Submitted:
02 March 2024
Posted:
04 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Immune Dysregulation in IBD
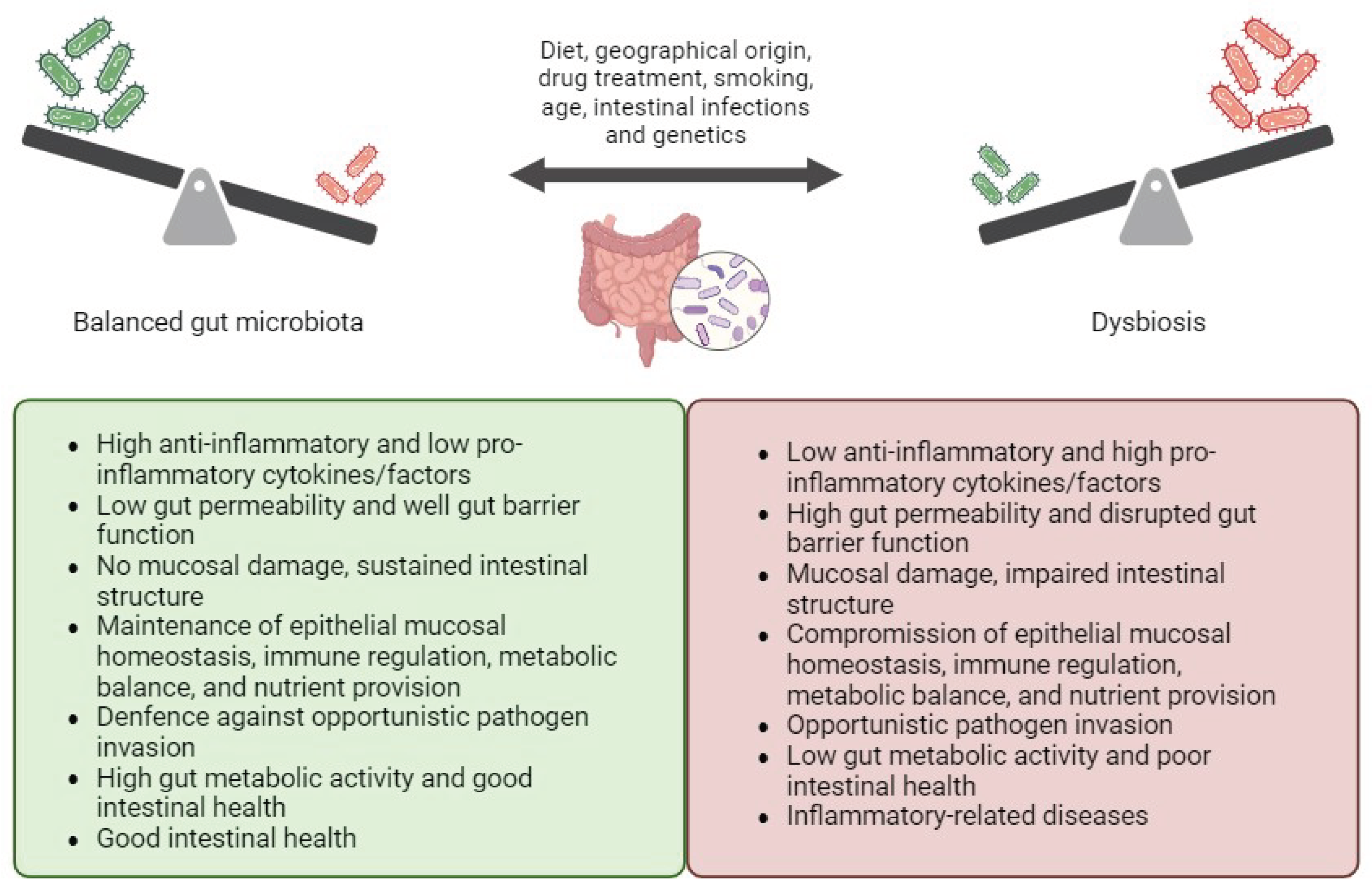
3. The Role of Gut Microbiota in IBD
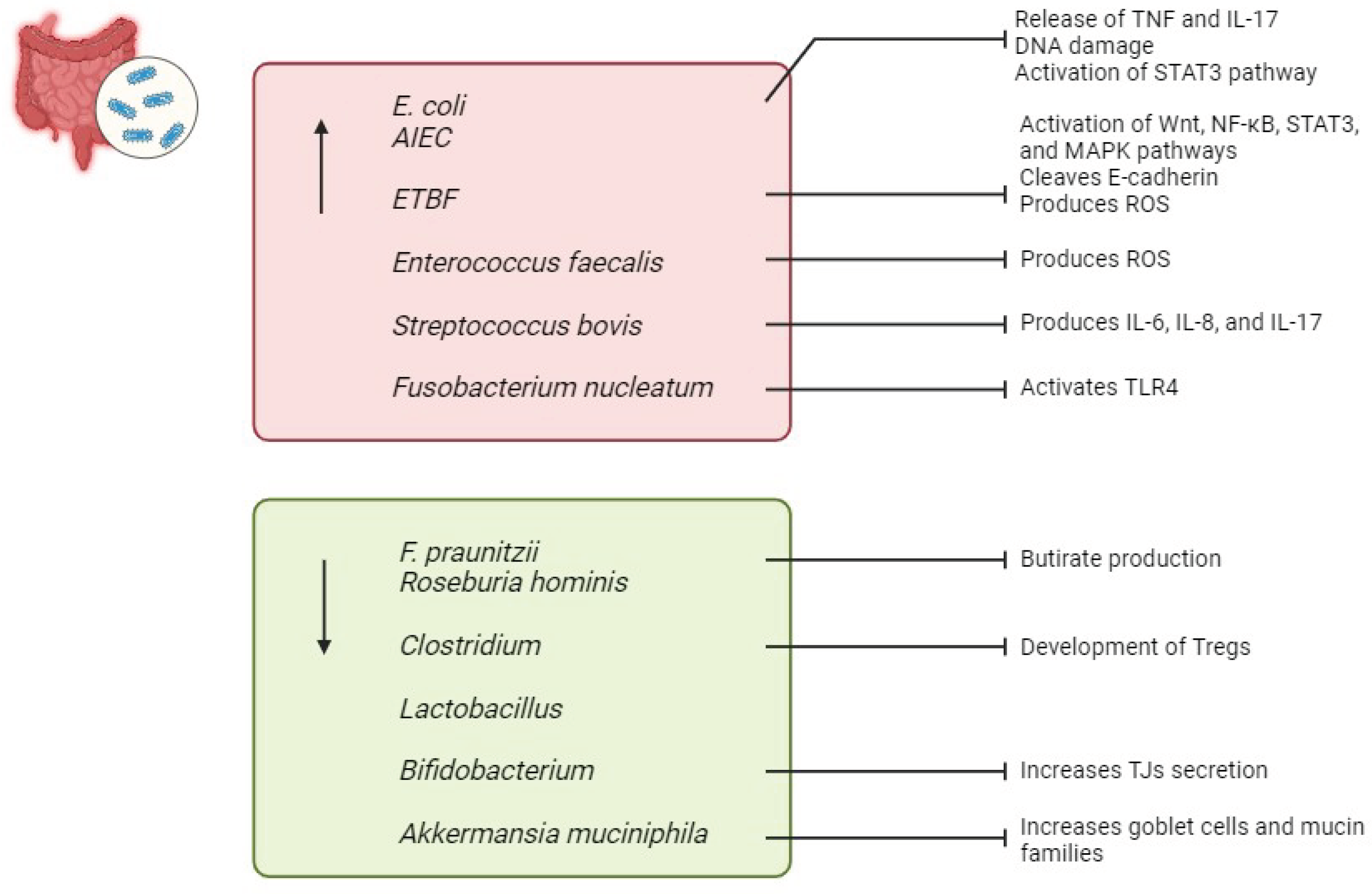
3.1. Bacteria in IBD
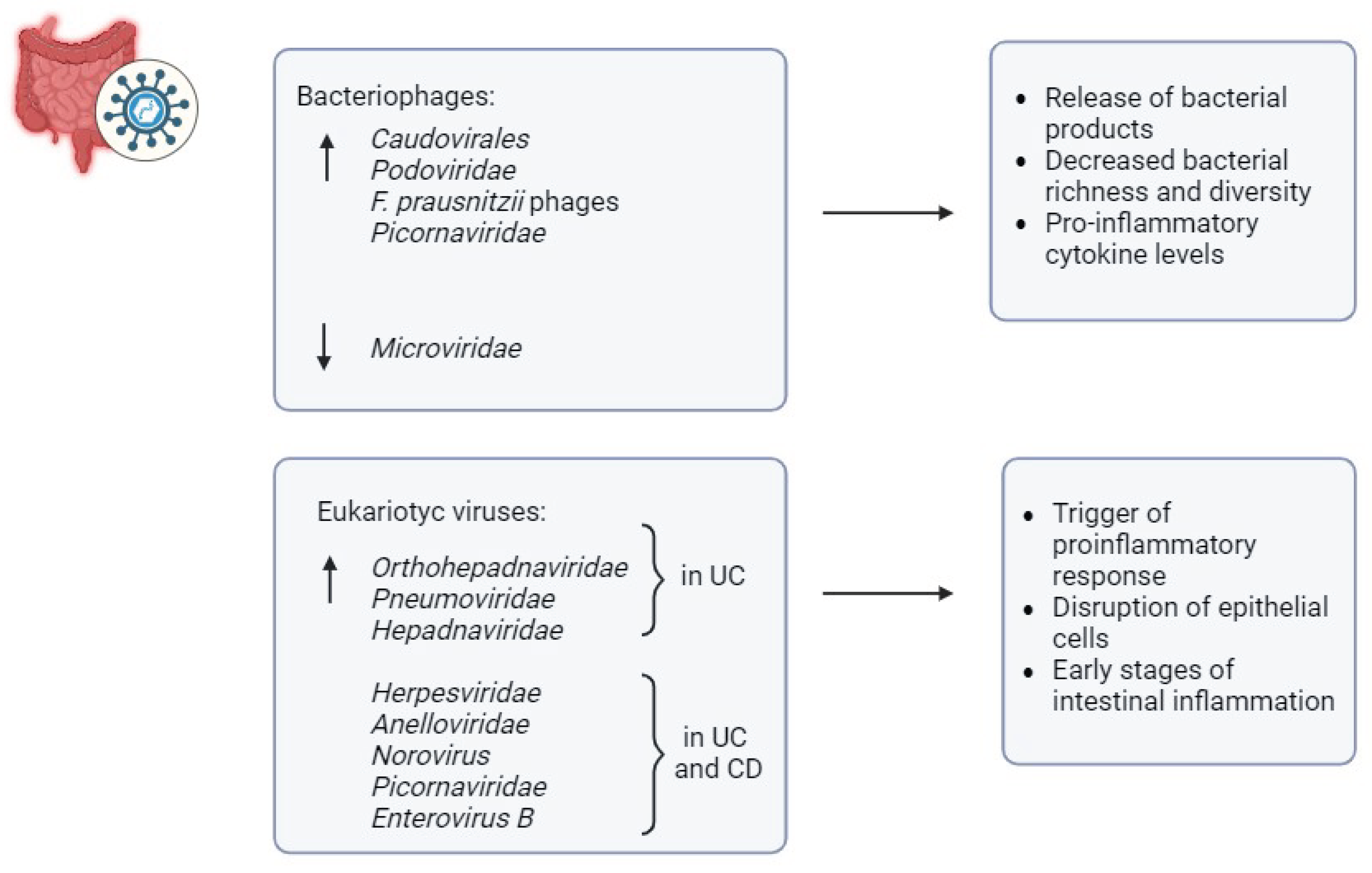
3.2. Viruses in IBD
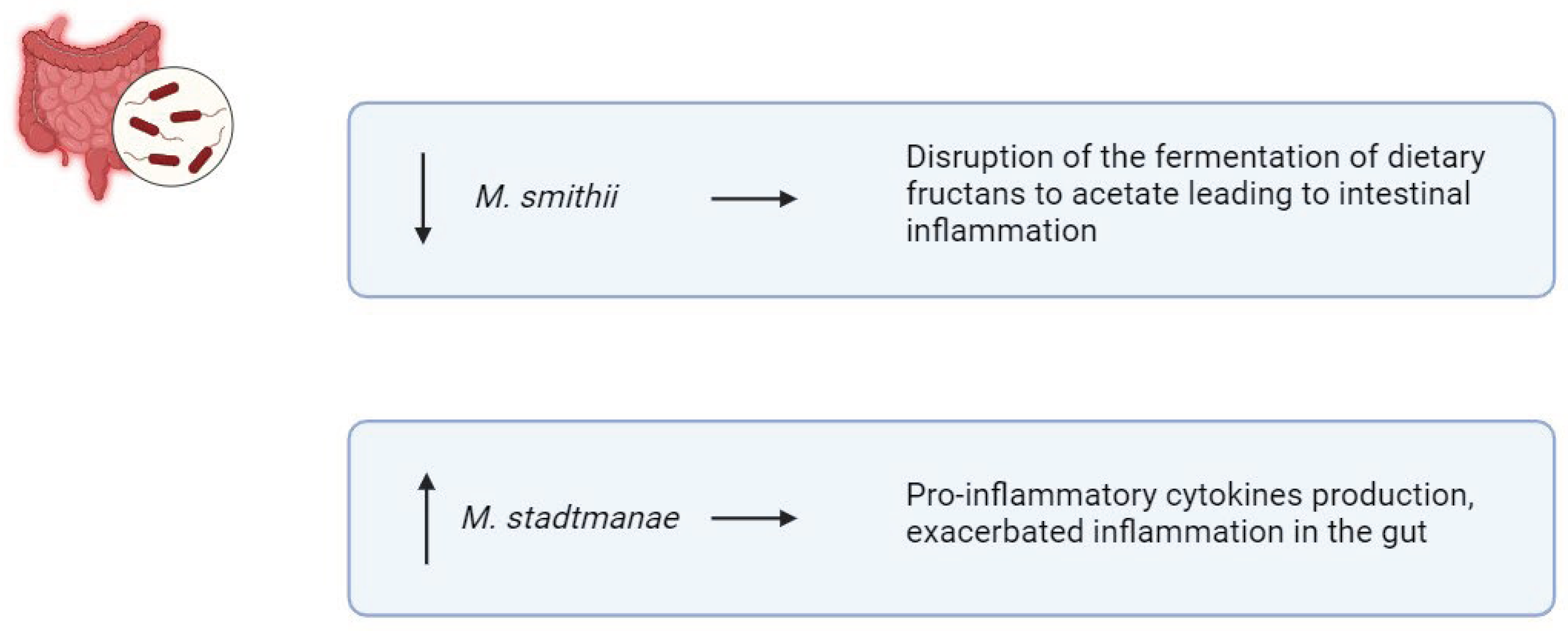
3.3. Archaea in IBD
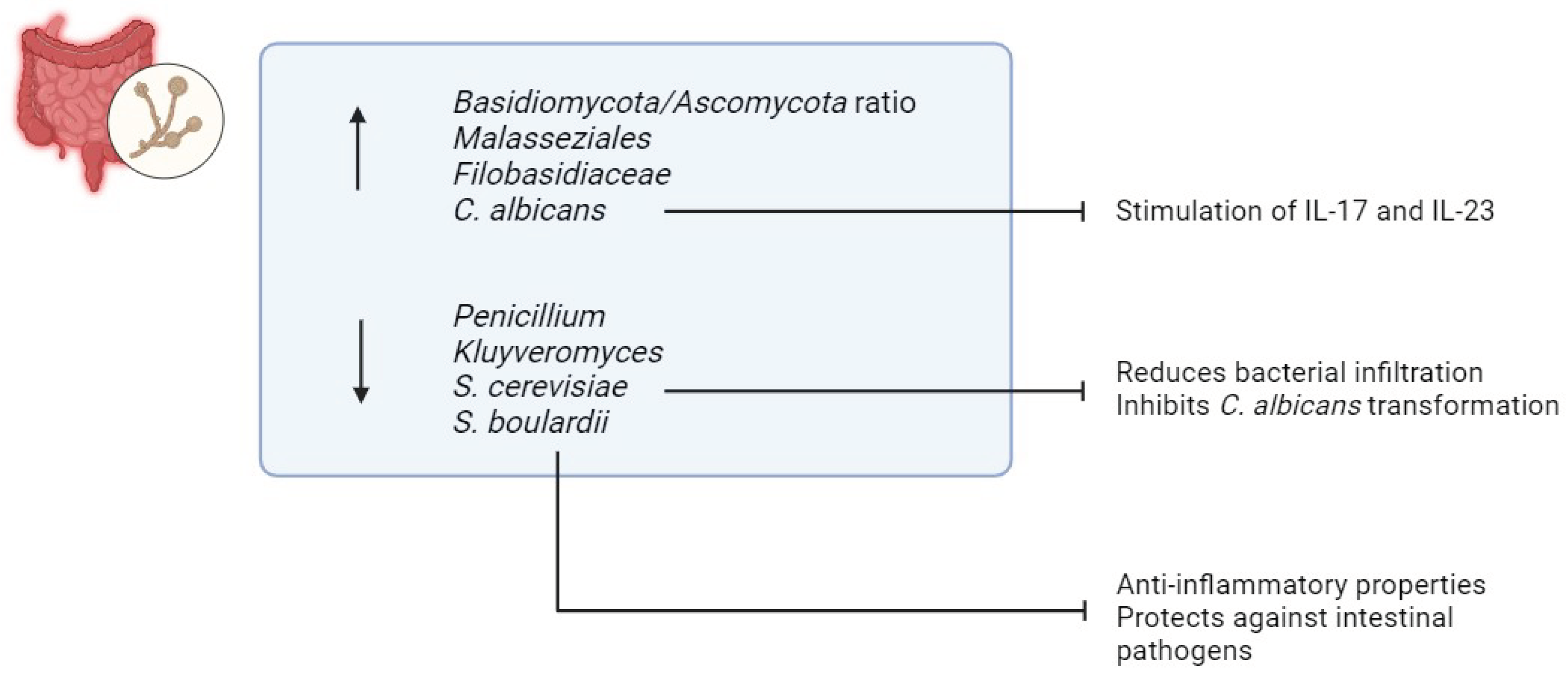
3.4. Fungi in IBD
3.5. Microbiota-Derived Metabolites Involved in IBD
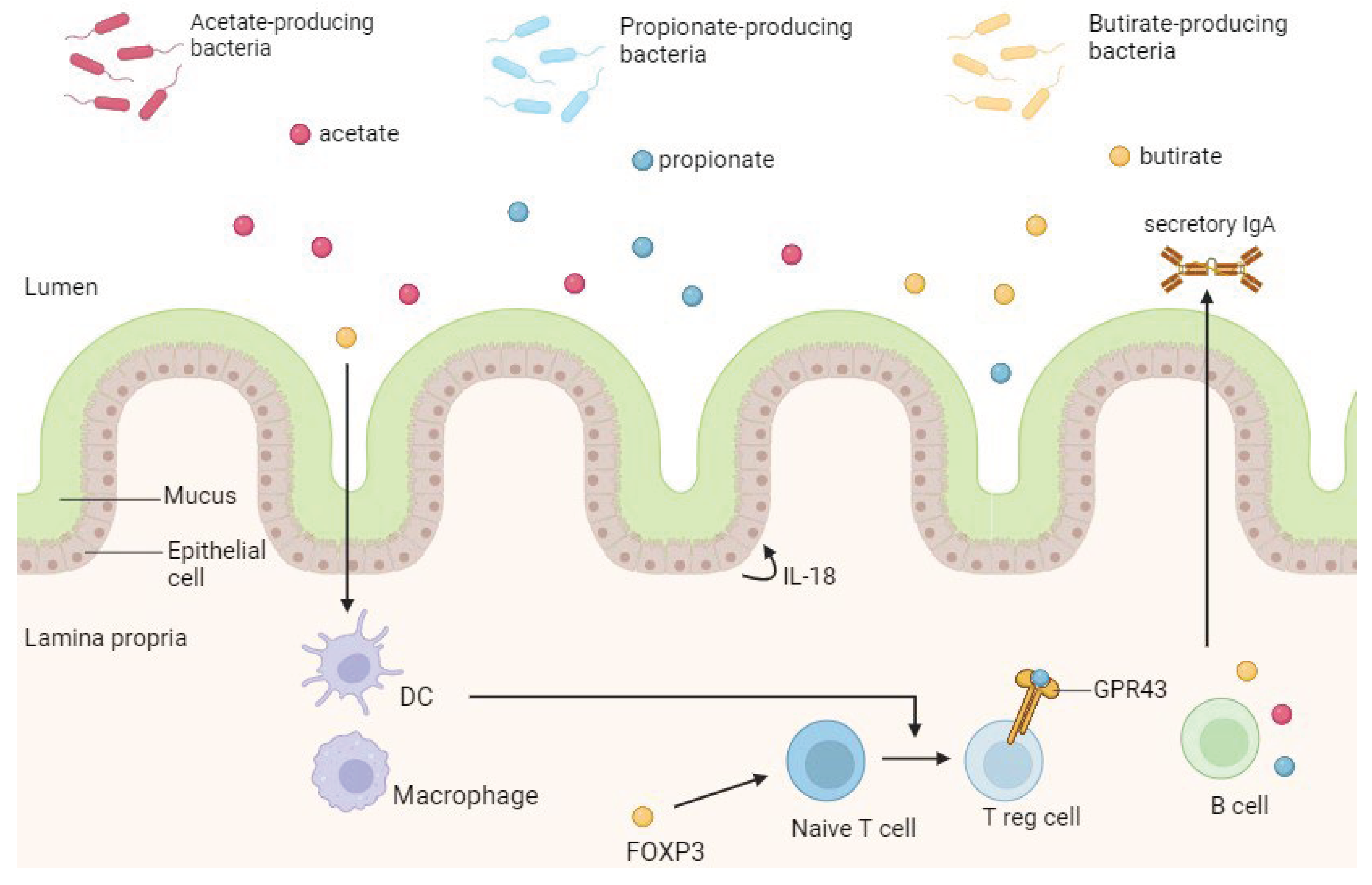
3.5.1. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
3.5.2. Bile Acids (BAs)
3.5.3. Bacterial Self-Metabolites
3.5.4. Vitamins
4. Manipulation of Microbiota as a Treatment Strategy in IBD
4.1. Diet
4.2. Prebiotics
4.3. Probiotics
4.4. Next Generation Probiotics (NGPs)
4.5. Synbiotics
4.6. Fecal Microbial Transplant (FMT)
4.7. Fecal Virome Transplant (FVT)
4.8. Phage Therapy
4.9. Targeting Archaeome
4.10. Targeting Micobiome
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomollón, F.; Dignass, A.; Annese, V.; et al. 3rd European Evidence-based Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Crohn’s Disease 2016: Part 1: Diagnosis and Medical Management. J Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Eliakim, R.; et al. Third European Evidence-based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 1: Definitions, Diagnosis, Extra-intestinal Manifestations, Pregnancy, Cancer Surveillance, Surgery, and Ileo-anal Pouch Disorders. J Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Panés, J.; Sandborn, W.J.; et al. Defining Disease Severity in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Current and Future Directions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc 2016, 14, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, S.R.; Graff, L.A.; Wilding, H.; et al. Quality of Life in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analyses-Part I. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2018, 24, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buie, M.J.; Quan, J.; Windsor, J.W.; et al. Global Hospitalization Trends for Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis in the 21st Century: A Systematic Review With Temporal Analyses. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc 2023, 21, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S.; Hernández, V.; Myrelid, P.; et al. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: results of the 3rd ECCO pathogenesis scientific workshop (I). J Crohns Colitis 2014, 8, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annese, V.; Duricova, D.; Gower-Rousseau, C.; et al. Impact of New Treatments on Hospitalisation, Surgery, Infection, and Mortality in IBD: a Focus Paper by the Epidemiology Committee of ECCO. J Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gönczi, L.; Lakatos, P.L.; et al. The Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Europe in 2020. J Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burisch, J.; Jess, T.; Martinato, M.; et al. The burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Europe. J Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q. A Comprehensive Review and Update on the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Immunol Res 2019, 2019, 7247238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, S.; Bernstein, C.N.; Sargent, M.; et al. Genome-wide analysis identifies rare copy number variations associated with inflammatory bowel disease. PloS One 2019, 14, e0217846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Wu, G.D.; Albenberg, L.; et al. Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 14, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geremia, A.; Biancheri, P.; Allan, P.; et al. Innate and adaptive immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun Rev 2014, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsialis, V.; Wall, S.; Liu, P.; et al. Single-Cell Analyses of Colon and Blood Reveal Distinct Immune Cell Signatures of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.C.; Chang, C.; Boschetti, G.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Crohn’s Disease Lesions Identifies a Pathogenic Cellular Module Associated with Resistance to Anti-TNF Therapy. Cell 2019, 178, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakase, H.; Sato, N.; Mizuno, N.; et al. The influence of cytokines on the complex pathology of ulcerative colitis. Autoimmun Rev 2022, 21, 103017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saez, A.; Herrero-Fernandez, B.; Gomez-Bris, R.; et al. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Innate Immune System. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, J.K.; Glapa-Nowak, A.; Banaszkiewicz, A.; et al. HLA-DQA1*05 Associates with Extensive Ulcerative Colitis at Diagnosis: An Observational Study in Children. Genes 2021, 12, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Bonen, D.K.; Inohara, N.; et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 2001, 411, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Ammitzboell, M.; Nys, K.; et al. ATG16L1: A multifunctional susceptibility factor in Crohn disease. Autophagy 2015, 11, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalischuk, L.D.; Buret, AG. A role for Campylobacter jejuni-induced enteritis in inflammatory bowel disease? Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2010, 298, G1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, B.M.; Paduro, C.A.; Salazar, G.A.; et al. A Potential Role of Salmonella Infection in the Onset of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. Association between TLR2 and TLR4 Gene Polymorphisms and the Susceptibility to Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis. PloS One 2015, 10, e0126803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidar, M.; Langevitz, P.; Shoenfeld, Y. The role of infection in inflammatory bowel disease: initiation, exacerbation and protection. Isr Med Assoc J IMAJ 2009, 11, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Bernstein, C.N.; Iliopoulos, D.; et al. Environmental triggers in IBD: a review of progress and evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018, 15, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasaly, N.; Gasaly, N.; de Hermoso, M.A.V.P. Impact of Bacterial Metabolites on Gut Barrier Function and Host Immunity: A Focus on Bacterial Metabolism and Its Relevance for Intestinal Inflammation. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 658354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Khan, MR. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 2019, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; et al. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, C.; Perillo, F.; Strati, F.; et al. The Role of Gut Microbiota Biomodulators on Mucosal Immunity and Intestinal Inflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merra, G.; Noce, A.; Marrone, G.; et al. Influence of Mediterranean Diet on Human Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2020, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, B.; Wolters, M.; Weyh, C.; et al. The Effects of Lifestyle and Diet on Gut Microbiota Composition, Inflammation and Muscle Performance in Our Aging Society. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglio, A.E.V.; Grillo, T.G.; De Oliveira, E.C.S.; et al. Gut microbiota, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2022, 28, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, N.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, FR. Intestinal Barrier in Human Health and Disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, SH. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, K.; Xu, C.; et al. Intestinal Claudin-7 deficiency impacts the intestinal microbiota in mice with colitis. BMC Gastroenterol 2022, 22, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barmeyer, C.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Claudin-related intestinal diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2015, 42, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christovich, A.; Luo, XM. Gut Microbiota, Leaky Gut, and Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 946248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, J.; Chang S-H, Ko Y-F, et al.; et al. Gut barrier disruption and chronic disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab TEM 2022, 33, 247–265. [CrossRef]
- Giambra, V.; Pagliari, D.; Rio, P.; et al. Gut Microbiota, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, and Cancer: The Role of Guardians of Innate Immunity. Cells 2023, 12, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyapati, R.K.; Rossi, A.G.; Satsangi, J.; et al. Gut mucosal DAMPs in IBD: from mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Mucosal Immunol 2016, 9, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.; McCarthy, J.; O’Driscoll, C.; et al. Pattern recognition receptors--molecular orchestrators of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2013, 24, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, A.B.R.; Ounit, R.; Afshinnekoo, E.; et al. Comprehensive benchmarking and ensemble approaches for metagenomic classifiers. Genome Biol 2017, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, F.; Ghosh, T.S.; O’Toole, PW. The Healthy Microbiome-What Is the Definition of a Healthy Gut Microbiome? Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBurney, M.I.; Davis, C.; Fraser, C.M.; et al. Establishing What Constitutes a Healthy Human Gut Microbiome: State of the Science, Regulatory Considerations, and Future Directions. J Nutr 2019, 149, 1882–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, G.; Tropini, C. The gut microbiota and its biogeography. Nat Rev Microbiol 2024, 22, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leimbach, A.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt U., E. coli as an all-rounder: the thin line between commensalism and pathogenicity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2013, 358, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmela, C.; Chevarin, C.; Xu, Z.; et al. Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2018, 67, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsepasi-Lauridsen, H.C.; Vallance, B.A.; Krogfelt, K.A.; et al. Escherichia coli Pathobionts Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 2019, 32, e00060–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkopf, N.; Pickert, G.; Billmeier, U.; et al. Activation of intestinal epithelial Stat3 orchestrates tissue defense during gastrointestinal infection. PloS One 2015, 10, e0118401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appunni, S.; Rubens, M.; Ramamoorthy, V.; et al. Emerging Evidence on the Effects of Dietary Factors on the Gut Microbiome in Colorectal Cancer. Front Nutr 2021, 8, 718389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, S. A tale of two habitats: Bacteroides fragilis, a lethal pathogen and resident in the human gastrointestinal microbiome. Microbiol Read Engl 2022, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y.; et al. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroidesfragilis Promotes Intestinal Inflammation and Malignancy by Inhibiting Exosome-Packaged miR-149-3p. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1552–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghi, F.; Goli, E.; Mirzaei, B.; et al. The association between fecal enterotoxigenic B. fragilis with colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teitelbaum, J.E.; Triantafyllopoulou, M. Inflammatory bowel disease and Streptococcus bovis. Dig Dis Sci 2006, 51, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Nakagawasai, O.; Nemoto, W.; et al. Effect of Enterococcus faecalis 2001 on colitis and depressive-like behavior in dextran sulfate sodium-treated mice: involvement of the brain-gut axis. J Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickertsson, J.A.B.; Desler, C.; Martin-Bertelsen, T.; et al. Enterococcus faecalis infection causes inflammation, intracellular oxphos-independent ROS production, and DNA damage in human gastric cancer cells. PloS One 2013, 8, e63147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan T-J, Goeser, L.; Lu, K.; et al. Enterococcus faecalis Glucosamine Metabolism Exacerbates Experimental Colitis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021, 12, 1373–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Miskeen, A.Y.; Hazari, Y.M.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum, inflammation, and immunity: the fire within human gut. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med 2016, 37, 2805–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Chen, Y.; Cao, P.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes the Development of Ulcerative Colitis by Inducing the Autophagic Cell Death of Intestinal Epithelial. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 594806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, A.; Selak, M.; Lantin, D.; et al. Bifidobacteria and Butyrate-Producing Colon Bacteria: Importance and Strategies for Their Stimulation in the Human Gut. Front Microbiol 2016, 7, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiels, K.; Joossens, M.; Sabino, J.; et al. A decrease of the butyrate-producing species Roseburia hominis and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii defines dysbiosis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 2014, 63, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; et al. prausnitzii and its supernatant increase SCFAs-producing bacteria to restore gut dysbiosis in TNBS-induced colitis. AMB Express 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, S.; Vitulo, N.; Calgaro, M.; et al. Microbiota changes induced by microencapsulated sodium butyrate in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2020, 32, e13914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Dharmaprakash, V.; Nighot, P.; et al. Bifidobacterium bifidum Enhances the Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junction Barrier and Protects against Intestinal Inflammation by Targeting the Toll-like Receptor-2 Pathway in an NF-κB-Independent Manner. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri, S.T.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F.; Amiri, M.M.; et al. Comparison of the prevalence of bacteriocin encoding genes in Lactobacillus spp. isolated from fecal samples of healthy volunteers, IBD-patient and IBD-recovered. Iran J Microbiol 2022, 14, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, K.R.; Liu, S.X.L.; Tian, R.; et al. Bifidobacteria stabilize claudins at tight junctions and prevent intestinal barrier dysfunction in mouse necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Pathol 2013, 182, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.F.; Elias-Oliveira, J.; Pereira, Í.S.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and Gut Immune System: A Good Friendship That Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Obesity, and Diabetes. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 934695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Cobián-Güemes, A.G.; Albenberg, L.; et al. The gut virome in inflammatory bowel diseases. Curr Opin Virol 2021, 51, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Aiewsakun, P. Virus classification - where do you draw the line? Arch Virol 2018, 163, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Handley, S.A.; Baldridge, M.T.; et al. Disease-specific alterations in the enteric virome in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 2015, 160, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Fan, D.; Sun, Y.; et al. The gut ileal mucosal virome is disturbed in patients with Crohn’s disease and exacerbates intestinal inflammation in mice. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornuault, J.K.; Petit M-A, Mariadassou, M.; et al. Phages infecting Faecalibacterium prausnitzii belong to novel viral genera that help to decipher intestinal viromes. Microbiome 2018, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, F.; Massimino, L.; Furfaro, F.