaccine effectiveness against JN.1. Based on these data, the CDC recommended that all persons aged ≥6 months should receive an updated COVID-19 vaccine dose. However, SGTF is the proxy for 69-70del in the N-terminal domain, not amino acid mutations in the RBD of the S-gene of SARS-CoV-2. Using the latter proxy as the proxy indicator of JN.1 is a highly imprecise approach to diagnose JN.1 because other non-JN.1 variants, such as the variants Alpha, Omicron BA.1, BA.4 and BA.5 as well as BA.2.86, the precursor of JN.1, that have circulated in the U. S. populations, also harbor 69-70del [
1].
This paper recommends that Sanger sequencing of a segment of the S-gene RBD [
8,
9] of JN.1 be used to verify the variant before each case is accepted as true JN.1 infection for statistics to generate the data based on which guidelines are made to direct vaccination policies and clinical practice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Specimens
Nasopharyngeal swab specimens from patients with clinical respiratory infection were collected by healthcare providers in the month of February 2024. The swabs were immersed in VTM or phosphate-buffered saline after collection and stored at -80°C temperature until testing in a CLIA-certified laboratory.
2.2. Extraction of Viral RNA from Infected Cells
As previously described in detail, the test was designed to detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the infected cells as well as in cell-free fluid [
9]. Briefly, about 1 mL of the nasopharyngeal swab rinse was centrifuged at ~16,000× g to pellet all cells and cellular debris. The pellet and 0.2 mL of the supernatant were digested in a proteinase K solution. The digestate was extracted by a phenol: chloroform:isoamyl alcohol mixture. The nucleic acids in the aqueous sample were precipitated in 70% ethanol and finally dissolved in 50 μL of diethylpyrocarbonate-treated water to be stored at -80°C temperature until RT-PCR.
2.3. Nested RT-PCR Conditions
To initiate the primary RT-PCR, a total volume of 25 μL mixture was made in a PCR tube containing 20 μL of ready-to-use LoTemp® PCR mix with denaturing chemicals (HiFi DNA Tech, LLC, Trumbull, CT, USA), 1 μL (200 units) of Invitrogen SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase, 1 μL (40 units) of Ambion™ RNase Inhibitor, 0.1 μL of Invitrogen 1 M DTT (dithiothreitol), 1 μL of 10 μmolar forward primer in TE buffer, 1 μL of 10 μmolar reverse primer in TE buffer and 1 μL of sample nucleic acid extract. The ramp rate of the thermal cycler was set to 0.9 °C/s. The program for the temperature steps was set as: 47°C for 30 min to generate the cDNA, 85°C 1 cycle for 10 min, followed by 30 cycles of 85°C 30 sec for denaturing, 50°C 30 sec for annealing, 65°C 1 min for primer extension, and final extension 65°C for 10 minutes. The nested PCR was conducted in a 25 μL volume of complete PCR mixture containing 20 μL of ready-to-use LoTemp® PCR mix, 1 μL of 10 μmolar forward primer, 1 μL of 10 μmolar reverse primer and 3 μL of molecular grade water. To initiate the nested PCR, a trace (about 0.2 μL) of primary PCR products was transferred by a micro-glass rod to the complete nested PCR mixture. The thermocycling steps were programmed to 85°C 1 cycle for 10 min, followed by 30 cycles of 85°C 30 sec for denaturing, 50°C 30 sec for annealing, 65°C 1 min for primer extension, and final extension 65°C for 10 minutes. Transferring of PCR products was carried out by micro-glass rods in a PCR station, not by micropipetting, to avoid aerosol contamination.
