1. Introduction
Stress refers to the physiological response induced in living organisms when they are exposed to adversity and try to adapt to it, a process known as allostasis [
1]. Non-adaptation generates allostatic overload in the brain, increasing vulnerability to mental disorders [
2]. In animal models, allostatic overload triggers morphological changes in neurons, such as dendritic atrophy and neurogenesis reduction in the hippocampus, dendritic arborization in the amygdala, and dendritic remodeling in the medial prefrontal cortex [
3,
4]. These morphological changes impact synaptic function, leading to cognitive and behavioral impairments [
5,
6]. The hippocampus is a brain area associated with episodic memory that is highly vulnerable to allostatic overload. Chronic stress induces dendritic atrophy in the hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons [
5,
7] and dendritic hypertrophy in the basolateral amygdala, both leading to spatial memory impairments [
4,
8] and enhancing anxiety [
9], respectively.
The adolescent brain is highly responsive and susceptible to environmental demands, i.e., stressors [
10]. For instance, higher plasma corticosterone levels was found in adolescent rats exposed to restraint stress than adult rats [
11]. The serum corticosterone levels of acute-stressed adolescent rats were elevated for twice as long as those of adult rats subjected to the same conditions [
12]. In humans, male and female adolescents also show an increased cortisol response in response to stress exposure compared to male and female children and adults [
13].
External factors, such as nutrition and exercise, can modulate vulnerability to stress [
14]. In line with this, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play an essential role in the development of the brain [
15] and promote anti-stress effects in rats [
14]. n-3 PUFA supplementation improves memory and GABAergic activity in the hippocampus, modulated by the cannabinoid receptor type 1 [
14]
. An optimal n-6:n-3 ratio (1:5) of PUFA promotes anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity in animal models [
16] and humans [
17]. Moreover, a high n-6:n-3 ratio is associated with depression symptoms, a stress-related disorder [
18]. As n-3 PUFAs consumption has decreased in the last years triggering a disbalance in the n-6:n-3 ratio, it is crucial to promote and study food high in these fatty acids [
19].
Quinoa (
Chenopodium quinoa, Wild) is an ancient grain from the Andean region with an exceptional nutritional value. Quinoa has a high content of unsaturated fatty acids, reaching 88% of total fatty acids, mainly oleic (OA, 18:1 n-9, 19.7–29.5 %), linoleic (LA: 18:2n-6, 49.0-56.4 %) and alpha-linolenic (ALA: 18:3 n-3, 8.7-11.7 %) [
20]. ALA and LA are essential fatty acids and their dietary intake is a source of PUFAs [
21]. Quinoa consumption has been associated with improved health and reduction of risk factors related to cardiovascular diseases [
22]. Recently, a red-quinoa seed extract prevented memory deficit induced by scopolamine in mice, suggesting that quinoa may have a neuroprotective effect [
23]. Considering that the hippocampal neurogenesis and maturation in the adolescent brain are particularly susceptible to stress, we aimed to evaluate the effects of a quinoa-based functional food intake in a repeated restrain stress protocol in adolescent rats. Anxiety, spatial memory, and dendritic length in long shaft pyramidal neurons of CA3 hippocampal were measured in rats supplemented with quinoa-based functional food and exposed to a restrain stress.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals and Restraint Protocols
Prepubertal male Sprague-Dawley rats, 21 postnatal days (PND), were housed in groups of three on a 12 h light/dark cycle (light: 350 lux at 8:00 am). All rats had ad libitum access to food and water in a temperature (21±1 ºC) and humidity-controlled (55%) room.