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of intestinal mucosa revealed a specific eukaryotic gut virome signature in early-diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Conrad, M.A.; Kelsen, J.R.; et al. Dynamics of the Stool Virome in Very Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis 2020, 14, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, M. Evidence from genetics for a role of autophagy and innate immunity in IBD pathogenesis. Dig Dis Basel Switz 2012, 30, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiamani, K.; Luo, S.; Schulz, S.; et al. The role of virome in the gastrointestinal tract and beyond. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2022, 46, fuac027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, N.A.; Hameed, S.A.; Agyei, E.K.; et al. Crosstalk between the Intestinal Virome and Other Components of the Microbiota, and Its Effect on Intestinal Mucosal Response and Diseases. J Immunol Res 2022, 2022, 7883945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Li, Y.; Mirzaei, M.K.; et al. Transplantation of bacteriophages from ulcerative colitis patients shifts the gut bacteriome and exacerbates the severity of DSS colitis. Microbiome 2022, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiliaghdam, F.; Amatullah, H.; Digumarthi, S.; et al. Human enteric viruses autonomously shape inflammatory bowel disease phenotype through divergent innate immunomodulation. Sci Immunol 2022, 7, eabn6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweere, J.M.; Van Belleghem, J.D.; Ishak, H.; et al. Bacteriophage trigger antiviral immunity and prevent clearance of bacterial infection. Science 2019, 363, eaat9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Feng, N.; Narváez, C.F.; et al. The influence of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells on the immune response to rotavirus infection. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5601–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eme, L.; Doolittle, WF. Archaea. Curr Biol CB 2015, 25, R851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymann, K.; Moeller, A.H.; Goodman, A.L.; et al. Unexplored Archaeal Diversity in the Great Ape Gut Microbiome. mSphere 2017, 2, e00026–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, S.B.; Rostami, E.; Sephay, A.A.; et al. Alterations of the human gut Methanobrevibacter smithii as a biomarker for inflammatory bowel diseases. Microb Pathog 2018, 117, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais Lecours, P.; Marsolais, D.; Cormier, Y.; et al. Increased prevalence of Methanosphaera stadtmanae in inflammatory bowel diseases. PloS One 2014, 9, e87734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxley, A.P.A.; Lanfranconi, M.P.; Würdemann, D.; et al. Halophilic archaea in the human intestinal mucosa. Environ Microbiol 2010, 12, 2398–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehoud, C.; Albenberg, L.G.; Judge, C.; et al. Fungal Signature in the Gut Microbiota of Pediatric Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2015, 21, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallen-Adams, H.E.; Suhr, MJ. Fungi in the healthy human gastrointestinal tract. Virulence 2017, 8, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, H.; Leducq, V.; Aschard, H.; et al. Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut 2017, 66, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, A.K.; Auchtung, T.A.; Wong, M.C.; et al. The gut mycobiome of the Human Microbiome Project healthy cohort. Microbiome 2017, 5, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhao, X.; Cui, X.; et al. Characterization of fungal and bacterial dysbiosis in young adult Chinese patients with Crohn’s disease. Ther Adv Gastroenterol 2020, 13, 1756284820971202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Fungal Microbiota is Associated With Mucosal Inflammation in Crohn’s Disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 2014, 48, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Liang, L.; et al. Lactic Acid-Producing Probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae Attenuates Ulcerative Colitis via Suppressing Macrophage Pyroptosis and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 777665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon. Comparative immunophenotyping of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida spp. strains from Crohn’s disease patients and their interactions with the gut microbiome - PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7388382/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; et al. Saccharomyces boulardii alleviates DSS-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation in humanized mice. Food Funct 2022, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivananthan, K.; Petersen, AM. Review of Saccharomyces boulardii as a treatment option in IBD. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2018, 40, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. Dietary fiber and SCFAs in the regulation of mucosal immunity - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36543697/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Parada Venegas, D.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; et al. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Chen, X.; Kwan, T.K.; et al. Dietary Fiber Protects against Diabetic Nephropathy through Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Mediated Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors GPR43 and GPR109A. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 2020, 31, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Potamitis, M.; et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv Immunol 2014, 121, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Esch BCAM van, Wagenaar, G.T.M.; et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids on immune and endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2018, 831, 52–59. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cheng, S.; Yao, J.; et al. Correlation between altered gut microbiota and elevated inflammation markers in patients with Crohn’s disease. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 947313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yutuc, E.; Griffiths, WJ. Cholesterol metabolism pathways - are the intermediates more important than the products? FEBS J 2021, 288, 3727–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Sun, L.; Gonzalez, FJ. Gut microbiota-derived bile acids in intestinal immunity, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.L.; Stine, J.G.; Bisanz, J.E.; et al. Bile acids and the gut microbiota: metabolic interactions and impacts on disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 21, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall H-U, et al.; et al. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darkoh, C.; Lichtenberger, L.M.; Ajami, N.; et al. Bile acids improve the antimicrobial effect of rifaximin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2010, 54, 3618–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajor, A.; Gillberg P-G, Abrahamsson H. Bile acids: short and long term effects in the intestine. Scand J Gastroenterol 2010, 45, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.Y.; Aleksunes, L.M.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Bile acids via FXR initiate the expression of major transporters involved in the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in newborn mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012, 302, G979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Hu, J.; Yan, X. Cross-talk between bile acids and intestinal microbiota in host metabolism and health. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2015, 16, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, A.; Nancey, S.; Reimund J-M, et al.; et al. Fecal microbiota and bile acids in IBD patients undergoing screening for colorectal cancer. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2078620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijmeijer, R.M.; Gadaleta, R.M.; Mil SWC van, et al. Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) activation and FXR genetic variation in inflammatory bowel disease. PloS One 2011, 6, e23745. [CrossRef]
- Labbé, A.; Ganopolsky, J.G.; Martoni, C.J.; et al. Bacterial bile metabolising gene abundance in Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis and type 2 diabetes metagenomes. PloS One 2014, 9, e115175. [CrossRef]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Ma, N.; He, T.; et al. Tryptophan (Trp) modulates gut homeostasis via aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020, 60, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connors, J.; Dawe, N.; Van Limbergen, J. The Role of Succinate in the Regulation of Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvornikova, K.A.; Platonova, O.N.; Bystrova, EY. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Crosstalk between Histamine, Immunity, and Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 9937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figliuolo, V.R.; Coutinho-Silva, R.; Coutinho, C.M.L.M. Contribution of sulfate-reducing bacteria to homeostasis disruption during intestinal inflammation. Life Sci 2018, 215, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinsky, V.; Dotan, I.; Gophna, U. Carriage of Colibactin-producing Bacteria and Colorectal Cancer Risk. Trends Microbiol 2020, 28, 874–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.Y.; Groer, M.; Dutra, S.V.O.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Immune System Interactions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.L.; Karl, J.P.; Oliverio, A.M.; et al. Dietary vitamin K is remodeled by gut microbiota and influences community composition. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Dold, S.; Rehman, A.; et al. Vitamins, the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal health in humans. Nutr Res N Y N 2021, 95, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, F.; Spisni, E.; Giovanardi, E.; et al. Implications of the Westernized Diet in the Onset and Progression of IBD. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernia, F.; Valvano, M.; Longo, S.; et al. Vitamin D in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Implications. Nutrients 2022, 14, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, W.; Garud, N.; Joshi, R. Role of inulin as prebiotics on inflammatory bowel disease. Drug Discov Ther 2019, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; et al. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drzymała-Czyż S, Banasiewicz, T.; Tubacka, M.; et al. Inulin supplementation in rat model of pouchitis. Acta Biochim Pol 2011, 58, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Yu, X.; Luo, Y.; et al. Effect of Fructooligosaccharides Supplementation on the Gut Microbiota in Human: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, HD. Dietary fiber and prebiotics and the gastrointestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng D-W, Li R-Q, An J-X, et al. Prebiotics-Encapsulated Probiotic Spores Regulate Gut Microbiota and Suppress Colon Cancer. Adv Mater Deerfield Beach Fla 2020, 32, e2004529. [CrossRef]
