Submitted:
06 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
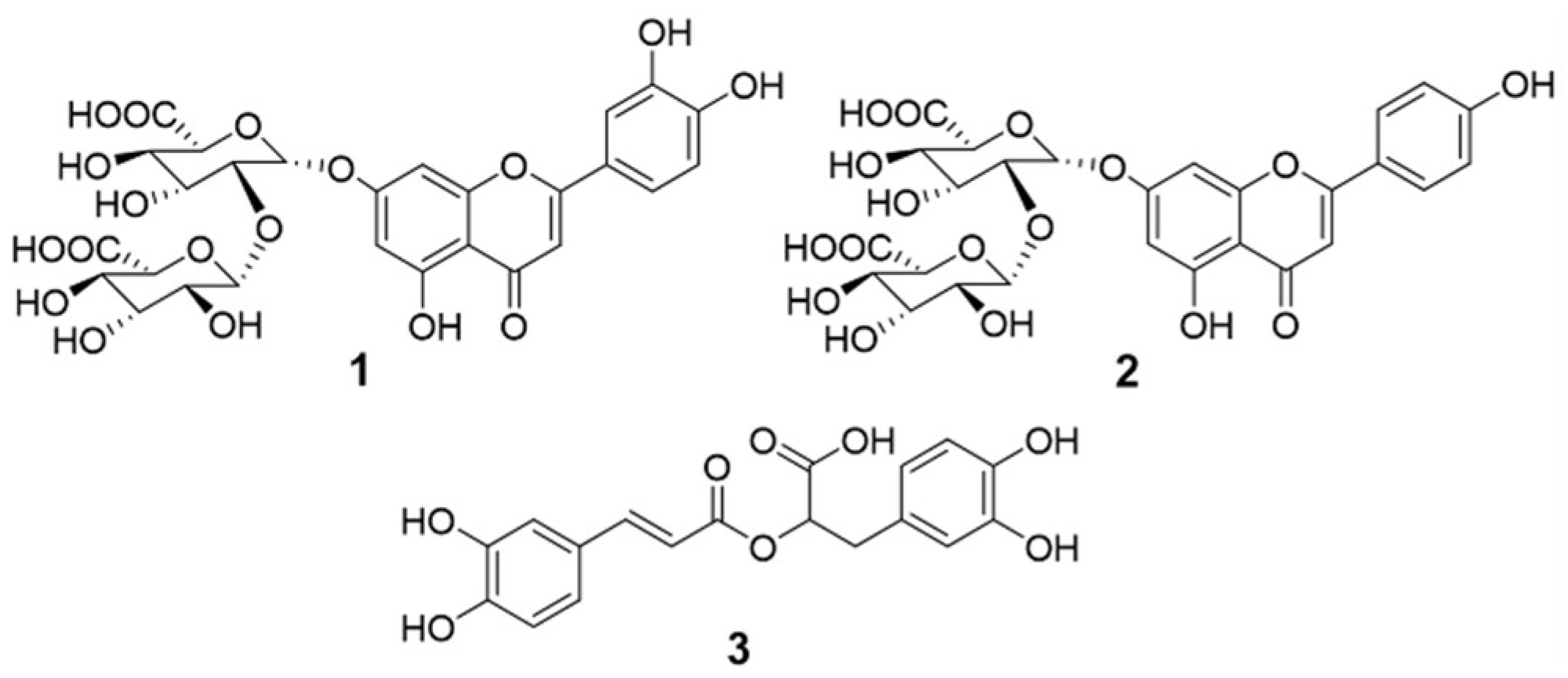
2.1. Isolation of the compounds
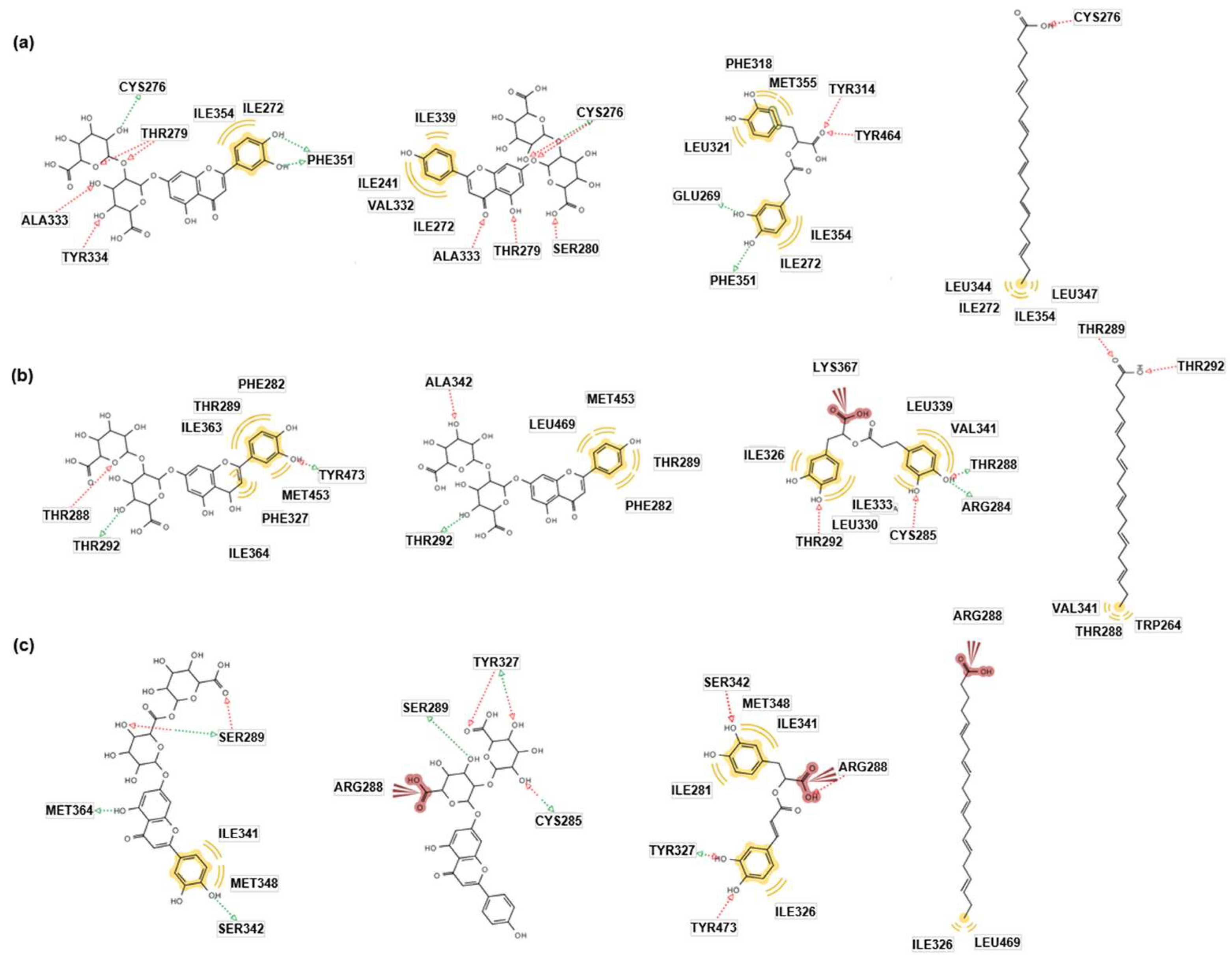