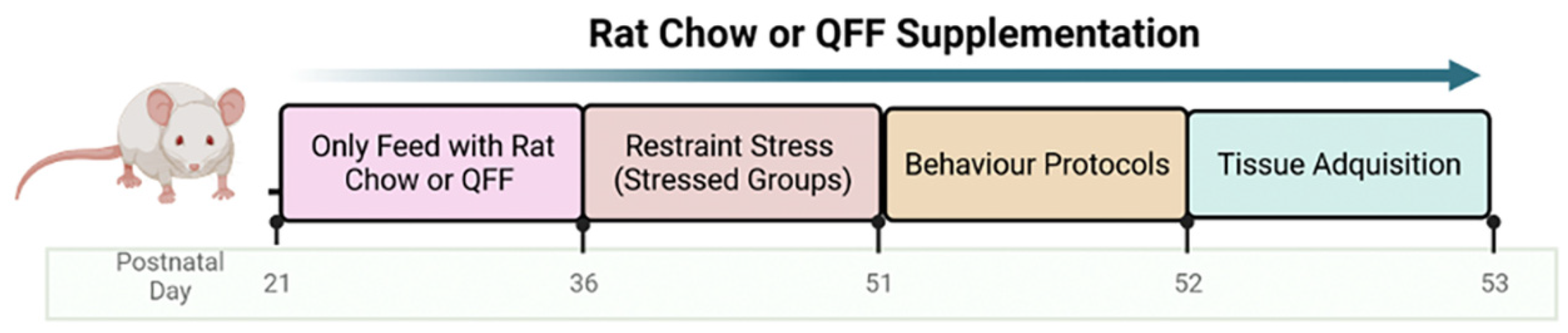
Table 1 shows the experimental groups and the number of rats used in each group. Non-stressed animals, littermates of the Stressed animals, were housed in separate rooms and cages, and not subjected to any experimental stress. Stressed groups were restrained during the light phase of the cycle at 10 am. Animals were placed in a custom-made plastic restrainer (12 cm long and 6 cm diameter x 20 cm long as the rats grew) in their home cages for two hours daily, from 36 to 51 PND (15 days). This protocol adapts the repeated restraint paradigm used by McLaughlin et. al. [
24]. Rats were fed with commercial rat chow (Champion
®, Chile) or quinoa functional food (QFF) for 31 or 32 days starting the weaning day (day 21). The stress protocol was initiated on PND 36 (15 days after weaning) (
Figure 1). To monitor the general effects of the stress protocol, we measured the weight gain in all the animals throughout the experiments.
2.2. Quinoa Functional Food: Raw Material and Formulation
The quinoa-supplemented rat food for QFF groups was prepared by mixing commercial rat chow (Champion S.A.
®, Chile) and quinoa in a 1:1 ratio, following previously described methods [
25]. Briefly, quinoa seeds were obtained from a crop grown in coastal central Chile at Cahuil, Region of O’Higgins. Quinoa seeds were washed under stirring in water for one hour to extract saponins. Then, 125 g of quinoa was blanched in 250 mL of water at 80ºC for 15 min. Finally, quinoa was mixed with an equal amount of rat chow (125 g each) and 300 ml of water. The mixture was homogenized in a Meat Mincer (TJ12 model, Australia) and molded into a pellet, like the commercial rat chow. The pellets were dried for 36 hours at 50 °C and 60% humidity in an industrial furnace.
2.3. Behavioral Procedures
