1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth most common cause of death worldwide (1). Several therapeutic agents have been developed in recent years for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (2) (3) (4) (5) (6), but the combination of atezolizumab (Atezo) + bevacizumab (Bev) is currently the only combination of a molecular targeting agent and an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) that is used therapeutically (7). This combination is regarded as a first-line treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in various guidelines (8) (9). Atezo+Bev was shown to be superior to sorafenib in the IMbrave 150 trial (7) (10), but ICIs have been shown to have a poor anti-tumor effect in mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and to cause fibrosis in non-cancerous tissue (11). The IMbrave 150 trial showed that Atezo+Bev treatment did not have the same overall survival (OS) benefit for patients with non-viral HCC than for those with viral HCC, and was associated with slightly poorer progression-free survival (PFS), but the objective response rates (ORRs) for non-viral and viral HCC were similar (10). Therefore, we performed an observational study to determine whether a reduction in liver reserve capacity might explain the difference in prognosis, despite comparable treatment efficacy.
2. Materials and Methods
Participants
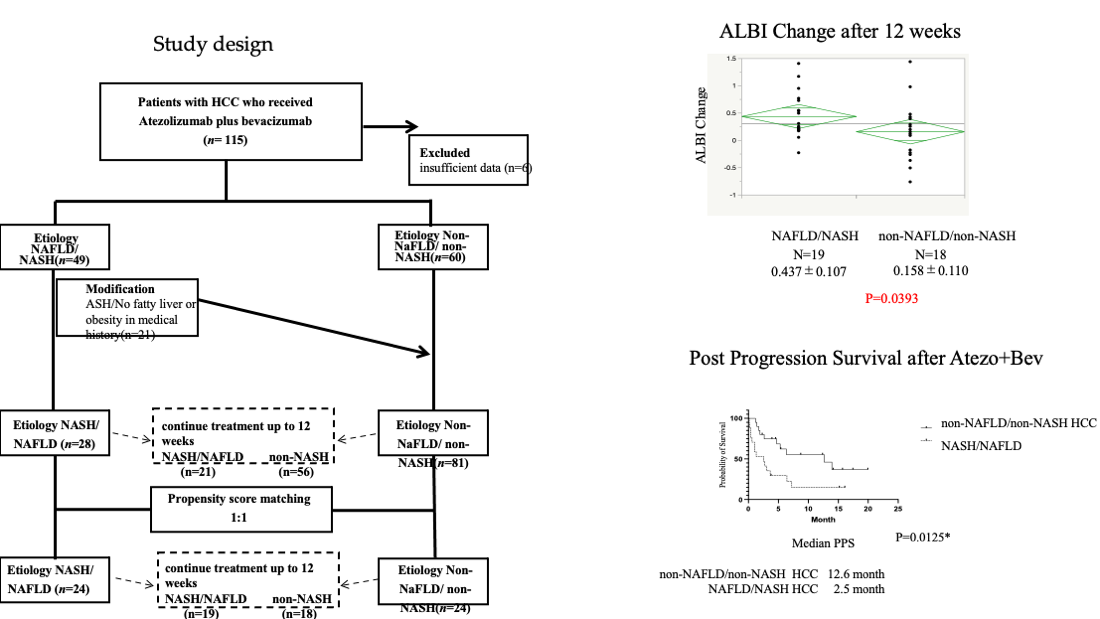
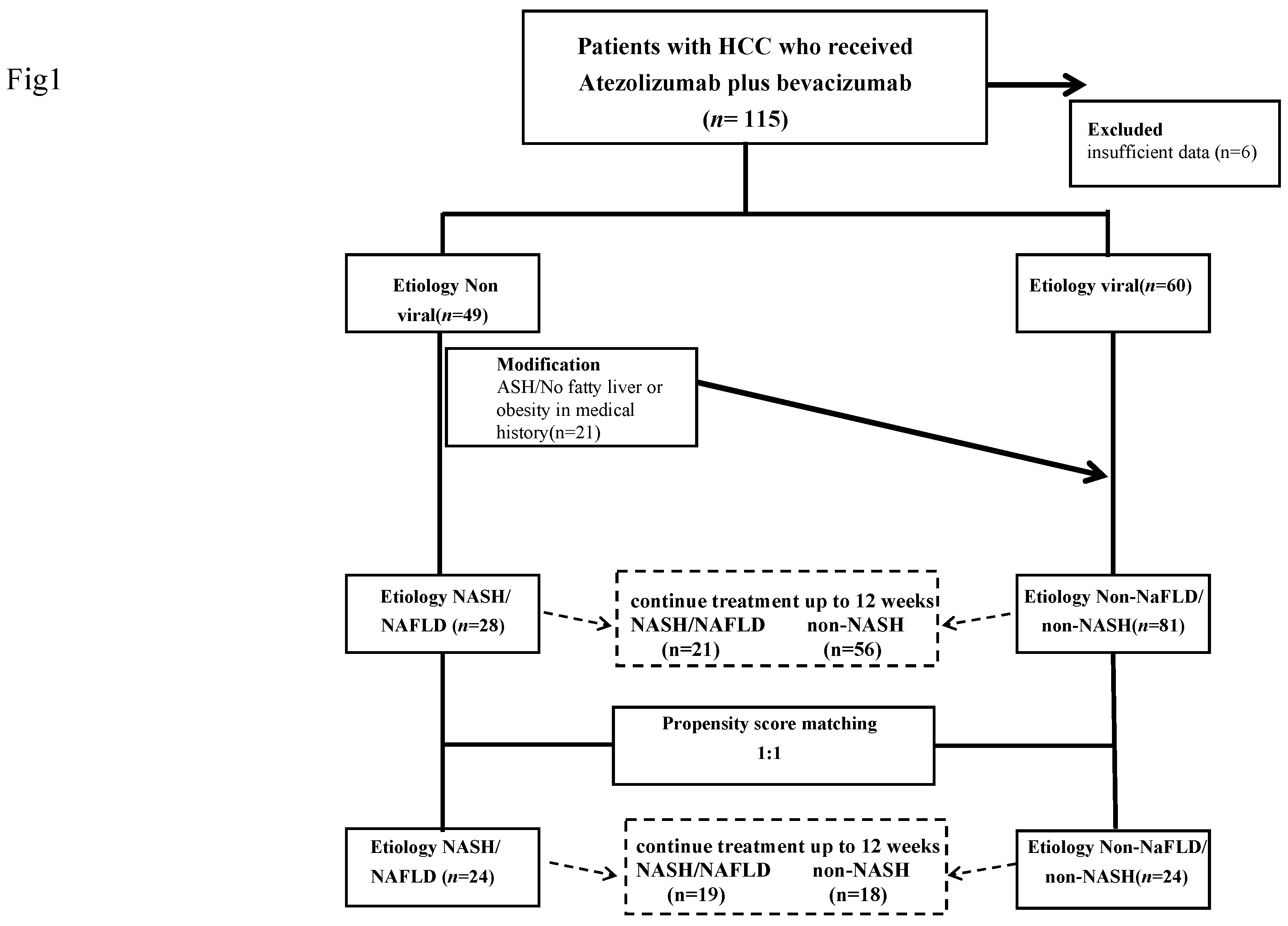
We recruited 115 patients with unresectable advanced HCC who were treated with Atezo+Bev between September 2019 and January 2022 at several centers. Following the initial evaluation, six patients with insufficient data were excluded from the analysis, and therefore the final analysis was of 109 patients. As a comparison, 181 patients who were treated with lenvatinib between January 2019 and January 2022 were also studied. The study was approved by the ethics committee of Kyushu Cancer Center (2018-16) and conformed to the principles of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki.