2.4. DNA Sequencing
The crude nested PCR products showing an expected amplicon at agarose gel electrophoresis were subjected to automated Sanger sequencing without further purification. To initiate the Sanger reaction, a trace (about 0.2 μL) of nested PCR products was transferred by a micro-glass rod into a thin-walled PCR tube containing 1 μL of 10 μmolar sequencing primer, 1 μL of BigDye® Terminator (v 1.1/Sequencing Standard Kit), 3.5 μL 5× buffer, and 14.5 μL water in a total volume of 20 μL. Twenty (20) enzymatic primer extension/termination reaction cycles were run according to the protocol supplied by the manufacturer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). After a dye-terminator cleanup, the Sanger reaction mixture was loaded in an Applied Biosystems SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer for automated sequencing. The sequences were visually analyzed for nucleotide deletions, mutations and indels.
2.5. PCR Primers
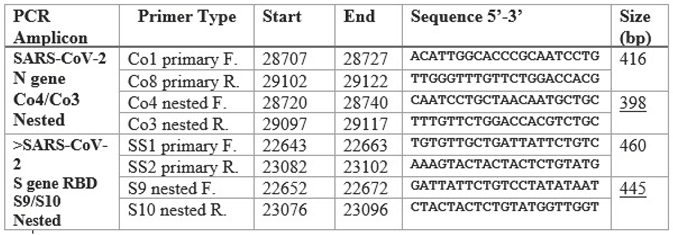
The sequences of the primary and nested PCR primers used in this study for amplification of the N gene and the RBD are summarized in the following table.
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.86 (+JN.1) N Gene Sequence
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 S-Gene RBD Sequence
3.2.1. S-gene RBD Forward Sequencing
3.2.2. S-gene RBD Reverse Sequencing
4. Discussion
The results presented in this paper confirm that implementation of routine sequencing of a 445-bp RT-PCR amplicon of the SARS-CoV-2 S-gene in CLIA-certified diagnostic laboratories can identify almost all the amino acid mutations in the RBD for accurate determination of SARS-CoV-2 variants [
9], including the latest dominant JN.1 variant by demonstrating its hallmark L455S mutation (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). Sequencing a 398-bp segment of the N-gene for molecular diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 can confirm the Omicron BA.2.82 (+LN.1) lineage because there is a unique Q229K mutation in this lineage (
Figure 1), but cannot verify JN.1. However, targeting the N-gene for SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR generates less primer failures because the N-gene mutates less frequently than the S-gene [
9].
The CDC’s relying on using TaqPath COVID-19 Combo Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) as the method to define JN.1 or non-JN.1 infections for statistical analysis to support the claim of effectiveness of updated monovalent XBB.1.5 COVID-19 vaccines against symptomatic infection with the JN.1 lineage [
7] is questionable. In a convoluted statement “
SARS-CoV-2–positive specimens with either null or reduced amplification of the S-gene (Ct for S-gene >4 cycles from the average of N and ORF1ab Ct values) were considered to have SGTF, an indication of a particular deletion in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which currently indicates an infection with BA.2.86, JN.1, and their sublineages” published in its report [
7], the CDC has admitted that the TaqPath COVID-19 Combo Kit cannot distinguish between BA.2.86 and JN.1. The rationale for using SGTF as the proxy indicator of JN.1 was based on CDC's National SARS-CoV-2 Strain Surveillance (NS3) program, which shows a very high JN.1/BA.2.86 proportion [
2], so that the possibility of detecting a BA.2.86 could be disregarded. However, the CDC’s SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance relies on using next generation sequencing technologies that require samples containing high viral loads (RT-qPCR Ct values ≤ 28) to generate quality sequence [
10]. As a result, all positive specimens submitted to the National SARS-CoV-2 Strain Surveillance (NS3) program for sequencing have a RT-qPCR Ct values ≤ 28 [
11]. But in real medical practice, most specimens testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR have a Ct value higher than 27, false positives included [
12]. In one comparative study, among 29 true SARS-CoV-2-positive specimens confirmed by Sanger sequencing, 13 of the 29 (~45%) had an RT-qPCR Ct>28 [
9]. In other words, about 45% of the specimens positive for a variant of SARS-CoV-2 are not being sequenced in the national genomic surveillance program because the viral loads in these specimens were not high enough for next generation sequencing, and these patient specimens with low viral loads may contain a non-JN.1 variant that is not included in the current COVID Data Tracker. The very high JN.1 percentage listed in the National SARS-CoV-2 Strain Surveillance may be the result of sample selection bias that cannot be extrapolated to using SGTF as the proxy indicator of JN.1 by statistic exclusion of other possible variants found in routine RT-qPCR testing.