All tests were performed between 8:00 and 12:00 a.m. Animals were naive to the tests, which were recorded by internet protocol cameras fixed above the behavioral apparatus and connected to a computer in an adjacent room. Videos were acquired by Nuuo software (Nuuo, Taiwan) and analyzed offline using EthoVision® XT 18 version (Noldus, Wageningen, The Netherlands). After each trial, all mazes were wiped clean thoroughly with 5% ethanol solution. Animals from all experimental groups were evaluated simultaneously, conducted in a sound-proof and temperature-controlled (21 ± 1 ºC) room. The background noise level in the room was 40 dB (Precision sound level meter, Quest Technologies, USA).
a) Open Field (OF)
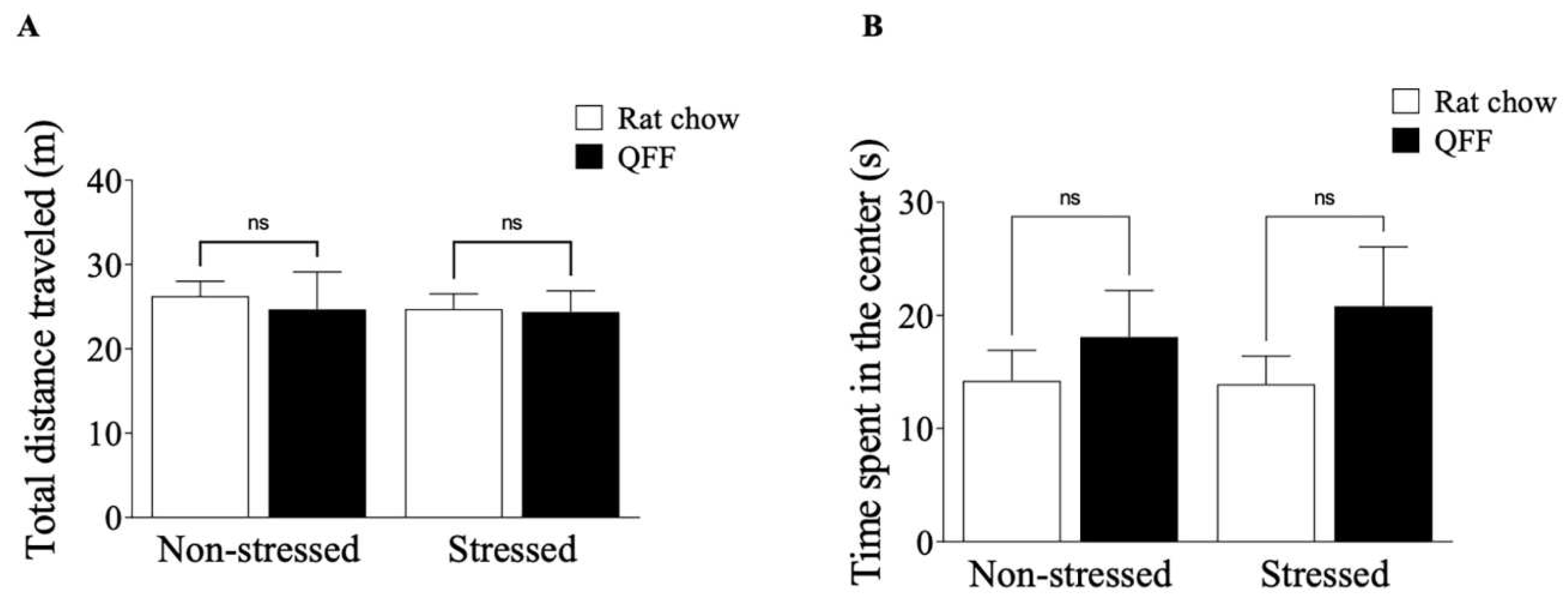
Locomotor activity was analyzed twenty-four hours after the last stress session for all experimental groups. The OF was performed by placing the animal in the center of a black Plexiglas cage (70x70x40 cm) for 5 minutes. The OF arena was digitally divided offline into 16 equal grids using the EthoVision® XT 18 version (Noldus, Wageningen, The Netherlands). The OF arena was illuminated to 300 luxs (Digital lux meter, Weafo Instrument Co., China). Total distance traveled and time spent in the center of the apparatus were measured as locomotor activity and anxiety-like behaviors, respectively. Immediately after the OF test, we measured the anxiety levels using the elevated plus maze (EPM) and the light-dark box test (LDB).
b) Elevated plus maze (EPM)
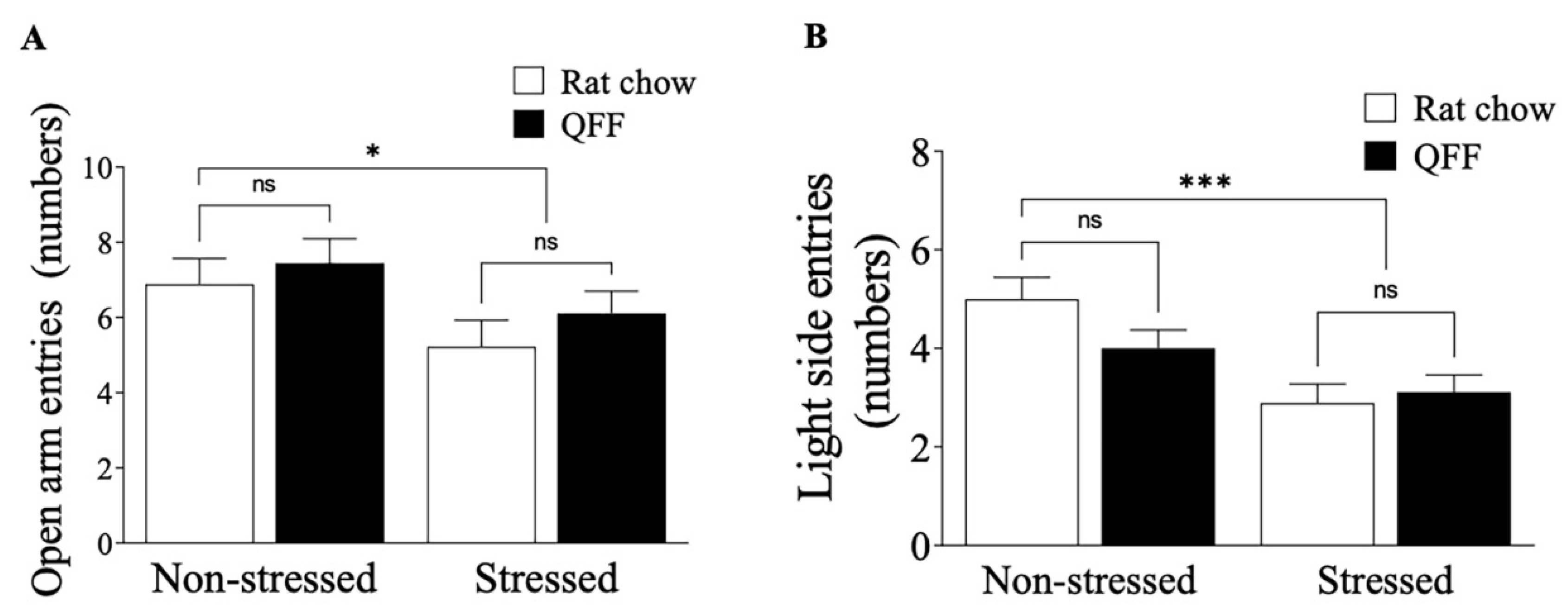
The EPM paradigm consists of two open arms (60 x 15 cm each) and, two closed arms (60 x 15 x 20 cm each) and a central platform (15 x 15 cm) arranged so two arms of each type were opposite of each other. The maze was elevated 100 cm above the floor and illuminated from the ceiling by a bulb giving 300 ± 10 lux in the open arms and 210 ± 10 lux in the closed arms. Each rat was placed at the maze’s center, facing always the same open arm, and the frequency of entries to the open and closed arms during a 5-minute test period were recorded. Entries into an arm were defined as having occurred when the animal placed 70 % of the body onto the arm. Open-arm entries were used as measures of anxiety level.