We examined the medical records of each participant and collected information on their clinical characteristics and therapeutic response, including their PFS, OS, and post-progression survival (PPS), and analyzed the data retrospectively. Participants who were positive for anti-hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibodies were judged to have HCC owing to HCV infection, those who were positive for hepatitis B virus surface antigen were judged to have HCC owing to hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, and those without either of these were judged to have cancer of a non-viral etiology. For participants with a non-viral etiology, NAFLD/NASH was diagnosed based on contemporaneous or prior imaging or histological examination showing evidence of fatty liver or steatohepatitis, in the absence of a history of alcohol consumption or the use of drugs known to cause fatty liver. Of the 49 patients who were classified as having HCC of non-viral origin, 28 were classified as having NAFLD/NASH.
Data for the 109 patients who were treated using Atezo+Bev were studied. The changes in ALBI in the two groups over a 12-week period were compared after the exclusion of those who were unable to continue treatment for 12 weeks. Seventy-seven participants were included in this analysis, and the changes in participants who were taking Atezo+Bev as their first-line treatment were also analyzed. In addition, PSM was performed for participants in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups, according to their round of treatment, tumor number and size, macrovascular invasion, extrahepatic metastasis, sex, age, ALBI score, and AFP at the start of treatment (
Figure 1). The change in ALBI during 12 weeks of treatment was compared among 24 pairs of participants who were propensity score-matched and able to continue treatment for 12 weeks. As a secondary analysis, the OS, PFS, and PPS of all the participants in the two groups were compared, including those who did not continue the treatment for the full 12 weeks. In addition, the OS, PFS, and PPS of the 24 propensity score-matched pairs of participants were compared.