2.2. In silico docking simulation
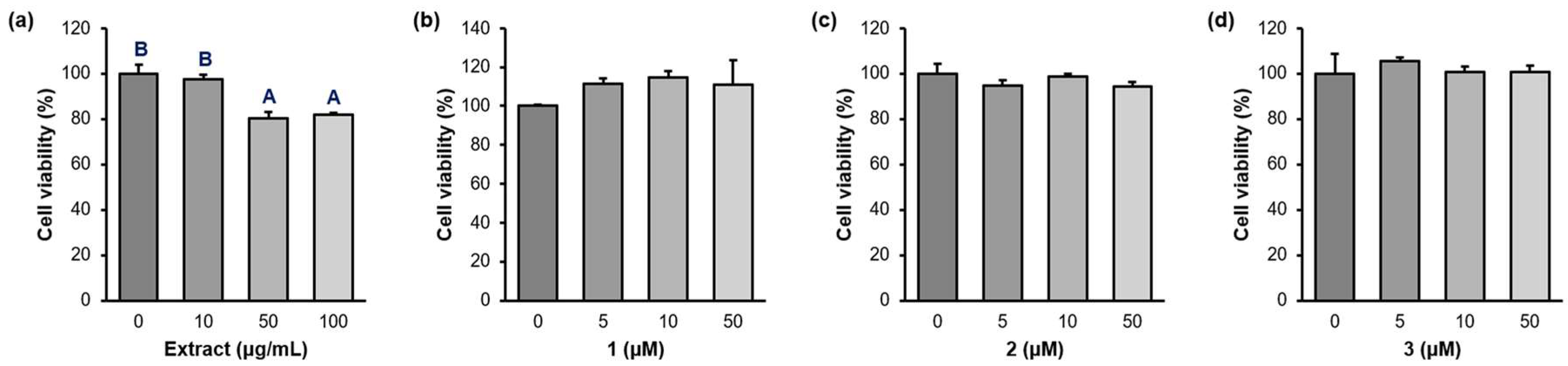
2.3. Cell viability
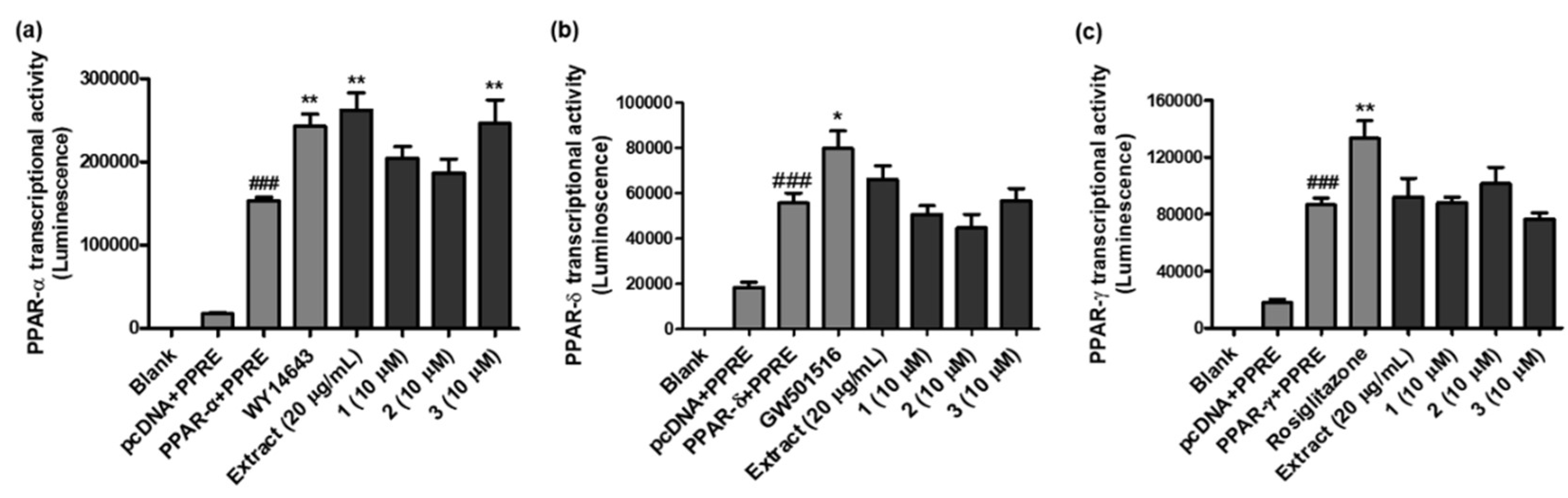
2.4. PPAR-α/δ/γ transcriptional activity