c) Light Dark Box (LDB) paradigm
Since the LDB paradigm has a different sensibility than EPM to evaluate anxiety levels [
26], a new group of rats was used to perform this test. LDB consists of a two-compartment Plexiglas box of 50 cm x 50 cm x 40 cm each. The lighted chamber was illuminated from above by a white light bulb (500 lux at floor level). The dark chamber was made with black Plexiglas with 5 lux of light intensity on the floor. Both chambers were separated by a black partition with a small opening (8 cm x 8 cm) at the bottom. Each rat was placed in the center of the lighted box facing the side away from the door and released during the 5-minute test. The full-body light side entry frequency was measured by the EthoVision
® XT 18 version (Noldus, Wageningen, The Netherlands).
d) Y-maze
Y-maze is a robust and well-documented test to measure spatial and working memory for chronically stressed rats [
4]. A new group of rats was subjected to the Y-maze task twenty-four hours after completing the locomotor activity and anxiety evaluations. Each rat was placed in the center of a black Plexiglass cage (70 × 70 × 40 cm) for 5 min. The arena was illuminated by 300 ± 20 lux. One arm of the maze was assigned as “novel arm” and the start and alternate arms were denominated as “other arm” which were counterbalanced among rats. Stressed and non-stressed rats were tested simultaneously in different rooms and mazes. The test was performed in two phases. First, a training session where the novel arm was blocked, and the animals were placed on the start arm to explore for 15 minutes the two free arms. After training, rats were returned to their home cages and the novel arm was unblocked. Four hours after training, rats were returned to the same start arm used during training and let to explore all three arms for 5 minutes. Entry into the arm was defined as when the animal placed all limbs or 70 percent of the body onto the arm. The number of entries in the novel and other arms was measured.
2.4. Morphological Data Analysis
Hippocampal morphology was determined in a new group of rats. Animals were killed one day after the end of the stress paradigm under deep anesthesia. The brain was removed and processed using the FD Rapid Golgi Stain kit (FD Neuro Technologies, Inc., USA). The brain tissue was processed by cutting in the coronal plane, maintaining the middle part containing the hippocampus. The coronal sections were cut in a cryostat (Microm International) and 150µm thick sections were collected onto super-frost plus slides. Afterward, the sections were collected serially,ydrated in a descendent alcohol battery, cleared in xylene, and cover-slipped. The drawing of stained cells (Long-shaft pyramidal of CA3 hippocampal neurons) was generated using Camera Lucida tracking (BX31-U-DAL 10X, Olympus Co., Japan). Random selection was made among neurons following the next criteria: (1) presence of untruncated dendrites, (2) consistent and dark impregnation along the entire dendritic field, and (3) relative isolation from neighboring impregnated neurons. The drawn cells were scanned (eight-bit grayscale TIFF images with 1200 d.p.i. resolution; EPSON ES-1000C) along with a calibrated scale for subsequent computerized image analysis. A researcher-made data analysis (dendritic arbor length per neuron) in a double-blind fashion. Image J software (NIH, USA) was used for the morphometric analysis of digitized images.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
First, all variables were analyzed for normal distribution using the Shapiro-Wilk test, whereas the homoscedasticity was analyzed using the Levene test. The differences in body weight gain were analyzed using two-way ANOVA [groups (stress, diet) × days (1, 5, 10, 15)] followed by Bonferroni post-test. Results from the OF (total distance traveled, time spent in the center), EPM (percentage of open-arm entries), LDB (light side entries), Y-maze tests (total entries into the novel arm), and dendritic morphology, were analyzed by two-way ANOVA for stress (non-stressed or stressed) and diet (rat chow or QFF), followed by a Bonferroni post-test. Statistical analyses were performed using Prism 7 software (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). Results are given as mean ± SEM, a probability level of 0.05 or less was accepted as significant.