For participants with non-viral hepatitis-related liver cancer, those with prior or contemporaneous imaging-based or histological evidence of fatty liver or steatohepatitis, in the absence of a history of alcohol consumption or the use of medication that might cause fatty liver, were diagnosed as having NAFLD/NASH-related cancer, and the others were classified as having non-NAFLD/non-NASH-related cancer. After excluding those who were unable to continue treatment for 12 weeks, data from 21 participants with NAFLD/NASH and 59 with non-NAFLD/non-NASH were analyzed. Participants in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups were propensity score-matched according to age, sex, tumor number and size, macrovascular invasion, extrahepatic metastasis, round of treatment, ALBI score, and AFP value; and 24 cases from each group were selected for comparison. NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; ASH, alcoholic liver disease; ALBI, albumin-bilirubin score; AFP, α-fetoprotein.
The same analysis was performed on 181 participants who had been treated with lenvatinib for comparison (
Figure S1). After the exclusion of participants with insufficient data, the total number studied was 175. The change in ALBI over the 12-week treatment period was also evaluated according to etiology, with the exclusion of participants who failed to continue treatment for the full 12 weeks, as for the participants who underwent treatment with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. Following the application of this criterion, 137 participants remained for inclusion in the analysis. We compared the OS, PFS, and PPS of the NASH and non-NASH groups. In addition, propensity score-matching was performed for participants in the NASH and non-NASH groups, based on treatment, sex, age, ALBI score at the start of treatment, maximum tumor diameter, the number of tumors with AFP, the presence or absence of substantial vascular invasion, and the presence or absence of extrahepatic metastases. The change in ALBI and the OS, PFS, and PPS before and 12 weeks after the initiation of treatment, according to etiology, were evaluated in participants selected by propensity score-matching.
Liver parameters
Liver reserve capacity was evaluated using the ALBI score, which is calculated using the circulating albumin and bilirubin concentrations (12) (13) (14), as ALBI-score = (log10 bilirubin (µmol/L) × 0.66) + (albumin (g/L) × −0.085). The ALBI grades were defined as <−2.60, ALBI grade 1; −2.60 to −1.391, ALBI grade 2; and ≥−1.39, ALBI grade 3. To further subdivide moderate liver injury, mALBI grades of 1, 2a, 2b, and 3 were assigned as follows: <−2.60, ALBI grade 1; −2.60 to −2.271, ALBI grade 2a; −2.270 to −1.391, ALBI grade 2b; and ≥−1.39, ALBI grade 3 (15).
Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
HCC was diagnosed using dynamic CT, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and/or pathological findings. Tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage, determined as previously reported for the staging of HCC by the Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan, 6th edition (16), was used to evaluate tumor progression. We also used the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage (17).
Statistical analysis
Continuous data are presented using medians and ranges. The changes in ALBI between baseline and week 12 in the NASH and non-NASH groups were compared using ANOVA/pooled t-test. Participants treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in the NAFLD/NASH (n=28) and non-NAFLD/NASH groups (n=59) were matched using PSM to reduce the influence of confounding factors. Eight factors that are thought to affect the prognosis of advanced liver cancer were included as baseline variables: age, sex, ALBI score, AFP value, the number of tumors, the size of the tumors, macrovascular invasion, extrahepatic metastasis, and the round of treatment. The propensity scores for the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD /NASH groups were 0.803 ± 4.699 and −1.476 ± 0.817, respectively (mean ± standard deviation (SD)). The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) was 0.7873. This propensity score was used for one-to-one nearest-neighbor matching, and the caliper was set at 0.20. This resulted in the selection of 24 participants from each of the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/NASH groups. The propensity scores after matching were −0.822 ± 0.833 and −0.825 ± 0.831 (mean ± SD). Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time between the start date of administration of Atezo+Bev and the date of death. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the time between the start date of administration of Atezo+Bev and the date of the final follow-up examination, disease progression, or death, whichever came first. Post-progression survival (PPS) was defined as the time between the date of completion of Atezo+Bev or the date of disease progression, whichever came first, and the date of death. OS, PFS, and PPS are reported as median values, expressed in months, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Survival curves were plotted using the Kaplan-Meier product-limit method. The roles of other variables were assessed using the log-rank test. P < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. Statistical analyses were performed using JMP Pro. version 15.1.0 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) and graphs were prepared using PRISM version 9.1.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
A similar approach was used to study the 175 participants who were treated with lenvatinib. The participants in the NAFLD/NASH (n=32) and non-NAFLD/NASH (n=141) groups were matched using PSM to reduce the influence of confounding factors. Eight factors were included as baseline variables: age, sex, ALBI score, AFP value, the number of tumors, the size of tumors, macrovascular invasion, extrahepatic metastasis, and the round of treatment. The mean ± standard deviation (SD) propensity scores for the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD /NASH groups were 0.229 ± 0.091 and 0.175± 0.092, respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) was 0.6797. This propensity score was used for one-to-one nearest-neighbor matching, with the caliper set at 0.20. This resulted in the selection of 30 participants from each of the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/NASH groups, and their mean ± SD propensity scores after matching were 0.2132 ± 0.067 and 0.2133 ± 0.068.