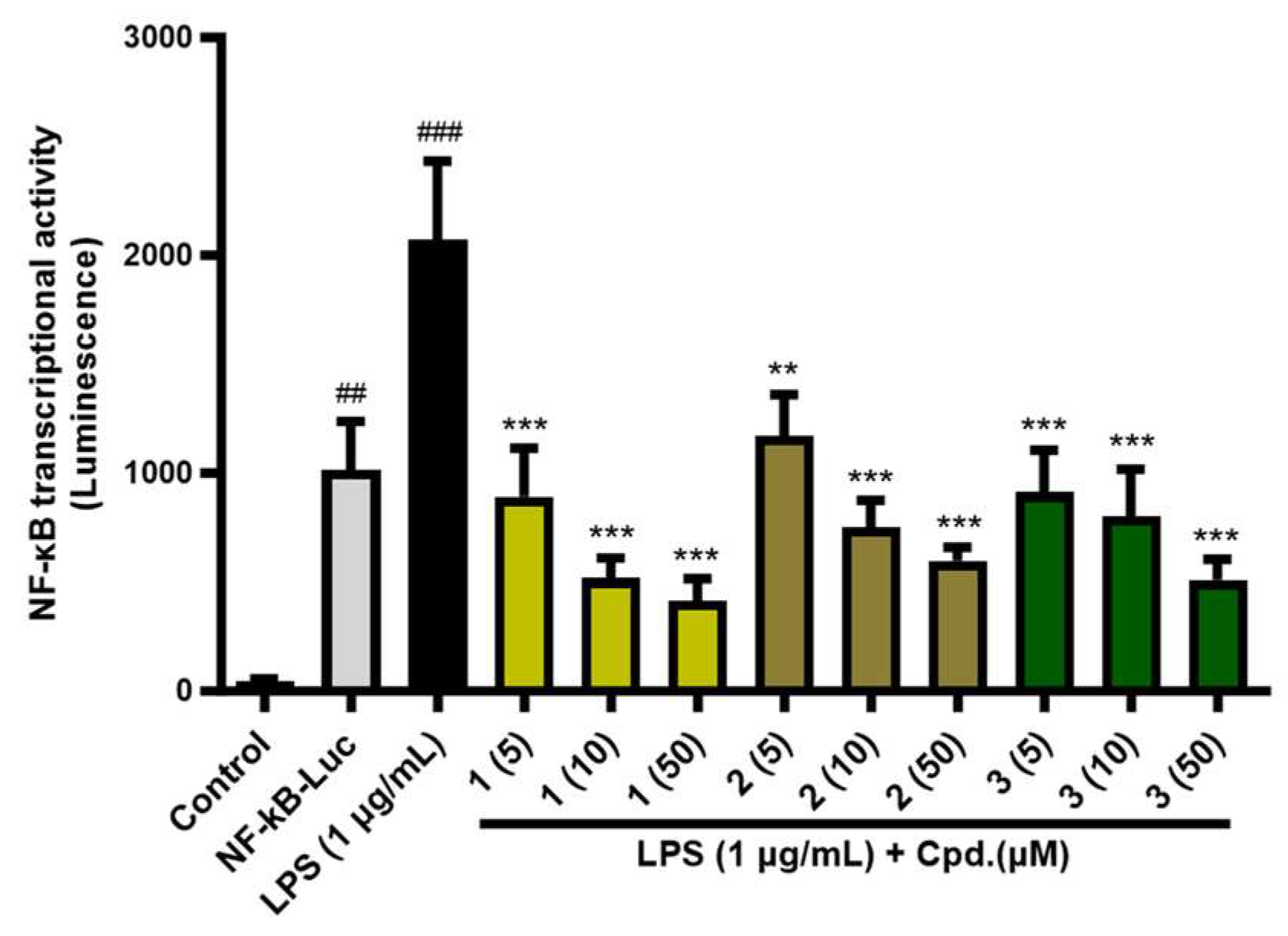
2.5. NF-κB transcriptional activity
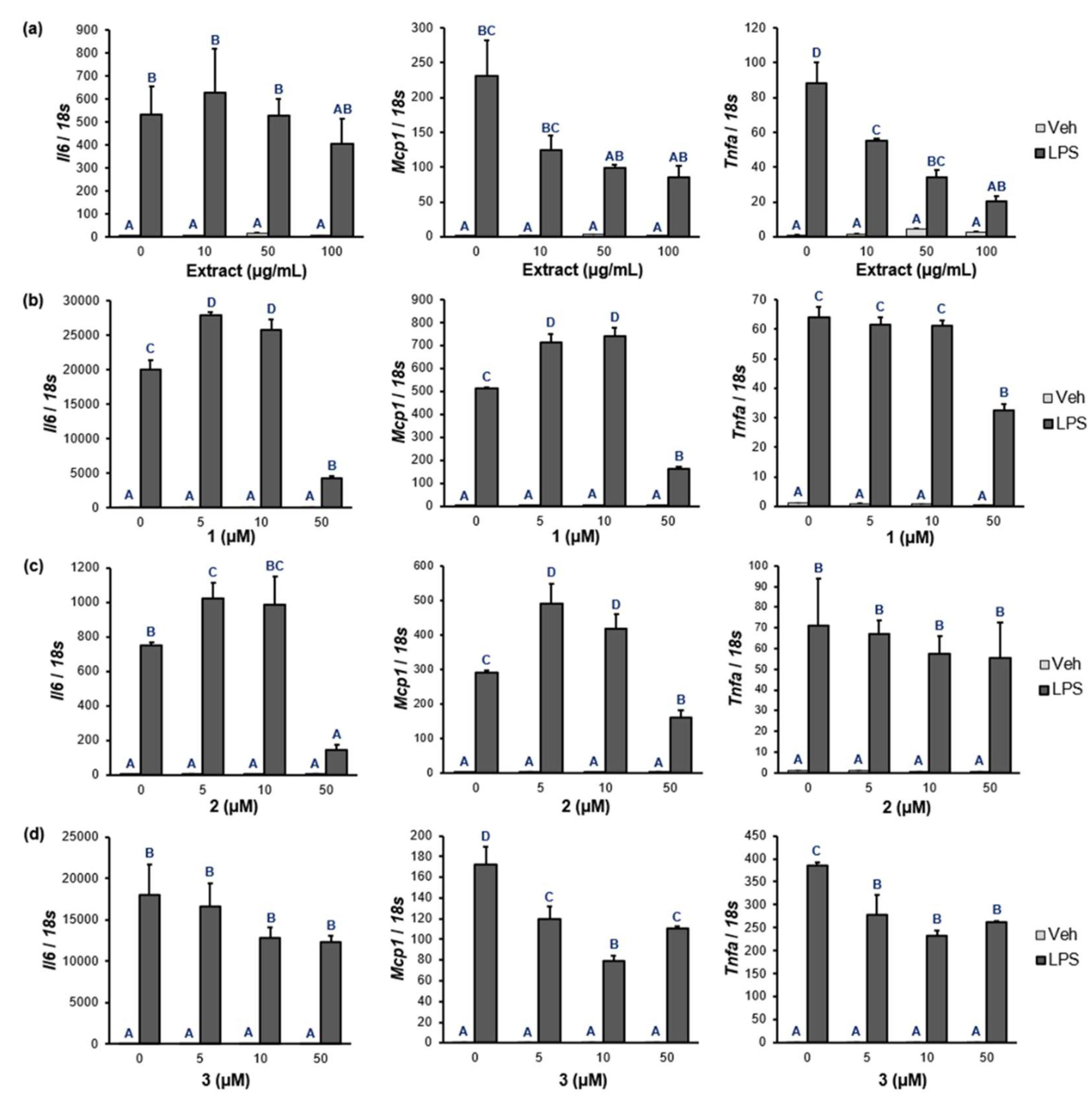
2.6. NF-κB target gene expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant material
4.2. General experimental procedures
4.3. Extraction and isolation
4.4. Molecular docking
4.5. Cell viability
4.6. PPAR and NF-κB transcriptional activity
4.7. NF-κB target gene expression
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plants of the World Online. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:190343-2 (accessed on 23 August, 2023).