4. Discussion
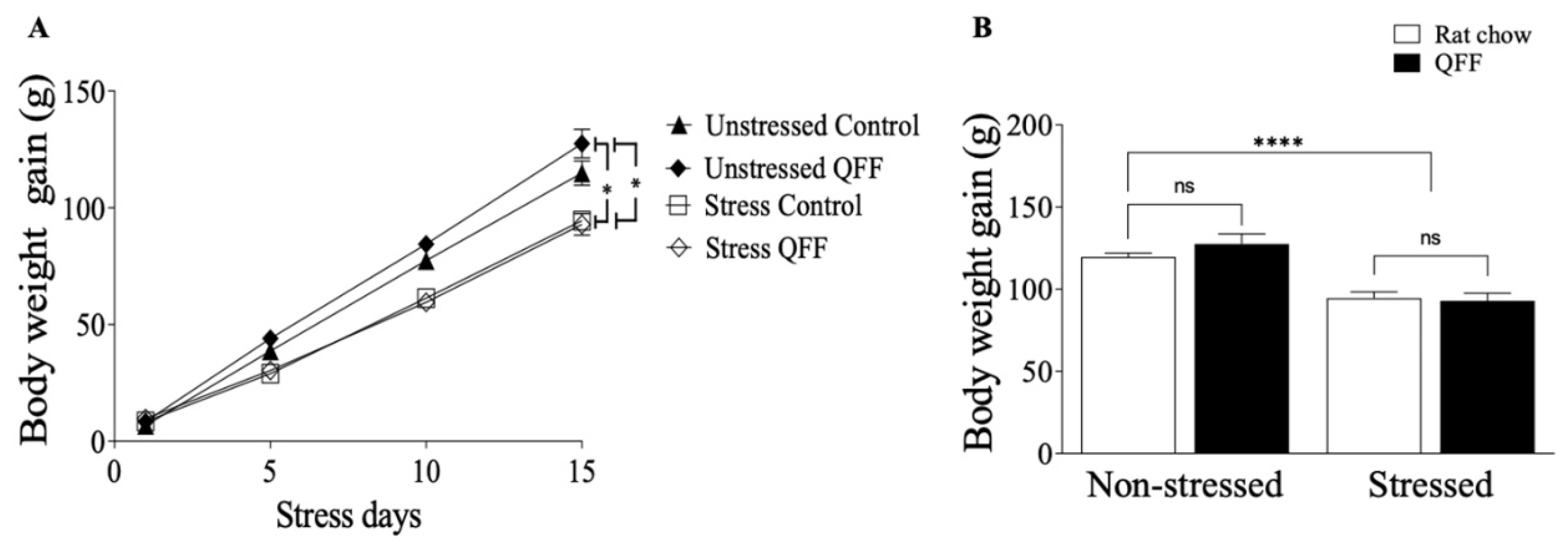
In this study, we show that the intake of quinoa-based food during adolescence improves the memory of stressed rats as well as counteracts the effects of stress-induced dendritic atrophy in the hippocampus. First, we investigated whether our stress protocol effectively triggered stress responses. Stressed rats of all experimental groups (rat chow and QFF) had less body weight gain than non-stressed rats. This suggests that the stress protocol used was effective and QFF intake did not prevent the loss of weight gain induced by restraint stress. However, other studies have shown that dietary supplementation of hydrolyzed quinoa (2000 mg/kg, 30 days) in sedentary Wistar rats decreased body weight gain, food intake, fat deposition, and triglycerides [
27], while supplementation with fermented or sprouted quinoa (47 days) reduced food intake, blood glucose and lipids levels on rats fed with high-carbohydrates diet (28). Both studies reported a decrease in weight gain after quinoa supplementation that may be associated with food intake reduction [
28] related to lower levels of ghrelin, leptin, and cholecystokinin [
29].
On the other hand, we did not observe changes in the body weight gain in the non-stressed group fed with QFF compared to rat chow, which could be explained by differences in food intake, forms of administration, and by nutritional properties of the food. We suggest that anxiogenic protocols administration (oral administration or orogastric gavage) and reduction in food intake translate into a less body weight gain. In support of this idea, previous studies have shown that oral administration of n-3 PUFAs is considered a stressor for rats due because it increases corticosterone levels in the non-stressed rats [
30], which reduces body weight gain. Moreover, feeding the animals with a solution of hydrolyzed quinoa through orogastric gavage reduces food intake and decreases body weight gain [
27].
Food intake is strongly influenced by stress and the composition of the diet. Rats subjected to stress consumed less commercial chow than the non-stressed rats [
31]. Interestingly, rats that could choose between two diets prefer high-caloric food [
31]. In our study, we found no difference in food intake. This may suggest that our form of administration of food is less stressful or that, due to nutritional characteristics, quinoa is more palatable for rats.