3. Results
The characteristics of the participants at the start of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab treatment are shown in Table 1. Twenty-eight patients comprised the NAFLD/NASH groups and 81 comprised the non-NAFLD/NASH group.
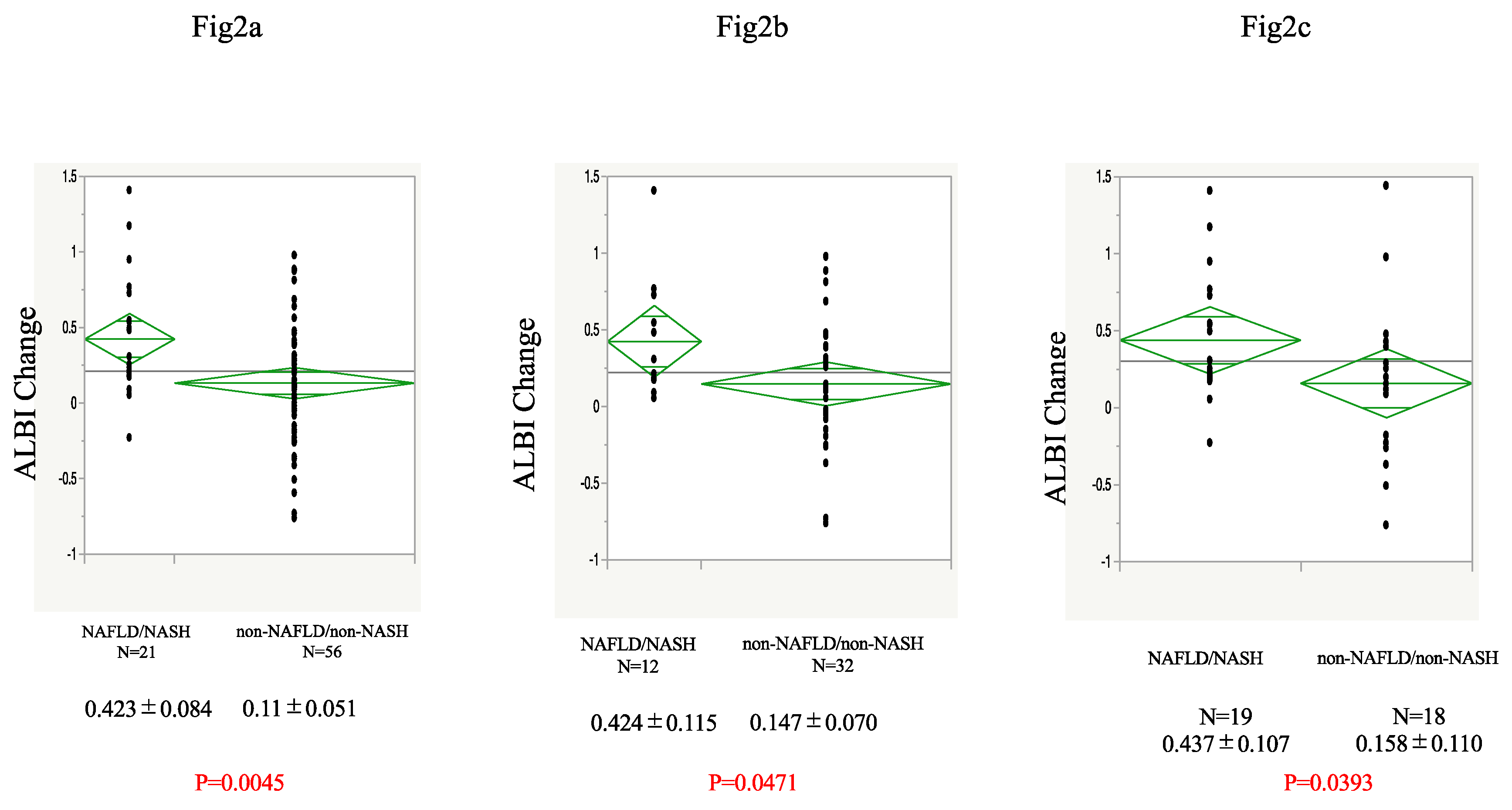
An analysis of the ALBI values at baseline and after 12 weeks of Atezo+Bev treatment is shown in
Figure 2a. Twenty-one participants with NASH and 56 without were able to continue treatment up to 12 weeks and had their ALBI calculated. The NAFLD/NASH group had a significantly worse mean ALBI score after 12 weeks than the non-NAFLD/non-NASH group. The analysis of the first-line treatment group also showed that the ALBI score was worse in the NAFLD/NASH group after 12 weeks of treatment than in the non-NAFLD/non-NASH group (
Figure 2b). In addition, after PSM of 24 participants according to round of treatment, tumor number and size, macrovascular invasion, extrahepatic metastasis, sex, age, ALBI score, and AFP at the start of treatment, we found that the NAFLD/NASH group had a significantly worse ALBI score than the non-NAFLD/non-NASH group (
Figure 2c).