- Ahmed, H.M. Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical, and pharmacological investigations of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Molecules, 2018; 24 , 102. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Qiu, J.-F.; Ma, L.-J.; Hu, Y.-J.; Li, P.; Wan, J.-B. Phytochemical and phytopharmacological review of Perilla frutescens L.(Labiatae), a traditional edible-medicinal herb in China. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017; 108, 375–391. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, H.; Yamazaki, M. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α production by orally administering a perilla leaf extract. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.P.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, S.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of Perilla frutescens leaf extract on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M. Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricote, M.; Li, A.C.; Willson, T.M.; Kelly, C.J.; Glass, C.K. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature 1998, 391, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mues, R. Species specific flavone glucuronides in Elodea species. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1983, 11, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aritomi, M.; Kumori, T.; Kawasaki, T. Cyanogenic glycosides in leaves of Perilla frutescens var. acuta. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 2438–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Furuta, Y.; Fujii, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Wakushima, H.; Saito, K.-i.; Kano, Y. Effect of oral treatment of Perilla frutescens and its constituents on Type-I allergy in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Guo, K.; Liu, L.; Tian, W.; Xie, X.; Wen, S.; Wen, C. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic data reveal the flavonoid biosynthesis metabolic pathway in Perilla frutescens (L.) leaves. Sci. Rep. 2020; 10, 16207. [Google Scholar]
- Aritomi, M. Chemical studies on the constituents of edible plants (Part 1). Phenolic compounds in leaves of Perilla frutescens BRITTON var. acuta KUDO f. viridis MAKINO. J. Home Econ. 1982, 33, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, M.; Simmonds, M.S. Rosmarinic acid. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Dos Santos, R.N.; Oliva, G.; Andricopulo, A.D. Molecular docking and structure-based drug design strategies. Molecules 2015, 20, 13384–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.H.; Stephens, E.; O'Brien, D.P.; Zhou, M. Understanding noncovalent interactions: Ligand binding energy and catalytic efficiency from ligand-induced reductions in motion within receptors and enzymes. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2004; 43, 6596–6616. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, N.; Zhang, X.; Sugiyama, E.; Kono, H.; Horiuchi, A.; Nakajima, T.; Kanbe, H.; Tanaka, E.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Aoyama, T. Eicosapentaenoic acid improves hepatic steatosis independent of PPAR-α activation through inhibition of SREBP-1 maturation in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Liu, W.; Shi, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gong, P. Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates LPS-stimulated inflammatory response by regulating the PPAR-γ/NF-κB pathways in primary bovine mammary epithelial cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 112, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, E.; Eyre, E.; Palomer, X.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β/δ (PPAR-β/δ) agonist GW501516 prevents TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in human HaCaT cells by reducing p65 acetylation through AMPK and SIRT1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, S.; Kooshki, M.; Zhao, W.; Hsu, F.-C.; Robbins, M.E. PPAR-α ligands inhibit radiation-induced microglial inflammatory responses by negatively regulating NF-κB and AP-1 pathways. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Wang, D.; Ye, L.; Li, P.; Hao, W.; Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, B.; Shang, J.; Li, D. Rosmarinic acid protects against inflammation and cardiomyocyte apoptosis during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Fang, N.