To justify using SGTF as proxy indicator of JN.1 for statistical analysis, the CDC should consider sequencing the S-gene RBD of 500 specimens tested positive by TaqPath COVID-19 Combo Kit regardless RT-qPCR Ct values, 250 with SGTF and 250 with SGTP, to prove that SGTF and SGTP are in fact the appropriate proxy indicators of the presence and absence of L455S, the hallmark mutation of JN.1. The cost for such a small project would be less than $100,000 that should be well within the CDC budget.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Written consents were obtained from the patients whose samples were positive for SARS-CoV-2 to allow their samples to be further analyzed for publication.
Conflicts of Interest
Sin Hang Lee is Director of the Milford Molecular Diagnostics Laboratory specialized in developing DNA sequencing-based diagnostic tests implementable in community hospital laboratories.
References
- ViralZone. Sars-CoV-2 circulating variants. https://viralzone.expasy.org/9556.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Covid Data Tracker. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update on SARS-CoV-2 Variant JN.1 Being Tracked by CDC December 8, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/ncird/whats-new/SARS-CoV-2-variant-JN.1.html?CDC_AA_refVal=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.cdc.gov%2Frespiratory-viruses%2Fwhats-new%2FSARS-CoV-2-variant-JN.1.html.
- Jeworowski LM, Mühlemann B, Walper F, et al. Humoral immune escape by current SARS-CoV-2 variants BA.2.86 and JN.1, December 2023. Euro Surveill. 2024;29(2):2300740. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10785204/. [CrossRef]
- Kaku Y, Okumura K, Padilla-Blanco M, et al. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 variant. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024;24(2):e82. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38184005/. [CrossRef]
- Yang S, Yu Y, Xu Y, et al. Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure [published correction appears in Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 3;:]. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024;24(2):e70-e72. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38109919/. [CrossRef]
- Link-Gelles R, Ciesla AA, Mak J, et al. Early Estimates of Updated 2023-2024 (Monovalent XBB.1.5) COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness Against Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Attributable to Co-Circulating Omicron Variants Among Immunocompetent Adults - Increasing Community Access to Testing Program, United States, September 2023-January 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73(4):77-83. Published 2024 Feb 1. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38300853/. [CrossRef]
- Lee SH. A Routine Sanger Sequencing Target Specific Mutation Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Interest. Viruses. 2021;13(12):2386. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8706074/. [CrossRef]
- Lee SH. Evidence-Based Evaluation of PCR Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 and the Omicron Variants by Gold Standard Sanger Sequencing. Science, Public Health Policy, and the Law. 2022; 4:144-189. https://www.publichealthpolicyjournal.com/_files/ugd/adf864_01b8d2e159014d53a342e807a540c143.pdf.
- Goswami C, Sheldon M, Bixby C, et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 variants using viral sequencing for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention genomic surveillance program. BMC Infect Dis. 2022;22(1):404. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35468749/. [CrossRef]
- SARS COV-2 Appendix 1: National SARS-CoV-2 Strain Surveillance (NS3) Submissions to CDC for SARSCoV-2 Positive Specimens (Recommended) (Updated 08/30/2023) https://www.aphl.org/programs/infectious_disease/Documents/NS3%20Guidance%20with%20Appendix%201%20.pdf.