a) Change in ALBI during Atezo+Bev treatment in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups in the participants who were able to continue treatment for 12 weeks. b) Change in ALBI in participants in each group undergoing first-line Atezo+Bev treatment. c) Change in ALBI in propensity score-matched participants who were treated using Atezo+Bev. Atezo+Bev, atezolizumab + bevacizumab; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; ALBI, albumin-bilirubin score.
The background factors after PSM are shown in Table 2. The mean ALBI score was also significantly worse for participants with non-viral liver cancer than for those with viral liver cancer (non-viral
vs. viral: 0.310±0.063
vs. 0.109±0.064,
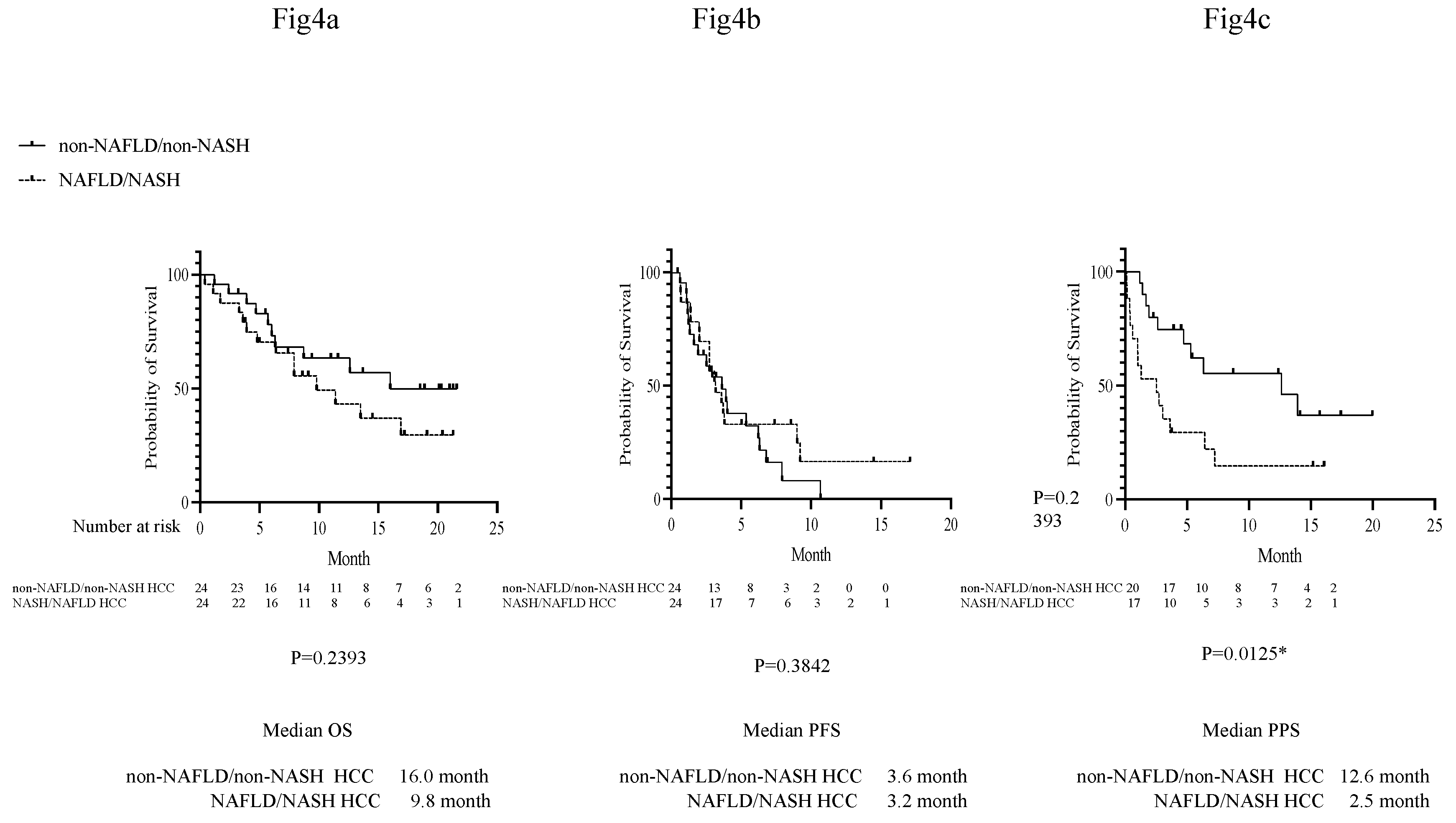
p=0.0289; data not shown). The OS, PFS, and PPS of the groups were also compared, and no differences in OS or PFS were found between the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups, but the NAFLD/NASH group had a significantly shorter mean PPS (
Figure 3a–c).
In addition, for the 24 propensity score-matched pairs, there were no differences in OS or PFS, but the participants with NAFLD/NASH had a significantly shorter PPS (
Figure 4a–c).
Kaplan-Meier curves were used for the analysis. a) Comparison of OS in propensity score-matched participants in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups. b) Comparison of PFS in propensity score-matched participants in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups. c) Comparison of PPS in propensity score-matched participants in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups. OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; PPS, post-progression survival; Atezo+Bev, atezolizumab + bevacizumab; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
The same study was conducted for participants taking lenvatinib for comparison.
Figure S2a shows the results of the analysis of ALBI at the start and after 12 weeks of lenvatinib treatment. The numbers of participants who were able to continue treatment for the full 12 weeks and had their ALBI calculated were 27 in the NASH group and 110 in the non-NASH group. There was no difference in the change in ALBI score over 12 weeks between the NASH and non-NASH groups. In addition, PSM was performed using age, sex, BCLC stage, pretreatment ALBI score, pre-treatment AFP value, maximum tumor diameter, the presence or absence of substantial vascular invasion, and the presence or absence of extrahepatic metastasis as covariates; and comparisons were made for each of the 30 participants selected. Similar to the results of the above analysis, there was no difference in ALBI between the NASH and non-NASH groups (