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, M.; Hou, Q. Perilla leaf extract (PLE) attenuates COPD airway inflammation via the TLR4/Syk/PKC/NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 763624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.-A.; Park, C.-S.; Ahn, H.-J.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.-M. Effect of Perilla frutescens var. acuta Kudo and rosmarinic acid on allergic inflammatory reactions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Banno, N.; Akihisa, T.; Tokuda, H.; Yasukawa, K.; Higashihara, H.; Ukiya, M.; Watanabe, K.; Kimura, Y.; Hasegawa, J.-i.; Nishino, H. Triterpene acids from the leaves of Perilla frutescens and their anti-inflammatory and antitumor-promoting effects. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, P.; Jayaraman, S.; Jh, S.F.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Laxman, P.A.; Muthaiah, V.P.K.; Tripathi, S.C.; Gugapriya, T.; Tarnekar, A.M.; Muthiyan, G.G. Molecular docking analysis of PPAR-γ with compounds from Ocimum tenuiflorum. Bioinformation 2021, 17, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, L.V.; Savova, M.S.; Tews, D.; Wabitsch, M.; Georgiev, M.I. Rosmarinic acid attenuates obesity and obesity-related inflammation in human adipocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, F.; Hoberg, J.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Keller, M.D.; Jones, D.R.; Frye, R.A.; Mayo, M.W. Modulation of NFBdependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lin, Q.; Lin, R.; Zhang, J.; Ren, F.; Zhang, J.; Ji, M.; Li, Y. PPAR-α agonist fenofibrate attenuates TNF-α-induced CD40 expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the SIRT1-dependent signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Rong, S.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, G. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist pioglitazone prevents NF-κB activation in cisplatin nephrotoxicity through the reduction of p65 acetylation via the AMPK-SIRT1/p300 pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 101, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delerive, P.; Gervois, P.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Staels, B. Induction of IκBα expression as a mechanism contributing to the anti-inflammatory activities of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α activators. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36703–36707. [Google Scholar]
- Scirpo, R.; Fiorotto, R.; Villani, A.; Amenduni, M.; Spirli, C.; Strazzabosco, M. Stimulation of nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor- limits NFBdependent inflammation in mouse cystic fibrosis biliary epithelium. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockert, J.; Wolf, A.; Kaddatz, K.; Schnitzer, E.; Finkernagel, F.; Meissner, W.; Müller-Brüsselbach, S.; Kracht, M.; Müller, R. Regulation of TAK1/TAB1-mediated IL-1β signaling by cytoplasmic PPAR-β/δ. PloS One 2013, 8, e63011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantsar, T.; Poso, A. Binding affinity via docking: Fact and fiction. Molecules 2018, 23, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Choi, H.; Jo, A.; Oh, D.-R.; Kim, Y.; Im, S.; Lee, S.-G.; Jeong, K.-I.; Ryu, G.-C. Aqueous extract of Perilla frutescens var. acuta relaxes the ciliary smooth muscle by increasing NO/cGMP content in vitro and in vivo. Molecules, 2018; 23, 1777. [Google Scholar]
- Aung, H.T.; Nikai, T.; Niwa, M.; Takaya, Y. Rosmarinic acid in Argusia argentea inhibits snake venom-induced hemorrhage. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 64, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Autodock Vina | Autodock 4 | Dock6 | |
| PPAR-α | EPA * | -6.7 | -7.8 | -35.5 |
| 1 | -7.2 | -13.2 | -41.5 | |
| 2 | -6.5 | -9.1 | -41.7 | |
| 3 | -8.6 | -9.7 | -43.0 | |
| PPAR-δ | EPA | -7.8 | -7.4 | -41.0 |
| 1 | -9.7 | -14.7 | -58.1 | |
| 2 | -9.4 | -13.2 | -43.3 | |
| 3 | -8.3 | -9.3 | -41.5 | |
| PPAR-γ | EPA | -6.8 | -8.1 | -37.2 |
| 1 | -5.8 | -9.7 | -57.1 | |
| 2 | -5.6 | -13.4 | -51.6 | |
| 3 | -7.6 | -8.9 | -40.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