- Tartof SY, Slezak JM, Fischer H, et al. Effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine up to 6 months in a large integrated health system in the USA: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2021;398(10309):1407-1416. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34619098/. [CrossRef]
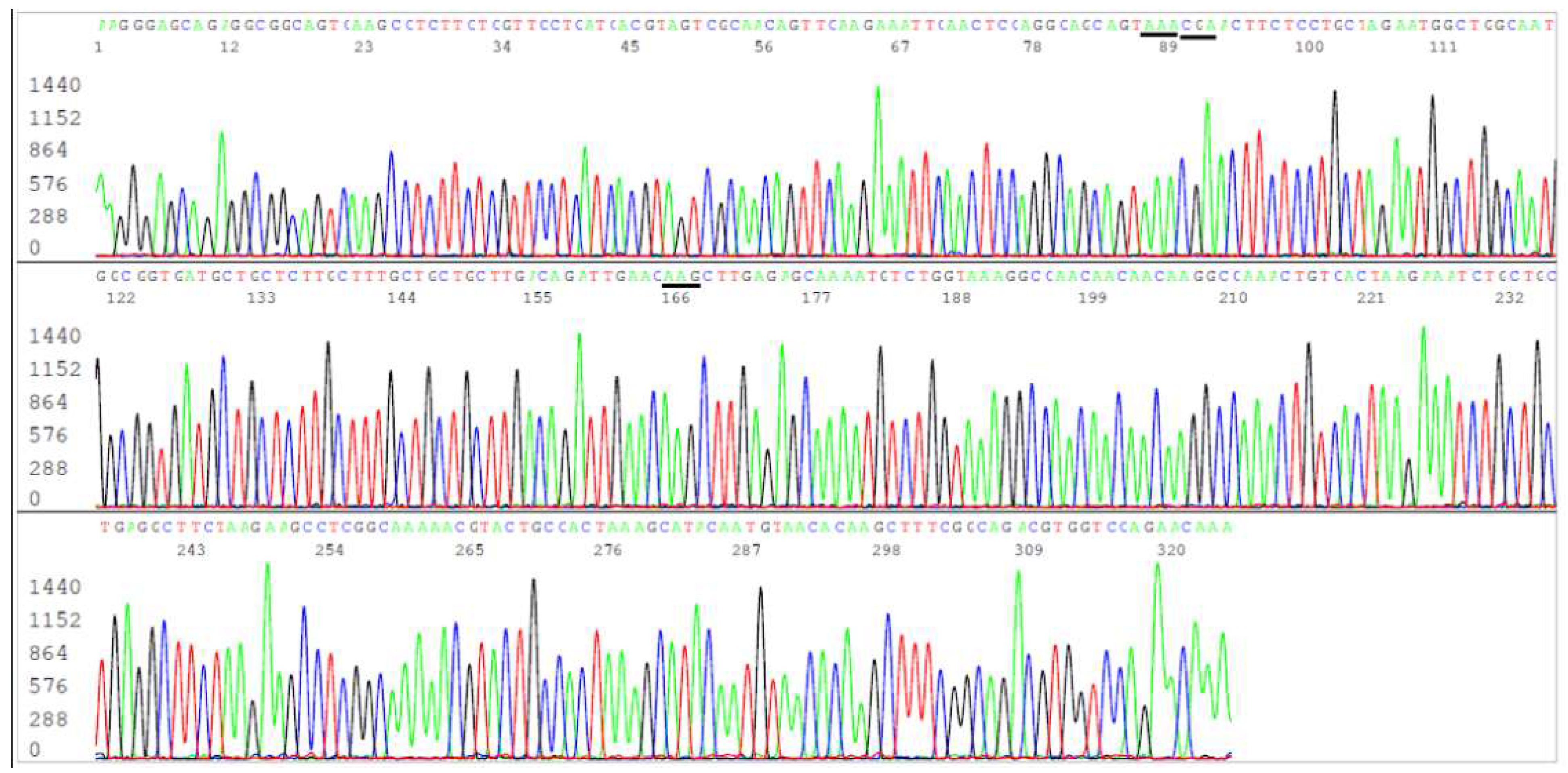
Figure 1.