Chronic stress-induced anxiety is produced by neuronal morphology alterations in the basolateral amygdala [
32]. In the brain, the medial prefrontal cortex and the amygdala are extensively interconnected and work in concert to tune the expression of emotions, such as fear and anxiety [
33]. It is possible that the chronic stress protocol used in our study induced hyperactivation of the basolateral amygdala and/or the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis [
33,
34], which increased anxiety. On the other hand, several studies have shown that n-3 PUFAs supplementation can reduce chronic stress-induced anxiety [
30,
35]. Indeed, the anxiolytic effect of n-3 PUFAs was significantly different to controls only in subgroups with a higher dosage (at least 2000 mg/d) and not in subgroups with a lower dosage (<2000mg/d) [
36]. This suggests that the anxiolytic effect depends on the concentration of PUFA, specifically docosahexaenoic acid (DHA: 22:6 n-3). In our experiments, QFF consumption did not affect anxiety on the EPM and LDB tests. Quinoa seeds have a high content of ALA [
37], but although humans can convert ALA into eicosapentaenoic (EPA: 20:5n-3) and DHA, the efficiency of this conversion is limited and thus EPA and DHA must also be obtained from the diet to maintain adequate levels [
38]. Therefore, we believe that due to the low concentration of DHA achieved from the conversion of ALA, it is not possible to obtain an anxiolytic effect.
Chronic restrain protocol induces atrophy in dendritic arborization of pyramidal neurons from the CA3 region of the hippocampus, characterized by a reduction in dendritic length and number of branch points [
39]. Moreover, dendrites atrophy has been associated with deficits in hippocampal-dependent spatial memory [
8,
39]. This evidence supports the results of this study where the restrain protocol induced a reduction in dendritic length and a deficit in spatial memory evaluated in the Y-maze. In the case of our study, QFF intake countered these changes, reducing the stress-induced damage in dendritic length and spatial memory. Previous studies have shown that a red-quinoa seeds extract prevented memory deficit induced by a scopolamine treatment in mice [
23], supporting our findings and establishing a protective role of a quinoa-supplemented diet in cognitive performance or/and behavioral alterations in rodents.
Diet has a great impact on anxiety behavior [
40], learning, and memory in rats [
41]. When combined with stress, a diet rich in saturated fatty acids induces the retraction of dendrites in neurons in the CA3 region of the hippocampus [
14], produces arterial hypertension, and increments levels of corticosterone [
42]. In contrast, n-6 and n-3 PUFAs consumption improve the cognitive and emotional state in rodents [
43] and humans [
44]. Quinoa seeds have a high content of ALA and LA, two essential fatty acids, which represent 55-63% of its lipid fraction [
45]. ALA has been related to health, reproduction, and development in mammals [
46]. Importantly, ALA can be converted to long-chain PUFAs (LCPUFA) in the liver, allowing the synthesis of EPA and DHA acids. DHA is the predominant fatty acid in the brain, constituting about 15% of the total fatty acid in that tissue [
47]. As well, low intake of DHA led to poor performance in attentions and learning tests [
48], along with elevated aggression and anxiety levels [
49] in rodents. Moreover, n-3 LCPUFA-deficient rats showed excessive stress, anxiety, and fear responses that were reverted after DHA supplementation [
50], while EPA and DHA supplementation improved memory and prevented hippocampal dendritic atrophy in chronically stressed rats [
51]. DHA may prevent stress-induced behavior through modulating GABA receptor activity [
50] and restoring GABA release probability in the CA1 region of the hippocampus [
51]. On the other hand, consumption of a fish oil-enriched diet (high in EPA and DHA) changes the phospholipid composition of the rat brain, increasing the levels of phosphatidylserine and changing cortical and striatal dopaminergic function, thus improving cognitive function, spatial memory, and locomotor activity in aged rats [
52]. Furthermore, n-3 PUFA induces the expression of genes involved in learning, memory, and neuronal metabolism [
53]. Interestingly, high ALA supplementation in rats did not change anxiety levels [
52,
54], which is in concordance with our results were QFF did not affect anxiety on the EPM and LDB test. Taken together, all this evidence suggests that the effects of QFF in the prevention of spatial memory and dendritic detriment induced by the restrain protocol may be due to the PUFA content in quinoa. The differences found between anxiety and memory could be due to different requirements in the concentration of PUFAs, but further studies are needed.
In addition to the lipidic profile of quinoa, it has also been proposed that its high antioxidants content may have a role in the neuroprotective effect of this seeds. Indeed, dietary supplementation with red quinoa extract, which is high in phenolic and flavonoids compounds, had a neuroprotective effect in mice treated with scopolamine [
23].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.T, P.M-L, E.M.; Methodology, G.T. M.A.P, P.M-L, A.D., A.D-S.; Formal Analysis, G.T., M.A.P, A.D, A.D-S.; Resources, P.M-L, E.M., A.D-S.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, G.T., M.A.P., PM-L.; Writing—Review & Editing, G.T., A.D., E.M., A.D-S.; Funding Acquisition, A.D-S.