Figure S2b). There were no differences in the OS, PFS, and PPS of the participants in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/NASH groups taking lenvatinib treatment (
Figure S3a–c), nor between the participants selected by PSM (
Figure S4a–c).
4. Discussion
The drug therapy for HCC has undergone significant changes in recent years. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab treatment was adopted as the first-line treatment for HCC after it was found to outperform sorafenib, which has long been a standard treatment, with respect to both OS and PFS, in the IMbrave150 trial (7). For HCC, as for other carcinomas, a number of drugs, including ICIs, have become available, and their efficacy and the importance of sequential treatment are now recognized. However, the treatment of HCC differs from that of other carcinomas, in that liver reserve has a larger effect on prognosis (18). Hepatic reserve has been identified to be an important prognostic factor in various analyses (19, 20), and the maintenance of hepatic reserve is a major challenge in the treatment of HCC.
Hepatitis C used to be a major background factor in patients with liver cancer, but its prevalence has been declining in recent years, whereas NASH/NAFLD-derived liver cancer has become very common. In the United States, the number of patients awaiting liver transplantation because of NASH increased by 170% between 2004 and 2013 (21), and in Japan, a rapid increase in the prevalence of NASH-related cancer has been reported (18). However, this differs in several ways from viral liver cancer, and there has been recent interest in whether there are differences in the therapeutic efficacy of immunotherapy between patients in NASH/NAFLD-related and non-NASH-related liver cancer or between those with non-viral or viral liver cancer. In a meta-analysis of subgroup analyses of the results of several drug development trials, Pfister et al. found that immunotherapy was associated with a poorer prognosis in patients with non-viral liver cancer than in those with viral liver cancer, and that in two real-world clinical cohorts, NAFLD-related liver cancer was associated with a poorer prognosis than non-NAFLD-related liver cancer in patients undergoing immunotherapy (11). In addition, a study of propensity score-matched patients showed that Atezo+Bev treatment is associated with worse OS and PFS than lenvatinib treatment in patients with NASH/NAFLD-related HCC, but not in those with non-NASH/NAFLD-related HCC (22). However, findings on the efficacy of ICI combination therapy in patients with NASH-related or non-NASH-related cancer have been conflicting (23).