This is an electropherogram showing an N gene forward sequence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 variant. The reverse Co3 primer is in the end of the sequence. The codons of the 3 amino acid mutations, R203K (AGG>AAA), G204R (GGA>CGA) and Q229K (CAG>AAG), usually associated with BA.2.86 (+JN.1) are underlined. An N-gene sequencing cannot distinguish JN.1 variant from its predecessor Omicron BA.2.86.
Figure 1.
This is an electropherogram showing an N gene forward sequence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 variant. The reverse Co3 primer is in the end of the sequence. The codons of the 3 amino acid mutations, R203K (AGG>AAA), G204R (GGA>CGA) and Q229K (CAG>AAG), usually associated with BA.2.86 (+JN.1) are underlined. An N-gene sequencing cannot distinguish JN.1 variant from its predecessor Omicron BA.2.86.
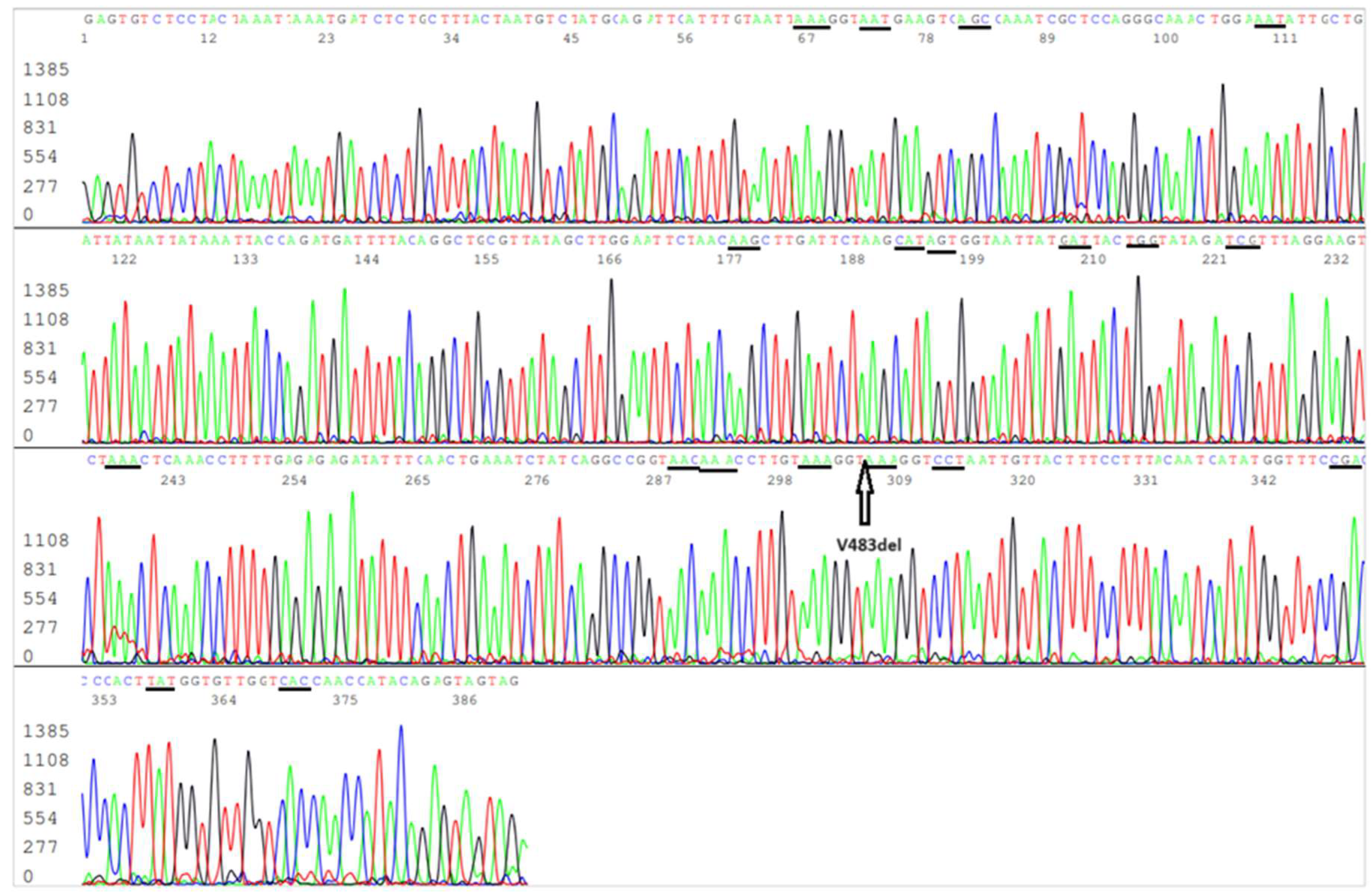
Figure 2.