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing of the experimental design. Male Sprague-Dawley rats of 21 postnatal days (PND) were fed either with rat chow or quinoa functional food (QFF, (50% rat chow + 50% dehydrated quinoa seeds)). At PND 36, animals were submitted to a restrain protocol for 2 hours per day for 15 days, establishing four groups (n=27 per experimental group): non-stressed (rat chow), non-stressed + QFF, stressed, and stressed + QFF. At PND 52, motor and anxiety behavior were evaluated on the Open field (OF), elevated plus maze (EPM), and light-dark box (LDB). Finally, at PND 53, the memory performance was evaluated on the Y-maze test, and brain tissue was used for Golgi staining. QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing of the experimental design. Male Sprague-Dawley rats of 21 postnatal days (PND) were fed either with rat chow or quinoa functional food (QFF, (50% rat chow + 50% dehydrated quinoa seeds)). At PND 36, animals were submitted to a restrain protocol for 2 hours per day for 15 days, establishing four groups (n=27 per experimental group): non-stressed (rat chow), non-stressed + QFF, stressed, and stressed + QFF. At PND 52, motor and anxiety behavior were evaluated on the Open field (OF), elevated plus maze (EPM), and light-dark box (LDB). Finally, at PND 53, the memory performance was evaluated on the Y-maze test, and brain tissue was used for Golgi staining. QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 2.
Effect of diet type in body weight gain during the stress protocol: (A) Daily measure of body weight during the 15 days of stress protocol and (B) Total body weight gain at the end of day 15 of the stress protocol. There are no significant differences in body weight gain induced by diet intake. However, exposure to the restraint stress protocol was associated with a significant reduction in body weight in both rat chow and QFF groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9). * p<0.05. Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 2.
Effect of diet type in body weight gain during the stress protocol: (A) Daily measure of body weight during the 15 days of stress protocol and (B) Total body weight gain at the end of day 15 of the stress protocol. There are no significant differences in body weight gain induced by diet intake. However, exposure to the restraint stress protocol was associated with a significant reduction in body weight in both rat chow and QFF groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9). * p<0.05. Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 3.
Effect of diet type in locomotor activity measured in the open field test (A) Total distance traveled (m) and (B) Time spent in the center in an open field test (s). Locomotor activity at PND 52 was not affected by the restraint stress protocol in any experimental group. The anxiety-like behavior measured by the time spent in the center of the field did not show a significant difference in any of the groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9). Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 3.
Effect of diet type in locomotor activity measured in the open field test (A) Total distance traveled (m) and (B) Time spent in the center in an open field test (s). Locomotor activity at PND 52 was not affected by the restraint stress protocol in any experimental group. The anxiety-like behavior measured by the time spent in the center of the field did not show a significant difference in any of the groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9). Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 4.
Effect of diet type in anxiety-like behavior measured in the elevated plus-maze and light-dark box test. (A) Total number of open arm entries made in the elevated plus-maze. Stress protocol significantly decreased the number of open-arm entries in both rat chow and QFF groups. Anxiety levels measured in the EPM were not affected by diet. (B) Total number of light side entries made in the light-dark box test. Stressed animals had a smaller number of entries to the light side compared to the non-stressed in both rat chow and QFF groups. Anxiety levels measured in LDB were not affected by diet between groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9). Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 4.
Effect of diet type in anxiety-like behavior measured in the elevated plus-maze and light-dark box test. (A) Total number of open arm entries made in the elevated plus-maze. Stress protocol significantly decreased the number of open-arm entries in both rat chow and QFF groups. Anxiety levels measured in the EPM were not affected by diet. (B) Total number of light side entries made in the light-dark box test. Stressed animals had a smaller number of entries to the light side compared to the non-stressed in both rat chow and QFF groups. Anxiety levels measured in LDB were not affected by diet between groups. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9). Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 5.
Influence of quinoa functional food diet on Y-maze performance. Total number of entries made in the novel arm in the Y-maze. Chronic stress protocol induced spatial memory impairment in the rat chow but not in the QFF group. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9), * p<0.05. Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 5.