- Matijašić, M.; Meštrović, T.; Perić, M.; et al. Modulating Composition and Metabolic Activity of the Gut Microbiota in IBD Patients. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greef, E.; Vandenplas, Y.; Hauser, B.; et al. Probiotics and IBD. Acta Gastro-Enterol Belg 2013, 76, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- La Fata, G.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, MH. Probiotics and the Gut Immune System: Indirect Regulation. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 2018, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwehand, AC. A review of dose-responses of probiotics in human studies. Benef Microbes 2017, 8, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Probiotic Escherichia coli NISSLE 1917 for inflammatory bowel disease applications. Food Funct 2022, 13, 5914–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon. Probiotics for induction of remission in Crohn’s disease - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32678465/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Scaldaferri, F.; Gerardi, V.; Mangiola, F.; et al. Role and mechanisms of action of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 in the maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis patients: An update. World J Gastroenterol 2016, 22, 5505–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, S.; Di Nardo, G.; Ferrari, F.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: the effectiveness of Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 rectal enema in children with active distal ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012, 35, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lyu, W.; Song, Y.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Clostridium butyricum-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Ulcerative Colitis: Impact on Host microRNAs Expressions and Gut Microbiome Profiles. Mol Nutr Food Res 2023, 67, e2200884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. Saccharomyces boulardii in maintenance treatment of Crohn’s disease - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10961730/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Pan, Y.; Ning, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. The Preventive Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum ZS62 on DSS-Induced IBD by Regulating Oxidative Stress and the Immune Response. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021, 2021, 9416794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng F-S, Pan, D.; Chang, B.; et al. Probiotic mixture VSL#3: An overview of basic and clinical studies in chronic diseases. World J Clin Cases 2020, 8, 1361–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursi, A.; Brandimarte, G.; Papa, A.; et al. Treatment of relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with the probiotic VSL#3 as adjunctive to a standard pharmaceutical treatment: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol 2010, 105, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, A.; Midha, V.; Makharia, G.K.; et al. The probiotic preparation, VSL#3 induces remission in patients with mild-to-moderately active ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc 2009, 7, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardini, H.E.; Grigorian, AY. Probiotic mix VSL#3 is effective adjunctive therapy for mild to moderately active ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2014, 20, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huynh, H.Q.; deBruyn, J.; Guan, L.; et al. Probiotic preparation VSL#3 induces remission in children with mild to moderate acute ulcerative colitis: a pilot study. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009, 15, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, E.; Pascarella, F.; Giannetti, E.; et al. Effect of a probiotic preparation (VSL#3) on induction and maintenance of remission in children with ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2009, 104, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumi, R.; Abdelouhab, K.; Rafa, H.; et al. Beneficial role of the probiotic mixture Ultrabiotique on maintaining the integrity of intestinal mucosal barrier in DSS-induced experimental colitis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2013, 35, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghyselinck, J.; Verstrepen, L.; Moens, F.; et al. A 4-strain probiotic supplement influences gut microbiota composition and gut wall function in patients with ulcerative colitis. Int J Pharm 2020, 587, 119648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, V.D.; Romeo, M.; Marino Gammazza, A.; et al. The long-term effects of probiotics in the therapy of ulcerative colitis: A clinical study. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czechoslov 2016, 160, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hong, G.; et al. Probiotic mixtures with aerobic constituent promoted the recovery of multi-barriers in DSS-induced chronic colitis. Life Sci 2020, 240, 117089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Deng, Y.; Guo, J.; et al. Effect of mesalazine combined with probiotics on inflammation and immune function of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Transl Res 2022, 14, 8234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martín, R.; Miquel, S.; Benevides, L.; et al. Functional Characterization of Novel Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Strains Isolated from Healthy Volunteers: A Step Forward in the Use of F. prausnitzii as a Next-Generation Probiotic. Front Microbiol 2017, 8, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Feng, S.; Arjan, N.; et al. A next generation probiotic, Akkermansia muciniphila. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2019, 59, 3227–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasueda, A.; Mizushima, T.; Nezu, R.; et al. The effect of Clostridium butyricum MIYAIRI on the prevention of pouchitis and alteration of the microbiota profile in patients with ulcerative colitis. Surg Today 2016, 46, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, D.; Landete, JM. Genetic engineering as a powerful tool to improve probiotic strains. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 2017, 33, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.P.; Goers, L.; Lesser, CF. Emerging strategies for engineering Escherichia coli Nissle 1917-based therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2022, 43, 772–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, T.C.; Nair, NU. Engineered lactobacilli display anti-biofilm and growth suppressing activities against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, F.; Chen, S.; Marcotte, H. Engineer probiotic bifidobacteria for food and biomedical applications - Current status and future prospective. Biotechnol Adv 2020, 45, 107654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darb Emamie, A.; Rajabpour, M.; Ghanavati, R.; et al. The effects of probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics on the reduction of IBD complications, a periodic review during 2009-2020. J Appl Microbiol 2021, 130, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskey, N.; Dahl, WJ. Synbiotic therapy: a promising new adjunctive therapy for ulcerative colitis. Nutr Rev 2006, 64, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steed, H.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Blackett, K.L.; et al. Clinical trial: the microbiological and immunological effects of synbiotic consumption - a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study in active Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010, 32, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, M.; Pu, J.; et al. Probiotics and Their Metabolites Ameliorate Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Critical Review. Infect Microbes Dis 2021, 3, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng Y-W, Fischer M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 2023, 36, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weingarden, A.R.; Vaughn, BP. Intestinal microbiota, fecal microbiota transplantation, and inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvas, C.L.; Dahl Jørgensen, S.M.; Jørgensen, S.P.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Is Superior to Fidaxomicin for Treatment of Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37189634/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Costello, S.P.; Hughes, P.A.; Waters, O.; et al. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on 8-Week Remission in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation for ulcerative colitis: a prospective clinical study. BMC Gastroenterol 2019, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, R.J.; Rubin, DT. Fecal microbiota transplantation as therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis 2014, 8, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramsothy, S.; Paramsothy, R.; Rubin, D.T.; et al. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation for Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 1180–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira L de, F.; Borba, H.H.; Tonin, F.S.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation in inflammatory bowel disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One 2020, 15, e0238910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayyedi, P.; Surette, M.G.; Kim, P.T.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Induces Remission in Patients With Active Ulcerative Colitis in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramsothy, S.; Kamm, M.A.; Kaakoush, N.O.; et al. Multidonor intensive faecal microbiota transplantation for active ulcerative colitis: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Lond Engl 2017, 389, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Li, P.; Xu, L.; et al. Step-up fecal microbiota transplantation strategy: a pilot study for steroid-dependent ulcerative colitis. J Transl Med 2015, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anon. Safety, tolerability, and clinical response after fecal transplantation in children and young adults with ulcerative colitis - PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23542823/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- He, Z.; Li, P.; Zhu, J.; et al. Multiple fresh fecal microbiota transplants induces and maintains clinical remission in Crohn’s disease complicated with inflammatory mass. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Bu, C.; Yuan, W.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplant via Endoscopic Delivering Through Small Intestine and Colon: No Difference for Crohn’s Disease. Dig Dis Sci 2020, 65, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, H.; Landman, C.; Seksik, P.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation to maintain remission in Crohn’s disease: a pilot randomized controlled study. Microbiome 2020, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellermayer, R.; Nagy-Szakal, D.; Harris, R.A.; et al. Serial fecal microbiota transplantation alters mucosal gene expression in pediatric ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2015, 110, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, S.; Virmani, S.; K Vuyyuru, S.; et al. Faecal microbiota transplantation with anti-inflammatory diet (FMT-AID) followed by anti-inflammatory diet alone is effective in inducing and maintaining remission over 1 year in mild to moderate ulcerative colitis: a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2022, 71, 2401–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okahara, K.; Ishikawa, D.; Nomura, K.; et al. Matching between Donors and Ulcerative Colitis Patients Is Important for Long-Term Maintenance after Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. J Clin Med 2020, 9, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelberger, S.; Reinisch, W.; Makristathis, A.; et al. Temporal bacterial community dynamics vary among ulcerative colitis patients after fecal microbiota transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol 2013, 108, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskind, D.L.; Singh, N.; Nielson, H.; et al. Fecal microbial transplant via nasogastric tube for active pediatric ulcerative colitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2015, 60, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, M.; Colville, A. Adverse events in faecal microbiota transplant: a review of the literature. J Hosp Infect 2016, 92, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.S.; Mentzel, C.M.J.; Kot, W.; et al. Faecal virome transplantation decreases symptoms of type 2 diabetes and obesity in a murine model. Gut 2020, 69, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, L.A.; Ryan, F.J.; Dalmasso, M.; et al. Autochthonous faecal viral transfer (FVT) impacts the murine microbiome after antibiotic perturbation. BMC Biol 2020, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, D.; Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; et al. Community Types of the Human Gut Virome are Associated with Endoscopic Outcome in Ulcerative Colitis. J Crohns Colitis 2023, 17, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, S.J.; Waetzig, G.H.; Rehman, A.; et al. Efficacy of Sterile Fecal Filtrate Transfer for Treating Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungaro, F.; Massimino, L.; D’Alessio, S.; et al. The gut virome in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: From metagenomics to novel therapeutic approaches. United Eur Gastroenterol J 2019, 7, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Guo, F.; Yu, Y.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes Chemoresistance to Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Autophagy. Cell 2017, 170, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Pan, P.; Zheng D-W, et al; et al. Bioinorganic hybrid bacteriophage for modulation of intestinal microbiota to remodel tumor-immune microenvironment against colorectal cancer. Sci Adv 2020, 6, eaba1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerte-Stone, J.; Mimee, M. Host happy hour: Phage cocktail targets IBD-associated microbes. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1352–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, S.; Kredo-Russo, S.; Valdés-Mas, R.; et al. Targeted suppression of human IBD-associated gut microbiota commensals by phage consortia for treatment of intestinal inflammation. Cell 2022, 185, 2879–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dridi, B.; Fardeau M-L, Ollivier, B.; et al. The antimicrobial resistance pattern of cultured human methanogens reflects the unique phylogenetic position of archaea. J Antimicrob Chemother 2011, 66, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, K.; Wacher, V.; Sliman, J.; et al. Review article: inhibition of methanogenic archaea by statins as a targeted management strategy for constipation and related disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016, 43, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plein, K.; Hotz, J. Therapeutic effects of Saccharomyces boulardii on mild residual symptoms in a stable phase of Crohn’s disease with special respect to chronic diarrhea--a pilot study. Z Gastroenterol 1993, 31, 129–134. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