Electropherogram showing an S-gene RBD forward sequence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 variant. The S10 reverse nested PCR primer is in the end of the sequence. The codons of the 19 amino acid mutations included in this sequence, namely R403K (AGA>AAA), D405N (GAT>AAT), R408S (AGA>AGC), K417N (AAG>AAT), N440K (AAT>AAG), V445H (GTT>CAT), G446S (GGT>AGT), N450D (AAT>GAT), L452W (CTG>TGG), L455S (TTG>TCG), N460K (AAT>AAA), S477N (AGC>AAC), T478K (ACA>AAA), N481K (AAT>AAA), E484K (GAA>AAA), F486P (TTT>CCT), Q498R (CAA>CGA), N501Y (AAT>TAT) and Y505H (TAC>CAC), are underlined. The position of V483del is pointed by an arrow. The L455S mutation in the RBD distinguishes JN.1 variant from its predecessor Omicron BA.2.86.
Figure 2.
Electropherogram showing an S-gene RBD forward sequence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 variant. The S10 reverse nested PCR primer is in the end of the sequence. The codons of the 19 amino acid mutations included in this sequence, namely R403K (AGA>AAA), D405N (GAT>AAT), R408S (AGA>AGC), K417N (AAG>AAT), N440K (AAT>AAG), V445H (GTT>CAT), G446S (GGT>AGT), N450D (AAT>GAT), L452W (CTG>TGG), L455S (TTG>TCG), N460K (AAT>AAA), S477N (AGC>AAC), T478K (ACA>AAA), N481K (AAT>AAA), E484K (GAA>AAA), F486P (TTT>CCT), Q498R (CAA>CGA), N501Y (AAT>TAT) and Y505H (TAC>CAC), are underlined. The position of V483del is pointed by an arrow. The L455S mutation in the RBD distinguishes JN.1 variant from its predecessor Omicron BA.2.86.