Influence of quinoa functional food diet on Y-maze performance. Total number of entries made in the novel arm in the Y-maze. Chronic stress protocol induced spatial memory impairment in the rat chow but not in the QFF group. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9), * p<0.05. Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
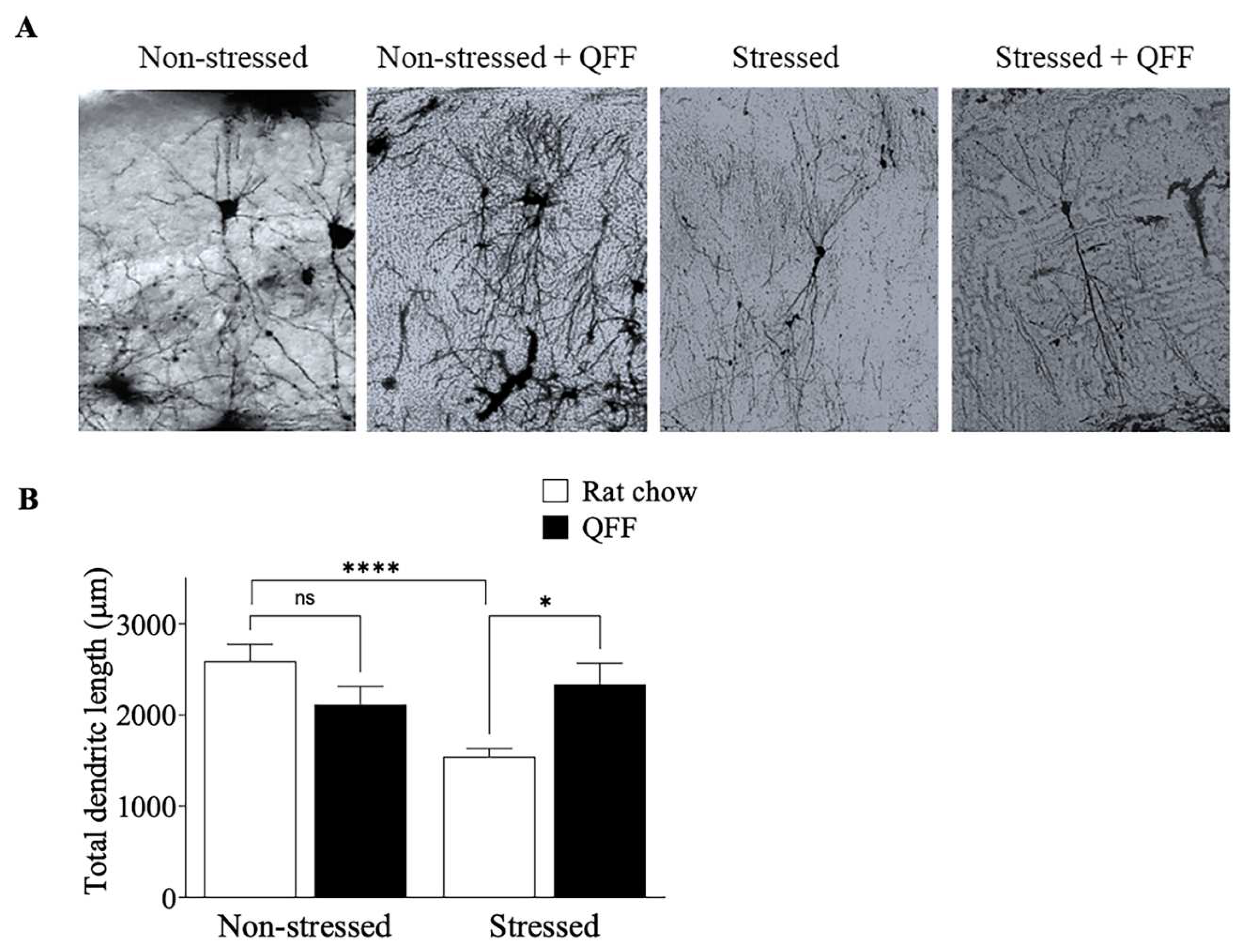
Figure 6.
Effect of quinoa functional food on CA3 dendritic morphology. A. representative photographs and B. quantification of the total dendritic length of CA3 pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus. QFF diet reduced the dendritic impairment induced by stress compared to the rat chow group. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9), * p<0.05. Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Figure 6.
Effect of quinoa functional food on CA3 dendritic morphology. A. representative photographs and B. quantification of the total dendritic length of CA3 pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus. QFF diet reduced the dendritic impairment induced by stress compared to the rat chow group. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=9), * p<0.05. Non-significant, n.s; QFF, Quinoa functional food.
Table 1.
Number of rats used in each experiment.
Table 1.
Number of rats used in each experiment.
| |
|
|
Experimental groups |
Total |
| Description |
|
|
Non- stressed |
Non-stressed + QFF |
Stressed |
Stressed + QFF |
|
| Locomotor activity and anxiety |
n=9 |
n=9 |
n=9 |
n=9 |
|
| Golgi Staining |
n=9 |
n=9 |
n=9 |
n=9 |
|
| Behavioral tasks |
n=9 |
n=9 |
n=9 |
n=9 |
|
| Total |
n=27 |
n=27 |
n=27
|
n=27 |
n=108 |