A number of studies have been conducted regarding the pre-carcinogenic immune response in NASH. It has been reported that in a mouse model of NAFLD, intrahepatic CD8 T cells are activated and express CD44 and CD69, which may result in liver damage through interactions with hepatocytes (21). It has also been reported that exhausted CD8 T cells are activated in the livers of patients with NASH and express high levels of PD-1, which promotes hepatocellular damage and the progression of fibrosis (24). In the present study, we measured the change in ALBI over the 12 weeks of treatment, and found that the NAFLD/NASH group had significantly poorer results than the non-NAFLD/non-NASH group. This may imply that the hepatic reserve of patients with NAFLD/NASH is worse than in those with other etiologies during Atezo+Bev treatment. One reason for this may be that checkpoint inhibitors increase inflammation and cytotoxicity in non-cancerous areas of the liver. Pfister et al. reported that in mice with NASH and HCC, anti-PD1 immunotherapy results in a slight reduction in circulating ALT activity, but an increase in fibrosis (11).
Although the immune responses of humans and mice differ, we believe that a similar response may explain the present findings. In the present study, we calculated ALBI 12 weeks after the start of treatment because it has been reported that it worsens slightly in the second month of lenvatinib treatment, but returns to its pre-treatment value by the third month (25). Hiraoka et al. also reported that ALBI worsens slightly after 3 weeks, but tends to improve after 6 weeks of Atezo+Bev treatment (26). This initial deterioration and subsequent improvement are thought to be the results of adverse events and fatigue during the early stages of treatment. On this basis, we conducted a comparison after 12 weeks, by which time the initial side effects and fatigue would be expected to have subsided to some extent. We found that ALBI after 12 weeks of Atezo+Bev treatment differed between the NASH and non-NASH groups, but not between participants in these groups who were undergoing lenvatinib treatment, as shown in the Supplementary data. Another reason for the difference in ALBI between the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups with respect to those undergoing Atezo+Bev treatment may be that NAFLD/NASH-related HCC is associated with a high incidence of cardiovascular complications (27), and Bev treatment may have worsened any hypertension, resulting in greater urinary protein loss and a consequent reduction in circulating albumin concentration. Irrespective of the actual reason, the ALBI after 12 weeks of Atezo+Bev treatment was worse in participants with NAFLD/NASH-related HCC than in those with non-NAFLD/non-NASH-related HCC. The prognosis of patients following Atezo+Bev treatment failure has been reported to correlate with hepatic reserve at the time of failure (28), and the worsening of ALBI may, at least in part, explain why the PPS associated with Atezo+Bev was worse in participants with NAFLD/NASH-related liver cancer than in those with non-NAFLD/non-NASH liver-related cancer in the present study.
The present study had several limitations. First, it was a retrospective study and participants were not randomly assigned. Instead, PSM was used, albeit of relatively few participants. In addition, markers of fibrosis and liver histology were not analyzed, and the cause of the worsening of the ALBI is unclear. In many cases, pre-treatment liver biopsies were not obtained and a definitive diagnosis of NASH was not made, but rather a diagnosis of NAFLD alone. Nevertheless, we believe that this is the first study to assess the ALBI of patients undergoing immunotherapy in combination with another treatment for NAFLD/NASH or non-NAFLD/non-NASH, and therefore the findings should be of great interest.