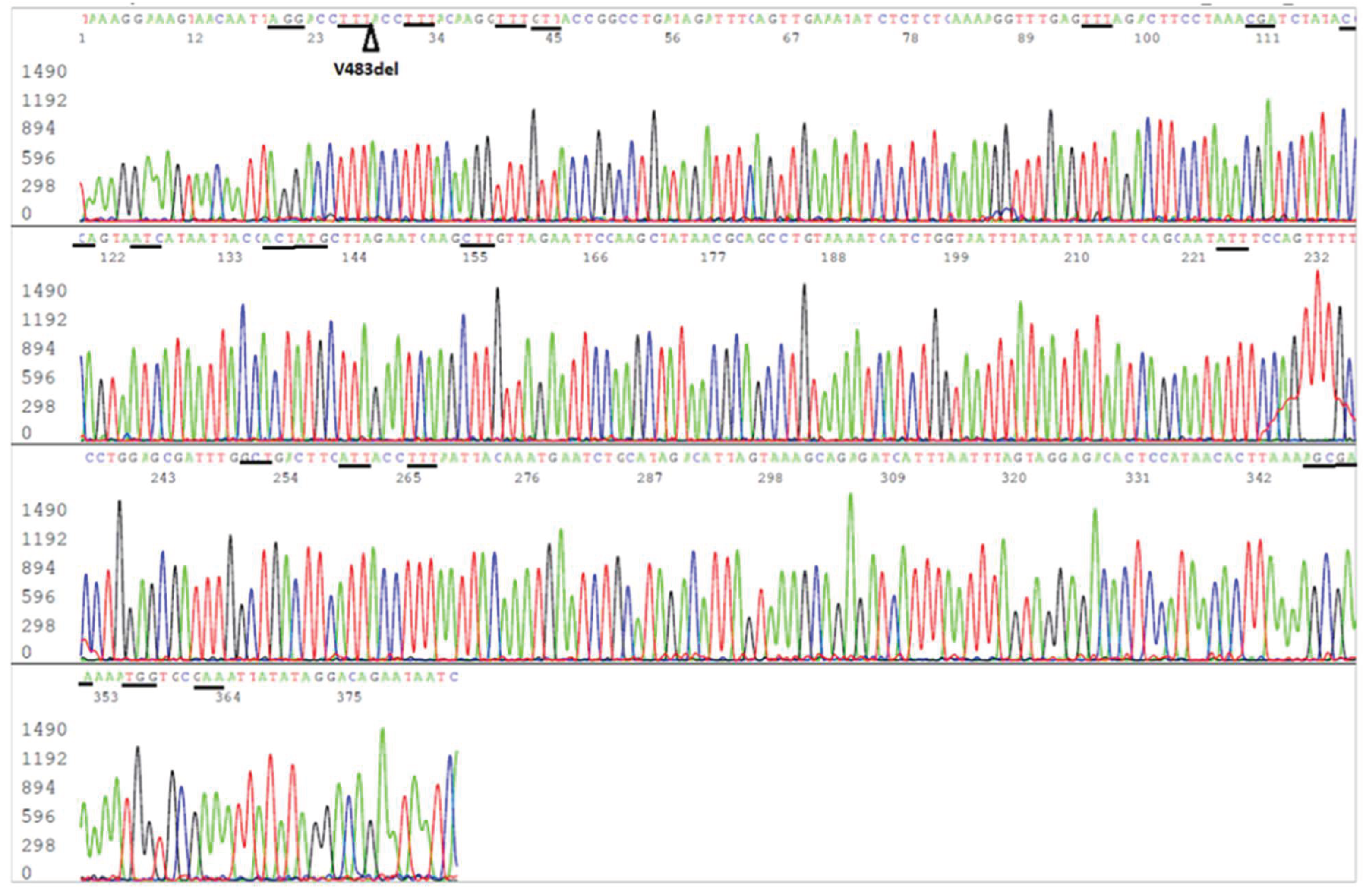
Figure 3.
Electropherogram showing an S-gene RBD reverse sequence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 variant. The S9 forward nested PCR primer is in the end of the sequence. The codons (in reverse complement) of the 20 amino acid mutations included in this sequence, namely F486P, E484K, N481K, T478K, S477N, N460K, L455S, L452W, N450D, G446S, V445H, N440K, K417N, R408S, D405N, R403K, T376A, S375F, S373P and S371F, are underlined. The position of V483del is pointed by an arrowhead.
Figure 3.
Electropherogram showing an S-gene RBD reverse sequence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 variant. The S9 forward nested PCR primer is in the end of the sequence. The codons (in reverse complement) of the 20 amino acid mutations included in this sequence, namely F486P, E484K, N481K, T478K, S477N, N460K, L455S, L452W, N450D, G446S, V445H, N440K, K417N, R408S, D405N, R403K, T376A, S375F, S373P and S371F, are underlined. The position of V483del is pointed by an arrowhead.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).