5. Conclusions
We found that the hepatic reserve of patients with NAFLD/NASH-related HCC undergoing Atezo+Bev treatment is worse than of those with non-NAFLD/non-NASH-related HCC. The PPS for patients with NAFLD/NASH-related liver cancer during Atezo+Bev treatment was also found to be poorer than that of patients with non-NAFLD/non-NASH-related liver cancer. This may indicate a worse prognosis for patients with NAFLD/NASH-related liver cancer who undergo Atezo+Bev treatment, probably because of deterioration in liver reserve.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1. Study design, patient inclusion, and propensity score-matching for lenvatinib-treated participants. Figure S2. Change in ALBI during lenvatinib treatment in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups. Figure S3. OS, PFS, and PPS of participants in the NAFLD/NASH and non-NAFLD/non-NASH groups during treatment with Lenvatinib. Fig.S4.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S. and K.M.; methodology, R.S.; software, R.S.; validation, R.S., T.S., Y.T., N.H., T.N., M.T., Y.A., A.O., T.G., A.K., K.K., U.M. and A.O.; formal analysis, R.S.; investigation, R.S.; resources, R.S.; data curation, R.S., M.O., S.Y., T.K., T.M., M.K., S.T., Y.A., T.Y., T.S., T.K., S.H., A.U., and M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.; writing—review and editing, R.S.,M.N. and M.K.; visualization, R.S.; supervision, R.S.; project administration, R.S.; funding acquisition R.S.,. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.” Please turn to the CRediT taxonomy for the term explanation. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Kyushu Cancer Center (2018-16) and conformed to the principles of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Written and verbal informed consent was obtained from all the participants with regard to their participation, the publication of the study, and the accompanying images. A copy of the written consent form is available for review upon request.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets obtained and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
RS and KM declare that they have received speaking fees from Chugai Pharm. Co. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kang, Y.K.; Yen, C.J.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.Y.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.L.; Altayar, O.; O'Shea, R.; Shah, R.; Estfan, B.; Wenzell, C.; et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Systemic Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Tateishi, R.; Kariyama, K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Japan: JSH Consensus Statements and Recommendations 2021 Update. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 181–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.; Núñez, N.G.; Pinyol, R.; Govaere, O.; Pinter, M.; Szydlowska, M.; et al. NASH limits anti-tumour surveillance in immunotherapy-treated HCC. Nature 2021, 592, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Michitaka, K.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Ueki, H.; et al. Usefulness of albumin-bilirubin grade for evaluation of prognosis of 2584 Japanese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Kudo, M.; Hirooka, M.; Tsuji, K.; Itobayashi, E.; et al. Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) Grade as Part of the Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline for HCC of the Japan Society of Hepatology: A Comparison with the Liver Damage and Child-Pugh Classifications. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Tsuji, K.; Takaguchi, K.; Itobayashi, E.; Kariyama, K.; et al. Validation of Modified ALBI Grade for More Detailed Assessment of Hepatic Function in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients: A Multicenter Analysis. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Kitano, M.; Sakurai, T.; Nishida, N. . General Rules for the Clinical and Pathological Study of Primary Liver Cancer, Nationwide Follow-Up Survey and Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Outstanding Achievements of the Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Reig, M.; Sherman, M. . Evidence-Based Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateishi, R.; Uchino, K.; Fujiwara, N.; Takehara, T.; Okanoue, T.; Seike, M.; et al. A nationwide survey on non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan: 2011-2015 update. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Hiraoka, A.; Atsukawa, M.; Hirooka, M.; Tsuji, K.; et al. Impact of modified albumin-bilirubin grade on survival in patients with HCC who received lenvatinib. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, T.; Naganuma, A.; Shibasaki, M.; Kohga, T.; Arai, Y.; Nagashima, T.; et al. The Role of the Albumin-Bilirubin Score for Predicting the Outcomes in Japanese Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Ramucirumab: A Real-World Study. Oncology 2021, 99, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.J.; Aguilar, M.; Cheung, R.; Perumpail, R.B.; Harrison, S.A.; Younossi, Z.M.; et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimini, M.; Rimassa, L.; Ueshima, K.; Burgio, V.; Shigeo, S.; Tada, T.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus lenvatinib or sorafenib in non-viral unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: an international propensity score matching analysis. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, T.; Jochheim, L.S.; Bathon, M.; Welland, S.; Scheiner, B.; Shmanko, K.; et al. Atezolizumab and bevacizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with impaired liver function and prior systemic therapy: a real-world experience. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359221080298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, M.; Pfister, D.; Donakonda, S.; Filpe, P.; Schneider, A.; Laschinger, M.; et al. Auto-aggressive CXCR6(+) CD8 T cells cause liver immune pathology in NASH. Nature 2021, 592, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Ueshima, K.; Chan, S.; Minami, T.; Chishina, H.; Aoki, T.; et al. Lenvatinib as an Initial Treatment in Patients with Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Beyond Up-To-Seven Criteria and Child-Pugh A Liver Function: A Proof-Of-Concept Study. Cancers 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Tada, T.; Hirooka, M.; Kariyama, K.; Tani, J.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Early clinical experience. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, P.; Martin, A.; Lang, S.; Kütting, F.; Goeser, T.; Demir, M.; et al. NAFLD and cardiovascular diseases: a clinical review. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Feng, Y.H.; Yen, C.J.; Chen, S.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Lu, L.C.; et al. Prognosis and treatment pattern of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after failure of first-line atezolizumab and bevacizumab treatment. Hepatol. Int. 2022, 16, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).